Analysis of early microscopic pore structure of electrolytic manganese residue modified polymer magnesium phosphate cement composites
-
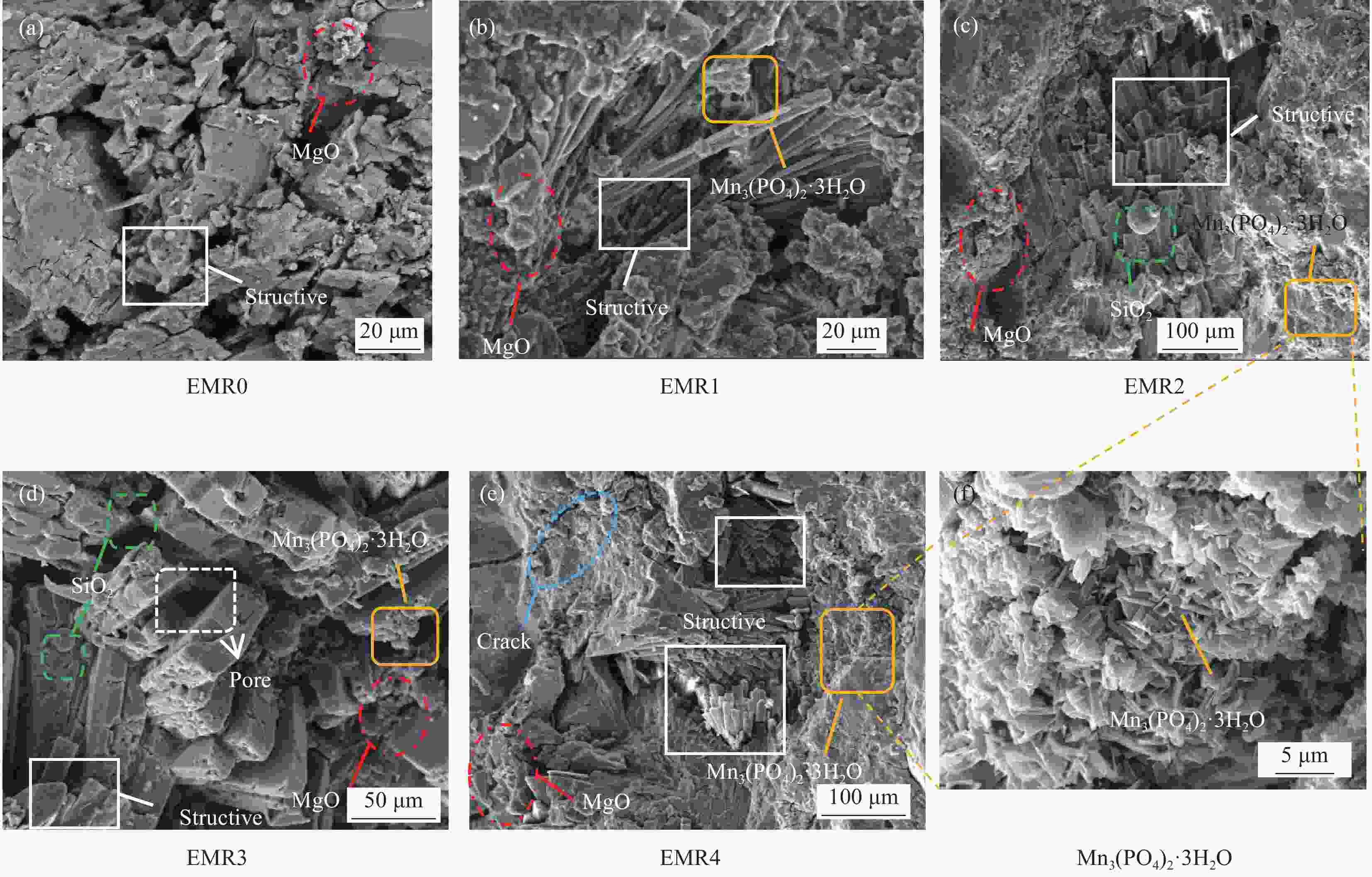
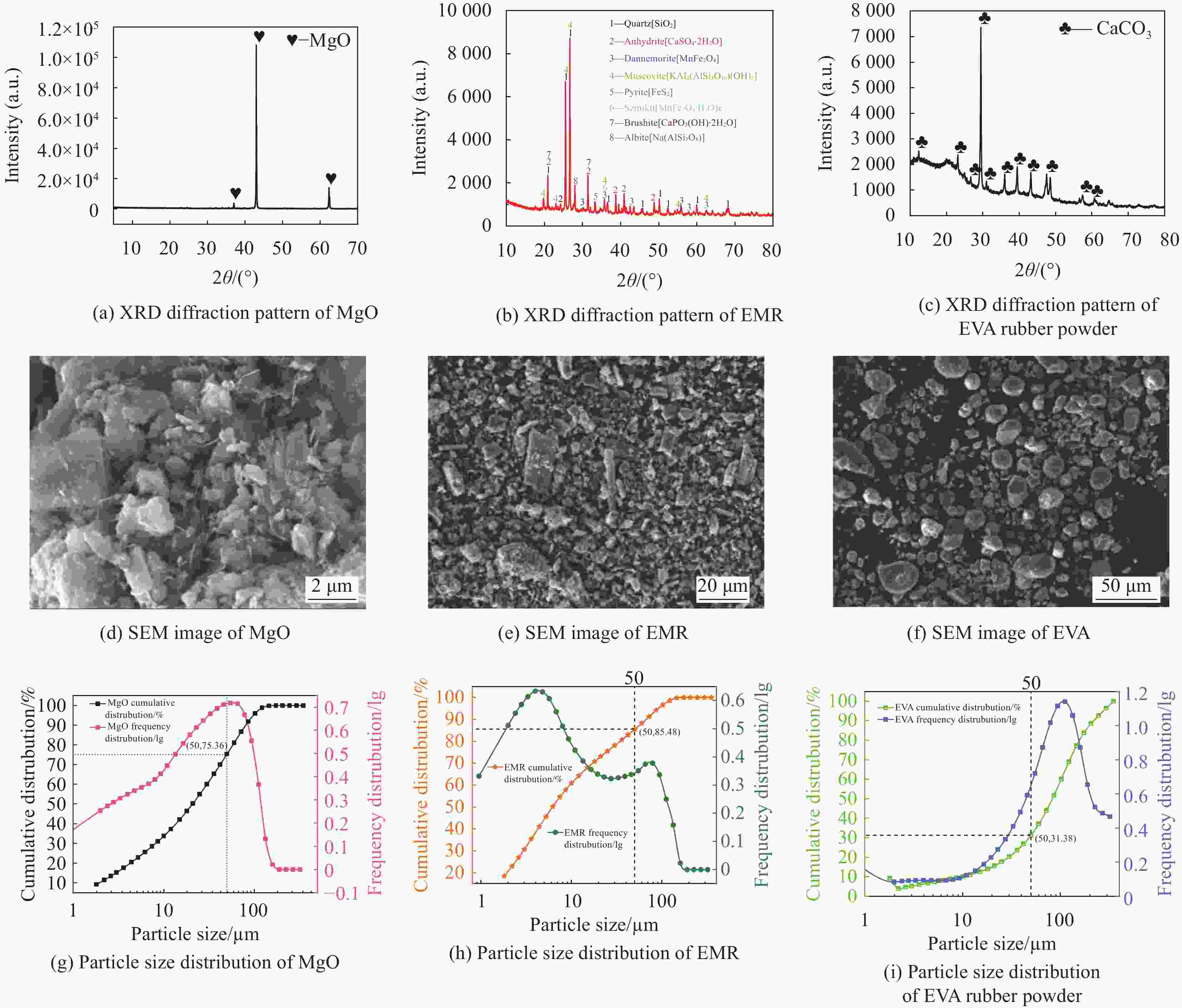
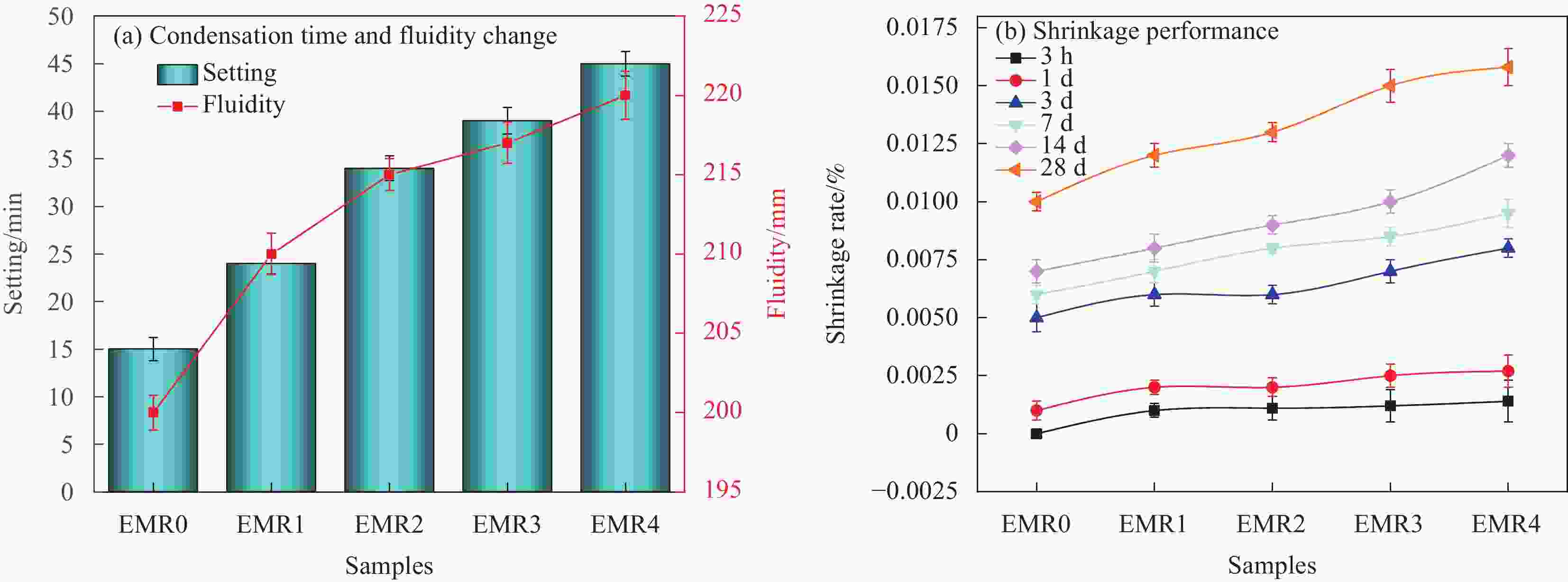
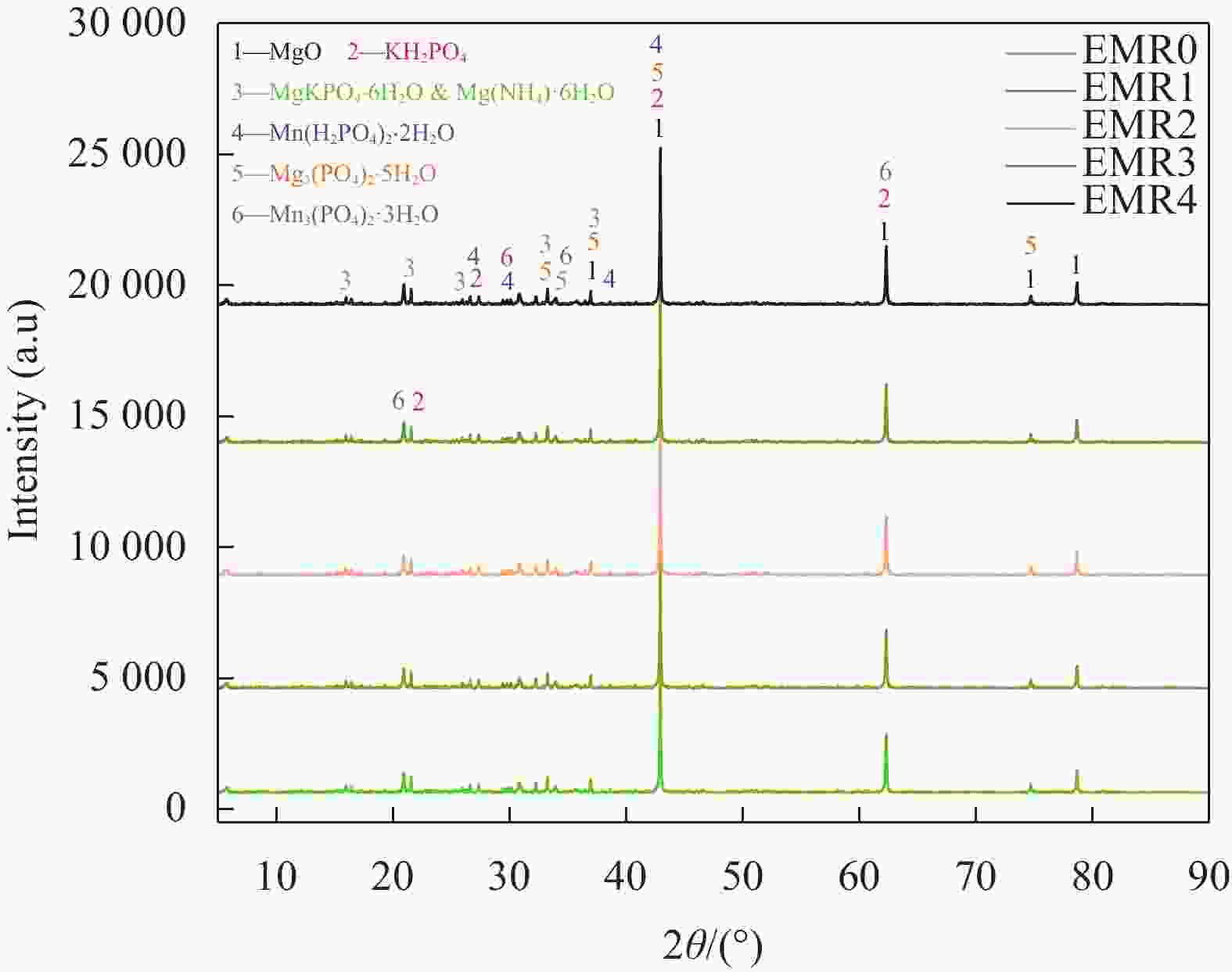
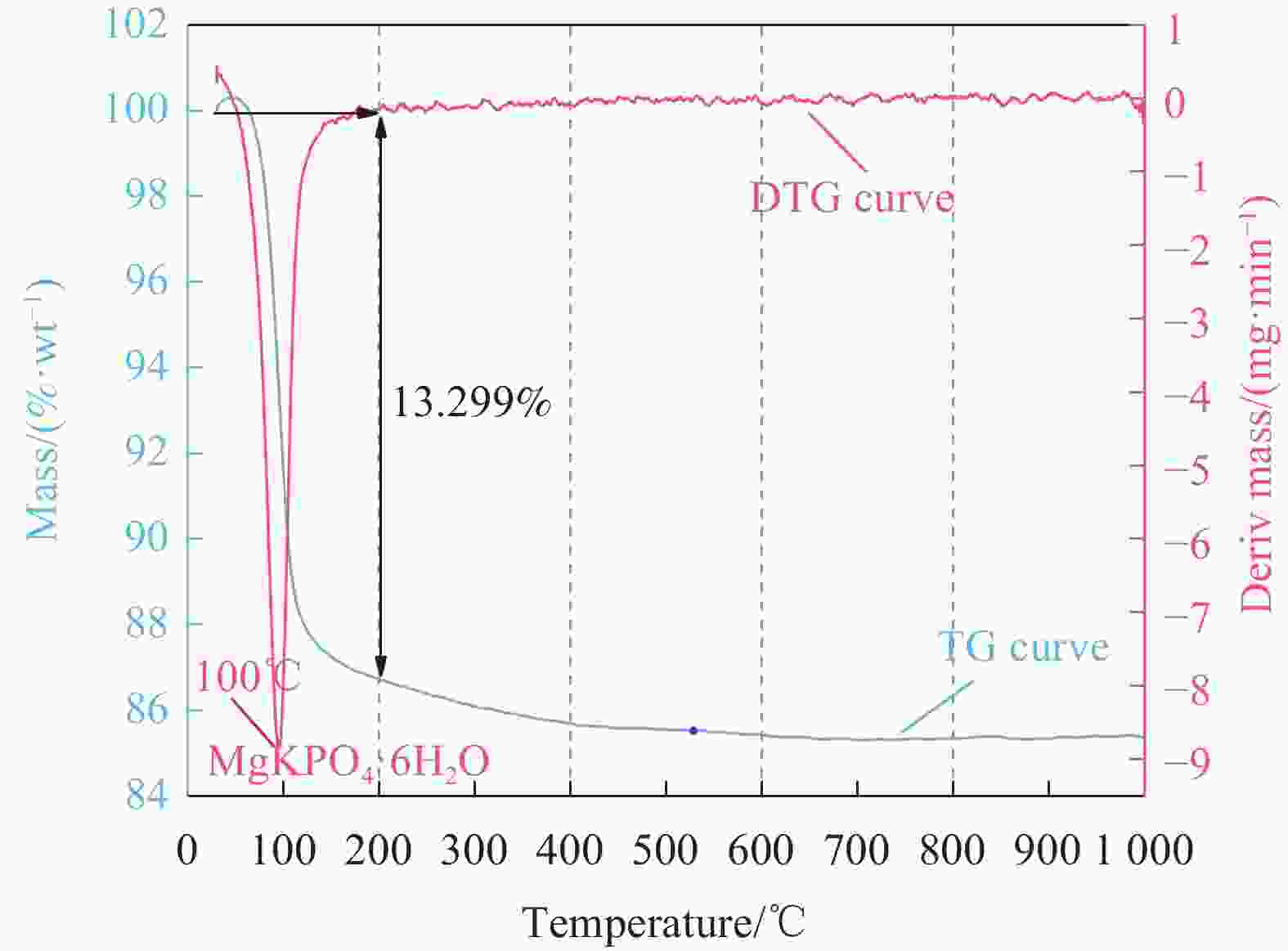
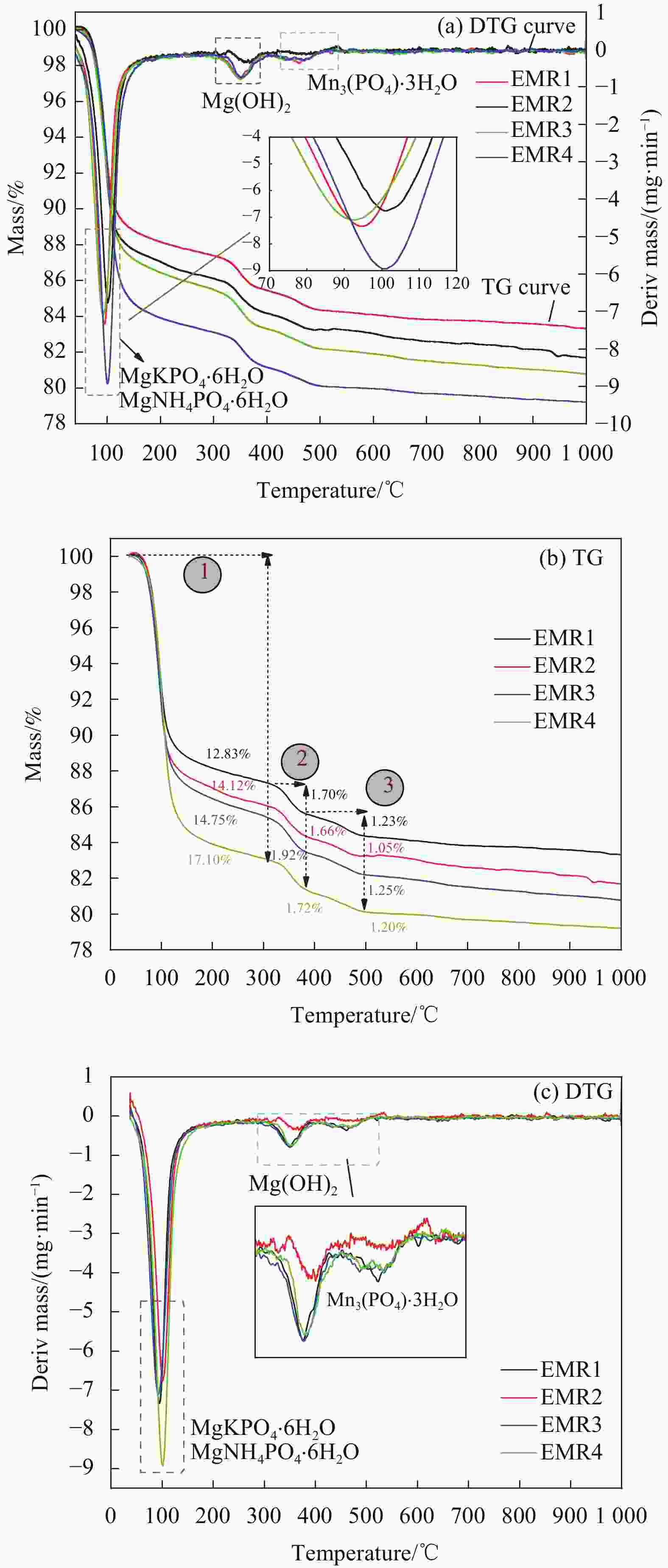
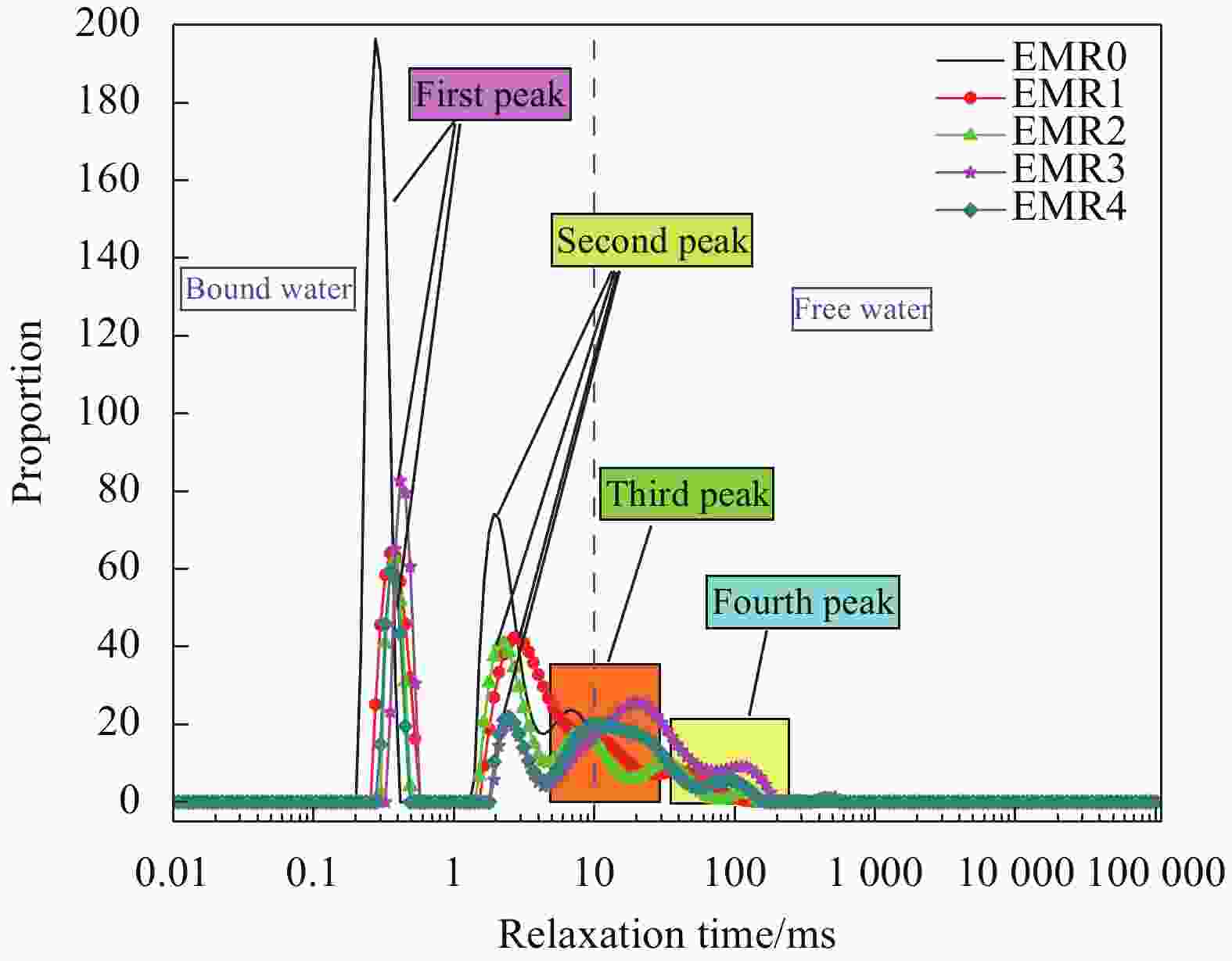
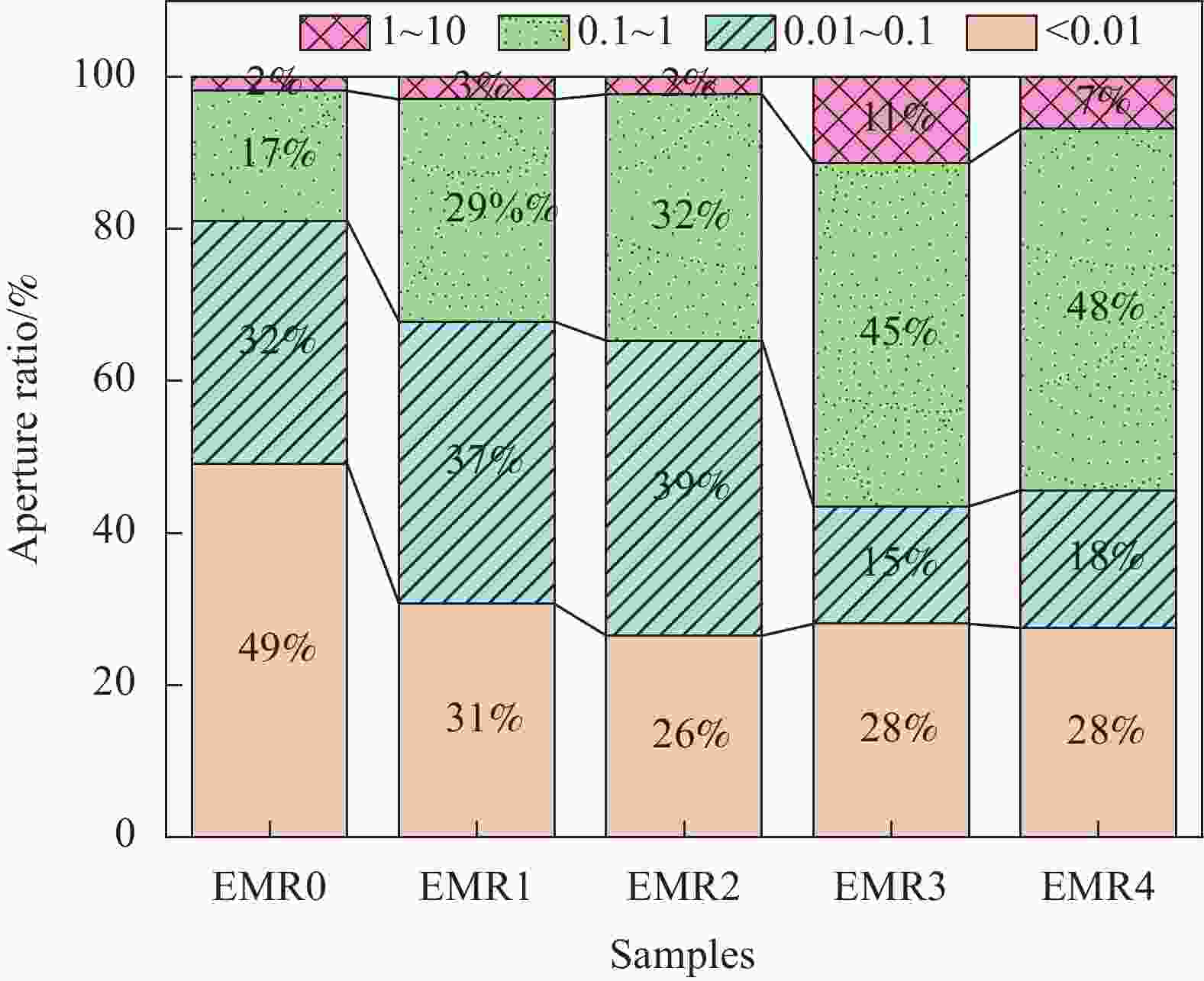
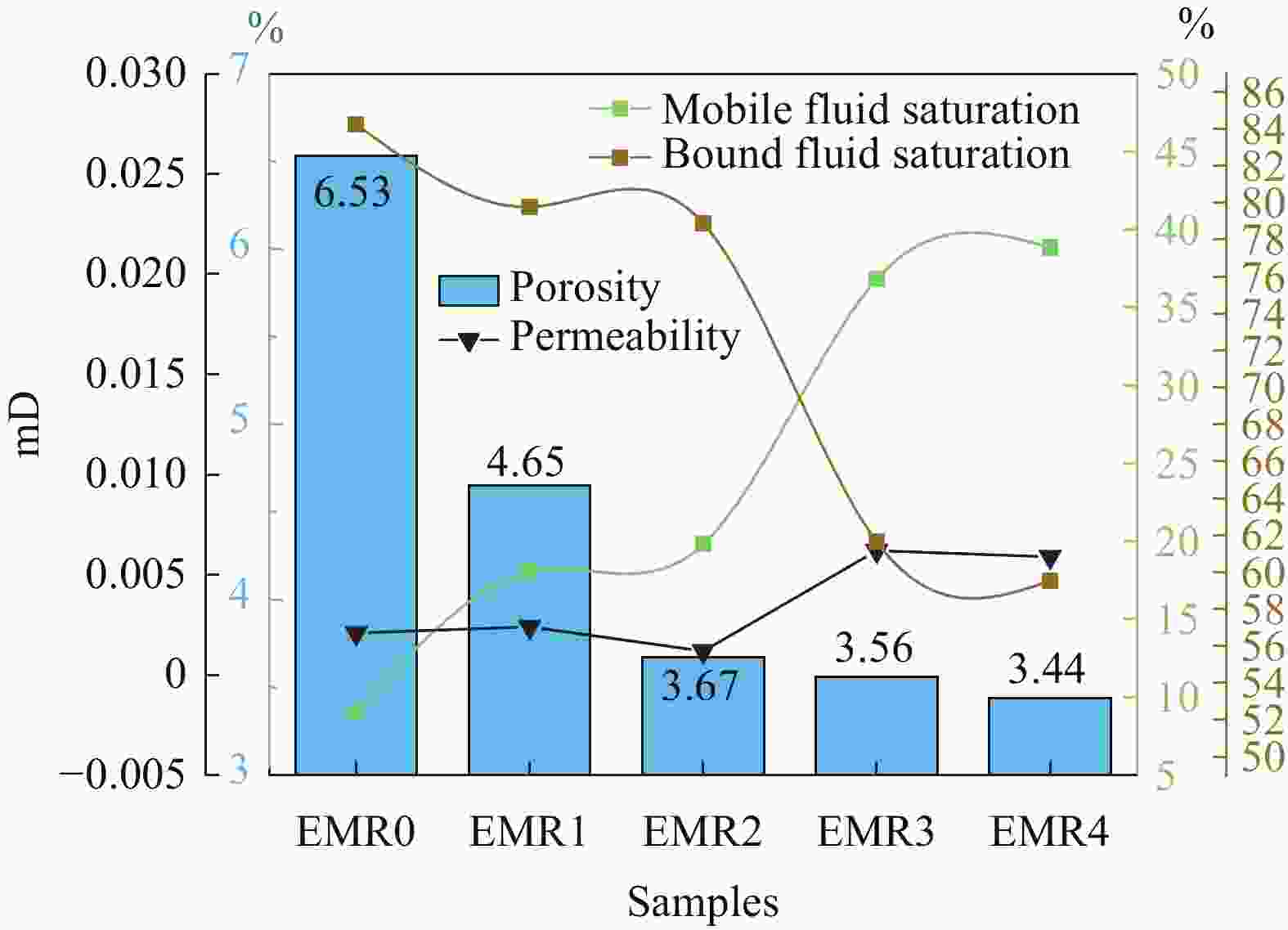
摘要: 利用电解锰渣(Electrolytic Manganese Residue,EMR)可减缓聚合物磷酸镁水泥复合材料水化速率,延长凝结时间,改善微细观结构等特点,通过宏观物理力学性能、工作性能,结合微观手段X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、同步热分析(TG-DTG)及低场核磁共振技术(NMR)等测试手段研究EMR掺量对聚合物磷酸镁水泥早期宏观和微细观孔隙结构性能影响机制。结果表明:加入EMR后能够改善浆体的工作性能,提升后期强度并有效细化孔隙结构;掺加2% EMR的28 d抗压强度值达到49.5 MPa,3%、4%掺量强度明显降低;水化产物除了长细条树状鸟粪石(Struvite,MgKPO4·6H2O&Mg[NH4]PO4·6H2O)和原料中片块状MgO外,Mn元素参与反应形成含锰化合物,水化产物相互搭接形成致密微细观结构细化了孔隙;TG-DTG曲线中在100℃出现明显的吸热峰对应鸟粪石的吸热脱水现象,质量损失率为13.299%;掺加EMR的试件出现3个吸热峰,包括Mn(OH)2和Mn3(PO4)·6H2O失去结合水的过程;T2谱弛豫时间会滞后,孔径在过渡孔和毛细孔的分布范围较大,总孔隙度随掺量增大降低,渗透率先减小后增大,1%和2%掺量的复合材料主要以凝胶孔和过渡孔分布,大孔分布面积较少,内部结构较密实,渗透率低,束缚流体饱和度高,自由流体饱和度较低。Abstract: Electrolytic manganese residue (EMR) can slow down the hydration rate of polymer magnesium phosphate cement composite mortar, prolong the setting time and improve the microstructure. Through macroscopic physical and mechanical properties, working performance, combined with microscopic means such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) simultaneous thermal analysis (TG-DTG) and low field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques were used to investigate the mechanism of the influence of EMR dosage on the early macroscopic and microscopic pore structure properties of magnesium phosphate cement. The results show that the addition of EMR can improve the working performance of the slurry, enhance the later strength and effectively refine the pore structure; The 28 d compressive strength value of adding 2% EMR reaches 49.5 MPa, and the strength of 3% and 4% additives is significantly reduced; In addition to the elongated tree like struvite (MgKPO4·6H2O) and block like MgO in the raw material, Mn elements participate in the reaction to form manganese containing compounds, and the hydration products overlap with each other to form a dense microstructure which refines the pores; TG-DTG curve at 100 ℃ appeared obvious heat-absorption peak corresponds to the heat-absorption dehydration phenomenon of guano stone, the mass loss rate is 13.299%; EMR-doped specimens appeared three heat-absorption peaks, including the process of the loss of bound water by Mn(OH)2 and Mn3(PO4)·6H2O; T2 spectra relaxation time will be lagging behind, the pore size in the range of the transition pores and the distribution of the capillary pores. The total porosity decreases with the increase of doping, and the permeability decreases first and then increases. The pores of composites with 1% and 2% doping are mainly distributed by gel pores and transition pores, the distribution area of macropores is less, the internal structure is more dense, and the permeability is low, the saturation of bound fluid is high, and the saturation of free fluid is low.
-
表 1 原材料的化学成分(wt%)
Table 1. Chemical composition of raw materials (wt%)
Component SiO2 Fe2O3 Al2O3 CaO MgO Na2O SO3 K2O MnO P2O5 TiOi2 MgO 2.1 0.4 0.4 1.7 95 0.21 0.02 0.01 0.06 0.43 0.03 Fly Ash(FA) 49.07 4.15 32.48 3.89 1.02 0.56 0.92 1.41 0.05 EVA 5010 4.28 0.39 2.72 19.35 0.34 0.18 0.11 0.10 0.02 0.03 0.34 Electrolytic Manganese Residue (EMR) 31.74 6.67 8.94 11.32 0.98 0.92 20.18 2.29 1.97 Na2B4O7·10H2O 0.13 0.01 0.11 0.10 0.19 13.34 0.24 0.03 - 0.06 - KH2PO4 0.36 0.03 0.11 0.18 0.02 2.13 0.09 31.87 - 42.77 - Defoaming Agent 27.73 0.04 0.10 0.09 0.02 0.24 0.45 0.05 - 0.08 - 表 2 EVA 5010胶粉的基本性能
Table 2. Basic properties of EVA 5010 rubber powder
Performance Appearance Apparent density/
(g·L−1)Solid content/% Stabilized system Main particle size/μm Minimum film forming temperature/℃ Target White powder 540+50 99+1 Polyvinyl alcohol 0.5-0.8 4 表 3 EMR-PMPC复合材料配合比(wt%)
Table 3. EMR-PMPC composite mortar mix ratio (wt%)
No. M/P FA/M BX/M W/B S/B EMR/B EVA/B DA/B Water reducer/% EMR0
2
0.1
0.4
0.2
10
4
0.10.50 EMR1 1 0.80 EMR2 2 1.20 EMR3 3 1.26 EMR4 4 1.30 Notes: B=M+P+FA,binder; M-MgO; P-KH2PO4; FA-Fly ash; BX-Na2B4O7·10H2O, borax; S-sand; W-mixing water; In order to be able to make the numbering well presented in the figure, the specimen numbers are abbreviated as composite material (EMR-PMPC), i.e., EMR0 is the abbreviation of EMR0-PMPC, EMR1 is the abbreviation of EMR1-PMPC, EMR2 is the abbreviation of EMR2-PMPC, EMR3 is the abbreviation of EMR3-PMPC, EMR4 is the abbreviation of EMR4-PMPC. 表 4 EMR-PMPC试件不同龄期抗压抗折强度增长率(%)
Table 4. Growth rate of compressive and flexural strength of EMR-PMPC specimens at different ages (%)
No. Age Growth rate of compressive strength% Growth rate of flexural strength% 3 h 1 d 3 d 7 d 14 d 28 d 3 h 1 d 3 d 7 d 14 d 28 d EMR0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 EMR1 −0.097 −0.11 −0.17 −0.13 −0.2 −0.25 −0.03 −0.136 −0.144 −0.29 −0.054 −0.11 EMR2 −0.118 −0.15 −0.18 −0.23 −0.2 −0.25 −0.05 −0.106 −0.118 −0.16 −0.175 −0.17 EMR3 −0.158 −0.18 −0.22 −0.25 −0.3 −0.32 −0.10 −0.166 −0.184 −0.24 −0.219 −0.24 EMR4 −0.165 −0.20 −0.28 −0.27 −0.37 −0.36 −0.16 −0.23 −0.24 −0.27 −0.25 −0.31 表 5 不同EMR-PMPC试件7 d龄期T2谱特征峰面积比
Table 5. Characteristic peak area ratio of T2 spectrum of different EMR-PMPC specimens at 7 d age
No. Peak area First peak Second peak Third peak Fourth peak Fifth peak Peak area Proportion Peak area Proportion Peak area Proportion Peak area Proportion Peak area Proportion EMR0 2054.131 1006.616 49.004 639.529 31.134 271.979 13.241 134.077 6.527 1.93 0.094 EMR1 1275.019 407.78 31.982 769.561 60.357 94.764 7.432 2.914 0.229 - - EMR2 954.739 252.912 26.49 370.708 38.828 213.308 22.342 105.579 11.058 2.233 1.281 EMR3 1110.128 341.543 30.766 136.631 12.308 547.628 49.33 81.395 7.332 2.931 0.264 EMR4 875.831 240.718 27.485 152.935 17.462 426.216 48.664 52.779 6.026 3.183 0.363 -
[1] 王建苗, 高越青, 詹培敏, 等. 磷酸钾镁水泥修补材料研究综述[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2021, 40(11): 3533-3543.WANG Jianmiao, GAO Yueqing, ZHAN Peimin, et al. Review of research on potassium magnesium phosphate cement repair materials[J]. Silicate Bulletin, 2021, 40(11): 3533-3543(in Chinese). [2] 汤云杰, 单春明, 顾华健, 等. 矿物掺合料对自流平磷酸钾镁水泥砂浆性能的影响[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2021, 39(4): 666-672.TANG Yunjie, SHAN Chunming, GU Huajian, et al. Effect of mineral admixtures on properties of self-leveling potassium magnesium phosphate cement mortar[J]. Material Science and Engineering, 2021, 39(4): 666-672(in Chinese). [3] 赵思勰, 晏华, 李云涛. 磷酸镁水泥水化热研究进展[J]. 材料保护, 2016, 49(S1): 148-152.ZHAO Sixie, YAN Hua, LI Yuntao. Research progress on hydration heat of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Material protection, 2016, 49(S1): 148-152(in Chinese). [4] 陶涛, 杨建明, 李涛, 等. 偏高岭土和粉煤灰对大流动性磷酸钾镁水泥抗盐冻性能的影响[J]. 混凝土, 2021, (4): 87-90+95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2021.04.021TAO Tao, YANG Jianming, LI Tao, et al. Effect of metakaolin and fly ash on salt-frost resistance of high fluidity potassium magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Concrete, 2021, (4): 87-90+95(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2021.04.021 [5] 缪汉良, 赵斌, 纪荣健, 等. 早龄期磷酸钾镁水泥砂浆的抗冻性评价[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2021, 40(4): 1128-1136.MIAO Hanliang, ZHAO Bin, JI Rongjian, et al. Evaluation of frost resistance of early age potassium magnesium phosphate cement mortar[J]. Silicate Bulletin, 2021, 40(4): 1128-1136(in Chinese). [6] 杨辉, 袁伟, 严思阳, 等. 超细掺合料改性高强磷酸镁水泥砂浆的性能研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2023, 50(3): 60-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2023.03.014YANG Hui, YUAN Wei, YAN Siyang, et al. Study on the properties of high strength magnesium phosphate cement mortar modified by ultrafine admixture[J]. New building materials, 2023, 50(3): 60-63(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2023.03.014 [7] 刘佳辉, 周新涛, 罗中秋. 镍铁渣基磷酸镁水泥的制备及其机理研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(2): 255-262.LIU Jiahui, ZHOU Xintao, LUO Zhongqiu. Preparation and mechanism of ferronickel slag-based magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(2): 255-262(in Chinese). [8] 赵思勰, 晏华, 汪宏涛等. 粉煤灰掺量对磷酸钾镁水泥水化动力学的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 2017, 31(11): 839-846. doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2017.274ZHAO Sixie, YAN Hua, WANG Hongtao and so on. Effect of fly ash content on hydration kinetics of magnesium potassium phosphate cement[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 31(11): 839-846(in Chinese). doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2017.274 [9] 何盛, 何兆益, 唐亮, 等. 磷酸镁水泥固化电解锰渣特性及机理研究[J]. 应用化工, 2023, 52(7): 2025-2029, 2035.HE Sheng, HE Zhaoyi, TANG Liang, et al. Study on the Characteristics and Mechanism of Magnesium Phosphate Cement Solidification of electrolytic manganese reside[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2023, 52(7): 2025-20292035. (in Chinese) [10] 沈君, 程寅, 于浩, 等. 固化/稳定化电解锰渣浸出毒性及强度特性试验研究[J]. 交通运输研究, 2023, 9(2): 63-71.SHEN Jun, CHENG Yin, YU Hao, et al. Experimental study on the leaching toxicity and strength characteristics of solidified/stabilized electrolytic manganese reside[J]. Transportation Research, 2023, 9(2): 63-71(in Chinese). [11] GB 50119-2013, 混凝土外加剂应用技术规范[S].GB 50119-2013, Technical Specification for Application of Concrete Admixtures[S]. (in Chinese) [12] JGJ/T 70-2009, 建筑砂浆基本性能试验方法标准[S].JGJ/T 70-2009, Standard for Test Methods of Basic Properties of Building Mortar[S]. (in Chinese) [13] 林玮, 孙伟, 李宗津. 磷酸镁水泥中的粉煤灰效应研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2010, 13(6): 716-721. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2010.06.003LIN Wei, SUN Wei, LI Zongjin. Study on fly ash effect in magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2010, 13(6): 716-721(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2010.06.003 [14] 王智, 高翠翠, 王庆珍. 电解锰渣复合胶凝材料的研制[J]. 非金属矿, 2013, 36(2): 51-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2013.02.015WANG Zhi, GAO Cuicui, WANG Qingzhen. Development of electrolytic manganese reside composite cementitious material[J]. Non metallic Mineral, 2013, 36(2): 51-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2013.02.015 [15] 曾辕, 谢芳圆, 龚奡, 等. 粉煤灰掺量对砂浆干缩性能影响的试验研究[J]. 城市建筑, 2022, 19(11): 129-132.ZENG yuan, XIE Fangyuan, GONG Xian, et al. Experimental study on the effect of fly ash content on dry shrinkage performance of mortar[J]. Urban Building, 2022, 19(11): 129-132(in Chinese). [16] SONG K W, CHEN G F, ZHANG H, SHI C L, YANG J. Mechanism Research of Drying Shrinkage of Cement Pastes Based on the Contact Angle[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 3558(670-671): 391-395. [17] 李刊, 魏智强, 乔宏霞, 等. 纳米SiO2改性聚合物水泥基复合材料早期微观结构及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(9): 2272-2284.LI Kan, WEI Zhiqiang, QIAO Hongxia, et al. Early microstructure and properties of nano-SiO2 modified polymer cement-based composites[J]. Journal of Composites, 2020, 37(9): 2272-2284(in Chinese). [18] 汤云杰. 磷酸钾镁水泥的早期水化特征及流变性能[D]. 安徽理工大学, 2021.TANG Yunjie. Early hydration characteristics and rheological properties of potassium magnesium phosphate cement[D]. Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2021. (in Chinese) [19] 韦宇, 周新涛, 黄静, 等. 缓凝剂对磷酸镁水泥性能及其水化机制影响研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(4): 77-83.WEI Yu, ZHOU Xintao, HUANG Jing, et al. Research progress on the effect of retarders on the properties and hydration mechanism of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Materials Report, 2022, 36(4): 77-83(in Chinese). [20] 马越, 周新涛, 黄静, 罗中秋, 符义忠, 母维宏, 王路星, 邵周军. 矿物掺合料对磷酸钾镁水泥性能影响及机理研究现状[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(6): 629-638. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220157MA Yue, ZHOU Xintao, HUANG Jing, LUO Zhongqiu, FU Yizhong, MU Weihong, Wang Luxing, Shao Zhoujun. Effect of mineral admixtures on properties of potassium magnesium phosphate cement and its mechanism[J]. Process Engineering Journal, 2021, 21(6): 629-638(in Chinese). doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220157 [21] 孙赫男, 关岩, 毕万利, 等. 烧结氧化镁粉的晶体特征对磷酸钾镁水泥力学性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2022, (19): 1-14.SUN Henan, GUAN Yan, BI Wanli, et al. Effect of Crystalline Characteristics of Sintered Magnesium Oxide Powder on Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Potassium Phosphate Cement[J]. Materials Guide, 2022, (19): 1-14(in Chinese). [22] 朱金才, 曹琪, 孟晓凯, 等. 矿物掺合料改性磷酸镁水泥力学和耐久性能研究进展[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2023, (1): 95-98. doi: 10.19761/j.1000-4637.2023.01.095.04ZHU Jincai, CAO Qi, MENG Xiaokai et al. Research progress on mechanical and durability properties of magnesium phosphate cement modified with mineral admixtures[J]. Concrete and Cement Products, 2023, (1): 95-98. doi: 10.19761/j.1000-4637.2023.01.095.04 [23] 李茂, 岳燕飞, 钱觉时, 等. 钢纤维增强磷酸镁水泥混凝土力学性能研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2022, 55(7): 691-698.LI Mao, YUE Yanfei, QIAN Jueshi, et al. Study on Mechanical Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Magnesium Phosphate Cement Concrete[J]. Journal of Wuhan University(Engineering Edition), 2022, 55(7): 691-698(in Chinese). [24] HUANG G P, WANG H, SHI F T. Coupling Effect of Salt Freeze-Thaw Cycles and Carbonation on the Mechanical Performance of Quick Hardening Sulphoaluminate Cement-Based Reactive Powder Concrete with Basalt Fibers[J]. Coatings, 2021, 11(9): 1142-1142. doi: 10.3390/coatings11091142 [25] 雒云龙, 母维宏, 周新涛等. 磷酸镁水泥固化/稳定化重金属性能及作用机理研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(12): 3875-3886. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072201LUO Yunlong, MU Weihong, ZHOU Xintao et al. Research progress on the properties and mechanism of heavy metals during solidification/stabilization of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(12): 3875-3886(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072201 [26] 何盛, 何兆益, 唐亮, 等. 磷酸镁水泥固化电解锰渣特性及机理研究[J]. 应用化工, 2023, 52(7): 2025-2029, 2035.HE Sheng, HE Zhaoyi, TANG Liang, et al. Study on the Characteristics and Mechanism of Magnesium Phosphate Cement Solidification of electrolytic manganese reside[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2023, 52(7): 2025-20292035. (in Chinese) [27] 高明, 刘宁, 陈兵. 硅灰改性磷酸镁水泥砂浆试验研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(1): 29-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.01.005GAO Ming, LIU Ning, CHEN Bing. Experimental study on micro silicon powder modified magnesium phosphate cement mortar[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(1): 29-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.01.005 [28] 秦继辉, 钱觉时, 宋庆, 等. 磷酸镁水泥的研究进展与应用[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2022, 50(6): 1592-1606.QIN Jihui, QIAN Jueshi, SONG Qing, et al. Research Progress and Application of Magnesium Phosphate Cement[J]. Acta Silicate Sinica, 2022, 50(6): 1592-1606(in Chinese). [29] 任强, 蒋正武, 马敬畏. 矿物掺和料对磷酸镁水泥基修补砂浆强度的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2016, 19(6): 1062-1067. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2016.06.019REN Qiang, JIANG Zhengwu, MA Jingwei. Effect of mineral admixtures on the strength of magnesium phosphate cement-based repair mortar[J]. Building Materials, 2016, 19(6): 1062-1067(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2016.06.019 [30] 丁涛, 刘铁, 蒋俊, 等. 磷酸镁水泥基多孔材料孔结构及性能研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2022, 44(8): 7-13. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2022.08.002DING Tao, LIU Tie, JIANG Jun, et al. Study on pore structure and properties of magnesium phosphate cement-based porous materials[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2022, 44(8): 7-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2022.08.002 [31] 叶飞. 磷酸钾镁水泥基材的性能优化及其固化能力研究[D]. 西南科技大学, 2023.YE Fei. Study on the Performance Optimization and Solidification Ability of Potassium Magnesium Phosphate Cement Substrate[D]. Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2023. (in Chinese) [32] 戴丰乐, 汪宏涛, 张时豪等. 固化模拟放射性核素Sr对磷酸镁水泥水化特性的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2017, 45(5): 651-656.DAI Fengle, WANG Hongtao, ZANG Shihao, et al. The effect of solidified simulated radioactive nuclide Sr on the hydration characteristics of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Journal of Portland, 2017, 45(5): 651-656(in Chinese). [33] 翟念, 刘方, 朱健等. 不同煅烧温度下白云岩砂性状变化及对电解锰渣中Mn2+的稳定效果[J]. 应用化工, 2023, 52(2): 451-455+463.ZHAI Nian, LIU Fang, ZHU Jian, et al. Changes in the properties of dolomite sand under different calcination temperatures and its stabilizing effect on Mn2+ in electrolytic manganese reside[J]. Applied Chemistry, 2023, 52(2): 451-455+463(in Chinese). [34] Liang T, Zhaoyi H, Kefan C, et al. Study of microscopic properties and heavy metal solidification mechanism of electrolytic manganese residue-based cementitious materials[J]. Environmental science and pollution research international, 2023, 30(48): 105056-105071. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-29772-3 [35] Guosheng Z, Qiang W, Yue L, et al. Microstructure and micromechanical properties of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2023, 172: 107227. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2023.107227 [36] 徐选臣, 杨建明, 谷明轩等. 海水浸泡养护对磷酸钾镁水泥浆体微观结构和性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2017, 20(5): 673-679. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.05.003XU Xuanchen, YANG Jianming, GU Mingxuan, et al. The effect of seawater immersion curing on the microstructure and properties of potassium magnesium phosphate cement slurry[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2017, 20(5): 673-679(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.05.003 [37] 范旭涵, 王炳楠, 汤世豪等. 磷酸镁水泥加固低液限粉土的pH和电导率响应与孔隙特征研究[J/OL]. 材料导报: 1-18[2023-11-07]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1078.tb.20230825.1535.009.html.FAN Xuhan, WANG Bingnan, TANG Shihao, et al. Study on pH and conductivity response and pore characteristics of low liquid limit silt reinforced with magnesium phosphate cement[J/OL]. Material Introduction: 1-18 [2023-11-07] http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1078.tb.20230825.1535.009.html. (in Chinese) [38] Xiaosa Y, Mingjiang D, Yingjie G, et al. Pore morphology based on graphene oxide modified steel fibre concrete for freeze–thaw resistance[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 409. [39] Hu F, Junhao L, Aofei G, et al. Development and design of ultra-high ductile magnesium phosphate cement-based composite using fly ash and silica fume[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2023, 137. [40] APUA M. NKAZI B C, DIAKANUA. Leaching of coal fly ash with sulphuric acid for synthesis of wastewater treatment composite coagulant[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2022, 61(3): 309-331. doi: 10.1080/00084433.2022.2044689 [41] GHERNOUTI Y, RABEHI B, MANSOUR S M. Mechanical Performance of Steam-Cured Self-Compacting Concrete Incorporating Silica Fume and Limestone Powder[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research in Africa, 2021, 64(2): 111-122. [42] 侯世伟, 张皓, 杨镇吉, 等. 磷酸钾镁水泥固化铜污染土的冻融稳定性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(S1): 3123-3129.HOU Shiwei, ZHANG Hao, YANG Zhenji, et al. Study on freeze-thaw stability of copper contaminated soil solidified by potassium magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Rock mechanics and engineering, 2020, 39(S1): 3123-3129(in Chinese). -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 45
- HTML全文浏览量: 25
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: