Effect of organic scaffold structure on properties of styrene butadiene rubber/ ethylene vinyl acetate composite foams
-
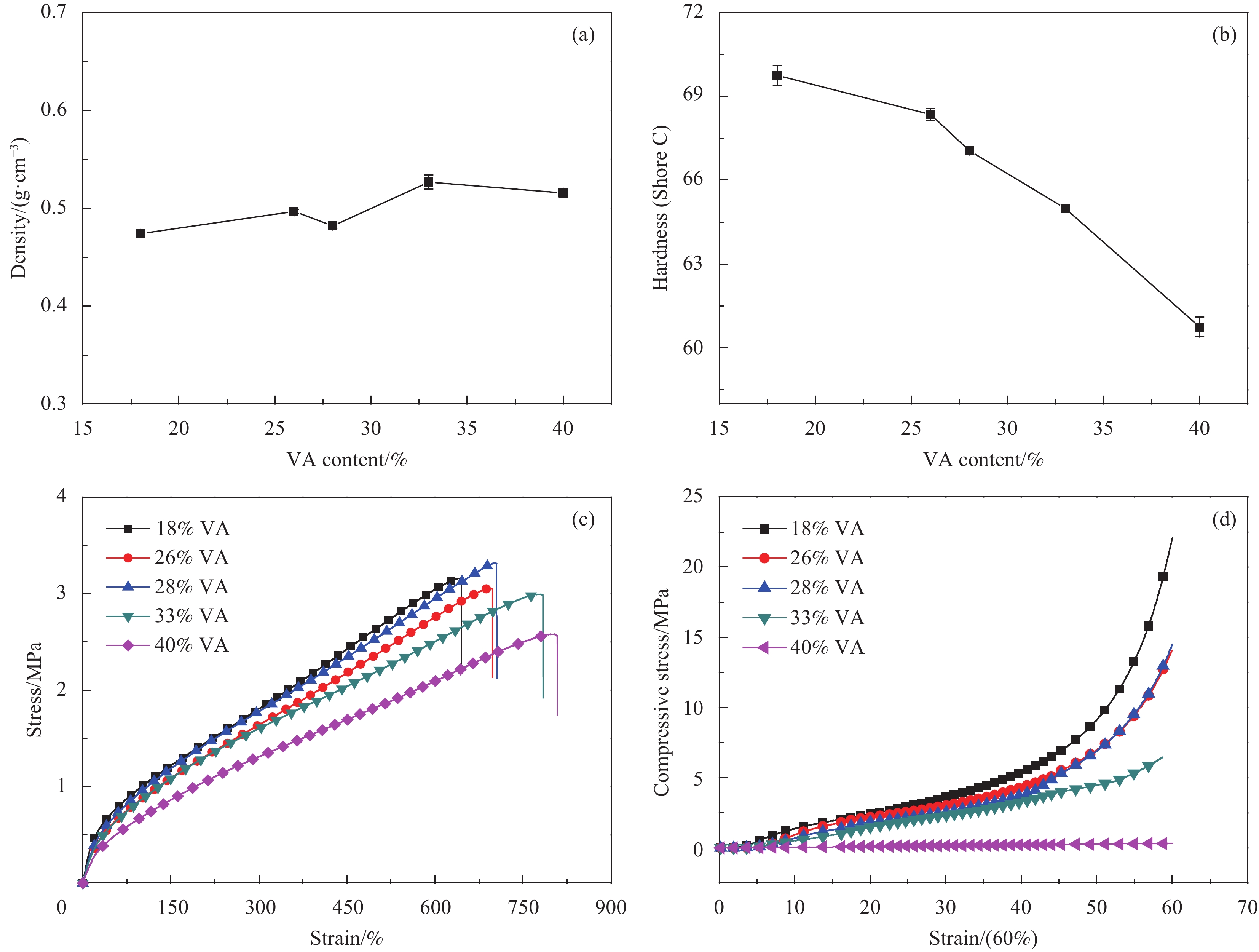
摘要: 为提高橡胶发泡材料尺寸稳定性及实现其广泛的工业化应用,基于硫磺和过氧化二异丙苯的交联体系,通过机械共混的方式,以具有结晶性的乙烯-醋酸乙烯共聚物(EVA)构筑有机支架结构,制备了高尺寸稳定性的丁苯橡胶(SBR)/EVA复合发泡材料。研究了不同醋酸乙烯(VA)含量的EVA对SBR/EVA复合材料结晶性、相容性、泡孔形貌、尺寸稳定性和力学性能的影响规律,并探明了EVA结晶区作为有机支架结构的抗收缩机制。结果表明:不同VA含量EVA的SBR/EVA复合材料都具有良好的发泡行为。高结晶度的EVA (VA含量为18%)使SBR/EVA复合发泡材料的收缩率减小至4.7%,硬度和压缩强度(60%)分别增加到70 Shore C和22 MPa。Abstract: In order to improve the dimensional stability of the rubber-based foam material and realize its wide industrialization, an organic scaffold structure was constructed with crystalline ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) to enhance the dimensional stability of styrene butadiene rubber (SBR)/EVA composite foam based on the cross-linked structure of sulfur and dicumyl peroxide through mechanical blending. The effects of different content of vinyl ester (VA) content on the crystallinity, compatibility, cell morphology, dimensional stability and mechanical properties of SBR/EVA composites were studied, and the anti-shrinkage mechanism of the EVA crystal area as an organic scaffold structure was explored. The results show that SBR/EVA composites with different VA content of EVA have good foaming behavior. The shrinkage of SBR/EVA composite foam with high crystallinity EVA (18% VA content) is reduced to 4.7% and its hardness and compression stress (60%) are increased to 70 Shore C and 22 MPa, respectively.
-
-
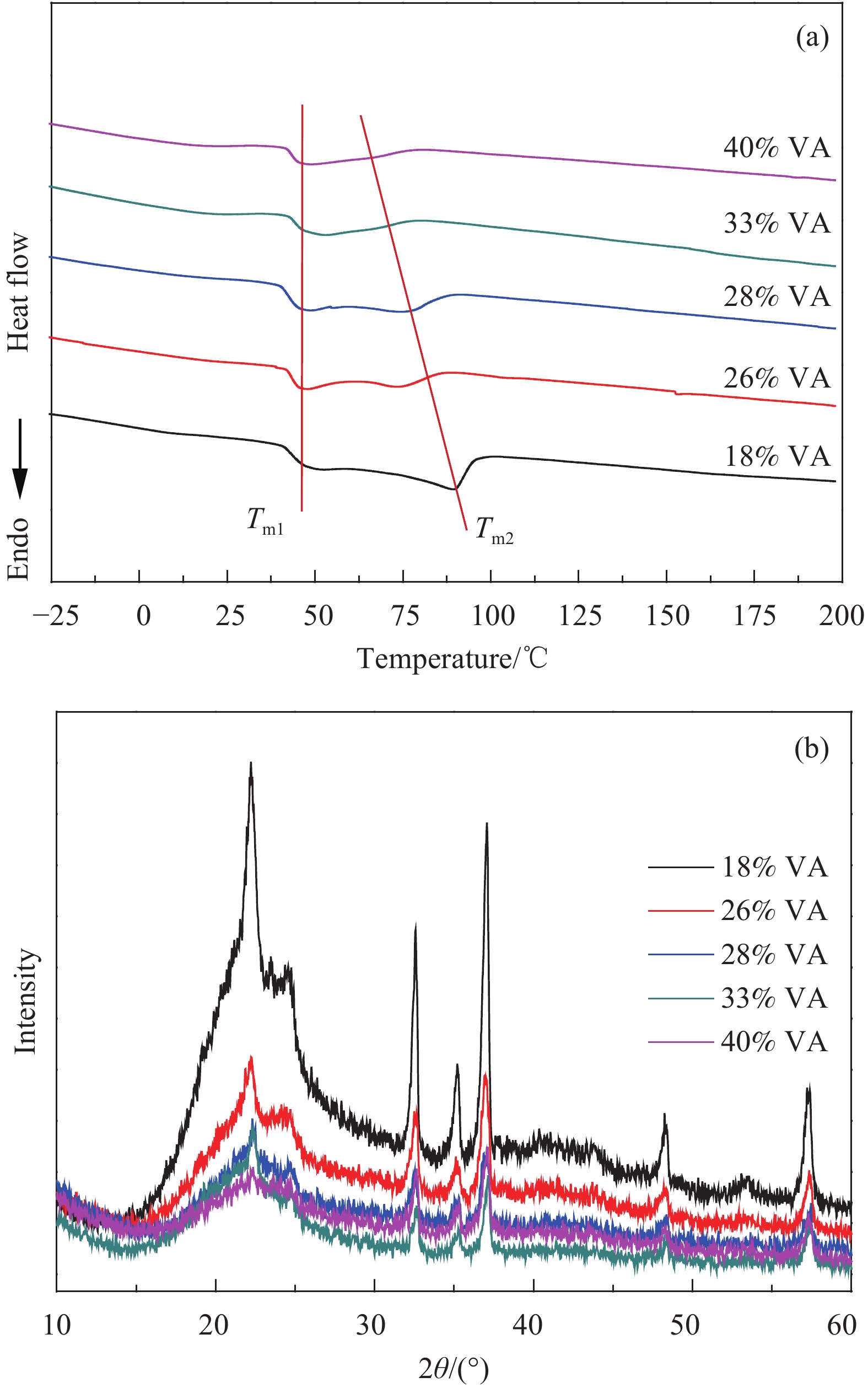
表 1 不同VA含量EVA的SBR/EVA复合材料的结晶行为
Table 1 Crystallization behavior of SBR/EVA composites with different VA content EVA
VA content/% ΔHf/(J·g−1) Tm1/℃ Tm2/℃ χc/% 18 524.8 50.1 89.4 8.15 26 128.4 52.4 73.9 1.99 28 107.3 50.3 75.3 1.67 33 79.7 48.5 66.0 1.24 40 72.3 48.3 — 1.12 Notes: ΔHf —Enthalpy of melting; Tm1, Tm2—Melting temperature; χc—Crystallinity. 表 2 VA含量为18%的SBR/EVA复合发泡材料与其他发泡材料的物理和力学性能对比[34-41]
Table 2 Comparison of physical and mechanical properties between SBR/EVA composite foam with VA content of 18% and other foam materials[34-41]
Material Density/(g·cm−3) Shrinkage/% Tensile/MPa Elongation/% Reference EVA/MWCNT 0.15 — 3.83 251 [34] EVA/POE 0.18 — 2.66 268 [35] EVA/CPE 0.12 7.2 1.05 200 [36] EVA/TPU 0.15 — 2.50 244 [37] BR/SBR/NR 0.89±0.006 — 11.10±0.3 538±18 [38] EPDM 0.29 — 2.44 626 [39] CPE — — 1.93 269 [40] SBS/SBR/PS 0.20 5.0 0.92 270 [41] SBR/EVA 0.47±0.03 4.7±0.35 3.15±0.17 642±5.52 This work Notes: MWCNT—Multiwalled carbon nanotube; POE—Polyolefin thermoplastic elastomer; CPE—Chlorinated polyethylene rubber; TPU—Thermoplastic polyurethane; BR—Butadiene rubber; NR—Nature rubber; EPDM—Ethylene-propylene-diene monomer; SBS—Styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer; PS—Polystyrene. -
[1] SAI H, TAN K W, HUR K, et al. Hierarchical porous polymer scaffolds from block copolymers[J]. Science,2013,341(6145):530-534. DOI: 10.1126/science.1238159
[2] XIANG B, DENG Z, ZANG F, et al. Microcellular silicone rubber foams: The influence of reinforcing agent on cellular morphology and nucleation[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science,2019,59(1):5-14. DOI: 10.1002/pen.24857
[3] XU Y, ZHANG S, PENG X, et al. Fabrication and mechanism of poly(butylene succinate) urethane ionomer microcellular foams with high thermal insulation and compressive feature[J]. European Polymer Journal,2018,99:250-258. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.12.032
[4] VAHIDIFAR A, ESMIZASEH E, ROSTAMI E, et al. Morphological, rheological, and mechanical properties of hybrid elastomeric foams based on natural rubber, nanoclay and nanocarbon black[J]. Polymer Composites,2019,40(11):4289-4299. DOI: 10.1002/pc.25290
[5] CHEN L, SCHADLER L S, OZISIK R. An experimental and theoretical investigation of the compressive properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube/poly(methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite foams[J]. Polymer,2011,52(13):2899-2909. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2011.04.050
[6] NOFAR M, AMELI A, PARK C B. Development of polylactide bead foams with double crystal melting peaks[J]. Polymer,2015,69:83-94. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2015.05.048
[7] SHRUDIN R W B, OHSHIMA M. Preparation of microcellular thermoplastic elastomer foams from polystyrene-b-ethylene-butylene-b-polystyrene (SEBS) and their blends with polystyrene[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2013,128(4):1-10.
[8] SHAO L, JI Z Y, MA Z, et al. The synergy of double cross-linking agents on the properties of styrene butadiene rubber foams[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6:36931. DOI: 10.1038/srep36931
[9] JI Z, MA J, QIN X, et al. Improved dimensional stability of styrene butadiene rubber/ethylene vinyl acetate composite foams with skeleton support structure based on alternately cross-linking process[J]. Polymer,2018,157:103-110. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2018.10.028
[10] PHIRI M, SIBEKO M A, PHIRI M J, et al. Effect of free foaming and pre-curing on the thermal, morphological and physical properties of reclaimed tyre rubber foam composites[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,218(1):65-672.
[11] GARANCHER J P, FERNYHOUGH A. Expansion and dimensional stability of semi-crystalline polylactic acid foams[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2014,100:21-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.12.037
[12] KAIRYT A, JELIS S. Evaluation of forming mixture composition impact on properties of water blown rigid polyurethane (PUR) foam from rapeseed oil polyol[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2015,66:210-215. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.12.032
[13] HOSSIENY N J, BSRZEGARI M R, NOFARM, et al. Crystallization of hard segment domains with the presence of butane for microcellular thermoplastic polyurethane foams[J]. Polymer,2014,55(2):651-662. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2013.12.028
[14] ZHANG R, HUANG K, HU S, et al. Improved cell morphology and reduced shrinkage ratio of ETPU beads by reactive blending[J]. Polymer Testing,2017,63:38-46. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.08.007
[15] JAMEL M M, KHOSHNOUD P, GUNASHEKARS, et al. Effect of E-glass fibers and phlogopite mica on the mechanical properties and dimensional stability of rigid PVC foams[J]. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering,2015,54(15):1560-1570. DOI: 10.1080/03602559.2015.1010222
[16] JAMEL M M, KHOSHNOUD P, GUNASHEKAR S, et al. Mechanical properties and dimensional stability of rigid PVC foam composites filled with high aspect ratio phlogopite mica[J]. Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering,2015,3(4):237-247. DOI: 10.4236/jmmce.2015.34026
[17] KWON M J, LIM D H, CHOI I C, et al. Preparation and properties of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer-based blend foams[J]. Journal of Elastomers and Plastics,2021,53(1):68-82. DOI: 10.1177/0095244319900375
[18] ZHANG B S, ZHANG Z X, LV X F, et al. Properties of chlorinated polyethylene rubber/ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer blend-based foam[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science,2011,52(1):218-224.
[19] WANG L, LANG F, DU F, et al. Zinc dimethacrylate-reinforced thermoplastic vulcanizates based on chlorinated polyethylene rubber/ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer[J]. Journal of Macromolecular Science Part B: Physics,2013,52(1):178-189. DOI: 10.1080/00222348.2012.695655
[20] HE Y X, MA J Z, LI Z, et al. Preparation and characterization of graft copolymer EVA-g-PU[J]. Polymer Plastics Technology and Engineering,2008,47(12):1214-1219. DOI: 10.1080/03602550802497123
[21] MA J Z, DUAN Z, XUE C, et al. Morphology and mechanical properties of EVA/OMMT nanocomposite foams[J]. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials,2013,26(4):555-569. DOI: 10.1177/0892705712458943
[22] DUAN Z. Foamed materials from POE/EVA blends[J]. Journal of Functional Biomaterials,2012,43(4):508-511.
[23] ZHAO Y F, XIAO M, WANG S J, et al. Preparation and properties of electrically conductive PPS/expanded graphite nanocomposites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2007,67(11):2528-34.
[24] SHIEH Y T, LIN Y G. Equilibrium solubility of CO2 in rubbery EVA over a wide pressure range: Effects of carbonyl group content and crystallinity[J]. Polymer,2002,43(6):1849-56. DOI: 10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00776-5
[25] LIU S, EIJKELENKAMP R, DUVIGNEAU J, et al. Silica-assisted nucleation of polymer foam cells with nanoscopic dimensions: Impact of particle size, line tension, and surface functionality[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,2017,9(43):37929-37940. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b11248
[26] LIU S, YIN S, DUVIGNEAU J, et al. Bubble seeding nanocavities: Multiple polymer foam cell nucleation by polydimethylsiloxane-grafted designer silica nanoparticles[J]. ACS Nano,2020,14(2):1623-1634. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.9b06837
[27] LIU S, PANDEY A, DUVIGNEAU J, et al. Size-dependent submerging of nanoparticles in polymer melts: Effect of line tension[J]. Macromolecules,2018,51:2411−2417.
[28] 王旭, 常素芹, 冯钠, 等. 不同发泡剂及工艺条件对BR/SBR/NR发泡材料相结构及尺寸稳定性的影响[J]. 弹性体, 2013, 23(1):58-64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3174.2013.01.015 WANG Xu, CHANG Suqin, FENG Na, et al. Effect of blowing agents and process technology on morphology and dimensional stability of BR/SBR/NR foams[J]. China Elastomeric,2013,23(1):58-64(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3174.2013.01.015
[29] 金雪华, 司朗诵, 朱旭, 等. 发泡剂对聚氨酯硬泡保温塑料低温尺寸稳定性的研究[J]. 化工技术与开发, 2010, 39(5):13-15, 20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9905.2010.05.005 JIN Xuehua, SI Langsong, ZHU Xu, et al. Effect of blowing agent on dimensional stability of polyurethane foam insulation plastic[J]. Technology and Development of Chemical Industry,2010,39(5):13-15, 20(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9905.2010.05.005
[30] 董懿嘉, 孙才英. 玉米秸秆粉对硬质聚氨酯泡沫尺寸稳定性的影响研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2017, 45(1):194-196. DONG Yijia, SUN Caiying. Influence of corn straw powders on the dimentional stability of RPUF[J]. New Chemical Materials,2017,45(1):194-196(in Chinese).
[31] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 软质泡沫聚合材料拉伸强度和断裂伸长率的测定: GB/T 6344—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Flexible cellular polymeric materials: Determination of tensile strength and elongation at break: GB/T 6344—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese).
[32] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 软质泡沫聚合材料模压和挤出海绵胶制品/成品的压缩性能试验: GB/T 20467—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Flexible cellular polymeric materials moulded and extruded sponge or expanded cellular rubber prodcuts Compressibility test on finished parts: GB/T 20467—2006[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2006(in Chinese).
[33] MA Z L, ZHANG G C, YANG Q, et al. Tailored morphologies and properties of high-performance microcellular poly(phenylene sulfide)/poly(ether sulfones) (PPS/PEEK) blends[J]. Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2018,132(40):116-128.
[34] PARK K W, KIM G H. Ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA)/multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) nanocomposite foams[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2009,112(3):1845-1849. DOI: 10.1002/app.29736
[35] DENG F Q, MA J Z, XUE C H, et al. Foamed materials from POE/EVA blends[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2012,43(4):508-511.
[36] ZHANG B S, ZHANG Z X, LV X F, et al. Properties of chlorinated polyethylene rubber/ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer blend-based foam[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science,2012,52(1):218-224. DOI: 10.1002/pen.22071
[37] MA J Z, SHAO L, XUE C H, et al. Compatibilization and properties of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) blend-based foam[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2014,71(9):2219-2234. DOI: 10.1007/s00289-014-1183-5
[38] WANG X, FENG N, CHANG S. Effect of precured degrees on morphology, thermal, and mechanical properties of BR/SBR/NR foams[J]. Polymer Composites,2013,34(6):849-859. DOI: 10.1002/pc.22489
[39] LEE K, CHANG Y W, KIM S W. Ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymer/halloysite nanocomposites: Thermal, mechanical properties, and foam processing[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2014,131(11):2928-2935.
[40] ZHANG B S, LV X F, ZHANG Z X, et al. Effect of carbon black content on microcellular structure and physical properties of chlorinated polyethylene rubber foams[J]. Materials and Design,2010,31(6):3106-3110. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.12.041
[41] SHIH R S, KUO S W, CHANG F C. Thermal and mechanical properties of microcellular thermoplastic SBS/PS/SBR blend: Effect of crosslinking[J]. Polymer,2011,52(3):752-759. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2010.12.026
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李滋阳,王思佳,邓文举. 陶瓷颗粒增强金属基复合材料研究进展. 轻工科技. 2021(04): 41-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈亚楠,金云学,牛牧野,陈洪美,杜文栋. Ni_3Al(Cr)合金室温干滑动摩擦磨损性能研究. 江苏科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(05): 18-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)
-




 下载:
下载: