Analyses on flexural behavior of GFRP-reinforced crumb rubber concrete beams
-
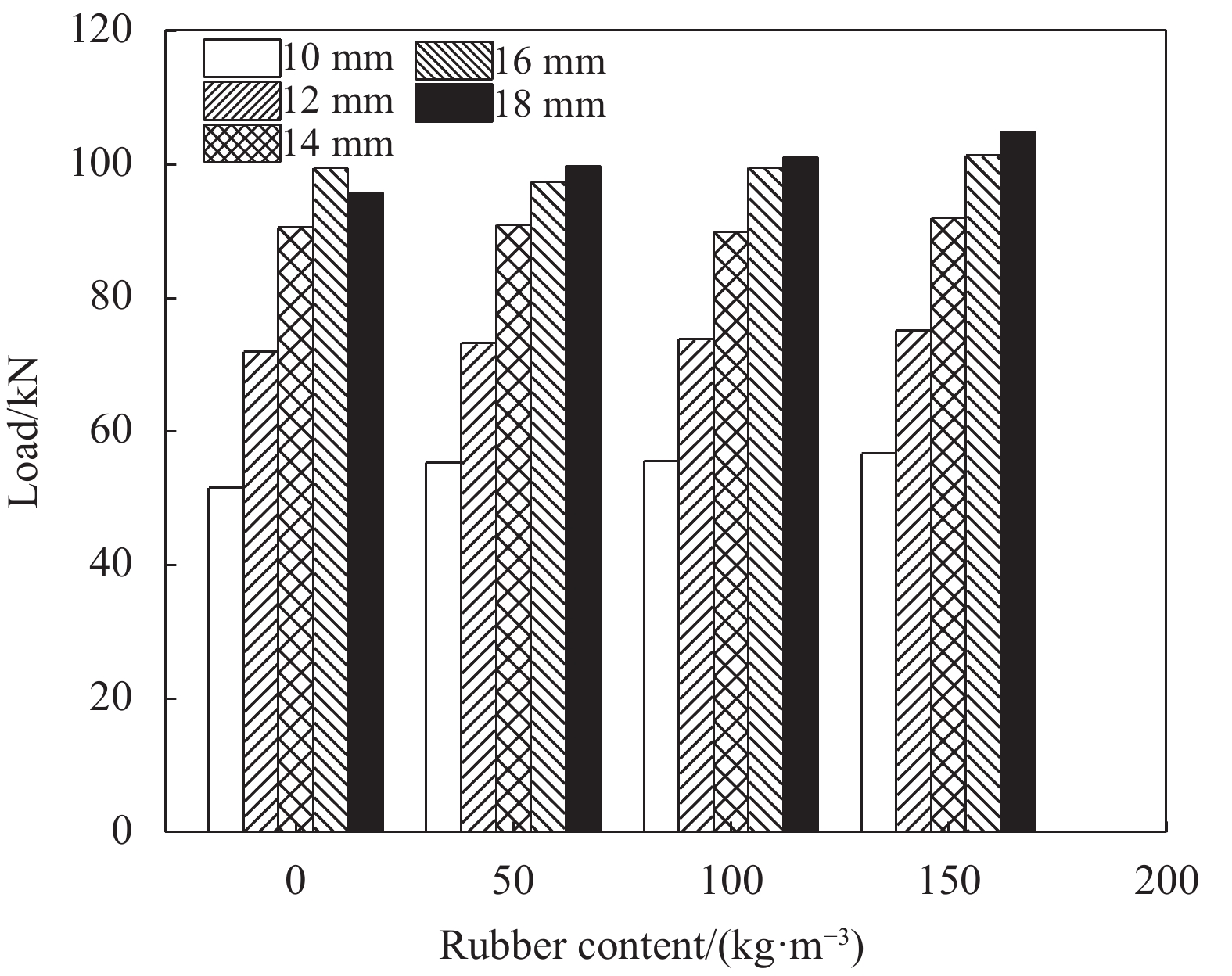
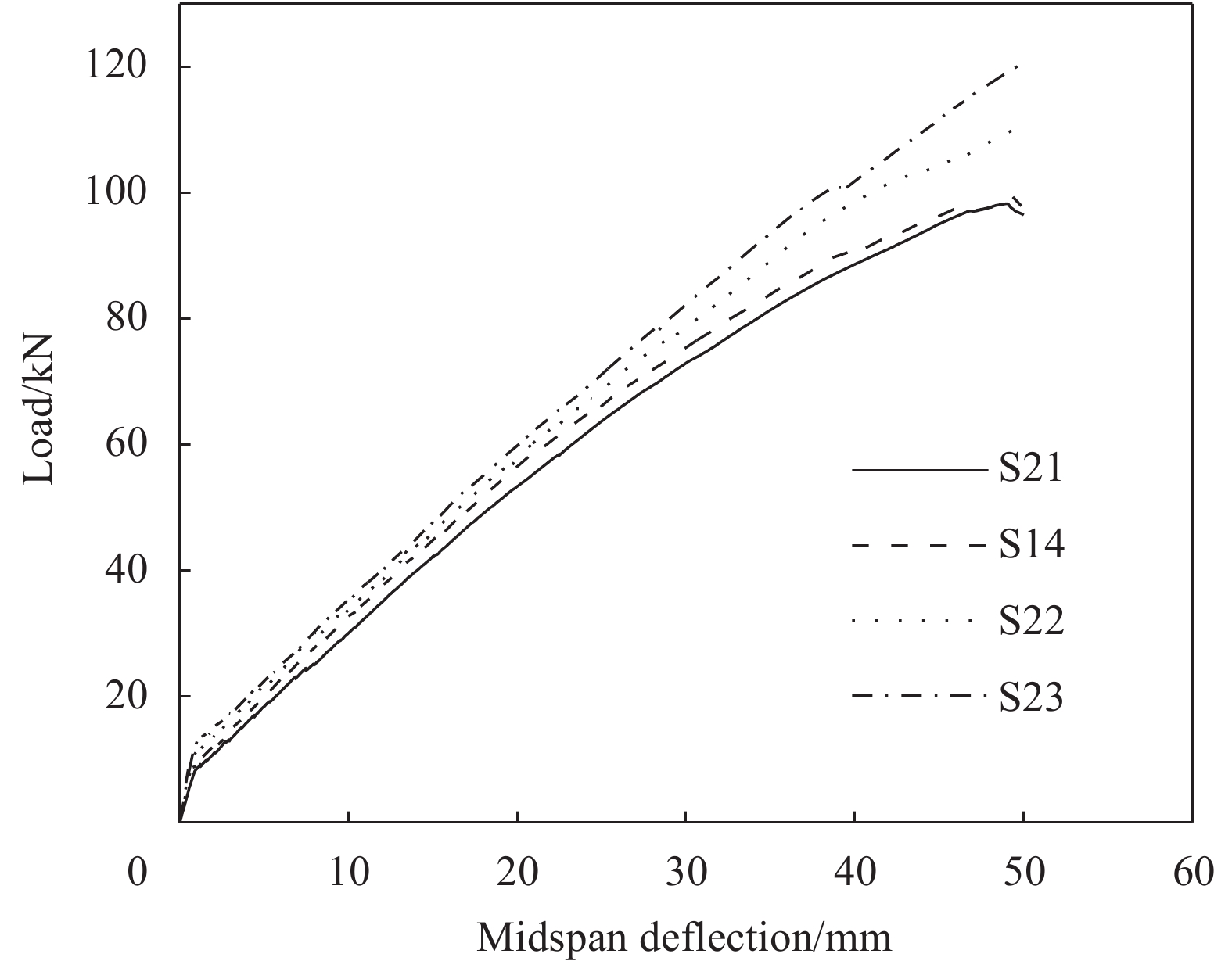
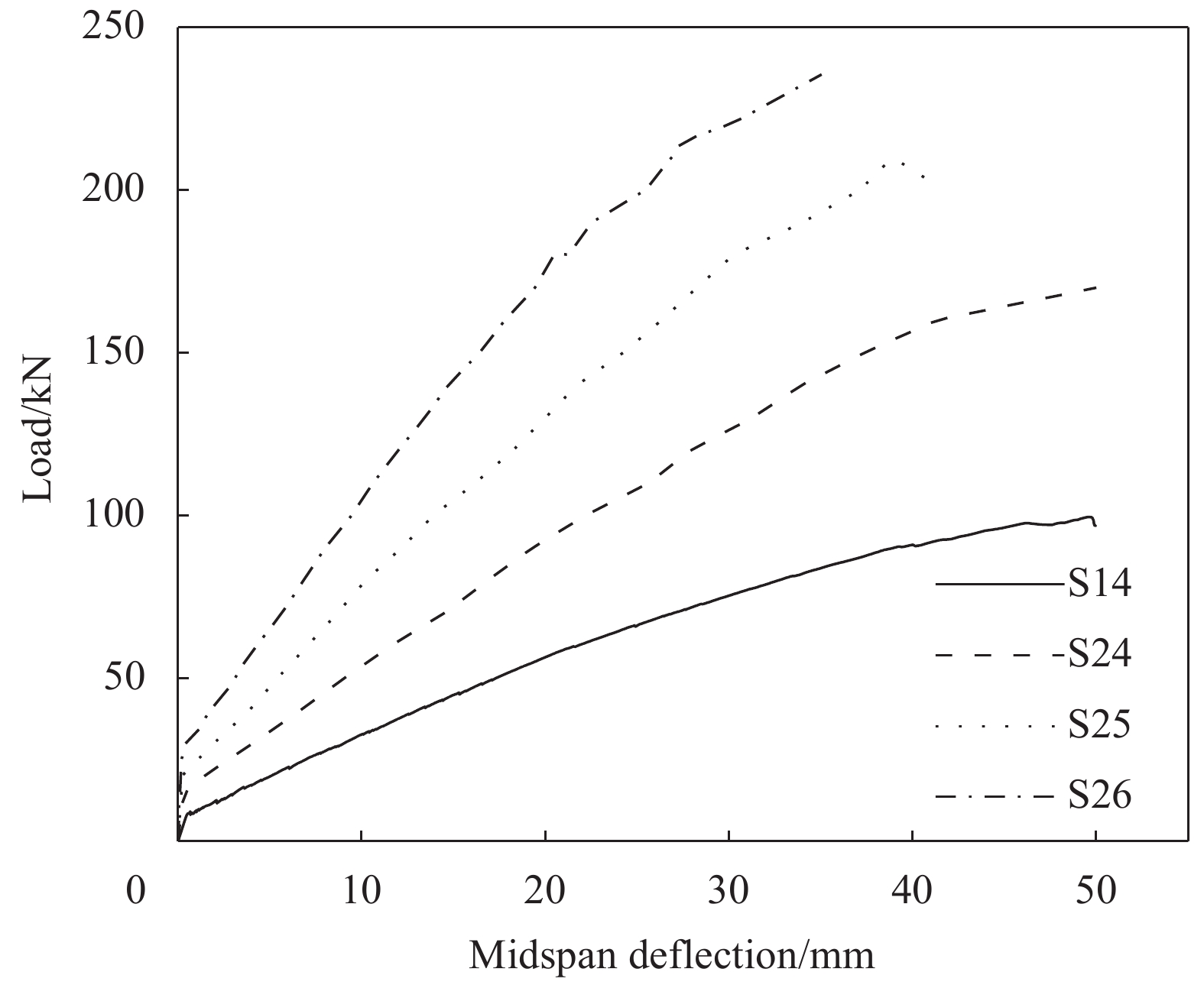
摘要: 为提高纤维增强聚合物复合材料(FRP)筋混凝土梁抗裂性能,改善其脆性破坏特征,将玻璃纤维增强聚合物复合材料(GFRP)筋与橡胶集料混凝土共同应用于梁构件中。采用ABAQUS对GFRP筋橡胶集料混凝土梁的受弯性能进行有限元模拟及参数分析,探究了橡胶掺量、GFRP筋配筋率、混凝土强度等级及截面高度对梁受弯性能的影响。结果表明:增加混凝土中橡胶颗粒的掺量可提高梁的开裂荷载,当橡胶掺量为15%时,开裂荷载提高了29%;增加配筋率可提高梁的开裂荷载和承载力,当受拉筋直径由10 mm增加至18 mm时,橡胶掺量为10%的GFRP筋橡胶混凝土梁开裂荷载提高了约15%,承载力提高了约85%,但配筋率增加至一定数值后,其影响不再明显;提高橡胶混凝土强度等级,可提高梁的开裂荷载及承载力,当橡胶混凝土强度等级由C25提高至C40时,开裂荷载提了高约53.7%,承载力提高了约23%;为更好地满足正常使用极限状态,GFRP筋橡胶混凝土梁的截面高度宜适当增加。Abstract: In order to improve the crack resistance capacity, and avoid the brittle failure of the fiber-reinforced polymer composite (FRP) reinforced concrete beams, a mixed-use of glass fiber-reinforced polymer composite (GFRP) bars and crumb rubber concrete was adopted in beam components under bending. Finite element analysis software ABAQUS was used to simulate the flexural behavior of GFRP-reinforced crumb rubber concrete beams. Parametric studies were conducted to study the influence of rubber content, reinforcement ratio, concrete strength grade, and cross-section height on the flexural behavior of GFRP-reinforced crumb rubber concrete beams. The results show that the cracking load of beam increases with the increase of rubber content. The cracking load of beam increases by 29% when the rubber content of concrete is 15%. Increasing the reinforcement ratio could improve the cracking load and flexural strength of the beam. The cracking load of the GFRP-reinforced crumb rubber concrete beam with rubber replacement ratio of 10% has a 15% increase and the flexural strength of the beam has 85% increase induced by increasing the diameter of the GFRP bar from 10 mm to 18 mm. However, when the reinforcement ratio reaches a certain value, the influence is no longer obvious. Increasing the crumb rubber concrete strength can improve the cracking load and flexural strength of the beam. Increasing the crumb rubber concrete strength from C25 to C40 results in approximately 53.7% increase in cracking load, and more than 23% increase in flexural strength. The beams with higher section height are more likely to meet the requirements at normal serviceable limit state.
-
-
表 1 不同橡胶掺量混凝土配合比
Table 1 Mix proportion of concrete with different rubber contents
Type Rubber/% Crumb
rubber/kgCement/
kgWater/
kgFine
aggregate/kgCoarse
aggregate/kgSuper
Plasticizer/%TC 0 0 300 165 839 1087 2.40 5% CRC 5 50 400 180 939 768 5.20 10% CRC 10 100 440 162 680 832 4.78 Notes: CRC—Crumb rubber concrete; TC—Traditional concrete. 表 2 不同橡胶掺量混凝土强度及弹性模量
Table 2 Strength and elastic modulus of concrete with different rubber contents
Type Cubic compressive
strength/MPaSplit tensile
strength/MPaAxial compressive
strength/MPaElastic
modulus/GPa7 d 28 d 50 d 28 d 50 d 50 d TC 23.5 29.8 31.0 2.11 25.5 30.8 5% CRC 22.7 29.1 29.9 1.82 24.7 27.9 10% CRC 24.9 32.9 33.2 2.00 25.5 30.6 表 3 玻璃纤维增强聚合物复合材料(GFRP)筋橡胶混凝土梁试件主要参数
Table 3 Key parameters of glass fiber-reinforced polymer composite (GFRP)-reinforced crumb rubber concrete beams
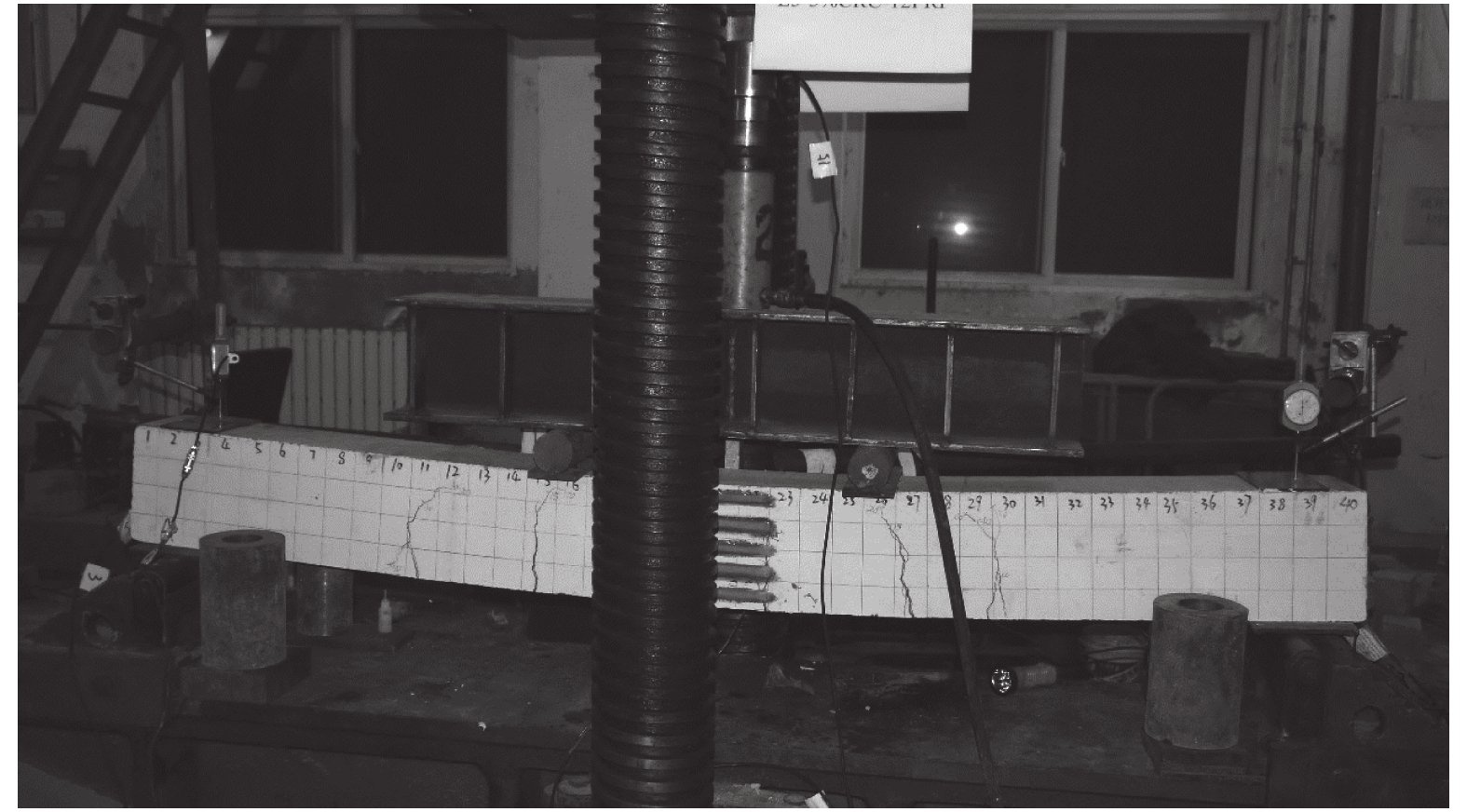
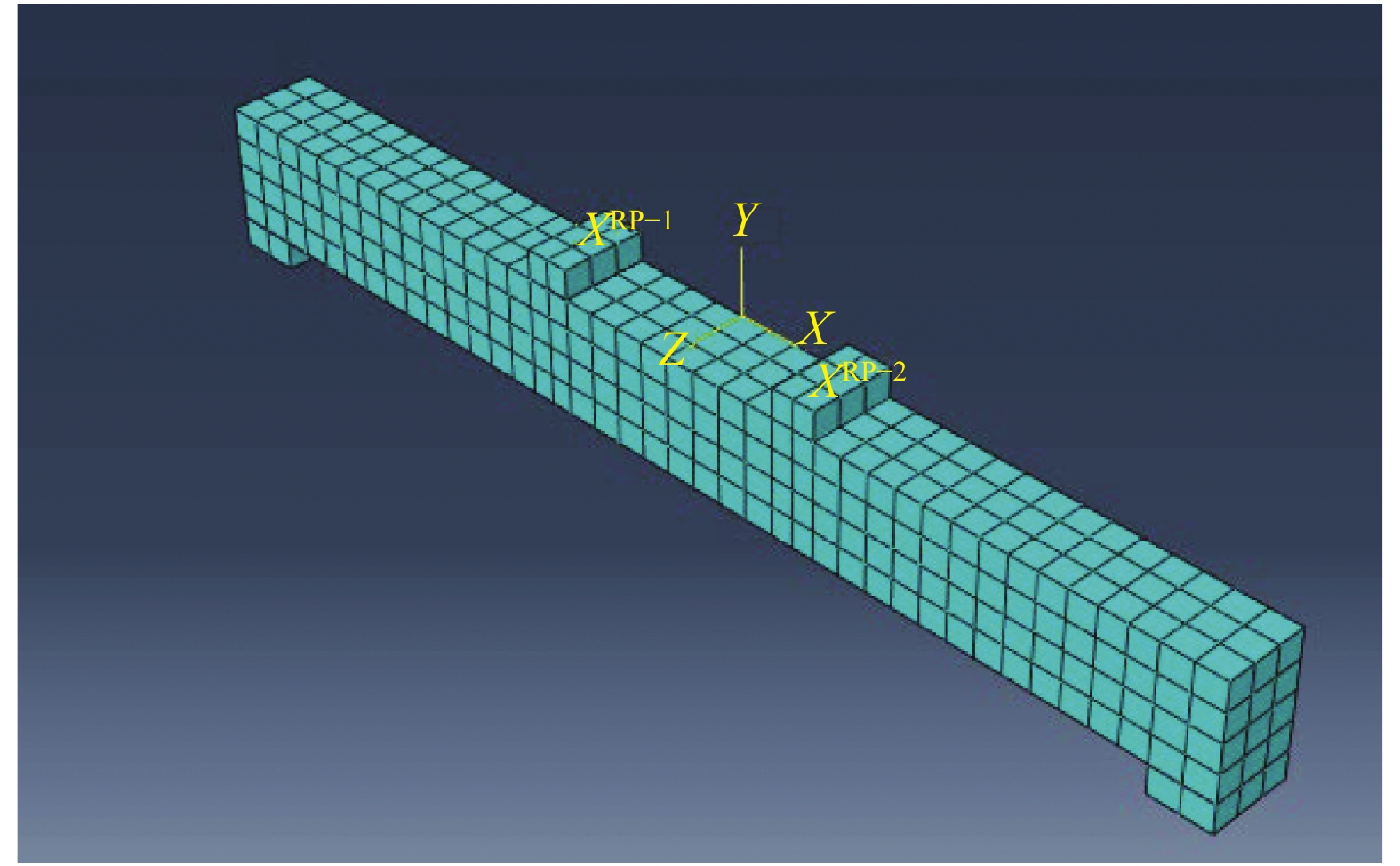
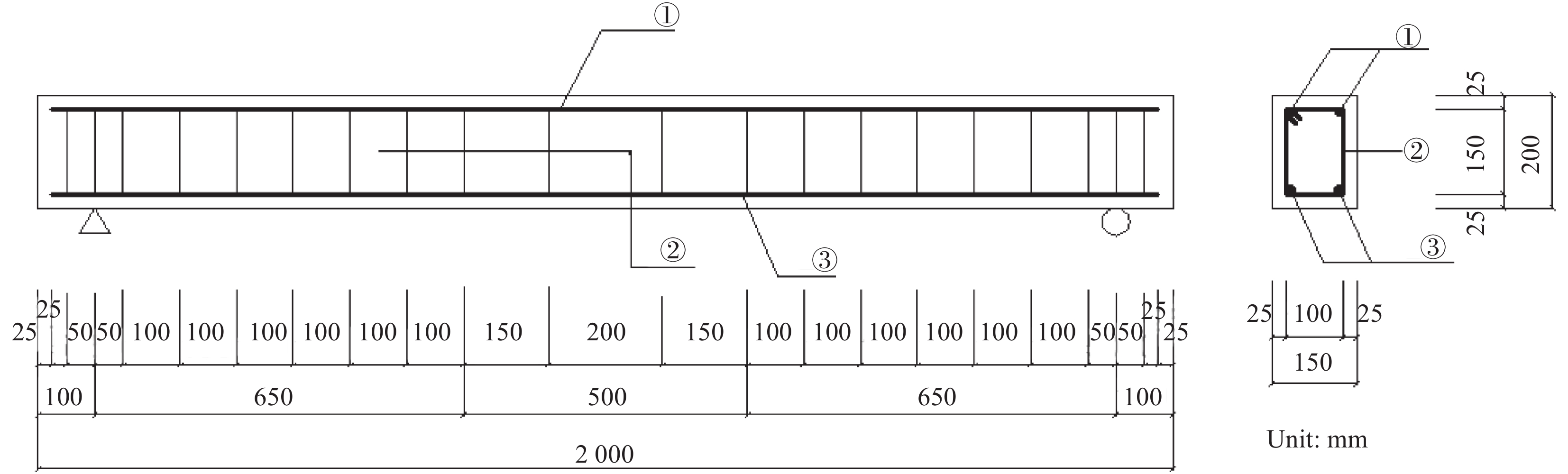
Specimen Span l0/
mmEffective height h0/
mmRubber
content of
concrete/%Erecting
bar ①Stirrup ② Longitudinal
reinforcement ③Longitudinal
reinforcement ratio/%Group 1 B1 (Steel/TC) 1800 161 0 2 

2 
1.665 B2 (GFRP/TC) 1800 163 0 2 

2-12FRP 0.924 B3 (GFRP/5% CRC) 1800 163 5 2 

2-12FRP 0.924 B4 (GFRP/10% CRC) 1800 163 10 2 

2-12FRP 0.924 Group 2 B5 (GFRP/5% CRC) 1800 161 5 2 

2-16FRP 1.665 B6 (GFRP/10% CRC) 1800 161 10 2 

2-16FRP 1.665 表 4 B1~B6试件的有限元分析和试验的开裂荷载和极限荷载
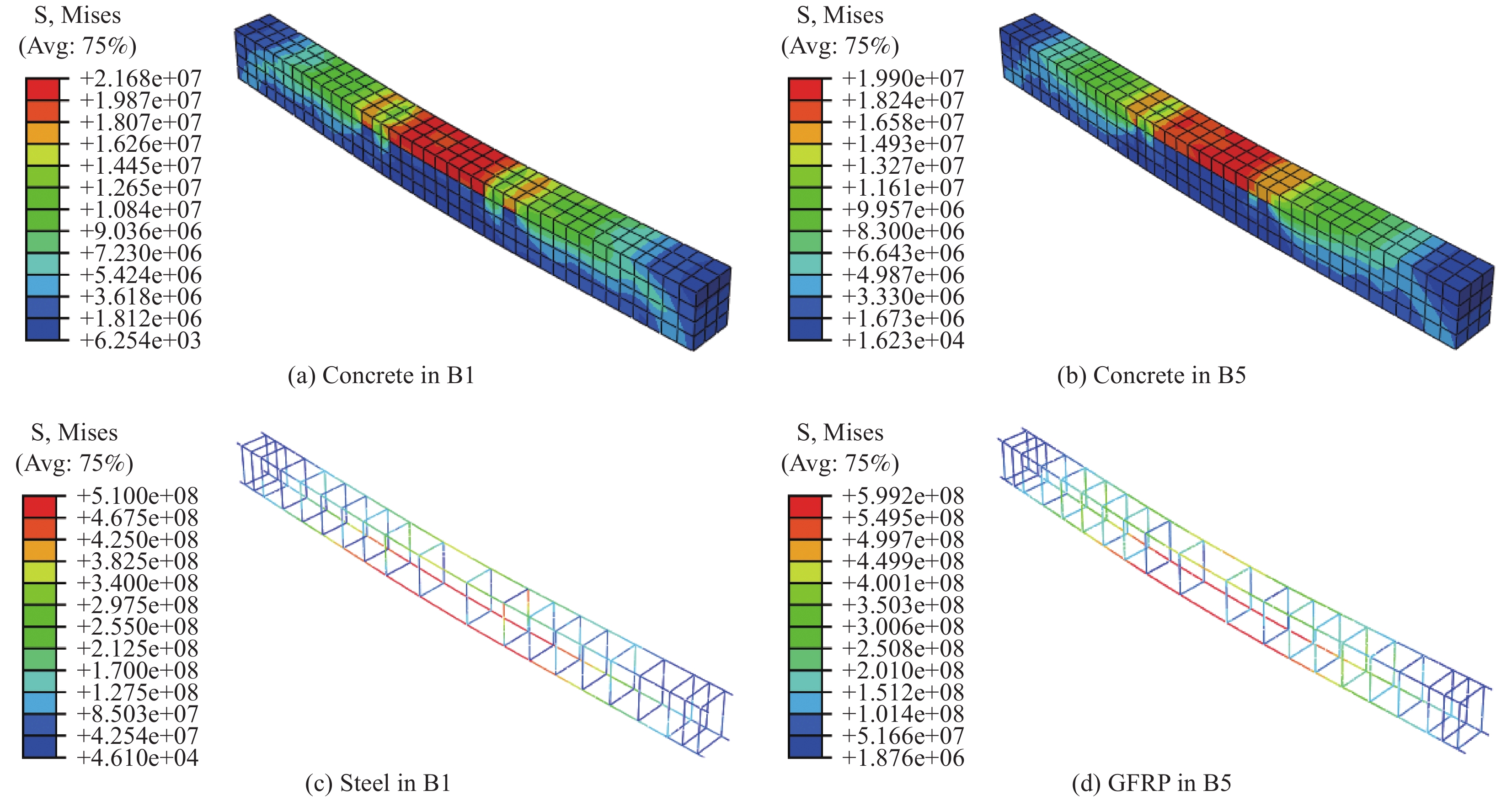
Table 4 Crack load and ultimate load of B1−B6 specimens by FEA and test
Specimen Load/kN Test value FEA value FEA/Test B1 (Steel/TC beam) Crack 18.5 14.9 0.81 Ultimate 92.0 90.3 0.98 B2 (GFRP/TC beam) Crack 8.5 8.2 0.96 Ultimate 77.0 74.2 0.96 B3 (GFRP/5% CRC beam) Crack 10.0 9.4 0.94 Ultimate 71.0 74.6 1.05 B4 (GFRP/10% CRC beam) Crack 10.5 10.2 0.97 Ultimate 81.0 79.2 0.98 B5 (GFRP/5% CRC beam) Crack 10.0 9.5 0.95 Ultimate 102.0 103.0 1.01 B6 (GFRP/10% CRC beam) Crack 10.5 10.3 0.98 Ultimate 99.0 116.0 1.17 表 5 有限元模型参数设计
Table 5 Parameter design of finite element models
Model Rubber content
of concrete/%FRP bar
diameter/mmStrength grade
of concreteBeam section
height/mmCracking
load/kNUltimate
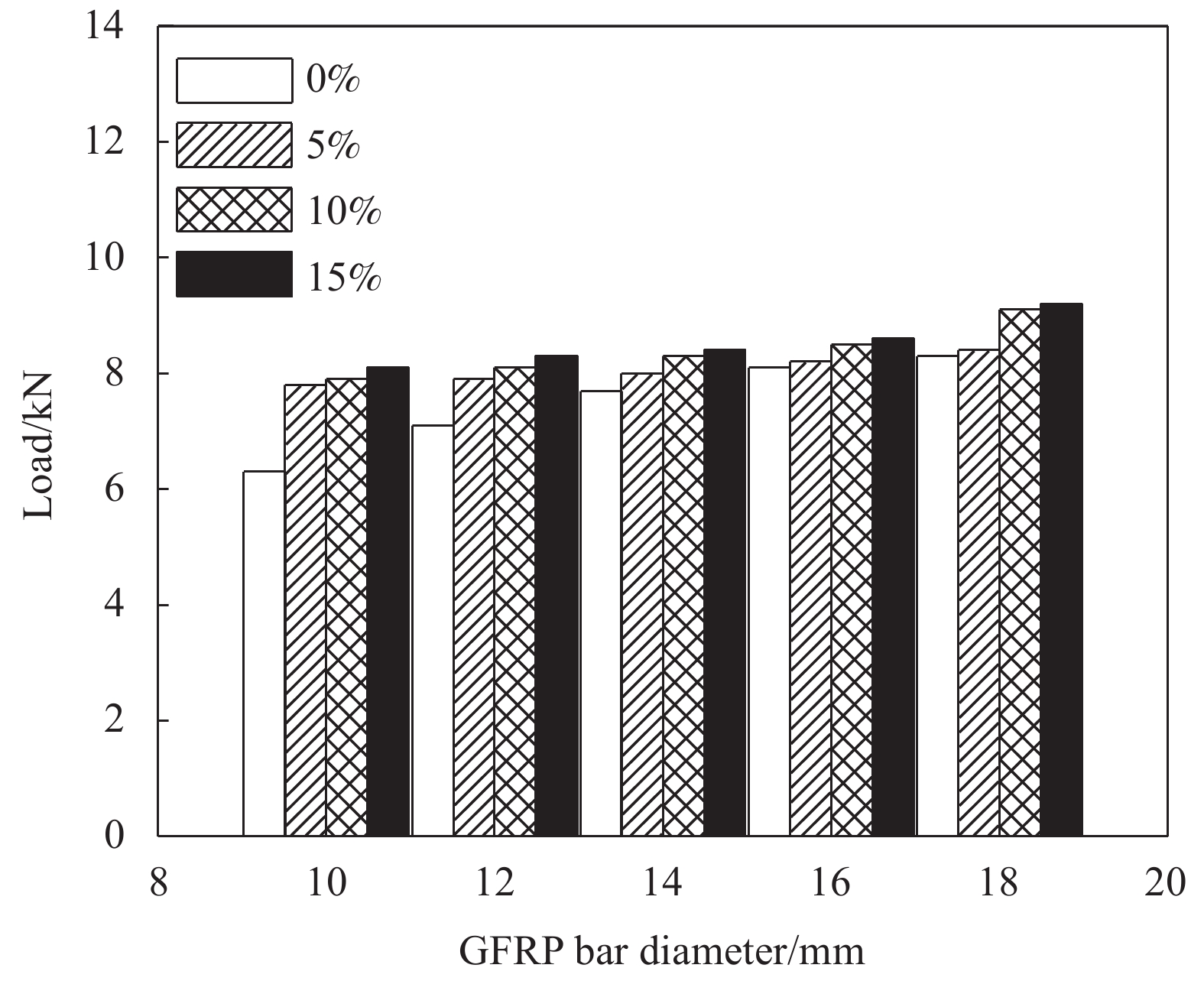
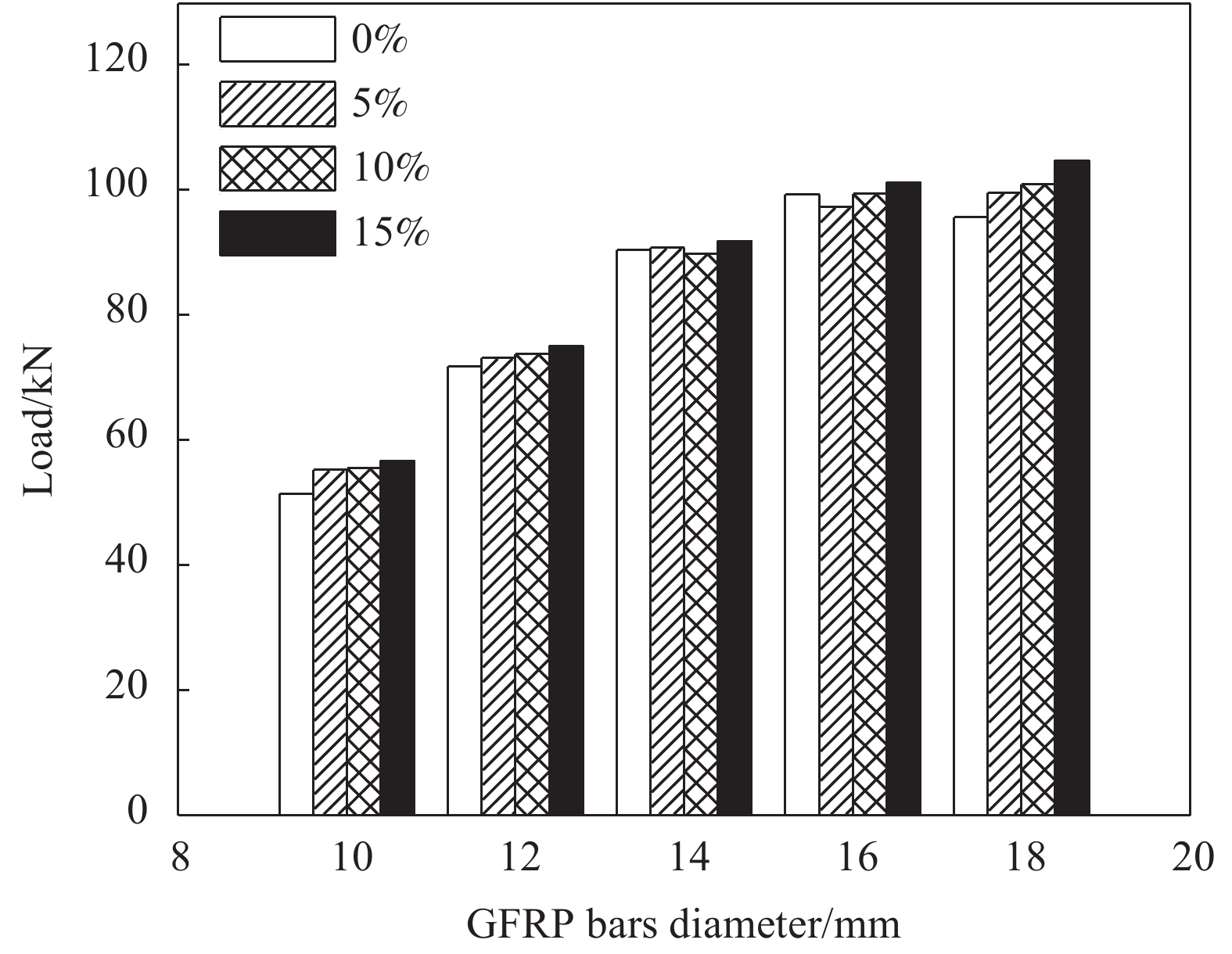
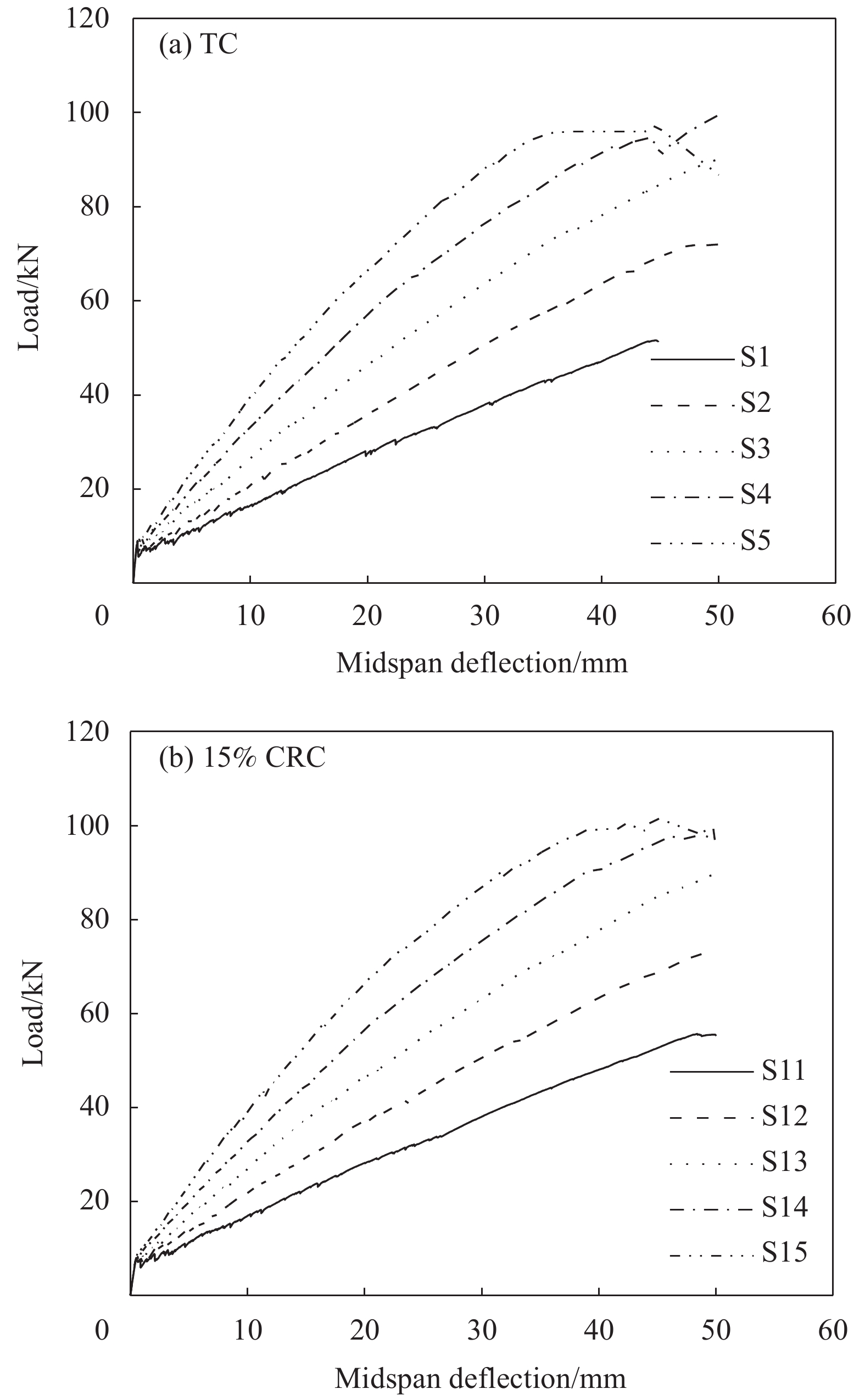
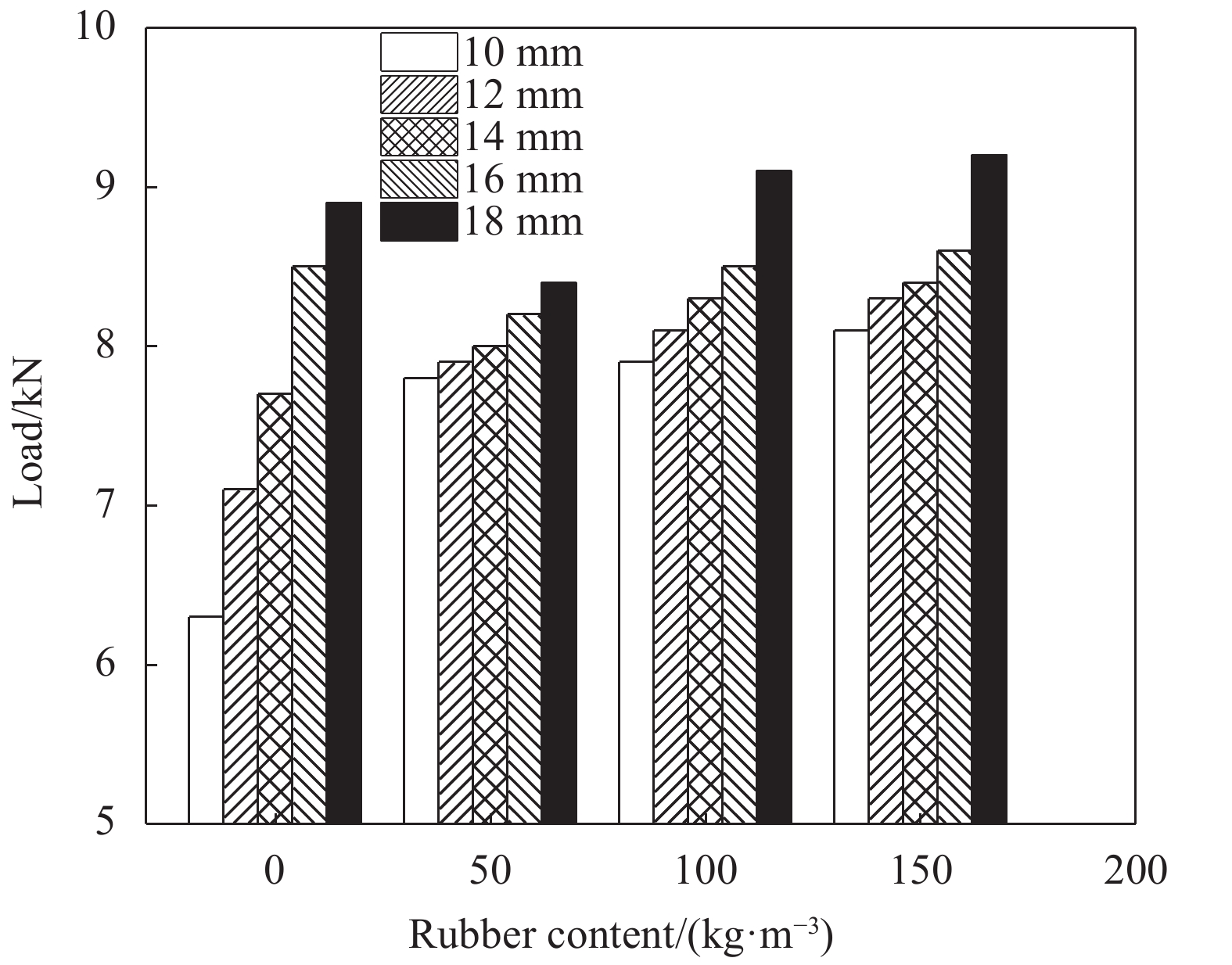
load/kNS1 0 10 C30 200 6.3 51.5 S2 0 12 C30 200 7.1 71.9 S3 0 14 C30 200 7.7 90.5 S4 0 16 C30 200 8.1 99.4 S5 0 18 C30 200 8.3 95.7 S6 5 10 C30 200 7.8 55.3 S7 5 12 C30 200 7.9 73.2 S8 5 14 C30 200 8.0 90.9 S9 5 16 C30 200 8.2 97.4 S10 5 18 C30 200 8.4 99.7 S11 10 10 C30 200 7.9 55.5 S12 10 12 C30 200 8.1 73.8 S13 10 14 C30 200 8.3 89.9 S14 10 16 C30 200 8.5 99.5 S15 10 18 C30 200 9.1 101.0 S16 15 10 C30 200 8.1 56.7 S17 15 12 C30 200 8.3 75.1 S18 15 14 C30 200 8.4 91.9 S19 15 16 C30 200 8.6 101.3 S20 15 18 C30 200 9.2 104.8 S21 10 16 C25 200 8.2 98.1 S22 10 16 C35 200 10.2 110.9 S23 10 16 C40 200 12.6 120.7 S24 10 16 C30 250 12.7 170.1 S25 10 16 C30 300 20.5 211.8 S26 10 16 C30 350 26.5 235.6 表 6 不同橡胶掺量混凝土本构参数
Table 6 Constitutive parameters of crumb rubber concret with different rubber contents
Type Peak strain/
10−6Axial compressive
strength/MPaβ TC 2 000 25 2.01 5% CRC 3400 25 2.01 10% CRC 4300 25 2.01 15% CRC 4500 25 2.01 Note: β—Ratio coefficient of plastic strain to inelastic strain. 表 7 极限受弯承载力FEA模拟值与理论值对比
Table 7 Comparison of ultimate flexural capacity from FEA and calculation
Specimen
and modelρf/ρfb Ultimate flexural capacity
from calculation Mt/(kN·m)Ultimate flexural capacity
form FEA Mn/(kN·m)Mn/Mt S6 0.86 17.400 17.973 1.03 S7 1.25 21.185 23.790 1.12 S8 1.72 23.298 29.543 1.27 S9 2.58 25.115 31.655 1.26 S10 3.28 26.673 32.403 1.21 S11 0.76 17.394 18.038 1.04 S12 1.11 22.498 23.985 1.07 S13 1.52 24.635 29.218 1.19 S14 2.27 26.448 32.338 1.22 S15 2.89 27.982 32.825 1.17 S16 0.77 17.373 18.428 1.06 S17 1.11 22.399 24.408 1.09 S18 1.52 24.500 29.868 1.22 S19 2.28 26.276 32.923 1.25 S20 2.91 27.773 34.060 1.23 S21 2.84 23.563 31.883 1.35 S22 1.89 28.910 36.043 1.25 S23 1.62 31.046 39.228 1.26 S24 1.74 41.489 55.283 1.33 S25 1.41 59.361 68.835 1.16 S26 1.18 79.535 76.570 0.96 B3 1.92 21.177 23.075 1.09 B4 1.25 22.490 26.325 1.17 B5 1.11 25.115 33.150 1.32 B6 2.58 26.448 32.175 1.22 Average value 1.184 Coefficient of variation 0.083 Notes: ρf-Reinforcement ratio of GFRP bars under longitudinal stress; ρfb-Balance reinforcement ratio of GFRP reinforced concrete beams. -
[1] 吕志涛. 高性能材料FRP应用于结构工程创新[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2005, 22(1):2-5. LV Zhitao. Application of high performance FRP and innovations of structure engineering[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering,2005,22(1):2-5(in Chinese).
[2] 叶列平, 冯鹏. FRP在工程结构中的应用与发展[J]. 土木工程学报, 2006, 39(3):24-36. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2006.03.004 YE Lieping, FENG Peng. Applications and development of fiber-reinforced polymer in engineering structures[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2006,39(3):24-36(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2006.03.004
[3] NAWY E G, NEUWERTH G E, PHILLIPS C J. Behavior of fiber glass reinforced concrete beams[J]. Journal of the Structural Division,1971,97(9):2203-2215.
[4] MASMOUDI R, THERIAULT M, BENMOKRANE B. Flexural behavior of concrete beams reinforced with deformed fiber reinforced plastic rods[J]. ACI Structural Journal,1998,95(6):665-676.
[5] THERIAULT M, BENMOKRANE B. Effects of FRP reinforced ration and concrete strength on flexural behavior of concrete beams[J]. Journal of Composites for Construction. February,1998,2(1):7-15. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0268(1998)2:1(7)
[6] 朱虹, 吴刚, 吴智深, 等. FRP筋混凝土梁的刚度试验研究和理论计算[J]. 土木工程学报, 2015, 48(11):44-53. ZHU Hong, WU Gang, WU Zhishen, et al. Experimental study and theoretical calculation on the flexural stiffness of concrete beams reinforced with FRP bars[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2015,48(11):44-53(in Chinese).
[7] 董志强, 吴刚. 基于试验数据分析的FRP筋混凝土受弯构件最大裂缝宽度计算方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2017, 50(10):1-8. DONG Zhiqiang, WU Gang. Calculation method for the maximum crack width of FRP bar reinforced concrete flexural member based on experimental data analysis[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2017,50(10):1-8(in Chinese).
[8] 徐新生. FRP筋力学性能及其混凝土梁受弯性能研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2007. XU Xinsheng. Research on mechanical property of FRP bars and flexural property of concrete beams with FRP bars[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2007(in Chinese).
[9] 屈妍. 橡胶集料混凝土力学性能试验研究[J]. 混凝土, 2012(2):96-98. QU Yan. Experimental study on mechanical properties of rubber aggregate concrete[J]. Concrete,2012(2):96-98(in Chinese).
[10] 董建伟, 袁琳, 朱涵. 橡胶集料混凝土的试验研究及工程应用[J]. 混凝土, 2006(7):74-76, 83. DONG Jianwei, YUAN Lin. ZHU Han. Experiment analysis and application of crumb rubber concrete[J]. Concrete,2006(7):74-76, 83(in Chinese).
[11] 李悦, 吴玉生, 杨玉红, 等. 钢筋橡胶集料混凝土结构性能研究[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2008, 34(12):1280-1285. LI Yue, WU Yusheng, YANG Yuhong, et, al. Study on the structure properties of steel reinforced crumb rubber concrete[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2008,34(12):1280-1285(in Chinese).
[12] 郭红梅, 朱涵. 钢筋橡胶集料混凝土梁的抗裂性能研究[J]. 混凝土, 2012(12):11-13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2012.12.005 GUO Hongmei, ZHU Han. Study on cracking resistance of reinforced crumb rubber concrete beam[J]. Concrete,2012(12):11-13(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2012.12.005
[13] 朱涵, 刘春生, 张永明, 等. 橡胶集料掺量对混凝土压弯性能的影响[J]. 天津大学学报, 2007, 40(7):761-765. ZHU Han, LIU Chunsheng, ZHANG Yongming, et, al. Effect of crumb rubber proportion on compressive and flexural behavior of concrete[J]. Journal of Tianjin University,2007,40(7):761-765(in Chinese).
[14] 刘锋, 潘东平, 李丽娟, 等. 低强橡胶混凝土单轴受压本构关系的试验研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2007, 10(4):407-411. LIU Feng, PAN Dongping, LI Lijuan, et, al. Experimental study on constitutive equation of crumb rubber concrete subject to uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2007,10(4):407-411(in Chinese).
[15] 赵秋红, 王菲, 朱涵. 结构用橡胶集料混凝土受压全曲线试验及其本构模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(8):2222-2234. ZHAO Qiuhong, WANG Fei, ZHU Han. Compression test on curves and constitutive model of crumb rubber concrete for structural purposes[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(8):2222-2234(in Chinese).
[16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构试验方法标准: GB/T 50152—2012[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for test methods of concrete structures: GB/T 50152—2012[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2012(in Chinese).
[17] 王菲. FRP筋橡胶集料混凝土梁受弯性能试验研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2017. WANG Fei. Experimental study on flexural behavior of FRP-reinforced crumb rubber concrete beams[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2017(in Chinese).
[18] XING Y, HAN Q, XU J, et al. Experimental and numerical study on static behavior of elastic concrete-steel composite beams[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2016,123:79-92. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.04.023
[19] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构设计规范: GB 50010—2010[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for design of concrete structures: GB 50010—2010[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2011(in Chinese).
[20] 方自虎, 周海俊, 赖少颖, 等. ABAQUS混凝土应力-应变关系选择[J]. 建筑结构, 2013, 43(s2):559-561. FANG Zihu, ZHOU Haijun, LAI Shaoying, et al. Choose of ABAQUS concrete stress-strain curve[J]. Building Structure,2013,43(s2):559-561(in Chinese).
[21] 刘劲松, 刘红军. ABAQUS钢筋混凝土有限元分析[J]. 装备制造技术, 2009(6):69-70. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-545X.2009.06.028 LIU Jinsong, LIU Hongjun. Finite element analysis of ABAQUS reinforced concrete[J]. Equipment Manufacturing Technology,2009(6):69-70(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-545X.2009.06.028
[22] 庄茁, 张帆, 岑松, 等. ABAQUS非线性有限元分析与实例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005. ZHUANG Zhuo, ZHANG Fan, CENG Song, et, al. ABAQUS nonlinear finite element analysis and examples[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005(in Chinese).
[23] CARREIRA D J, CHU K H. Stress-strain relationship for plain concrete in compression[J]. Journal of the American Concrete Institute,1985,82(6):797-804.
[24] YAN J B, LI Z X, XIE J. Numerical and parametric studies on steel-elastic concrete composite structures[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2017,133:84-96. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2017.02.010
[25] HAN Q H, WANG Y H, XU J, et al. Static behavior of stud shear connectors in elastic concrete-steel composite beams[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2015,113:115-126.
[26] EL-NEMR A, AHMED E A, BENMOKRANE B. Flexural behavior and serviceability of normal- and high-strength concrete beams reinforced with glass fiber-reinforced polymer bars[J]. ACI Structural Journal,2013,110(6):1077-1087.
[27] American Concrete Institute Committee 440. Guide for the design and construction of structural concrete reinforced with fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) bars: ACI 440.1R—15[S]. Farmington Hills: American Concrete Institute, 2015.
[28] Canadian Standard Association. Design and construction of building structures with fiber reinforced polymers: CSA S806—12[S]. Ontario: Canadian Standard Association, 2012.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 张有茶,贾成厂,贾鹏. 中间相碳微球/氰酸酯树脂复合材料的导电导热性能. 复合材料学报. 2019(03): 602-610 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张新庄,张书勤,闫鹏,裴婷,窦倩,董昭,王姗姗. 聚丙烯基石墨烯改性复合材料的导电及热稳定性. 化学工业与工程. 2019(06): 60-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 胡荣杰,甯尤军,肖藤,雷玲,阿拉木斯,胡宁. 石墨烯/环氧树脂纳米复合材料的制备与热膨胀特性分析. 重庆大学学报. 2018(06): 50-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 洪新密,肖小亭,吴雅莎,杨洁,何穗华. 超声振动对闪光铝颜料填充HDPE复合材料流变行为和性能的影响. 高分子材料科学与工程. 2018(04): 82-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐子威,张婧婧,何穗华,赖永健,杨涛,余浩斌. 螺杆剪切对聚丙烯/石墨烯微片纳米复合材料形态和性能的影响. 塑料科技. 2018(02): 56-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)
-




 下载:
下载: