Numerical research on magnetostrictive deformation of hard magnetic soft materials
-
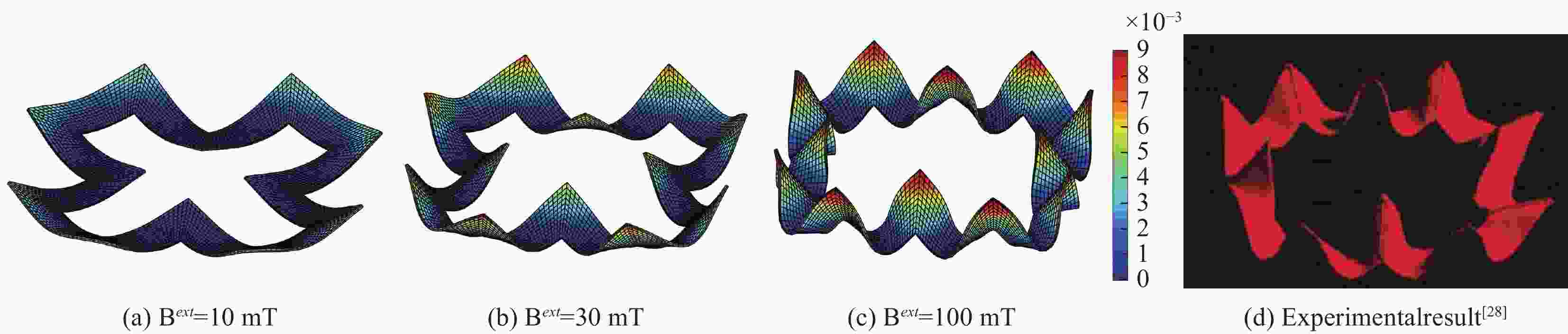
摘要: 光滑有限元基于光滑应变技术,在进行数值积分时避免使用等参变换,在模拟软材料大变形问题具有一定的优势。建立了基于光滑应变技术的硬磁软材料大变形模拟的数值格式,给出了数值格式中所需要的应力张量和本构张量。采用该数值格式研究了不同长高比下的硬磁软材料梁在外部磁场激励下的弯曲特性, 得到的磁载荷-位移曲线和试验结果进行了对比;模拟了含有不同残余磁场方向分布的硬磁软材料结构在外磁场作用下的形态演化过程,计算的最终变形形态与试验结果进行比较。计算结果表明:采用该数值格式得到的结果与试验结果吻合较好;在不受约束的前提下,硬磁软材料内部残余磁场方向突变处变形较大。研究结果可为由硬磁软材料组成的软体机器人和智能柔性结构的力学分析与变形调控设计提供参考。Abstract: Smoothed finite element method is based on strain-smoothed technology; it avoids using the isoparametric transformations during numerical integration, and has certain advantages in simulating large deformation problems of soft materials. A numerical format for simulating large deformation of hard magnetic soft materials based on strain-smoothed technology has been established, and the necessary stress tensors and constitutive tensors have been provided. The bending characteristics of hard magnetic soft material beams with different aspect ratios under external magnetic field were studied, and the magnetic load displacement curves obtained were compared with experimental results; evolution process of the morphological of hard magnetic soft material structures with different directions of residual magnetic field under the action of an external magnetic field was simulated, and the calculated final deformation morphology was compared with experimental results. The numerical results indicate that the results obtained by using this numerical format are in good agreement with the experimental results; there is significant deformation at the sudden change in the direction of the residual magnetic field inside hard magnetic soft materials. The research results can provide reference for the mechanical analysis and deformation control design of soft robots and intelligent flexible structures composed of hard magnetic soft materials.
-
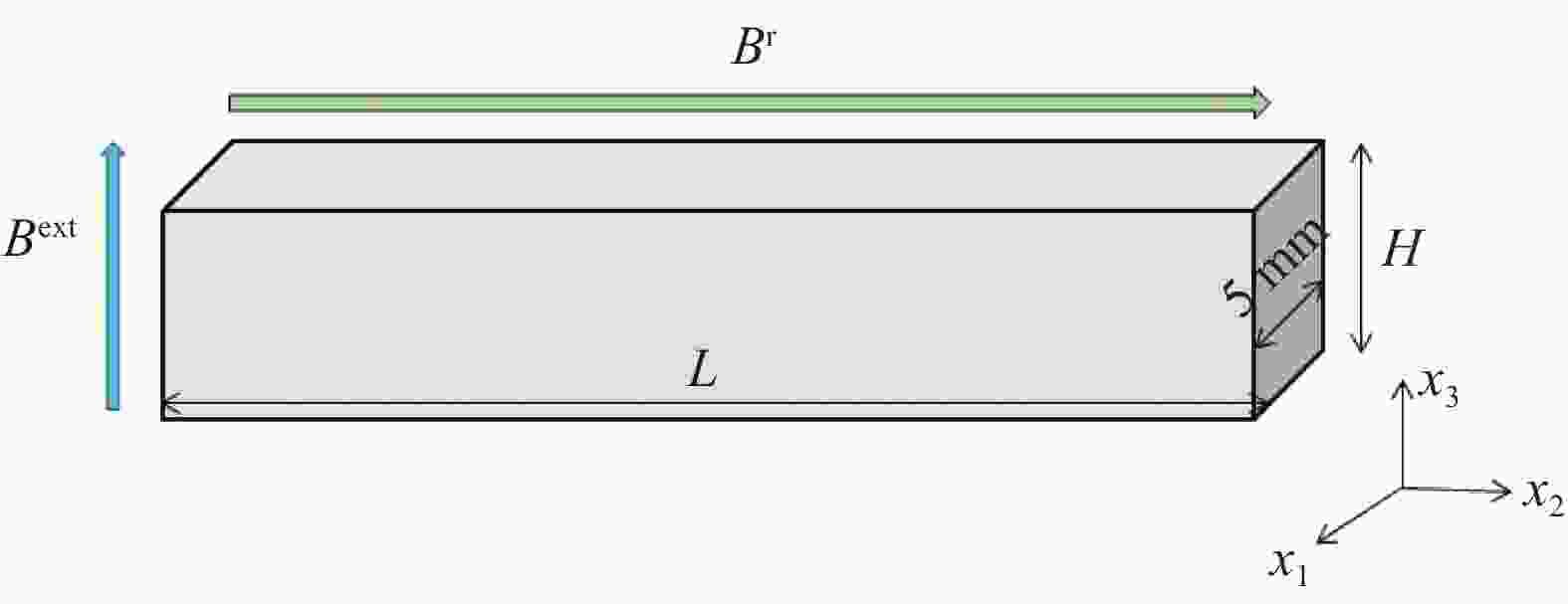
图 2 硬磁软材料梁的几何尺寸、外磁场和残余磁场方向
Figure 2. Geometric size, direction of external magnetic field, and residual magnetic field of hard magnetic soft material beams
$ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{{\text{ext}}}} $and$ {{\boldsymbol{\tilde B}}^{\text{r}}} $denote external magnetic field and residual magnetic field respectively
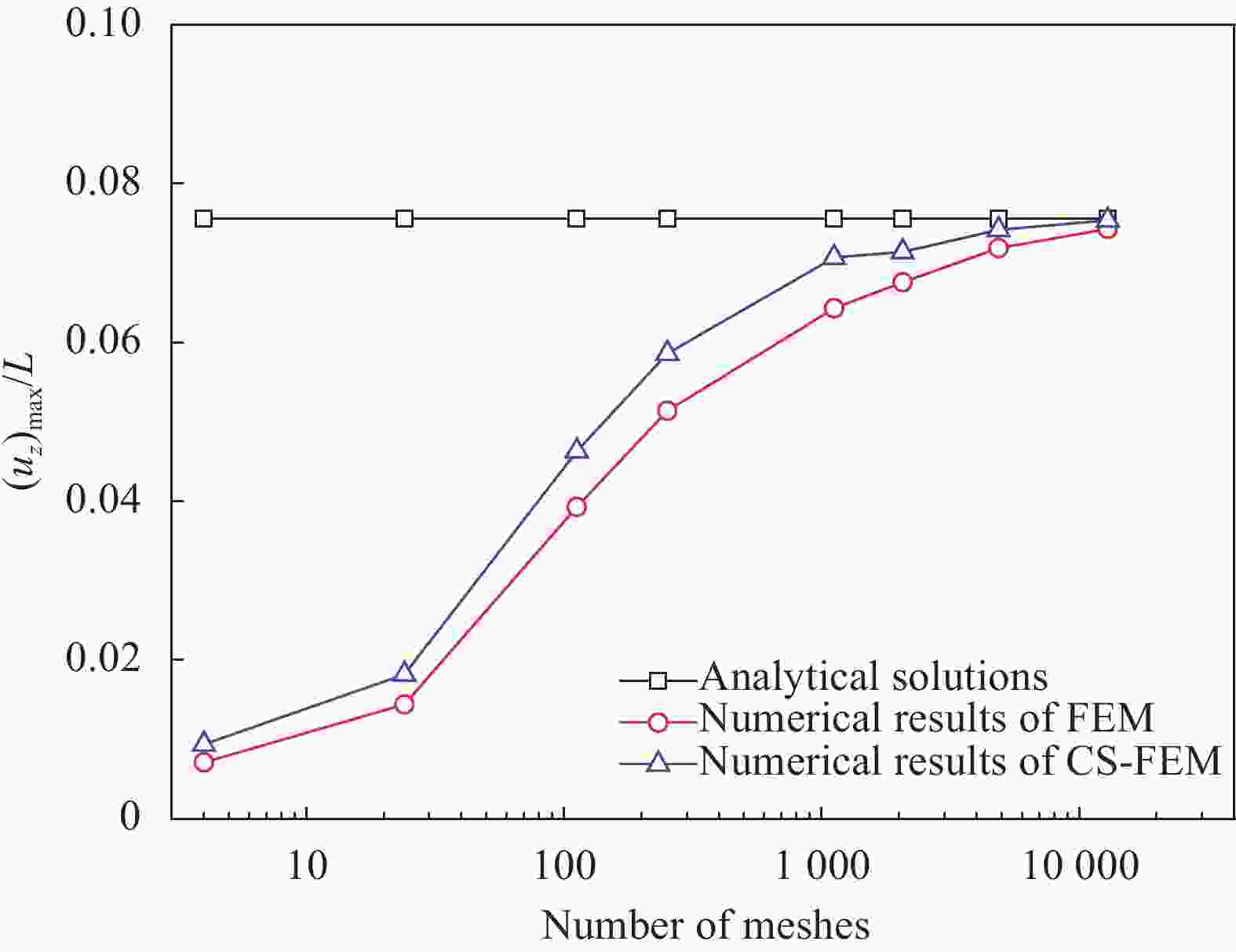
图 6 两种硬磁软材料梁的磁载荷-位移曲线
Figure 6. Magnetic loading-displacement curves of two kinds of hard magnetic soft material beams
(uz)max/L stands for the ratio of deflection-to-span; $ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{{\text{ext}}}} $ and $ {{\boldsymbol{\tilde B}}^{\text{r}}} $ denote external magnetic field and residual magnetic field respectively; $ \mu $is the shear modulus; $ {\mu _0} $ is permeability
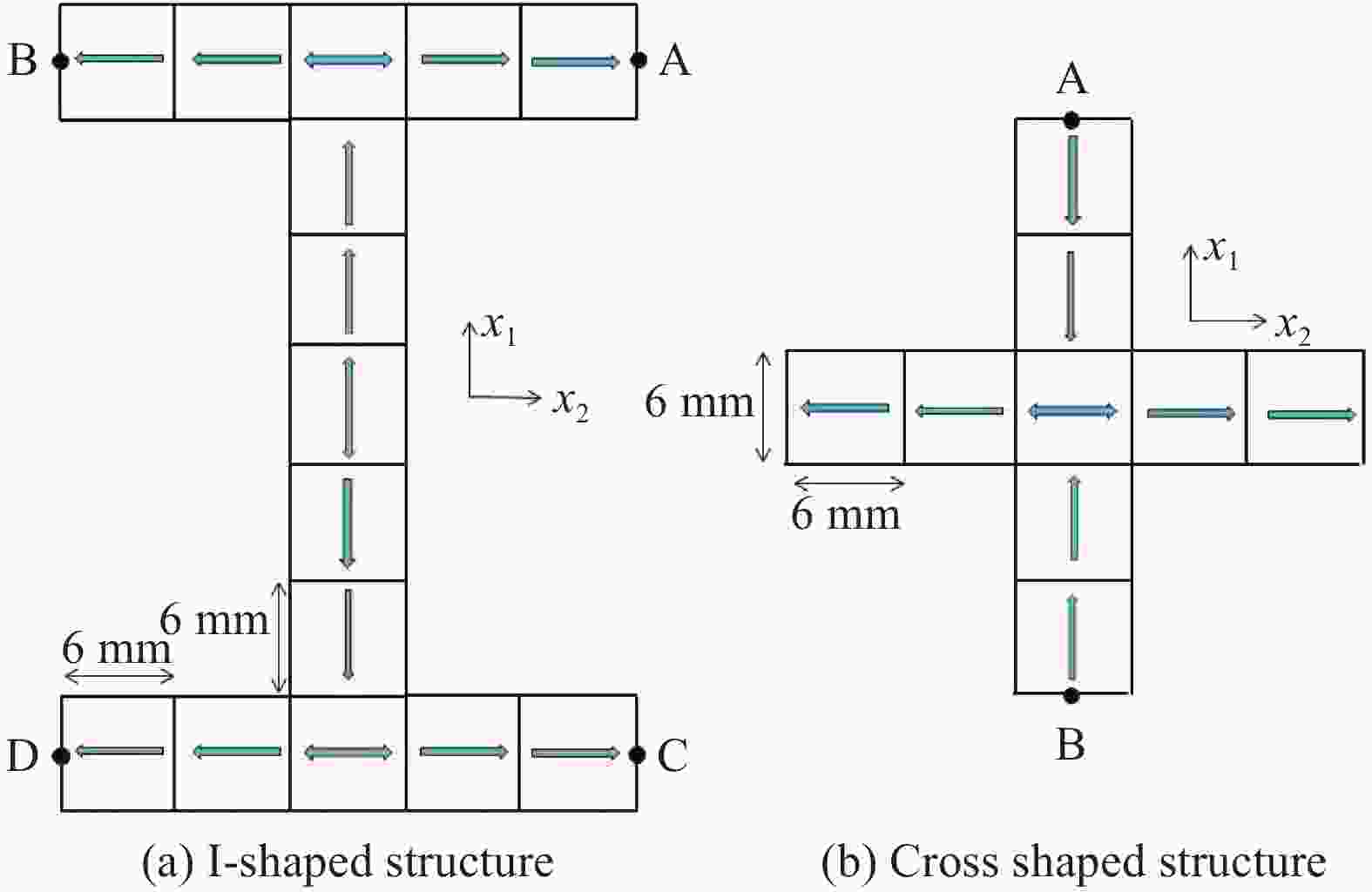
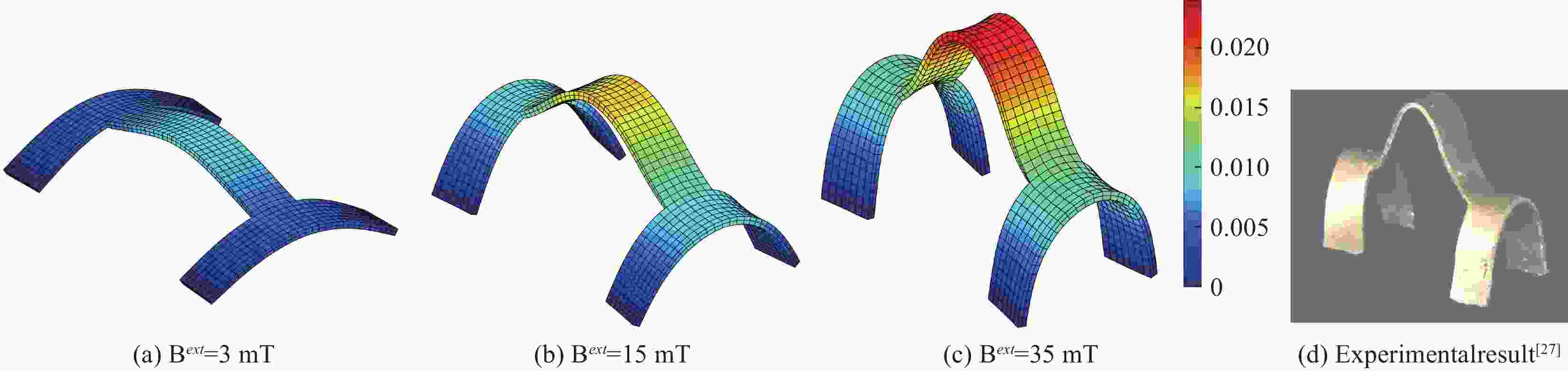
图 8 H形结构在不同外磁通量下的变形响应和最终试验结果[27]
Figure 8. Deformation response of H-shaped structure under different external magnetic fluxes and final experimental result[27]
(a) $ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{ext}} $=3 mT (b) $ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{ext}} $=15 mT (c) $ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{ext}} $=35 mT (d) Experimental result [27]
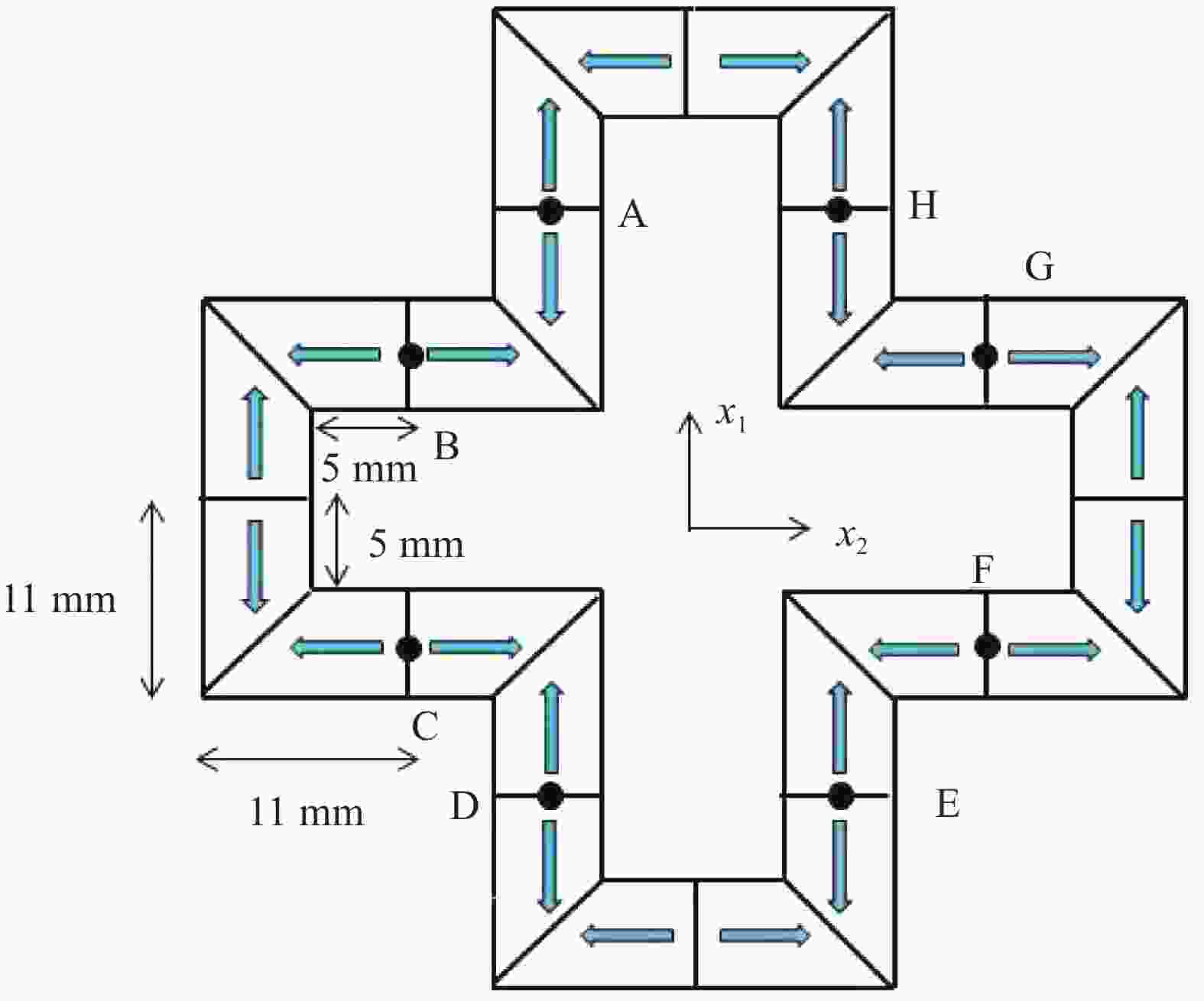
图 9 十字形结构在不同外磁通量下的变形响应和最终试验结果[27]
Figure 9. Deformation response of cross shaped structure under different external magnetic fluxes and final experimental result[27]
(a) $ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{ext}} $=5 mT (b) $ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{ext}} $=15 mT (c) $ {{\boldsymbol{B}}^{ext}} $=40 mT (d) Experimental result [27]
-
[1] DADGAR-RAD F, HOSSAIN M. Finite deformation analysis of hard-magnetic soft materials based on micropolar continuum theory[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 251: 111747. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2022.111747 [2] LUCARINI S, HOSSAIN M, GONZALEZ D, et al. Recent advances in hard-magnetic soft composites: Synthesis, characterization, computational modeling, and applications[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 279: 114800. [3] WEN H, SUN Y, LIU R et al. Reprogrammable magnetization pattern and shape morphing of phase-change magnetic soft composites[J]. Composites Communications, 2023, 40: 101618. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2023.101618 [4] 李茂源, 杨易凡, 程柘, 等. 硬磁软曲梁大变形力学模型[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67: 4080-4091LI M Y, YANG Y F, CHENG Z, et al. A model of hard-magnetic soft curved beams at large deformation[J]. Chinese Science Bullet, 2022, 67: 4080-4091(in Chinese). [5] PARK S J, GAZZOLA M, PARK K S, et al. Phototactic guidance of a tissue-engineered soft-robotic ray[J]. Science, 2016, 353: 158-162. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf4292 [6] GARCIA-GONZALEZ D, TER-YESAYANTS T, MORENO-MATEOS M. Hard-magnetic phenomena enable autonomous self-healing elastomers[J]. Composites Part B, 2023, 248: 110357. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110357 [7] 圣宇, 欧兴成, 黄嘉琪, 等. 3D打印磁控柔性抓手[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(5): 2670-2679.SHENG Yu, OU Xingcheng, HUANG Jiaqi, et al. 3D printing magnetic soft gripper[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(5): 2670-2679 (in Chinese). [8] ZHANG S, BELLINGER A M, GLETTIG D L, et al. A pH-responsive supramolecular polymer gel as an enteric elastomer for use in gastric devices[J]. Nature Materials, 2015, 14: 1065-1071. doi: 10.1038/nmat4355 [9] KIM C C, LEE H H, OH K H, et al. Highly stretchable, transparent ionic touch panel[J]. Science, 2016, 353: 682-687. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf8810 [10] XIA L, HU Z, SUN L, et al. Multiscale numerical modeling of magneto-hyperelasticity of magnetorheological elastomeric composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2022, 224(33): 109443. [11] YANG Y, LI M, XU F. A 3D hard-magnetic rod model based on co-rotational formulations[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2022, 38: 222085. doi: 10.1007/s10409-022-22085-x [12] LIU J T, YANG Y F, LI M Y, et al. A meshfree model of hard-magnetic soft materials[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2023, 258(15): 108566. [13] 刘俊廷, 杨易凡, 李茂源, 等. 硬磁软材料的三维无网格模型[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2023.LIU J T, YANG Y F, LI M Y, et al. A 3D meshfree model of hard-magnetic soft materials. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2023. [14] CHEN W, WANG L, YAN Z, et al. Three-dimensional large-deformation model of hard-magnetic soft beams[J]. Composite Structure, 2021, 266: 113822. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113822 [15] ZHAO R, KIM, Y, CHESTER A S, et al. Mechanics of hard-magnetic soft materials[J]. Journal of the mechanics and physics of solids, 2019, 124: 244-263. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2018.10.008 [16] WANG L, KIM Y, GUO G F, et al. Hard-magnetic elastica[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2020, 142: 10404. [17] NARAYANAN P, PRAMANIK R, AROCKIARAJAN A. Micromechanics-based constitutive modeling of hard-magnetic soft materials[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2023, 184: 104722. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2023.104722 [18] ZENG W, LIU G R. Smoothed Finite Element Methods (S-FEM): An Overview and Recent Developments[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2018, 25(2): 397-435. doi: 10.1007/s11831-016-9202-3 [19] LIU G, NGUYEN T, DAI K, et al. Theoretical aspects of the smoothed finite element method (SFEM)[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2007, 71(8): 902-930. doi: 10.1002/nme.1968 [20] LIU G R, DAI K, NGUYEN-THOI T. A smoothed finite element method for mechanics problems[J]. Computational Mechanic, 2007, 39: 859-877. doi: 10.1007/s00466-006-0075-4 [21] NGUYEN-THOI T, LIU G, DAI K, et al. Selective smoothed finite element method[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2007, 12(5): 497-508. doi: 10.1016/S1007-0214(07)70125-6 [22] NGUYEN-THOI T, PHUNG-VANP, RABCZUK T, et al. Free and forced vibration analysis using then-sided polygonal cell-based smoothed finite element method (nCS-FEM)[J]. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2013, 10(1): 43-51. [23] 蔡斌, 周立明. 非均匀材料界面裂纹的 Cell-Based光滑有限元法[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(1): 175-182.CAI B, ZHOU L M. Research on Cell-Based smoothed finite element method of inhomogeneous material interface crack[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(1): 175-182(inChinese). [24] 周立明, 蔡斌, 孟广伟, 等. 含裂纹压电材料的 Cell-Based光滑扩展有限元法[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(4): 929-938.ZHOU L M, CAI B, MENG G W , et al. Cell-Based smoothed extended finite element method for piezoelectric materials with cracks[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(1): 175-182. (inChinese). [25] ZHOU L M, LI M, CAI Y, et al. The multi-physic cell-based smoothed finite element method for dynamic characterization of magneto-electro-elastic structures under thermal conditions[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 240: 112045. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112045 [26] ZHOU L M, REN S, MA Z. A valid inhomogeneous cell-based smoothed finite element model for the transient characteristics of functionally graded magneto-electro-elastic structures[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 208(15): 298-313. [27] KUANG X, WU S, ZE Q, et al. Magnetic dynamic polymers for modular assembling and reconfigurable morphing architectures[J]. Advanced Material, 2021, 33: 2102113. doi: 10.1002/adma.202102113 [28] KIM Y, YUK H, ZHAO R, et al. Printing ferromagnetic domains for untethered fast-transforming soft materials[J]. Nature, 2018, 558: 274-279. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0185-0 -






 下载:
下载: