Mechanical properties of jujube pit/linear low density polyethylene composites
-
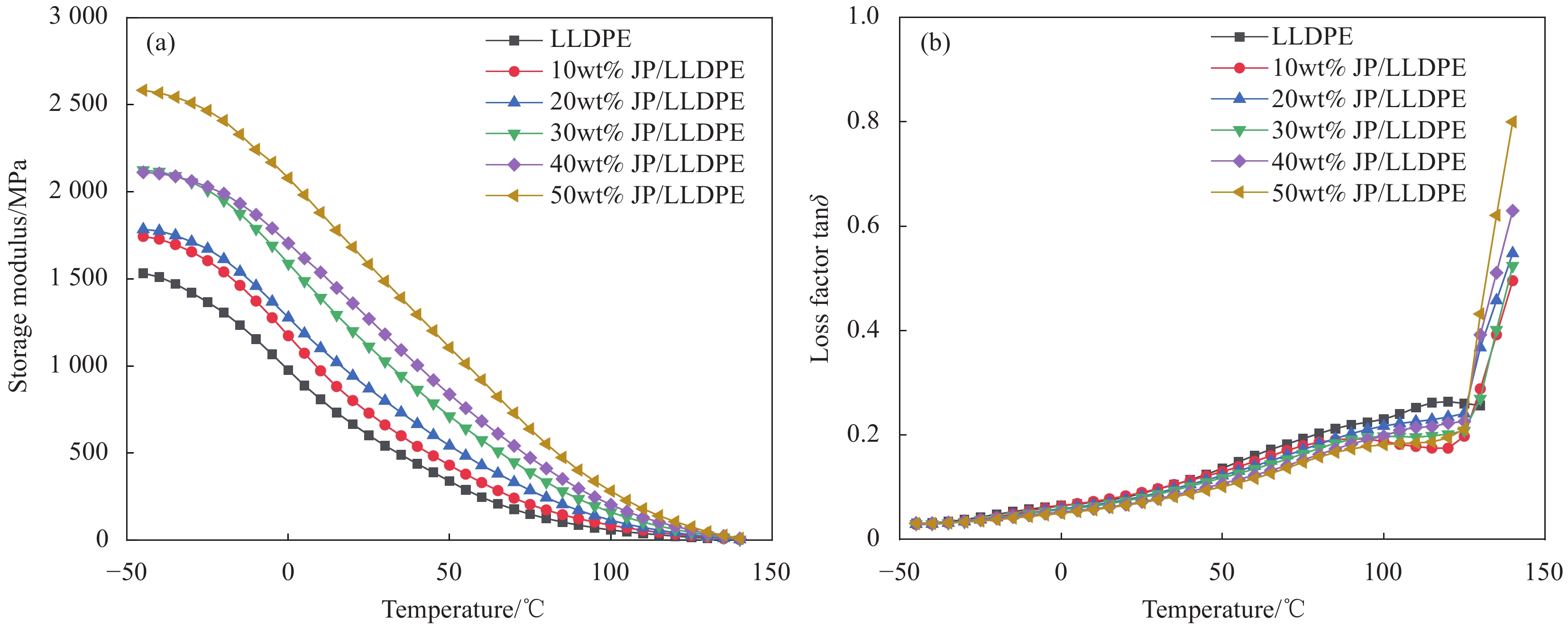
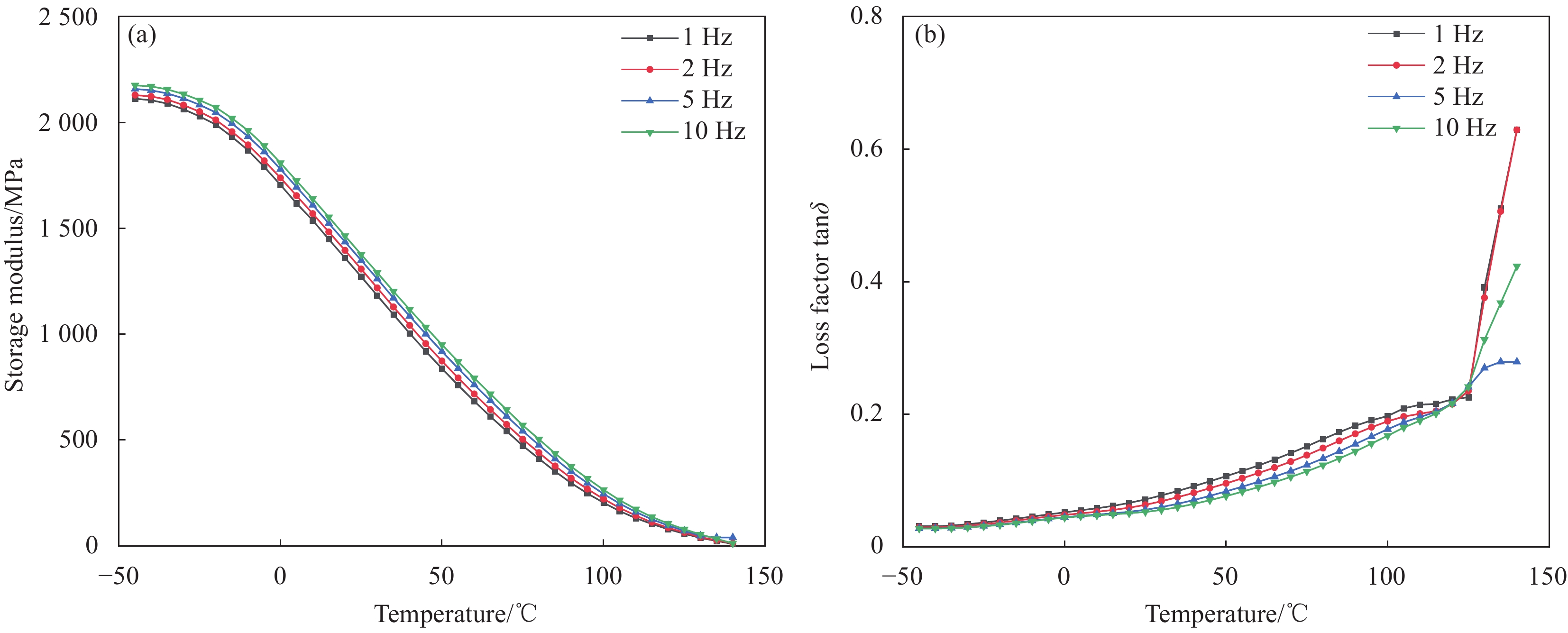
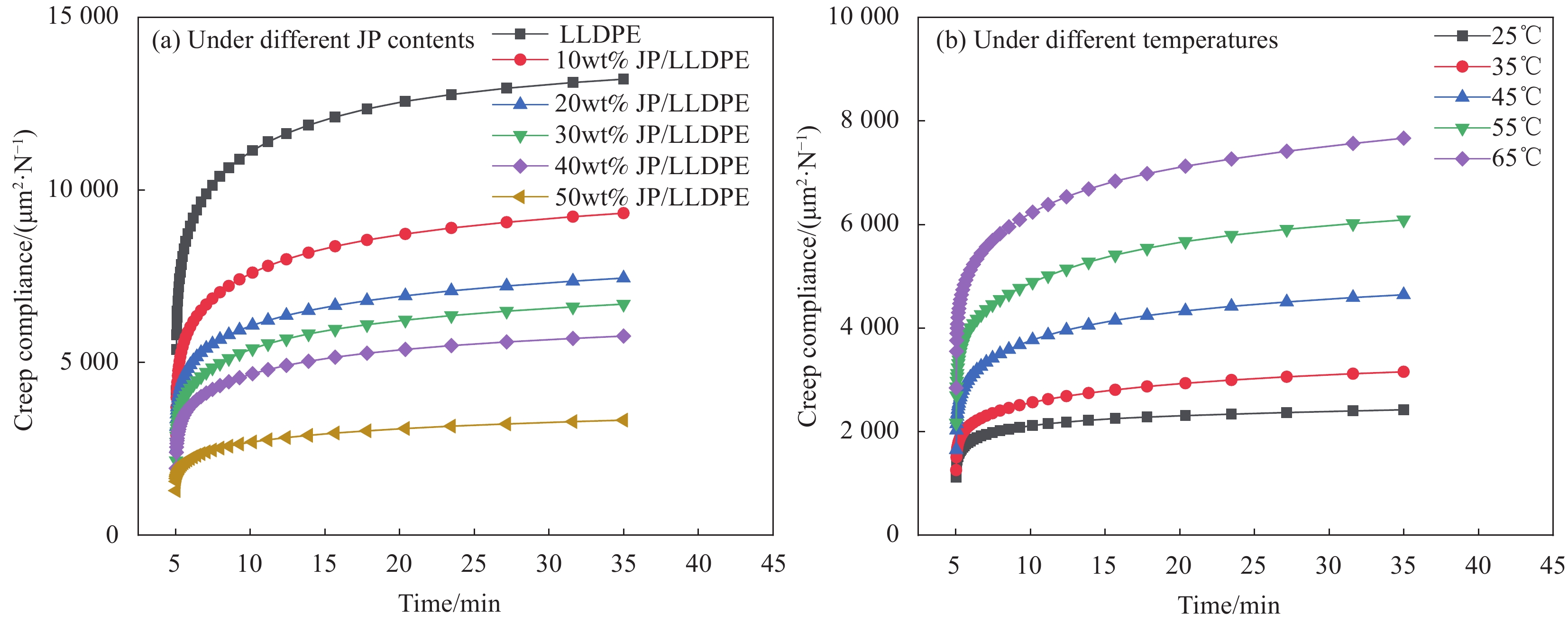
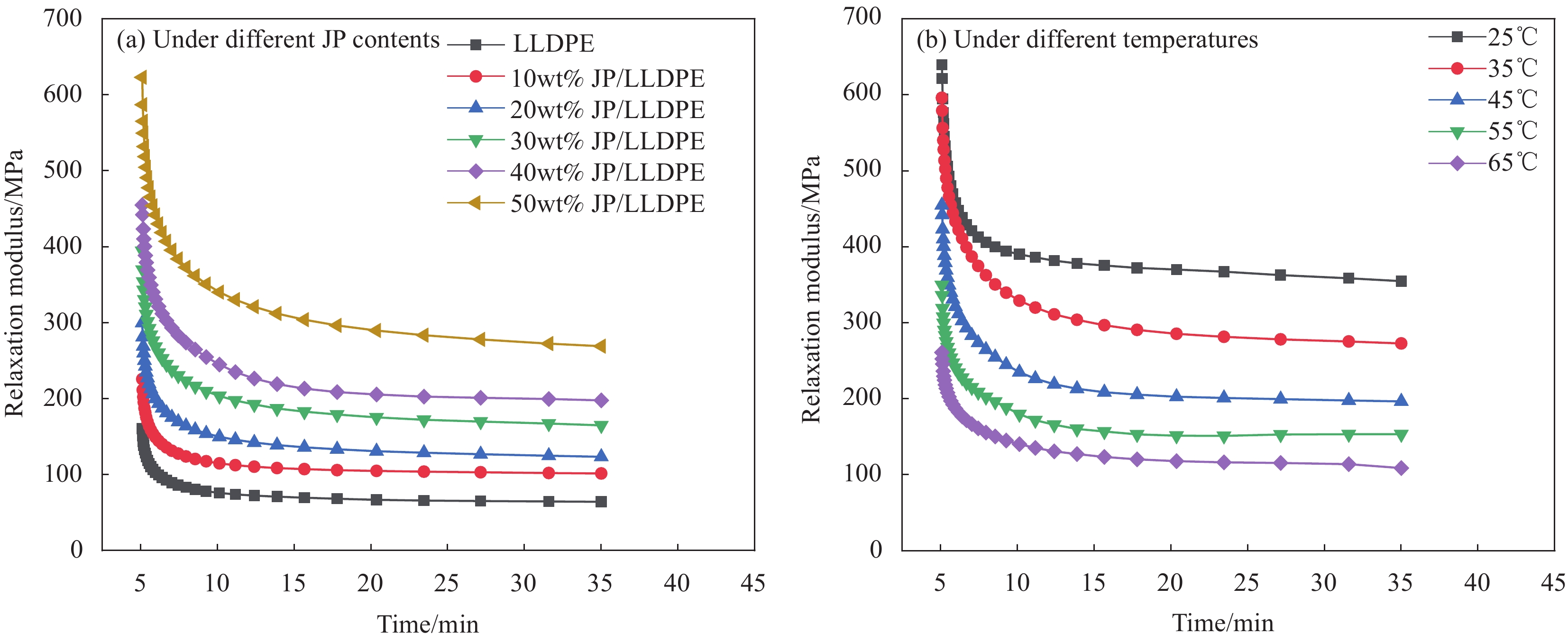
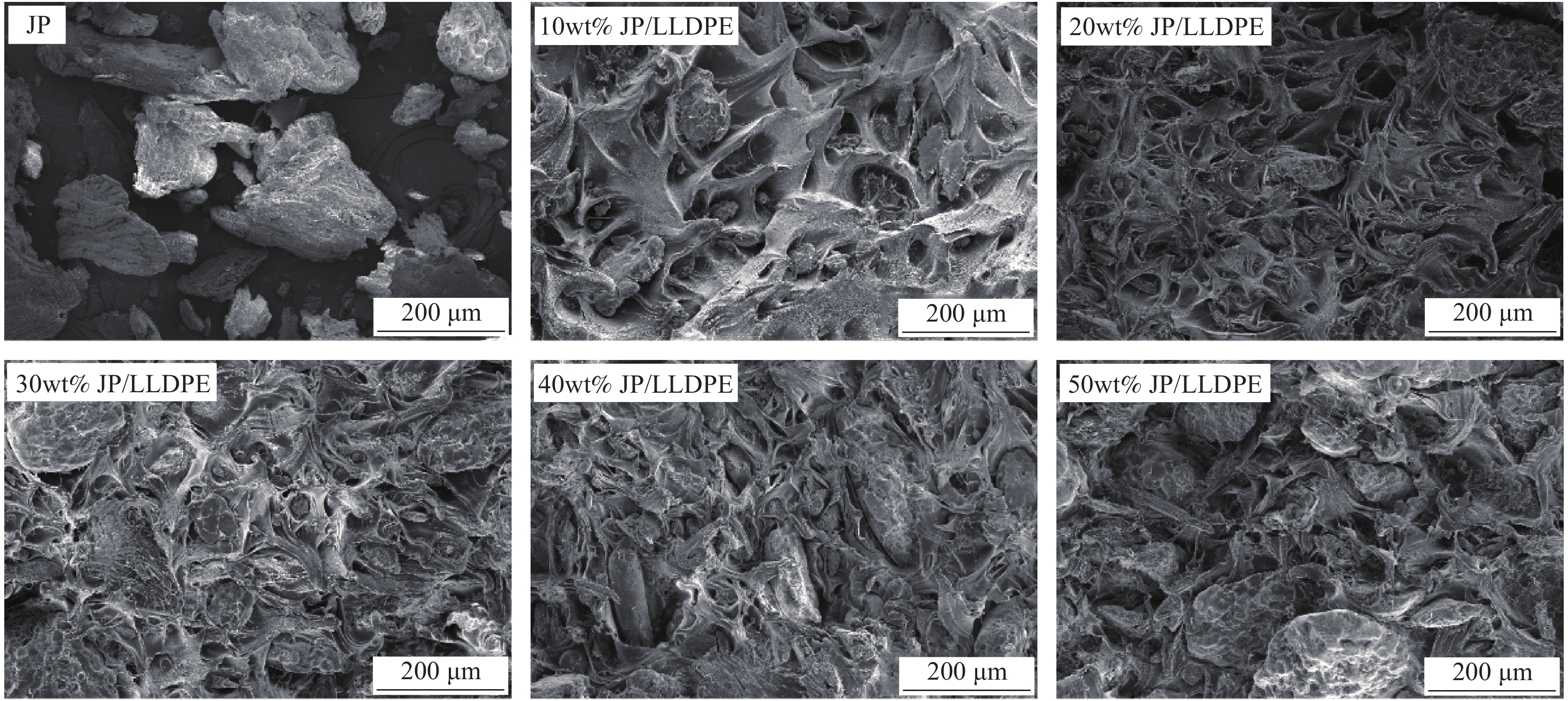
摘要: 为充分利用红枣精深加工产生的废弃物,以枣核(JP)和低密度聚乙烯(LLDPE)为主要材料,采用注塑成型法制备JP/LLDPE复合材料,并对其静态力学性能(拉伸、弯曲和冲击)和动态力学性能(动态黏弹性、蠕变行为和应力松弛行为)进行系统测试分析。静态力学性能分析表明,随JP含量的增加,JP/LLDPE复合材料的拉伸强度和冲击强度逐渐降低,但复合材料的弯曲强度得到明显的提升。当JP添加量为20wt%时,JP/LLDPE复合材料的弯曲强度最高,较纯LLDPE的弯曲强度提高63.57%;动态力学分析表明,JP含量的增加有利于提高JP/LLDPE复合材料的刚性、抗蠕变性能和抗应力松弛性能,而温度的升高会对JP/LLDPE复合材料的抗蠕变性能和抗应力松弛性能产生不利的影响。Abstract: In order to make full use of the waste generated during the deep processing of red jujube, jujube pit (JP) and linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) composites were prepared by injection molding method with JP and LLDPE as the main components. The static mechanical properties (tensile, flexural and impact) and dynamic mechanical properties (dynamic viscoelastic, creep behavior and stress relaxation behavior) were fully tested and analyzed. The static mechanical properties analysis show that the tensile and impact strength of JP/LLDPE composites are decreased as the JP contents increase, while the flexural strength of the composites is obviously improved. When the addition contents of JP reach 20wt%, the JP/LLDPE composite exhibit optimal flexural strength, which is 63.57% higher than that of pure LLDPE. Dynamic mechanical analysis confirms that the increase of JP contents is beneficial to improve the rigidity, creep resistance and stress relaxation of JP/LLDPE composites, but the increase of temperature adversely affects the creep resistance and stress relaxation resistance of JP/LLDPE composites.
-
Keywords:
- jujube pit /
- low density polyethylene /
- composites /
- waste utilization /
- mechanical properties
-
-
表 1 枣核/低密度聚乙烯(JP/LLDPE)复合材料配方
Table 1 Formulations of jujube pit/linear low density polyethylene (JP/LLDPE) composites
wt% No. 10wt% JP/LLDPE 20wt% JP/LLDPE 30wt% JP/LLDPE 40wt% JP/LLDPE 50wt% JP/LLDPE JP 10 20 30 40 50 LLDPE 80 70 60 50 40 TPW604 2 2 2 2 2 Calcium stearate 2 2 2 2 2 MAPE 6 6 6 6 6 Note: MAPE—Maleic anhydride grafted polyethylene. 表 2 JP的组成成分
Table 2 Composition of JP
wt% Cellulose Hemicellulose Lignin Ash Water extract 29.73±0.51 28.48±0.75 31.60±0.45 1.35±0.36 8.84±0.58 -
[1] 康宁波, 尚梦玉, 何建国, 等. 链式气动冲切自动化干红枣去核机设计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(22):19-26. DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.22.003 KANG N B, SHANG M Y, HE J G, et al. Design of chained pneumatic punching automatic dried jujube pit removing machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2018,34(22):19-26(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.22.003
[2] 马朝锋, 刘凯, 杨军良, 等. 红枣去核机技术研究进展[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2019, 40(3):108-116. MA Z F, LIU K, YANG J L, et al. Progress on the technology of the red jujube kernel removing machine[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization,2019,40(3):108-116(in Chinese).
[3] 周靖博, 张淑娟, 孙海霞, 等. 我国红枣去核机的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 山西农业科学, 2014, 42(2):199-202. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2014.02.25 ZHOU J B, ZHANG S J, SUN H X, et al. Research status and development trend of jujube kernel removing machine in China[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2014,42(2):199-202(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2014.02.25
[4] PANDHARIPADE S L, MOHARKAR Y, THAKUR R. Synthesis of adsorbents from waste materials such as ziziphus jujube seed & mango kernel[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications,2012:1337-1341.
[5] 王清文, 易欣, 沈静. 木塑复合材料在家具制造领域的发展机遇[J]. 林业工程学报, 2016, 1(3):1-8. WANG Q W, YI X, SHEN J. Tailoring wood-plastic composites for furniture production: Possibilities and opportunities[J]. China Forestry Science and Technology,2016,1(3):1-8(in Chinese).
[6] 申婷文, 孙亚楠, 刘一楠, 等. 单板贴面木粉/高密度聚乙烯复合材制备及表面胶合性能研究[J]. 林业工程学报, 2020, 5(4): 101-107. SHEN T W, SUN Y N, LIU Y N, et al. Study on preparation and adhesion property of veneer overlaid wood flour/high density polyethylene composites [J]. China Forestry Science and Technology, 2020, 5(4): 101-107(in Chinese).
[7] 张庆法, 杨科研, 蔡红珍, 等. 稻壳/高密度聚乙烯复合材料与稻壳炭/高密度聚乙烯复合材料性能对比[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11):3044-3050. ZHANG Q F, YANG K Y, CAI H Z, et al. Comparison of properties between rice husk/high density polyethylene and rice husk biochar/high density polyethylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(11):3044-3050(in Chinese).
[8] MU B, WANG H, HAO X, et al. Morphology, mechanical properties and dimensional stability of biomass particles/high density polyethylene composites: Effect of species and composition[J]. Polymers,2018,10(3):308.
[9] 朱碧华, 何春霞, 石峰, 等. 三种壳类植物纤维/聚氯乙烯复合材料性能比较[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(2):291-297. ZHU B H, HE C X, SHI F, et al. Performance comparison of three kinds of husk’s fibers/polyvinyl chloride composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(2):291-297(in Chinese).
[10] 杨莉, 王孝锋, 邹梨花, 等. 混杂工艺对椰壳-大麻/聚丙烯复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(9):2093-2100. YANG L, WANG X F, ZHOU L H, et al. Effects of hybrid process on mechanical properties of coir-hemp/polypropylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(9):2093-2100(in Chinese).
[11] 周吓星, 苏国基, 陈礼辉. 竹粉热处理改善竹粉/聚丙烯复合材料的防霉性能[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(24):308-314. DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.24.040 ZHOU X X, SU G J, CHEN L H. Heat-treated bamboo powder improves anti-mold performance of bamboo powder/polypropylene composites[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2017,33(24):308-314(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.24.040
[12] 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 塑料拉伸性能的测定第 2 部分: 模塑和挤塑塑料的试验条件: GB/T 1040.2—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. Standardization Administration of People’s Republic of China. Plastics determination of tensile properties-Part 2: Test conditions for moulding and extrusion plastics: GB/T 1040.2—2006[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2006(in Chinese).
[13] 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 塑料弯曲性能的测定: GB/T 9341—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. Standardization Administration of People’s Republic of China. Plastics-Determination of flexural properties: GB/T 9341—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese).
[14] 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 塑料悬臂梁冲击强度的测定: GB/T 1843—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. Standardization Administration of People’s Republic of China. Plastics-Determination of izod impact strength: GB/T 1843—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese).
[15] 张东红, 周亮, 任夏瑾, 等. 山楂核/聚乙烯复合材料的力学性能与热性能[J]. 塑料科技, 2020, 48(5):71-76. ZHANG D H, ZHOU L, REN X J, et al. Mechanical and thermal properties of hawthorn seed/polyethylene composites[J]. Plastics Science and Technology,2020,48(5):71-76(in Chinese).
[16] ARORA A, NANDAL P, SINGH J, et al. Nanobiotechnological advancements in lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment[J]. Materials Science for Energy Technologies,2020,3:308-318.
[17] 王博闻, 路琴. 聚氯乙烯/秸秆粉木塑复合材料的性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2017, 31(9):62-67. WANG B W, LU Q. Study on properties of poly (vinyl chloride)/wheat straw composites[J]. China Plastics,2017,31(9):62-67(in Chinese).
[18] GAO H, XIE Y, OU R, et al. Grafting effects of polypropylene/polyethylene blends with maleic anhydride on the properties of the resulting wood-plastic composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(1):150-157.
[19] HAO X, ZHOU H, WANG Q, et al. Reinforcement of wood flour/HDPE composite with a copolyester of p-hydroxy benzoic acid and 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid: Reinforcement of wood flour/HDPE composite with a copolyester of p-hydroxy benzoic acid and 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2019,136(15):47338.
[20] LUO Z, LI P, CAI D, et al. Comparison of performances of corn fiber plastic composites made from different parts of corn stalk[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2017,95:521-527.
[21] 龚维, 高家诚, 何力, 等. 微发泡聚丙烯/晶须复合材料的发泡行为与力学性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2011, 27(3):67-70, 75. GONG W, GAO J C, HE L, et al. Foam behavior and mechanical property of PP/whisker microcellular foam composites[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering,2011,27(3):67-70, 75(in Chinese).
[22] REN W, ZHANG D, WANG G, et al. Mechanical and thermal properties of bamboo pulp fiber reinforced polyethylene composites[J]. Bioresources,2014,9(3):4117-4127.
[23] 王翠翠, 程海涛, 羡瑜, 等. 纳米CaCO3增强竹浆纤维/环氧树脂复合材料的动态力学性能[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(6):281-287. DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.06.036 WANG C C, CHENG H T, XIAN Y, et al. Improving dynamic mechanical property of bamboo pulp fiber reinforced epoxy resin composite treated by nano calcium carbonate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2017,33(6):281-287(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.06.036
[24] 郝建秀, 杜凤, 王伟宏. 短切碳纤维表面处理对木粉/高密度聚乙烯复合材料性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(2):298-303. HAO J X, DU F, WANG W H. Effect of surface treatment of short carbon fibers on the properties of wood flour/high density polyethylene composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(2):298-303(in Chinese).
[25] 邵笑, 何春霞, 姜彩昀. 木质纤维/PVC复合材料的蠕变和热稳定性[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2019, 37(6):991-995. SHAO X, HE C X, JIANG C Y. Study on creep and thermal stability of wood fiber/PVC composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering,2019,37(6):991-995(in Chinese).
[26] TAMRAKAR S, LOPEZANIDO R, KIZILTAS A, et al. Time and temperature dependent response of a wood-polypropylene composite[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2011,42(7):834-842.
[27] 韦春, 曾思华, 黄绍军, 等. 剑麻纤维素微晶增强酚醛树脂复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(S1):306-310. WEI C, ZENG S H, HUANG S J, et al. Preparation and properties of sisal fiber cellulose microcrystal reinforced phenol-formaldehyde resins composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(S1):306-310(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 柯俊,李志虎,秦玉林. 金属主簧-复合材料副簧复合刚度计算模型. 汽车实用技术. 2021(05): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾婷,王咏莉,尹忠旺,苏婷慧,师志峰,饶猛. 端面凸轮下压机构支承轴承冲击失效分析及优化(英文). 机床与液压. 2017(24): 37-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)
-




 下载:
下载: