Tailoring the dielectric properties of silicone particles/poly(vinylidene fluoride) composites based on interface structures
-
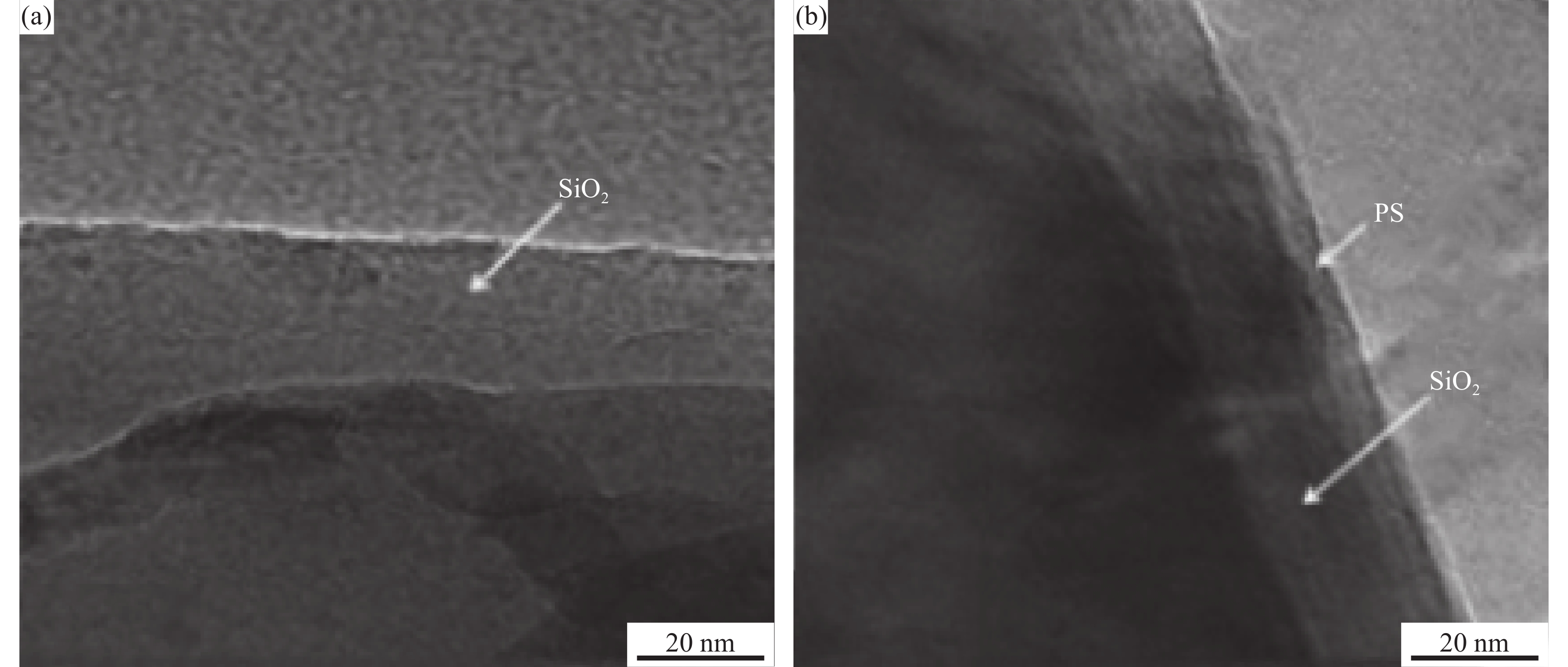
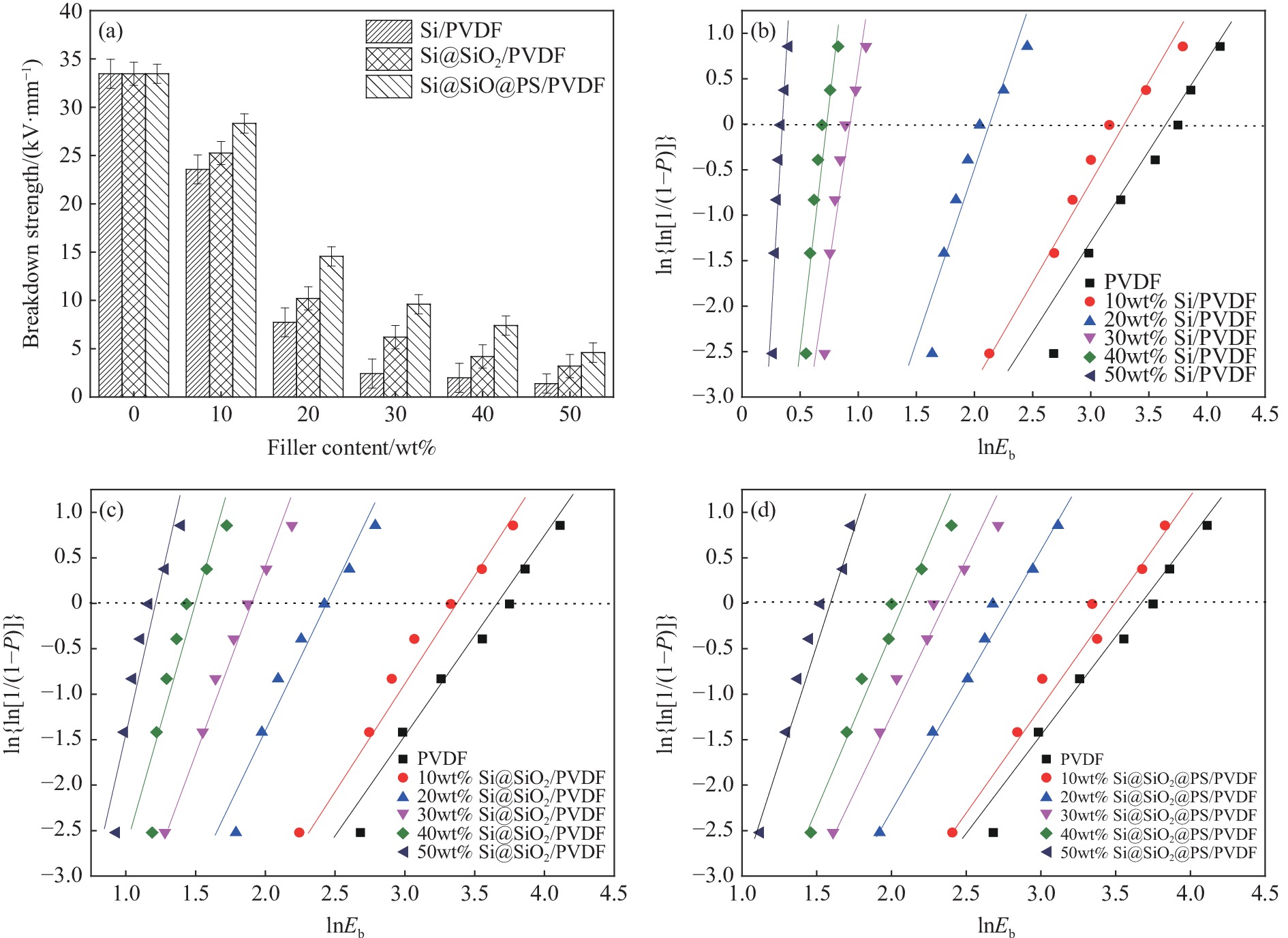
摘要: 为降低硅粒子/聚偏氟乙烯(Si/PVDF)复合材料体系的介电损耗(tanδ)及提高其击穿强度(Eb),采用高温氧化及聚苯乙烯(PS)包覆法,制备出两种分别具有SiO2单壳及SiO2@PS双壳的Si@SiO2和Si@SiO2@PS核壳结构粒子。采用FTIR、XRD和TEM分析测试了核壳粒子的壳层结构。分析测试证明,Si粒子表面存在SiO2和PS壳层。结果表明,相比未改性Si/PVDF复合材料,SiO2外壳显著降低和抑制了Si@SiO2/PVDF复合材料的tanδ和漏导电流;PS层改进了Si/PVDF复合材料的界面相容性,促进其在基体中均匀分散。双壳结构Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF复合材料呈现出最低tanδ和最高Eb。Si@SiO2/PVDF和Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF复合材料介电性能的改善归因于Si表面SiO2及SiO2@PS绝缘界面层有效阻止了半导体Si粒子间的直接接触,极大抑制了损耗。此外,Si/PVDF复合材料相界面缺陷减少及界面相容性改善均有效降低了局部电场畸变,提高了体系的Eb。Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF复合材料在1 kHz下介电常数高达48,tanδ低至0.07,Eb约为6 kV/mm,在微电子器件及电力设备领域具有潜在的应用价值。Abstract: To reduce the dielectric loss(tanδ) and increase the dielectric breakdown strength(Eb) of silicon particles/poly(vinylidene fluoride)(Si/PVDF) composites, two kinds of core-shell structured Si particles, i.e., Si@SiO2 and Si@SiO2@PS were prepared by high temperature oxidation and polystyrene(PS) coating. The FTIR, XRD and TEM measurements were used to characterize the formed shell structure. The measurements results verify the existence of SiO2 and SiO2@PS shells on the surface of Si. The results show that the Si@SiO2 interlayer significantly suppresses the tanδ and reduces the leakage conductivity of the Si@SiO2/PVDF composites compared with Si/PVDF composites, and the double-shell Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF composites exhibit the lowest tanδ and the highest Eb among the three composites because the organic PS interlayer enhances the interfacial compatibility and promotes the fillers’ homogeneous dispersion in PVDF. The improvement in dielectric properties of Si@SiO2/PVDF and Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF composites can be ascribed to the facts that the insulating SiO2 and SiO2@PS shells effectively prevent the semi-conducting Si particles from direct contacting, thereby remarkably reducing the tanδ. The enhanced phase interfacial compatibility between the Si@SiO2 or Si@SiO2@PS and PVDF matrix reduces the interface defects and suppresses the local electrical field distortion, thereby improving Eb of the core-shell structured Si/PVDF composites. The prepared Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF composites with a high dielectric constant of 48 and tanδ of 0.07, Eb of 6 kV/mm, have potential applications in the field of microelectronic devices and power equipment.
-
Keywords:
- Si /
- poly(vinylidene fluoride) /
- interface structure /
- core-shell structure /
- composites /
- dielectric properties
-
再生粗骨料混凝土(RAC)采用再生粗骨料(RCA)替代天然粗骨料(NCA),可减少对自然资源的消耗,实现固体废弃物的回收利用。由于混凝土是一种非均质材料,骨料力学性质的离散性及其位置的随机性、胶凝材料水化进程中引发的力学性质的离散性、初始缺陷的随机位置等诸多因素导致其在抗压强度方面存在一定的离散性[1]。若忽略混凝土离散性对其力学性能的影响,极有可能在实际工程中造成安全隐患。因此,准确评估抗压强度离散性对于结构设计和可靠性分析至关重要。
目前,许多学者对于RAC进行了大量静动态力学性能研究,由于RCA经机械破碎后产生大量微裂纹,表面附着大量松散老砂浆,相较普通混凝土(NAC)存在更多初始缺陷[2],在准静态压缩下,RAC的抗压强度普遍低于NAC[3-5],在动态荷载下RAC动态抗压强度随着RCA替代率增大而减小,动态增强因子(DIF)随RCA替代率的增加而增加[6-8]。这些研究进一步加深了对RAC力学性能的理解,然而仅使用抗压强度评价RAC力学性能是不充分的,还应关注其抗压强度的离散性程度。有学者开展了RAC在准静态压缩下的抗压强度离散性研究,陈海霞等[9]认为RAC相较于NAC表现出更强的离散性,赵雨等[10]认为RCA替代率为50%时,再生保温混凝土的抗压强度离散性最大。动态荷载下RAC抗压强度离散性的研究较少,且往往只关注平均值,忽视抗压强度离散性有可能导致结构设计存在安全风险,因此研究抗压强度离散性对于深入理解且合理利用混凝土材料的力学行为具有重要意义。
鉴于此,本文对不同RCA替代率的RAC试件进行准静态压缩和霍普金森压杆(SHPB)试验,得到静动态荷载下RCA替代率与应变率对RAC抗压强度离散性的影响规律。基于修正的Weibull分布模型,提出了在任意保证率下具有不同RCA替代率的RAC动态抗压强度预测公式。
1. 试验设计
1.1 原材料与配合比
采用普通硅酸盐水泥P·O 42.5,其矿物成分见表1。细骨料为河砂,最大粒径为4.75 mm,表观密度为2590 kg/m3。天然粗骨料(NCA)选取天然碎石,再生粗骨料(RCA)由北京格林雷斯环保科技有限公司提供,来源为附近废弃建筑物粉碎后的建筑垃圾,考虑到其杂质含量较高,试验前对其进行了多次筛分和清洗。根据我国发布的《混凝土用再生粗骨料》(GB/T 25177—2010)[11],本次试验中粗骨料分类为Class II,粗骨料性能指标见表2。由于RCA的吸水率较高[12],需加入额外的搅拌水以保证相同的有效水灰比,具体配合比见表3。采用两阶段混合法制备RCA替代率为0%、50%、100%的RAC试件,分别命名为RAC-0、RAC-50、RAC-100。所有试件在标准养护条件下养护28天。试验前,所有试件的两端都进行了打磨处理,其中SHPB试验试件不平行度≤0.02 mm。
表 1 普通硅酸盐水泥 P·O 42.5的矿物成分Table 1. Mineral components of ordinary Portland cement P·O 42.5Al2O3/wt% SiO2/wt% Fe2O3/wt% CaO/wt% SO3/wt% R2O/wt% MgO/wt% Other/wt% 4.42 21.65 2.61 62.93 2.27 0.83 2.92 2.37 Note: R2O—Basic oxide ( Na2O, K2O). 表 2 粗骨料性能指标Table 2. Performance index of coarse aggregatesAggregate type Gradation/mm Apparent density/(kg·m−3) Crush index/% Mortar content/% Water absorption/% NCA 5-12.5 2814 8.8 0 0.40 RCA 5-12.5 2640 17.7 34 3.85 Notes: NCA—Natural coarse aggregate; RCA—Recycled coarse aggregate. 表 3 试验配合比 (kg/m3)Table 3. Mix design proportions of tests (kg/m3)Specimen Cement Sand NCA RCA Water Extra water RAC-0 462.5 596.09 1156.41 0 185 0 RAC-50 462.5 596.09 578.21 578.21 185 17.35 RAC-100 462.5 596.09 0 1156.41 185 34.69 Notes: RAC-0, RAC-50, RAC-100—Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) with 0%, 50%, 100% substitute rate of recycled coarse aggregate, respectively. 1.2 试验设备与试验方法
1.2.1 准静态压缩试验
试件尺寸为直径ϕ70 mm×140 mm,共3组,每组准备40个。使用美特斯工业系统(中国)有限公司提供的MTS Exceed E45试验机(最大负载能力为300 kN)对RAC试件进行准静态压缩试验,采用等速位移的加载方式,加载速率为0.1 mm/min (等效应变速率为1.2×10−5 s−1)。
1.2.2 SHPB试验
SHPB试验基于一维应力波和应力均匀性两个基本假定[13],试件尺寸为ϕ70 mm×35 mm,采用直径10 mm的橡胶圆片作为波形整形器延长入射波上升沿并消除应力波高频振荡。试验时在杆端涂抹润滑剂防止对应变率效应的高估[14-15]。试验设备是由合肥姜水动态力学实验室提供的直径为75 mm的SHPB系统,冲击速度分为4组:Group 1 (4.3 m/s)、Group 2 (5.2 m/s)、Group 3 (5.7 m/s)、Group 4 (6.2 m/s),对应应变率分别为50 s−1、70 s−1、90 s−1和120 s−1,共12组,每组准备40个试件。
2. 试验结果及分析
2.1 准静态压缩试验结果
2.1.1 破坏模式
图1展示了在准静态压缩下具有不同RCA替代率的RAC的破坏模式。全部RAC试件表现出相似的破坏模式。试件中部首先出现纵向裂缝,随着荷载的增加,裂纹沿纵向扩展到顶部和底部,中部混凝土膨胀剥落,直至试件丧失承载能力。随着RCA替代率的增加,试件破坏更快,表现出更强的脆性。RCA的加入使试件中旧砂浆与粗骨料界面和旧砂浆与新砂浆界面增加,荷载作用下大量裂缝在界面处发展,RAC更容易发生裂纹和断裂[16]。
2.1.2 抗压强度
图2绘制了具有不同RCA替代率的RAC试件的120组抗压强度结果。随着RCA替代率的增加,RAC的抗压强度下降,RAC-50与RAC-100的抗压强度相较RAC-0分别下降了6.35%和16.94%。此外,不同RCA替代率下的RAC试件的抗压强度表现出不同的离散程度。
2.2 SHPB试验结果
2.2.1 破坏模式
采用最大应力的75%至100%范围的线性斜率代表应变率[17]。各组试件破坏模式如图3所示。不同RCA替代率的RAC试件在不同应变率下破坏模式相似。当应变率较低时,试件破坏主要由贯穿主裂缝引起,试件能大体保持其完整性。随着应变率的增加,试件出现了更多更细密的裂缝,当应变率达到90 s−1以上时,试件破裂成碎片并向四周飞溅,破坏形式与准静态压缩与低应变率下显著不同[18]。由于高应变率下裂纹没有足够的时间通过砂浆基底的薄弱层路径传播,大量裂缝贯穿骨料。而在低应变率下因砂浆基底较低的强度,裂缝主要穿透骨料间的砂浆。
2.2.2 抗压强度
图4为不同RCA替代率下RAC试件的动态抗压强度随应变率的变化情况,表明具有不同RCA替代率的RAC试件均表现出显著的应变率效应,其动态破坏机制主要表现为3个方面[19]:(1) 热活化机制。随着应变率的增高,裂缝的扩展演化发生变化,准静态压缩中裂缝有时间沿最薄弱面进行发展,随着荷载的增大,裂缝会穿透粗骨料颗粒导致强度增大;(2) 孔隙水作用。微孔隙中自由水表现出的类似Stefan效应会使混凝土加固。此外,随着应变率的增加,自由水对裂纹作用模式逐渐从张拉模式转化为约束模式[20],抑制裂缝的拓展;(3) 惯性效应。由于粒子加速度运动产生沿加载方向的惯性力及泊松效应和端部摩擦带来的侧向约束效应会限制混凝土试件的侧向变形[21]。在各应变率下,随着RCA替代率的增加,试件的抗压强度降低。同一替代率下,应变率从50 s−1增加至120 s−1时,RAC-0、RAC-50和RAC-100试件的动态抗压强度分别增加了30.42%、35.55%和37.40%,表明随着RCA替代率的提高,试件表现出更明显的应变率效应[5, 14, 22]。此外,不同RCA替代率的RAC试件动态抗压强度表现出不同程度的离散性,这是由于不同的裂缝开展路径和损伤区域[23],低应变率下试件内部初始缺陷程度对于裂缝优先开展路径和损伤开始区域有着重要影响,高应变率下由于裂缝发展时间短,损伤区域扩大到整个试件,初始缺陷的影响会减小。
3. 讨 论
3.1 考虑RCA替代率的RAC准静态抗压强度预测
3.1.1 分布模型的确定
采用正态分布[24]、Weibull分布[25]和对数正态分布[26]分别对RAC抗压强度按下式进行分布拟合,结果见图5:
![]() 图 5 准静态压缩试验下RAC抗压强度分布Figure 5. Distribution of compressive strength of RAC under quasi-static compressionμ1, σ1—Mean and standard deviation of the normal distribution; m, β—Shape and scale parameters of the Weibull distribution; μ2, σ2—Location and scale parameters of the lognormal distribution; R2—Goodness of fit
图 5 准静态压缩试验下RAC抗压强度分布Figure 5. Distribution of compressive strength of RAC under quasi-static compressionμ1, σ1—Mean and standard deviation of the normal distribution; m, β—Shape and scale parameters of the Weibull distribution; μ2, σ2—Location and scale parameters of the lognormal distribution; R2—Goodness of fitf(σ)=1√2πσ1exp[−12(σ−μ1σ1)2] (1a) f(σ)=mβ(σβ)m−1exp[−(σβ)m] (1b) f(σ)=1σ√2πσ2exp[−12(ln(σ)−μ2σ2)2] (1c) 式中:σ 为试件抗压强度值;μ1、σ1为正态分布的均值和标准差;m和β为Weibull分布的形状参数和尺度参数;μ2、σ2为对数正态分布的位置参数和尺度参数。
由图5发现,这3种分布均可描述RAC在准静态压缩下的强度分布,但观察拟合优度参数R2得到,在对RAC-50的描述中正态分布与对数正态分布表现较差(R2=0.85),相比较而言Weibull分布(R2=0.93)能够提供更准确的结果。
3.1.2 Weibull分布回归分析
基于式(2),取两次对数后[27],得到式(3):
Pf(σ)=1−exp[−(σβ)m] ln[−ln(1−Pf(σ))]=mlnσ−mlnβ (3) 其中,Pf(σ)为试样在σ应力下破坏的概率。式(3)可简化为一般线性方程的形式,m可视为以lnσ为横坐标和ln[−ln(1−Pf(σ))]为纵坐标时直线的拟合斜率。为了确定每个强度值的失效概率,将强度值升序排列后第i个强度值对应的概率Pf(σi)近似为第i个样本数据与总样本数据N的关系:
Pf(σi)=i−0.5N (4) 图6给出了根据式(3)和式(4)拟合的RAC抗压强度的Weibull图,估计参数总结在表4。对于具有不同RCA替代率的RAC,线性回归结果与实测强度数据表现出良好的一致性。采用Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S)拟合优度检验[28]进一步验证回归结果的准确性。最大偏差Dn为观测样本的累积频率Pf,E(σi)与回归的Weibull概率分布Pf,W(σi)的最大差值,如下式所示:
Dn=max[|Pf,E(σi)−Pf,W(σi)|]<Dnα (5) 其中,Dnα为n个数据在显著水平为α下的临界值,此处为40组数据在α=0.05时的临界值取0.215[28]。由表4可知Dn均小于Dnα,说明RAC准静态抗压强度均服从Weibull分布。
此外,Weibull分布下RAC抗压强度的数学期望值E(σ)、标准差S与离散系数C的计算方法见下式,结果见表4:
E(σ)=∫∞0σdPf(σ)dσdσ =βΓ(1+1m) (6a) S=∫∞0(σ−E(σ))2dPf(σ)dσdσ=β[Γ(1+2m)−Γ2(1+1m)]1/2 (6b) C=SE(σ) (6c) 其中,Γ代表Gamma函数。Weibull分布中,除离散系数C外,形状参数m也可以表示一组数据的分散情况,m值越低,强度变异性越高[29]。由表4可知在准静态压缩情况下,随着RCA替代率的增加,RAC的离散系数差异并不明显,但随RCA替代率的增加,RAC抗压强度的离散性表现出先增加后降低的趋势。RAC试件抗压强度离散性可以归结于砂浆的离散性、粗骨料位置的随机性及内部缺陷的数量。值得注意的是,本研究中骨料来源单一,若骨料来源不同会增大试验结果的离散性[5, 30],需对这一趋势予以重视。在准静态压缩条件下,根据Weibull分布可靠度函数可计算出在任意保证率R下不同RCA替代率的RAC抗压强度σR,如下式所示:
σR=β(ln1R)1/m RAC在保证率为0.75、0.85和0.95下的抗压强度统计在表5。
3.2 考虑RCA替代率的RAC动态抗压强度预测
3.2.1 修正的Weibull分布回归分析
为考虑应变率效应的影响,将双参数Weibull分布模型进行了修正,加入了应变率效应参数。采用修正的Weibull分布模型对RAC动态抗压强度进行分析[31],如下式:
PM(σ)=1−exp[−˙εηδγ(σβ)m] 其中: ˙ε为应变率; η为应变率效应参数;γ为RCA替代率百分数;δ为替代率参数。将式(8)简化为线性形式,如下式所示:
ln[−ln(1−PM(σ))]=ηln˙ε+γlnδ+mlnσ−mlnβ 对该方程进行回归分析,如图7所示。m可由斜率求得,β、η和δ由截距项求得。具体拟合参数结果见表6,可知,R2系数均在0.90~0.98之间,表明具有不同RCA替代率的RAC在不同应变率下的回归结果与试验结果吻合较好。采用Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S)进行检验,最大偏差Dn均在合理范围内,修正的Weibull分布可准确描述在不同RCA替代率和应变率下RAC的动态强度分布。此外,计算了RAC动态抗压强度的数学期望值EM(σ)、标准差SM与离散系数CM,如下式所示:
表 4 准静态压缩下RAC抗压强度Weibull参数Table 4. Weibull parameters for compressive strength of RAC under quasi-static compressionSpecimen Linear fitting equation
Y=aX+bWeibull parameter E(σ)/MPa S/MPa C K-S
goodness-of-testa b R2 m β Dn Dnα RAC-0 22.80 79.43 0.92 22.80 32.58 31.817 1.737 0.054 0.103 0.215 RAC-50 21.47 73.41 0.93 21.47 30.54 29.783 1.723 0.058 0.104 RAC-100 22.61 74.55 0.98 22.61 27.06 26.415 1.454 0.055 0.069 Notes: E(σ)—Mathematical expectation; S—Variance; C—Dispersion coefficient; K-S—Kolmogorov-Smirnov; a, b—Slope and intercept of the linear fitting equation; Dn—Maximum deviation; Dnα—Critical values for n data at a confidence level of α. 表 5 不同保证率下的RAC抗压强度Table 5. Compressive strength of RAC at different levels of reliabilitySpecimen σmean/MPa σ0.75/MPa σ0.85/MPa σ0.95/MPa RAC-0 31.82 30.85 30.09 28.60 RAC-50 29.78 28.82 28.06 25.47 RAC-100 26.42 25.61 24.97 22.77 Notes: σmean—Mean compressive strength; σ0.75, σ0.85, σ0.95—Compressive strength with a guarantee of 0.75, 0.85, 0.95, respectively. 表 6 SHPB试验下RAC抗压强度修正Weibull参数Table 6. Modified Weibull parameters for compressive strength of RAC in SHPB testSpecimen Strain
rate/s−1Fitting curve Modified Weibull parameter R2 EM(σ)/
MPaSM/
MPaCM K-S goodness-of-test Dn Dnα m β η δ RAC-0 50.4 Y=10.62X−42.67 10.62 13.53 −3.79 1.5 0.92 52.20 0.74 0.014 0.099 0.215 68.0 Y=11.05X−45.18 11.05 13.89 −3.82 0.97 57.06 0.71 0.012 0.111 89.1 Y=11.46X−47.85 11.46 14.37 −3.85 0.98 62.11 0.70 0.011 0.095 117.3 Y=12.08X−51.68 12.07 15.48 −3.90 0.98 69.20 0.70 0.010 0.094 RAC-50 50.8 Y=8.34X−32.79 8.34 13.05 −2.94 0.94 49.23 0.85 0.018 0.135 68.7 Y=10.15X−40.66 10.15 13.36 −3.43 0.97 53.13 0.75 0.014 0.123 88.6 Y=10.88X−44.93 10.88 14.30 −3.62 0.92 60.70 0.73 0.012 0.087 118.2 Y=11.86X−50.07 11.86 15.43 −3.72 0.96 66.03 0.73 0.011 0.134 RAC-100 53.2 Y=7.19X−27.95 7.19 12.66 −2.53 0.96 45.37 0.96 0.022 0.119 70.5 Y=8.12X−32.24 8.12 13.99 −2.62 0.94 49.47 1.00 0.020 0.095 89.2 Y=10.55X−43.06 10.55 14.73 −3.35 0.97 56.23 0.80 0.014 0.142 121.3 Y=11.24X−47.02 11.24 15.84 −3.42 0.98 62.86 0.80 0.013 0.073 Notes: EM(σ), SM, and CM—Mathematical expectation, variance, and dispersion coefficient based on the modified model; η—Strain rate effect parameter; δ—Substitute rate parameter. EM(σ)=∫∞0σdPM(σ)dσdσ=β˙ε−ηmδ−γmΓ(1+1m) (10a) SM=∫∞0(σ−EM(σ))2dPM(σ)dσdσ=β˙εηmδγm[Γ(1+2m)−Γ2(1+1m)]1/2 (10b) CM = SMEM (10c) 图8给出了不同RCA替代率下RAC动态抗压强度与应变率的关系。可知,在相同的应变率下,随着RCA替代率的增加,RAC动态强度离散程度也随之增加。在相同的RCA替代率下,强度离散程度随应变率的增加而降低。同一应变率下,RCA的增加会导致混凝土内部缺陷增多,由于在高应变率下材料惯性效应增强,缺陷会阻碍应力波的传播,加剧能量的耗散[32],导致材料在较大缺陷处更容易发生局部应力集中,使RAC在动态加载下的破坏行为受缺陷大小的影响更显著。对于同一替代率的RAC,应变率的增加会使RAC变形速率增加,内部变形差异减小,且在高应变率下骨料的穿透行为会减弱界面过渡区对于RAC的破坏影响[32],导致离散性降低。
3.2.2 RAC动态强度预测公式
通过表6发现,RAC的替代率和应变率会对修正后Weibull分布的特征参数有一定程度的影响,将m、β、η分别与应变率和替代率进行拟合,可得到在一定应变率下RAC的动态平均抗压强度σmean预测公式,如下式所示:
σmean=β˙ε−ηmδ−γmΓ(1+1m), 50s−1⩽ 图9为预测平均抗压强度与试验平均抗压强度的比较结果,平均误差为1.37%,最大误差为3.96%,修正后的Weibull模型能够较好预测不同RCA替代率γ下的RAC平均动态抗压强度。
在实际工程中,为确保结构的安全性和可靠性,常采用更高保证率下的抗压强度。根据修正Weibull分布的可靠度函数可求出在任意保证率R下的RAC动态抗压强度σR,如下式:
\sigma_R=\beta\left[\frac{\ln\left(1/R\right)}{\dot{\varepsilon}^{\eta}\delta^{\gamma}}\right]^{1/m},\text{ 5}0\; \text{s}^{-1}\leqslant\text{ }\dot{\varepsilon}\leqslant120\; \text{s}^{-1} (12) 图10展示了在保证率为0.75、0.85和0.95下RAC动态抗压强度与平均值的比值。随着应变率的增加比值趋近于1,这意味着高应变率下RAC动态抗压强度离散性减小。对于不同RCA替代率,随着保证率增加,RAC动态抗压强度变化幅度增大,表明RAC-100试件动态抗压强度表现出更强的离散性,与试验结果相符。
4. 结 论
对不同再生粗骨料(RCA)替代率的再生粗骨料混凝土(RAC)试件进行准静态压缩和霍普金森压杆(SHPB)试验,研究了静动态荷载下,RCA替代率与应变率对RAC抗压强度离散性的影响规律。此外,基于修正的Weibull分布模型,提出了任意保证率下具有不同RCA替代率的RAC动态抗压强度预测公式。主要结论如下:
(1) 采用3种分布模型对准静态压缩下的RAC抗压强度进行拟合,发现Weibull分布可提供较准确的描述,结果表明3种RCA替代率的RAC抗压强度离散性分别为0.054、0.058、0.055,随RCA替代率的增加,表现出先增加后减小的趋势,但差异不显著;
(2) SHPB试验应变率为50~120 s−1时,RAC动态抗压强度离散性同时受到RCA替代率和应变率的影响。在相同的应变率下,随着RCA替代率的增加,RAC动态强度离散性也随之增加。在相同的RCA替代率下,随着应变率的增加,强度离散性降低;
(3) 基于修正的Weibull分布,提出了单一配合比下任意保证率下不同RCA替代率的RAC动态抗压强度预测公式,计算预测平均抗压强度与试验值比较最大误差为3.96%,修正后的Weibull模型能较好预测不同RCA替代率下的RAC动态抗压强度,为实际工程中RAC结构的设计提供参考。需要说明的是,本研究中动态抗压强度预测公式适用于应变率为50~120 s−1的情况。对于多种配合比与多种强度情况有待于进一步研究。
-
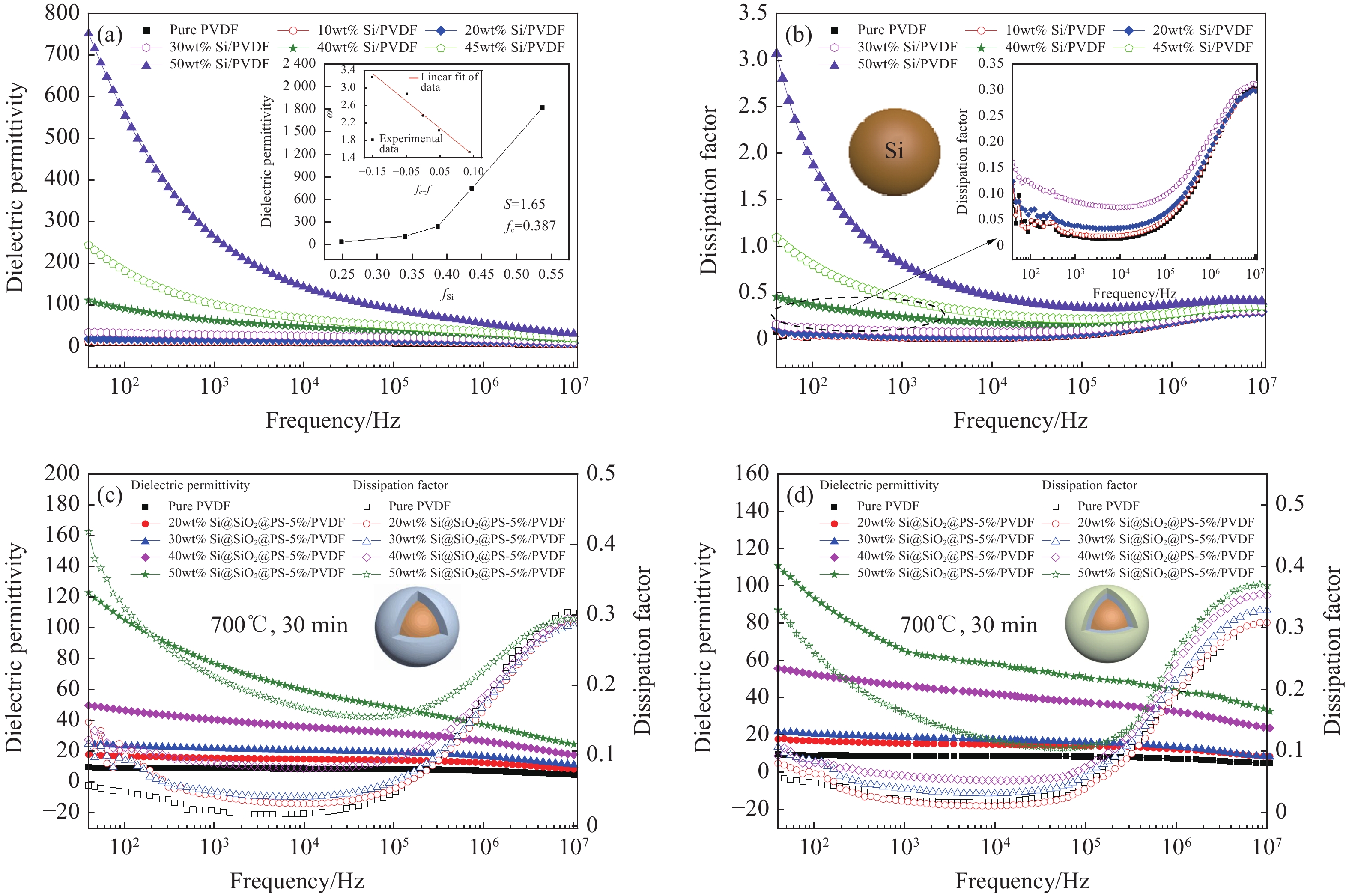
图 4 Si/PVDF、Si@SiO2/PVDF、Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF复合材料的介电性能(内图分别为Si/PVDF复合材料介电常数渗流理论计算及不同结构的核壳粒子结构示意图)
Figure 4. Dielectric properties of Si/PVD SiO2/PVDF and Si@SiO2@PS/PVDF composites(Insets in Fig. 4 show the theoretical calculation diagram of permittivity of Si/PVDF composites and the schematic diagram of core-shell particles with different structures)
-
[1] DANG Z M, ZHENG M S, ZHA J W. 1D/2D carbon nanomaterial-polymer dielectric composites with high permittivity for power energy storage applications[J]. Small,2016,12(13):1688-1701. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201503193
[2] WANG Z, HAN N M, WU Y, et al. Ultrahigh dielectric constant and low loss of highly-aligned graphene aerogel/poly(vinyl alcohol) composites with insulating barriers[J]. Carbon,2017,123:385-394. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.07.079
[3] ZHOU W Y, KOU Y J, YUAN M X, et al. Polymer composites filled with core@double-shell structured fillers: Effects of multiple shells on dielectric and thermal properties[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,181:107686. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107686
[4] CHEN Y, ZHANG H B, YANG Y B, et al. High-performance epoxy nanocomposites reinforced with three-dimensional carbon nanotube sponge for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2016,26(3):447-455. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201503782
[5] DANG Z M, WANG L, WANG H Y, et al. Rescaled temperature dependence of dielectric behavior of ferroelectric polymer composites[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2005,86(17):172905.
[6] QI L, LEE B I, CHEN S, et al. High-dielectric-constant silver-epoxy composites as embedded dielectrics[J]. Advanced Materials,2005,17(14):1777-1781. DOI: 10.1002/adma.200401816
[7] HE F, LAU S, CHAN H L, et al. High dielectric percolation threshold in nanocomposites based on poly(vinylidene fluoride) and exfoliated graphite nanoplates[J]. Advanced Materials,2009,21(6):710-715. DOI: 10.1002/adma.200801758
[8] ZHAO Y H, LUO L, TANG H F, et al. Preparation of high-k composites with low dielectric loss based on the double-layer coaxial structure of inorganic/polymer[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2018,135(21):46299. DOI: 10.1002/app.46299
[9] WANG L, DANG Z M. Carbon nanotube composites with high delectric constant at low percolation threshold[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2005,87(4):042903. DOI: 10.1063/1.1996842
[10] WU Y, LIN X, SHEN X, et al. Exceptional dielectric properties of chlorine-doped graphene oxide/poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites[J]. Carbon,2015,89:102-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.02.074
[11] ZHOU W Y, GONG Y, TU L, et al. Dielectric properties and thermal conductivity of core-shell structured Ni@NiO/poly(vinylidene fluoride) composites[J]. Journal of Alloys <italic>&</italic> Compounds,2017,693:1-8.
[12] WANG D, BAO Y, ZHA J W, et al. Improved dielectric properties of nanocomposites based on poly(vinylidene fluoride) and poly(vinyl alcohol)-functionalized graphene[J]. ACS Applied Materials <italic>&</italic> Interfaces,2012,4(11):6273-6279. DOI: 10.1021/am3018652
[13] GONG Y, ZHOU W Y, WANG Z J, et al. Towards suppressing dielectric loss of GO/PVDF nanocomposites with TA-Fe coordination complexes as an interface layer[J]. Journal of Materials Science <italic>&</italic> Technology,2018,34(12):2415-2423.
[14] LI Y, HUANG X, HU Z, et al. Large dielectric constant and high thermal conductivity in poly(vinylidene fluoride)/barium titanate/silicon carbide three-phase nanocomposites[J]. ACS Applied Materials <italic>&</italic> Interfaces,2011,3(11):4396-4403.
[15] WEI H, WU Y, LUN N, et al. Preparation and photocatalysis of TiO<sub>2</sub> nanoparticles co-doped with nitrogen and lanthanum[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2004,39(4):1305-1308. DOI: 10.1023/B:JMSC.0000013889.63705.f3
[16] XIE L, HUANG X, HUANG Y, et al. Core@double-shell structured BaTiO<sub>3</sub>-polymer nanocomposites with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss for energy storage application[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2013,117(44):22525-22537. DOI: 10.1021/jp407340n
[17] XU X L, YANG C J, YANG J H, et al. Excellent dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) composites based on partially reduced graphene oxide[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,109:91-100. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.10.056
[18] LI Q, HAN K, GADINSKI M R, et al. High energy and power density capacitors from solution-processed ternary ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites[J]. Advanced Materials,2014,26(36):6244-6249. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201402106
[19] THAKA T, KOZAKO M, FUSE N, et al. Proposal of a multi-core model for polymer nanocomposite dielectrics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2005,12(4):669-681. DOI: 10.1109/TDEI.2005.1511092
[20] XU H P, DANG Z M, JIANG M J, et al. Enhanced dielectric properties and positive temperature coeffcient effect in the binary polymer composites with surface modified carbon black[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2008,18(2):229-234. DOI: 10.1039/B713857A
[21] LIU L P, LV F Z, ZHANG Y H, et al. Enhanced dielectric performance of polyimide composites with modified sandwich-like SiO<sub>2</sub>@GO hybrids[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,99:41-47. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.03.029
[22] DANG Z M, YUAN J K, ZHA J W, et al. Fundamentals, processes and applications of high-permittivity polymer-matrix composites[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2012,57(4):660-672. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2011.08.001
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-




 下载:
下载: