Preparation and performance of modified SiO2 gel coating filter material
-
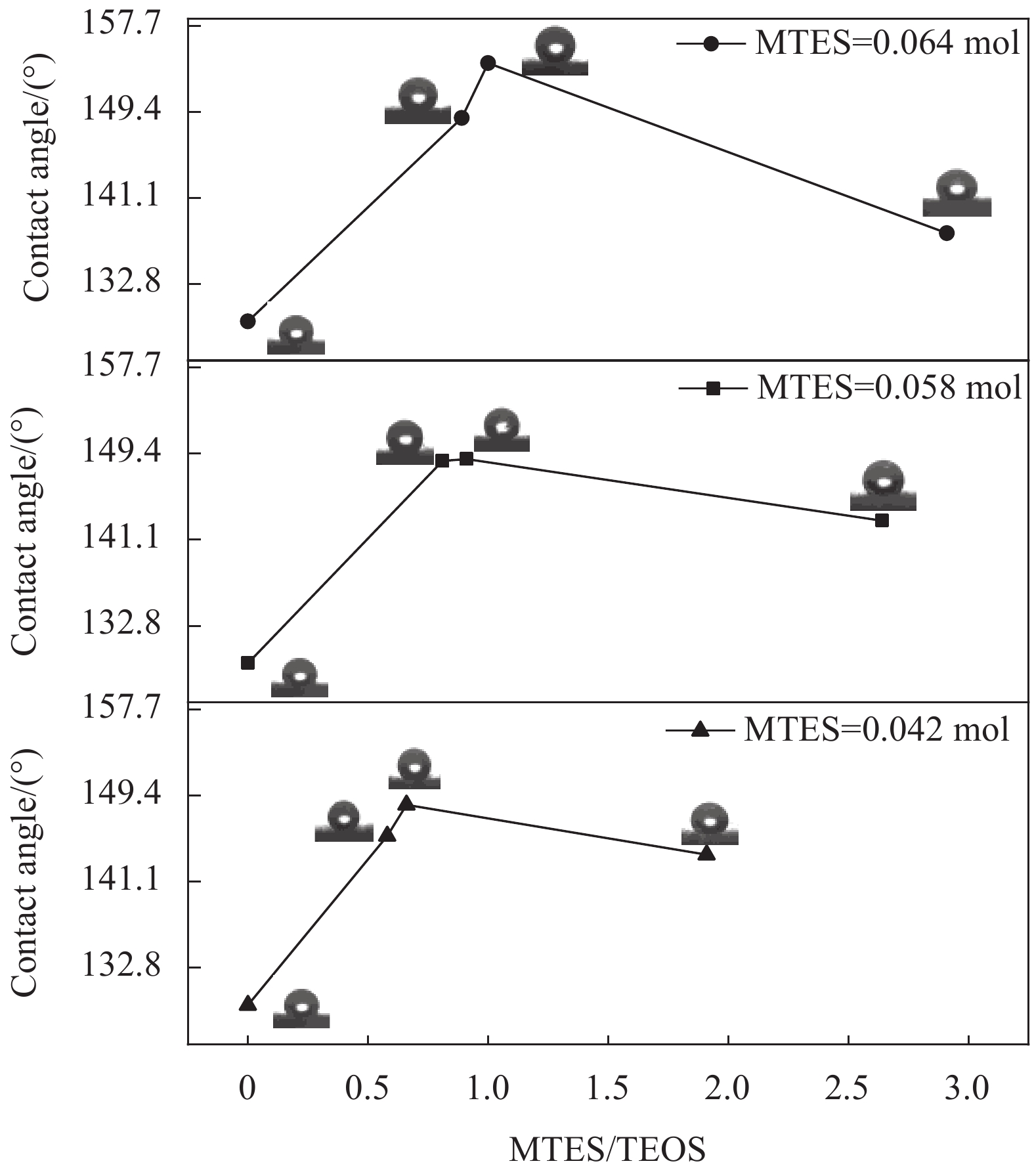
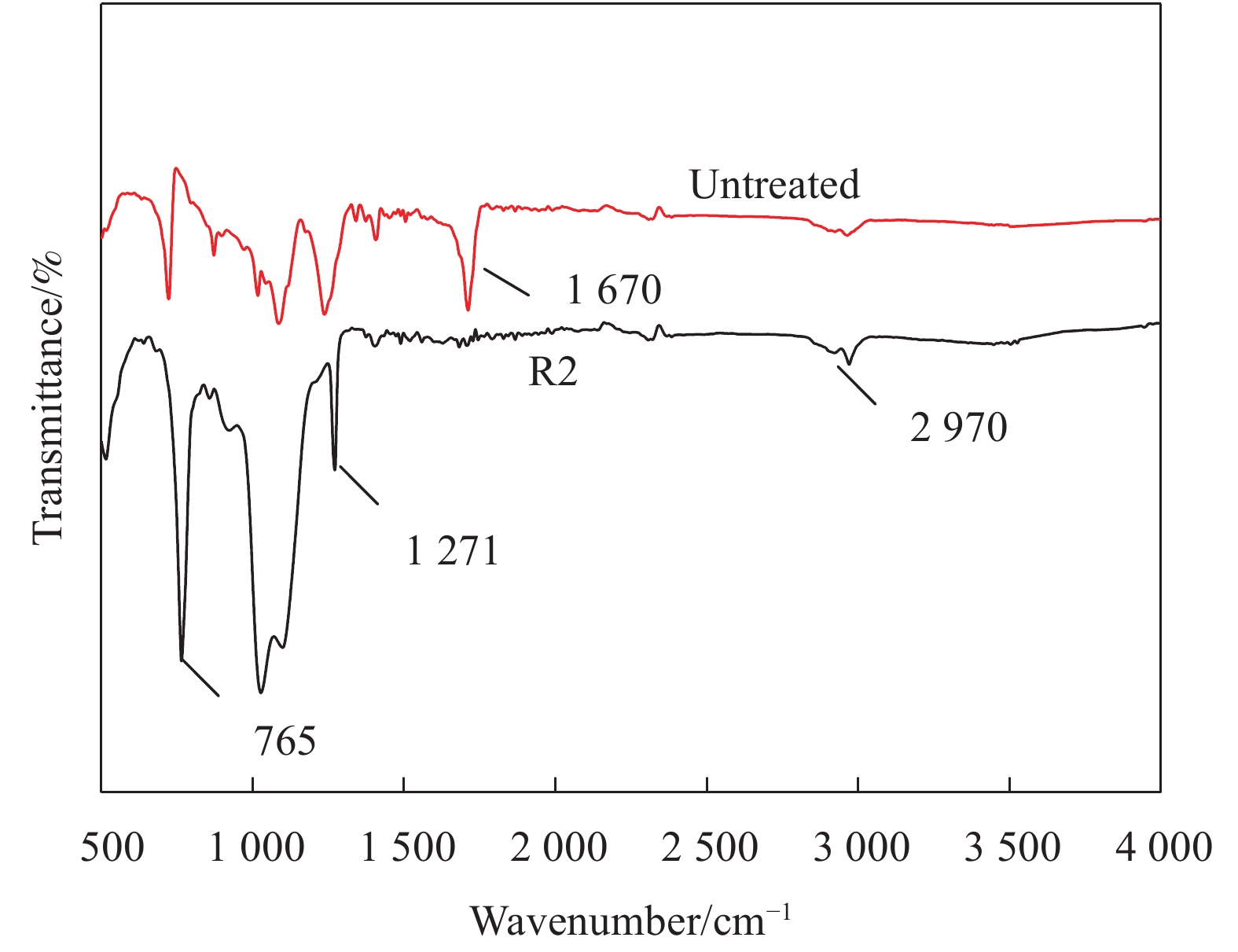
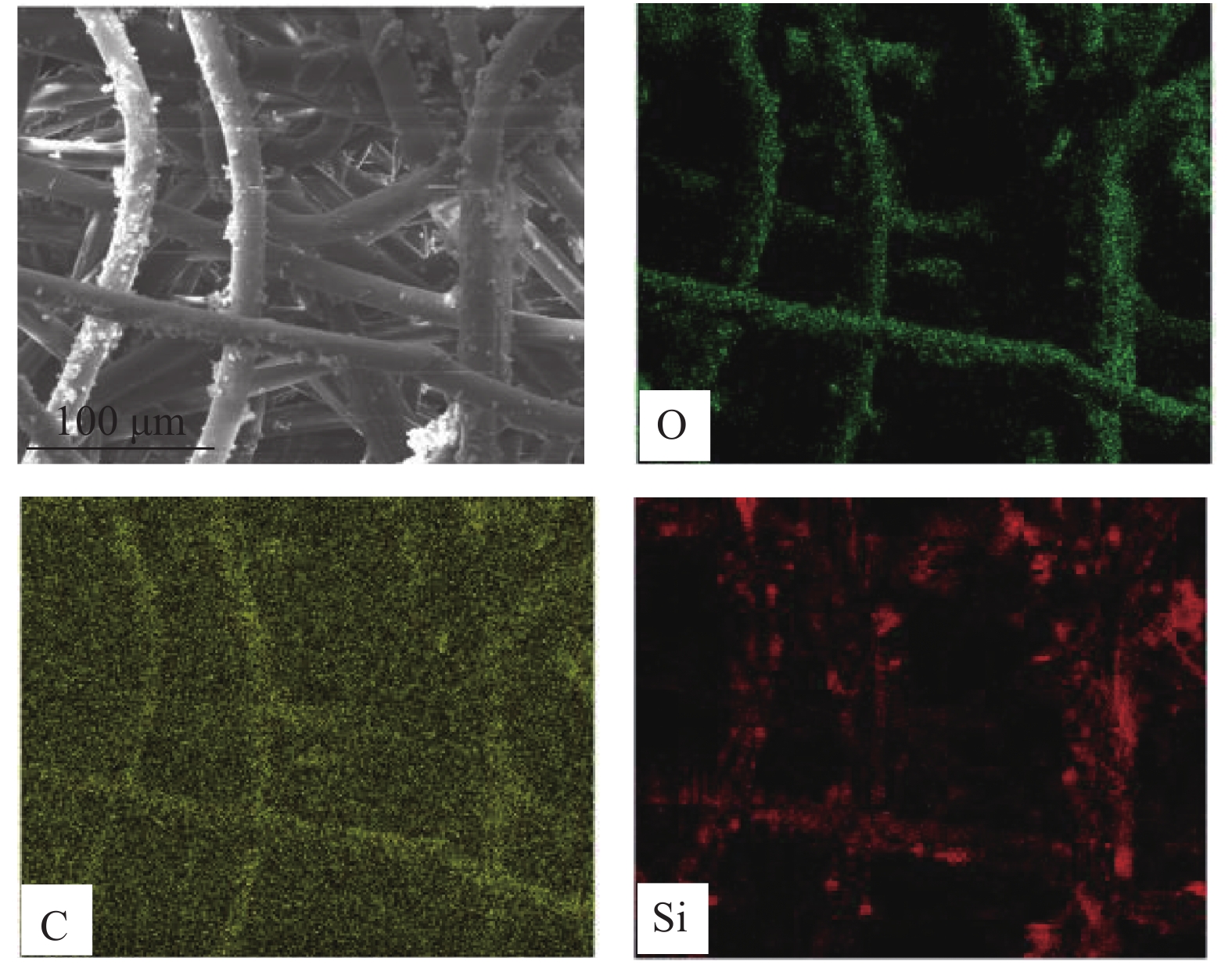
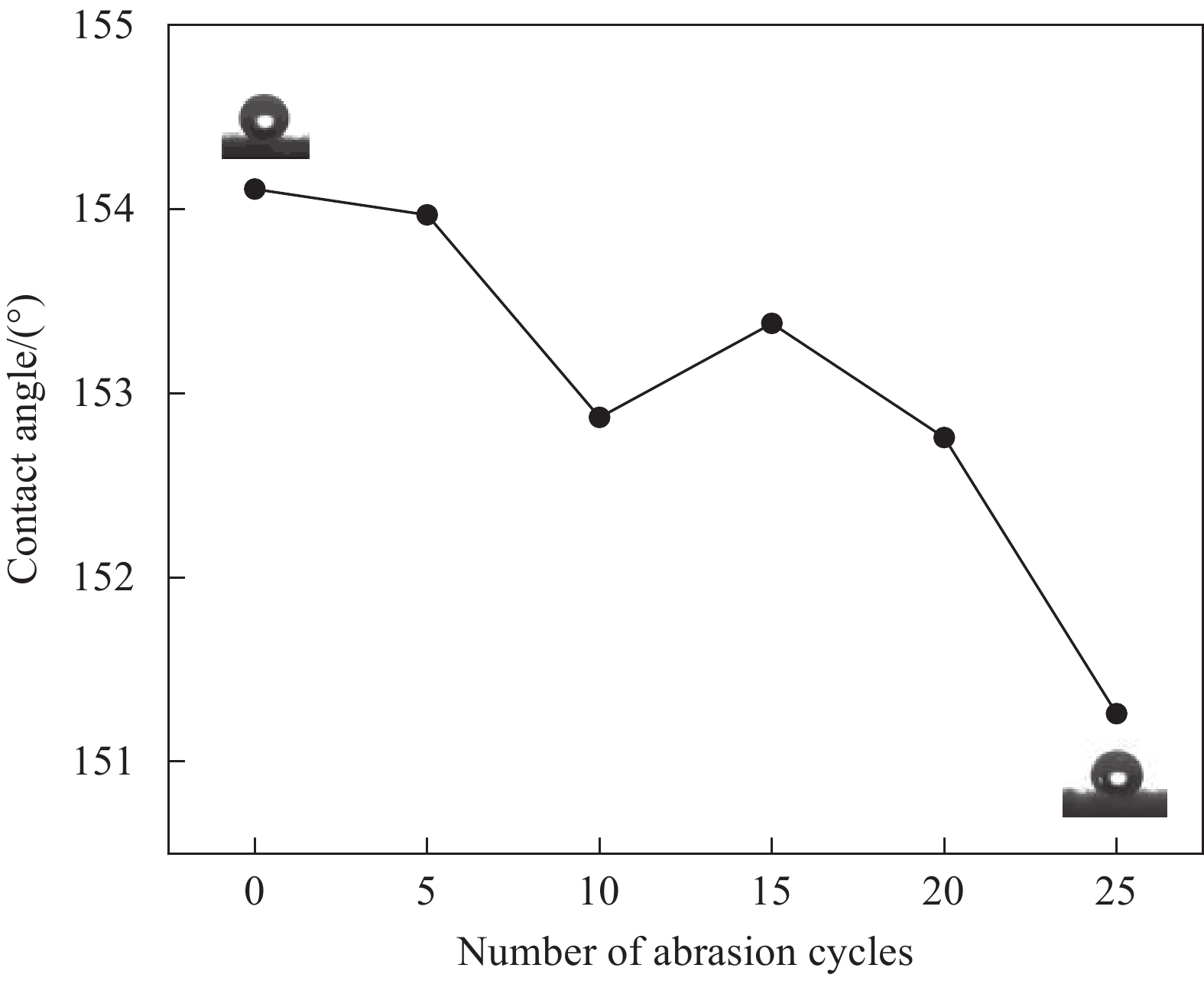
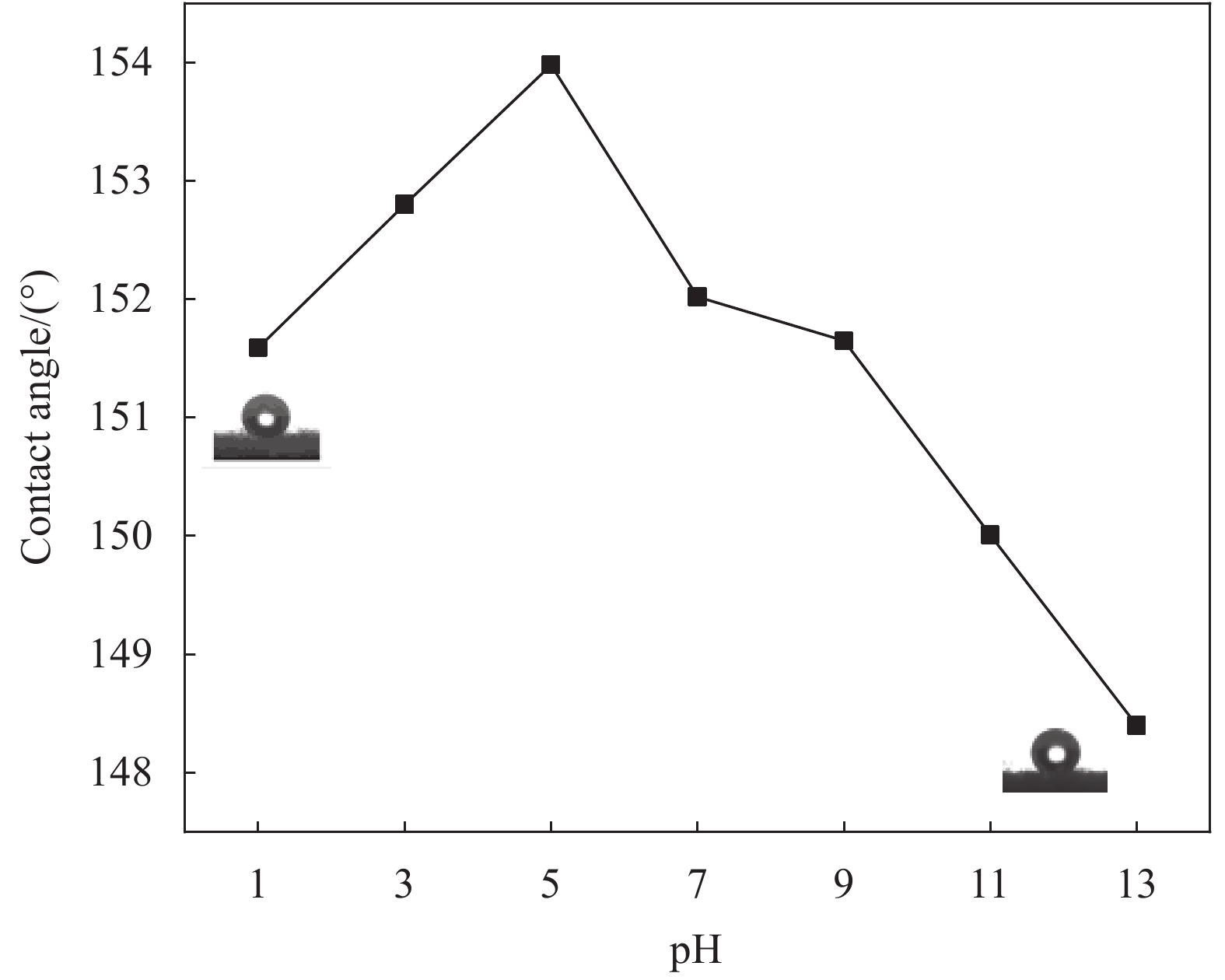
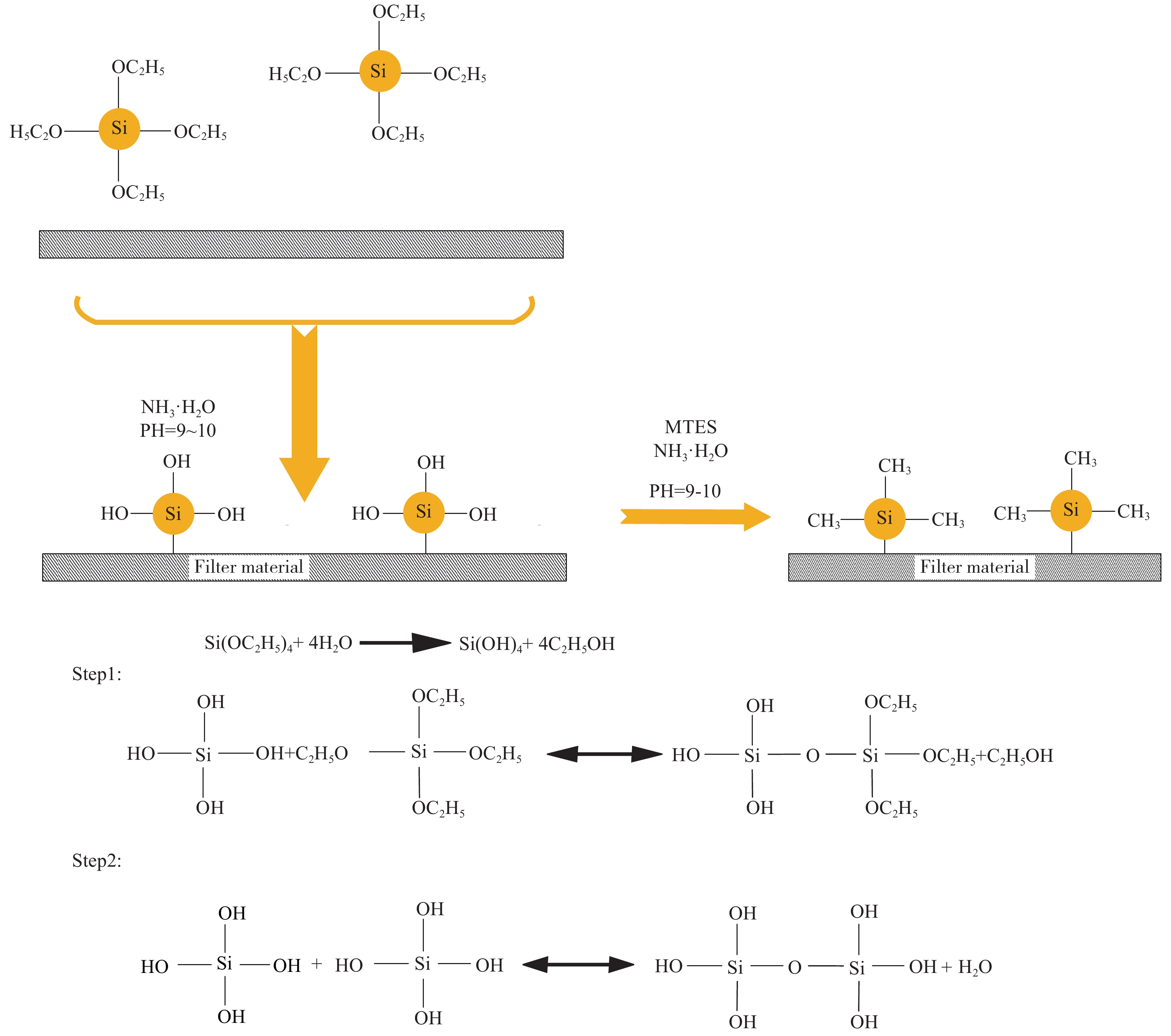
摘要: 从滤料表面改性的角度对提高滤料在高湿环境中运行的稳定性进行研究。以聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)滤料为基材、正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)为前驱体、甲基三乙氧基硅烷(MTES)为低表面能物质,采用溶胶-凝胶法,在滤料表面原位生成SiO2纳米粒子,制备改性SiO2凝胶涂层滤料。采用FESEM- EDS、FTIR和接触角测量仪分析了PET滤料表面化学成分、润湿性能及表面形貌的变化。结果表明:整理后PET滤料表面生成SiO2纳米粒子,经MTES改性处理后滤料表面布满疏水的甲基基团,滤料疏水性能显著提高,其表面水接触角达154.11°。SiO2颗粒在滤料表面均匀分布,凝胶聚合物仅在纤维交叉处沉积,使滤料透气性得以保证,过滤效率由97.0595%增加到99.2028%,过滤品质因数由0.02124增加到0.02761,提升了30%。
-
关键词:
- 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)纤维滤料 /
- 超疏水特性 /
- 过滤性能 /
- 高湿黏性颗粒 /
- 溶胶-凝胶法
Abstract: In this paper, from the perspective of surface modification of filter material, how to improve its stability in high humidity environment has been studied. Using polyethylene terephthalate (PET) filter material as the substrate, ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as the precursor, and methyltriethoxysilane (MTES) as the low surface energy substance, the sol-gel method was used to generate in-situ on the surface of the filter material SiO2 nanoparticles to prepare modified SiO2 gel-coated filter material. Then, FESEM-EDS, FTIR and a contact angle measuring instrument were used to analyze the changes in the surface chemical composition, wettability and surface morphology of the PET filter material. The results show that SiO2 nanoparticles are formed on the surface after finishing, and the surface is covered with hydrophobic methyl groups after MTES modification treatment. Thus, its hydrophobic property is significantly improved, and its surface water contact angle reaches 154.11°. At the same time, the SiO2 particles are evenly distributed on the surface, and the gel polymer is only deposited at the intersection of the fibers, which ensures air permeability, and the filtration efficiency increases from 97.0595% to 99.2028%, and the filtration quality factor increases by 30%, from 0.02124 to 0.02761. -
-
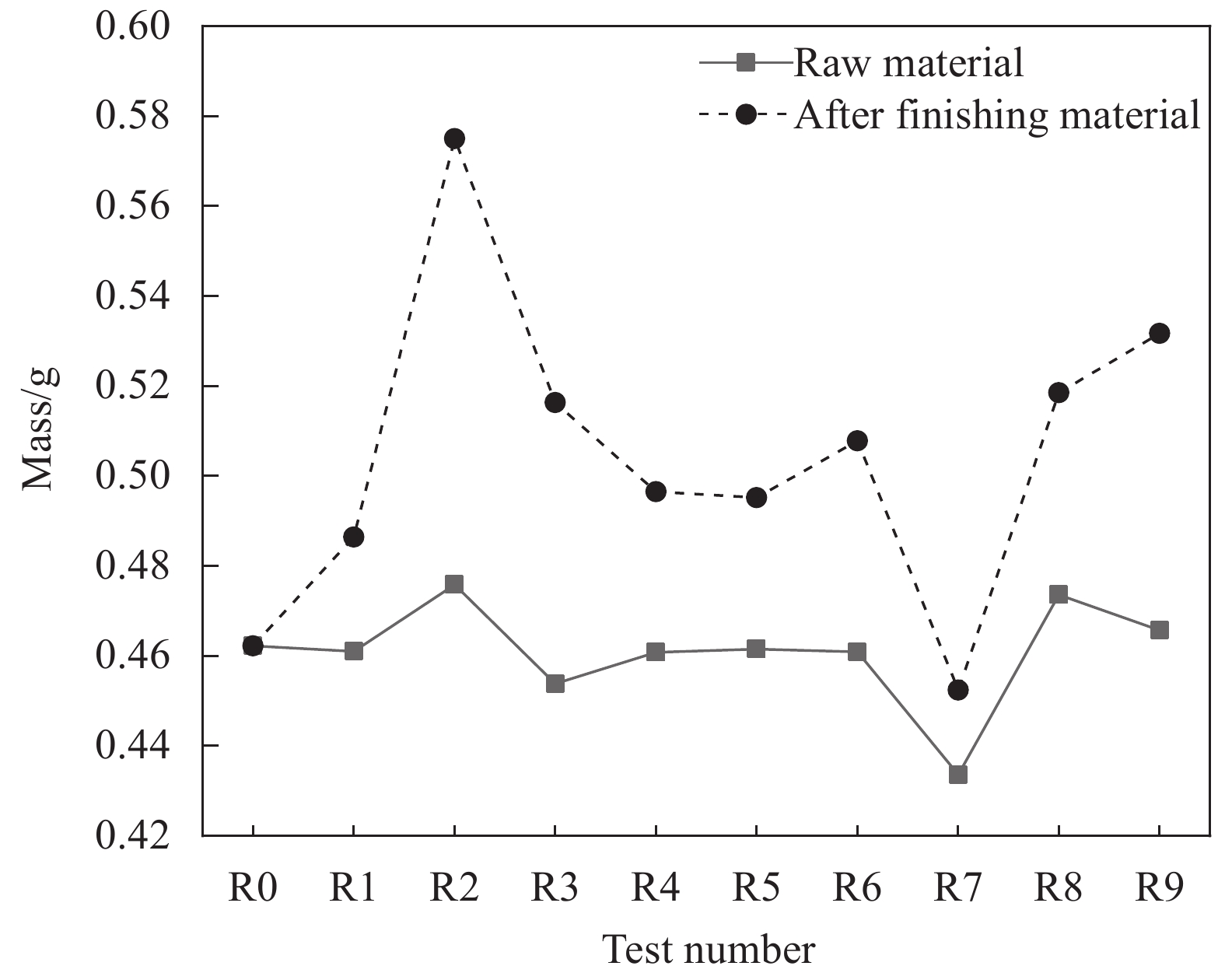
表 1 不同改性SiO2凝胶的正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)、甲基三乙氧基硅烷(MTES)配比
Table 1 Ratio of ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and methyltriethoxysilane (MTES) of different modified SiO2 gels
Test number R0 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 R9 TEOS/mol 0 0.022 0.064 0.072 0.022 0.064 0.072 0.022 0.064 0.072 MTES/mol 0 0.042 0.064 0.058 0.064 0.058 0.042 0.058 0.042 0.064 表 2 改性后滤料表面主要元素含量
Table 2 Content of main elements on the surface of modified filter material
Element C O Si Content/wt% 82.05 16.71 1.24 表 3 改性前后滤料过滤性能变化
Table 3 Change of filter performance before and after modification
Untreated PET filter material R2 Filtration efficiency/% 97.0595 99.2028 Filter resistance/Pa 166 175 Quality factor 0.02124 0.02761 -
[1] CAO B W, WANG S L, DONG W, et al. Investigation of the filtration performance for fibrous media: Coupling of a semi-analytical model with CFD on Voronoi-based microstructure[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 251: 117364.
[2] LI J L, ZHOU F B, LI S H. Experimental study on the dust filtration performance with participation of water mist[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2017,109:357-364. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.04.006
[3] ANDERSEN B O, NIELSEN N F, WALTHER J H. Numerical and experimental study of pulse jet cleaning in fabric filters[J]. Powder Technology,2016,291:284-298. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2015.12.028
[4] FINDANIS N, SOUTHAM M. Control and management of particulate emissions using improved reverse pulse-jet cleaning systems[J]. Procedia Engineering,2012,49:228-238. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.10.132
[5] 陈路敏, 钱付平, 叶蒙蒙, 等. 脉冲喷吹清灰高湿粉尘剥落的数学模型研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(S2):683-690. CHEN L M, QIAN F P, YE M M, et al. Research on mathematical model of high humidity dust spalling by pulse jet cleaning[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(S2):683-690(in Chinese).
[6] SRIRAMULU D, REED E L, ANNAMALAI M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of superhydrophobic, self-cleaning NIR-reflective silica nanoparticles[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6(1):35593.
[7] CAO C Y, GE M Z, HUANG J Y, et al. Robust fluorine-free superhydrophobic PDMS-ormosil@fabrics for highly effective self-cleaning and efficient oil-water separation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2016,4(31):12179-12187. DOI: 10.1039/C6TA04420D
[8] LU Y, SATHASIVAM S, SONG J, et al. Robust self-cleaning surfaces that function when exposed to either air or oil[J]. Science,2015,347(6226):1123-1135.
[9] SAM E K, SAM D K, LV X, et al. Recent development in the fabrication of self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,373:531-546. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.077
[10] LU S, ZHAO Y, HU X, et al. Biomimetic fabrication of micron/nano-meter assembled superhydrophobic polymer fiber fabrics for oil/water separation[J]. Materials Letters,2019,262:127152.
[11] HAO L F, GAO T T, XU W, et al. Preparation of crosslinked polysiloxane/SiO2 nanocomposite via in-situ condensation and its surface modification on cotton fabrics[J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,371:281-288. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.204
[12] KUMAR D, WU X, FU Q T, et al. Development of durable self-cleaning coatings using organic inorganic hybrid sol-gel method[J]. Applied Surface Science,2015,344:205-212. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.105
[13] KONG X, ZHU C, LV J, et al. Robust fluorine free superhydrophobic coating on polyester fabrics by spraying commercial adhesive and hydrophobic fumed SiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2020,138:105342. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.105342
[14] WU X H, FU Q T, KUMAR D, et al. Mechanically robust superhydrophobic and superhydrophobic coatings derived by sol-gel method[J]. Materials and Design,2016,89:1302-1309. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.053
[15] 张旋宇, 徐丽慧, 沈勇, 等. 疏水SiO2气凝胶的常压制备及其在棉织物上的应用研究[J]. 功能材料, 2018, 49(3):3118-3123. ZHANG X Y, XU L H, SHEN Y, et al. Preparation of hydrophobic SiO2 aerogel at atmospheric pressure and its application on cotton fabrics[J]. Functional Materials,2018,49(3):3118-3123(in Chinese).
[16] LATTHE S S, SUTAR R S, KODAG V S, et al. Self-cleaning superhydrophobic coatings: Potential industrial applications[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2019,128:52-58. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2018.12.008
[17] YANG J, PU Y, HE H, et al. Superhydrophobic cotton nonwoven fabrics through atmospheric plasma treatment for applications in self-cleaning and oil-water separation[J]. Cellulose,2019,26(12):7507-7522.
[18] 郭颖赫, 赫伟东, 柳静献. 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯纳米纤维膜/涤纶针刺毡过滤复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(3):572-577. GUO Y H, HE W D, LIU J X. preparation and properties of polyethylene terephthalate nanofiber membrane/polyester needled felt filter composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(3):572-577(in Chinese).
[19] 徐林, 任煜, 张红阳, 等. 涤纶织物表面TiO2/氟硅烷超疏水层构筑及其性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2019, 40(12):86-92. XU L, REN Y, ZHANG H Y, et al. Construction and performance of TiO2/fluorosilane superhydrophobic layer on polyester fabric surface[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2019,40(12):86-92(in Chinese).
[20] SUN H X, XU Y Y, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Preparation of superhydrophobic nanocomposite fiber membranes by electrospinning poly (vinylidene fluoride)/silane coupling agent modified SiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2017,134(13):44501.
[21] 欧阳舴艋, 李双双, 石琢, 等. 改性纳米SiO2/硅橡胶复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(7):1700-1707. OUYANG Z M, LI S S, SHI Z, et al. Preparation and properties of modified nano-SiO2/silicone rubber composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(7):1700-1707(in Chinese).
[22] RAO A V, GURAV A B, LATTHE S S, et al. Water repellent porous silica films by sol-gel dip coating method[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2010,352(1):30-35. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.08.003
[23] HA T, CHOI S G, JUNG S, et al. The improvement of mechanical and dielectric properties of ordered mesoporous silica film using TEOS-MTES mixed silica precursor[J]. Ceramics International,2008,34(4):947-951. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.09.070
[24] 罗文. 超浸润空气过滤织物的制备及其性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. LUO W. Preparation and performance study of super-soaked air filter fabric[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2018(in Chinese).
[25] 董伟, 钱付平, 李晴, 等. 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯滤料超疏水表面的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(12): 3017-3025. DONG W, QIAN F P, LI Q, et al. Preparation and properties of polyethylene terephthalate filter material superhydrophobic surface [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(12): 3017-3025(in Chinese).
[26] 齐春红. 基于低表面能二氧化硅超疏水表面的制备及其防结冰性能研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2020. QI C H. Study on the preparation and anti-icing performance of low surface energy silica superhydrophobic surface[D]. Taiyuan: North China University, 2020(in Chinese).
[27] 李晓霞. 超疏水二氧化硅溶胶的制备及性能应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020. LI X X. Preparation and Application of superhydrophobic silica sol[D]. Ji'nan: Shandong University, 2020(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 徐康康,程蹈,刘点,陈玉霞,涂道伍,郭勇,吴自成. 无损检测技术在纤维增强聚合物复合材料机械损伤监测中的应用进展. 塑料工业. 2024(02): 8-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孟凌霄,石文泽,卢超,黄良,凌建. 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料气瓶电磁超声在线监测方法及失效机制. 复合材料学报. 2024(04): 1820-1829 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 熊政辉,陈俊超,肖树坤,荆砚,何喜,陈尧. 应用于斜楔块的子孔径虚拟源全聚焦成像. 应用声学. 2024(03): 625-634 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曹欢庆,朱启民,赵培含,何梓科,郭师峰. 复杂型面结构超声成像检测研究进展. 仪器仪表学报. 2024(06): 42-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李荣光,朱甜甜,孙伶,陈斯迅,周文彬,周正干. 管道碳纤维复合材料修复层阵列超声检测方法提高检测精度. 石油钻采工艺. 2024(06): 728-742 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 夏玉秀,张义凤,薛峰. 相控阵超声检测技术在航空领域应用研究进展. 无损探伤. 2023(04): 6-10+38 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 杨红娟,杨正岩,杨雷,单一男,林奎旭,武湛君. 碳纤维复合材料损伤的超声检测与成像方法研究进展. 复合材料学报. 2023(08): 4295-4317 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 陈学宽,龙盛蓉,宋奕霖,邹越豪,李志农. 基于二维等效声速的频域全聚焦超声成像研究. 仪器仪表学报. 2023(08): 130-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)
-




 下载:
下载: