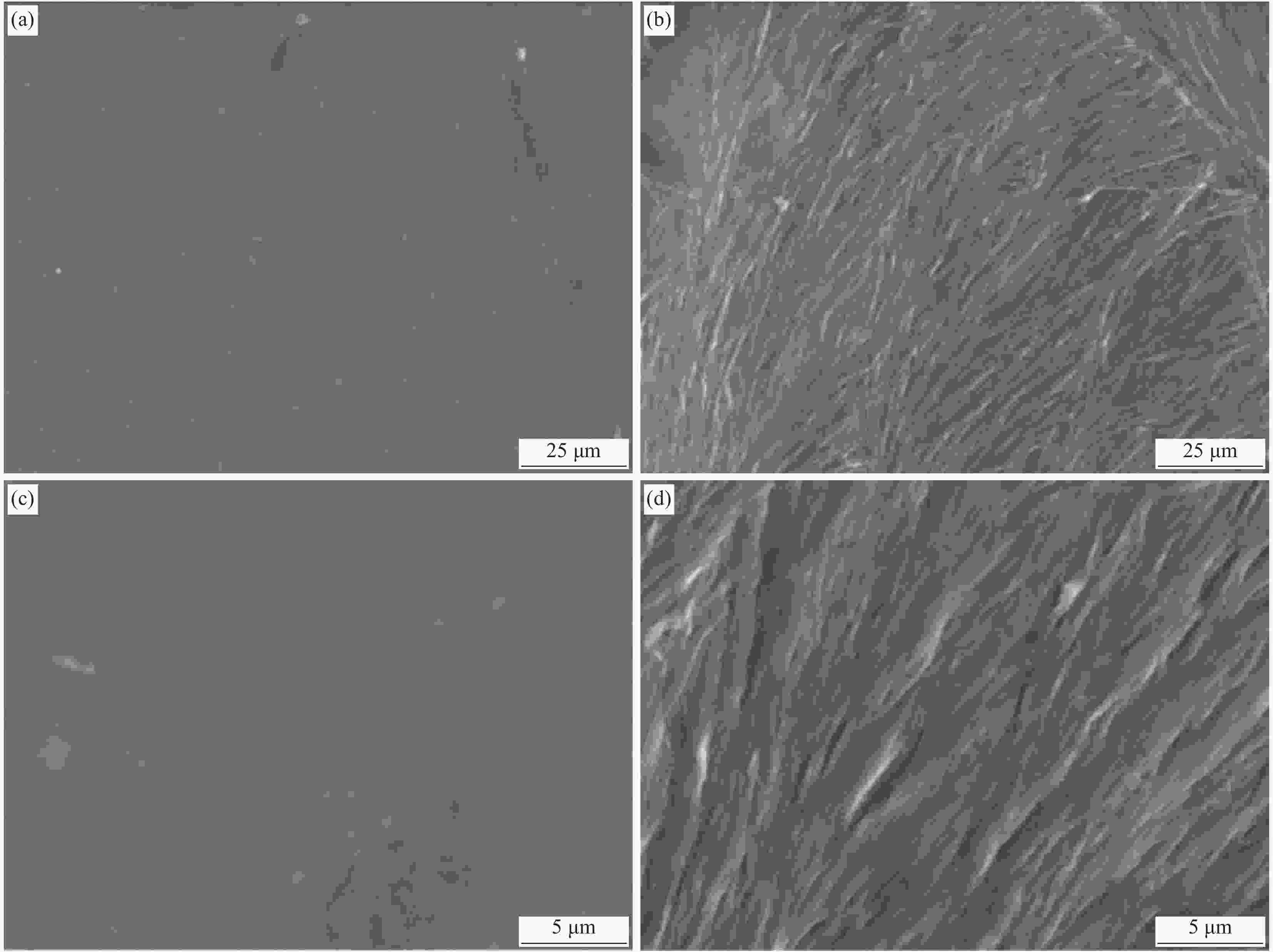
Preparation of conductive molecularly imprinted membrane chemically modified electrode and electrochemical detection of Ponceau 4R
-
摘要: 报道了一种聚丙烯酰胺(PAAM)-植酸(PA)-聚多巴胺(PDA)导电分子印迹膜(PAAM-PA-PDA MIP)化学修饰电极的制备、表征及其在电化学定量检测食品添加剂胭脂红(P4R)中的应用。即通过原位电聚合和碱液洗脱的方法在玻碳电极(GCE)表面制得具有分子识别作用的导电分子印迹膜(PAAM-PA-PDA MIP)化学修饰电极,并利用SEM、循环伏安法(CV)及交流阻抗法(EIS)对该导电分子印迹膜化学修饰电极的表面形貌和电化学性能进行表征。研究结果表明该方法所制备的导电分子印迹膜化学修饰电极具有良好的电化学检测性能和应用前景,其对P4R的线性检测区间为10~200 μmol/L,灵敏度为0.085 A/mol/L,检测限可达23.6 nmol/L,并可有效地应用于P4R实际样品的分析检测。Abstract: A polyacrylamide-phytic acid-polydopamine conductive molecularly imprinted membrane (PAAM-PA-PDA MIP) chemically modified electrode was prepared, characterized and applied to the quantitative detection of food additive Ponceau 4R (P4R). Based on the in-situ electrochemical polymerization and alkaline elution, a PAAM-PA-PDA MIP chemically modified electrode with molecular recognition was prepared by the modification of surface of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) with PAAM-PA-PDA MIP. In addition, as-prepared PAAM-PA-PDA MIP chemically modified electrode was characterized by SEM, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). It is found that the PAAM-PA-PDA MIP chemically modified electrode could be applied in the electrochemical detection of P4R with linear detection range from 10 μmol/L to 200 μmol/L, high sensitivity of 0.085 A/mol/L and low detection limit of 23.6 nmol/L, which presents potential application in the practical detection of P4R.
-
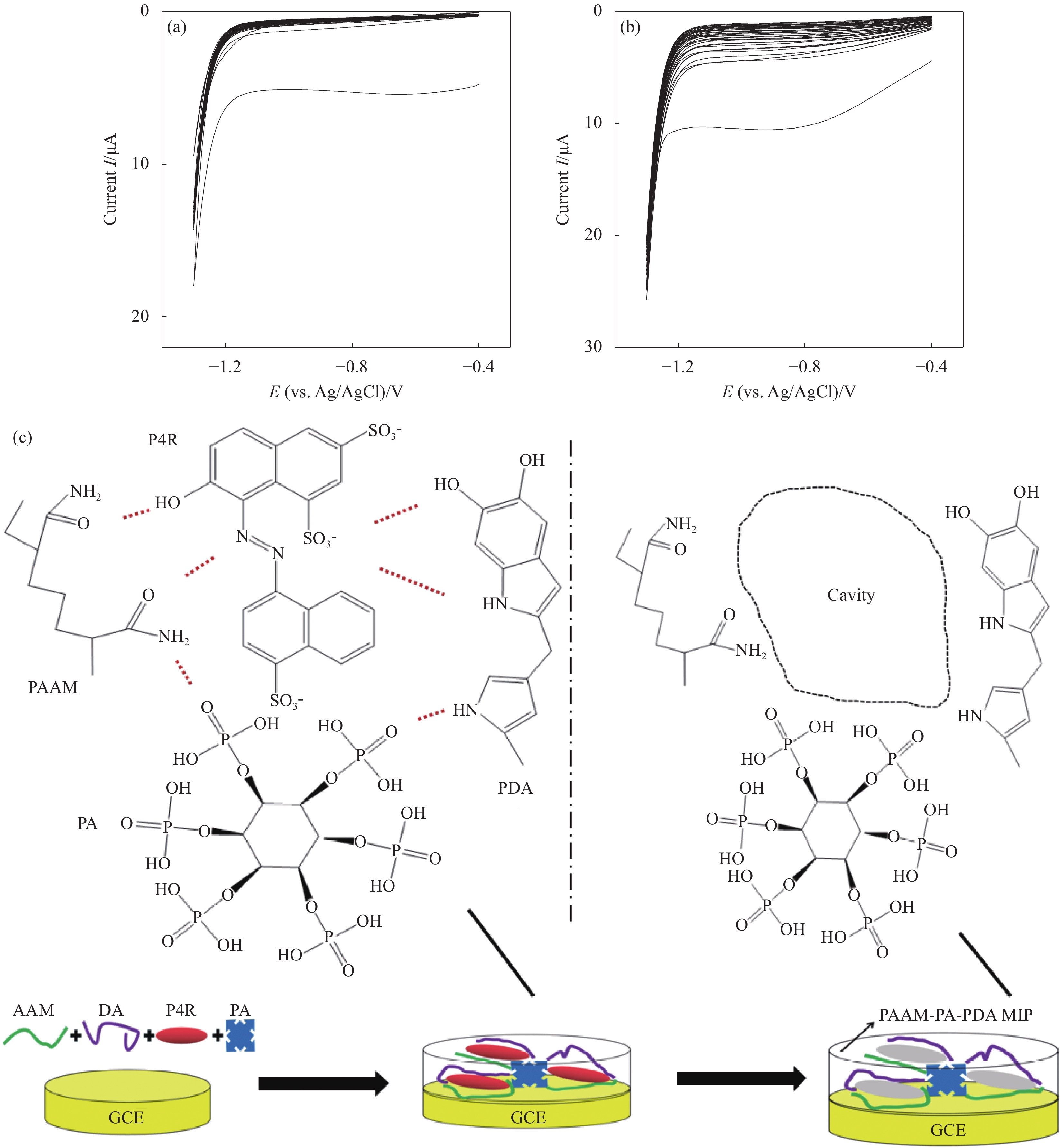
图 1 原位聚合聚丙烯酰胺(PAAM) (a)、原位聚合PAAM-植酸(PA)-聚多巴胺(PDA)导电分子印迹膜(MIP)的循环伏安图 (b),PAAM-PA-PDA MIP原位电聚合结合碱液洗脱的示意图 (c)
Figure 1. In-situ electrochemical polymerization of polyacrylamide (PAAM) (a), in-situ electrochemical polymerization of PAAM-phytic acid (PA)-polydopamine (PDA) conductive molecularly imprinted membrane (MIP) (b) by CV curves; schematic illustration of PAAM-PA-PDA MIP using the in-situ electrochemical polymerization and alkaline elution (c)
GCE—Glassy carbon electrode; PA—Polyamide; DA—Dopareine; AAM—Acrylamide; P4R—Ponceau 4R
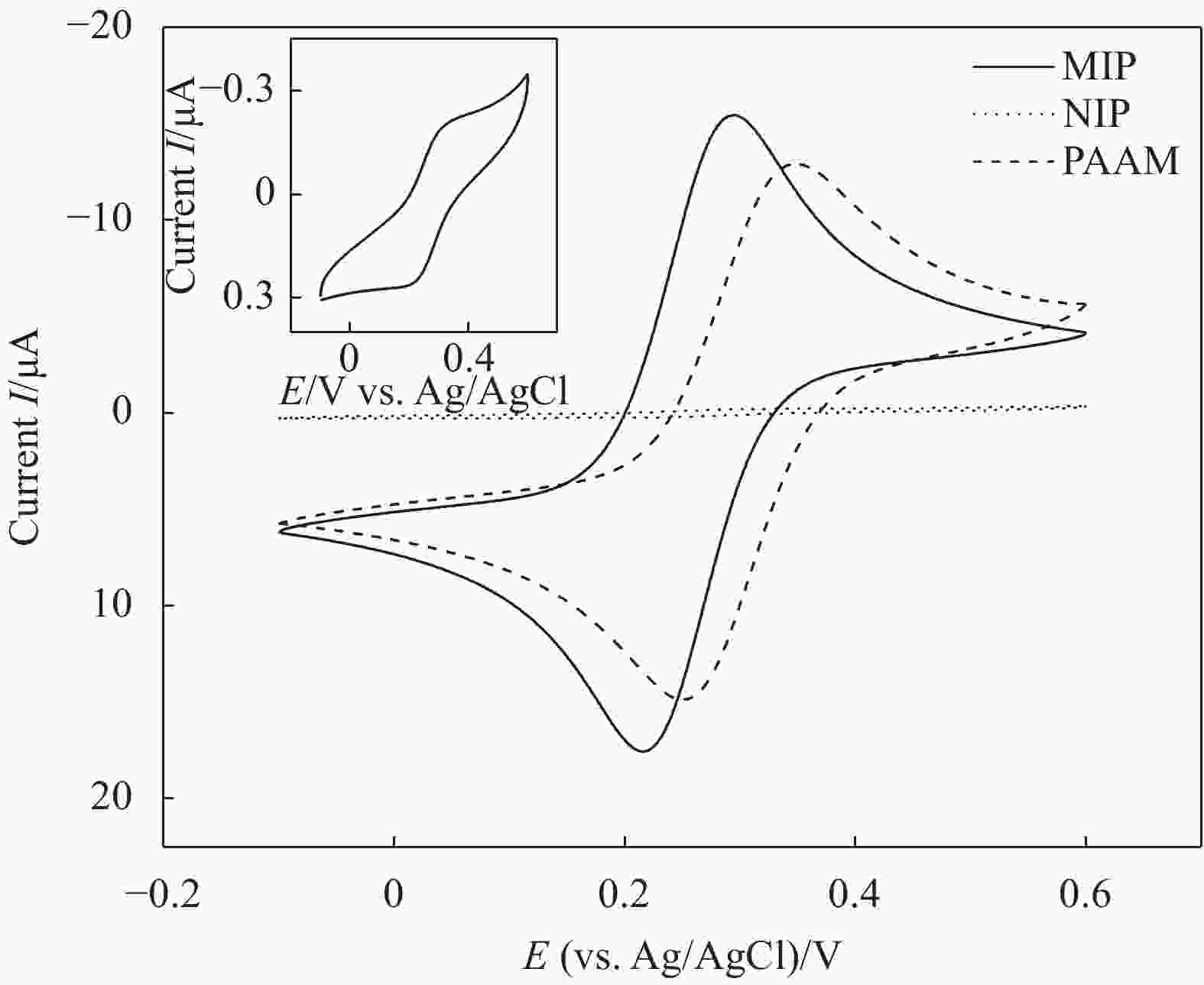
图 3 [Fe(CN)6]3−探针离子在PAAM修饰电极、PAAM-PA-PDAMIP修饰电极和非分子印迹膜(NIP)修饰电极上的循环伏安曲线(插图为PAAM修饰电极的循环伏安曲线)
Figure 3. CV curves obtained for the [Fe(CN)6]3− as electrochemical probe ion on the PAAM modified electrode, PAAM-PA-PDA MIP modified electrode and non-molecularly imprinted (NIP) modified electrode (Inset is the CV curve of PAAM modified electrode)
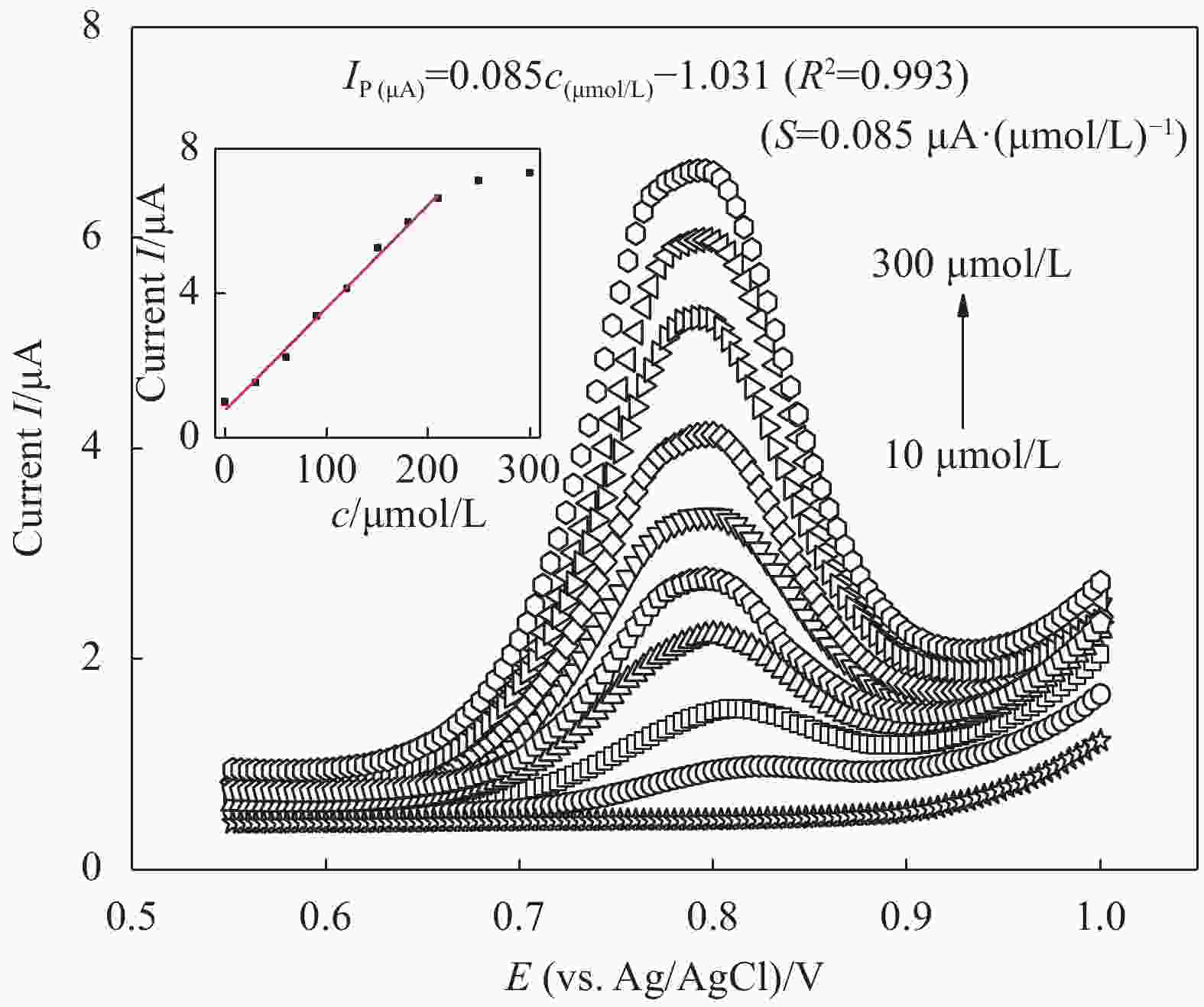
图 5 不同浓度下(10~300 μmol/L)P4R在PAAM-PA-PDA MIP修饰电极上的DPV曲线(插图为DPV峰电流与P4R浓度之间的标准曲线)
Figure 5. DPV curves obtained for the different P4R concentrations (10-300 μmol/L) at the PAAM-PA-PDA MIP modified electrode (Inset is the standard curve based on the relationship between peak current and P4R concentration)
表 1 与其他检测P4R的文献报道进行性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of the proposed electrode with other electrodes for the determination of P4R
-
[1] QU D, GU Y, FENG L, et al. High content analysis technology for evaluating the joint toxicity of sunset yellow and sodium sulfite in vitro[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,233:135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.102 [2] TANAKA T. Reproductive and neurobehavioural toxicity study of Ponceau 4R administered to mice in the diet[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2006,44(10):1651-1658. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2006.05.001 [3] MINIOTI K S, SAKELLARIOU C F, THOMAIDIS N S. Determination of 13 synthetic food colorants in water-soluble foods by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2007,583(1):103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2006.10.002 [4] YI J, ZENG L, WU Q, et al. Sensitive simultaneous determination of synthetic food colorants in preserved fruit samples by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2018,11(6):1608-1618. doi: 10.1007/s12161-017-1141-6 [5] BEVZIUK K, CHEBOTAREV A, SNIGUR D, et al. Spectrophotometric and theoretical studies of the protonation of Allura Red AC and Ponceau 4R[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2017,1144:216-224. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.05.001 [6] BENVIDI A, ABBASI S, GHARAGHANI S, et al. Spectrophotometric determination of synthetic colorants using PSO-GA-ANN[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,220:377-384. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.010 [7] IAMMARINO M, MENTANA A, CENTONZE D, et al. Dye use in fresh meat preparations and meat products: A survey by a validated method based on HPLC-UV-diode array detection as a contribution to risk assessment[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2020,55(3):1126-1135. [8] MASARBO R S, NIRANJANA S R, MONISHA T R, et al. Efficient decolorization and detoxification of sulphonated azo dye Ponceau 4R by using single and mixed bacterial consortia[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation,2019,37(5):367-376. doi: 10.1080/10242422.2019.1568414 [9] HUANG J, ZENG Q, WANG L. Ultrasensitive electrochemical determination of Ponceau 4R with a novel ε-MnO2 microspheres/chitosan modified glassy carbon electrode[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2016,206:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.04.142 [10] YANG X, SUN D, ZENG R, et al. Trace analysis of ponceau 4R based on the signal amplification of copper-based metal-organic framework modified electrode[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2017,794:229-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.04.038 [11] ZHANG J, ZHANG S, WANG X, et al. Simultaneous determination of Ponceau-4R and Allura Red in soft drinks based on the ionic liquid modified expanded graphite paste electrode[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry,2015,95(7):581-591. doi: 10.1080/03067319.2015.1046055 [12] ALEXANDER C, ANDERSSON H S, ANDERSSON L I, et al. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years up to and including 2003[J]. Journal of Molecular Recognition: An Interdisciplinary Journal,2006,19(2):106-180. doi: 10.1002/jmr.760 [13] FISCHER E. Einfluss der configuration auf die wirkung der enzyme[J]. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft,1894,27(3):2985-2993. doi: 10.1002/cber.18940270364 [14] ASHLEY J, SHAHBAZI M A, KANT K, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation and biosensing in food analysis: Progress and perspectives[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2017,91:606-615. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.018 [15] HAN Q, SHEN X, ZHU W, et al. Magnetic sensing film based on Fe3O4@Au-GSH molecularly imprinted polymers for the electrochemical detection of estradiol[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2016,79:180-186. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.017 [16] KAN X, ZHANG T, ZHONG M, et al. CD/AuNPs/MWCNTs based electrochemical sensor for quercetin dual-signal detection[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2016,77:638-643. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.10.033 [17] LI J, XU Z, LIU M, et al. Ag/N-doped reduced graphene oxide incorporated with molecularly imprinted polymer: An advanced electrochemical sensing platform for salbutamol determination[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2017,90:210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.016 [18] WU Y, LU J, MENG M, et al. Bioinspired synthesis of PDA/SiO2-based porous ciprofloxacin-imprinted nanocomposite membrane by a polydopamine-assisted organic-inorganic method[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,309:263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.044 [19] WEI M, CHEN H, WANG S, et al. Synthesis and characterization of hybrid molecularly imprinted membrane with blending SiO2 nanoparticles for ferulic acid[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials,2017,27(2):586-597. doi: 10.1007/s10904-017-0502-3 [20] ZHOU Z, HE L, MAO Y, et al. Green preparation and selective permeation of d-Tryptophan imprinted composite membrane for racemic tryptophan[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,310:63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.070 [21] DELANEY T L, ZIMIN D, RAHM M, et al. Capacitive detection in ultrathin chemosensors prepared by molecularly imprinted grafting photopolymerization[J]. Analytical chemistry,2007,79(8):3220-3225. doi: 10.1021/ac062143v [22] TAMAYO F G, TURIEL E, MARTIN E A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction and solid-phase microextraction: recent developments and future trends[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2007,1152(1-2):32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.08.095 [23] ALVAREZ L C, CONCHEIRO A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for drug delivery[J]. Journal of Chromatography B,2004,804(1):231-245. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.12.032 [24] PAN J, XUE X, WANG J, et al. Recognition property and preparation of Staphylococcus aureus protein A-imprinted polyacrylamide polymers by inverse-phase suspension and bulk polymerization[J]. Polymer,2009,50(11):2365-2372. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2009.04.004 [25] MADDOCK S C, PASETTO P, RESMIMI M. Novel imprinted soluble microgels with hydrolytic catalytic activity[J]. Chemical Communications,2004(5):536-537. doi: 10.1039/b312631e [26] LI H, XIE C, LI S, et al. Electropolymerized molecular imprinting on gold nanoparticle-carbon nanotube modified electrode for electrochemical detection of triazophos[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2012,89:175-181. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.09.010 [27] BAI H, WANG C, CHEN J, et al. Graphene@ AuNPs modified molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the determination of colchicine in pharmaceuticals and serum[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2018,816:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.02.061 [28] WANG H H, CHEN X J, LI W T, et al. ZnO nanotubes supported molecularly imprinted polymers arrays as sensing materials for electrochemical detection of dopamine[J]. Talanta,2018,176:573-581. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.083 [29] DUAN D, YANG H, DING Y, et al. Three-dimensional molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on Au NPs@Ti-based metal-organic frameworks for ultra-trace detection of bovine serum albumin[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2018,261:160-166. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.12.146 [30] ZHAO Z, CHEN H, ZHANG H, et al. Polyacrylamide-phytic acid-polydopamine conducting porous hydrogel for rapid detection and removal of copper (II) ions[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2017,91:306-312. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.047 [31] ARVAND M, ZAMANI M, ARDAKI M S. Rapid electrochemical synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers on functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective recognition of sunset yellow in food samples[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical,2017,243:927-939. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.077 [32] LIU Y, AI K, LU L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields[J]. Chemical Reviews,2014,114(9):5057-5115. doi: 10.1021/cr400407a [33] GAO Z, WANG L, SU R, et al. A carbon dot-based “off-on” fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of phytic acid[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2015,70:232-238. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.03.043 [34] LI Y, LI Y, HONG M, et al. Highly sensitive protein molecularly imprinted electro-chemical sensor based on gold microdendrites electrode and prussian blue mediatedamplification[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2013,42:612-617. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2012.10.069 [35] BECK F. Electrodeposition of polymer coatings[J]. Electrochimica Acta,1988,33(7):839-850. doi: 10.1016/0013-4686(88)80080-X [36] LIAN W, LIU S, YU J, et al. Electrochemical sensor using neomycin-imprinted film as recognition element based on chitosan-silver nanoparticles/graphene-multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites modified electrode[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2013,44:70-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.01.002 [37] YANG Y, YI C, LUO J, et al. Glucose sensors based on electrodeposition of molecularly imprinted polymeric micelles: A novel strategy for MIP sensors[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2011,26(5):2607-2612. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.11.015 [38] HUANG J, XING X, ZHANG X, et al. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotube-gold nanoparticle composites and chitosan for the detection of tyramine[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(1):276-281. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.10.020 [39] BARD A. Electrochemical merhods: Fundamentals and applications[M]. 4th ed. New York: Academik Press Inc, 1980: 290. [40] ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, LU X, et al. Multi-wall carbon nanotube film-based electrochemical sensor for rapid detection of Ponceau 4R and Allura Red[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,122(3):909-913. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.035 [41] YANG X, QIN H, GAO M, et al. Simultaneous detection of Ponceat 4R and tartrazine in food using adsorptive stripping voltammetry on an acetylene black nanoparticle-modified electrode[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2011,91(15):2821-2825. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4527 [42] ZHANG J, WANG M, SHENTU C, et al. Simultaneous determination of the isomers of Ponceau 4R and Amaranth using an expanded graphite paste electrode[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,160:11-15. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.03.078 [43] ZHAO Z, CHEN H, MA L, et al. A label-free electrochemical impedance aptasensor for cylindrospermopsin detection based on thionine-graphene nanocomposites[J]. Analyst,2015,140(16):5570-5577. doi: 10.1039/C5AN00704F -






 下载:
下载: