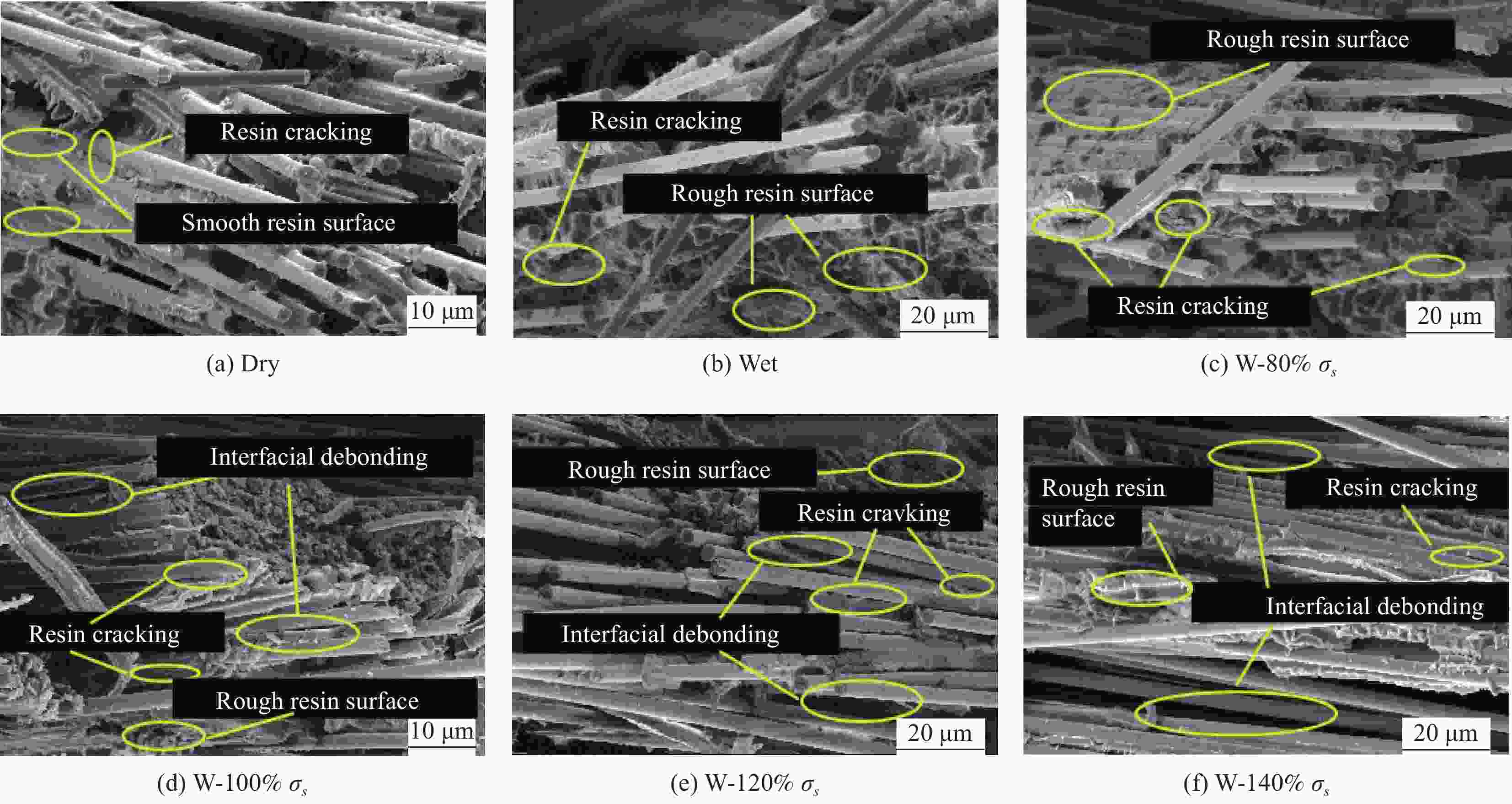
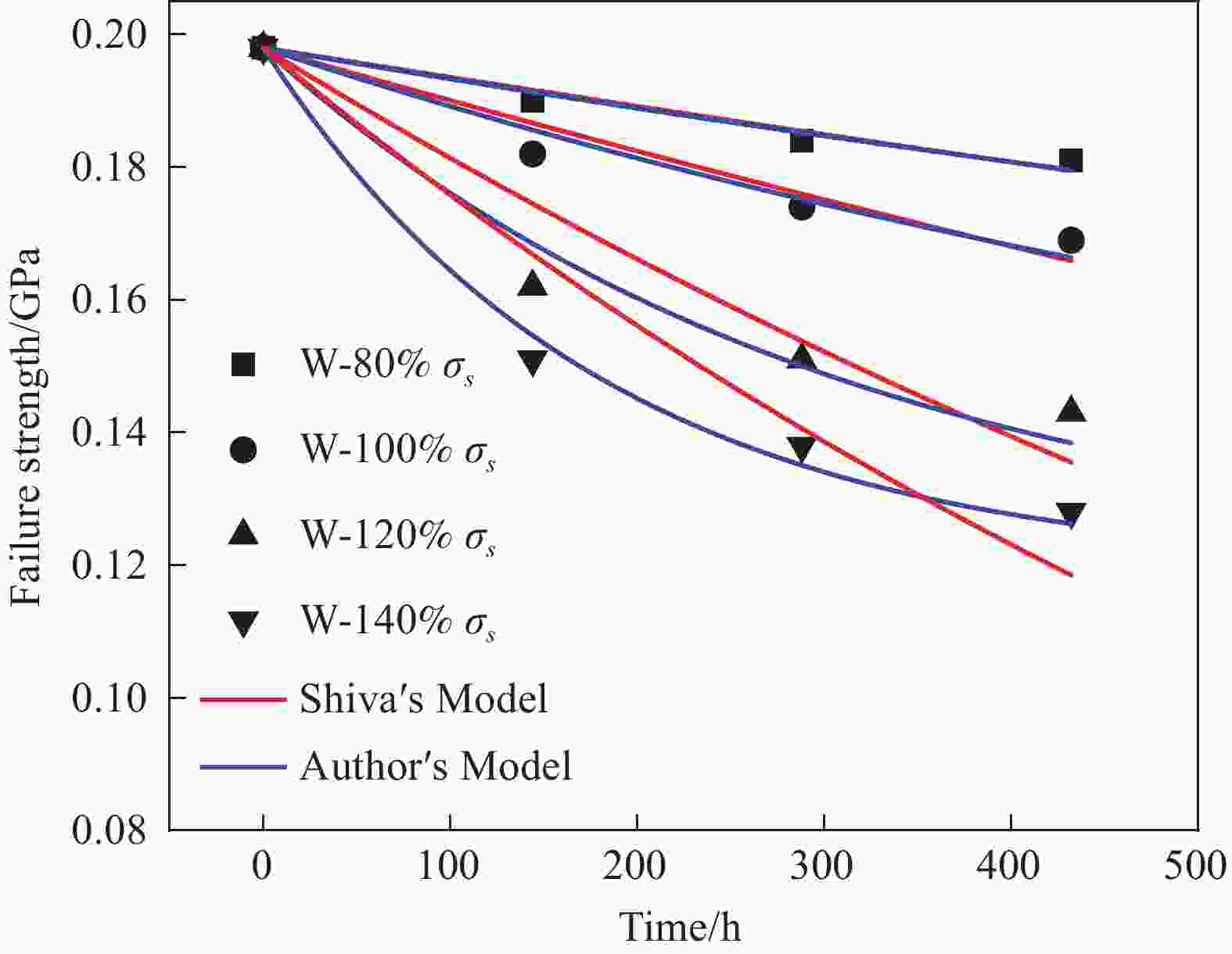
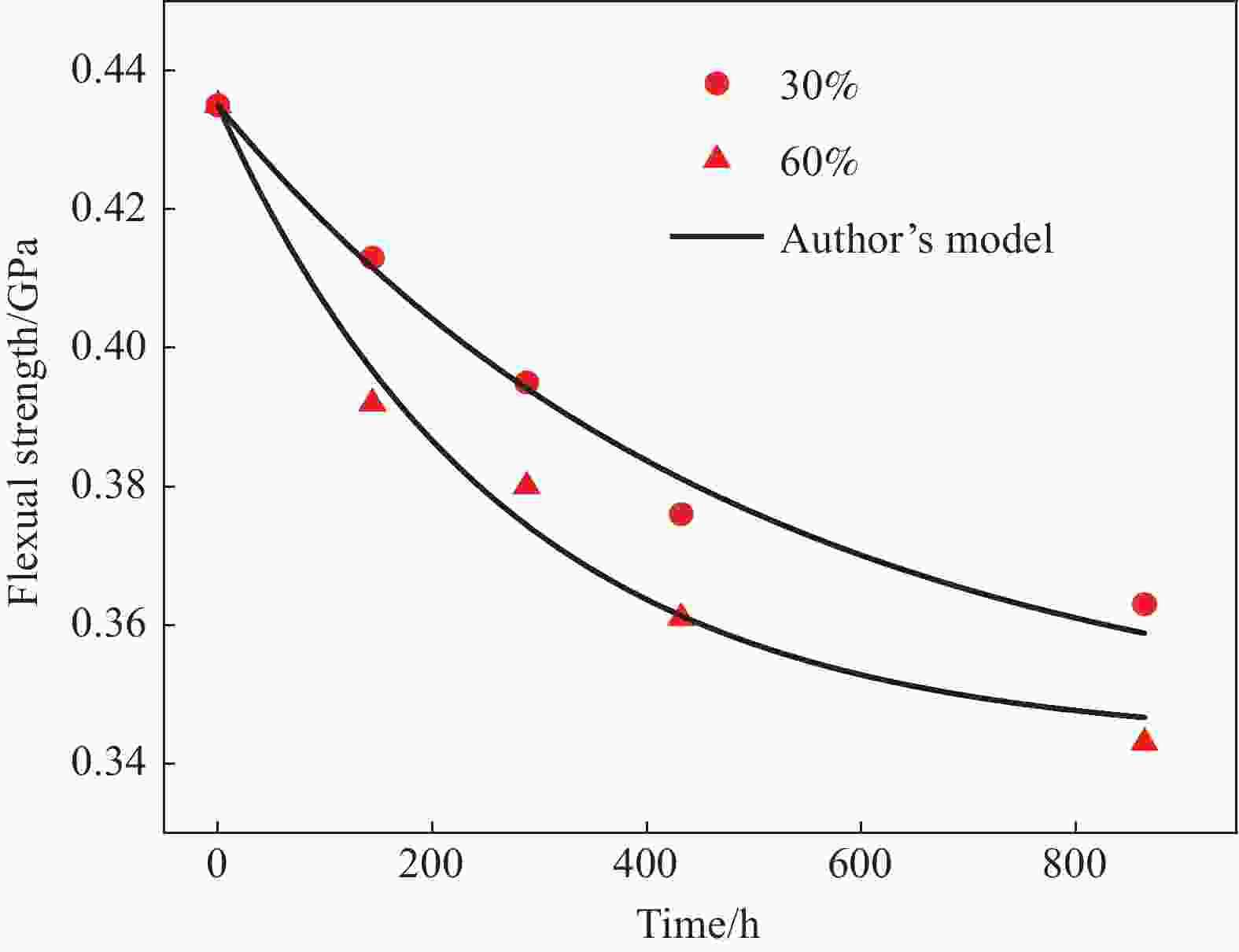
Mechanical behavior of 2D braided composites under the coupling effect of moisture and load
-
摘要: 为了研究长期水分-载荷耦合作用下2D编织复合材料的吸湿行为及性能劣化规律,设计了水分-载荷耦合环境老化装置,开展了不同应力水平下T300/H69 平纹编织复合材料的吸湿试验及吸湿后的拉伸试验。结果表明:T300/H69 编织复合材料的吸湿量与拉伸预应力总体上呈现正相关,随着拉伸预应力的增大而增大;相对于水分单独作用,水分-载荷耦合作用下材料的弹性模量和强度退化更为明显,在140% σs预应力下作用432小时后,编织复合材料的弹性模量及失效强度分别下降达55.9%和35.4%。此外,通过宏微观断面分析,进一步揭示长期水分-载荷耦合作用下编织复合材料性能的退化机制,并基于Shiva剩余强度理论,改进了水分-载荷作用下复合材料的剩余强度模型,预测结果良好,为复杂环境下复合材料耐久性设计提供指导。Abstract: In order to study the moisture absorption behavior and performance degradation law of 2D braided composites under long-term moisture-load coupling, a moisture-load coupled aging device was designed. The moisture absorption test and tensile test after moisture absorption of T300/H69 plain woven composite material under different stress levels were carried out. The results show that the moisture absorption of T300/H69 braided composites is positively correlated with the tensile prestress, and increases with the increase of tensile prestress. Compared with the effect of water alone, the elastic modulus and strength degradation of the material under moisture -load coupling are more obvious. After 432 hours at 140% σs prestress, the elastic modulus and failure strength of the braided composites decreased by 55.9% and 35.4%, respectively. In addition, the degradation mechanism of braided composites under long-term moisture-load coupling is further revealed by macro and micro section analysis. Based on Shiva 's residual strength theory, the residual strength model of composites under moisture-load is improved, and the prediction results are good, which provides guidance for the durability design of composites in complex environment.
-
表 1 T300/H69复合材料的基本力学性能参数
Table 1. Basic mechanical properties of T300 / H69 composites
Engineering constants Value Engineering constants Value E1/GPa 55.90 XT/MPa 602 E2/GPa 54.60 XC/MPa 431 E3/GPa 7.220 YT/MPa 597 G12/GPa 3.812 YC/MPa 422 G13/GPa 3.122 ZT/MPa 60 G23/GPa 3.122 ZC/MPa 152 $ \nu _{12}$ 0.068 S12/MPa 83 $ \nu _{13}$ 0.310 S13/MPa 49 $ \nu_{23} $ 0.310 S23/MPa 49 Notes:E1,E2 and E1 are the elastic modulus in different directions. G12, G13 and G23 are shear modulus in different directions. $ \nu_{12} $, $ \nu_{12} $ and $ \nu_{12} $ are the Poisson 's ratio of the material. XT, XC, YT, YC, ZT, ZC are axial tension, axial compression, transverse tension, transverse compression, normal tension, normal tension. S12, S13, S23 are the corresponding in-plane shear strength. 表 2 试验矩阵
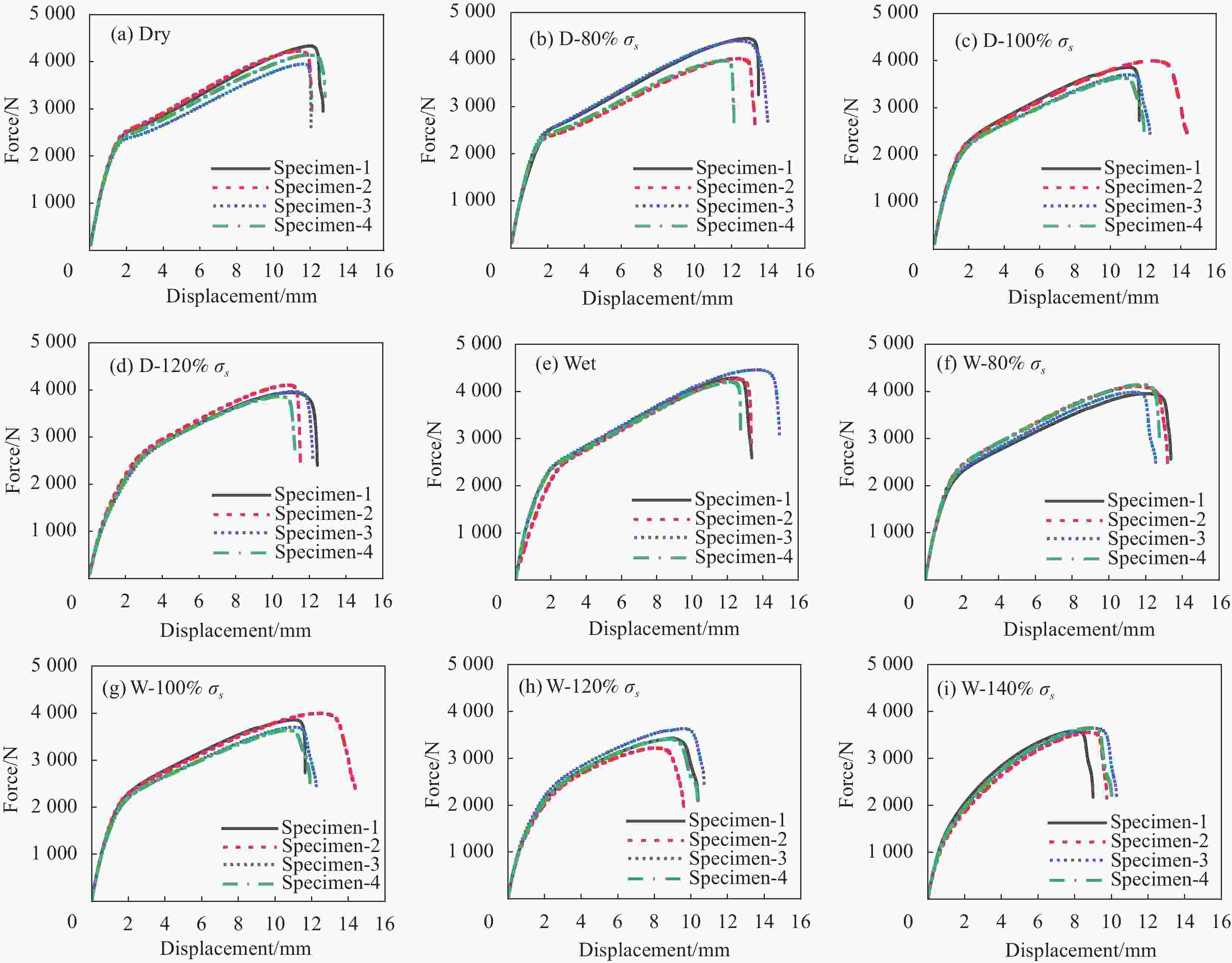
Table 2. Test matrix
Pretreated Specimen group Test time / h Untreated Dry 0 Moisture Wet 144,288,432 Load D-80% σs 288 D-110% σs 288 D-120% σs 288 Moisture- load W-80% σs 144,288,432 W-100% σs 144,288,432 W-120% σs 144,288,432 W-140% σs 144,288,432 Notes:D and W are the dry state and moisture absorption state of the material; σs—yield stress. 表 3 Fick吸湿模型的相关参数
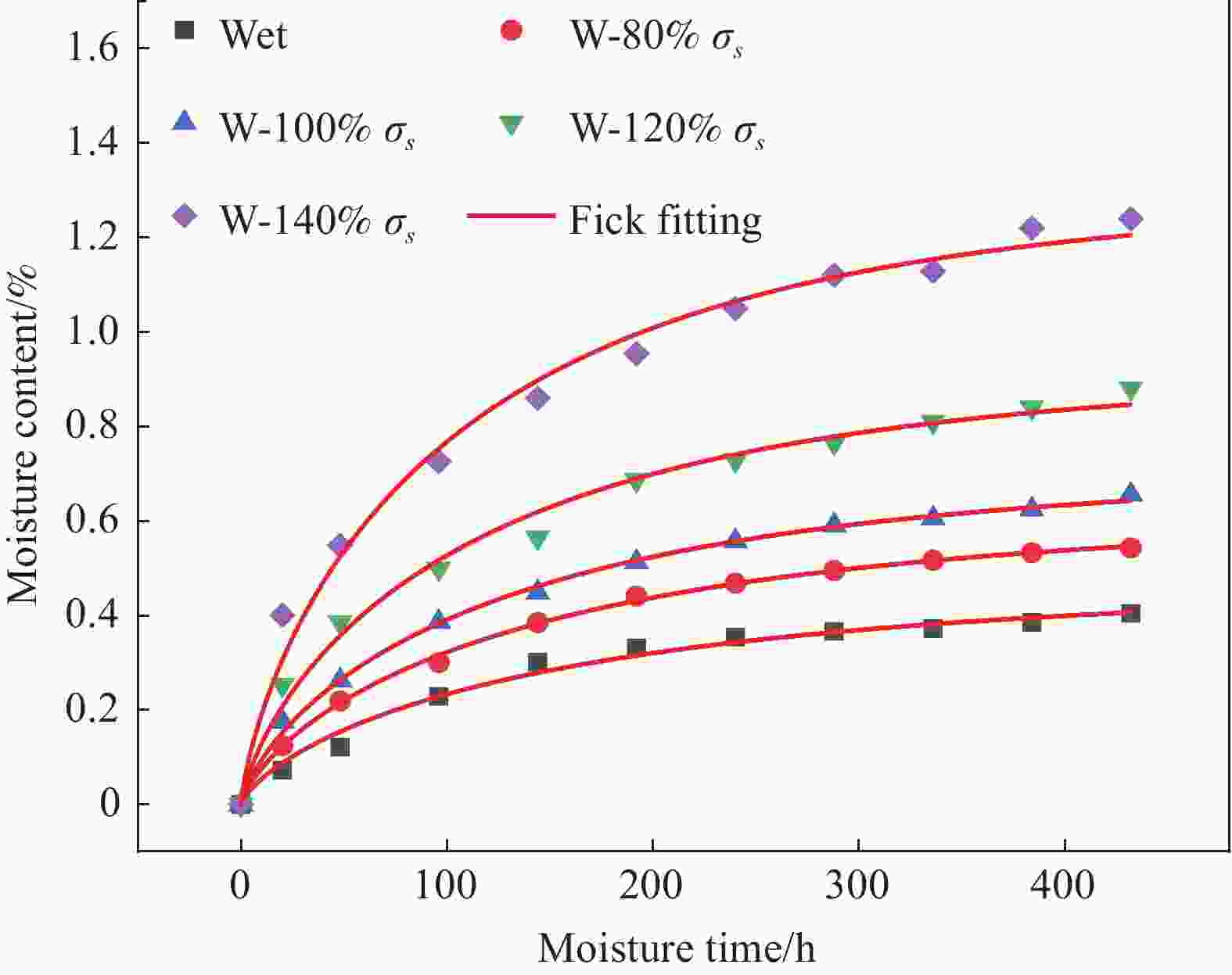
Table 3. The relevant parameters of Fick moisture absorption
Tensile prestress Diffusion coefficient D/(mm2/h) Balanced moisture
contentM∞/%0 0.00175 0.464 80% σs 0.00192 0.612 100% σs 0.00213 0.706 120% σs 0.00229 0.917 140% σs 0.00257 1.297 表 4 T300/H69编织复合材料的弹性模量及强度
Table 4. Elastic modulus and strength of T300 / H69 braided composites
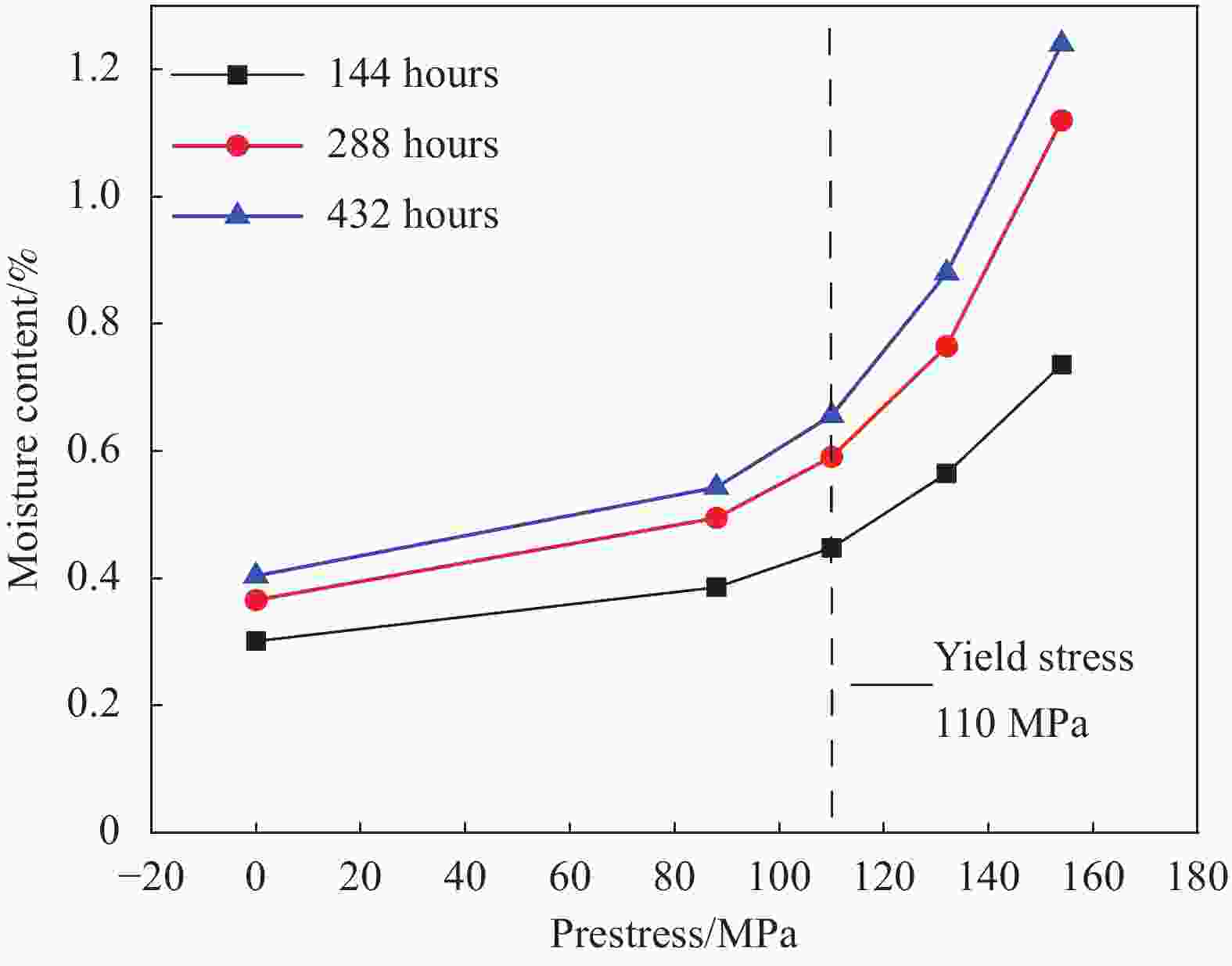
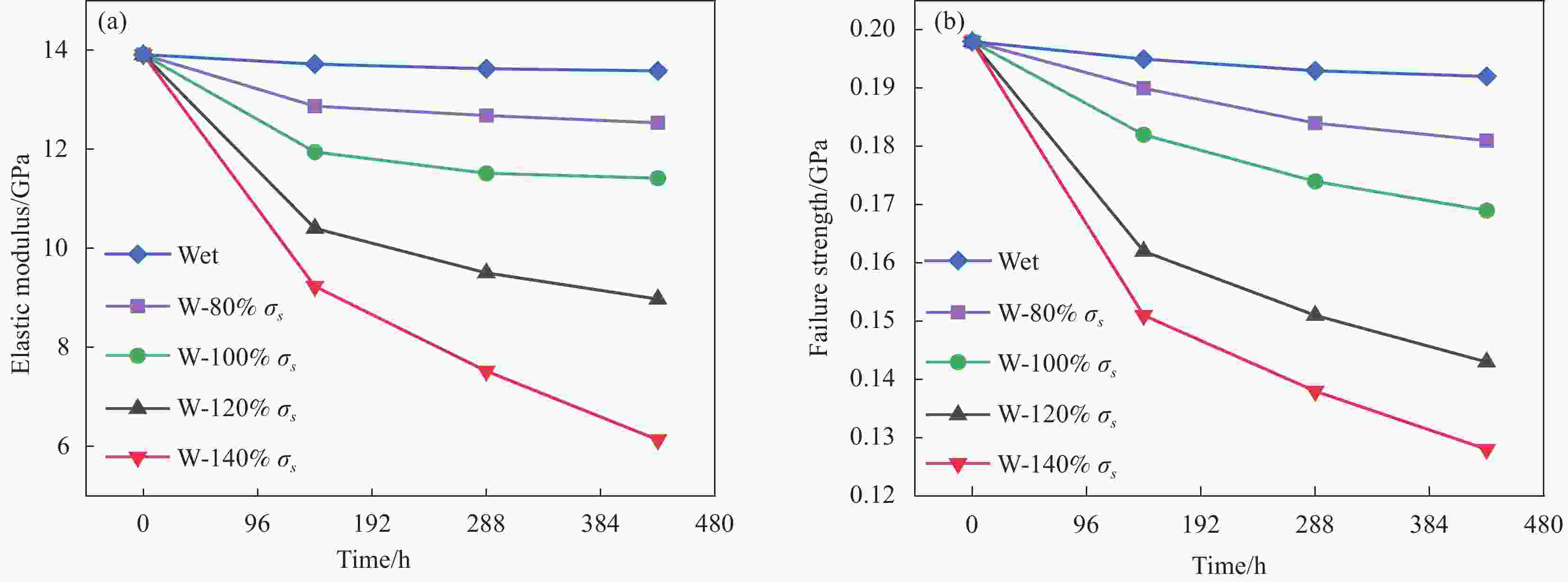
Category 144 hours 288 hours 432 hours E/GPa σf /GPa E/GPa σf /GPa E/GPa σf /GPa Moisture Average 13.721 0.195 13.627 0.193 13.586 0.192 CV 2.13% 2.31% 4.61% 2.01% 1.09% 1.82% D-80%σs Average / / 13.204 0.191 / / CV / / 2.61% 2.30% / / D-100%σs Average / / 12.715 0.187 / / CV / / 1.89% 1.6% / / D-120%σs Average / / 10.643 0.180 / / CV / / 3.64% 1.78% / / W-80%σs Average 12.873 0.190 12.682 0.184 12.535 0.181 CV 2.05% 0.74% 3.01% 1.36% 2.43% 1.88% W-100%σs Average 11.947 0.182 11.516 0.174 11.419 0.169 CV 4.19% 2.58% 3.32% 2.82% 5.08% 3.02% W-120%σs Average 10.404 0.162 9.506 0.151 8.975 0.143 CV 3.27% 3.33% 4.12% 3.88% 5.39% 2.66% W-140%σs Average 9.232 0.151 7.521 0.138 6.136 0.128 CV 4.78% 2.72% 5.66% 3.38% 7.12% 4.11% Notes:E is the elastic modulus of the material, σf is the failure strength of the material, CV is the coefficient of variation. -
[1] HAN Wei, ZHANG Hong-ping, TAVAKOLI J, et al. Polydopamine as Sizing on Carbon Fiber Surfaces for Enhancement of Epoxy Laminated Composites[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2018, 107: 626-632. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.02.003 [2] RANI M, CHOUDHARY P, KRISHNAN V, et al. A Review on Recycling and Reuse Methods for Carbon Fiber/Glass Fiber Composites Waste from Wind Turbine Blades[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2021, 215: 108768. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108768 [3] CHEN Junlin, WANG Kai, ZHAO Yan. E-nhanced Interfacial Interactions of Carbon F-iber Reinforced PEEK Composites by Regulating PEI and Graphene Oxide Complex Sizing at the Interface[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018, 154: 175-186. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.11.005 [4] LIU B, HAN Q, ZHONG X P, et al. The impact damage and residual load capacity of composite stepped bonding repairs and joints[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 158: 339-351. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.09.096 [5] CHEN C, ZHANG C, LIU C, et al. Rate-dependent tensile failure behavior of short fiber reinforced PEEK[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2018, 136: 187-196. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.10.031 [6] 张月欣, 杨明君, 王崇杰, 等. 干湿环境对环氧树脂/碳纤维复合材料层合板老化性能的影响[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2022, 50(04): 124-129.ZHANG Yuexin, YANG Mingjun, WANG Chongjie, et al. Effects of Dry/Wet Environment on Aging Properties of Epoxy Resin/Carbon Fiber Composite Laminates[J]. ENGINEERING PLASTI-CS APPLICATION, 2022, 50(04): 124-129(in Chinese). [7] 李佳楠, 姜亚明, 项赫, 等. 高性能纤维增强树脂基复合材料湿热老化研究进展 [J/OL]. 化工新型材料: 1-9.LI Jianan, JIANG Yaming, XIANG He, et al. Research progress in the hydrot-hermal aging of high-performance fiber reinforced plastic [J/OL]. New Chemical Materials: 1-9(in Chinese). [8] BLACKBURN B P, TATAR J, DOUGLAS E P, et al. Effects of hygrothermal conditioning on epoxy adhesives used in FRP composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 96: 679-689. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.056 [9] PRADIP S, ASHOK M. Experimental and numerical study on moisture diffusion phenomenon of natural fiber based on composites[J]. Materials today:Proceedings, 2017, 4(9): 10293-10297. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.06.367 [10] ROCHA I B C M , RAIJMAEKERS S , VAN d M F P, et al. Combined experimental/numerical investigation of directional moisture diffusion in glass/epoxy composites. Composite Science and Technology, 2017, 151: 16-24. [11] 齐士杰, 张纪奎, 程小全. 吸湿后复合材料层合板快速加热分层扩展数值模拟[J]. 复合材料报, 2016, 33(08): 1687-1693.QI Shijie , ZHANG Jikui , CHENG Xiaoquan. Numerical simulation of rapid heating induced delamination growth of composite laminates after moisture absorption[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2016, 33(08): 1687-1693(in Chinese). [12] 张先航, 李曙林, 常飞, 等. BA9916-II/CCF复合材料加筋板吸湿特性[J]. 航空材料学报, 2017, 37(5): 63-69.ZHANG Xianhang LI Shulin CHANG fei, et al. BA9916-II/CCF300 Composite Stiffened Plate Hygroscopic Characteristics[J]. JOUR-NAL OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS, 2017, 37(5): 63-69(in Chinese). [13] 吴以婷, 葛东云, 李辰. 湿热环境下Carbon/Epo-xy复合材料层合板动态压缩性能[J]. 复合材学报, 2016, 33(02): 259-264.WU Yiting, GE Dongyun, LI Chen. Dynamic compressive properties of Carbon/Epoxy composite laminates under hygrothermal environment[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2016, 33(02): 259-264(in Chinese). [14] SHETTY K, SRIHARI S, MANJUNATHA C M. Effect of hygrothermal aging on the interlaminar shear strength of a carbon fibre composite[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2019, 14: 849-854. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2019.07.063 [15] 张裕恒, 王继辉, 魏建辉, 等. 湿热环境下碳纤维增强乙烯基树脂复合材料长期力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(03): 1406-1416.ZHANG Yuheng , WANG Jihui , WEI Jianhui, et al. Long-term mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced v-inyl resin composites in hygrothermal environment[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(03): 1406-1416(in Chinese). [16] 王登霞, 孙岩, 谢可勇, 等. 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料模拟海洋环境长期老化及失效行为[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(03): 1353-1362.WANG Dengxia , SUN Yan, XIE Keyong, et al. Long term aging and failure behaviors of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites in simulated marine environments[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(03): 1353-1362(in Chinese). [17] 许良, 涂宜鸣, 崔浩, 等. 海水环境下老化周期对T800碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2022, 50(12): 89-94.XU Liang, TU Yiming, CUI Hao, et al. Effect of aging cycle on T800 carbon fiber / epoxy resin composites in seawater environment[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2022, 50(12): 89-94(in Chinese). [18] HUMEAU C, DAVIES P, JACQUEMIN F. An Experimental Study of Moisture Diffusion in Carbon/epoxy Composites Under Static Tensile Stress[J]. Composites Part A, 2018, 107: 94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.12.016 [19] 李彪, 李家兴, 贾彬, 等. 海水浸泡与应力耦合作用下碳纤维复材网格单肢拉伸力学性能试验研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2020, 50(11): 178-183.LI Biao, LI Jiaxing, JIA Bin, et al. Experimental study on tensile propertiesof CFRP grids under the coupling of seawater immersion and stress[J]. Industrial Construction, 2020, 50(11): 178-183(in Chinese). [20] 南田田. 湿热环境下弯曲载荷对CFRP性能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.NAN Tiantian. Influence of bending load on the CFRP under hygrothermal environment [D]. Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [21] 马晓红, 田文强, 夏燕茂. 二维编织复合材料的结构及力学性能研究[J]. 上海纺织科技, 2016, 44(05): 27-29.MA Xiaohong, TIAN Wenqiang, XIA Yanmao. Structure and mechanical properties of 2D braided composites[J]. Shanghai Textile Science & Technology, 2016, 44(05): 27-29(in Chinese). [22] GB/T 1447-2005, 纤维增强塑料拉伸性能试验方法[S].GB/T 1447-2005, Test method for tensile properties of fiber reinforced plastics [S] (in Chinese). [23] HB 7401-2020, 航空用聚合物基复合材料吸湿试验方法[S].HB 7401-2020, Moisture absorption test method of polymer matrix composites for aviation [S] (in Chinese). [24] SHEN C H, SPRINGER G S. Moisture Absorption and Desorption of Composite Materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1976, 10(1): 2-20. doi: 10.1177/002199837601000101 [25] XU J, HENK K, FRANS B. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in pultruded fibre reinforced polymer composites of bridge decks[J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 37: 304-312. [26] SHIVA E, FATHOLLAH T B, FARID T. Long-term hygrothermal response of perforated GFRP plates with/without application of constant external loading[J]. Polymer Composites, 2012, 33(4): 467-475. doi: 10.1002/pc.22150 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 83
- HTML全文浏览量: 58
- 被引次数: 0




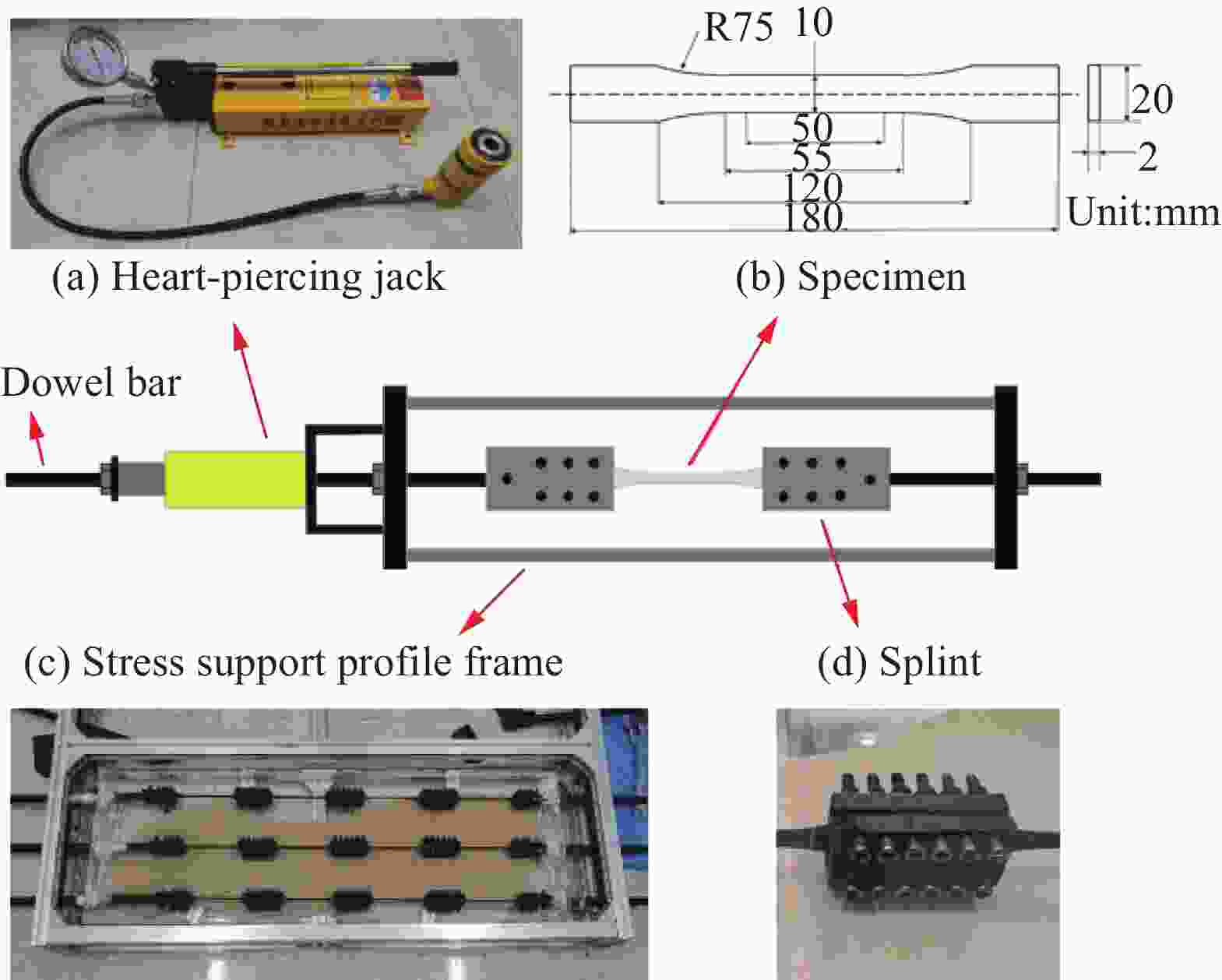
 下载:
下载: