Interlaminar aligned carbon nanotubes spraying process and fracture toughness of CFRP
-
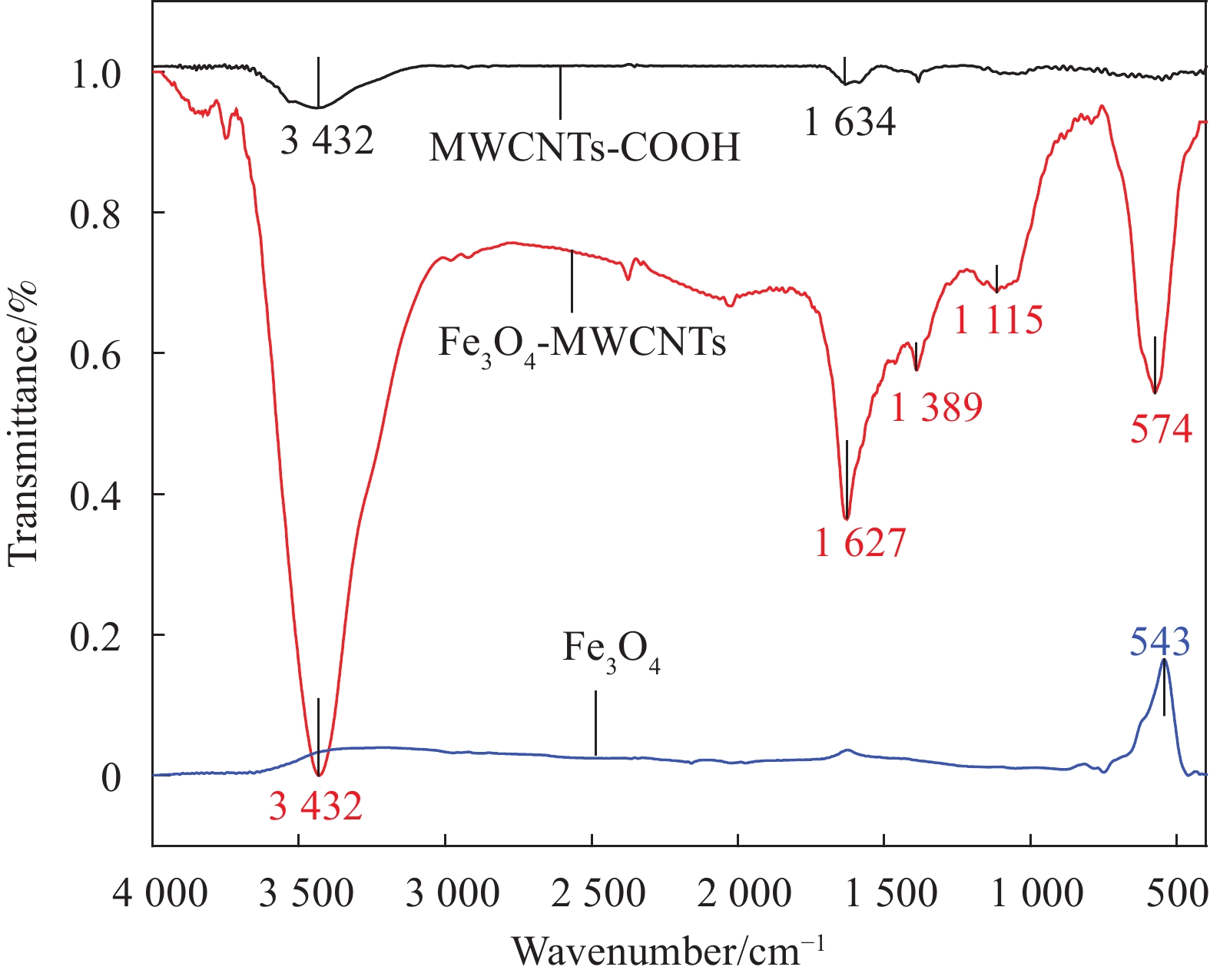
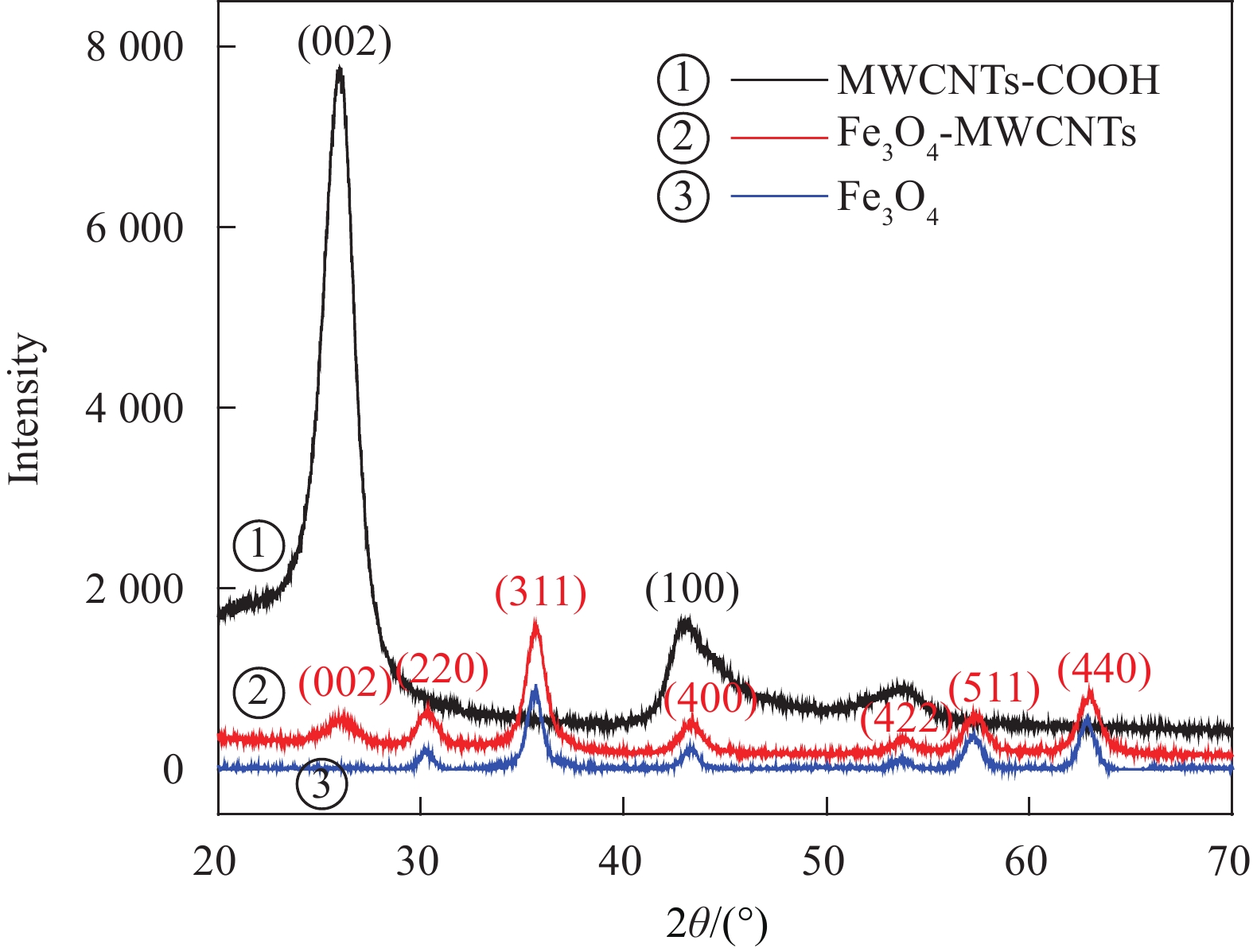
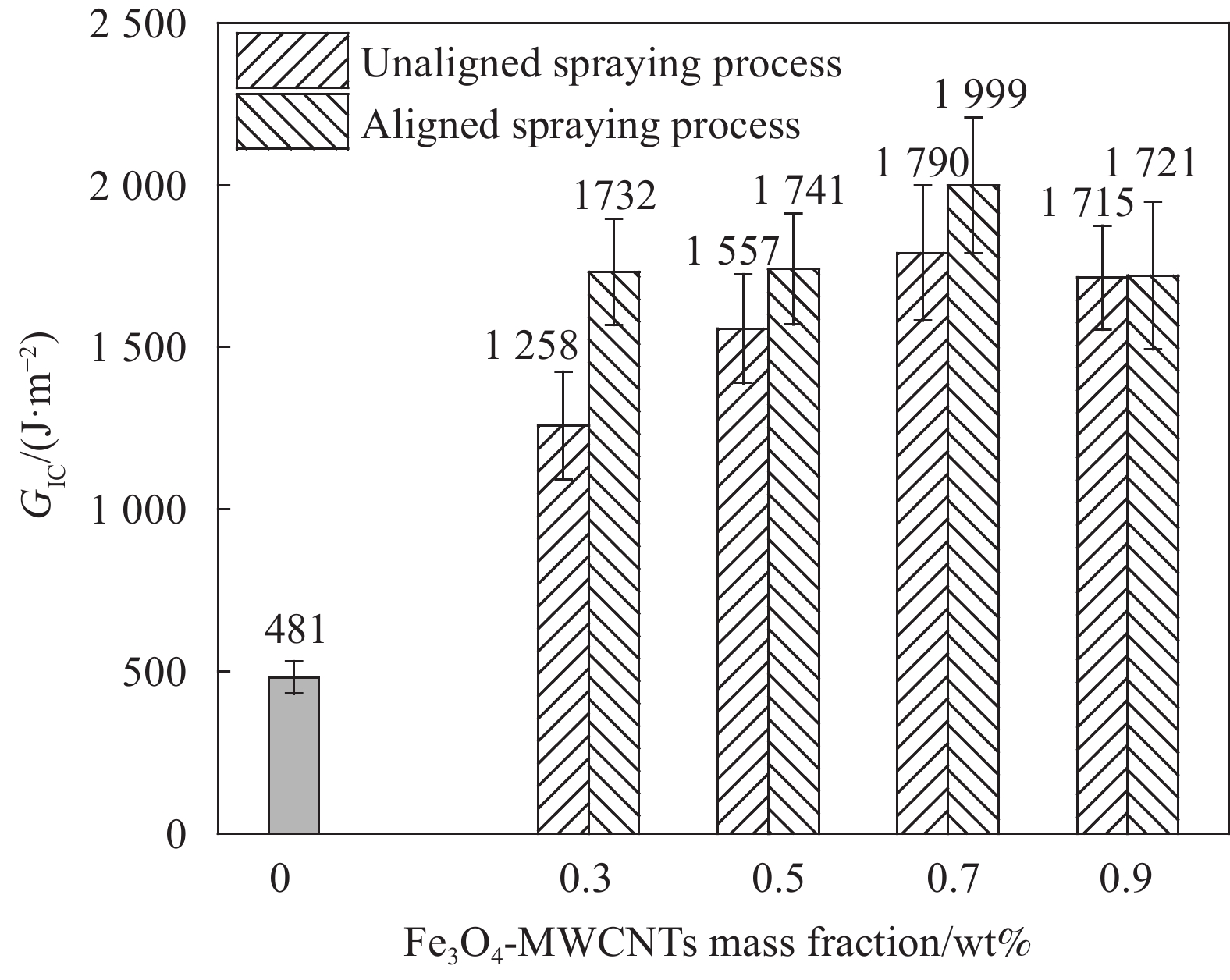
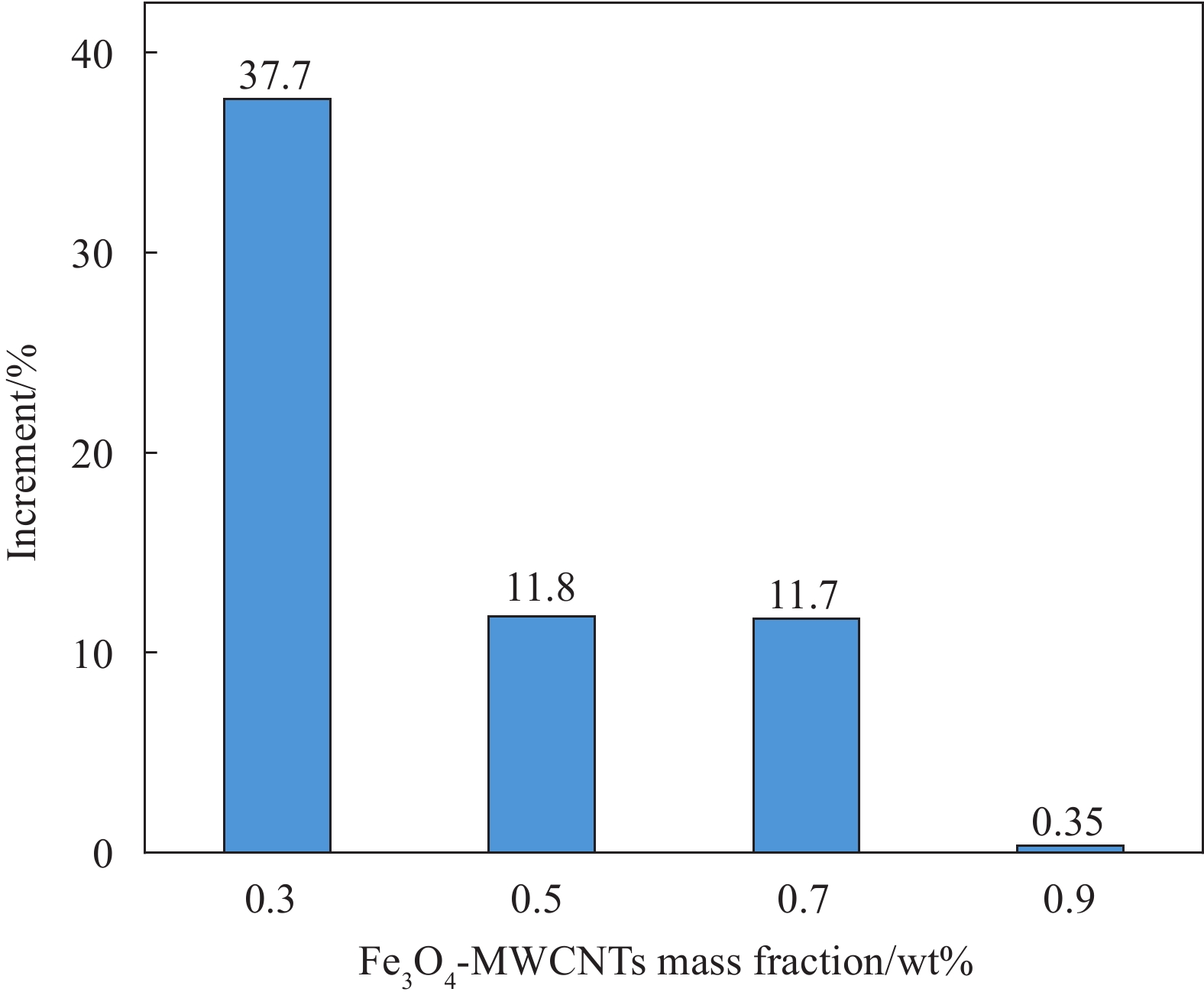
摘要: 为了提高碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料(CFRP)层间性能,采用共沉淀法在碳纳米管上接枝磁性Fe3O4粒子,通过定向喷涂工艺使磁性碳纳米管(Fe3O4-MWCNTs)在碳纤维表面取向一致,并喷涂树脂加以固定,形成碳纤维-定向碳纳米管-树脂界面,采用真空辅助树脂渗透成形(Vacuum assisted resin infusion, VARI)工艺制备层间性能优异的Fe3O4-MWCNTs层间定向增强CFRP。试验结果表明,喷涂树脂可改善和巩固定向喷涂工艺。与未加磁场喷涂工艺相比,当Fe3O4-MWCNTs的质量分数为0.3wt%时,采用定向喷涂工艺试件的I型层间断裂韧性(GIC)提升幅度最大,GIC提高了37.7%。断面形貌分析表明其增强机制以树脂的塑性变形、Fe3O4-MWCNTs棒状聚集体的拔出及树脂塑性孔洞的生长为主。该研究为具有可控定向行为的磁性碳纳米管改性CFRP层间力学性能提供了新思路与方法。Abstract: Co-precipitation method was applied for grafting magnetic Fe3O4 particles on carbon nanotubes. In order to improve the interlayer properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP), the magnetic carbon nanotubes (Fe3O4-MWCNTs) were aligned on the surface of carbon fiber by spraying process after exposure to magnetic field to form ‘carbon fiber-aligned carbon nanotubes-resin’ interface, and were fixed by spraying the resin. Aligned Fe3O4-MWCNTs-reinforced CFRP with excellent interlaminar properties was prepared by vacuum assisted resin infusion (VARI) molding. The test results show spraying resin plays an important role in consolidating and improving aligned spraying process. Compared with non-magnetic spraying process, when the mass fraction of Fe3O4-MWCNTs is 0.3wt%, the mode I interlaminar fracture toughness (GIC) increases by up to 37.7%. The main toughening mechanisms, which are pull-out and rupture of Fe3O4-MWCNTs aggregates, plastic deformation and plastic void growth of resin, are revealed by the fracture surface morphology. The research provides a new idea and method for interface modification of CFRP by adding Fe3O4-MWCNTs with controlled aligned behavior.
-
Keywords:
- CFRP /
- magnetic carbon nanotubes /
- spraying process /
- interface modification /
- fracture toughness
-
纤维增强树脂复合材料拥有高强、轻质、耐腐蚀、抗疲劳、吸波隐身等优异性能,在航空航天、军工、汽车、化工及电子等先进工业领域得到广泛应用[1-4]。按树脂基体性质可以将纤维增强树脂复合材料分为两大类,即热固性树脂基复合材料和热塑性树脂基复合材料;相较而言,热塑性树脂基复合材料具有:(1)韧性好,疲劳强度高,冲击损伤容限高;(2)预浸料和热塑性树脂存储没有期限要求;(3)热成型工艺性好,成型周期短,生产效率高;(4)边角料或废料可再熔融成型或回收利用,环境友好[5]。因此,热塑性树脂基复合材料随着工业技术发展越来越受到青睐。以聚醚醚酮(PEEK)、聚醚酮酮(PEKK)、聚苯硫醚(PPS)和聚醚酰亚胺(PEI)等为代表的高性能热塑性树脂基复合材料的出现,为航空航天结构材料选材提供了富有竞争性的解决方案,且随着产品线的延伸和技术成熟度的不断提高,高性能热塑性树脂基复合材料在航空航天结构材料体系中的地位越来越重要,并逐渐打破以环氧树脂及双马来酰亚胺树脂等为代表的传统热固性树脂基复合材料的垄断地位。
航空航天结构大而复杂,在制造和装配时需要通过连接技术将不同的部件连接在一起来实现,因此需要可靠、自动化和经济的连接技术。机械连接是目前航空结构的主要连接方法,具有制造工艺简单、厚度方向起到增强作用和便于拆装等优点;但也引入许多问题,特别是钻孔存在应力集中、孔边分层、纤维损伤、重量增加和热膨胀系数不匹配等问题[6-7]。胶接连接使连接应力集中最小化,具有优越的抗疲劳性能,但胶接需要严格的表面处理,对污染和环境非常敏感(如粉尘、水分和加工油污等),胶粘剂有存储寿命、胶接工艺复杂和周期长等问题[8]。热塑性树脂基复合材料具有可焊性,其焊接工艺已被认为是热塑性树脂基复合材料连接的有效替代技术,利用热塑性树脂基复合材料焊接可以在很大程度上消除这些问题。最具潜力的焊接方法主要有超声波焊接[9]、感应焊[10]、电阻焊[11]和激光焊[12]等。
热塑性树脂基复合材料焊接在国外已经有较长的研究历程,且相应成果已经成功应用于民用客机及战斗机结构中[2],而国内热塑性树脂基复合材料的制造及相应技术尚处于起步阶段[13]。因此,本文针对航空结构用碳纤维/聚苯硫醚(CF/PPS)热塑性复合材料,采用CF/PPS复合材料混编织物电阻元件对其织物层压板进行电阻焊接;电流、压力和加热时间是电阻焊接的重要工艺参数,采用正交实验、Taguchi方法和方差分析(ANOVA)研究分析CF/PPS热塑性复合材料电阻焊接最佳工艺参数和其对接头强度的影响,同时对其焊接接头单搭接剪切强度和断口进行测试分析,获取其失效机制。该方法也是热塑性树脂基复合材料焊接技术的有益探索。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
碳纤维/聚苯硫醚(CF/PPS)复合材料层压板是利用加拿大Barrday公司提供的AS4 3K 5HS CF织物/PPS树脂预浸料在XLB-660.660.3型平板硫化机上热压成型;热压工艺为:温度为320℃±10℃,保温时间为30 min,压力为2 MPa,冷却速率为5℃/min,压制过程排气两次;试板铺层结构为[0]8,试板厚度为2 mm,CF体积分数约为54vol%。AS4 3K 5HS CF/PPS复合材料混编织物的混编方式如图1所示,PPS树脂薄膜由日本东丽公司提供,PPS树脂膜厚度为50 μm。
1.2 电阻焊接装置
采用中国民航大学自主研制的复合材料焊接设备(CAUC-CW100),如图2所示,该设备能进行多种形式电载荷施加(直流、交流和脉冲电流),采用伺服电子压力缸进行多段恒位移或压力压装控制,数据采集器可进行焊接件的焊接接头温度、压力和位移变化的信息实时采集等功能。
电阻焊接:利用CF电热特性,在试样的焊接表面放置CF混编织物,并在焊接件上下焊接表面放置PPS树脂薄膜,CF在电热作用时产生焦耳热,熔融被焊接的焊接表面及PPS树脂薄膜,并在压力作用下形成焊接接头。在焊缝中间布置K型伯劳焊点热电偶,对焊缝温度检测,焊接示意图及尺寸如图3所示。
1.3 Taguchi方法和实验设计
Taguchi方法是以正交表为基础来获取可得到CF/PPS复合材料层板焊接质量的优化工艺方案,与传统正交实验相比,该方法利用信噪比(S/N)来衡量指标的波动[14-16]。本研究质量特性为CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接单搭接的剪切强度,3个关键焊接工艺参数即电流、压力和焊接时间作为因素,基于相同比例给出水平变化,如表1所示;因此优化目标即是获得最大的信噪比。CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接剪切强度属于越大越优的质量指标,其信噪比公式为[11]
表 1 因素和水平Table 1. Factors and levelsParameters Levels 1 2 3 4 Factor A(Current/A) 8 10 12 14 Factor B(Pressure/MPa) 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 Factor C(Time/min) 10 20 30 40 η=−10lg[1nn∑i=11Xi2] (1) 式中:η是CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接质量特性,即信噪比(dB);Xi是第i个CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接试样剪切强度(MPa);n是每组试验中的重复数(本研究n=6)。
设计L16实验,得到各次CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接实验的焊接剪切强度,然后利用式(1)计算出各次实验的信噪比,结果如表2所示。
表 2 CF/PPS复合材料层板的正交实验参数及结果Table 2. Input parameters of orthogonal arrays and performance characteristics of CF/PPS composite laminatesExpt.run Factor Performance Current
A/APressure
B/MPaTime
C/minLSS/MPa η 1 8 0.5 10 3.68 11.32 2 8 1.0 20 5.34 14.55 3 8 1.5 30 6.86 16.73 4 8 2.0 40 5.37 14.60 5 10 0.5 20 9.02 19.10 6 10 1.0 10 8.65 18.74 7 10 1.5 40 12.46 21.91 8 10 2.0 30 10.34 20.29 9 12 0.5 30 13.05 22.31 10 12 1.0 40 16.78 24.50 11 12 1.5 10 14.28 23.09 12 12 2.0 20 12.15 21.69 13 14 0.5 40 7.49 17.49 14 14 1.0 30 9.65 19.69 15 14 1.5 20 9.84 19.86 16 14 2.0 10 7.51 17.51 Average η 18.96 Notes: LSS—Lap shear strength; η—Signal to noise ratio. 同时,采用方差分析(ANOVA)来获取CF/PPS热塑性复合材料层板电阻焊接各个工艺参数对其剪切强度影响的贡献度。
1.4 焊接接头力学性能测试
参考ASTM D1002—10标准[17],采用Instron5982电子万能材料试验机对CF/PPS复合材料层板焊接的单搭接剪切强度(LSS)进行测试,试验件尺寸如图4所示。
剪切强度τ(MPa)
计算如下: τ=FmaxLb (2) 式中:L为搭接长度(mm);b为搭接宽度(mm);Fmax为最大拉伸力(N)。
1.5 剪切断口分析
采用激光共聚焦显微镜(OLYMPUS 4100)和SEM(Quanta FEG250)对Taguchi方法优化最佳焊接参数的焊接试样(记为H-LSS)和本实验方案中较低剪切强度试样(记为L-LSS)的截面形貌和剪切测试断口形貌进行观察,分析焊缝结构、铺展形态及其失效形式和机制。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 CF/PPS复合材料的焊接
图5为CF/PPS复合材料电阻焊接控制过程。可知,CF/PPS复合材料电阻焊接控制过程主要为五个阶段。第Ⅰ阶段:通电,以一定速率增加电流强度,CF/PPS复合材料混编织物电热作用产生的焦耳热也随之增加,PPS膜及焊接件表面受热软化变形,达到PPS树脂热熔温度(Tm);第Ⅱ阶段:初始压紧(预压力Ps),释放焊接件焊接界面与CF/PPS复合材料混编织物间的间隙,保证受热均匀;第Ⅲ阶段:增加焊接压力(达到额定压力Pm),保持恒温恒压,焊接件的焊接界面及PPS膜热熔,在压力作用下热塑性树脂流动,分子链热运动和扩散缠结;第Ⅳ阶段:调节电流以一定冷却速率(Tf,本实验Tf≈5℃/min)冷却,固化;第Ⅴ阶段:采用压缩空气冷却,焊接接头热收缩,完成焊接。在第Ⅱ和第Ⅲ阶段施加压力时会出现温度小幅度迅速升高后降低,这是由于施加压力使焊缝紧密,焦耳热集聚增加,随后在热传导和热扩散作用下又缓慢减小,同时压力也增大,这是由于高温使焊接接头自由体积膨胀。依据表2焊接参数完成试样焊接,如图6所示,CF/PPS复合材料层板焊接接头无明显变形。
![]() 图 5 CF/PPS复合材料电阻焊接控制过程Figure 5. Resistance welding control process of CF/PPS composites (Tm—PPS hot melt temperature; Ps—Pre-pressure during welding; Pm—Rated pressure during welding; Tf—Cooling rate; RT—Room temperature; t1—Temperature rise time of resistance welding; t2—Pre-pressure time; t 3—Constant temperature and pressure time; t4—Cooling time at Tf rate; t5—Natural cooling time)
图 5 CF/PPS复合材料电阻焊接控制过程Figure 5. Resistance welding control process of CF/PPS composites (Tm—PPS hot melt temperature; Ps—Pre-pressure during welding; Pm—Rated pressure during welding; Tf—Cooling rate; RT—Room temperature; t1—Temperature rise time of resistance welding; t2—Pre-pressure time; t 3—Constant temperature and pressure time; t4—Cooling time at Tf rate; t5—Natural cooling time)2.2 CF/PPS复合材料的工艺参数优化与性能预测
预测CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接工艺参数最优组合需要计算各个因素的信噪比均值,计算如下:
mfi=1Nn∑i=1ηi (3) 式中:f是因素;i是水平;N是实验次数;η是信噪比。
利用式(3)计算得到各因素的信噪比,比较得到该因素下的最大值是该因素的主效应,所有因素都取主效应即是预测的最优组合。CF/PPS复合材料电阻焊接工艺参数主效应图如图7所示。
可以看出,随着焊接电流、压力和焊接时间的增加,CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接单搭接剪切强度均呈先增大后减小的变化趋势,获得最优焊接参数水平为A3、B3、C3 (即电流为12 A,压力为1.5 MPa,时间为30 min),其信噪比为[11]
ηA3B3C3=m+(mA3−m)+(mB3−m)+(mC3−m) (4) 式中:ηA3B3C3为优化因素水平的预测信噪比;m为总体信噪比均值;mA3、mB3、mC3分别为因素的主效应。
由式(1)、式(3)、式(4)可得,预测最优因素水平焊接参数的CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接单搭接剪切强度为18.07 MPa,同时用实验对预测结果进行验证,采用预测最优化焊接参数焊接CF/PPS复合材料单搭接试样,并测试了其剪切强度,如表3所示,可以看出,CF/PPS复合材料单搭接试样剪切强度均值为17.88 MPa,Taguchi方法预测剪切强度和实验测试剪切强度非常接近,表明Taguchi方法可有效应用到热塑性树脂基复合材料焊接工艺参数优化中。
表 3 CF/PPS复合材料Taguchi方法预测最优因子水平、焊接接头剪切强度和实验验证结果Table 3. Taguchi method for predicting optimal factor level, weld joint shear strength and experimental verification results of CF/PPS compositesFactor A Factor B Factor C Optimal parameter 12 1.5 30 Taguchi method predicted optimum shear strength/MPa 18.07 Verification experiment results shear strength/MPa 17.88 为了更准确地研究各焊接工艺参数对CF/PPS热塑性复合材料层压板焊接接头质量影响的大小,对表2中信噪比(S/N)进行方差分析,如表4所示。可以看出,各参数方差均值和贡献分数表明焊接电流强度为CF/PPS热塑性复合材料焊接剪切强度的最主要影响因素,其贡献值为83.37%,压力其次,贡献值为9.55%,时间贡献值为6.02%。同时所有参数均具有90%以上的置信度。
表 4 CF/PPS复合材料层压板焊接接头信噪比方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance of signal-to-noise ratio of CF/PPS composite laminate welded jointsANOVA-Signal-to-noise ratio values Process parameters Level mean value SS df Variance F Sig. P Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Factor A(Current) 14.30 20.01 22.90 18.64 153.704 3 51.235 156.957 0 83.37 Factor B(Pressure) 17.56 19.37 20.40 18.52 17.600 3 5.867 17.972 0.02 9.55 Factor C(Time) 17.67 18.80 19.75 19.62 11.107 3 3.702 11.343 0.05 6.02 Errors – – – – 1.959 6 0.326 – – 1.06 Total – – – – 184.370 15 – – – 100.00 Notes: SS—Sum of squares of mean deviation; df—Degrees of freedom; F—F statistics; Sig.—Significance; P—Probability. 2.3 CF/PPS复合材料电阻焊接剪切断口的微观形貌
图8和图9为H-LSS和L-LSS两类试样的截面形貌和剪切断口形貌。
从图8可以看出,最佳焊接工艺参数焊接的H-LSS试样焊接接头中CF/PPS复合材料混编织物、PPS膜及接层板紧密结合,焊缝中无空隙及脱黏区域等缺陷,CF/PPS复合材料混编织物很好地植入到焊接层板结合界面,且PPS膜和层板PPS基体很好地融合、扩渗及结合。而L-LSS试样的焊缝中存在空隙,CF/PPS复合材料混编织物中CF和PPS树脂的浸润较差,有大量裸纤维存在,表明其焊缝结合较差。
由图9 可以看出,植入的CF/PPS复合材料混编织物断裂,焊接层板的焊接界面也有纤维拔出和断裂,表明焊接接头在剪切力作用时,CF/PPS复合材料混编织物起到了焊缝增强相作用,且与焊接层板很好地结合,是典型复合材料层板层间失效断裂破坏模式,即焊接层板和CF/PPS复合材料混编织物都受损失效。H-LSS试样中植入的CF/PPS复合材料混编织物的纤维断裂平齐,纤维上黏附大量树脂,与之对应黏结的层板表面树脂基体在纤维拔出后出现明显破碎和塑性变形,证明CF/PPS复合材料混编织物、PPS膜及层板焊接界面间树脂与纤维充分浸润、扩渗链接和结合,保证了力的有效传递。而 L-LSS试样在剪切力作用下焊接接头失效形式为CF/PPS复合材料混编织物与焊接层板界面脱黏失效,即CF/PPS复合材料混编织物和被焊接层板的焊接界面胶层脱黏。这是由于在该工艺参数下树脂和纤维的浸润差,焊缝区域边缘处有部分PPS膜未完全熔化,焊缝区域存在大量空隙和裸纤维(如图8 中L-LSS试样),在剪切力作用下诱发裂纹产生,导致接头性能较低;由图9 也可看出,L-LSS试样中CF/PPS复合材料混编织物的纤维与树脂的浸润和包裹较差,拔出纤维上树脂附着很少且不均匀,与之黏接的层板树脂基体上有明显纤维压痕,在剪切力作用下,CF/PPS复合材料混编织物中的纤维拔出,而层板树脂无明显形变,表明其结合强度较弱,剪切强度低。
由上述实验结果及分析可知,CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接工艺参数(电流、压力和时间)的变化直接影响着焊接接头的性能。随着电流强度的增加,焊接接头剪切强度呈先增大后减小的趋势,这是由于在较低电流时,CF混编织物电阻元件电热作用产生的焦耳热不足以充分软化和熔化PPS树脂,使焊缝处树脂扩渗和黏接不够充分,导致焊接接头剪切强度低;在较大电流时,CF电阻元件产生足够的焦耳热,使被焊接件的焊接界面充分均匀受热,PPS树脂充分受热软化、流动、扩渗和熔融胶接,使焊接接头剪切强度增大。但电流强度过大,产生热量过大,会使PPS树脂产生分子链断裂、热降解和烧蚀变性等不良影响[7],使焊接接头性能下降。CF/PPS复合材料层板电阻焊接需要一定的压力,由于熔融态PPS黏度较大,且流动困难,其流动是若干分子链段运动推动另一部分分子链段再运动并形成整个大分子重心移动[18],因此焊接压力是热塑性树脂基复合材料焊接的重要因素之一,压力过低时,不足以使受热软化和熔融的树脂充分流动与纤维浸润,无法排除焊缝中的气体,会增加焊缝中空隙等缺陷[19-20];而压力过高,会使焊缝软化和热熔树脂挤压排出,使焊缝的树脂含量过低,从而影响焊缝的有效黏接,因此,焊接压力过高或过低都会导致其剪切强度减小。焊接时间为电流流经CF混编织物电阻元件产生热量持续的过程,保证焊接接头所需热量,其对焊接接头性能的影响与焊接压力类似,焊接时间短,会引起树脂流动、扩渗和浸润不充分;焊接时间过长会导致焊接件的焊接界面树脂热解和烧蚀,同时引起焊接接头整体软化及纤维排布变形,使剪切强度减小。
3. 结 论
对航空结构用碳纤维/聚苯硫醚(CF/PPS)热塑性复合材料层压板,通过植入CF/PPS复合材料混编织物电阻元件进行电阻焊接技术研究。
(1)采用植入CF/PPS复合材料混编织物电阻元件对CF/PPS复合材料层板进行电阻焊接,工艺简单,设备成本低,焊接接头无异质材料引入,无明显应力集中。
(2) Taguchi方法可用于CF/PPS复合材料电阻焊接工艺参数设计和优化分析中,优化预测得到最佳焊接工艺参数为:电流为12 A,压力为1.5 MPa,时间为30 min,剪切强度为18.07 MPa;采用该参数验证CF/PPS复合材料层板焊接剪切强度为17.88 MPa,与其预测结果相近。方差分析得到CF/PPS复合材料层压板电阻焊接工艺参数电流贡献率最高,为83.37%,其次是压力,为9.55%,时间贡献率为6.02%。
(3) CF/PPS复合材料层压板电阻焊接接头横截面和剪切断口观察分析表明,最佳参数焊接试样(H-LSS)焊接接头界面结合良好,CF/PPS复合材料混编织物很好融合进焊缝,主要剪切失效形式为层间失效。较低剪切强度试样(L-LSS)焊接接头失效形式主要为界面脱黏失效。
(4)电阻焊接技术可以推广于商业和工业任何类型热塑性树脂基复合材料的连接。
-
表 1 不同Fe3O4-MWCNTs质量分数下采用不同工艺成型的试件
Table 1 Manufactured specimens by different processes with different mass farctions of Fe3O4-MWCNTs
Process Specimen Mass fraction of Fe3O4-MWCNTs/wt% Without spraying process Unmodified CFRP 0 − − − Aligned spraying process without resin Comparison CFRP 0.5 − − − Unaligned spraying process with resin Unaligned Fe3O4-MWCNTs-reinforced CFRP 0.3 0.5 0.7 0.9 Aligned spraying process with resin Aligned Fe3O4-MWCNTs-reinforced CFRP 0.3 0.5 0.7 0.9 Note: CFRP—Carbon fiber reinforced polymer. -
[1] 杜善义. 先进复合材料与航空航天[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(1):1-12. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001 DU S Y. Advanced composite materials and aerospace engineering[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2007,24(1):1-12(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001
[2] 张娜, 龙春光, 何宏燕, 等. 碳纳米纤维纸-玻纤/环氧复合材料对风力发电叶片的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(1):90-95. ZHANG N, LONG C G, HE H Y, et al. Effect of carbon nano-fiber paper-glass fiber/epoxy composite used for wind turbineblade[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(1):90-95(in Chinese).
[3] 拓宏亮, 马晓平, 卢智先. 基于连续介质损伤力学的复合材料层合板低速冲击损伤模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7):1878-1888. TUO H L, MA X P, LU Z X. A model for low velocity impact damage analysis of composite laminates based on con-tinuum damage mechanics[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(7):1878-1888(in Chinese).
[4] KHAN S U, KIM J K. Impact and delamination failure of multiscale carbon nanotube-fiber reinforced polymer composites: A review[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical & Space Sciences,2011,12(2):115-133.
[5] STORCK S, MALECKI H, SHAH T, et al. Improvements in interlaminar strength: A carbon nano-tube approach[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2011,42(6):1508-1516. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.04.039
[6] WARRIER A, GODARA A, ROCHEZ O, et al. The effect of adding carbon nanotubes to glass/epoxy composites in the fibre sizing and/or the matrix[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2010,41(4):532-538. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.01.001
[7] FAN Z, SANTARE M H, ADVANI S G. Interlaminar shear strength of glass fiber reinforced epoxy composites enhanced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Compo-sites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing (Incorporating Composites and Composites Manufacturing),2008,39(3):540-554. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2007.11.013
[8] IIJIMA S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon[J]. Nature,1991,354(6348):56-58. DOI: 10.1038/354056a0
[9] CHOU T W, GAO L, THOSTENSON E T, et al. An assessment of the science and technology of carbon nanotube-based fibers and composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2010,70(1):1-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.10.004
[10] SAGER R J, KLEIN P J, LAGOUDAS D C, et al. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the interfacial shear strength of T650 carbon fiber in an epoxy matrix[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2009,69(7-8):898-904. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2008.12.021
[11] LV P, FENG Y Y, ZHANG P, et al. Increasing the interfacial strength in carbon fiber/epoxy composites by controlling the orientation and length of carbon nanotubes grown on the fibers[J]. Carbon,2011,49(14):4665-4673. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2011.06.064
[12] AN F, LU C, GUO J, et al. Preparation of vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays grown onto carbon fiber fabric and evaluating its wettability on effect of composite[J]. Applied Surface Science,2011,258(3):1069-1076. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.09.003
[13] SEYHAN A T, TANOGLU M, SCHULTE K. Mode I and mode II fracture toughness of E-glass non-crimp fabric/carbon nanotube (CNT) modified polymer based composites[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2008,75(18):5151-5162. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2008.08.003
[14] SHAN F L, GU Y Z, LI M, et al. Effect of deposited carbon nanotubes on interlaminar properties of carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy composites using a developed spraying processing[J]. Polymer Composites,2013,34(1):41-50. DOI: 10.1002/pc.22375
[15] WILLIAMS J, GRADDAGE N, RAHATEKAR S. Effects of plasma modified carbon nanotube interlaminar coating on crack propagation in glass epoxy composites[J]. Compo-sites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2013,54(54):173-181.
[16] 赫玉欣, 杨松, 张丽, 等. 碳纳米管有序排列对碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料低温性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(8):1693-1703. HE Y X, YANG S, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of aligned carbon nanotubes in matrix on mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites at cryogenic tempera-ture[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(8):1693-1703(in Chinese).
[17] RAVINDRAN A R, LADANI R B, WU S Y, et al. Multi-scale toughening of epoxy composites via electric field alignment of carbon nanofibres and short carbon fibres[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2018(167):115-125.
[18] 周还潮, 马传国, 张晶晶. 弱磁场对EP/MWCNTs-Fe3O4复合材料结构与性能的影响[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2015, 43(10):7-12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2015.10.002 ZHOU H C, MA C G, ZHANG J J, et al. Effects of low magnetic field on structure and properties of epoxy/MWCNTS-Fe3O4 composites[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2015,43(10):7-12(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2015.10.002
[19] 董怀斌, 李长青, 任攀, 等. 碳纳米管定向排列增强碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料制备及力学性能[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2017(7):22-28. DONG H B, LI C Q, REN P, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube aligned carbon fiber/epoxy composites[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Compo-sites,2017(7):22-28(in Chinese).
[20] 陈伟, 郑亚萍. Fe3O4-MWCNTs在环氧树脂中的定向排列[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(6):54-59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3851.2013.06.008 CHEN W, ZHENG Y P. Alignment of Fe3O4-MWCNTs in epoxy resin[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(6):54-59(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3851.2013.06.008
[21] MA C G, LIU H Y, DU X S, et al. Fracture resistance, thermal and electrical properties of epoxy composites containing aligned carbon nanotubes by low magnetic field[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2015(114):126-135.
[22] THAKRE P R, LAGOUDAS D C, RIDDICK J C, et al. Investigation of the effect of single wall carbon nanotubes on interlaminar fracture toughness of woven carbon fiber-epoxy composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2011,45(10):1091-1107. DOI: 10.1177/0021998310389088
[23] 中国航空工业总公司, 碳纤维复合材料层合板I型层间断裂韧性GIC试验方法: HB 7402—1996[S]. 北京: 中国航空工业总公司, 1996. Aviation Industry Corporation of China. Test method for mode I interlaminar fracture toughness GIC of CFRP laminates: HB 7402—1996[S]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Corporation of China, 1996(in Chinese).
[24] CUNHA C, PANSERI S, IANNAZZO D, et al. Hybrid composites made of multiwalled carbon nanotubes functionalized with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for tissue engineering applications[J]. Nanotechnology,2012,23(46):465102. DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/46/465102
[25] RAVINDRAN A R, LADANI R B, WU S, et al. Multi-scale toughening of epoxy composites via electric field alignment oi carbon nanofibres and short carbon fibres[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2018,167(OCT. 20):115-125.
[26] ISLAM M F, ROJAS E, BERGEY D M, et al. High weight fraction surfactant solubilization of single-wall carbon nanotubes in water[J]. Nano Letters,2003,3(2):269-273. DOI: 10.1021/nl025924u
[27] SIDDIQUI N A, KHAN S U, KIM J K. Experimental torsional shear properties of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy compo-sites containing carbon nanotubes[J]. Composite Structures,2013,104(5):230-238.
[28] ELISA B, ESLAM S, USAMA K, et al. Interlaminar fracture toughness of CFRP laminates incorporating multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Polymers,2015,7(6):1020-1045. DOI: 10.3390/polym7061020
[29] KHAN S U, POTHNIS J R, KIM J K. Effects of carbon nanotube alignment on electrical and mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied science and Manufacturing,2013,49:26-34. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.01.015
[30] WU S Y, LADANI R B, ZHANG J, et al. Epoxy nanocompo-sites containing magnetite-carbon nanofibers aligned using a weak magnetic field[J]. Polymer,2015,68:25-34. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2015.04.080
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 钱小琴. 基于3D打印的热塑性聚氨酯防护材料性能分析及应用. 粘接. 2025(03): 111-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李世雄,侯琳,蔡普宁,刘泱,樊威. 纺织用X射线防护材料的研究进展. 棉纺织技术. 2024(03): 89-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李昊,吴承承,王志新,王亚平,廖学品,石碧. 钆-钡/天然皮革复合可穿戴X射线屏蔽材料的制备及性能. 皮革科学与工程. 2024(03): 9-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 邱淑秀,马杨,汤新颖. 一种屏蔽X射线的新型纳米复材性能测试及应用效果研究. 粘接. 2024(06): 115-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 雷超,许维星,曾运航,石碧. 硅烷改性胶原纤维/聚氯乙烯复合材料的界面相容性及其高弹抗蠕变性研究. 复合材料学报. 2024(06): 2923-2934 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 王博宇,张栋栋,袁继龙,陆地,王琦,刘洋. 无铅柔性高分子复合材料X射线屏蔽性能研究. 辐射防护. 2024(06): 695-704 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 冯斯涵,韩刘佳,陈长洁,王新厚. 纤维基轻质高效X射线防护材料的制备及性能探究. 产业用纺织品. 2024(12): 20-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载: