Effect of sulfate corrosion on the fracture properties of PVA fiber reinforced cement-based composite materials with steel slag powder
-
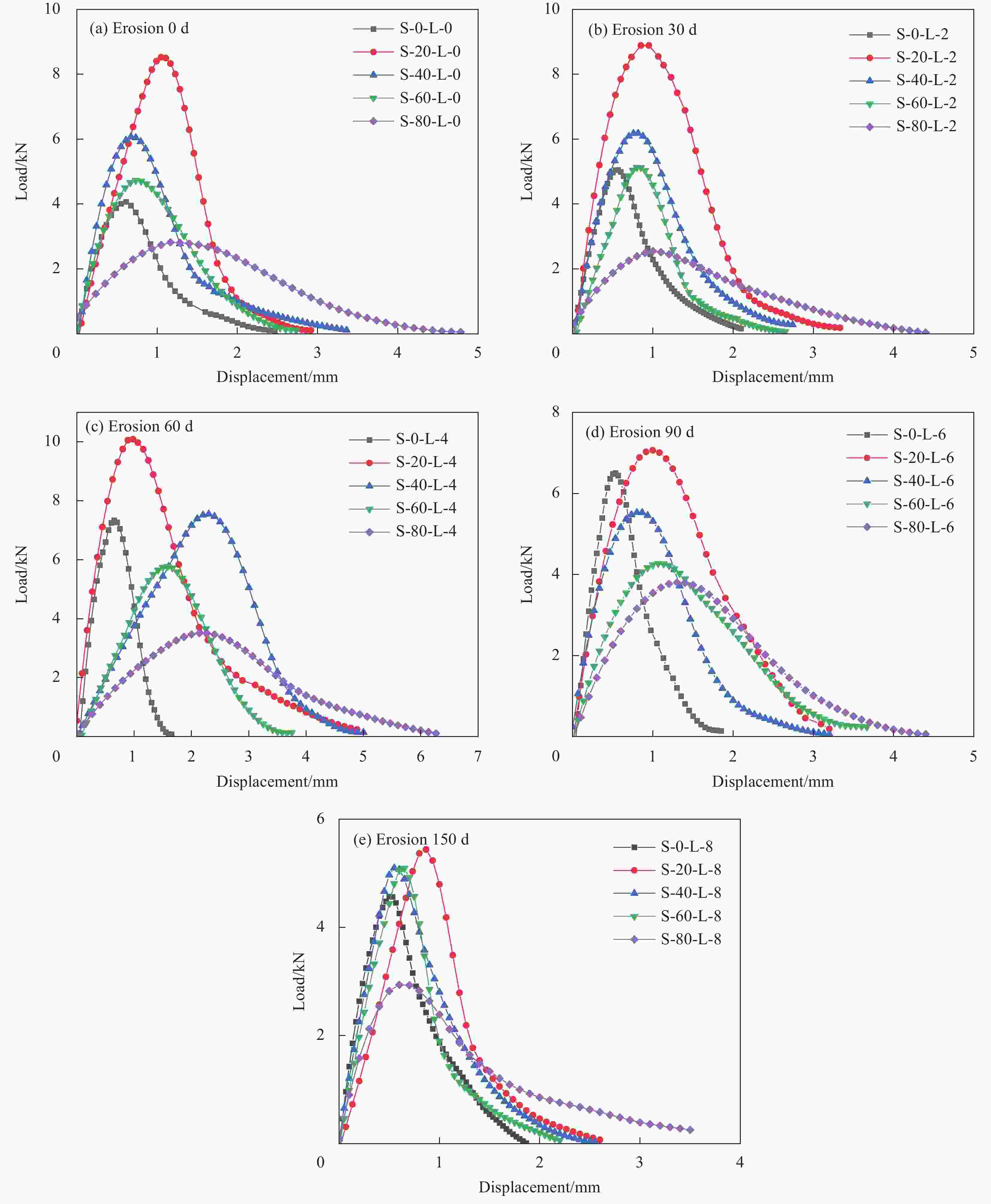
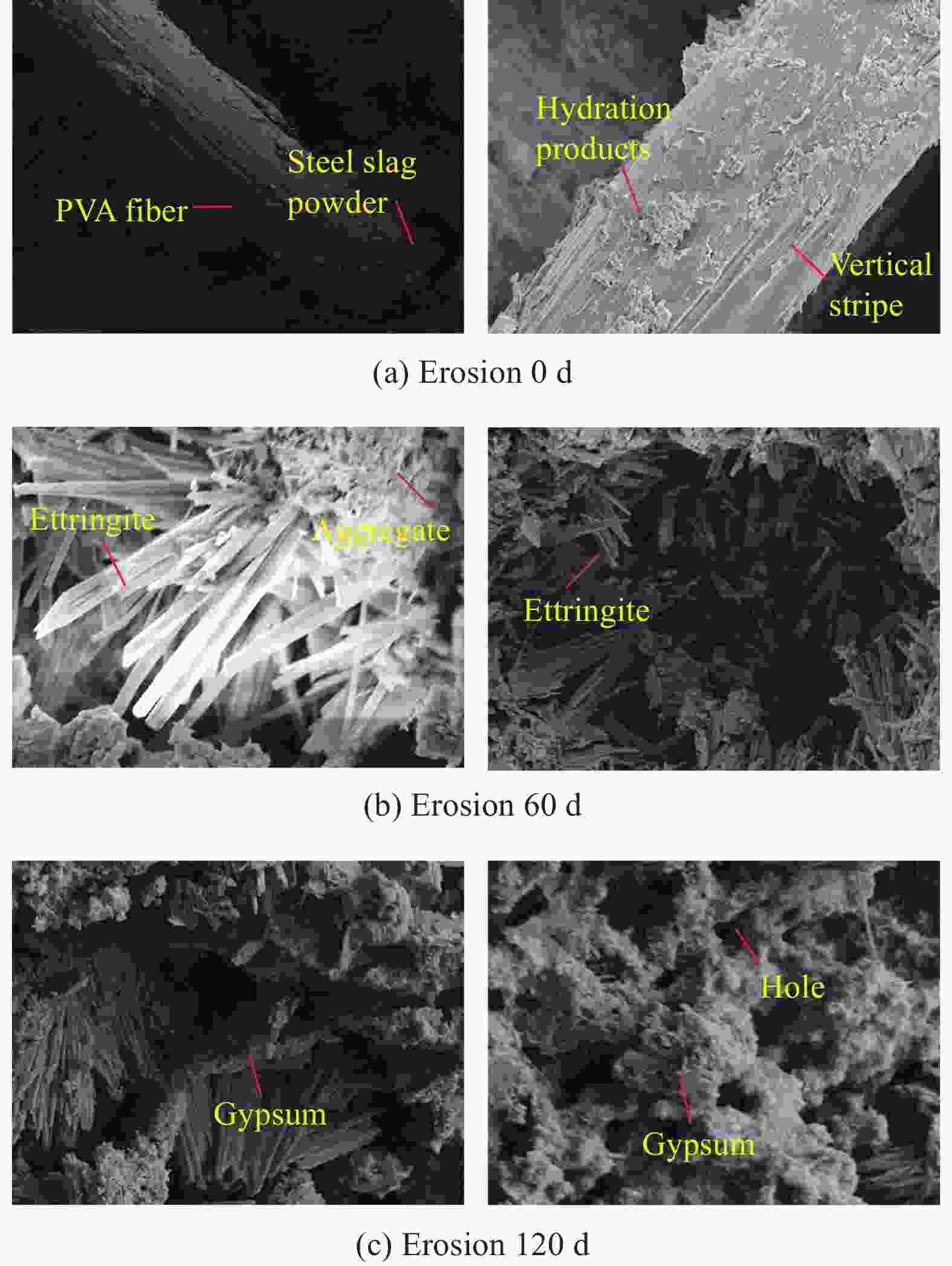
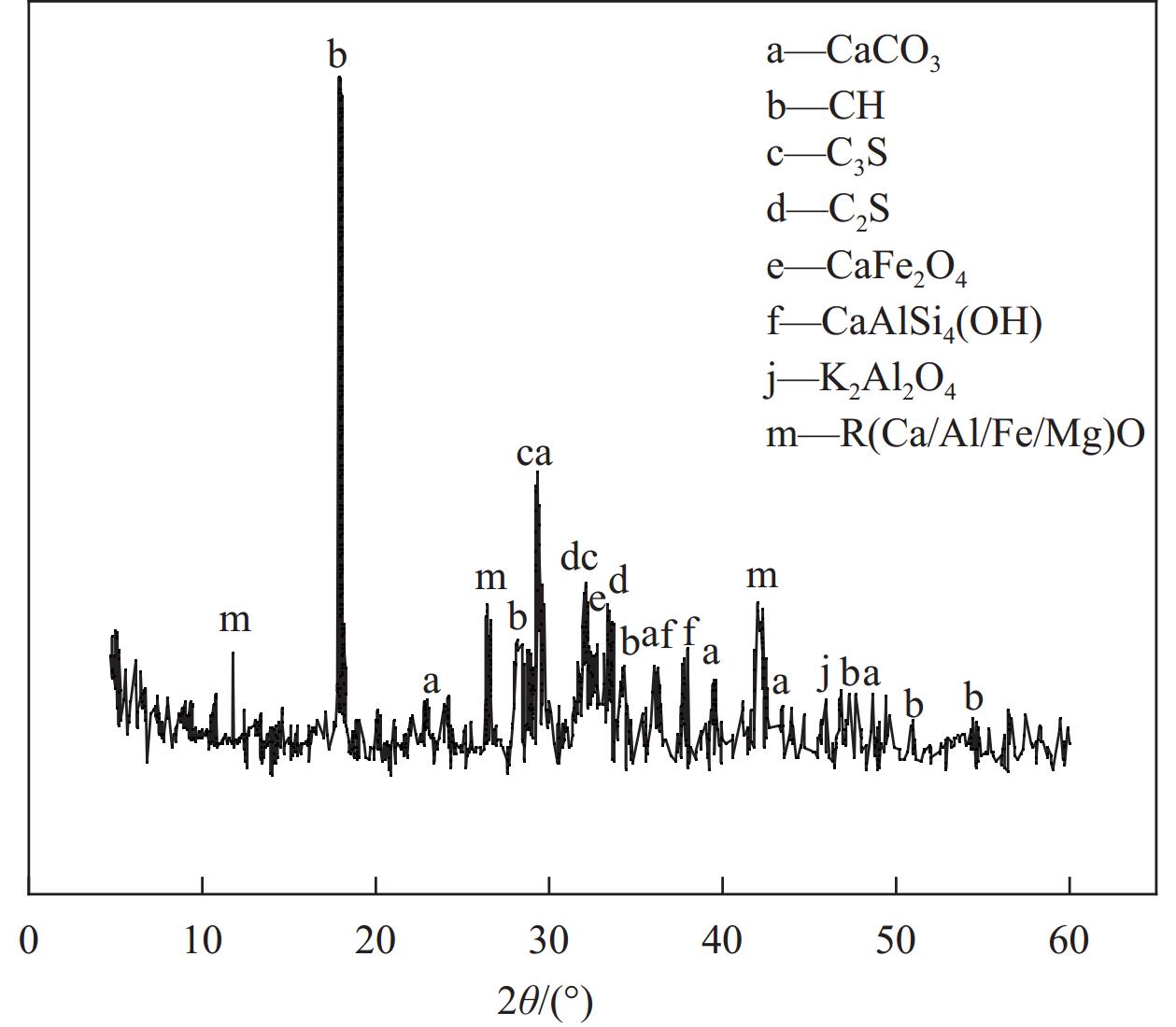
摘要: 为研究固体废料钢渣以及硫酸盐溶液侵蚀作用下水泥基复合材料断裂特性,本文设计掺入不同质量分数的钢渣粉制备PVA纤维增强水泥基复合材料,通过对硫酸盐侵蚀后的预制初始裂缝梁式试件进行三点弯曲性能试验,同时结合掺钢渣粉PVA/ECC在Na2SO4溶液(质量分数为5%)中的表观形态和微观结构特征,探究硫酸盐侵蚀对钢渣粉PVA/ECC断裂性能的影响。结果表明:在未受硫酸盐侵蚀钢渣粉掺量为20%时,试件起裂荷载、失稳荷载提升效果最佳,较未掺钢渣粉试件分别提高约61%、110%;PVA/ECC断裂韧度随侵蚀时间先增大后减小,侵蚀60d到达峰值,120d后S80组劣化最明显,起裂韧度$ {K}^{\mathrm{u}\mathrm{n}} $和失稳韧度$ {K}^{\mathrm{u}\mathrm{n}} $分别减小了约23%、13%;适量钢渣粉的掺入能有效缓解PVA纤维增强水泥基复合材料的侵蚀损伤,钢渣粉掺量不超过60%时在试验研究的龄期范围内材料未出现明显劣化。在此基础上通过Weibull分布模型预测试件耐久性寿命,其中钢渣粉掺量为20%的PVA/ECC使用寿命最长,可达到444次左右。Abstract: In order to study the fracture characteristics of cement-based composite materials under the solid waste steel slag and erosion of sulfate solution, the PVA fiber reinforced cement-based composite materials were prepared by adding different mass fractions of steel slag powder. Three-point bending performance test was conducted on prefabricated initial crack beam specimens after sulfate erosion. Combined with the apparent morphology and microstructure characteristics of steel slag powder PVA/ECC in Na2SO4 solution (mass fraction of 5%), the effect of sulfate corrosion on the fracture performance of steel slag powder PVA/ECC was investigated. The results show that when the content of steel slag powder without sulfate attack is 20%, the cracking load and instability load of the specimen are the best, with an increase of about 61% and 110% compared to the specimens without steel slag powder, respectively; The fracture toughness of PVA/ECC first increases and then decreases with erosion time, reaching its peak after 60 days of erosion. After 120 days, the S80 group shows the most obvious degradation, with the initiation toughness $ {K}^{\mathrm{u}\mathrm{n}} $and instability toughness $ {K}^{\mathrm{u}\mathrm{n}} $decreasing by about 23% and 13%, respectively; The addition of an appropriate amount of steel slag powder can effectively alleviate the erosion damage of PVA fiber reinforced cement-based composite materials. When the amount of steel slag powder does not exceed 60%, there is no significant deterioration of the material within the age range of the experimental study. On this basis, the durability life of the specimens was predicted using a Weibull distribution model, PVA/ECC with a 20% steel slag powder content having the longest service life, reaching around 444 cycles.
-
Key words:
- PVA fiber /
- steel slag powder /
- sulfate erosion /
- dry and wet cycle /
- fracture toughness /
- durability performance
-
表 1 水泥化学组成(wt%)
Table 1. Chemical composition of cement (wt%)
SiO2 CaO Fe2O3 Al2O3 K2O Na2O MgO P2O5 TiO2 SO3 17.63 65.39 4.11 5.35 0.70 0.20 1.43 0.16 0.33 3.51 表 2 钢渣粉的基本性能
Table 2. Basic properties of steel slag powder
Name Density/(g·cm−3) Specific surface area (m2·kg−1) Activity index 7 d 28 d Steel slag powder 5.3 400 71.63% 84.27% Specification ≥3.2 - ≥65 ≥80 表 3 钢渣粉XRF检测结果(%)
Table 3. XRF testing results of steel slag powder (%)
CaO SiO2 Fe2O3 Al2O3 MgO Na2O SO3 P2O5 43.55 14.22 24.26 2.86 4.34 2.98 1.39 1.24 表 4 钢渣粉的粒度分布结果
Table 4. Particle size distribution results of steel slag powder
Particle size/μm 0-2 2-5 5-10 10-20 20-30 30-40 40-45 >45 Content/wt% 13.2 14.1 14.3 33.3 9.1 5.6 1.4 9.1 表 5 PVA纤维物理性能指标
Table 5. Physical Performance Indicators of PVA Fibers
Length/mm Diameter /mm Aspect ratio Tensile strength/MPa Elongation rate/% Tensile modulus of elasticity/GPa Density /(g·cm−3) 12 40 300 1600 7 42 1.3 表 6 掺钢渣粉PVA/ECC材料配合比
Table 6. Mix proportion of PVA/ECC material mixed with steel slag powder
Group Cement Silica fume Steel slag powder Water Sand Water reducing agent PVA dosage S0 0.98 0.02 0 0.25 0.2 1% 2% S20 0.78 0.02 0.2 0.25 0.2 1% 2% S40 0.58 0.02 0.4 0.25 0.2 1% 2% S60 0.38 0.02 0.6 0.25 0.2 1% 2% S80 0.18 0.02 0.8 0.25 0.2 1% 2% Notes: S0 indicates that the amount of steel slag powder added is 0; In the table, except for the volume ratio of PVA content, all others are mass ratios. 表 7 掺钢渣粉PVA/ECC材料试件编号
Table 7. Number of PVA/ECC material specimens mixed with steel slag powder
Group Steel slag powder
dosage(wt%)Number of wet
and dry cyclesL0 0 L2 2 L4 4 L6 6 L8 8 S0 0 S20 20 S40 40 S60 60 S80 80 表 8 Weibull分布两参数
Table 8. Two parameters of Weibull distribution
Number Shape parameter$ m $ Scaling parameter$ \theta $ S0 3.614 127.966 S20 2.198 161.564 S40 2.525 131.077 S60 4.112 125.191 S80 3.91 108.872 -
[1] 杨波, 史林. 钢渣混凝土研究现状分析[J]. 中国新技术新产品, 2011, 197(7): 11-12.YANG Bo, SHI Lin Analysis of the current research status of steel slag concrete[J]. China New Technologies and Products, 2011, 197 (7): 11-12 (in Chinese). [2] 於林锋, 徐兵, 王琼, 等. 钢渣混凝土性能的试验研究及应用前景分析[J]. 混凝土, 2014, 291(1): 79-81.YU Linfeng, XU Bing, WANG Qiong, et al. Experimental study and application-benefit analysis of steel slag concrete[J]. Concrete, 2014, 291 (1): 79-81(in Chinese). [3] 涂昆, 刘家祥, 邓侃. 钢渣粉和钢渣水泥的活性及水化机理研究[J] . 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版) , 2015, 42(1) : 62-68.TU Kun, LUI Jiaxiang, DENG Kan. Study of the hydration behaviour of steel slag and steel slag cement complex powders[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 42 (1): 62-68(in Chinese). [4] 万江凯, 张朝晖, 刘佰龙, 等. 钢渣在混凝土中的应用[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(12): 4020-4024.WAN Jiangkai, ZHANG Chaohui, LIU Bailong, et al. Application of steel slag in concrete[J]. Bulletin of The Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 35 (12): 4020-4024(in Chinese). [5] 陈苗苗, 冯春花, 李东旭. 钢渣作为混凝土掺合料的可行性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2011, 30(4): 751-754.CHEN Miaomiao, FENG Chunhua, LI Dongxu. Research on feasibility of using steel slag as mineral admixture in concrete[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2011, 30(4): 751-754(in Chinese). [6] 徐世烺, 李贺东. 超高韧性水泥基复合材料研究进展及其工程应用[J]. 土木工程学报, 2008, 41(6): 45-60.XU Shiyan, LI Hedong. A review on the development of research and application of ultra high toughness cementitious composites[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2008, 41 (6): 45-60(in Chinese). [7] 刘俊, 牛荻涛, 宋华. 掺合料对混凝土抗硫酸盐侵蚀性能的影响[J]. 混凝土, 2014, (3): 79-83.LIU Jun, NIU Ditao, SONG Hua. Influences brought by admixtures to the sulfate corrosion of concrete[J]. Concrete, 2014, (3): 79-83(in Chinese). [8] 高润东, 赵顺波, 李庆斌, 等. 干湿循环作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀劣化机理试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2010, 43(2): 48-54. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2010.02.018GAO Rundong, ZHAO Shunbo, LI Qingbin, et al. Experimental study of the deterioration mechanism of concrete under sulfate attack in wet-dry cycles[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2010, 43(2): 48-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2010.02.018 [9] 徐世烺, 赵国藩. 混凝土结构裂缝扩展的双K断裂准则[J]. 土木工程学报, 1992, (2): 32-38. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.1992.02.005XU Shixuan, ZHAO Guofan. A double-k fracture criterion for the crack propagatiom in goncrete structures[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1992, (2): 32-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.1992.02.005 [10] 钱维民, 苏骏, 赵家玉, 等. 超低温作用对超高韧性水泥基复合材料断裂性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(9): 901-909, 916.QIAN Weimin, SU Jun, ZHAO Jiayu, et al. Effect of ultra-low temperature on fracture behavior of ultra-high toughness cementitious composites[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2022, 25(9): 901-909, 916(in Chinese). [11] 甘磊, 沈振中, 徐力群, 等. 不同pH值硫酸盐侵蚀下水泥砂浆断裂韧度[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2023, 31(3): 690-702.GAN Lei, SHEN Zhenzhong, XU Liqun, et al. Fracture toughness of cement mortar under sulfate attack at different pH values[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2023, 31(3): 690-702(in Chinese). [12] 肖建庄, 许金校, 罗素蓉, 等. 剑麻纤维对再生骨料混凝土断裂性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2023, 26(6): 587-595. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.06.003XIAO Jianzhuang, XU Jinxiao, LUO Surong, et al. The effect of sisal fiber on the fracture performance of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2023, 26(6): 587-595(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.06.003 [13] LIU H Z, ZHANG Q, LI V, et al. Durability study on engineered cementitious composites (ECC) under sulfate and chloride environment[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2017, 133: 171-181. [14] WANG Y M, HU S W, HE Z. Mechanical and fracture properties of geopolymer concrete with basalt fiber using digital image correlation[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 112: 102909. doi: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2021.102909 [15] 冷发光, 马孝轩, 田冠飞. 混凝土抗硫酸盐侵蚀试验方法[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 36(S2): 45-48.LENG Faguang, MA Xiaoxuan, TIAN Guanfei. Investigation of test methods of concrete under sulfate corrosion[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 36(S2): 45-48(in Chinese). [16] 董宜森. 硫酸盐侵蚀环境下混凝土耐久性能试验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011.DONG Yisen. Experimental research on the durability of concrete exposed to sulfate environment[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011(in Chinese). [17] 中国工程建设协会. 纤维混凝土试验方法标准: CECS 13: 2009[S]. 北京: 计划出版社, 2010.China Engineering Construction Association. Standard for test methods for fiber reinforced concrete: CECS 13: 2009[S]. Beijing: Planning Press, 2010(in Chinese). [18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构试验方法标准: GB/T 50152-2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012.Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. Standard for test methods of concrete structures: GB/T 50152-2012[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2012(in Chinese). [19] 韦选纯, 汤盛文, 何真, 等. 聚乙烯醇纤维增强钢渣粉-水泥复合材料基本力学性能及微观结构[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(8): 1918-1925. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20181108.008WEI Xuanchun, TANG Shengwen, HE Zhen, et al. Mechanical and microstructural characteristics of polyvinyl alcohol fiber reinforced cementitious composites containing steel slag powder[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(8): 1918-1925(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20181108.008 [20] 史占崇, 苏庆田, 邵长宇, 等. 粗骨料UHPC的基本力学性能及弯曲韧性评价方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(12): 86-97.SHI Zhanchong, SU Qingtian, SHAO Changyu, et al. Basic mechanical behavior and flexural toughness evaluation method of coarse aggregate UHPC[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(12): 86-97(in Chinese). [21] 陈红莉. 干湿循环下混凝土受硫酸盐腐蚀断裂性能试验研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2016.CHEN Hongli. Experimental research on anti-sulfate corrosion fracture properties of concrete under wet and dry cycles[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2016(in Chinese). [22] GUINEA G V, PASTOR J Y, PLANAS J, et al. Stress intensity factor, compliance and CMOD for a general three-point-bend beam[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1998, 89(2): 103-116. doi: 10.1023/A:1007498132504 [23] 乔宏霞. 高性能混凝土抗硫酸盐侵蚀试验研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2003.QIAO Hongxia. Experimental study on sulfate attack resistance of high-performance concrete[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2003(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: