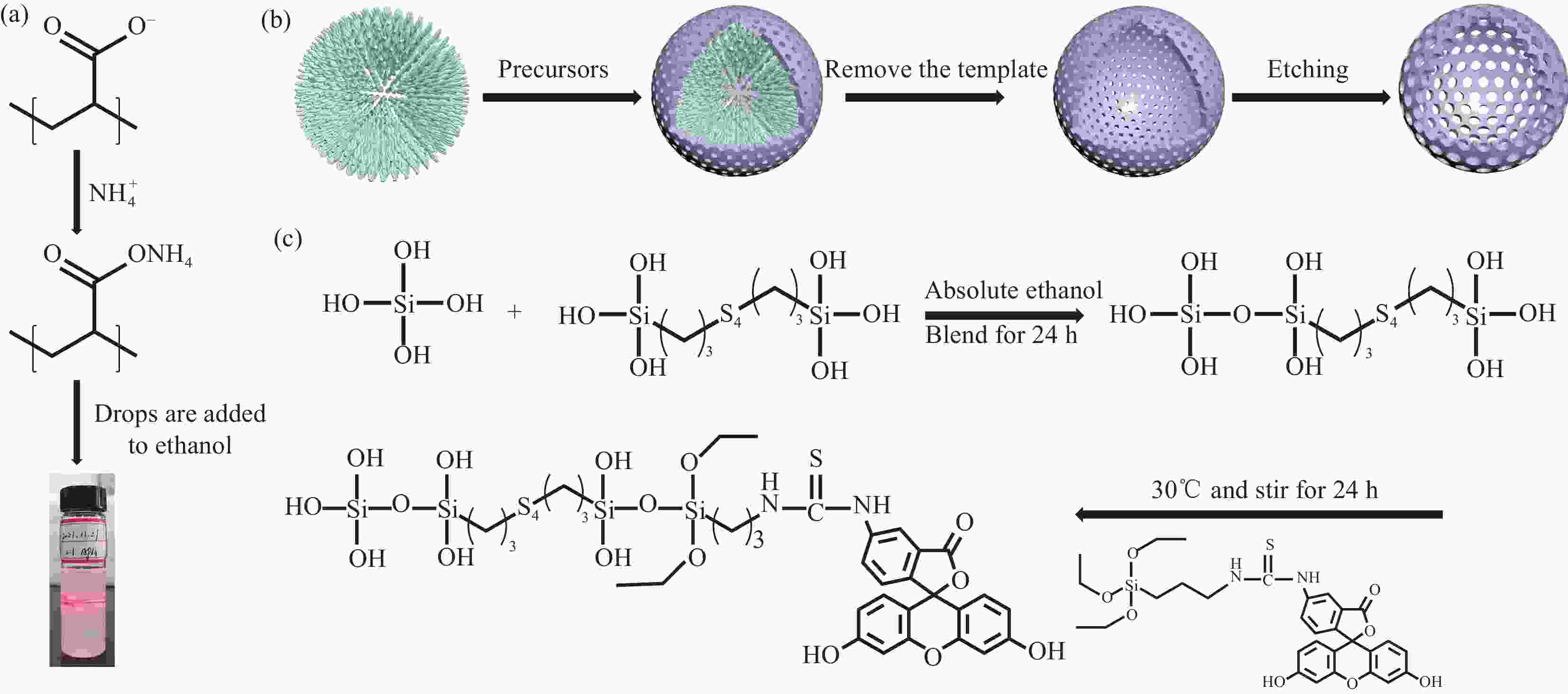
Design and performance of hollow mesoporous SiO2-based nanodrug carrier materials with controllable particle size
-
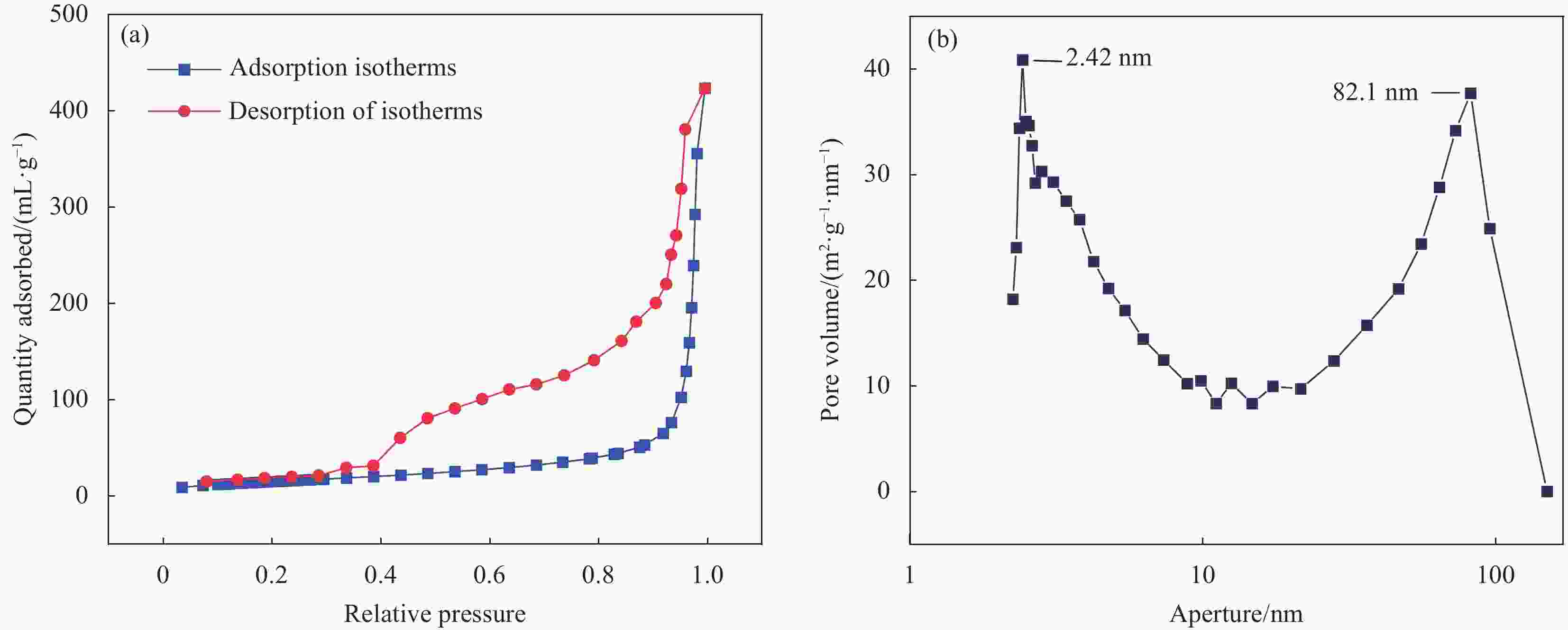
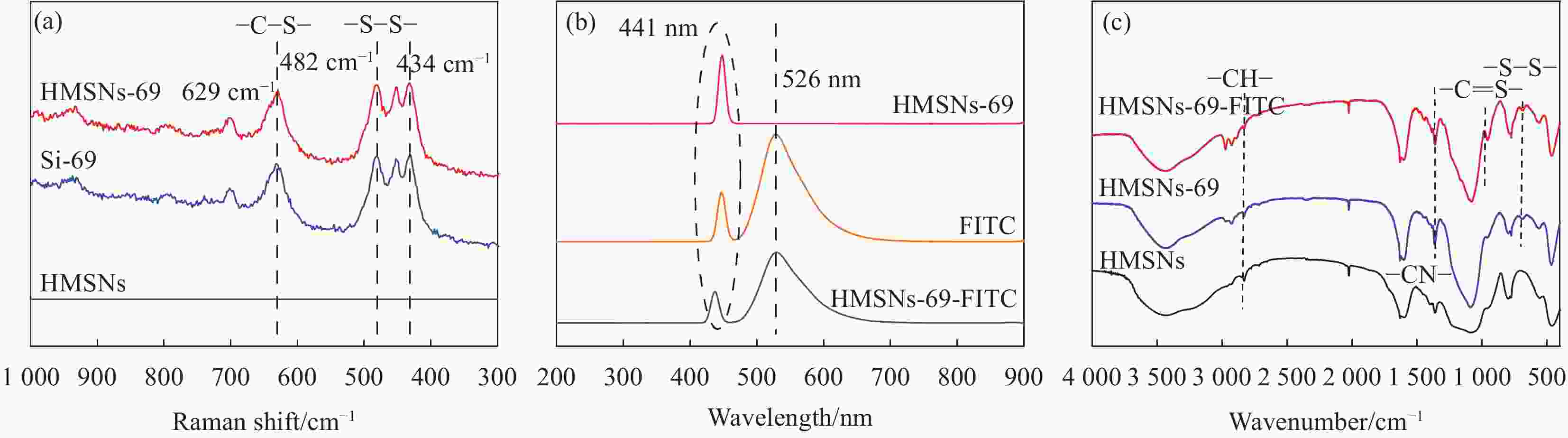
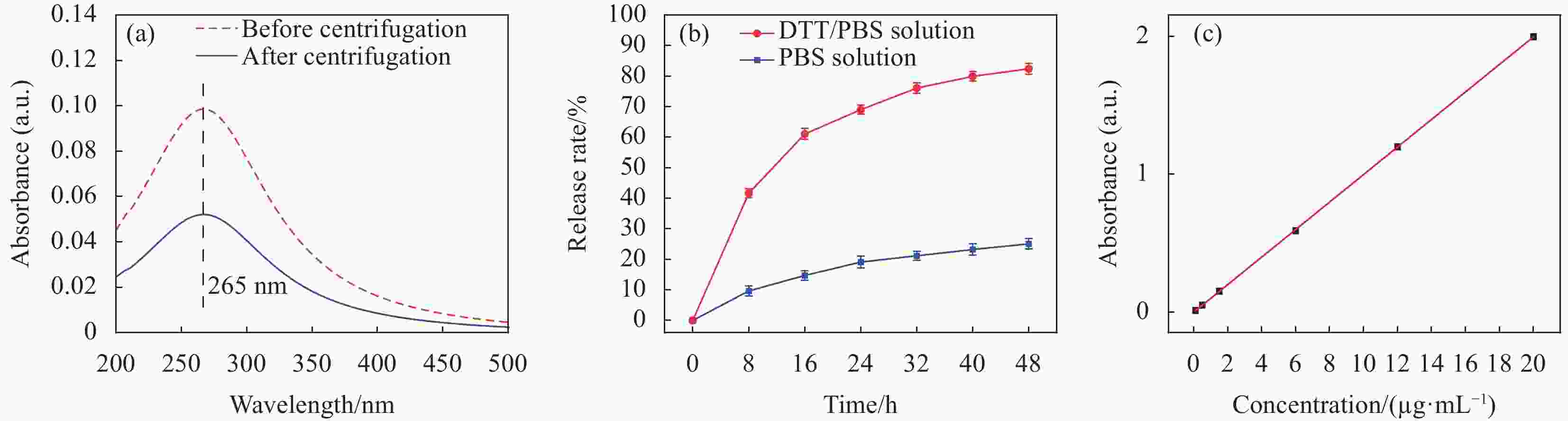
摘要: 本文分别以聚丙烯酸(PAA)、正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)、硅烷偶联剂Si-69,异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)为软模板,主要原料为荧光剂,利用自模板法制备具有荧光标记的中空介孔SiO2纳米载体(HMSNs-69-FITC)。通过FTIR、DLS、BET、Raman和TEM对纳米载体的结构、粒径进行测定,用紫外分光光度计和TEM对其还原敏感性能进行表征,用溶剂挥发法负载索拉非尼(SOR),并计算其负载效率。研究结果表明,调控PAA的量可以实现HMSNs在25~380 nm范围内粒径可控,其中,0.024 g/mL PAA、平均粒径100 nm的HMSNs稳定性能优良,HMSNS-69-FITC对SOR的负载效率为280.0 μg/mg,在含有0.0083 g/mL二硫苏糖醇(DTT)的PBS溶液中,48 h累计释放率约为82.4%;而无DTT时,48 h累计释放率约为25.1%,该载体具有二硫键还原敏感性。此研究工作有助于推动粒径可控的、还原敏感型SiO2纳米载体领域的研究。Abstract: In this study, polyacrylic acid (PAA), ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), silane coupling agent Si-69, fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) were used as soft templates, the main raw materials, fluorescent agents, and fluorescent agents were used to prepare hollow mesoporous SiO2 nanocarriers (HMSNs-69-FITC) with fluorescent labeling by self-template method. The structure and particle size of nanocarriers were determined by FTIR, DLS, BET, Raman and TEM, their reduction-sensitive properties were characterized by ultraviolet spectrophotometer and TEM, and sorafenib (SOR) was loaded with solvent volatilization, and calculate its load efficiency. The results show that the amount of regulating PAA can achieve controllable particle size of HMSNs in the range of 25-380 nm, among which, HMSNs with 0.024 g/mL PAA and an average particle size of 100 nm have excellent stability performance, HMSNs-69-FITC has a loading efficiency of 280.0 μg/mg for SOR, and in PBS solution containing 0.0083 g/mL dithiothreitol (DTT), the cumulative release rate of 48 h is about 82.4%. In the absence of DTT, the cumulative release rate at 48 h is about 25.1%, which has significant disulfide bond reduction sensitivity. This work helps advance research in the field of particle size controllable and reduction-sensitive SiO2 nanocarriers.
-
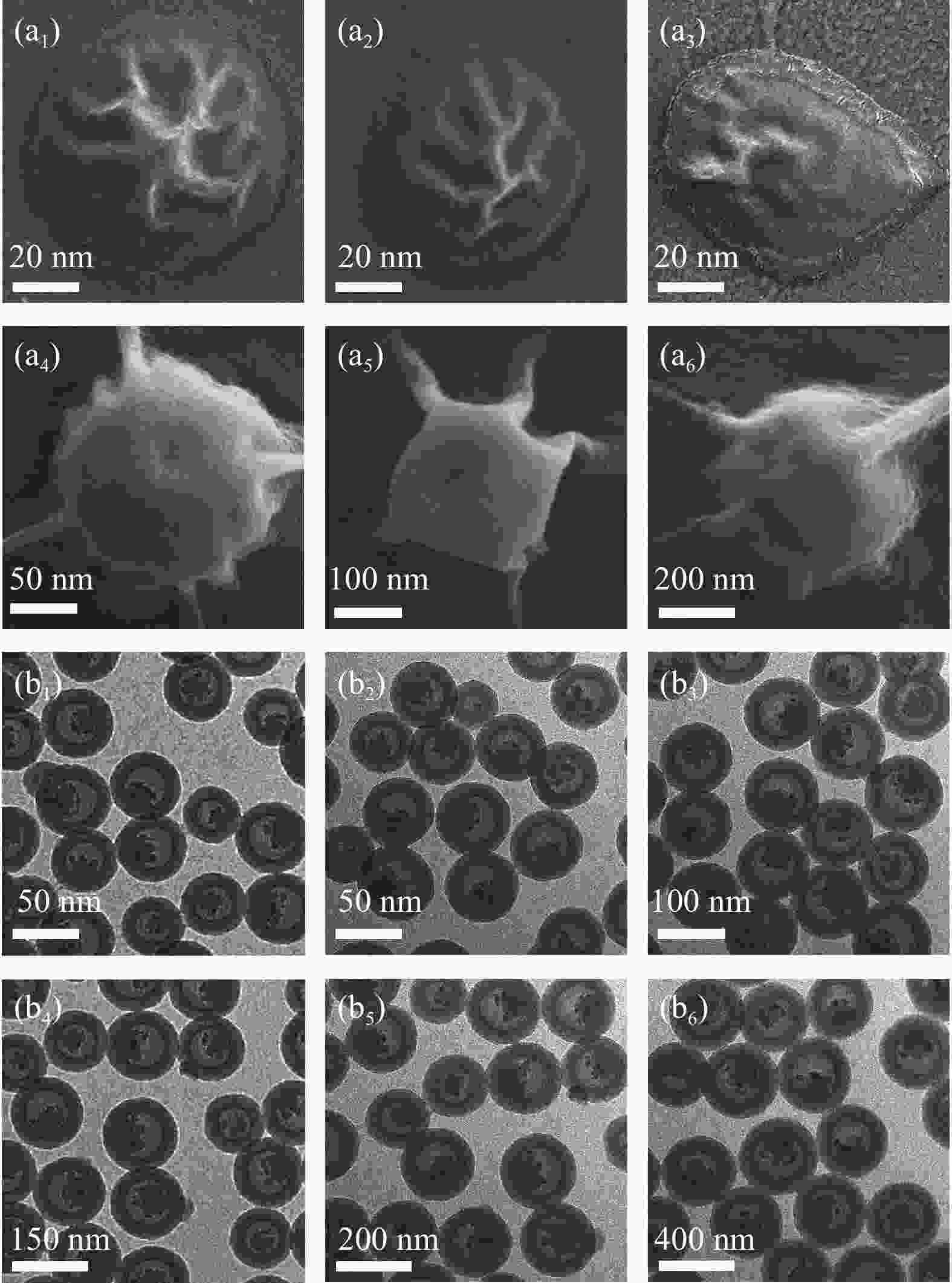
图 2 不同聚丙烯酸(PAA)含量的软模板的SEM图像: 0.02 g (a1)、0.12 g (a2)、0.22 g (a3)、0.32 g (a4)、0.42 g (a5)、0.52 g (a6);不同PAA含量制备得HMSNs的TEM图像:0.02 g (b1)、0.12 g (b2)、0.22 g (b3)、0.32 g (b4)、0.42 g (b5)、0.52 g (b6)
Figure 2. SEM images of soft template with different contents of polyacrylic acid (PAA): 0.02 g (a1), 0.12 g (a2), 0.22 g (a3), 0.32 g (a4), 0.42 g (a5), and 0.52 g (a6); TEM images of HMSNs with different contents of PAA: 0.02 g (b1), 0.12 g (b2), 0.22 g (b3), 0.32 g (b4), 0.42 g (b5), and 0.52 g (b6)
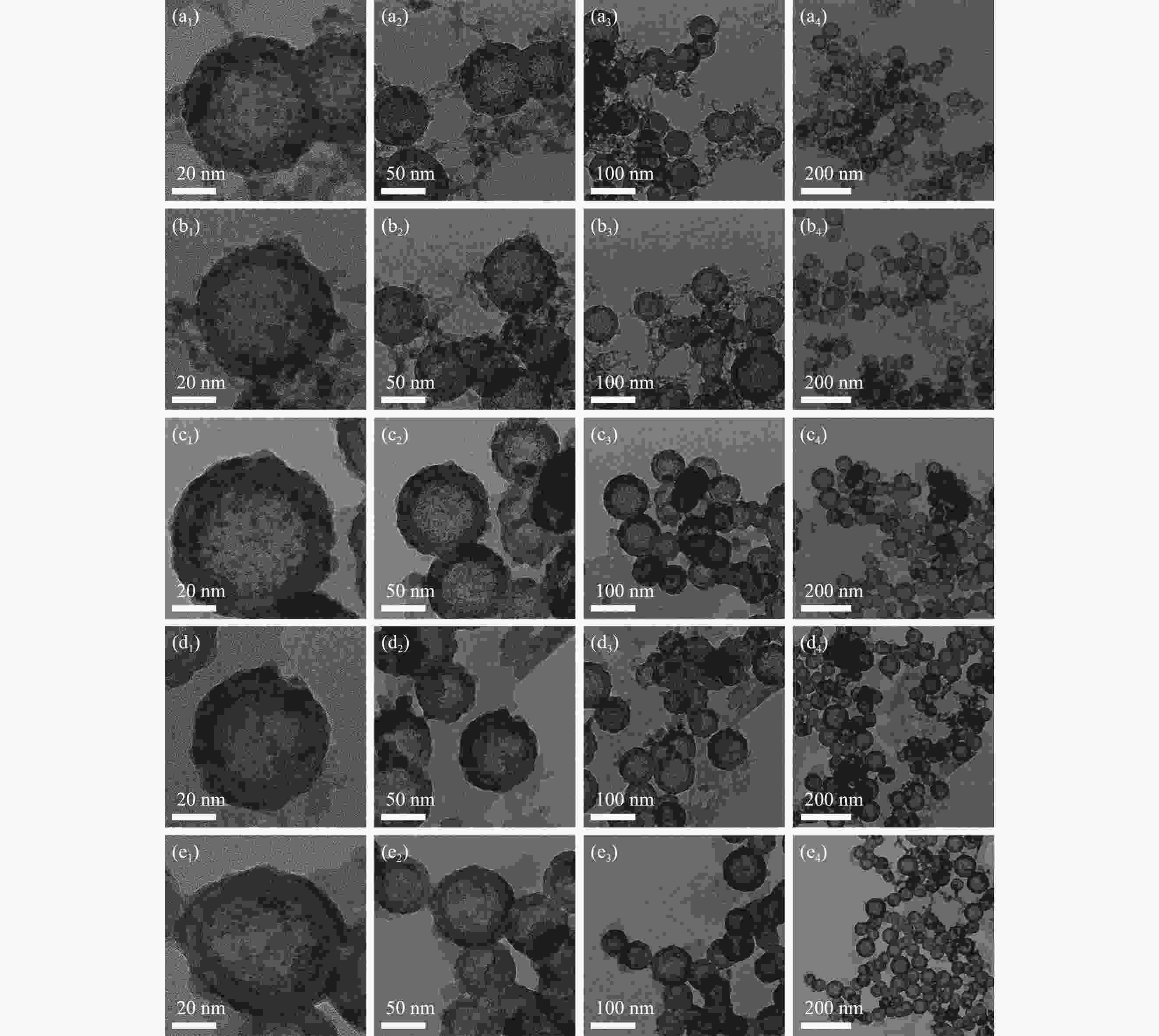
图 5 不同正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)/硅烷偶联剂Si-69体积比制得HMSNs-69的TEM图像:1.2/1.8 ((a1)~(a4))、1.5/1.5 ((b1)~(b4))、1.8/1.2 ((c1)~(c4))、2.2/0.8 ((d1)~(d4))、2.6/0.4 ((e1)~(e4))
Figure 5. TEM images of HMSNs-69 prepared by volume ratios of different ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS)/silane coupling agent Si-69: 1.2/1.8 ((a1)-(a4)), 1.5/1.5 ((b1)-(b4)), 1.8/1.2 ((c1)-(c4)), 2.2/0.8 ((d1)-(d4)), and 2.6/0.4 ((e1)-(e4))
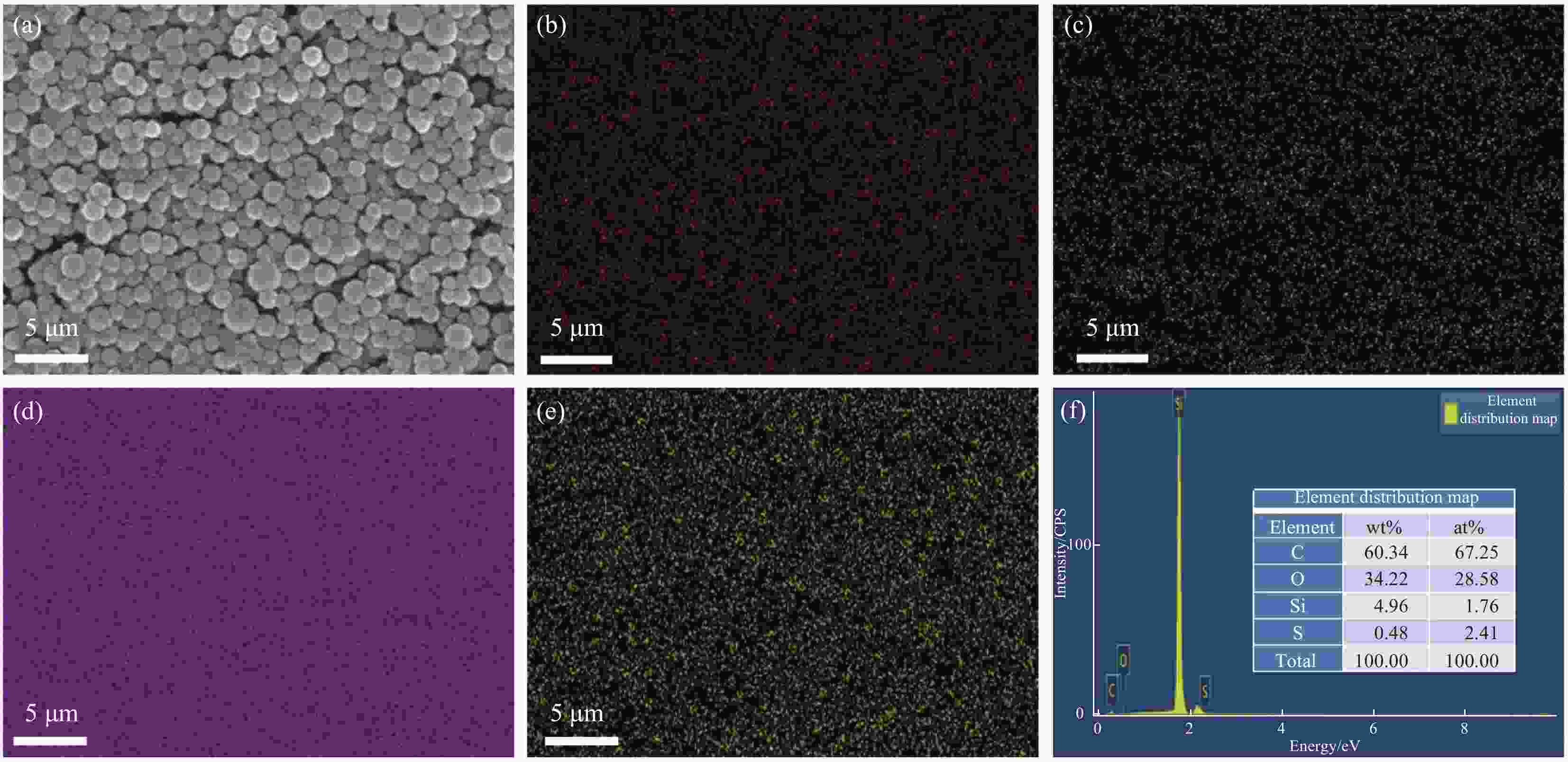
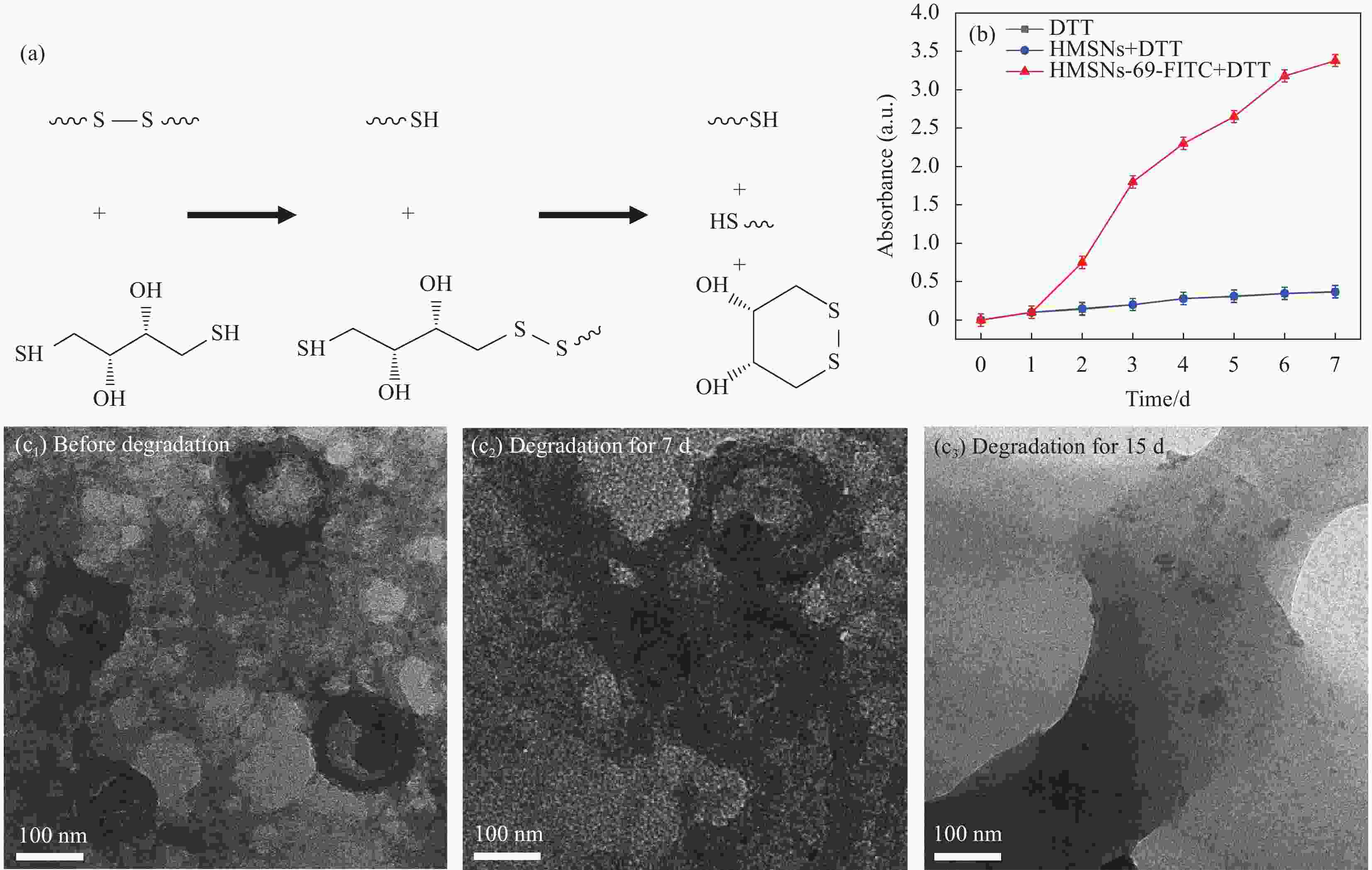
图 9 —S—S—和二硫苏糖醇(DTT)的氧化还原反应过程[30]、实验组和对照组的紫外吸收强度随时间的变化情况(b)、HMSNs-69-FITC降解前(c1)、降解7天(c2)、降解15天(c3)的SEM图像
Figure 9. —S—S— and dithiothreitol (DTT) redox reaction process[30](a), changes of UV absorption intensity over time in the experimental group and the control group (b), SEM images of HMSNs-69-FITC before degradation (c1), after degradation 7 days (c2), and 15 days (c3)
-
[1] YANG T, ZHANG J, YU Y, et al. Preparation, pharmacokinetic and application of gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) in tumor treatment[J]. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 28(34): 6990-7005. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210331145134 [2] 尹付琳, 刘超, 陈雨鑫, 等. 低CMC纳米载体PEGMA-b-PLLA-b-PCL的制备及其药物缓释性能[J]. 精细化工, 2023, 40(11): 2503-2515, 2521.YIN Fulin, LIU Chao, CHEN Yuxin, et al. Preparation and drug sustained release performance of low CMC nanocarrier PEGMA-b-PLLA-b-PCL[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2023, 40(11): 2503-2515, 2521(in Chinese). [3] KAMALY N, YAMEEN B, WU J, et al. Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: Mechanisms of controlling drug release[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(4): 2602-2663. [4] HÖRMANN K, ZIMMER A. Drug delivery and drug targeting with parenteral lipid nanoemulsions—A review[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 223(10): 85-98. [5] CHENG L, WANG X W, GONG F, et al. 2D nanomaterials for cancer theranostic applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(13): 1902333. [6] LI Y S, SHI J L. Hollow-structured mesoporous materials: Chemical synthesis, functionalization and applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(20): 3176-3205. doi: 10.1002/adma.201305319 [7] LIN L S, SONG J B, YANG H H, et al. Yolk-shell nanostructures: Design, synthesis, and biomedical applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(6): 1704639. doi: 10.1002/adma.201704639 [8] 王环江, 杨启亮, 张雨晨, 等. 芳香性聚氨基酸破乳剂的制备及性能评价[J/OL]. 材料导报, 2024: 1-16. doi: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1078.TB.20230419.1453.006.html.WANG Huanjiang, YANG Qiliang, ZHANG Yuchen, et al. Preparation and performance evaluation of aromatic polyamino acid demulsifier[J/OL]. Material Reports, 2024: 1-16(in Chinese). doi: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1078.TB.20230419.1453.006.html. [9] 王环江, 杨启亮, 张雨晨, 等. 原位接枝纳米炭黑水包油型破乳剂制备与性能评价[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(4): 241-246. doi: 10.11896/cldb.21070242WANG Huanjiang, YANG Qiliang, ZHANG Yuchen, et al. Synthesis and performance evaluation of in-situ grafted carbon black nanoparticle as demulsifier for treating crude oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(4): 241-246(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.21070242 [10] 汤琦龙, 傅晶依, 窦信, 等. 改性壳聚糖磁性纳米材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3): 1017-1025. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210830.003TANG Qilong, FU Jingyi, DOU Xin, et al. Research progress of modified chitosan magnetic nanomaterials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(3): 1017-1025(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210830.003 [11] 卢英, 荀晓伟, 杨志伟, 等. 纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合材料作为药物载体的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(12): 2953-2965. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200814.002LU Ying, XUN Xiaowei, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Research progress of nano-hydroxyapatite and its composite materials as drug carriers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(12): 2953-2965(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200814.002 [12] DANAEI M, DEHGHANKHOLD M, ATAEI S, et al. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2018, 10(2): 57. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10020057 [13] ZHOU Y M, XU Q N, LI C H, et al. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers employed in cancer therapy: A review[J]. Frontiers of Materials Science, 2020, 14(4): 373-386. doi: 10.1007/s11706-020-0526-4 [14] CUI L, LIU W T, LIU H, et al. pH-triggered charge-reversal mesoporous silica nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan oligosaccharide/carboxymethyl chitosan hybrids for effective intracellular delivery of doxorubicin[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2019, 2(5): 1907-1919. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.8b00830 [15] TAO G J, HE W J, WANG Y, et al. Dispersity, mesoporous structure and particle size modulation of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with excellent adsorption performance[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2018, 47(38): 13345-13352. doi: 10.1039/C8DT01940A [16] LIN C H, CHANG J H, YEH Y Q, et al. Formation of hollow silica nanospheres by reverse microemulsion[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(21): 9614-9626. doi: 10.1039/C5NR01395J [17] 兰海, 姚棋, 游经鹏, 等. 中空介孔氧化硅纳米颗粒的制备及应用进展[J]. 精细化工, 2020, 37(7): 1297-1303. doi: 10.13550/j.jxhg.20200015LAN Hai, YAO Qi, YOU Jingpeng, et al. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Preparation methods and applications[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2020, 37(7): 1297-1303(in Chinese). doi: 10.13550/j.jxhg.20200015 [18] 付欣, 张玉苍, 李瑞松, 等. 气溶胶辅助自组装制备中空球形二氧化硅材料的机理及应用[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(1): 327-335.FU Xin, ZHANG Yucang, LI Ruisong, et al. Mechanism and application of aerosol assisted self-assembly to prepare hollow spherical silica materials[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(1): 327-335(in Chinese). [19] DONG J J, YAO X Y, SUN S A, et al. In vivo targeting of breast cancer with a vasculature-specific GQDs/hMSN nanoplatform[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(20): 11576-11584. doi: 10.1039/C9RA01833F [20] 葛界芳, 熊向源. 抑制癌症治疗多药耐药性的纳米药物递送体系[J]. 精细化工, 2023, 40(5): 989-999.GE Jiefang, XIONG Xiangyuan. Nanodrug delivery system for inhibiting multidrug resistance in cancer treatment[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2023, 40(5): 989-999(in Chinese). [21] GUO L Y, PING J T, QIN J L, et al. A comprehensive study of drug loading in hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Impacting factors and loading efficiency[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(5): 1293. doi: 10.3390/nano11051293 [22] ZHOU Y M, XU Q N, LI C H, et al. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers employed in cancer therapy: A review[J]. Frontiers of Materials Science, 2020, 14(4): 373-386. [23] 李晴, 钱付平, 薛沚怡, 等. 改性SiO2凝胶涂层滤料制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(8): 2489-2496.LI Qing, QIAN Fuping, XUE Zhiyi, et al. Preparation and properties of modified SiO2 gel-coated filter media[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(8): 2489-2496(in Chinese). [24] 杨梦然, 尚宏周, 来士胜, 等. 中空介孔硅基刺激响应型纳米药物载体的研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2022, 42(4): 58-61. doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2022.04.012YANG Mengran, SHANG Hongzhou, LAI Shisheng, et al. Research progress on hollow mesoporous silicon-based stimulus responsive nano drug carriers[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2022, 42(4): 58-61(in Chinese). doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2022.04.012 [25] 余丽丽, 刘乾, 姚琳, 等. 氧化 还原敏感型胶束的构建和药物控释性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2018, 34(9): 20-25.YU Lili, LIU Qian, YAO Lin, et al. Construction and controlled release properties of redox responsive micelles[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 34(9): 20-25(in Chinese). [26] PENG X, LIANG Y T, YIN Y, et al. Development of a hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles vaccine to protect against house dust mite induced allergic inflammation[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2018, 549(1-2): 115-123. [27] XU X Y, DUAN J L, LAN Q, et al. A dual-sensitive poly(amino acid)/hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based anticancer drug delivery system with a rapid charge-reversal property[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2021, 66: 102817. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102817 [28] LI Z M, YANG Y, WEI H X, et al. Charge-reversal biodegradable MSNs for tumor synergetic chemo/photothermal and visualized therapy[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2021, 338: 719-730. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.09.005 [29] 韩伟豪, 宫玉梅, 张辰, 等. 不同铁源制备磁性中空介孔硅铁复合微球及应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(5): 1123-1129. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190730.005HAN Weihao, GONG Yumei, ZHANG Chen, et al. Preparation and application of magnetic hollow mesoporous SiO2-Fe x O y microspheres from different Fe sources[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(5): 1123-1129(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190730.005 [30] CAO L D, ZHANG H R, ZHOU Z L, et al. Fluorophore-free luminescent double-shelled hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pesticide delivery vehicles[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(43): 20354-20365. doi: 10.1039/C8NR04626C [31] DU Q Q, LIU Q. ROS-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with Glabridin for anti-pigmentation properties[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 327: 111429. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111429 [32] GUO L Y, PING J T, QIN J L, et al. A comprehensive study of drug loading in hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Impacting factors and loading efficiency[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(5): 1293. doi: 10.3390/nano11051293 -





 下载:
下载: