Research progress on microwave absorption stealth technology of honeycomb sandwich structure composites
-
摘要: 随着探测技术的快速发展与作战性能的需求,对雷达隐身技术提出了更高的要求,蜂窝夹层结构作为经典的结构型吸波材料近年来取得了长足的发展,本文旨在综合分析和总结国内外蜂窝夹层结构复合材料在吸波隐身技术领域的特点、研究现状及应用情况,重点探讨了影响蜂窝夹层结构吸波性能的关键因素,包括吸波剂性能、蜂窝结构设计和蒙皮的透波性能等,并就吸波带宽、吸收率等关键指标分析了不同蜂窝夹层结构吸波材料的优缺点。此外,总结了蜂窝夹层结构吸波隐身复合材料目前的发展趋势,归纳了发展现状,并对未来的发展方向进行了展望。Abstract: With the rapid development of detection technology and the demand for operational performance, higher requirements have been put forward for radar stealth technology, honeycomb sandwich structure as a classical structural wave-absorbing material has made great development in recent years, this paper aims to comprehensively analyse and summarize the characteristics, research status and application of honeycomb sandwich structure composites in the field of wave-absorbing stealth technology at home and abroad. This paper focuses on the key factors affecting the wave-absorbing performance of honeycomb sandwich structures, including the performance of absorbers, the design of honeycomb structures and the wave-transparent performance of skins, etc. It also analyses the advantages and disadvantages of different honeycomb sandwich structure wave-absorbing materials with respect to the key indexes of wave-absorbing bandwidth and absorption rate. In addition, this paper summarises the current development trend of honeycomb sandwich structure wave-absorbing stealth composites, summarises the current status of development, and gives an outlook on the future development direction.
-
图 2 (a) 石墨烯纳米片(GNP)包覆蜂窝(HC)材料的制备工艺流程[34];(b) 电介质涂层的复介电常数的实部($ {\varepsilon' }$)和虚部($ {\varepsilon'' } $)及介电损耗角正切值($ \mathrm{tan}{\delta }_{\varepsilon } $);(c) 蜂窝吸波材料(HMAMs)的有效介电常数的实部($ {\varepsilon '}_{{\mathrm{eff}}} $)和虚部($ {\varepsilon'' }_{{\mathrm{eff}}} $)及相应的介电损耗正切值($ \mathrm{tan}{\delta }_{{\mathrm{eff}}} $);(d) 实际试验、有限元法和有效介质法得到的反射损耗(RL)曲线[35];(e) 蜂窝芯浸渍量对吸波性能的影响;(f) 碳纤维频率选择表面(FSS)尺寸对吸波性能的影响;(g) 加入碳纤维FSS后,蜂窝芯浸渍量对吸波性能的影响[36]
Figure 2. (a) Preparation process of graphene nanosheet (GNP) coated honeycomb (HC) material[34]; (b) Real part (ε') and imaginary part (ε'') of relative complex permittivity and dielectric dissipation factor (tanδε) of the dielectric coating; (c) Real part ($ {\varepsilon' }_{{\mathrm{eff}}} $) and imaginary part ($ {\varepsilon ''}_{{\mathrm{eff}}} $) of the relative complex effective permittivity and effective dielectric dissipation factor ($ \mathrm{tan}{\delta }_{{\mathrm{eff}}} $) of the HMAMs; (d) Reflection loss (RL) curves of the HMAMs obtained by the real test, finite element and effective medium methods[35];(e) Effect of impregnation amount of honeycomb core on absorbing performance; (f) Effect of size of carbon fiber FSS on absorbing properties; (g) Effect of impregnation amount of honeycomb core on absorbing properties after adding carbon fiber FSS[36]
WEGs—Wormlike expanded graphite; PVA—Polyvinyl-alcohol; GNP—Graphene nanoplatelet; HC—Honeycomb; PEC—Perfectly electric conducting; HMAM—Honeycomb microwave absorbing materials; FSS—Frequency selective surface; d—Coating thickness; r—Honeycomb pore radius; h—Honeycomb height; MLG—Multilayer graphene microsheets; RAM—Radar absorbing material
图 3 (a) 单层HC复合材料的RL;(b)多层HC复合材料的RL;(c) 夹层结构HC吸波材料的力学性能[37];(d) 单层碳纳米管(CNTs)/炭黑(CB)/聚氨酯(PU) HC复合材料的RL;双层(e)和三层(f) HC复合材料的RL;双层(g)和三层(h)夹层结构HC复合材料的RL;双层(i)和三层(j)夹层结构HC复合材料的力学性能[38]
Figure 3. (a) RL of single-layer HC composites; (b) RL of multi-layer HC composites; (c) Mechanical properties of sandwich HC absorber[37]; (d) RL of single-layer carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/carbon black (CB)/polyurethane (PU) HC composites; RL of double-layer (e) and three-layer (f) HC composites; RL of double-layer (g) and three-layer (h) HC sandwich composites; Mechanical properties of double-layer (i) and three-layer (j) HC sandwich composites[38]
RGO—Reduced graphene oxide; H, h—HC; S, s—sandwich HC
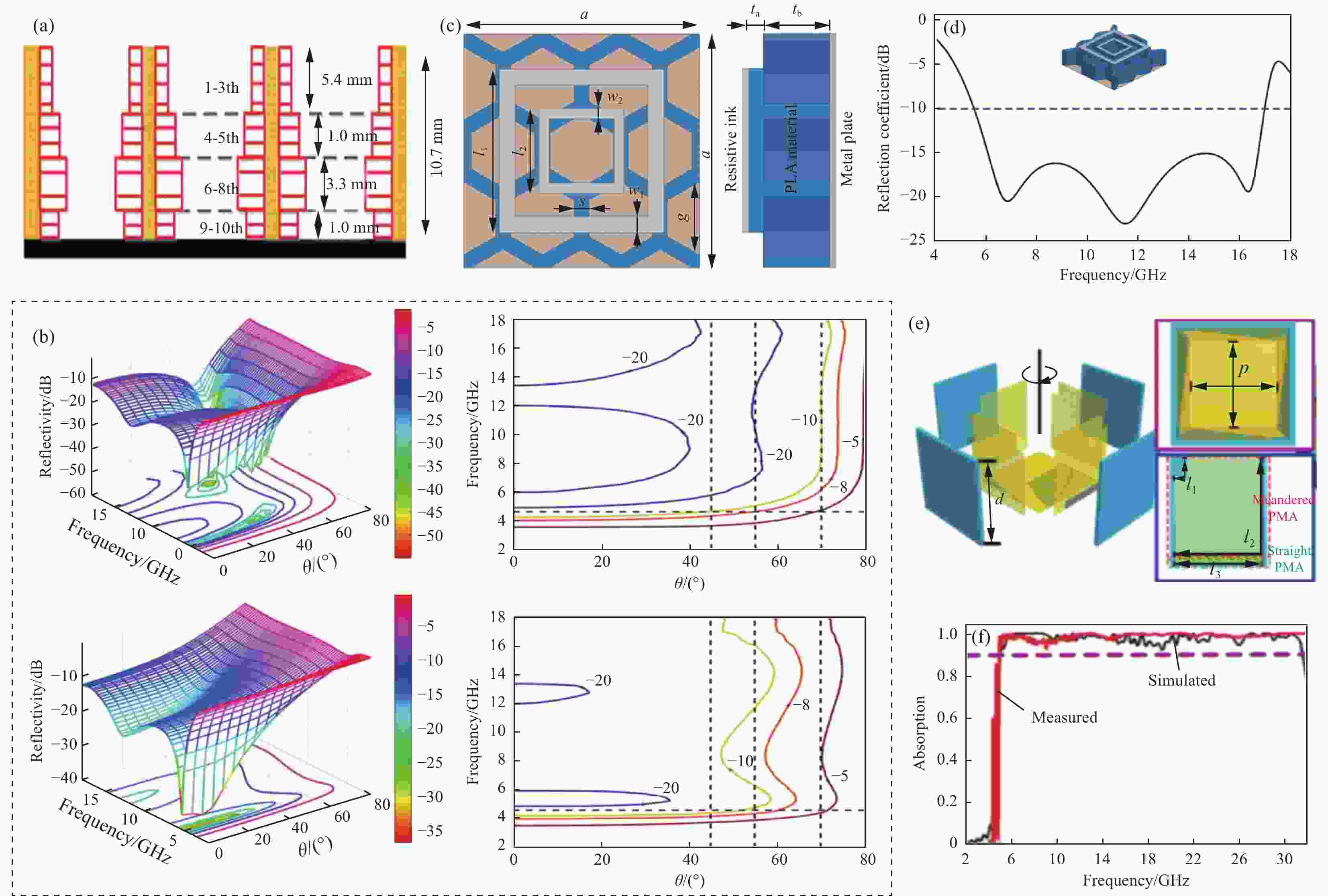
图 4 (a) 梯度蜂窝雷达吸波结构(RAS)设计结果;(b) 优化后的梯度蜂窝RAS的反射率[41];(c) 沉积电阻涂料拓扑结构的俯视图和侧视图;(d) 宽带吸收效果[42];(e) 多层弯折线等离子结构示意图;(f) 对于垂直入射电磁波的吸波性能[43]
Figure 4. (a) Graded honeycomb radar absorbing structure (RAS) design result; (b) Reflectivity of the optimized graded honeycomb RAS[41]; (c) Top view and side view of the topological structure of the deposition resistance coating; (d) Wide-band absorption effect[42]; (e) Schematic diagram of multilayer curved line plasma structure; (f) Absorption properties for vertical incident electromagnetic waves[43]
PLA—Polylactic acid; a, l1, l2, w1, w2, s, g, ta, tb—Optimized dimensions of the structure; PMA—Perfect metamaterial absorber; d—Height; p—Length; l1, l2—Total length of meandered wire; l3—Length of straight wire
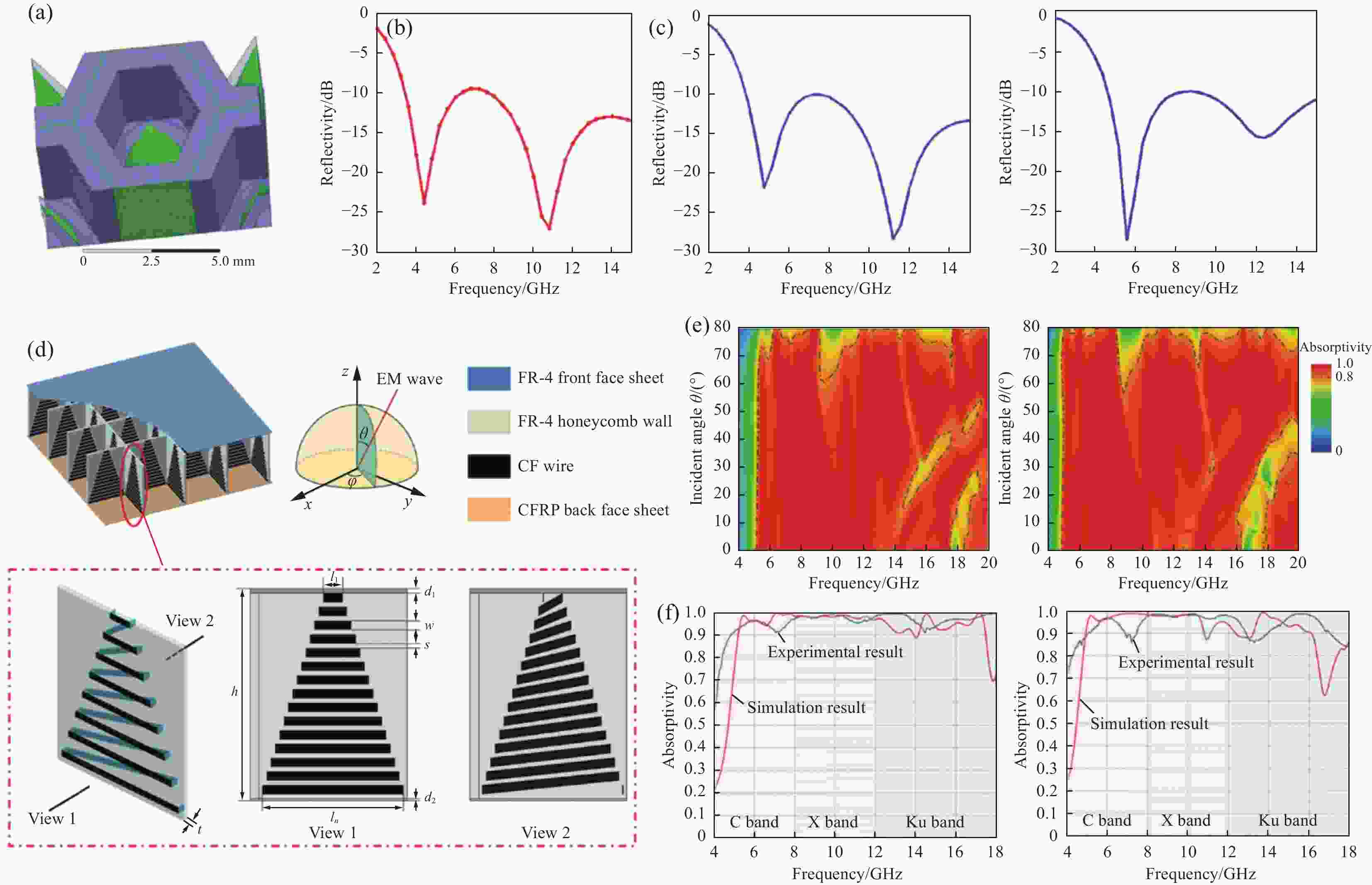
图 5 (a) 异形蜂窝结构设计模型;(b) 优化后垂直入射的反射率;(c) 优化后斜入射角的反射率[26];(d) 连续方形格栅吸波材料(SHS)原理图;(e) 连续SHS和聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺(PMI)泡沫填充的连续SHS在不同入射角θ时的吸收光谱;(f) 测量和模拟连续SHS和PMI泡沫填充连续SHS的电磁(EM)波吸收率[44]
Figure 5. (a) Designing model for special-shaped honeycomb structure; (b) Reflectivity of perpendicularly incident angle for the optimized multi-absorbing structure; (c) Reflectivity of obliquely incident angle for the optimised multi-absorbing structure[26]; (d) Schematic diagram of interlocked squarehoneycomb structure (SHS); (e) Absorptivity spectra with different incident angle θ of interlocked SHS and polymethacrylimide (PMI) foam-filled interlocked SHS; (f) Measured and simulated EM wave absorptivity of interlocked SHS and PMI foam-filled interlocked SHS[44]
EM—Electromagnetic; CF—Carbon fiber; CFRP—Carbon fiber reinforced plastics; φ—Incident direction; h, t—Height and thickness of honeycomb walls; w, s—Width of CF wire and the spacing between two adjacent CF wires; d1, d2—Thickness of FR-4 front face sheet and CFRP composite back face sheet; l1, ln—Shortest and longest of CF wire; FR-4—Glass fiber reinforced composite
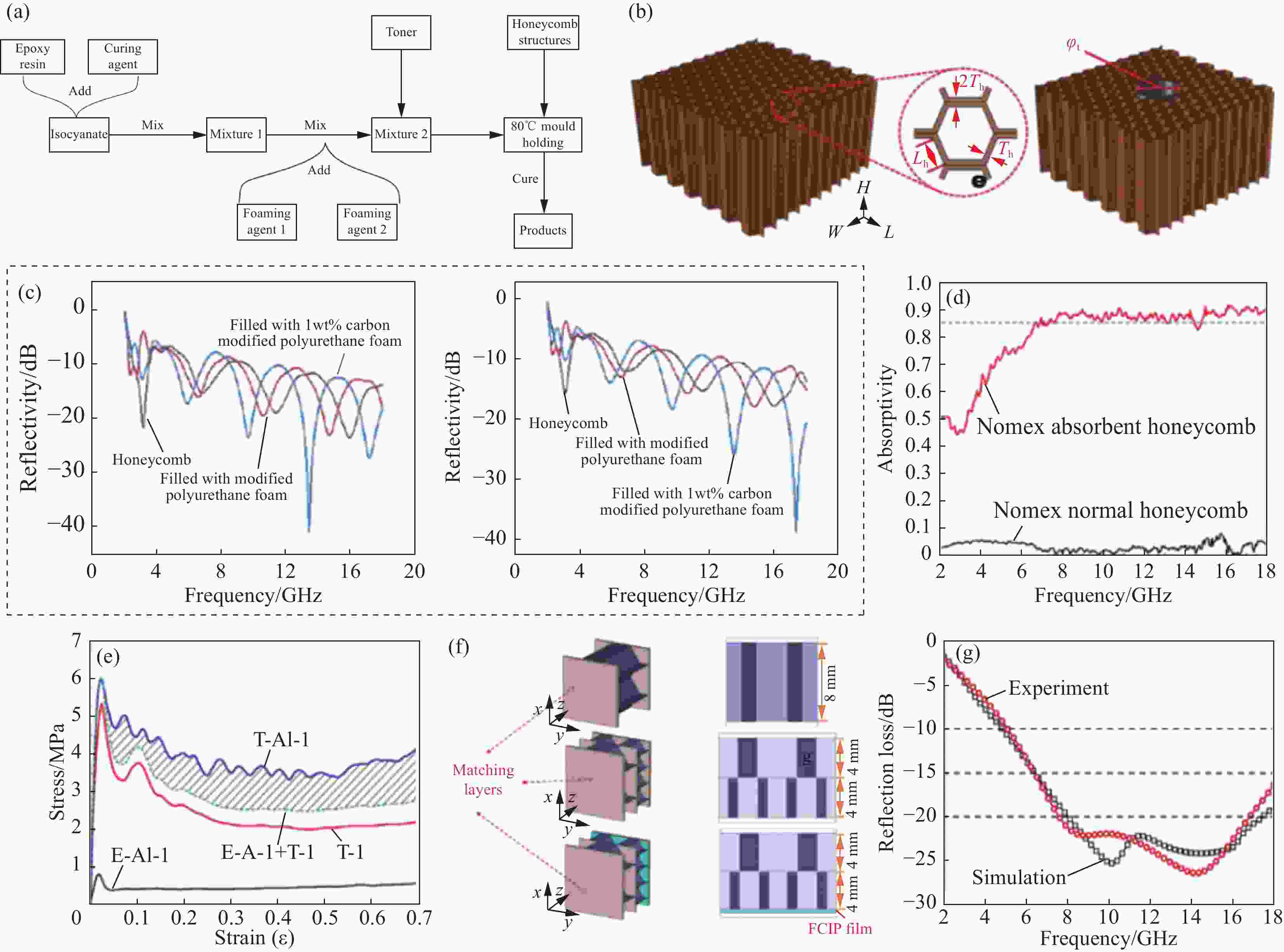
图 6 (a) 改性聚氨酯泡沫的制备流程图;(b) 空蜂窝及管状增强蜂窝芯示意图及参数;(c) 垂直极化(VV)与水平极化(HH)下的反射率曲线[46];(d) 垂直入射波反射率;(e) 空吸波蜂窝(E-A1-1)、CFRP管(T-1)、管增强吸波蜂窝(T-A1-1)及空吸波蜂窝与CFRP管之和在单轴压缩下的应力-应变曲线[47];(f) 两种不同孔径规格蜂窝的几何形状与设计参数;(g) 双层蜂窝结构吸波材料(THSSA)的宽带反射损耗[48]
Figure 6. (a) Flow chart of preparation of modified polyurethane foam; (b) Schematic and parameters of empty honeycomb and tube-reinforced honeycomb core; (c) Reflectance curves under vertical sending and vertical recieving (VV) polarization and horizontal sending and horizontal recieving (HH) polarization[46]; (d) Experimental results of reflectivity for vertical incident waves; (e) Nominal stress-strain curves of empty absorbent honeycomb (E-A1-1), CFRP tube (T-1), tube-reinforced absorbent honeycomb (T-A1-1) and sum of empty absorbent honeycomb and CFRP tube under uniaxial compression[47]; (f) Geometry and design parameters of two kinds of honeycomb with different aperture specifications; (g) Measured broadband reflection loss of fabricated two-layer honey-comb sandwich structure absorber (THSSA)[48]
φt—Outside diameter of CFRP tubes; Th—Wall thickness of honeycomb core; Lh—Hexagon side length; FCIP—Flaky carbonyl iron powder
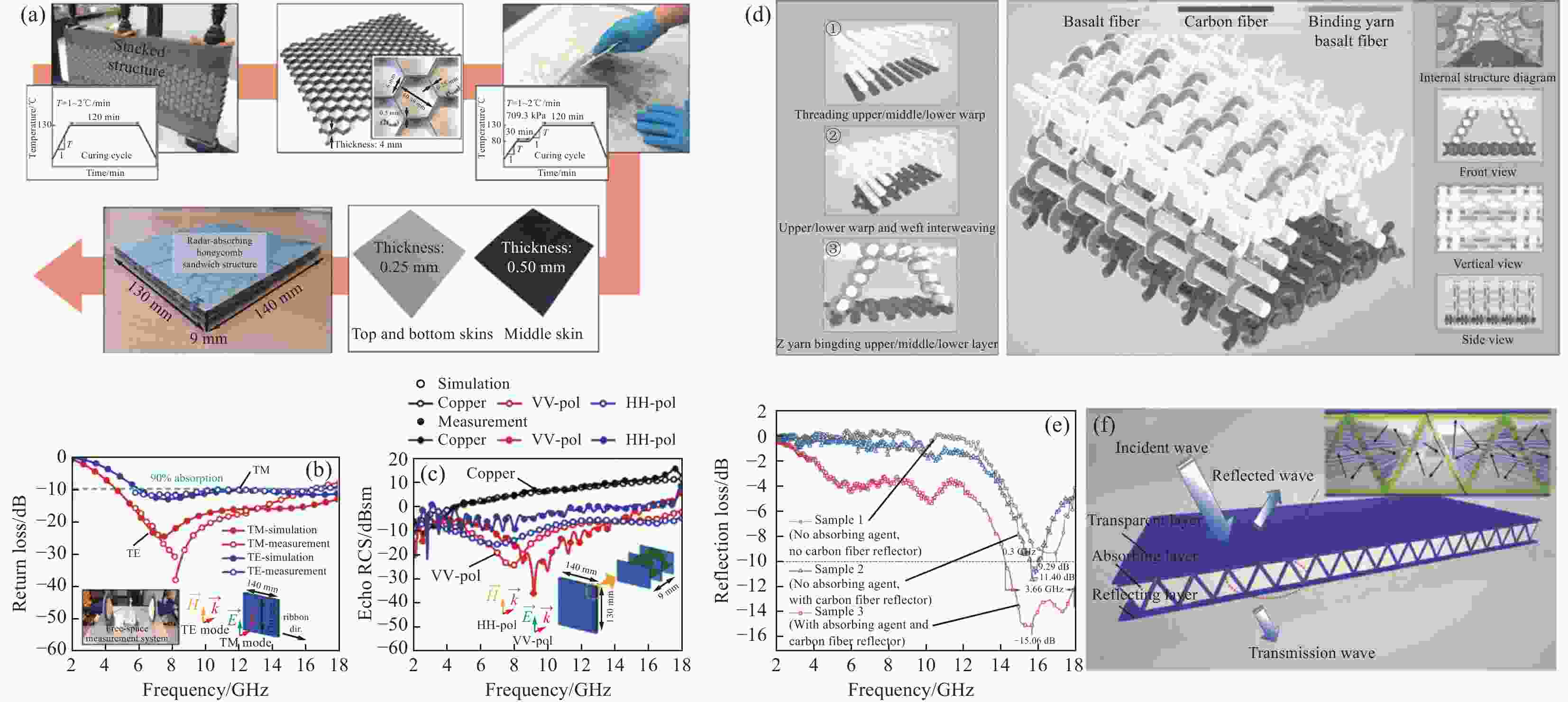
图 7 (a) 镀镍玻璃纤维蜂窝吸波夹层复合材料的完整制造过程;(b) 雷达吸波蜂窝夹层复合材料回波损耗的实测与仿真结果;(c) 在VV和HH极化下,铜板和所提出结构的单稳态雷达横截面(RCS)的仿真和测量结果[49];(d) 蜂窝状三维整体机织结构型吸波织物单胞示意图;(e) 蜂窝状三维整体机织结构型吸波复合材料的吸波损耗曲线;(f) 蜂窝状三维整体机织结构型吸波复合材料的吸波机制示意图[50]
Figure 7. (a) Complete manufacturing process of the radar-absorbing honeycomb sandwich composite with a nickel-coated glass fabric; (b) Measured return loss of the fabricated radar-absorbing honeycomb sandwich composite along with the simulation results; (c) Simulation and measurement results of the monostatic radar cross-section (RCS) for a copper plate and for the proposed structure under VV and HH polarizations[49]; (d) Cell diagram of honeycomb 3D integral woven structure microwave absorbing fabric; (e) Reflection loss curves of honeycomb 3D woven structure microwave absorbing composites; (f) Schematic diagram of microwave absorbing mechanism of honeycomb 3D integral woven structure microwave absorbing composite[50]
TE—Transverse electric; TM—Transverse magnetic; T—Temperature rate; $\vec H $—Perpendicular to glass fabric; $\vec E$—Lengthways; $\vec k $—Crosswise
图 8 (a) 吸波蜂窝复合石英/环氧蒙皮前后的反射率;(b) A型蒙皮复合吸波蜂窝结构;(c) A型蒙皮复合吸波蜂窝的反射率测试值[55];(d) 含超材料蜂窝夹层结构吸波复合材料结构示意图;(e) 超材料单元结构示意图;(f) 含超材料单元与不含超材料单元的透波面板在1~18 GHz 频率范围内的透波率曲线;(g) 含碳纤维超材料单元与不含超材料单元的吸波蜂窝夹层结构的L波段反射率曲线[56]
Figure 8. (a) Reflectivity of absorbing honeycomb with and without quartz/epoxy skin; (b) Structure of absorbing honeycomb with A-type skin; (c) Reflectance values of absorbing honeycomb with A-type skin[55]; (d) Schematic structure of the honeycomb sandwich composite containing metamaterial; (e) Schematic diagram of metamaterial unit structure; (f) Transmittivity curves of the wave-transmitting skin with/without metamaterial units in the frequency range of 1-18 GHz; (g) Reflectivity curves of the wave-absorbing honeycomb sandwich composites with/without carbon fiber metamaterials in the L-band[56]
表 1 不同吸波剂所制备的蜂窝夹层吸波体参数
Table 1. Parameters of honeycomb sandwich absorbers prepared with different absorbers
Category Total thickness of
the absorber/mmAbsorbing
bandwidth/GHzAbsorptivity Extreme electromagnetic
loss/dBRef. PVA/GNP 32.6 8-12 ≥99% −36 [34] CB/epoxy resin 18.4 2.5-4.3; 7-18 ≥90% −25 [35] Acetylene CB/PU (Carbon fiber FSS is added
between the layers)≈10 6.8-11.5 ≥90% −14 [36] CNT/CB/RGO/PU 15 2.2-18 ≥90% −35 [37] CNTs/CB/PU 15 2.2-17.7 ≥90% −26.4 [38] 表 2 不同结构类型的蜂窝夹层吸波体参数
Table 2. Parameters of honeycomb sandwich absorbers with different structure types
Categories Total thickness of
the absorber/mmAbsorbing
bandwidth/GHzAbsorptivity Ref. Structural design Nested cone-shaped scattering
configuration≈6 3-4 ≥90% [26] SHS 23.2 5-20 ≥90% [44] Double-layer honeycomb 10 4.5-48 ≥90% [45] Foam-filled honeycomb 30 5-7; 8.5-11; 12-20 ≥90% [46] CFRP tube-reinforced absorbent honeycomb 20 7-18 ≥90% [47] THSSA 9 4.8-18 ≥90% [48] Improvement of
raw materialsNickel-coated glass/epoxy honeycomb 4 5.8-16.3 ≥90% [49] Honeycomb 3D integral woven structure 7.5 14.34-18 ≥90% [50] PBCs 30 2-2.5; 4.4-18 ≥90% [51] Note: PBC—Paper-based composites. 表 3 含超材料的蜂窝夹层吸波体参数
Table 3. Parameters of honeycomb sandwich absorbers containing metamaterials
Cycle size Dielectric substrate material Total thickness of the
absorber/mmAbsorbing
bandwidth/GHzAbsorptivity Ref. 16 mm×16 mm PLA perforated dielectric made from honeycomb 5.5 5.52-16.92 ≥90% [42] 22.5 mm×15 mm FR-4 honeycomb walls 23.2 5-20 ≥90% [44] 70 mm×70 mm Wave-permeable prepreg 52 1-1.96 ≥90% [56] Thickness
10-15 μmWave-permeable prepreg 31 1.1-1.9; 4.5-18 ≥90% [57] Note: PLA—Polylactic acid. -
[1] 石智成, 孙凌夫, 李海豹, 等. 兼容性隐身材料的研究进展[J]. 激光与红外, 2022, 52(9): 1267-1273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.09.001SHI Zhicheng, SUN Lingfu, LI Haibao, et al. Research progress of compatible stealthy materials[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2022, 52(9): 1267-1273(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.09.001 [2] 张钊, 王峰, 张新全, 等. 低频宽带薄层吸波材料研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2019, 50(6): 6038-6045. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2019.06.007ZHANG Zhao, WANG Feng, ZHANG Xinquan, et al. Recent advances of broadband and thin microwave absorbing materials for low frequency[J]. Functional Materials, 2019, 50(6): 6038-6045(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2019.06.007 [3] 胡嘉龙, 卞美琴, 崔炎, 等. 吸波涂料在雷达隐身领域的应用[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2023, 45(2): 56-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3849.2023.02.009HU Jialong, BIAN Meiqin, CUI Yan, et al. Application of absorbing coatings in radar stealth field[J]. Plating and Finishing, 2023, 45(2): 56-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3849.2023.02.009 [4] 韩敏阳, 韦国科, 周明, 等. 低频雷达吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(4): 1363-1377.HAN Minyang, WEI Guoke, ZHOU Ming, et al. Research progress of low-frequency radar absorbents[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(4): 1363-1377(in Chinese). [5] 孔静, 高鸿, 李岩, 等. 电磁屏蔽机理及轻质宽频吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(9): 9055-9063. doi: 10.11896/cldb.18110163KONG Jing, GAO Hong, LI Yan, et al. Research progress of electromagnetic shielding mechanism and lightweight and broadband wave-absorbing materials[J]. Material Guide, 2020, 34(9): 9055-9063(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.18110163 [6] 李俊燕, 陈平. 结构型吸波复合材料的研究进展[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2012, 29(2): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2012.02.004LI Junyan, CHEN Ping. Development in structural absorbing composites[J]. Fiber Composites, 2012, 29(2): 11-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2012.02.004 [7] FAN Q, HUANG Y, CHEN M, et al. Integrated design of component and configuration for a flexible and ultrabroadband radar absorbing composite[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2019, 176: 81-89. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.04.008 [8] 刘雄飞, 王壮, 吴尧尧, 等. 电磁吸波结构研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(22): 19-26.LIU Xiongfei, WANG Zhuang, WU Yaoyao, et al. A review of electromagnetic wave absorbing structures[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(22): 19-26. [9] 温凯. 玻纤布/环氧结构功能一体化隐身复合材料制备及性能研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2022.WEN Kai. Preparation and properties of glass fiber cloth/epoxy structural-functional integrated stealth composites[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2022(in Chinese). [10] 李雅茹, 卫海鹏, 高学斌, 等. 结构型微波吸收复合材料的研究进展[J]. 山西化工, 2019, 39(3): 22-25.LI Yaru, WEI Haipeng, GAO Xuebin, et al. Recnet developments in the study on structural microwave absorbing composites[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(3): 22-25(in Chinese). [11] 张亚中. 基于多机制复合的宽带隐身超材料设计与性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2019.ZHANG Yazhong. Design and electromagnetic properties of broadband stealth metamaterials based on multiple mechanisms[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [12] 任鑫. 高效雷达吸波蜂窝设计及制备研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020.REN Xin. A research on design and preparation of high-efficiency radar absorbing honeycomb[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020(in Chinese). [13] 孟庆杰, 马秘辉, 鞠长滨, 等. SKuF吸波蜂窝夹层复合材料构件制造的研究[C]//第九届中国航空学会青年科技论坛论文集. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2020: 5.MENG Qingjie, MA Mihui, JU Changbin, et al. Research on SKuF wave-absorbing honeycomb sandwich structure composite parts manufacturing[C]//Proceedings of the 9th Youth Science and Technology Forum of Chinese Society of Aeronautics. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2020: 5(in Chinese). [14] MUNK B A. Frequency selective surfaces: Theory and design[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2005: 36. [15] SADEGHI R, SHARIFI A, ORLOWSKA M, et al. Investigation of microwave absorption performance of CoFe2O4/NiFe2O4/carbon fiber composite coated with polypyrrole in X-band frequency[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(9): 809. doi: 10.3390/mi11090809 [16] PAN K W, LENG T, SONG J, et al. Controlled reduction of graphene oxide laminate and its applications for ultra-wideband microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2020, 160: 307-316. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.12.062 [17] 徐义成. GNPs改性树脂涂覆蜂窝芯复材吸波结构电磁与力学性能研究 [D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022.XU Yicheng. Study on the electromagnetic and mechanical properties of GNPs modified resin-coated honeycomb core composite absorbing structures[D]. Chengdu: School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022(in Chinese). [18] 胡婉欣, 尹洪峰, 袁蝴蝶, 等. 纤维增强树脂基吸波复合材料的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(10): 178-189 doi: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2022.10.024HU Wanxin, YIN Hongfeng, YUAN Hudie, et al. Research progress in fiber-reinforced-resin matrix microwave absorbing composites[J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(10): 178-189(in Chinese). doi: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2022.10.024 [19] 曹波, 徐伟伟, 刘雨杭, 等. 结构/隐身一体化宽频聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺吸波泡沫的制备与性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2023, 39(4): 129-138.CAO Bo, XU Weiwei, LIU Yuhang, et al. Preparation and performance of structural/stealth integrated broadband polymethacrylimide (PMI) wave absorbing foam[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2023, 39(4): 129-138(in Chinese). [20] 郭文娇, 于雯霞, 党春蕾, 等. 导电聚氨酯泡沫材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2023, 37(3): 113-122.GUO Wenjiao, YU Wenxia, DANG Chunlei, et al. Research progress in conductive polyurethane foams[J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(3): 113-122(in Chinese). [21] QIU Q L, YANG X, ZHANG P H, et al. Effect of fiber surface treatment on the structure and properties of rigid bagasse fibers/polyurethane composite foams[J]. Polymer Composites, 2021, 42(6): 2766-2773. doi: 10.1002/pc.26011 [22] 马科峰, 张广成, 刘良威, 等. 夹层结构复合材料的吸波隐身技术研究进展[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2010, 25(6): 53-57.MA Kefeng, ZHANG Guangcheng, LIU Liangwei, et al. Research progress of technology for sandwich structural absorbing stealthy composite materials[J]. Material Development and Application, 2010, 25(6): 53-57(in Chinese). [23] 马向雨, 邢孟达, 张耀辉, 等. 无反射层泡沫夹层结构设计及吸波性能研究[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(2): 94-99. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000980MA Xiangyu, XIN Mengda, ZHANG Yaohui, et al. Design and electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of foam sandwich structure without reflective layer[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2020, 48(2): 94-99(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000980 [24] 孙鹏程, 王良模, 王陶, 等. 双层吸波蜂窝复合材料结构优化设计[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(4): 58-64.SUN Pengcheng, WANG Liangmo, WANG Tao, et al. Structural optimization of the design of a double-layer absorbing honeycomb composite[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science), 2019, 46(4): 58-64(in Chinese). [25] WANG P, ZHANG Y, CHEN H, et al. Broadband radar absorption and mechanical behaviors of bendable over-expanded honeycomb panels[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018, 162: 33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.04.015 [26] WANG M L, LIU J Q, LIU X, et al. Research on influence of special-shaped honeycomb radar absorbing structure for wide-band absorbing design[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(20): 6723-6728. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0292 [27] LI M, CAO X J, ZHENG S R, et al. Ternary composites RGO/MoS2@Fe3O4: Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28(22): 16802-16812. [28] CUI X Q, LIANG X H, LIU W, et al. Stable microwave absorber derived from 1D customized heterogeneous structures of Fe3N@C[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122589. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122589 [29] XU J, SHU R W, WAN Z L, et al. Construction of three-dimensional hierarchical porous nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/hollow cobalt ferrite composite aerogels toward highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 132: 193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2022.05.050 [30] YUAN W, CHENG L C, XIA T R, et al. Effect of Fe doping on the lattice structure, microscopic morphology and microwave absorption properties of LaCo1− xFe xO3[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 926: 166839. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166839 [31] 高翔, 宿静, 刘宏伟, 等. 新型吸波材料设计与电磁性能研究[J]. 电源技术, 2016, 40(7): 1467-1468, 1500.GAO Xiang, XU Jing, LIU Hongwei, et al. Design and electromagnetic performance analysis of new absorbing materials[J]. Power Technology, 2016, 40(7): 1467-1468, 1500(in Chinese). [32] YI P S, ZHANG X F, JIN L Q, et al. Regulating pyrolysis strategy to construct CNTs-linked porous cubic Prussian blue analogue derivatives for lightweight and broadband microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 132879. [33] 徐东卫, 王瑞琪, 陈平. 石墨烯基吸波复合材料研究进展[J]. 材料研究学报, 2024, 38(1): 1-13.XU Weidong, WANG Ruiqi, CHEN Ping. Research progress of graphene-based absorbing composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2024, 38(1): 1-13(in Chinese). [34] RINALDI A, PROIETTI A, TAMBURRANO A, et al. Graphene-coated honeycomb for broadband lightweight absorbers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2018, 60(5): 1454-1462. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2017.2775660 [35] LI W, XU L, ZHANG X, et al. Investigating the effect of honeycomb structure composite on microwave absorption properties[J]. Composites Communications, 2020, 19: 182-188. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2020.04.003 [36] 巴金满, 陆泽涛. 碳纤维FSS应用于蜂窝夹层吸波材料[J]. 河南科技, 2020(14): 116-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2020.14.048BA Jinman, LU Zetao. Carbon fiber FSS applied in honeycomb sandwich absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Henan Science and Technology, 2020(14): 116-118(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2020.14.048 [37] BI S, SONG Y Z, HOU G L, et al. Lightweight and compression-resistant carbon-based sandwich honeycomb absorber with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(15): 2622. doi: 10.3390/nano12152622 [38] BI S, SONG Y Z, HOU G L, et al. Sandwich nanoarchitectonics of heterogenous CB/CNTs honeycomb composite for impedance matching design and microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 943: 169154. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169154 [39] 孟真, 李广德, 崔光振, 等. 基于超材料的红外/雷达兼容隐身材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(21): 5-12.MENG Zhen, LI Guangde, CUI Guangzhen, et al. Research progress of infrared/radar compatible stealth materials based on metamaterials[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(21): 5-12(in Chinese). [40] 沈杨, 王甲富, 张介秋, 等. 基于超材料的雷达吸波材料研究进展[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 19(6): 39-47.SHEN Yang, WANG Jiafu, ZHANG Jieqiu, et al. Research progressses in radar absorbing materials based on meta-material[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 19(6): 39-47(in Chinese). [41] ZHAO Y C, REN F, HE L, et al. Design of graded honeycomb radar absorbing structure with wide-band and wide-angle properties[J]. International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies, 2019, 11(2): 143-150. doi: 10.1017/S1759078718001460 [42] GHOSH S, LIM S. Perforated lightweight broadband metamaterial absorber based on 3-D printed honeycomb[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(12): 2379-2383. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2018.2876023 [43] SHEN Y, ZHANG J Q, MENG Y Y, et al. Merging absorption bands of plasmonic structures via dispersion engineering[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112(25): 254103. doi: 10.1063/1.5040067 [44] CHENG L H, SI Y, JI Z J, et al. A novel linear gradient carbon fiber array integrated square honeycomb structure with electromagnetic wave absorption and enhanced mechanical performances[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 305: 116510. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116510 [45] 赵彦凯, 毕松, 侯根良, 等. 轻质蜂窝夹层复合材料的制备及其吸波性能研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(5): 93-96, 101.ZHAO Yankai, BI Song, HOU Genliang, et al. Preparation and microwave absorption property of lightweight honeycomb sandwich composite[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2021, 49(5): 93-96, 101(in Chinese). [46] 孙启峰. 复合蜂窝吸波结构电磁力学一体化研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022.SUN Qifeng. Integrated research on electromagnetic and mechanical properties of composite honeycomb absorbing structure[D]. Chengdu: School of Electronic Science and Engineering, 2022(in Chinese). [47] YAN L, ZHU K, CHEN N, et al. Energy-absorption characteristics of tube-reinforced absorbent honeycomb sandwich structure[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 255: 112946. [48] LUO H, CHEN F, WANG X, et al. A novel two-layer honeycomb sandwich structure absorber with high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2019, 119: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.01.015 [49] KWAK B S, CHOI W H, NOH Y H, et al. Nickel-coated glass/epoxy honeycomb sandwich composite for broadband RCS reduction[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 191: 107952-107952. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107952 [50] 吕丽华, 王荣蕊, 刘文迪, 等. 蜂窝状三维整体机织结构型吸波复合材料的设计、制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(3): 1477-1483. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220425.001LYU Lihua, WANG Rongrui, LIU Wendi, et al. Design, preparation and properties of honeycomb 3D integral woven structure microwave absorbing composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(3): 1477-1483(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220425.001 [51] WANG H, XIU X, WANG Y, et al. Paper-based composites as a dual-functional material for ultralight broadband radar absorbing honeycombs[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 202: 108378. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108378 [52] ZHANG K L, ZHANG J Y, HOU Z L, et al. Multifunctional broadband microwave absorption of flexible graphene composites[J]. Carbon, 2019, 141: 608-617. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.10.024 [53] 阮心怡, 张恒宇, 王妮, 等. 周期结构电磁超材料吸波体的设计及最新进展[J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(3): 35-45.RUAN Xinyi, ZHANG Hengyu, WANG Ni, et al. Design and recent progress of periodically structured electromagnetic metamaterial absorbers[J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(3): 35-45(in Chinese). [54] WANG C, CHEN M, LEI H, et al. Frequency-selective-surface based sandwich structure for both effective loadbearing and customizable microwave absorption[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 235: 111792. [55] 邢孟达, 马向雨, 宫元勋, 等. A型蒙皮复合蜂窝结构设计及其吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3): 1180-1185.XING Mengda, MA Xiangyu, GONG Yuanxun, et al. Design and wave absorbing properties of honeycomb with A-type skin[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(3): 1180-1185(in Chinese). [56] 鹿海军, 礼嵩明, 黄浩, 等. 宽频蜂窝夹层结构吸波复合材料的低频隐身介质超材料研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(1): 188-195.LU Haijun, LI Chongming, HUANG Hao, et al. Study on the low frequency radar-stealth dielectric metamaterial of broadband wave-absorbing honeycomb sandwich composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(1): 188-195(in Chinese). [57] 礼嵩明, 吴思保, 王甲富, 等. 含超材料的新型蜂窝夹层结构吸波复合材料[J]. 航空材料学报, 2019, 39(3): 94-99. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2019.000052LI Chongming, WU Sibao, WANG Jiafu, et al. Novel honeycomb sandwich structure wave-absorbing composites with metamaterials[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2019, 39(3): 94-99(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2019.000052 [58] WANG Y, CHEN S J, LIU S S, et al. A novel ultra-broadband absorber based on carbon-coated honeycomb panels combined with metamaterials[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2022, 55(45): 455106. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ac90cf [59] INDRUSIAK T, SOARES B G, PEREIRA I M, et al. Low cost and easily scalable microwave absorbing material based on three-layer honeycomb sandwich structures[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 35: 105955. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105955 -






 下载:
下载: