Preparation and properties of strong polyaniline-polyacrylic acid/polyacrylamide conductive hydrogel
-
摘要: 将导电聚合物引入到水凝胶网络中的导电高分子基导电水凝胶,因结合了水凝胶的三维网络结构、良好的生物相容性、优异的力学性能等和导电高分子良好电学性能等优点而被广泛研究,特别是以聚苯胺(PANI)为导电高分子的导电水凝胶。但PANI不溶于水,因此很难制备PANI基导电水凝胶。本文以制备高强度PANI基导电水凝胶为目的,尝试将PANI接枝在亲水性聚合物聚丙烯酸(PAA)上,获得能在水中均匀分散的PANI-PAA导电复合物,再使其与丙烯酰胺(AM)聚合得到高强度的PANI-PAA/PAM导电水凝胶。通过力学性能及电化学性能测试,发现该导电水凝胶具有良好的力学性能和电化学性能。当以十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)为分散剂时,其电导率可达4.63 S·m−1,可承受压缩应力1.33 MPa (压缩耗散能为85.50 kJ·m−3),拉伸断裂伸长率达964%,相应的断裂强度为0.25 MPa;而以NaOH为分散剂时,凝胶的电导率可达4.19 S·m−1,可承受压缩应力1.13 MPa (压缩耗散能为73.45 kJ·m−3),拉伸断裂伸长率达896%;相应的断裂强度为 0.14 MPa。该研究为高强度聚苯胺基导电水凝胶的制备提供了思路。Abstract: The conductive polymer-based conductive hydrogels which introduced conductive polymers into the hydrogel network have been extensively studied because of the combination of three-dimensional network structure, good biocompatibility, excellent mechanical properties and electrical properties, especially the conductive hydrogels with polyaniline (PANI) as conductive polymer. However, PANI is insoluble in water, so it is difficult to prepare PANI-based conductive hydrogels. In order to prepare high-strength PANI based conductive hydrogels, this paper attempted to graft PANI onto the hydrophilic polymer polyacrylic acid (PAA) to obtain a PANI-PAA conductive composite that could be uniformly dispersed in water, and then it was polymerized with polyacrylamide (PAM) to obtain a strong PANI-PAA/PAM conductive hydrogel. Through mechanical and electrochemical tests, it is found that the conductive hydrogel has good mechanical and electrochemical properties. When SDS was used as dispersant, the conductivity could reach 4.63 S·m−1, meanwhile, it could withstand compression stress of 1.33 MPa (corresponding dissipation energy of compression is 85.50 kJ·m−3), the elongation at break is 964%, and the corresponding breaking strength is 0.25 MPa. Under the condition of NaOH as dispersant, the conductivity could reach 4.19 S·m−1, and it could bear the compression stress of 1.13 MPa (corresponding dissipation energy of compression is 73.45 kJ·m−3), the tensile elongation at break reaches 896%, and the corresponding fracture strength is 0.14 MPa. This study provides ideas for the preparation of high-strength polyaniline-based conductive hydrogels.
-
Keywords:
- conductive hydrogels /
- strong hydrogels /
- polyaniline /
- polyacrylic acid /
- conductive complex
-
随着现代电子和通讯技术的高速发展及各类电子、电气设备的普及,无形的电磁波改变了人类的生产和生活方式。作为信息的重要载体,电磁波被广泛运用于移动通讯、卫星通信、雷达探测等领域,为人们的生产和生活带来了前所未有的便利。但是,电磁污染也对人体健康和电子设备的正常运行带来了日益严重的危害[1-3]。相关研究表明,长期的电磁辐射会造成细胞癌变或基因突变,对人体健康产生不可逆的损伤;电磁波还会对设备中的各类电子元器件产生电磁干扰,使之无法正常运行甚至失效[4-6]。电磁波已成为继废气、废水和噪声之后的第四大污染源,引起了社会和科学界的广泛关注。使用电磁屏蔽材料“阻断”电磁波的传输路径,可以有效保护敏感对象不受电磁辐射的影响,是解决电磁污染问题的主要方式[7-8]。传统的电磁屏蔽材料,如金属或合金,存在密度大、易腐蚀、柔韧性差等缺点,难以满足日益复杂的电磁环境[9-10]。因此,开发新型电磁屏蔽材料成为当今科学界的研究热点。
石墨烯是一种由碳六元环组成的二维蜂窝状结构的纳米材料,每个碳原子均为sp2杂化,贡献p轨道上剩余的一个电子形成大π键,π电子可以自由移动,赋予了石墨烯良好的导电性。此外,石墨烯薄膜拥有轻质、化学稳定性强、柔韧性好等传统电磁屏蔽材料所不具备的优良性质,使其在电磁屏蔽领域展现出巨大的应用潜力 [11-13]。Shen等[14]采用直接蒸发法制备了氧化石墨烯薄膜,并通过高温热处理得到石墨烯薄膜。该薄膜厚度约8.4 μm,在X波段的屏蔽效能为20 dB。材料的电磁屏蔽性能与其趋肤深度(Skin depth)密切相关,它表示电磁波从入射材料表面至能量衰减为表面值的1/e时所传输的距离。为了获得高屏蔽效能,材料的厚度通常需大于其趋肤深度。相比传统的金属基电磁屏蔽材料,石墨烯薄膜的趋肤深度较大,要获得高屏蔽效能需要更大的厚度。Xi等[15]采用刮涂和热还原相结合的方法制备了凝胶型石墨烯薄膜。该薄膜的屏蔽效能随厚度发生明显变化,厚度为0.3 mm时,其0.1~3 GHz的屏蔽效能达105 dB;当厚度压缩为0.05 mm时,屏蔽效能迅速衰减为45 dB。因此,单一的石墨烯薄膜很难兼顾高屏蔽效能和超薄的厚度。
根据传输线理论,当电磁波从一种介质传向另一种介质时,会在界面处发生反射和透射,反射系数与两种介质的阻抗相关,当两种介质阻抗匹配时,电磁波在界面处几乎不发生反射;两种介质的阻抗相差越大,电磁波在界面处的反射越强。如果在材料内部构筑多层异质界面,可以增加电磁波在材料内部的多次反射,延长电磁波在材料内部的传输路径,有利于电磁波的损耗[16]。基于上述理论,本文对石墨烯薄膜进行多层结构设计,构建金属-石墨烯多层异质结构模型并进行电磁场仿真优化。以结构模型为基础,通过磁控溅射技术制备了Ag-石墨烯-Ag三明治结构复合薄膜(Ag-graphene-Ag composite film,A-G-A CF),并研究了其电磁屏蔽性能及屏蔽机制。
1. 研究方法
1.1 模型构建与仿真
使用CST Studio Suite电磁场仿真软件建立金属-石墨烯多层异质结构模型,如图1所示。将金属类型、石墨烯层厚度dG、金属层厚度dM及周期数n等参数作为变量;将电磁波入射方向(z方向)的边界条件设置为开放空间,xy方向的边界条件设置为周期边界,频率设置为4~18 GHz。采用四面体网格剖分结构模型,并进行电磁场仿真,获得不同结构参数物理模型的理论屏蔽效能,研究了各变量对复合薄膜屏蔽性能的影响。
1.2 材料制备
(1)氧化石墨烯(GO)薄膜的制备
采用真空抽滤方式制备GO薄膜。具体过程如下:将GO纳米片分散于去离子水中,并超声10 min获得相应的GO分散液;将浓度约0.25 mg/mL的GO分散液倒入装有聚四氟乙烯滤膜(孔径为0.45 μm)的真空抽滤装置中,打开循环水泵抽真空使GO分散液固液分离,GO纳米片在外力作用下在聚四氟乙烯滤膜上定向组装;最后,在烘箱中干燥后,将滤膜剥离得到GO薄膜。
(2)石墨烯薄膜的制备
采用化学还原和热还原相结合的方式处理GO薄膜。具体过程如下:将抗坏血酸加入去离子水中混合均匀,获得10 mg·mL−1的分散液。然后将GO薄膜置于抗坏血酸溶液中并加热至60℃,持续8 h,获得还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)薄膜。最后,用去离子水洗涤RGO薄膜并在鼓风干燥箱中烘干。将RGO薄膜置于石墨化炉中,在高纯氩气气氛下,以2℃·min−1的加热速率升温至800℃,保温30 min;然后以5℃·min−1的加热速率升温至
2000 ℃,保温2 h,获得高结晶石墨烯薄膜。(3) A-G-A CF的制备
使用多靶磁控溅射镀膜机(JCP-350,北京泰科诺科技有限公司)制备A-G-A CF。典型过程如下:将石墨烯薄膜作为基底安装在磁控溅射系统中,以高纯度银靶作为溅射靶材,然后抽真空至5×10−4 Pa后通入高纯氩气作为工作气体,气流量为60 mL·min−1,当气体压强达到1.0 Pa后,在室温下开始进行磁控溅射,溅射功率为200 W,在石墨烯薄膜的一个表面沉积Ag镀层,获得Ag-石墨烯复合薄膜(A-G CF);然后以另一个未镀膜的表面作为溅射基底,再次进行上述磁控溅射操作,获得A-G-A CF。通过控制磁控溅射的时间改变A-G-A CF的金属镀层厚度。
1.3 材料表征
采用日本JEOL公司的JSM-7001F型场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察样品表面形貌和微观结构的演变。使用德国Bruker公司的D8型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析了样品的物相组成和晶体结构,以Cu Kα (λ=0.154184 nm)辐射源,扫描角度为10°~80°,扫描速率为5°·min−1。采用美国Thermo公司的Scientific K-Alpha型X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)对样品的元素组成及化学价态进行分析。使用Al Kα (hν=
1486.6 eV)作为X射激发源,工作电压12 kV,灯丝电流6 mA。使用江苏天瑞仪器股份有限公司生产的Thick 800A镀层测厚仪测量金属镀层的厚度。采用苏州晶格电子有限公司生产的ST-2258A型四探针测试仪获得样品的方块电阻(Rs,Ω·sq−1),使用螺旋测微器测量样品的厚度(d,mm),并通过以下公式计算样品的电导率(σ,S·m−1)。σ=1000Rsd (1) 基于微带传输线法,使用矢量网络分析仪测试样品的相对磁导率μr,并通过以下公式计算样品的趋肤深度δ[17-18]。
μ=μrμ0 (2) δ=1√πfμσ (3) 式中:f为电磁波的频率;μ为样品的磁导率;μ0为真空磁导率,4π×10−7 H·m−1。
1.4 电磁屏蔽性能测试
采用波导法通过美国Agilent公司的N5247A型矢量网络分析仪测试样品的散射参数(S11和S21)。通过下列公式分别计算样品的总屏蔽效能(SEtotal)、反射衰减(SER)和吸收衰减(SEA)[19-20]。
SEtotal =−10lgT=−10lg(|S21|2) (4) SER=−10lg(1−R)=−10lg(1−|S11|2) (5) SEA=−10lg(T1−R)=−10lg(|S21|21−|S11|2) (6) 式中,T和R分别是电磁波的透射系数和反射系数。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 仿真结果分析
在保持复合薄膜的金属层与石墨烯层厚度一致的条件下,对不同金属类型(Ag、Cu、Al、Ni)的金属-石墨烯复合薄膜(dM=500 nm、dG=20 μm、n=1)的屏蔽性能进行了仿真模拟,结果如图3(a)所示。在4~18 GHz范围内,Ag-石墨烯复合薄膜的屏蔽效能为48.9 dB,高于其他类型的金属-石墨烯复合薄膜,这是由于Ag具有比其他金属更高的电导率(6.30×107 S·m−1),对电磁波中的电场有极强的屏蔽能力。由于Cu的电导率与Ag接近,Cu-石墨烯复合薄膜的屏蔽效能(48.1 dB)仅次于Ag-石墨烯复合薄膜。而Al的电导率约为3.77×107 S·m−1,Al-石墨烯复合薄膜的屏蔽效能下降为45.0 dB。值得注意的是,Ni的电导率虽然只有1.65×107 S·m−1,但Ni-石墨烯复合薄膜的屏蔽效能(45.7 dB)却高于Al-石墨烯复合薄膜,这是由于Ni原子的3d电子层拥有大量未成对电子,这些电子的自旋和轨道运动产生了较大的磁矩,在宏观上表现为较高的磁导率,对电磁波中的磁场起到有效的阻隔作用[21-22],进而在一定程度上提高屏蔽效能。上述仿真结果表明,金属材质的电导率和磁导率共同影响着复合薄膜的屏蔽效能。
![]() 图 3 金属-石墨烯多层复合薄膜的屏蔽效能仿真结果:金属类型(a)、石墨烯层厚度(b) 、金属层厚度(c)、周期数(d)对屏蔽效能的影响Figure 3. Simulation results of shielding effectiveness for metal-graphene multilayer composite films: The influence of metal type (a), thickness of graphene layer (b), thickness of metal layer (c) and period number (d) on shielding effectiveness
图 3 金属-石墨烯多层复合薄膜的屏蔽效能仿真结果:金属类型(a)、石墨烯层厚度(b) 、金属层厚度(c)、周期数(d)对屏蔽效能的影响Figure 3. Simulation results of shielding effectiveness for metal-graphene multilayer composite films: The influence of metal type (a), thickness of graphene layer (b), thickness of metal layer (c) and period number (d) on shielding effectiveness以Ag-石墨烯复合薄膜的结构模型为例,研究了石墨烯层和金属层厚度对复合薄膜屏蔽效能的影响。图3(b)展示了复合薄膜(dM=200 nm,n=1)的屏蔽效能与石墨烯层厚度之间的关系。随着石墨烯层的厚度从10 μm增加至50 μm,复合薄膜的屏蔽效能从37.5 dB增加至42.9 dB,但升高幅度逐渐下降。这是由于当石墨烯层厚度小于趋肤深度时,厚度对屏蔽效能影响较大;当厚度超过趋肤深度后,厚度对屏蔽效能的提升作用显著减弱。图3(c)展示了复合薄膜的屏蔽效能与金属层厚度之间的关系(dG=50 μm,n=1)。与石墨烯层厚度的作用类似,复合薄膜的屏蔽效能随金属层厚度的增加而非线性增加。当金属层厚度从200 nm增加至500 nm时,屏蔽效能从42.9 dB提高至50.8 dB。
Ag-石墨烯复合薄膜(dM=500 nm,dG=50 μm)的屏蔽效能随周期数的变化规律如图3(d)所示。这里,0.5个周期代表在整数周期的基础上额外增加一个金属层。在保持石墨烯层总厚度和金属层总厚度一致的条件下,改变复合薄膜的周期数。当周期数为1时,复合薄膜的屏蔽效能约50.8 dB;当增加一层金属后,复合薄膜的屏蔽效能提高至53.1 dB,特别是高频区域,增加幅度更加明显。类似地,其他周期数为n+0.5的多层复合薄膜的屏蔽效能普遍高于周期数n的复合薄膜,这个现象可用传输线理论解释,如图4所示。由于金属与石墨烯之间的阻抗失配,导致电磁波在上下两层金属之间发生多次反射,相当于延长电磁波的传输路径,增加了电磁波的传输损耗。此外,周期数由1增加为2或由1.5增加为2.5时,屏蔽效能明显提高;但随着周期数进一步增加,屏蔽效能提升受限,甚至有所降低,这可能与金属单层厚度降低有关。当金属单层厚度低于其趋肤深度时,部分电磁波能量将穿透金属单层,对电磁波的束缚作用反而减弱,造成了屏蔽效能的略微降低。
2.2 材料结构与组成分析
图5(a)是A-G-A CF的实物图,在磁控溅射镀Ag后,复合薄膜保持了石墨烯薄膜良好的柔韧性。图5(b)和图5(c)分别是A-G-A CF的横截面SEM图像及其能量分布面扫描分析(EDS-mapping)。石墨烯薄膜的上下表面成功被Ag镀层覆盖,呈现出典型的三明治结构。Ag镀层与石墨烯基底之间展现了良好的界面结合性能,在弯曲和折叠时,Ag镀层不会脱落或产生裂纹。这主要有以下两方面原因:首先,经还原和热处理后的石墨烯表面仍然含有一定数量的羟基、羰基等含氧官能团,Ag原子与这些含氧官能团通过氧诱导的共价相互作用在界面处形成金属/氧化物过渡层,大大改善了Ag与石墨烯之间的相容性[23];其次,在磁控溅射镀膜过程中,溅射的Ag原子具有非常高的能量,它们轰击基材表面使其产生大量缺陷,同时石墨烯薄膜表面本身也存在一定结构缺陷,这些缺陷为Ag原子提供了形核位点,对Ag镀层产生机械“锚定”作用[24],进一步提高了Ag镀层与石墨烯薄膜之间的界面结合能力。图5(d)~图5(f)是不同溅射时间制备的A-G-A CF样品表面的SEM图像。可以看出,薄膜表面被覆盖了一层致密的纳米颗粒,且纳米颗粒的尺寸随溅射内部时间的延长而逐渐增大,当溅射时间为10 min时,纳米金属颗粒的粒径细小且均匀,镀层表面非常平整;当溅射时间为20 min时,部分晶粒长大,表面开始变得凹凸不平;当溅射时间为30 min时,部分晶粒向外生长凝聚为孤岛形的豆状颗粒,颗粒尺寸约100~200 nm左右。
![]() 图 5 A-G-A CF的实物图(a)、横截面SEM图像(b)、横截面EDS mapping图(c);不同溅射时间制备的A-G-A CF的表面形貌:(d) 10 min;(e) 20 min;(f) 30 minFigure 5. Photograph (a), cross-section SEM image (b), cross-section EDS mapping (c) of A-G-A CF; Surface morphologies of A-G-A CF at different sputtering times: (d) 10 min; (e) 20 min; (f) 30 min
图 5 A-G-A CF的实物图(a)、横截面SEM图像(b)、横截面EDS mapping图(c);不同溅射时间制备的A-G-A CF的表面形貌:(d) 10 min;(e) 20 min;(f) 30 minFigure 5. Photograph (a), cross-section SEM image (b), cross-section EDS mapping (c) of A-G-A CF; Surface morphologies of A-G-A CF at different sputtering times: (d) 10 min; (e) 20 min; (f) 30 min图6(a)是所制备的A-G-A CF的XRD图谱。可以看出,样品在2θ=26.7°和54.6°出现了两个强衍射峰,分别对应于C的(002)和(004)晶面,表明所制备的石墨烯薄膜结晶度非常高。在2θ=38.3°出现一个较小的峰,对应于Ag的(111)晶面[25-26]。由于Ag镀层的厚度非常小,含量远远低于石墨烯,因此,Ag的衍射峰强度远低于C。图6(b)是不同溅射时间制备的复合薄膜的Ag(111)晶面衍射峰的高分辨率XRD图谱。可以看出,Ag(111)衍射峰的强度随着溅射时间的延长而逐渐增大,峰宽则逐渐变窄,这归因于Ag镀层厚度及纳米Ag晶粒尺寸的增大。
图6(c)是不同溅射时间制备的A-G-A CF的XPS图谱。除了285 eV出现的C1s峰外,所有样品在368 eV分别出现了Ag的3d特征峰[27],并且随着溅射时间的延长,Ag特征峰的强度逐渐提高。此外,各样品在532 eV出现了O1s峰,这可能来自于石墨烯表面残余的含氧官能团和Ag镀层的部分氧化。图6(d)是复合薄膜Ag3d峰的高分辨率XPS图谱,Ag3d峰是由368.5 eV和374.5 eV两个特征峰构成,分别属于Ag3d5/2和Ag3d3/2轨道。每个特征峰又可以分解为两个峰,较强的峰代表Ag单质,较弱的峰来自于Ag+,证实了少量Ag单质被氧化为Ag2O[28]。
2.3 电磁屏蔽性能分析
表1展示了石墨烯薄膜(1#)、不同溅射时间制备的A-G CF(2#~6#)及A-G-A CF(7#~11#)的镀层厚度和电导率。由表可知,石墨烯薄膜表面沉积Ag镀层后,电导率提高了近两个数量级。随着溅射时间的延长,镀层厚线性增加,电导率进一步提高。图7(a)展示了石墨烯薄膜(1#)、A-G CF (2#)和A-G-A CF (7#)的趋肤深度随频率的变化规律。随着频率的增加,各样品的趋肤深度呈现下降趋势。在4~18 GHz范围内,A-G CF和A-G-A CF的趋肤深度在4~10 μm之间,比石墨烯薄膜(27~60 μm)低一个数量级。在相同频率下,A-G-A CF的电导率略小于相同镀层厚度的A-G CF,而趋肤深度略微增加。
表 1 石墨烯薄膜、不同溅射时间制备的Ag-石墨烯复合薄膜(A-G CF)和A-G-A CF的镀层厚度和导电性能Table 1. Coating thickness and conductivity of graphene film, Ag-graphene composite films (A-G CF) and A-G-A CF prepared with different sputtering timeSample Sputtering time/min Coating thickness/μm Conductivity/(S·m−1) 1# Graphene film — 0 1.9×104 2# A-G CF 20 0.20 7.8×105 3# A-G CF 30 0.29 9.0×105 4# A-G CF 40 0.38 1.0×106 5# A-G CF 50 0.49 1.3×106 6# A-G CF 60 0.58 1.6×106 7# A-G-A CF 2×10 0.20 7.1×105 8# A-G-A CF 2×15 0.28 8.1×105 9# A-G-A CF 2×20 0.36 9.3×105 10# A-G-A CF 2×25 0.48 1.1×106 11# A-G-A CF 2×30 0.58 1.4×106 ![]() 图 7 石墨烯薄膜、A-G CF和A-G-A CF的屏蔽性能: (a) 趋肤深度;(b) 屏蔽效能;(d) 总屏蔽效能(SEtotal)、反射衰减(SER)和吸收衰减(SEA);(e) 透射系数T、反射系数R和吸收系数A;不同溅射时间制备的A-G-A CF的屏蔽性能:(c) 屏蔽效能;(f) SER、SEA和SEtotal值Figure 7. Shielding properties of graphene film, A-G CF and A-G-A CF: (a) Skin depth; (b) Shielding effectiveness; (d) Total shielding effectiveness (SEtotal), reflection attenuation (SER) and absorption (SEA); (e) Transmittance T, reflectance R and absorbance A; Shielding properties of A-G-A CF with different magnetron sputtering time: (c) Shielding effectiveness; (f) SER, SEA and SEtotal values
图 7 石墨烯薄膜、A-G CF和A-G-A CF的屏蔽性能: (a) 趋肤深度;(b) 屏蔽效能;(d) 总屏蔽效能(SEtotal)、反射衰减(SER)和吸收衰减(SEA);(e) 透射系数T、反射系数R和吸收系数A;不同溅射时间制备的A-G-A CF的屏蔽性能:(c) 屏蔽效能;(f) SER、SEA和SEtotal值Figure 7. Shielding properties of graphene film, A-G CF and A-G-A CF: (a) Skin depth; (b) Shielding effectiveness; (d) Total shielding effectiveness (SEtotal), reflection attenuation (SER) and absorption (SEA); (e) Transmittance T, reflectance R and absorbance A; Shielding properties of A-G-A CF with different magnetron sputtering time: (c) Shielding effectiveness; (f) SER, SEA and SEtotal values为了探索Ag镀层和三明治结构对复合薄膜电磁屏蔽性能的影响,对比了厚度接近(~26 μm)的石墨烯薄膜(1#)、A-G CF(2#)和A-G-A CF(7#)的屏蔽效能,结果如图7(b)所示。石墨烯薄膜的平均屏蔽效能仅24 dB,这是由于它的厚度小于趋肤深度。石墨烯薄膜单面镀Ag后,趋肤深度减小至10 μm以下,远小于薄膜厚度,因而屏蔽效能显著增加至44 dB。在相同频率下,A-G-A CF的趋肤深度略高于A-G CF,但其平均屏蔽效能却提高至51 dB,特别是高频区域(14~18 GHz)的屏蔽效能比A-G CF高10 dB左右,这主要得益于三明治结构中的多重异质界面,使电磁波被束缚在金属层之间发生多次反射,相当于延长电磁波在石墨烯薄膜中的传输路径,进而使更多电磁能被损耗。此外,石墨烯薄膜的屏蔽效能随频率增加而降低,而A-G CF和A-G-A CF的屏蔽效能随着频率的增加而提高,这是由于屏蔽效能随频率的变化规律受材料电导率、磁导率、厚度及趋肤深度等因素的影响[29]。石墨烯薄膜镀银后,材料的电导率和趋肤深度均显著变化,因而,复合薄膜的屏蔽效能随频率的变化趋势也发生明显改变。图7(c)展示了不同溅射时间制备的A-G-A CF的电磁屏蔽性能。随着溅射时间的延长,金属镀层的厚度增加,复合薄膜的平均屏蔽效能逐渐从51 dB增加至65 dB,这与金属-石墨烯多层异质结构模型的电磁场仿真结果相匹配。表2对比了A-G-A CF和其他石墨烯基复合材料的电磁屏蔽性能,如碘掺杂石墨烯薄膜[30]、纤维素纳米纤维(CNF)/石墨烯@Ni复合薄膜[22]、Fe3O4/石墨烯复合薄膜[17]、Cu/石墨烯复合薄膜、石墨烯/聚酰亚胺复合薄膜[31]、石墨烯/MXene复合薄膜[32]等。可以看出,所制备的A-G-A CF的屏蔽效能优于报道的大部分石墨烯基复合材料。并且,A-G-A CF的厚度仅26 μm,展示了其在高集成度便携式电子设备中的潜在应用价值。
为了揭示A-G-A CF屏蔽机制,本文对比石墨烯薄膜(1#)、A-G CF(4#)和A-G-A CF(7#)的SER、SEA和SEtotal,结果如图7(d)所示。石墨烯薄膜的SER大于SEA,屏蔽机制以反射损耗为主。石墨烯薄膜单面镀Ag后,电导率大幅度提升,对电磁波的反射能力进一步增强。构筑三明治结构后,SER由34 dB降低至28 dB,SEA由10 dB提高为23 dB,对电磁波的吸收能力增强,这主要得益于电磁波在三明治结构中多次反射而带来的传输损耗。利用公式T=|S21|2,R=|S11|2,A=1–T–R,分别计算了石墨烯薄膜、A-G CF和A-G-A CF的透射系数T、反射系数R和吸收系数A,结果如图7(e)所示。可以看出,各样品的反射系数都非常接近1,表明绝大部分入射电磁波都在样品表面被反射,没有进入材料内部;而吸收系数远高于透射系数,说明进入材料内部的电磁波大部分被吸收,只有极少部分电磁波穿透样品,特别是A-G-A CF的吸收系数比其透射系数高近3个数量级,表现了更强的吸收损耗能力。
表 2 A-G-A CF与先前报道的石墨烯基复合薄膜的电磁屏蔽性能(EMI)对比Table 2. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding performance of graphene-based composite film reported in previous references and A-G-A CFSample Thickness/μm Shielding effectiveness/dB Frequency range/GHz Ref. Graphene film 8.4 20 8-12 [14] Fe3O4/graphene film 50 52.76 8-12 [17] CNF/RGO@Ni film 15~20 32.2 8-12 [22] Iodine-doped graphene film 12.5 52.2 8-18 [30] Cu/graphene film 7.8 52 1-18 Graphene/polyimide composite films 151 31.37 8-12 [31] Graphene/MXene composite films 100 96.3 8-12 [32] A-G-A CF 26 65 4-18 This work Notes: CNF—Cellulose nanofibers; RGO—Reduced graphene oxide. 图7(f)展示了镀层厚度对A-G-A CF屏蔽机制的影响。随着溅射时间延长,镀层厚度线性增加,SER由28 dB增加至46 dB,而SEA则有下降趋势,这可能是由于镀层厚度增加提高了复合薄膜的电导率,导致复合薄膜与空气之间的阻抗匹配程度下降,使更多电磁波被Ag镀层直接反射而无法进入三明治结构内部,进而影响了复合薄膜对电磁波的吸收。
3. 结 论
本文基于传输线理论,对石墨烯薄膜进行了表面修饰和多重异质界面设计,建立金属-石墨烯多层异质结构模型并进行电磁场仿真,探索了模型的结构参数对金属-石墨烯多层复合薄膜屏蔽效能的影响规律;基于仿真模拟结果,采用磁控溅射方法在石墨烯薄膜表面沉积Ag镀层获得了Ag-石墨烯-Ag三明治结构复合薄膜(A-G-A CF),并对其结构形貌和电磁屏蔽性能进行分析,揭示了其屏蔽机制。主要结论如下:
(1)根据仿真结果,n+0.5周期的金属-石墨烯多层结构的屏蔽效能高于n周期的金属-石墨烯多层结构。并且,增加周期数可以提高金属-石墨烯多层结构的屏蔽效能,但在总厚度不变的情况下,周期数过多会导致单个金属层厚度过小,反而不利于阻隔电磁波;
(2) A-G-A CF的电磁屏蔽效能高于相同厚度的Ag-石墨烯复合薄膜(A-G CF),尤其是吸收损耗远高于A-G CF,这得益于A-G-A CF的三明治结构使电磁波被束缚在金属层之间发生多次反射,延长了电磁波在石墨烯薄膜中的传输路径,进而将更多电磁能转化为热能而耗散;
(3) A-G-A CF的电磁屏蔽效能与Ag镀层厚度呈正相关关系,当金属镀层总厚度为580 nm时,所制备复合薄膜在4~18 GHz的平均屏蔽效能达65 dB。
-
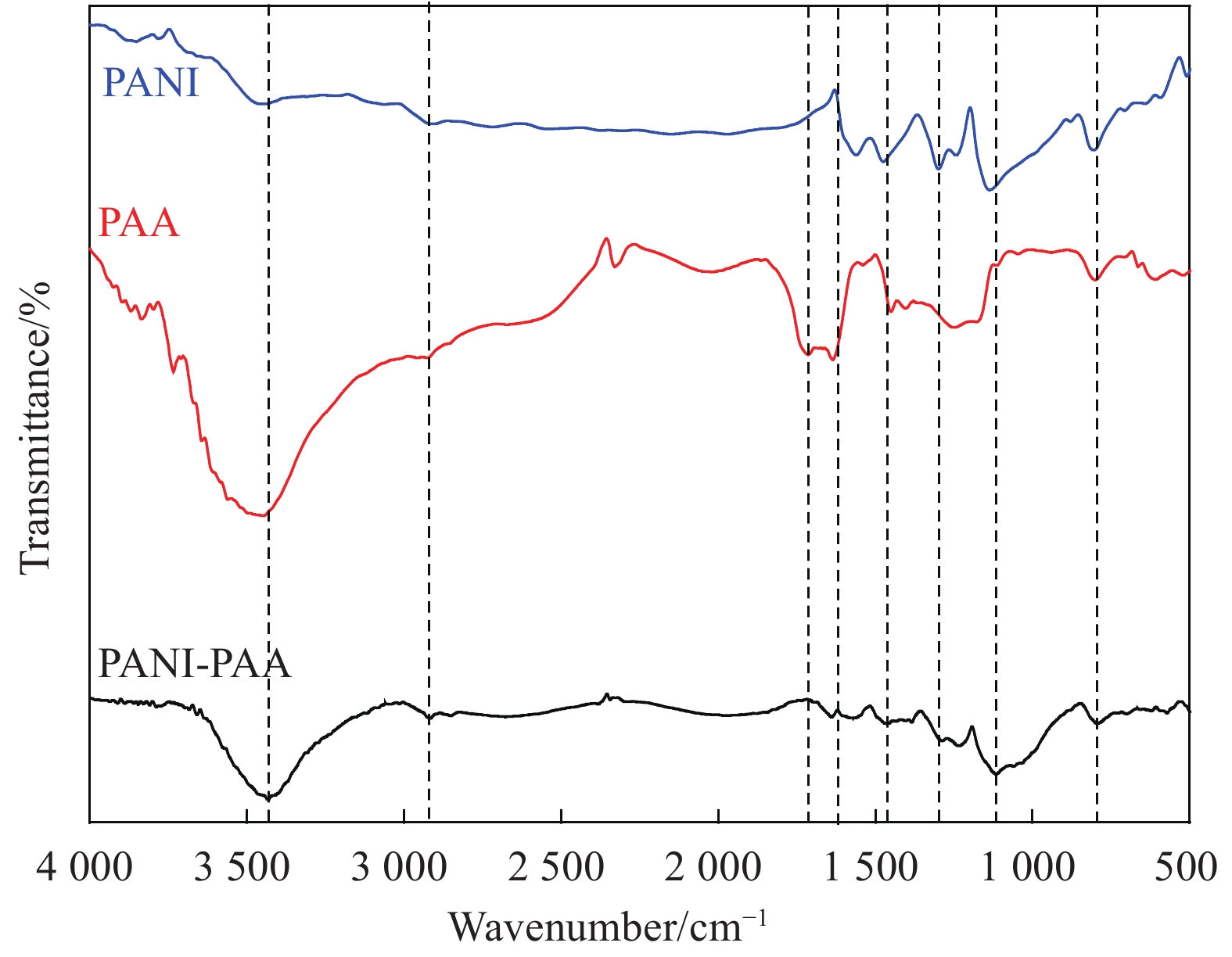
图 3 以SDS ((a)~(d)) 和NaOH ((e)~(g)) 为分散剂制备PANI-PAA/PAM导电水凝胶
Figure 3. Preparation of PANI-PAA/PAM conductive hydrogel with SDS ((a)-(d)) and NaOH ((e)-(g)) as dispersant, respectively ((a) PANI-PAA/SDS; (b) PANI-PAA/SDS; (c) PANI-PAA/SDS/AM; (e) PANI-PAA/NaOH solution; (f) PANI-PAA/NaOH dispersion; (g) PANI-PAA/NaOH/AM dispersion; ((d), (h)) PANI-PAA/PAM conducting hydrogel)
表 1 聚苯胺-聚丙烯酸/聚丙烯酰胺 (PANI-PAA/PAM) 导电水凝胶的配方
Table 1 Formula of polyaniline-polyacrylic acid/polyacrylamide (PANI-PAA/PAM) conductive hydrogels
PANI-PAA/g H2O/g SDS/g NaOH/g AM/g MBA(0.25wt%)/μL APS/g TEMED/μL 0 5 0.01 — 1.5 1 100 0.02 100 0.01 5 0.01 — 1.5 1 100 0.02 100 0.02 5 0.02 — 1.5 1 100 0.04 100 0.03 5 0.03 — 1.5 1 100 0.06 100 0 5 — 0.03 1.5 1 100 0.025 100 0.05 5 — 0.03 1.5 1 100 0.025 100 0.075 5 — 0.0475 1.5 1 100 0.0375 100 0.1 5 — 0.06 1.5 1 100 0.05 100 Notes: SDS—Sodium dodecyl sulfate; AM—Acrylamide; MBA—N, N'-methylene bisacrylamide; APS—Ammonium persulfate; TEMED—Tetramethylethylenediamine. 表 2 PANI-PAA/PAM导电水凝胶的压缩性能
Table 2 Compression properties of PANI-PAA/PAM conductive hydrogels
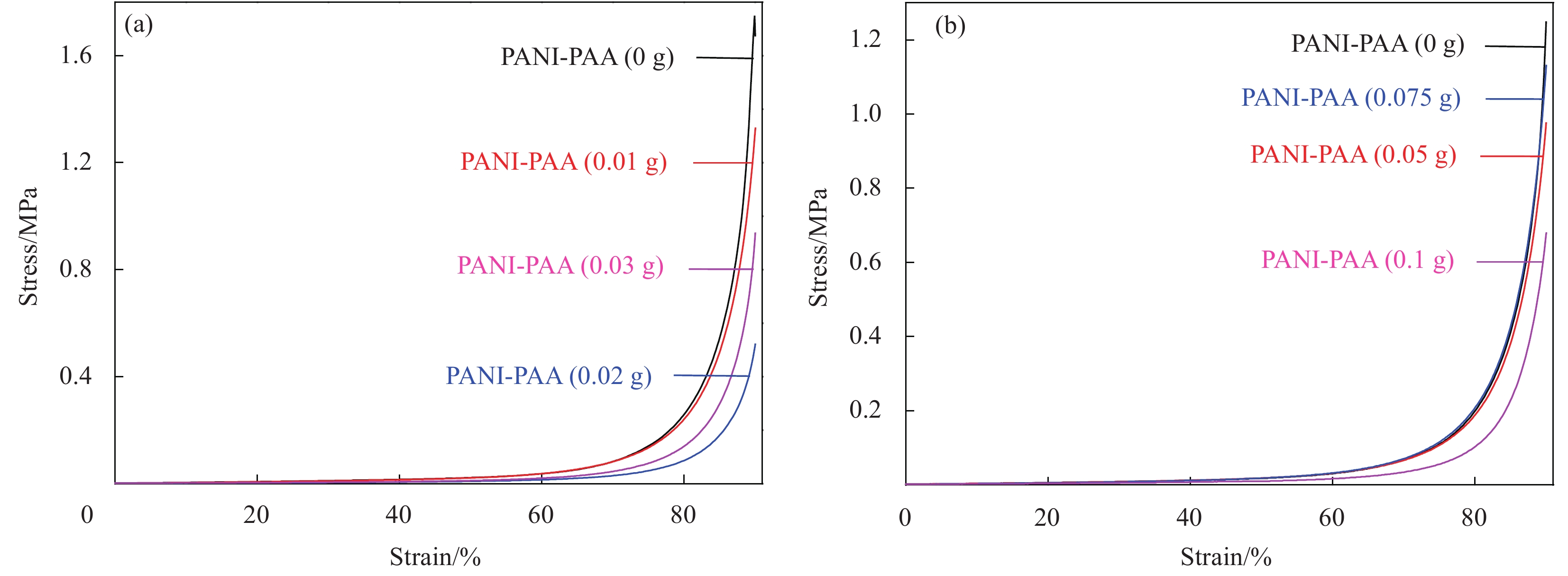
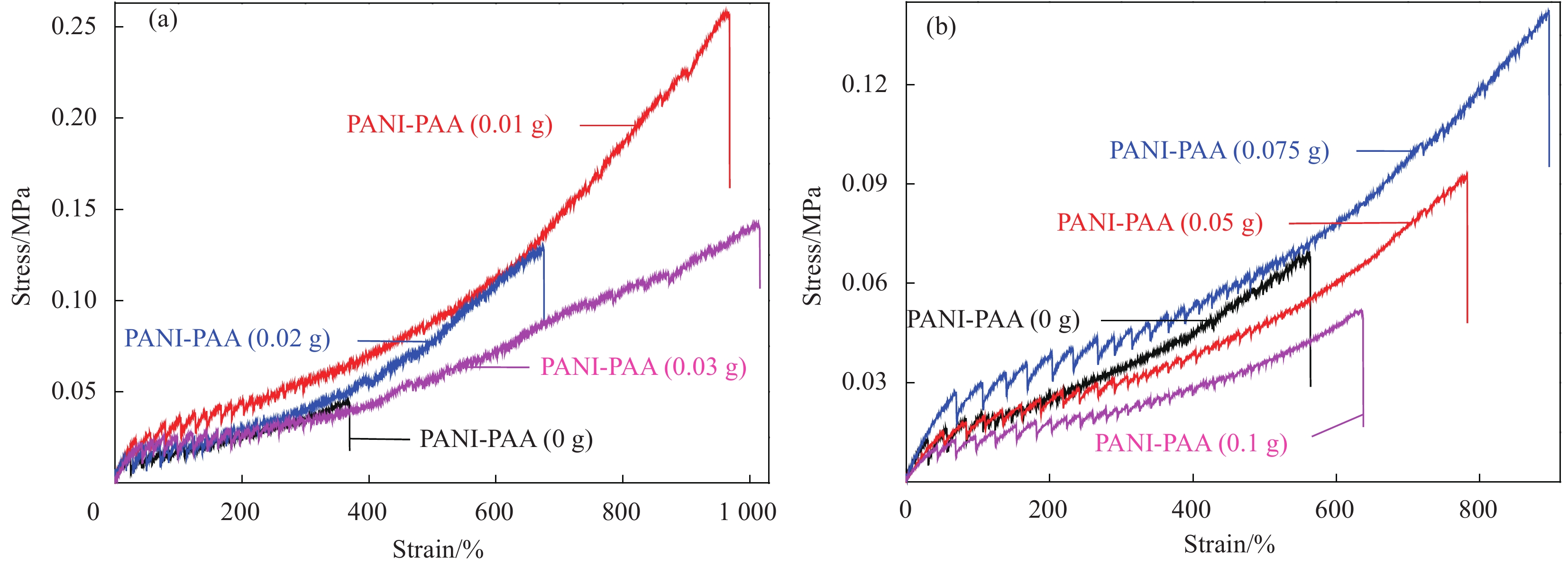
Dispersant PANI-PAA/g Compressive stress/MPa Elastic modulus/Pa Dissipated energy/(kJ·m−3) SDS 0 1.75 282.00 96.13 0.01 1.33 251.33 85.50 0.02 0.52 75.47 32.13 0.03 0.94 109.33 51.71 NaOH 0 1.25 220.79 71.86 0.05 0.98 214.10 66.79 0.075 1.13 183.48 73.45 0.1 0.68 111.09 39.96 表 3 PANI-PAA/PAM导电水凝胶的电导率
Table 3 Conductivity of PANI-PAA/PAM conducting hydrogel
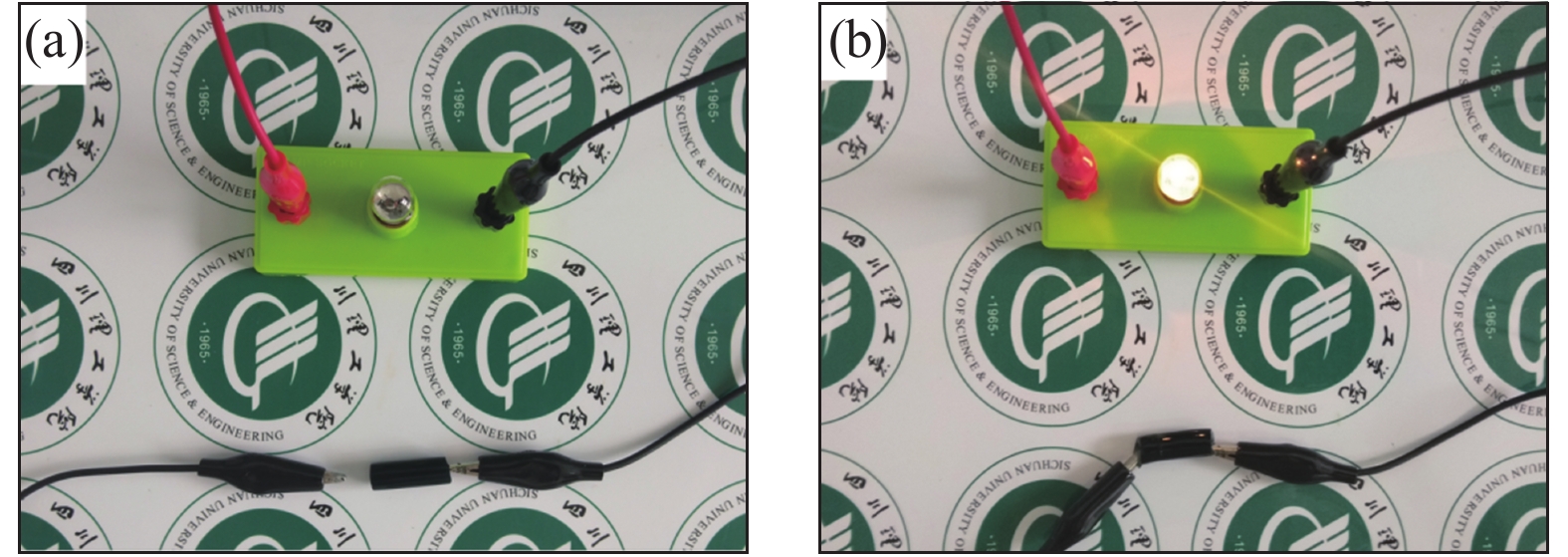
Dispersant PANI-PAA/g Conductivity/(S·m−1) SDS 0 0.023 0.01 2.38 0.02 2.69 0.03 4.63 NaOH 0 0.015 0.05 3.53 0.075 3.07 0.1 4.19 -
[1] BAI R B, YANG J W, SUO Z G. Fatigue of hydrogels[J]. European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids,2019,74:337-370. DOI: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2018.12.001
[2] ZHANG W, FENG P, CHEN J, et al. Electrically conductive hydrogels for flexible energy storage systems[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2019,88:220-240. DOI: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.09.001
[3] YUK H, LU B Y, LIN, S, et al. 3D printing of conducting polymers[J]. Nature Communications,2020,11:1604. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15316-7
[4] ZHAO F, SHI Y, PAN L J, et al. Multifunctional nanostructured conductive polymer gels: Synthesis, properties, and applications[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research,2017,50:1734-1743. DOI: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00191
[5] PAN L J, YU G H, ZHAI D Y, et al. Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrochemical activity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2012,109:9287-9292. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1202636109
[6] MA Z, CHEN P, CHENG W, et al. Highly sensitive, printable nanostructured conductive polymer wireless sensor for food spoilage detection[J]. Nano Letters,2018,18:4570-4575. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01825
[7] WU H, YU G H, PAN L J, et al. Stable Li-ion battery anodes by in-situ polymerization of conducting hydrogel to conformally coat silicon nanoparticles[J]. Nature Communications,2013,4:1943. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2941
[8] LI P P, JIN Z Y, PENG L L, et al. Stretchable all-gel-state fiber-shaped supercapacitors enabled by macromolecularly interconnected 3D graphene/nanostructured conductive polymer hydrogels[J]. Advanced Materials,2018,30:1800124. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201800124
[9] LI W W, GAO F X, WANG X Q, et al. Strong and robust polyaniline-based supramolecular hydrogels for flexible supercapacitors[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2016,55:9196-9201. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201603417
[10] LI W W, LU H, ZHANG N, et al. Enhancing the properties of conductive polymer hydrogels by freeze-thaw cycles for high-performance flexible supercapacitors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9:20142-20149.
[11] KIM H, ABDALA A A, MACOSKO C W. Graphene/polymer nanocomposites[J]. Macromolecules,2010,43:6515-6530. DOI: 10.1021/ma100572e
[12] 陈卉, 马会茹, 官建国. 水溶性导电聚苯胺的制备[J]. 化学进展, 2007, 19:1770-1775. CHEN Hui, MA Huiru, GUAN Jianguo. Preparation of water-soluble conducting polyanilines[J]. Progress in Chemistry,2007,19:1770-1775(in Chinese).
[13] GUPTA B, PRAKASH R. Synthesis of processible doped polyaniline-polyacrylic acid composites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2009,114(2):874-882. DOI: 10.1002/app.30554
[14] 郑春晓, 朱赛玲, 陆亚梅, 等. 纳米纤维素/聚丙烯酸-聚丙烯酰胺双网络导电水凝胶的合成与表征[J]. 林业工程学报, 2020, 5:127-134. ZHENG Chunxiao, ZHU Sailing, LU Yamei, et al. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose nanofibers/polyacrylicacid-polyacrylamide double network electroconductive hydrogel[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2020,5:127-134(in Chinese).
[15] HAN J Q, WANG S W, ZHU S L, et al. Electrospun core-shell nanofibrous membranes with nanocellulose-stabilized carbon nanotubes for use as high-performance flexible supercapacitor electrodes with enhanced water resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical toughness[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(47):44624-44635.
[16] HAN J Q, DING Q Q, MEI C T, et al. An intrinsically self-healing and biocompatible electroconductive hydrogel based on nanostructured nanocellulose-polyaniline complexes embedded in a viscoelastic polymer network towards flexible conductors and electrodes[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2019,318:660-672. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.06.132
[17] SYED JA, TANG S, LU H, et al. Water-soluble polyaniline-polyacrylicacid composites as efficient corrosion inhibitors for 316SS[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2015,54:2950-2959.
[18] HAN J Q, LU K Y, YUE Y Y, et al. Nanocellulose-templated assembly of polyaniline in natural rubber-based hybrid elastomers toward flexible electronic conductors[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2019,128:94-107. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.11.004
[19] DU J, WANG D, XuS M, et al. Stretchable dual nanocompo-site hydrogels strengthened by physical interaction between inorganic hybrid crosslinker and polymers[J]. Applied Clay Science,2017,150:71-80. DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.09.008
-





 下载:
下载: