Stiffness prediction for injection molded fiber reinforced thermoplastics composite
-
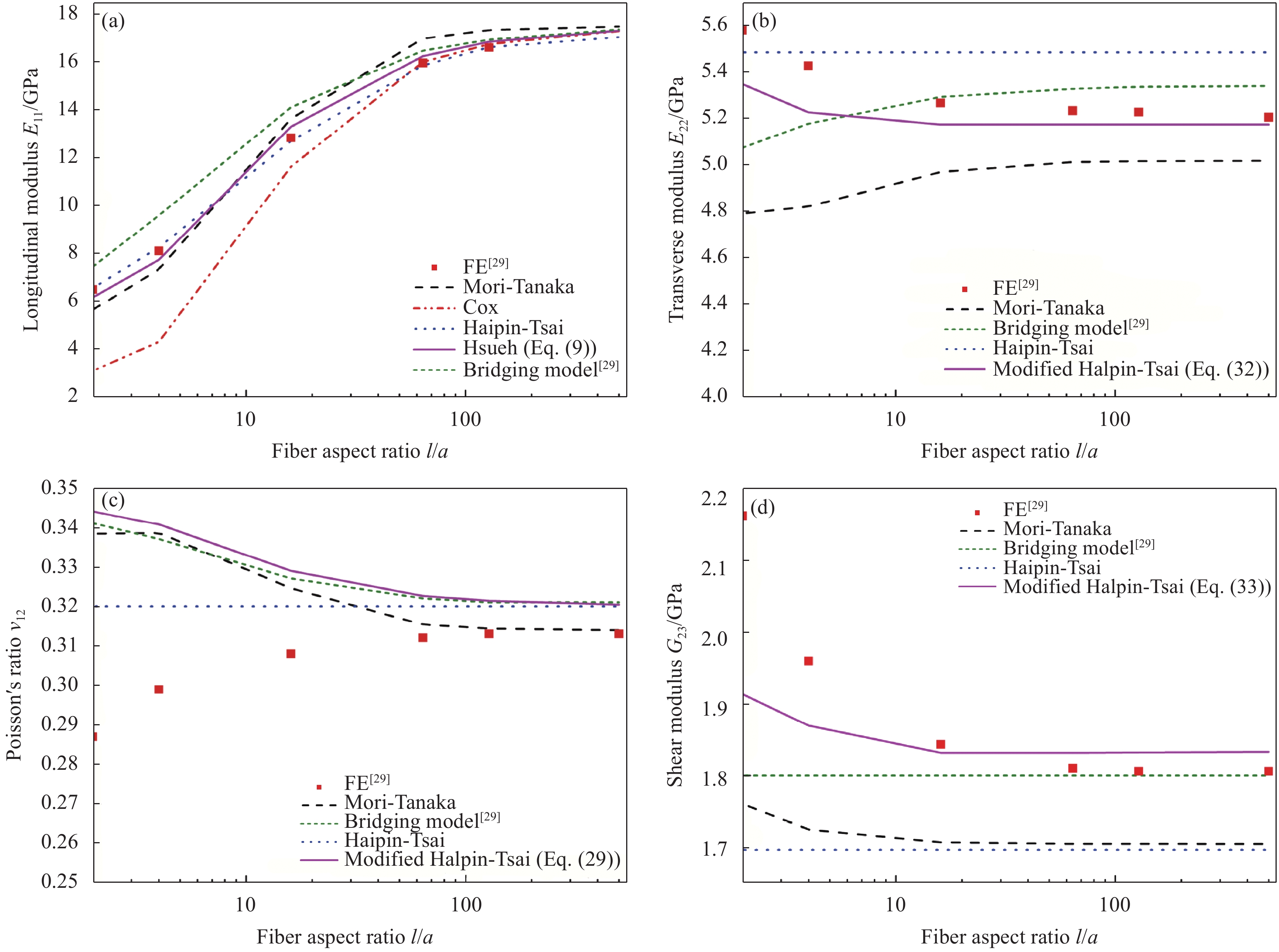
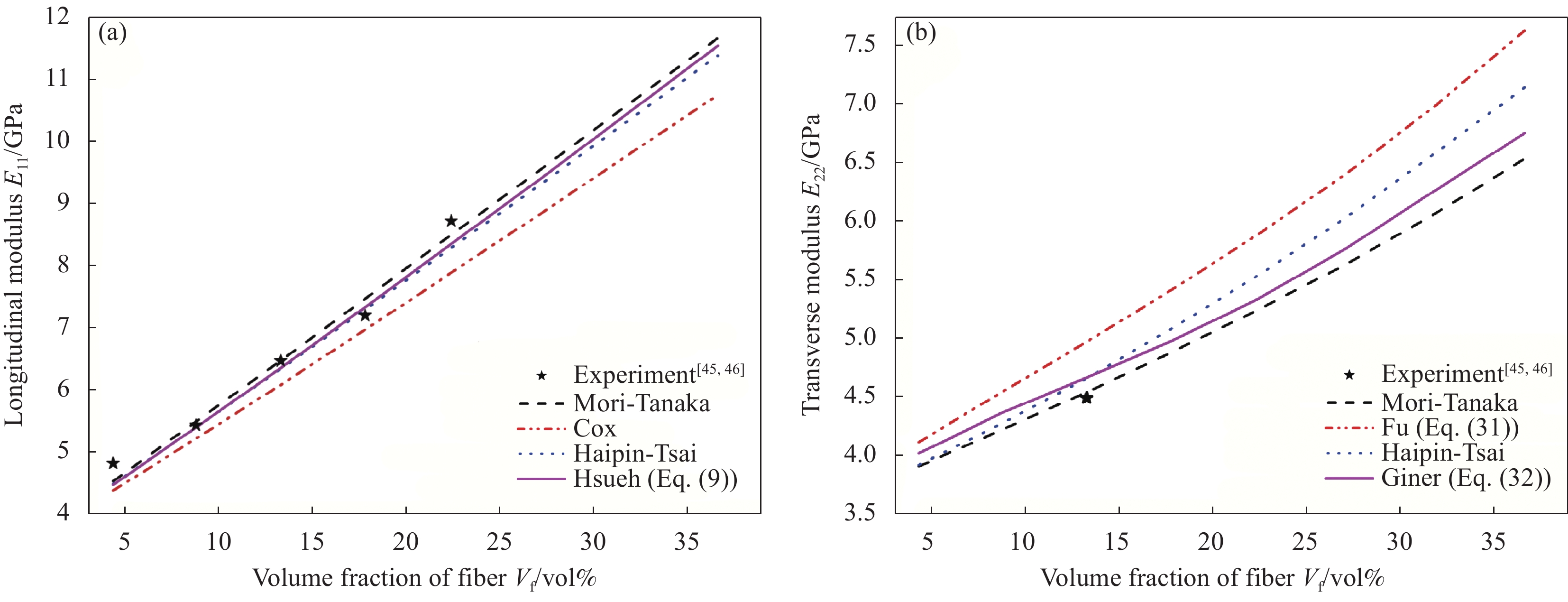
摘要: 基于Hsueh模型的应力场分布,采用代表性体积单元(RVE)平均近似方法,推导出可以退化成Halpin-Tsai模型的泊松比ν12的显性表达式,与桥联模型基本重合。结合Fu模型和Giner模型,引入与纤维长径比(l/a)相关的指数衰减函数得到横向模量E22修正的Halpin-Tsai模型,与自洽模型重合。基于泊松比各向同性假设而推导出的泊松比ν23与有限元结果逼近,远优于Halpin-Tsai模型;基于逆向工程,修正了被Halpin-Tsai模型低估的剪切模量G23。基于经典的层合板分析方法(LAA),引入纤维长度分布(FLD)及纤维取向广义分布函数,对两种注塑成型短玻璃纤维增强热塑性树脂(FRT)复合材料的弹性常数进行预测。结果表明:4个微观力学组合模型均很好地预测了复合材料的弹性常数,但纤维长度质量分布的预测结果比纤维长度数量分布的结果更为合理,特别是对于纵向杨氏模量EL的改进效果大于5%。
-
关键词:
- 刚度预测 /
- 微观力学 /
- 层合板分析方法(LAA) /
- 纤维增强热塑性复合材料 /
- 纤维长度分布(FLD) /
- 纤维取向分布(FOD)
Abstract: Based on the stress distribution in representative volume element (RVE) for Hsueh model, the explicit expression of Poisson’s ratio ν12, which can be reduced to the Halpin-Tsai model, was derived from average approximation method, and it basically coincides with the Bridging model. The modified Halpin-Tsai model for transverse modulus E22 was developed by introducing an exponential decay function of l/a related to the Fu and Giner models, and coincides with the self-consistent model. Based on the assumption of Poisson’s ratio properties, the deduced results better than the Halpin-Tsai model are close to the finite element results for Poisson’s ratio ν23, and then the underestimation of shear modulus G23 was corrected by the modified Halpin-Tsai model for ν23 based on reverse engineering. Based on the laminate analogy approach (LAA) in conjunction with fiber length distribution (FLD) and generalized fiber orientation distribution (FOD) functions, the elastic moduli for two kinds of injection molded short glass fiber reinforced thermoplastics (FRT) composite were predicted. The results show that the four combined micromechanical models all predict the elastic moduli of the composites well, but the prediction results of weight distribution of fiber lengths are more reasonable than that of number distribution of fiber lengths, especially more than 5% in the improvement effect of longitudinal Young’s modulus EL. -
-
表 1 FE分析中组分材料的物理和力学性能
Table 1 Physical and mechanical properties of materials used in FE
表 2 层合板分析方法(LAA)中组分材料的物理和力学性能[50]
Table 2 Mechanical and physical properties of materials used in laminate analogy approach (LAA)[50]
Property Short glass fiber/polyamide-6 Short glass fiber/polybutylene terephthalate S-glass fiber Polyamide-6 S-glass fiber Polybutylene terephthalate Mass fraction/wt% 35 65 30 70 Volume fraction/vol% 18 82 19 81 Tensile strength/MPa 3620 52.7 3620 64 Elastic modulus/GPa 72.4 1.92 72.4 3.0 Poisson’s ratio 0.22 0.4 0.22 0.4 表 3 注塑成型短玻璃纤维/(PBT)和短玻璃纤维/(PA6)复合材料的拉伸性能[50]
Table 3 Tensile properties of injection molded short glass fiber/polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and short glass fiber/ polyamide-6 (PA6) composites[50]
Composite Longitudinal
modulus EL/MPaTransverse
modulus ET/MPaShear modulus
GLT/MPaPoisson’s ratio
νLTCore thickness
ratio hc/%Short glass fiber/PA6 7816 (s=743) 4507 (s=678) 1641 0.3676a 13 Short glass fiber/PBT 9739 (s=916) 5846 (s=702) 2051 0.3658a 16 Notes: a—Rule of mixtures; s—Standard deviation. 表 4 短玻璃纤维/PBT和短玻璃纤维/PA6复合材料的弹性模量预测值与实验值的对比
Table 4 Comparisons of elastic moduli predictions with experiments for short glass fiber/PBT and short glass fiber/PA6 composites
Elastic modulus PA6-SGF35 PBT-SGF30 H-T* H-T G-H-T mH-T-H F-L H-T* H-T G-H-T mH-T-H F-L EL/MPa 7250
e=−7.2%7818
e= 0.0%7798
e=−0.3%8239
e=5.4%7949
e=1.7%9424
e=−3.2%9943
e=2.1%9906
e=1.7%10239
e=5.1%9770
e=0.3%ET/MPa 3844
e=−14.7%3960
e=−12.1%3838
e=−14.9%3952
e=−12.3%3991
e=−11.4%5822
e=−0.4%5949
e=1.8%5771
e=1.3%5885
e=0.7%5910
e=1.1%GLT/MPa 1463
e=−10.8%1522
e=−7.3%1516
e=−7.6%1561
e=−4.9%1.536
e=−6.4%2111
e=2.9%2165
e=5.6%2156
e=5.2%2190
e=6.8%2146
e=4.6%νLT 0.3991
e=8.6%0.4009
e=9.1%0.3971
e=8.0%0.4050
e=10.2%0.4016
e=9.2%0.3820
e=4.4%0.3820
e=4.4%0.3771
e=3.1%0.3828
e=4.6%0.3820
e=4.4%Notes: *—Eq.(34); e—Relative error; H-T—Halpin-Tsai model; G-H-T—Giner and Halpin-Tsai models; mH-T-H—Modified Halpin-Tsai and Hsueh models; F-L—Fu-Lauke model. -
[1] NING H B, LU N, HASSEN A A, et al. A review of long fibre-reinforced thermoplastic or long fibre thermoplastic (LFT) composites[J]. International Materials Reviews,2020,65(3):164-188.
[2] ISHIKAWA T, AMAOKA K, MASUBUCHI Y, et al. Overview of automotive structural composites technology developments in Japan[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2018,155:221-246. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.09.015
[3] MORTAZAVIAN S, FATEMI A. Fatigue behavior and modeling of short fiber reinforced polymer composites: A literature review[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2015,70:297-321.
[4] SONSINO C M, HEIM R, MELZ T. Lightweight-structural durability design by consideration of variable amplitude loading[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2016,91:328-336. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2015.07.030
[5] 孙宏雨, 吕兴聪, 郭垂根, 等. 杨木纤维/聚乙烯复合材料拉伸性能微观力学模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(1):155-164. SUN Hongyu, LV Xingcong, GUO Chuigen, et al. Micromechanical model of tensile properties of poplar fiber/polyethylene composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(1):155-164(in Chinese).
[6] FRIEDRICH K. Mesoscopic aspects of polymer composites: Processing, structure and properties[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1998,33(23):5535-5556. DOI: 10.1023/A:1004495611093
[7] 丁智平, 黄达勇, 荣继刚, 等. 长玻纤增强复合材料注塑成型构件强度分析[J]. 材料工程, 2018, 46(4):111-119. DING Zhiping, HUANG Dayong, RONG Jigang, et al. Strength analysis of long glass fiber reinforced composite injection molding components[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2018,46(4):111-119(in Chinese).
[8] NGUYEN B N, BAPANAPALLI S K, HOLBERY J D, et al. Fiber length and orientation in long-fiber injection-molded thermoplastics Part Ⅰ: Modeling of microstructure and elastic properties[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2008,42(10):1003-1029. DOI: 10.1177/0021998308088606
[9] HUANG D Y, ZHAO X Q. Novel modified distribution functions of fiber length in fiber reinforced thermoplastics[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,182:107749. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107749
[10] HUANG D Y, ZHAO X Q. A generalized distribution function of fiber orientation for injection molded composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2020,188:107999. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.107999
[11] FU S Y, LAUKE B, MAI Y W. Science and engineering of short fibre reinforced polymer composites[M]. New York: CRC Press, 2009.
[12] CHIN W K, LIU H T, LEE Y D. Effects of fiber length and orientation distribution on the elastic modulus of short fiber reinforced thermoplastics[J]. Polymer Composites,1988,9(1):27-35. DOI: 10.1002/pc.750090105
[13] XIA M, HAMADA H, MAEKAWA Z. Flexural stiffness of injection molded glass fiber reinforced thermoplastics[J]. International Polymer Processing,1995,10(1):74-81.
[14] FU S Y, LAUKE B. Effects of fiber length and fiber orientation distributions on the tensile strength of short-fiber-reinforced polymers[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1996,56(10):1179-1190. DOI: 10.1016/S0266-3538(96)00072-3
[15] 丁智平, 黄达勇, 荣继刚, 等. 注塑成型短玻纤增强复合材料各向异性弹性常数预测方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(24):126-134. DOI: 10.3901/JME.2017.24.126 DING Zhiping, HUANG Dayong, RONG Jigang, et al. Predicting method of anisotropic elastic constants for injection molded short glass fiber reinforced composites[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2017,53(24):126-134(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3901/JME.2017.24.126
[16] TSENG H C, CHANG R Y, HSU C H. Numerical prediction of fiber orientation and mechanical performance for short/long glass and carbon fiber-reinforced composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,144:51-56. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.02.020
[17] TSENG H C, CHANG R Y, HSU C H. Numerical predictions of fiber orientation and mechanical properties for injection-molded long-glass-fiber thermoplastic composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,150:181-186. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.07.026
[18] GARESCI F, FLIEGENER S. Young’s modulus prediction of long fiber reinforced thermoplastics[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2013,85:142-147. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.06.009
[19] SHOKRIEH M M, MOSHREFZADEH-SANI H. A novel laminate analogy to calculate the strength of two-dimensional randomly oriented short-fiber composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,147:22-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.04.034
[20] MISHUROVA T, RACHMATULIN N, FONTANA P, et al. Evaluation of the probability density of inhomogeneous fiber orientations by computed tomography and its application to the calculation of the effective properties of a fiber-reinforced composite[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science,2018,122:14-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2017.10.002
[21] FU S Y, LAUKE B. The elastic modulus of misaligned short-fiber-reinforced polymers[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1998,58(3-4):389-400. DOI: 10.1016/S0266-3538(97)00129-2
[22] FU S Y, LAUKE B, YUE C Y. The flexural modulus of misaligned short-fiber-reinforced polymers[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1999,59(10):1533-1542. DOI: 10.1016/S0266-3538(99)00022-6
[23] SEVOSTIANOV I, KACHANOV M. Modeling of the anisotropic elastic properties of plasma-sprayed coatings in relation to their microstructure[J]. Acta Materialia,2000,48(6):1361-1370. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-6454(99)00384-5
[24] SEVOSTIANOV I, GIRAUD A. Generalization of Maxwell homogenization scheme for elastic material containing inhomogeneities of diverse shape[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science,2013,64:23-36. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2012.12.004
[25] SEVOSTIANOV I. On the shape of effective inclusion in the Maxwell homogenization scheme for anisotropic elastic composites[J]. Mechanics of Materials,2014,75:45-59. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2014.03.003
[26] SEVOSTIANOV I, MOGILEVSKAYA S G, KUSHCH V I. Maxwell’s methodology of estimating effective properties: Alive and well[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science,2019,140:35-88. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2019.05.001
[27] TUCKER III C L, LIANG E. Stiffness predictions for unidirectional short-fiber composites: Review and evaluation[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1999,59(5):655-671. DOI: 10.1016/S0266-3538(98)00120-1
[28] HSUEH C H. Young’s modulus of unidirectional discontinuous-fibre composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2000,60(14):2671-2680. DOI: 10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00128-7
[29] HUANG Z M, ZHANG C C, XUE Y D. Stiffness prediction of short fiber reinforced composites[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2019,161–162:105068.
[30] CHOU T W, NOMURA S, TAYA M. A self-consistent approach to the elastic stiffness of short fibre composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1980,14(2):178-188.
[31] HALPIN J C, KARDOS J L. The Halpin-Tsai equations: A review[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science,1976,16(5):344-352. DOI: 10.1002/pen.760160512
[32] COX H L. The elasticity and strength of paper and other fibrous materials[J]. British Journal of Applied Physics,1952,3(3):72-79.
[33] MORI T, TANAKA K. Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions[J]. Acta Materialia,1973,21(5):571-574. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(73)90064-3
[34] TANDON G P, WENG G J. The effect of aspect ratio of inclusions on the elastic properties of unidirectionally aligned composites[J]. Polymer Composites,1984,5(4):327-333.
[35] BENVENISTE Y. A new approach to the application of Mori-Tanaka’s theory in composite materials[J]. Mechanics of Materials,1987,6(2):147-157. DOI: 10.1016/0167-6636(87)90005-6
[36] VIGNOLI L L, SAVI M A, PACHEC P, et al. Comparative analysis of micromechanical models for the elastic composite laminate[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,174:106961. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106961
[37] HSUEH C H. Analytical analyses of stress transfer in fibre-reinforced composites with bonded and debonded fibre ends[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters,1989,24(12):4475-4482. DOI: 10.1007/BF00544532
[38] HSUEH C H. A modified analysis for stress transfer in fibre-reinforced composites with bonded fibre ends[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1995,30(1):219-224.
[39] 张斌, 顾伯勤, 宇晓明. 大模量比短纤维增强复合材料应力分布预测[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 37(2):65-69. ZHANG Bin, GU Boqin, YU Xiaoming. Prediction of stress distribution in short-fiber-reinforced composites of large modulus ratio[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2015,37(2):65-69(in Chinese).
[40] 任超, 陈建钧, 潘红良. 纤维增强复合材料黏弹性行为的预测模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(1):162-168. REN Chao, CHEN Jianjun, PAN Hongliang. Prediction model for visco-elastic behavior of fiber reinforced composites[J]. Acta Materiac Compositae Sinica,2012,29(1):162-168(in Chinese).
[41] 任超, 陈建钧, 潘红良. 随机短纤维增强复合材料弹性模量预测模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(4):191-194. REN Chao, CHEN Jianjun, PAN Hongliang. Prediction model for elastic modulus of random short fiber reinforced composites[J]. Acta Materiac Compositae Sinica,2012,29(4):191-194(in Chinese).
[42] GINER E, VERCHER A, MARCO M, et al. Estimation of the reinforced factor ξ for calculating the transverse E2 with the Halpin-Tsai equations using the finite element method[J]. Composite Structures,2015,124:402-408. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.01.008
[43] FU S Y, HU X, YUE C Y. A new model for the transverse modulus of unidirectional fiber composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1998,33(20):4953-4960. DOI: 10.1023/A:1004442520797
[44] MONTE M D, QUARESIMIN M, LAZZARIN P. Modelling of fatigue strength data for a short fibre reinforced polyamide 6.6 based on local strain energy density[C]//16th International Conference on Composite Materials. Kyoto: ICCM, 2007.
[45] PICKERING K L, EFENDY M G A. Preparation and mechanical properties of novel bio-composite made of dynamically sheet formed discontinuous harakeke and hemp fibre mat reinforced PLA composites for structural applications[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2016,84:139-50. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.02.005
[46] PICKERING K L, EFENDY M G A. Comparison of strength and Young modulus of aligned discontinuous fibre PLA composites obtained experimentally and from theoretical prediction models[J]. Composite Structures,2019,208:566-573. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.10.057
[47] SHOKRIEH M M, MOSHREFZADEH-SANI H. An optimized representative volume element to predict the stiffness of aligned short fiber composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2015,50(23):3301-3310.
[48] PIGGOTT M R, KO M, CHUANG H Y. Aligned short-fibre reinforced thermosets: Experiments and analysis lend little support for established theory[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1993,48(1-4):291-299. DOI: 10.1016/0266-3538(93)90146-8
[49] YU H, POTTER K D, WISNOM M R. A novel manufacturing method for aligned discontinuous fibre composites (high performance-discontinuous fibre method)[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2014,65:175-185.
[50] MORTAZAVIAN S, FATEMI A. Effects of fiber orientation and anisotropy on tensile strength and elastic modulus of short fiber reinforced polymer composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2015,72:116-129.
-





 下载:
下载: