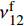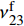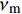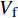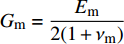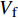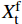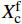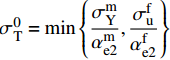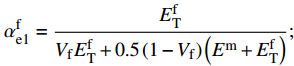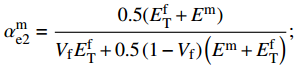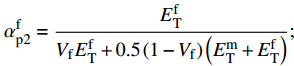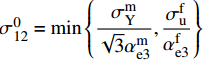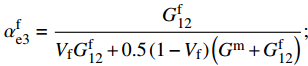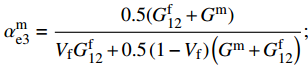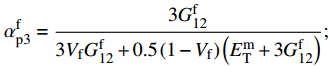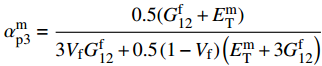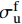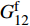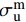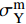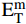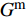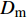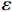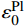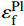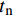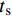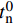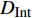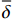Mechanical behavior and failure mechanism of the 3D angle interlocking woven reinforced aluminum matrix composites under in-plane tensile loading
-
摘要: 针对真空压力浸渗法制备的三维角联锁机织铝基复合材料,采用细观力学有限元模拟与试验结合的方法研究了其面内拉伸变形损伤与断裂力学行为。结果表明:复合材料拉伸应力-应变曲线的计算与试验结果吻合较好,经(纬)向拉伸初始弹性模量、极限强度和断裂应变的计算误差分别为3.96%(1.11%)、1.40%(6.86%)和−5.49%(3.73%);经向拉伸载荷作用下,经纱界面及其邻近基体合金先后发生损伤,随拉伸应变增加损伤累积和交互作用依次引发界面、基体和纬纱失效,变形后期经纱的断裂最终导致复合材料经向拉伸失效;纬向拉伸变形前期,经纱界面和经纬纱之间薄弱的基体合金相继产生损伤和失效现象,经纱在变形中期即出现横向破坏,起主要承载作用的纬纱轴向断裂是纬向拉伸的主要失效机制,由于三维角联锁机织体中纬纱体分远低于经纱,复合材料纬向拉伸模量和强度分别仅为经向的81.8%和56.5%。Abstract: 3D angle interlocking fabric reinforced aluminum composites were prepared by the vacuum assisted pressure infiltration method. The mechanical properties and damage behavior of the composites subjected to in-plane tensile loading were investigated using the micromechanical finite element simulation and experimental method. The results show that the tensile stress-strain curve from simulation is in agreement with the testing curves, where the calculation errors of the initial modulus, ultimate strength and fracture strain in warp (weft) direction are 3.96%(1.11%), 1.40%(6.86%) and −5.49%(3.73%), respectively. Under the warp directional tension condition, the interface on warp yarns and the adjoint matrix alloy damage successively. With the increase of tensile strain, these damage zones accumulate and interact with each other, leading to the failure of interface, matrix and weft yarns in sequence. The fracture of warp yarns in the terminate stage induces the ultimate failure of the composites. During the weft directional tensile process, the interface on warp yarns and the thin matrix alloy between yarns damage and fail firstly. The transverse fracture of warp yarns occurs in the middle stage of tensile deformation. The axial fracture of weft yarns, which sustain the loading stress at the end of deformation process, is the main failure mechanism of the composites under weft directional tensile condition. The tensile modulus and strength in weft direction are 81.8% and 56.5% times than those in warp direction, owing to the lower volume fraction of weft yarns in the 3D angle interlocking fabric.
-
连续碳(石墨)纤维增强铝基(CF/Al)复合材料具有比强度和比模量高、热膨胀系数低、耐热性好和抗老化等优良性能,其作为航空航天领域传统结构材料的有力竞争者甚至替代者而备受国内外研究者重视[1-3]。大量研究表明,CF/Al复合材料具有极高的轴向强度和模量,而其横向性能较差[4-6],从而限制了其工程应用[7-9]。近年来出现的各种织物CF/Al复合材料[10-12],不仅继承了CF/Al复合材料的优点,而且编织纤维结构使其具有良好的结构和性能可设计性,是满足航空航天结构整体化、轻量化和结构/性能一体化需求的新一代铝基复合材料。
Zhang等[13]制备了2D机织碳布增强铝基复合材料,纤维分布均匀且界面结合良好,面内拉伸强度和模量分别为366.2 MPa和110.7 GPa,拉伸时存在界面脱粘和部分纤维拔出现象。MA等[14]和周计明等[15]制备的2D正交铺层碳布增强铝基复合材料比重仅为铝合金的0.82倍,面内铺层0°/90°的抗拉强度为254 MPa(约为铸态基体合金2倍),面外压缩强度约为面内的2.5倍,面外压缩破坏表现为纤维剪切失效,而面内失效为界面脱粘和纵向开裂。Hufenbach等[16]采用气压辅助液态浸渗技术实现了2D机织布增强铝基复合材料的精密成形,基体合金中镀镍碳纤维分布均匀且织物结构良好。Yang等[17-18]将镀铜碳纤维布与ZL205铝板叠层后采用等离子烧结(SPS)法制备了铝基复合材料,其弯曲强度、延伸率和断裂能均显著高于基体铝合金。Zhang等[19-20]采用电磁浸渗法和半固态铸轧法制备的平纹碳布增强铝基复合材料面内弯曲强度分别达到了212 MPa和317 MPa,基体合金裂纹扩展和碳布界面分层是弯曲失效的主要原因。Lee等[21]根据2D机织碳布增强铝基复合材料的细观特征建立细观结构模型,计算预测了复合材料宏观弹性性能常数并通过超声共振光谱测量试验验证了理论计算结果。McWilliams等[22]基于多尺度力学框架对2D正交Al2O3纤维布增强铝基复合材料室温拉伸变形行为(包括渐进损伤和破坏)进行了数值模拟,结果表明界面损伤与脱粘对其力学行为有显著影响,界面横向开裂是其主要的室温拉伸破坏机制,复合材料面内抗拉强度在280~353 MPa范围内。综上文献来看,目前有关织物CF/Al复合材料的研究主要集中在2D织物CF/Al复合材料制备、力学性能及破坏的实验研究方面,而有关3D织物CF/Al复合材料的研究则非常少见[23]。周珍珍等[11]和王振军等[24]近年来开发了3D织物结构的CF/Al复合材料,并开展了其微观组织及断裂力学性能的实验探索,但目前仍缺乏其承载变形条件下损伤与失效行为机制的认识。
本研究通过室温拉伸试验,研究了真空压力浸渗法制备的三维角联锁机织CF/Al复合材料的面内经向和纬向拉伸变形力学行为,采用渐进损伤细观力学有限元法模拟分析了复合材料拉伸变形力学行为和损伤演化过程,并进一步结合试验和模拟结果分析了复合材料经向和纬向拉伸时的断裂失效机制,以期为复合材料设计和高性能制备提供理论指导。
1. 实验材料及方法
本文研究对象是浅交直联结构的三维角联锁机织CF/Al复合材料,增强体材料为日本东丽公司的高模碳纤维M40J,基体合金为北京航空材料研究院提供的铝合金ZL301,浅交直联结构的三维角联锁机织体由江苏宜兴新立织造公司织造,其纤维体积分数为42vol%,结构参数如表1所示。
表 1 三维角联锁机织体结构参数Table 1. Structural parameters of the 3D angle interlocking woven fabricFabric thickness/mm Yarn specification Warp density/(yarns·(10 mm)−1) Weft density/(yarns·(10 mm)−1) Fiber content/vol% 4.0 195Tex×2 8.0 4.0 42 采用真空压力浸渗法制备浅交直联结构三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料[24],机织物预热温度560℃,铝熔体浸渗温度720℃,浸渗压力8 MPa,保压时间30 min。
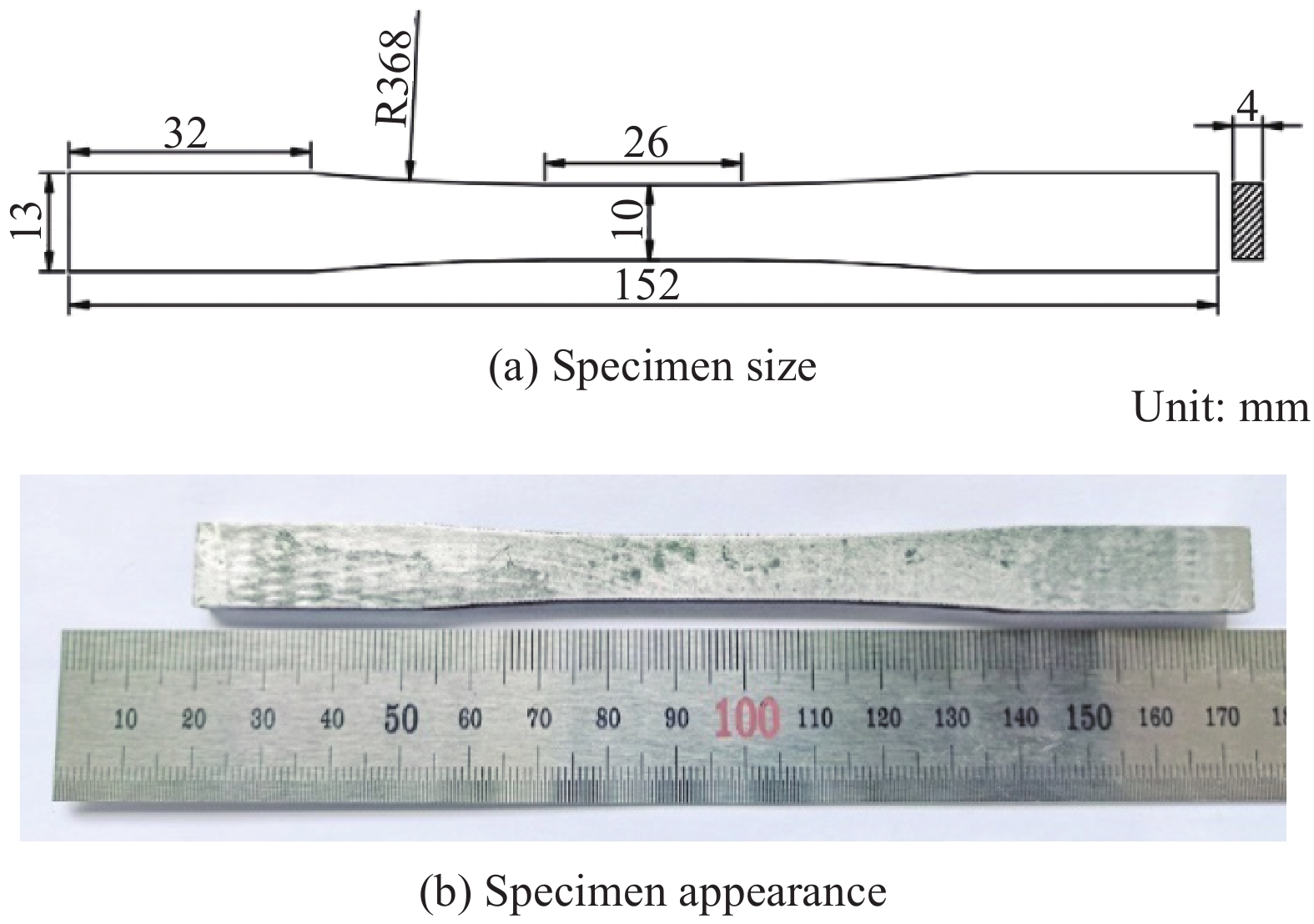
根据标准ASTM D3552—96[25]纤维增强金属基复合材料拉伸性能试验方法设计试样尺寸,如图1(a)所示。采用DK7745Z线切割机(江苏泰州雄峰机械厂)按照试样尺寸对复合材料板加工得到拉伸试样,如图1(b)所示。将试样在180℃下进行8 h人工时效处理以尽可能减小加工残余应力。为了避免试样夹持端在拉伸试验过程中试样打滑和有非正常开裂现象,试验前在试样夹持端的表面上粘贴厚度为1 mm的纯铝加强片。采用美国英斯特朗公司的Instron5569电子万能拉伸试验机进行室温拉伸试验,拉伸速率为0.5 mm/min,直至将试样拉伸至断裂失效状态。利用引伸计测量获得试样的工程应变数据,根据试验机采集的载荷数据计算其工程应力,从而绘制生成复合材料的拉伸应力-应变曲线。采用南京崛宇精密仪器有限公司的IM300金相显微镜和美国FEI公司生产的Quanta2000型扫描电镜(SEM)观察复合材料的微观组织形貌及试样的拉伸断口形貌。
2. 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料细观力学有限元模型
2.1 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料细观结构模型
图2(a)是浅交直联结构三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料的金相显微组织。可以看出,复合材料中纱线束分布状态与复合材料制备前的三维角联锁机织结构能够较好地吻和,并且基体合金无裂纹与孔洞等缺陷。图2(b)是复合材料纱线束内的微观组织,基体铝合金致密无缩孔缩松等铸造缺陷,纤维较均匀地分布在基体铝合金中,通过Image Pro Plus软件测定总面积和纤维所占面积,计算得到复合材料纱线束内纤维的体积分数约为75vol%。
不失一般性,假设三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料中经纱和纬纱均具有特定的横截面形状和尺寸,而且二者在基体合金中具有周期性分布特征,根据定量金相显微镜测量的经纬纱线截面尺寸及其之间的间距分布尺寸,采用三维建模软件Catia建立的浅交直联三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料细观结构模型如图3所示。
2.2 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料材料模型
从图2可知,三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料内部经向和纬向纱线束实质为纤维体积分数为75vol%的单向CF/Al复合材料。对于单向CF/Al复合材料,前期实验研究发现基体合金ZL301较高的Mg含量可显著抑制界面反应和Al4C3界面相生成[6, 26]。因此本文计算CF/Al纱线束力学性能时忽略其内部界面层的影响,采用混合法则(式(1))计算纱线束的横观各向同性弹性常数:
E11=VfEf11+(1−Vf)EmE22=E33=EmEf22/((1−Vf)Ef22+VfEm)G12=G13=GmGf12/(VfGm+(1−Vf)Gf12)G23=Gm/(1−Vf(1−Gm/Gf23)))ν12=ν13=Vfνf12+(1−Vf)νmν23=Vfνf23+(2νm−ν12) (1) 式中:
Ef11 、Ef22 为纤维轴向、横向弹性模量;Gf12 、Gf23 为纤维轴向、横向剪切模量;Em 为基体弹性模量;Gm 为基体剪切模量;νf12 、νf23 为纤维轴向、横向泊松比;νm 为基体泊松比,Vf 为纱线束纤维体积分数,其中Gm=Em2(1+νm) 。采用Chamis[27]提出的经验公式计算纱线束的轴向极限强度:
Xt=VfXftXc=VfXfc (2) 式中:
Vf 为纱线束纤维体积分数;Xft 为纤维拉伸强度;Xfc 为纤维压缩强度。采用桥联模型[28]计算纱线束的横向强度和剪切强度,其横向强度计算公式如下:
σuT=min (3) 式中:
\sigma _{\rm{T}}^0 = \min \left\{ {\dfrac{{\sigma _{\rm{Y}}^{\rm{m}}}}{{\alpha _{{\rm{e}}2}^{\rm{m}}}},\dfrac{{\sigma _{\rm{u}}^{\rm{f}}}}{{\alpha _{{\rm{e}}2}^{\rm{f}}}}} \right\} ;\alpha _{{\rm{e}}1}^{\rm{f}} = \frac{{E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}}}}{{{V_{\rm{f}}}E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}} + 0.5\left(1 - {V_{\rm{f}}}\right)\left({E^{\rm{m}}} + E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}}\right)}}; \alpha _{{\rm{e}}2}^{\rm{m}} = \frac{{0.5(E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}} + {E^{\rm{m}}})}}{{{V_{\rm{f}}}E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}} + 0.5\left(1 - {V_{\rm{f}}}\right)\left({E^{\rm{m}}} + E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}}\right)}}; \alpha _{{\rm{p}}2}^{\rm{f}} = \frac{{E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}}}}{{{V_{\rm{f}}}E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}} + 0.5\left(1 - {V_{\rm{f}}}\right)\left(E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{m}} + E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{f}}\right)}}; 纱线束的剪切强度计算公式如下:
{\sigma }_{\rm{12}}^{\rm{u}}={\min}\left\{ {\frac{{\sigma }_{\rm{u}}^{\rm{f}}-({\alpha }_{\rm{e3}}^{\rm{f}}-{\alpha }_{\rm{p3}}^{\rm{f}}){\sigma }_{\rm{12}}^{0}}{{\alpha }_{\rm{p3}}^{\rm{f}}},\;\frac{{\sigma }_{\rm{u}}^{\rm{m}}-({\alpha }_{\rm{e3}}^{\rm{m}}-{\alpha }_{\rm{p3}}^{\rm{m}}){\sigma }_{\rm{12}}^{0}}{{\alpha }_{\rm{p3}}^{\rm{m}}}} \right\} (4) 式中:
\sigma _{{\rm{12}}}^0 = \min \left\{ {\dfrac{{\sigma _{\rm{Y}}^{\rm{m}}}}{{\sqrt 3 \alpha _{{\rm{e3}}}^{\rm{m}}}},\dfrac{{\sigma _{\rm{u}}^{\rm{f}}}}{{\alpha _{{\rm{e3}}}^{\rm{f}}}}} \right\} ;\alpha _{{\rm{e3}}}^{\rm{f}} = \frac{{G_{{\rm{12}}}^{\rm{f}}}}{{{V_{\rm{f}}}G_{{\rm{12}}}^{\rm{f}} + 0.5\left(1 - {V_{\rm{f}}}\right)\left({G^{\rm{m}}} + G_{{\rm{12}}}^{\rm{f}}\right)}}; \alpha _{{\rm{e3}}}^{\rm{m}} = \frac{{0.5(G_{{\rm{12}}}^{\rm{f}} + {G^{\rm{m}}})}}{{{V_{\rm{f}}}G_{{\rm{12}}}^{\rm{f}} + 0.5\left(1 - {V_{\rm{f}}}\right)\left({G^{\rm{m}}} + G_{{\rm{12}}}^{\rm{f}}\right)}}; \alpha _{{\rm{p}}3}^{\rm{f}} = \frac{{3G_{12}^{\rm{f}}}}{{3{V_{\rm{f}}}G_{12}^{\rm{f}} + 0.5\left(1 - {V_{\rm{f}}}\right)\left(E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{m}} + 3G_{12}^{\rm{f}}\right)}}; \alpha _{{\rm{p3}}}^{\rm{m}} = \frac{{0.5(G_{12}^{\rm{f}} + E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{m}})}}{{3{V_{\rm{f}}}G_{12}^{\rm{f}} + 0.5\left(1 - {V_{\rm{f}}}\right)\left(E_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{m}} + 3G_{12}^{\rm{f}}\right)}} 式中:
{\rm{\sigma }}_{\rm{u}}^{\rm{f}} 、G_{{\rm{12}}}^{\rm{f}} 为纤维的横向拉伸极限强度和剪切模量;\sigma _{\rm{u}}^{\rm{m}} 、\sigma _{\rm{Y}}^{\rm{m}} 、{\rm{E}}_{\rm{T}}^{\rm{m}} 、{G^{\rm{m}}} 分别为基体合金拉伸极限强度、屈服极限、加工硬化模量和剪切模量。根据前期实验和数值分析研究获得的单向CF/Al复合材料中碳纤维和基体合金的弹性和强度性能参数[29],利用式(1)计算得到纱线束的弹性常数如表2所示,利用式(2)~(4)计算得到纱线束的强度性能参数如表3所示。细观力学有限元模型中将纱线束视为横观各向同性的单向复合材料,采用最大应力强度准则作为其失效判据,即纱线束3个主轴方向上的各应力分量大于或等于各自的极限强度常数时(表3),纱线束将发生失效,通过定义用户材料子程序(UMAT)实现纱线束失效判定。纱线束失效前满足由弹性常数(表2)定义的横观各向同性的线弹性力学本构关系,采用刚度降解法处理纱线束失效后的力学行为,目的是保证其有限元计算中的应力连续性和计算收敛性。
表 2 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料纱线束弹性性能参数Table 2. Elastic constant parameters of the yarns in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite{E}_{11} /MPa {E}_{22} /MPa {G}_{12} /MPa {G}_{23} /MPa {\nu }_{12} {\nu }_{23} 302700 23500 14700 10000 0.28 0.41 Notes: {E}_{11} —Elastic modulus in axial direction; {E}_{22} —Elastic modulus in transverse direction; {G}_{12} —Longitudinal shear modulus; {G}_{23} —Transverse shear modulus; {\nu }_{12} —Axial Poisson's ratio; {\nu }_{23} —Transverse Poisson's ratio. 表 3 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料纱线束极限强度性能参数Table 3. Strength parameters of the yarns in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite{X}_{\rm{t}} /MPa {X}_{\rm{c}} /MPa {Y}_{\rm{t}} /MPa {Y}_{\rm{c}} /MPa {S}_{\!{12}}/MPa {S}_{\!{23}}/MPa 1350 660 26.8 102.4 82.7 13.6 Notes: {X}_{\rm{t}} —Tensile strength in axial direction; {X}_{\rm{c}} —Compressive strength in axial direction; {Y}_{\rm{t}} —Tensile strength in transverse direction; {Y}_{\rm{c}} —Compressive strength in transverse direction; {S}_{\!{12}}—Longitudinal shear strength; {S}_{\!{23}}—Transverse shear strength. 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料基体合金为各向同性的弹塑性材料,其室温下的弹塑性力学性能参数如表4所示[30]。采用延性损伤模型定义其塑性变形后期因微裂纹萌生、扩展和聚集引起的损伤演化和失效行为,基体合金塑性损伤演化因子
{D}_{\rm{m}} :表 4 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料基体合金的弹塑性力学性能参数Table 4. Elastoplastic properties of the matrix alloy in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite{E}_{\rm{m}} /MPa {\nu }_{\rm{m}} {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{y}} /MPa {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{u}} /MPa {\varepsilon }_{0}^{\rm{Pl}} {\varepsilon }_{f}^{\rm{Pl}} 79700 0.33 100.0 159.1 0.15 0.75 Notes: {E}_{\rm{m}} —Young's modulus; {\nu }_{\rm{m}} —Poisson’s ratio; {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{y}} —Yield strength; {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{u}} —Ultimate strength; {\varepsilon }_{0}^{\rm{Pl}} —Critical strain for damage initiation; {\varepsilon }_{f}^{\rm{Pl}} —Critical strain for failure. {D}_{\rm{m}}=\frac{\varepsilon -{\varepsilon }_{0}^{\rm{Pl}}}{{\varepsilon }_{{\rm{f}}}^{\rm{Pl}}-{\varepsilon }_{0}^{\rm{Pl}}} (5) 式中:
\varepsilon 为等效塑性应变;{\varepsilon }_{0}^{\rm{Pl}} 与{\varepsilon }_{{\rm{f}}}^{\rm{Pl}} 分别为初始损伤(D=0)与完全损伤(D=1)时的等效塑性应变。基体合金完全损伤后对其弹性常数进行折减(折减因子0.1),表征其失效后的应力-应变力学本构行为。从图2可以看出,纱线束表面的纤维与基体合金之间形成纱线束/基体合金结合界面,其具有与纱线束内部纤维/基体合金界面相同的性质,采用的界面结合性能参数如表5所示[31]。考虑基体合金/纱线束的界面厚度远小于纱线束的特点,有限元建模时利用零厚度内聚力界面单元(Cohesive element)描述基体合金与纱线束之间的损伤和脱粘力学行为。采用最大名义应力准则作为界面单元损伤判据,即
表 5 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料基体合金/纱线束界面结合性能参数Table 5. Interfacial bonding properties between matrix alloy and yarns in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite{t}_{\rm{n}}^{0} /MPa {t}_{\rm{s}}^{0} /MPa {t}_{\rm{t}}^{0} /MPa {\bar {\delta }}^{0} /10−6 m {\bar {\delta }}^{\rm{f}} /10−6 m 16.0 9.5 9.5 0.08 0.72 Notes: {t}_{\rm{n}}^{0} —Peak stress purely normal to interface; {t}_{\rm{s}}^{0} —Peak stress in the first shear direction; {t}_{\rm{t}}^{0} —Peak stress in the second shear direction; {\bar {\delta }}^{0} —Critical separation displacement for damage initiation; {\bar {\delta }}^{\rm{f}} —Critical separation displacement for failure. {\rm{Max}}\left\{ {\frac{{\left\langle {{t_{\rm{n}}}} \right\rangle }}{{{t_{\rm{n}}}^0}}} \right.,\frac{{{t_{\rm{s}}}}}{{{t_{\rm{s}}}^0}},\left. {\frac{{{t_{\rm{t}}}}}{{{t_{\rm{t}}}^0}}} \right\} = 1 (6) 式中:
{t}_{\rm{n}} 、{t}_{\rm{s}} 、{t}_{\rm{t}} 为界面单元的法向和切向应力分量;{t}_{\rm{n}}^{0} 、{t}_{\rm{s}}^{0} 、{t}_{\rm{t}}^{0} 分别为相应的界面极限强度。内聚力界面单元满足损伤判据后,令界面强度随分离位移增加而线性衰减[31],衰减率通过界面损伤因子
{D_{{\rm{Int}}}} 定义:{D_{{\rm{Int}}}} = \frac{{\overline \delta ^{\rm{f}}({{\overline \delta }} - \overline \delta ^0)}}{{\overline \delta (\overline \delta ^{\rm{f}} - \overline \delta ^0)}} (7) 式中:
\overline {\delta } 为界面等效分离位移;{\overline {\delta }}^{f} 为失效临界等效分离位移;{\overline {\delta }}^{0} 为初始损伤临界等效分离位移。3. 结果与讨论
3.1 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料面内拉伸变形力学行为
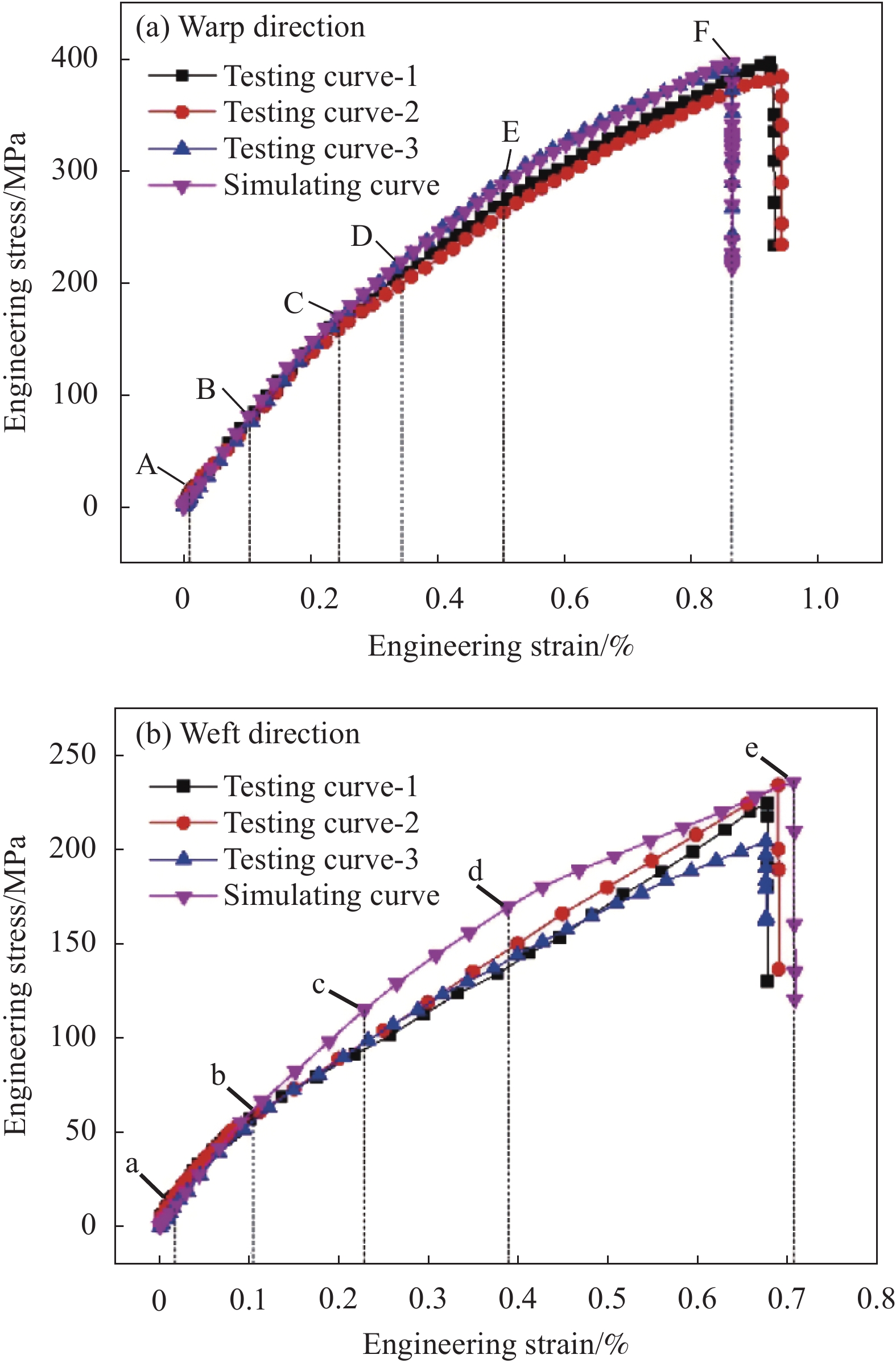
利用上一节建立的细观力学有限元模型,采用Abaqus软件模拟计算了三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料经向和纬向拉伸变形过程中的工程应力-应变曲线,并与拉伸试验曲线进行了对比,结果如图4所示。其中图4(a)为3条经向拉伸试验曲线与模拟曲线的对比,图4(b)为纬向拉伸获得的3条试验曲线与模拟曲线的对比。在拉伸初始变形阶段,由于基体中的经向纱线束呈卷曲状态,拉伸载荷主要由基体合金承担,因此复合材料表现出与基体合金相近的弹性模量(对比表4和表6)。随着拉伸变形量的增加,卷曲的纱线束逐渐伸直并开始发挥承载作用,随后发生界面脱粘、基体损伤及纱线断裂等过程,因此拉伸变形中后期复合材料表现出较显著的非线性力学行为。而三维角联锁机织结构的树脂基复合材料经纬向拉伸均表现出显著的线弹性特性[32]。这可能是由于三维角联锁机织铝基复合材料变形中后期出现了组元结构(基体合金、纱线束及其界面)的损伤累积并引发局部失效的结果。
表6为三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料经向和纬向拉伸力学性能的试验与模拟结果。可以看出,无论是在经向还是在纬向拉伸条件下,测试得到的复合材料三条拉伸试验力学曲线均表现出不完全重合的现象,这可能是三维角联锁机织物中不同部位纱线编织结构存在一定差异的结果[33]。通过试验曲线和数值模拟曲线的对比可见,细观力学模拟得到的两个方向的拉伸弹性模量和极限强度均高于试验测试结果的均值。其原因在于如下两个方面:(1) 复合材料纱线束间和束内基体合金可能存在微观缩松缺陷,而细观力学有限元模型未考虑微观缺陷对复合材料宏观拉伸力学性能的影响;(2) 经验公式预测纱线束性能无法考虑束内纤维/基体界面层影响,因此细观力学模型采用的纱线束弹性常数和强度性能高于纱线束实际性能,导致细观力学模拟得到的复合材料宏观力学性能偏高。
表 6 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料经向和纬向拉伸力学性能模拟与试验结果Table 6. Testing and simulating results of the mechanical properties of 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite at warp and weft directionResult Warp direction tension Weft direction tension Initial modulus/GPa Tensile strength/MPa Fracture strain/% Initial modulus/MPa Tensile strength/MPa Fracture strain/% Testing 70.29±0.86 391.59±5.55 0.91±0.05 57.52±2.62 221.08±16.6 0.68±0.01 Simulating 73.07 397.06 0.86 58.16 236.24 0.7086 Error/% 3.96 1.40 −5.49 1.11 6.86 3.73 3.2 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料经向拉伸损伤与失效过程
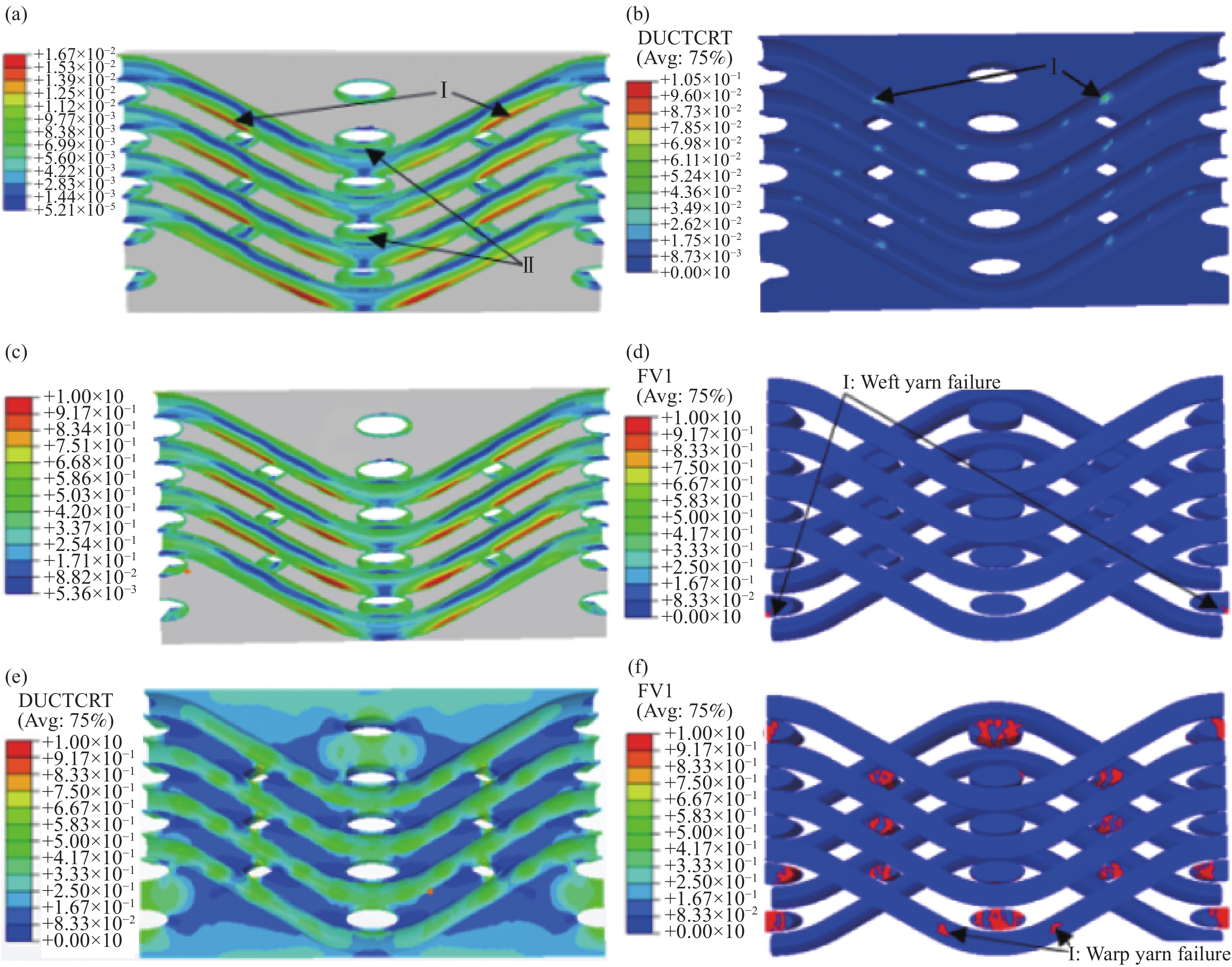
三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料经向拉伸细观损伤演化过程如图5所示。当拉伸应变为0.007%时(图4(a)中A点),经纱与基体间界面受剪应力作用开始出现明显损伤,如图5(a)的I处,而纬纱界面还未受损伤(图5(a)的II处);当应变达到0.1041%时(图4(a)中B点),经纱表面的基体合金发生损伤,如图5(b)中I处;当应变增加到0.2436%时(图4(a)中C点),经纱与基体间的界面开始局部失效,纬纱与基体间的界面损伤程度加重,如图5(c);随着拉伸变形量增加,界面和基体合金的损伤不断累积(对比图5(a)和图5(c)中的界面损伤因子及图5(b)和图5(e)中的基体损伤因子)。当应变为0.3436%时(图4(a)中D点),纬纱部分开始出现失效现象,见图5(d)中I点,而此时经纱未失效,这是由于经向拉伸载荷作用下纬纱受横向拉伸载荷,而其横向力学性能相对轴向较差[30-31],因此纬纱比经纱更易失效;当拉伸应变为0.5036%时,介于经纱和纬纱之间的基体合金发生失效,纱线间较薄的铝合金承载时非常容易因应力集中而失效,如图5(e);在拉伸应变达到0.8658%时,多数纬纱已经发生破坏,同时经纱上临近纬纱部位因受弯矩较大而开始产生局部失效现象,如图5(f)中I点,此时拉伸应力开始出现快速下降(图4(a)中F点),表明此时复合材料在经向上失去了对拉伸载荷的承载能力。
图6为三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料受经向拉伸载荷作用下的断口形貌。由图6(a)可以看出,经纱断裂发生在其与纬纱搭接处,同时纱线搭接处的纬纱发生横向开裂现象,这与数值模拟结果基本吻合。从经向拉伸模拟结果(图5(f))也可看出经纬纱搭接处经纱局部失效现象明显。由于此处经纱处于最大弯曲状态而易产生严重的剪切应力,一旦其超过纱线束的极限强度就会引起经纱束的断裂。图6(b)为经纱束拉伸断裂后的内部微观形貌。可以看出,纤维与基体界面发生失效后,部分纤维断裂并从基体合金中拔出,在基体合金中留下显著的空洞。综上可知,拉伸变形中界面与基体合金损伤逐渐累积并交互作用,从而导致纬纱开裂和基体合金失效,这使纱线搭接处弯曲的经纱束因剪切应力集中而发生局部断裂,这是该复合材料经向拉伸时的主要失效机制。
3.3 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料纬向拉伸损伤与失效过程
图7为三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料纬向拉伸损伤演化过程。在拉伸应变为0.018% (图4(b)中a点),基体与经纱之间界面开始出现损伤,且损伤区域垂直拉伸方向,图7(a)中I点,此时纬纱的界面并未发生损伤,如图7(a)中II点;随着拉伸载荷逐渐增大,应变为0.1005% (图4(b)中b点)时,经纱与纬纱搭接处的薄弱部分开始出现基体损伤,如图7(b)所示;当应变达到0.2287%时(图4(b)中c点),经纱与基体合金间的界面出现局部失效,且纬纱与基体的界面损伤程度增大(图7(c)),相比经向拉伸,纬向拉伸时界面失效出现较晚,这是由于界面主要受法向拉应力作用。
随着拉伸变形量增加基体合金损伤程度不断增加,在应变为0.3887% (图4(b)中d点)时,经纬纱线之间薄弱的基体合金出现失效,如图7(d)中I点,这可能是此处基体合金损伤萌生的裂纹扩展的空间受限的结果[29, 34]。与此同时,部分经纱发生失效而纬纱未见失效,纬向拉伸载荷下经纱主要处于横向应力状态而纬纱处于轴向应力状态,较差的横向强度致使经纱比纬纱更易失效,如图7(e)所示;此后拉伸应力随着应变增加而持续增长,应变达到0.7099%时,纬纱开始出现失效,由于此前经纱和基体均已发生失效,载荷主要由纬纱承担,纬纱的失效导致拉伸应力开始急剧下降(图4(b)中e点),这表明复合材料失去了承受纬向拉伸载荷的能力。
图8为三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料试样的纬向拉伸断口形貌。从图8(a)可以明显看出,在纬向拉伸变形中处于弯曲状态的经纱发生横向开裂,并出现部分纤维折断现象。纱线搭接处纬纱则发生轴向拉伸断裂现象,这是由于该处基体合金厚度最小,基体合金易产生失效导致应力集中使该处的纬纱产生较高的应力而导致局部失效,这可从纬向拉伸后期模拟结果(图7(f))中得到验证。从图8(b)可以发现,纬纱断口内部纤维断裂后拔出较少,其较平整的断口也说明纬纱发生了轴向拉伸断裂。由此可见,界面与基体合金产生损伤累积而失效后,引起其附近的经纱发生横向开裂,平行于拉伸方向的纬纱在拉伸变形中起主要载荷承担作用,经纬纱搭接处较高应力水平引起的纬纱轴向断裂是导致复合材料纬向拉伸失效的主要原因。
4. 结 论
(1) 细观力学模型对三维角联锁碳纤维增强铝基(CF/Al)复合材料经(纬)向拉伸模量、强度和断裂应变的计算误差分别为3.96%(1.11%)、1.40%(6.86%)和−5.49%(3.73%),具有较好的计算有效性。
(2) 经向拉伸变形初期界面与基体合金发生损伤累积和交互作用,先后引起界面失效、纬纱横向开裂和基体合金失效,变形后期经纱弯曲部位剪切应力引发的纱线断裂导致复合材料发生经向拉伸破坏。
(3) 纬向拉伸过程中界面与基体合金的损伤演化和累积,依次引起界面脱粘、基体合金失效和经纱横向开裂,变形后期纬纱起主要载荷承担作用,纱线交织处的纬纱因应力集中而发生轴向断裂是复合材料纬向拉伸失效的主要原因。
(4) 复合材料经向拉伸初始模量、极限强度和断裂应变分别为70.29 GPa、391.59 MPa和0.91%,而其纬向拉伸性能分别为经向的81.8%、56.5%和74.7%。
-
表 1 三维角联锁机织体结构参数
Table 1 Structural parameters of the 3D angle interlocking woven fabric
Fabric thickness/mm Yarn specification Warp density/(yarns·(10 mm)−1) Weft density/(yarns·(10 mm)−1) Fiber content/vol% 4.0 195Tex×2 8.0 4.0 42 表 2 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料纱线束弹性性能参数
Table 2 Elastic constant parameters of the yarns in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite
{E}_{11} /MPa {E}_{22} /MPa {G}_{12} /MPa {G}_{23} /MPa {\nu }_{12} {\nu }_{23} 302700 23500 14700 10000 0.28 0.41 Notes: {E}_{11} —Elastic modulus in axial direction; {E}_{22} —Elastic modulus in transverse direction; {G}_{12} —Longitudinal shear modulus; {G}_{23} —Transverse shear modulus; {\nu }_{12} —Axial Poisson's ratio; {\nu }_{23} —Transverse Poisson's ratio. 表 3 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料纱线束极限强度性能参数
Table 3 Strength parameters of the yarns in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite
{X}_{\rm{t}} /MPa {X}_{\rm{c}} /MPa {Y}_{\rm{t}} /MPa {Y}_{\rm{c}} /MPa {S}_{\!{12}}/MPa {S}_{\!{23}}/MPa 1350 660 26.8 102.4 82.7 13.6 Notes: {X}_{\rm{t}} —Tensile strength in axial direction; {X}_{\rm{c}} —Compressive strength in axial direction; {Y}_{\rm{t}} —Tensile strength in transverse direction; {Y}_{\rm{c}} —Compressive strength in transverse direction; {S}_{\!{12}}—Longitudinal shear strength; {S}_{\!{23}}—Transverse shear strength. 表 4 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料基体合金的弹塑性力学性能参数
Table 4 Elastoplastic properties of the matrix alloy in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite
{E}_{\rm{m}} /MPa {\nu }_{\rm{m}} {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{y}} /MPa {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{u}} /MPa {\varepsilon }_{0}^{\rm{Pl}} {\varepsilon }_{f}^{\rm{Pl}} 79700 0.33 100.0 159.1 0.15 0.75 Notes: {E}_{\rm{m}} —Young's modulus; {\nu }_{\rm{m}} —Poisson’s ratio; {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{y}} —Yield strength; {\sigma }_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{u}} —Ultimate strength; {\varepsilon }_{0}^{\rm{Pl}} —Critical strain for damage initiation; {\varepsilon }_{f}^{\rm{Pl}} —Critical strain for failure. 表 5 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料基体合金/纱线束界面结合性能参数
Table 5 Interfacial bonding properties between matrix alloy and yarns in 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite
{t}_{\rm{n}}^{0} /MPa {t}_{\rm{s}}^{0} /MPa {t}_{\rm{t}}^{0} /MPa {\bar {\delta }}^{0} /10−6 m {\bar {\delta }}^{\rm{f}} /10−6 m 16.0 9.5 9.5 0.08 0.72 Notes: {t}_{\rm{n}}^{0} —Peak stress purely normal to interface; {t}_{\rm{s}}^{0} —Peak stress in the first shear direction; {t}_{\rm{t}}^{0} —Peak stress in the second shear direction; {\bar {\delta }}^{0} —Critical separation displacement for damage initiation; {\bar {\delta }}^{\rm{f}} —Critical separation displacement for failure. 表 6 三维角联锁CF/Al复合材料经向和纬向拉伸力学性能模拟与试验结果
Table 6 Testing and simulating results of the mechanical properties of 3D angle interlocking woven CF/Al composite at warp and weft direction
Result Warp direction tension Weft direction tension Initial modulus/GPa Tensile strength/MPa Fracture strain/% Initial modulus/MPa Tensile strength/MPa Fracture strain/% Testing 70.29±0.86 391.59±5.55 0.91±0.05 57.52±2.62 221.08±16.6 0.68±0.01 Simulating 73.07 397.06 0.86 58.16 236.24 0.7086 Error/% 3.96 1.40 −5.49 1.11 6.86 3.73 -
[1] RAWAL S P. Metal-matrix composites for space applications[J]. The Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society,2001,53(4):14-17.
[2] LI D, CHEN G, JIANG L, et al. Effect of thermal cycling on the mechanical properties of CF/Al composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2013,586(1):330-337.
[3] LEE M, CHOI Y, SUGIO K, et al. Effect of aluminum carbide on thermal conductivity of the unidirectional CF/Al composites fabricated by low pressure infiltration process[J]. Composite Science and Technology,2014,97(16):1-5.
[4] ZHOU Y, WANG W, XIA Y, et al. An experimental study on the tensile behavior of a unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced aluminum composite at different strain rates[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2003,362(1-2):112-117. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00214-4
[5] JAQUESSON M, GIRARD A, VIALSETIF M H, et al. Tensile and fatigue behavior of Al-based metal matrix composites reinforced with continuous carbon or alumina fibers: Part I. quasi-unidirectional composites[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,2004,35:3289-3305. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-004-0071-2
[6] WANG X, JIANG D, WU G, et al. Effect of Mg content on the mechanical properties and microstructure of Grf/Al composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2008,497(1-2):31-36. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2008.07.022
[7] EVERETT R K. Metal matrix composites: Processing and Interfaces[M]. Pittsburgh: Academic Press, 1991.
[8] DYZIA M, GROSZ A D, SLEZIONA J, HUFENBACH W, et al. Infiltration test of carbon fibres textile by modiefied AlSi9Cu(Fe) alloy[J]. Composites,2009,9(3):201-213.
[9] ZHANG Y, YAN L, MIAO M, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of z-pinned carbon fiber reinforced aluminum alloy composites[J]. Material and Design,2015,86(5):872-877.
[10] ALHASHMY H A, NGANBE M. Laminate squeeze casting of carbon fiber reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Material and Design,2015,67:154-158. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.11.034
[11] 周珍珍, 徐志锋, 余欢, 等. 编织结构对3D-Cf/Al 复合材料显微组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(4):773-781. ZHOU Zhenzhen, XU Zhifeng, YU Huan, et al. Effects of braiding structures on microstructure and mechanical properties of 3D-Cf/Al composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2016,26(4):773-781(in Chinese).
[12] 胡银生, 余欢, 王振军, 等. 织物结构对2.5D-Cf/Al复合材料微观组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(12):2512-2522. HU Yinsheng, YU Huan, WANG Zhenjun, et al. Effect of woven fabric structure on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2.5D-Cf/Al composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2018,28(12):2512-2522(in Chinese).
[13] ZHANG Y, WU G, CHEN G, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 2D woven Grf/Al composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2006,16:1509-1512.
[14] MA YQ, QI L H, ZHENG W Q, et al. Effect of specific pressure on fabrication of 2D-Cf/Al composite by vacuum and pressure infiltration[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2013,23:1915-1921. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62677-1
[15] 周计明, 郑武强, 齐乐华, 等. 真空吸渗挤压二维正交铺层复合材料压缩失效机制[J]. 上海大学学报, 2014, 20(1):75-82. ZHOU Jiming, ZHENG Wuqiang, QI Lehua, et al. Investigation on compressive failure mechanism of 2D cross-ply Cf/Al composites by extrusion directly following vacuum pressure infiltration process[J]. Journal of Shanghai University,2014,20(1):75-82(in Chinese).
[16] HUFENBACH W, GUDE M, CZULAK A. Development of textile-reinforced carbon fibre aluminium composites manufactured with gas pressure infiltration methods[J]. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering,2009,2(35):177-183.
[17] YANG Q R, LIU J X, LI S K, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of Cu-coated woven carbon fibers reinforced aluminum alloy composite[J]. Materials & Design,2014,57:442-448.
[18] YANG Q R, LIU J X, LI S K, et al. Bending mechanical property and failure mechanisms of woven carbon fiber-reinforced aluminum alloy composite[J]. Rare Metals,2016,35(12):915-919. DOI: 10.1007/s12598-014-0271-x
[19] ZHANG J, LIU S, ZHANG Y, et al. Fabrication of woven carbon fibers reinforced Al-Mg (95-5wt%) matrix composites by an electromagnetic casting process[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2015,226:78-84. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.06.040
[20] ZHANG J, LIU S, LU Y, et al. Semisolid-rolling and annealing process of woven carbon fiber reinforced Al-matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2017,33:623-629.
[21] LEE S K, BYUN J H, HONG S H. Effect of fiber geometry on the elastic constants of the plain woven fabric reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2003,347:346-358. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00614-7
[22] MCWILLIAMS B, DIBELKA J, YEN C. Multiscale modeling and characterization of inelastic deformation mechanisms in continuous fiber and 2D woven fabric reinforced metal matrix composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2014,618:142-152. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.08.063
[23] SHIRVANIMOGHADDAM K, HAMIM S U, AKBARI M, et al. Carbon fiber reinforced metal matrix composites: Fabrication processes and properties[J]. Composites: Part A,2017,92:70-96. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.10.032
[24] 王振军, 董敬涛, WANG Gui, 等. 2.5维织物Cf/Al复合材料制备及其经纬向拉伸变形力学行为研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(12):3744-3752. WANG Zhenjun, DONG Jingtao, WANG Gui, et al. Research on the preparation of 2.5D woven fabric Cf/Al composite and its tensile deformation behavior in warp/weft direction[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2017,46(12):3744-3752(in Chinese).
[25] ASTM. Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Fiber Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites: ASTM D3552-96[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2007.
[26] 聂明明, 徐志锋, 余欢, 等. 基体合金对连续M40石墨纤维/Al复合材料纤维损伤及断裂机制的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(12):2797-2806. NIE Mingming, XU Zhifeng, YU Huan, et al. Effect of matrix alloy on fiber damage and fracture mechanism of continuous graphite fiber M40/Al composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(12):2797-2806(in Chinese).
[27] CHAMIS C C. Simplified composite micromechanics equations for strength, fracture toughness, impact resistance and environmental effects, TM-83696[R]. Washington: NASA, 1984.
[28] WANG Y C, HUANG Z M. Analytical micromechanics models for elastoplastic behavior of long fibrous composites: A critical review and comparative study[J]. Materials,2018,11:10.
[29] 周金秋, 王振军, 杨思远, 等. 连续石墨纤维增强铝基复合材料准静态拉伸损伤演化与断裂力学行为[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(4):907-918. ZHOU Jinqiu, WANG Zhenjun, YANG Siyuan, et al. Damage evolution and fracture behaviors of continuous CF/Al composites subjected to quasi-static tensile loading[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(4):907-918(in Chinese).
[30] WANG Z J, WANG Z Y, XIONG B W, et al. Micromechanics analysis on the microscopic damage mechanism and mechanical behavior of graphite fiber-reinforced aluminum composites under transverse tension loading[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,815:152459. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152459
[31] WANG Z J, YANG S Y, DU Z H, et al. Micromechanical modeling of damage evolution and mechanical behaviors of CF/Al composites under transverse and longitudinal Tensile Loadings[J]. Materials,2019,12(19):3133. DOI: 10.3390/ma12193133
[32] SONG J, WEN W D, CUI H T. Experimental and numerical investigation of mechanical behaviors of 2.5D woven composites at ambient and un-ambient temperatures[J]. Composite Structures,2018,201:699-720. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.06.054
[33] LU Z X, ZHOU Y, YANG Z Y, et al. Multi-scale finite element analysis of 2.5D woven fabric composites under on-axis and off-axis tension[J]. Computational Materials Science,2013,79:485-494. DOI: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.07.003
[34] OKABE T, NISHIKAWA M, TOYOSHIMA H. A periodic unit-cell simulation of fiber arrangement dependence on the transverse tensile failure in unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced composites[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2011,48:2948-2959. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2011.06.012
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 李存静,陶洋,逄增媛,张典堂. 2.5D机织碳纤维-玻璃纤维/双马来酰亚胺树脂复合材料高温力学行为及损伤机制. 复合材料学报. 2024(01): 144-154 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 徐瑞,王颖杰,张伟,王海楼. 三维角联锁衬经机织复合材料的纱线形态及力学性能分析. 南通大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(02): 74-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李聪聪,钟林,金礼月,黄晓梅,曹海建. 深角联芳纶1414织物复合材料拉伸性能研究. 棉纺织技术. 2023(04): 57-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王颖杰,王海楼,张伟. 不同衬经纱占比的三维角联锁机织增强复合材料弯曲性能. 复合材料学报. 2023(06): 3291-3301 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 胡嘉彬,徐自立,余联庆,刘海量. 3D-CF/Al复合材料宏细观结构与力学性能研究进展. 制造技术与机床. 2023(09): 131-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 童德,蔡长春,王振军,刘燕武,张益豪,余欢,徐志锋. 2.5D机织C_f/Al复合材料热残余应力与热变形细观力学分析. 航空材料学报. 2022(02): 73-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 朱超,吴宁,张一帆,焦亚男,陈利,刘刚. 三维角联锁机织铺层复合材料的拉伸性能与失效机制. 复合材料学报. 2022(07): 3167-3177 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 李聪聪,黄晓梅,曹海建,陈红霞. 三维深角联Kevlar/PA装甲材料拉伸性能的模拟分析. 化工新型材料. 2022(08): 126-129+134 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-




 下载:
下载: