High sensitivity flexible piezoresistive sensor of PDMS porous elastomer decorated by MXene-PEDOT:PSS
-
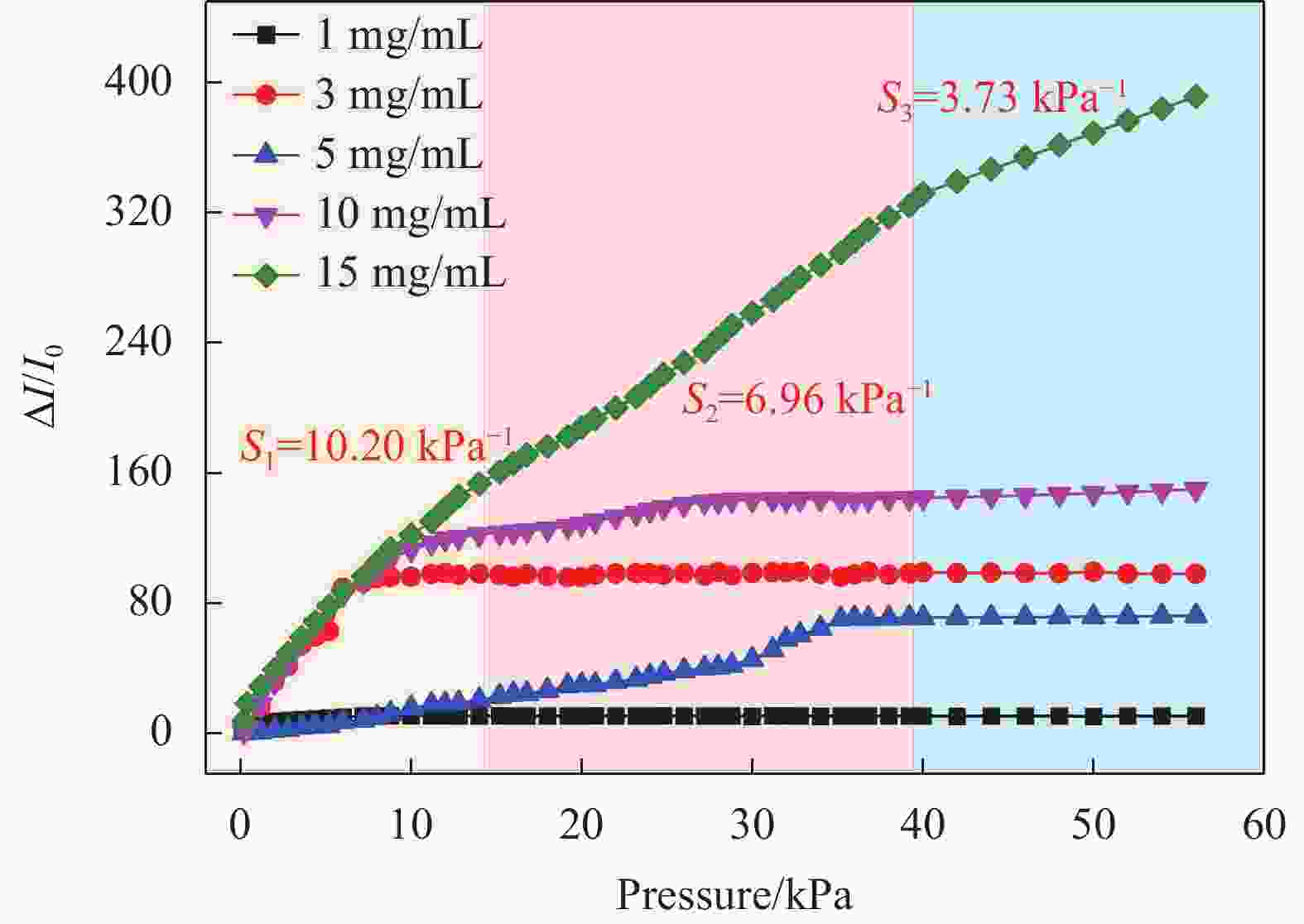
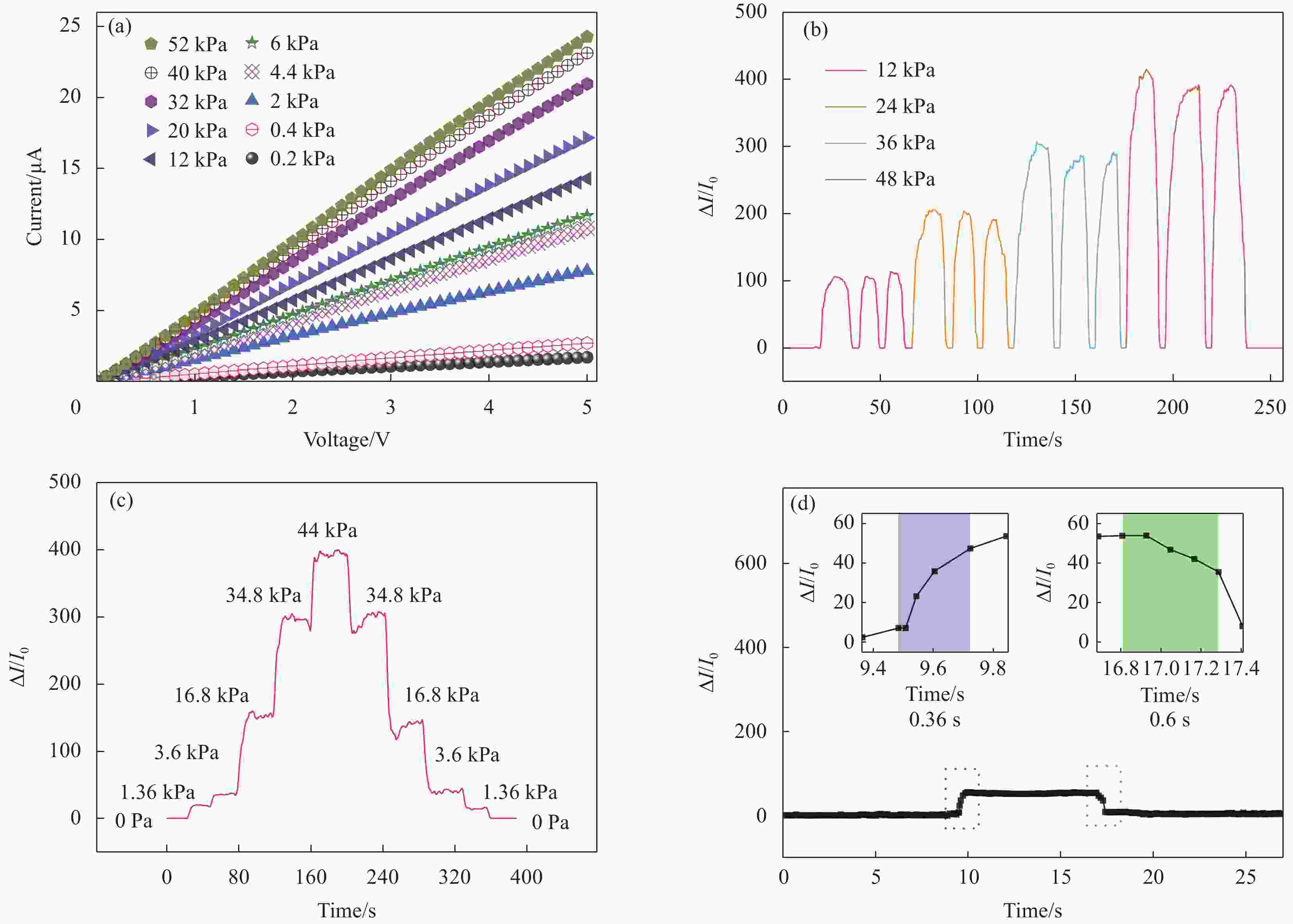
摘要: 柔性压阻传感器在可穿戴式设备、电子皮肤、人机交互等领域有着极大的应用需求。常见的柔性压阻传感器导电敏感介质存在成本高、制备工艺复杂的问题,限制了其实用化进程和批量化生产。本文以明胶为牺牲剂制备了具有多孔结构的聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)弹性体,再采用浸渍法获得了聚(3,4-亚乙基二氧噻吩):聚(苯乙烯磺酸盐)(PEDOT:PSS)和MXene复合修饰的PDMS柔性压阻传感器。实验表明,当PEDOT:PSS和MXene复合浓度分别为15 mg/mL和10 mg/mL时,传感器灵敏度获得最大值,在12~40 kPa压力范围内,灵敏度达29.1 kPa−1。经测试,所制备的传感器响应时间为0.36 s,回复时间为0.6 s。该传感器可以检测人体关节(手指、肘部、膝盖)运动,表明开发的压力传感器在智能衣物、柔性可穿戴电子设备及人机交互领域具有良好的应用前景。Abstract: Flexible piezoresistive sensors have great application demands in wearable devices, electronic skins, man-computer interaction, and other fields. The common conductive sensitive media of flexible piezoresistive sensors suffer from high cost and complex preparation processes, which limit their practical application and mass production. A porous polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer was prepared using gelatin as a sacrificial agent, and a MXene- Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS)/PDMS composite piezoresistive sensor was obtained by impregnation method. Experimental results demonstrated that when the composite concentrations of PEDOT:PSS and MXene are 15 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL, respectively, the sensor has the highest sensitivity, reaching up to 29.1 kPa−1 under the force range of 12-40 kPa. The response and recovery time of the piezoresistive sensor are 0.36 s and 0.6 s, respectively. After verification, the sensor can detect the movement of human joints (finger, elbow and knee), indicating that the developed piezoresistive sensor exhibits good application prospects in the fields of smart clothing, flexible wearable electronic devices, and human-computer interaction.
-
图 1 负载不同浓度PEDOT:PSS的PEDOT:PSS/PDMS弹性体SEM图. (a) 0 mg/mL; (b) 1 mg/mL; (c) 3 mg/mL; (d) 5 mg/mL; (e) 10 mg/mL;(f) 15 mg/mL
Figure 1. SEM images of PEDOT:PSS/PDMS porous elastomer after loading different concentrations of PEDOT:PSS (a) 0 mg/mL; (b) 1 mg/mL;(c) 3 mg/mL; (d) 5 mg/mL; (e) 10 mg/mL; (f) 15 mg/mL.
PDMS—polydimethylsiloxane; PEDOT:PSS—Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (styrene sulfonate)
图 2 负载不同浓度MXene的MXene-PEDOT:PSS/PDMS弹性体SEM图. (a) 0 mg/mL; (b) 1 mg/mL; (c) 3 mg/mL; (d) 5 mg/mL; (e) 10 mg/mL; (f) 15 mg/mL
Figure 2. SEM images of MXene-PEDOT:PSS/PDMS porous elastomer after loading different concentrations of MXene. (a) 0 mg/mL; (b) 1 mg/mL; (c) 3 mg/mL; (d) 5 mg/mL; (e) 10 mg/mL; (f) 15 mg/mL.
表 1 柔性压阻式压力传感器性能比较
Table 1. Performance comparison of flexible piezoresistive sensor
Materials Detection range/kPa Sensitivity/kPa−1 Response/recovery time/ms Reference PDMS@MWCNTs/PP 2-7 16.6 74/64 [18] MXene@PDMS 0-40 1.96 40/40 [19] CNT/PDMS 0-9.2 5.1 54/65 [20] MXene/NWF 15-150 6.31 300/260 [21] PANI/BC/CH 0-0.3 1.41 >1000 [22] MXene-PEDOT:PSS/PDMS 0-12 14.4 360/600 This work Notes: PP-Polypropylene; MWCNT-Multiwall carbon nanotube; NWF-nonwoven fabric; PANI/BC/CH-Polyaniline/bacterial cellulose/chitosan. -
[1] SHI L, LI Z, CHEN M, et al. Ultrasensitive and ultraprecise pressure sensors for soft systems[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(10): 2210091. doi: 10.1002/adma.202210091 [2] QU X Y, LI J, HAN Z L, et al. Highly sensitive fiber pressure sensors over a wide pressure range enabled by resistive-capacitive hybrid response[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(15): 14904-14915. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03484 [3] LIU H, LI Y L, DAI K, et al. Electrically conductive thermoplastic elastomer nanocomposites at ultralow graphene loading levels for strain sensor applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(1): 157-166. doi: 10.1039/C5TC02751A [4] HUANG J R, YANG X X, LIU J T, et al. Vibration monitoring based on flexible multi-walled carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane film sensor and the application on motion signal acquisition[J]. Nanotechnology, 2020, 31(33): 335504. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab8edd [5] ARAROMI O A, GRAULE M A, DORSEY K L, et al. Ultra-sensitive and resilient compliant strain gauges for soft machines[J]. Nature, 2020, 587: 219-224. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2892-6 [6] ZHANG X Y, HU Y G, GU H, et al. A highly sensitive and cost-effective flexible pressure sensor with micropillar arrays fabricated by novel metal-assisted chemical etching for wearable electronics[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(9): 1900367. doi: 10.1002/admt.201900367 [7] CHEN S, SONG Y J, XU F. Flexible and highly sensitive resistive pressure sensor based on carbonized crepe paper with corrugated structure[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(40): 34646-34654. [8] ZHAO S F, RAN W H, WANG D P, et al. 3D dielectric layer enabled highly sensitive capacitive pressure sensors for wearable electronics[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(28): 32023-32030. [9] CHEN M R, LUO W F, XU Z Q, et al. An ultrahigh resolution pressure sensor based on percolative metal nanoparticle arrays[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4024. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12030-x [10] YANG N, YIN X Y, LIU H L, et al. Dual-layer all-textile flexible pressure sensor coupled by silver nanowires with Ti3C2-Mxene for monitoring athletic motion during sports and transmitting information[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(36): 42992-43002. [11] HAMEDI M M, CAMPBELL V E, ROTHEMUND P, et al. Electrically activated paper actuators[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(15): 2446-2453. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201505123 [12] JIA P T, ARGUN A A, XU J W, et al. High-contrast electrochromic thin films via layer-by-layer assembly of starlike and sulfonated polyaniline[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(22): 6085-6091. doi: 10.1021/cm101683c [13] ZHENG X H, ZHANG S L, ZHOU M J, et al. MXene functionalized, highly breathable and sensitive pressure sensors with multi-layered porous structure[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(19): 2214880. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202214880 [14] LIU Z R , ZHANG Y L, SONG Y X, et al. A wearable 3D pressure sensor based on electrostatic self-assembly MXene/chitosan sponge and insulating PVP spacer[J]. Nanotechnology, 2023, 34(45): 455502. [15] CHEN Y, LIU H S, YU L, et al. Superhydrophobic modification on starch film using PDMS and ball-milled MMT coating[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 8(28): 10423-10430. [16] ZHENG D Y, JIN H H, LIAO Y C, et al. Bi2Te3 nanowires tuning PEDOT: PSS structure for significant enhancing electrical transport property[J]. Materials Letters, 2023, 338: 134019. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2023.134019 [17] LU Z, WEI Y Y, DENG J J, et al. Correction to “self-crosslinked MXene (Ti3C2Tx) membranes with good antiswelling property for monovalent metal ion exclusion”[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 13(9): 10535-10544. [18] LI H B, LUO R B, HU J B, et al. Self-assembled gel-assisted preparation of high-performance hydrophobic PDMS@MWCNTs/PEDOT: PSS composite aerogels for wearable piezoresistive sensors[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 182: 22-32. [19] CHEN B D, ZHANG L, LI H Q, et al. Skin-inspired flexible and high-performance MXene@polydimethylsiloxane piezoresistive pressure sensor for human motion detection[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 617: 478-488. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.03.013 [20] HE Y X, LU X S, WU D Y, et al. CNT/PDMS conductive foam-based piezoresistive sensors with low detection limits, excellent durability, and multifunctional sensing capability[J]. Sensors and Actuators: A. Physical, 2023, 358: 114408. [21] YU Q H, SU C L, BI S Y, et al. Ti3C2Tx@nonwoven fabric composite: Promising MXene-coated fabric for wearable piezoresistive pressure sensors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(7): 9632-9643. [22] HUANG J Y, LI D E, ZHAO M, et al. Flexible electrically conductive biomass-based aerogels for piezoresistive pressure/strain sensors[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 373: 1357-1366. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.136 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 112
- HTML全文浏览量: 74
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: