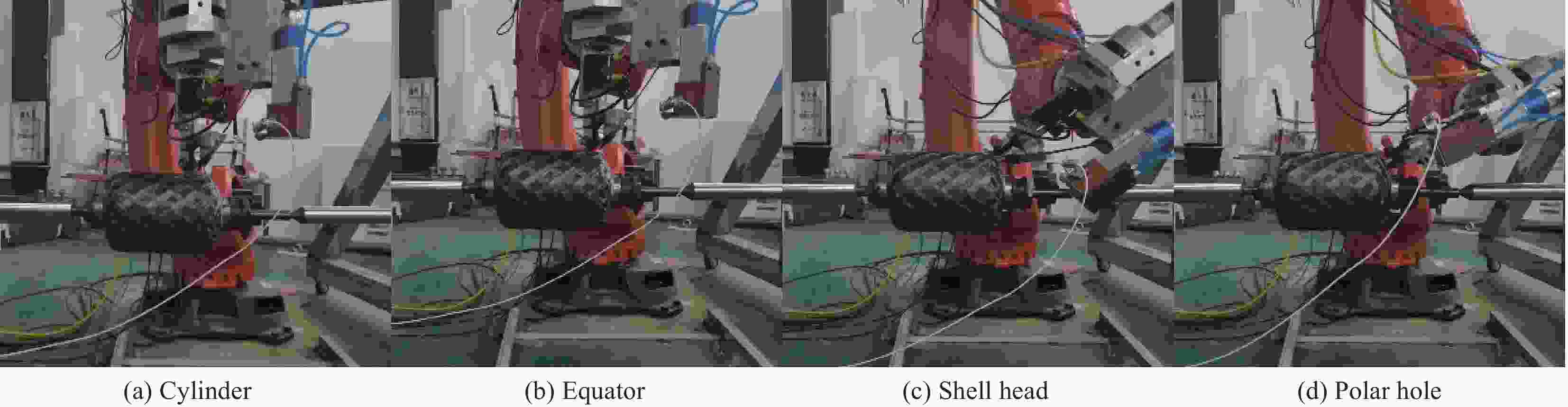
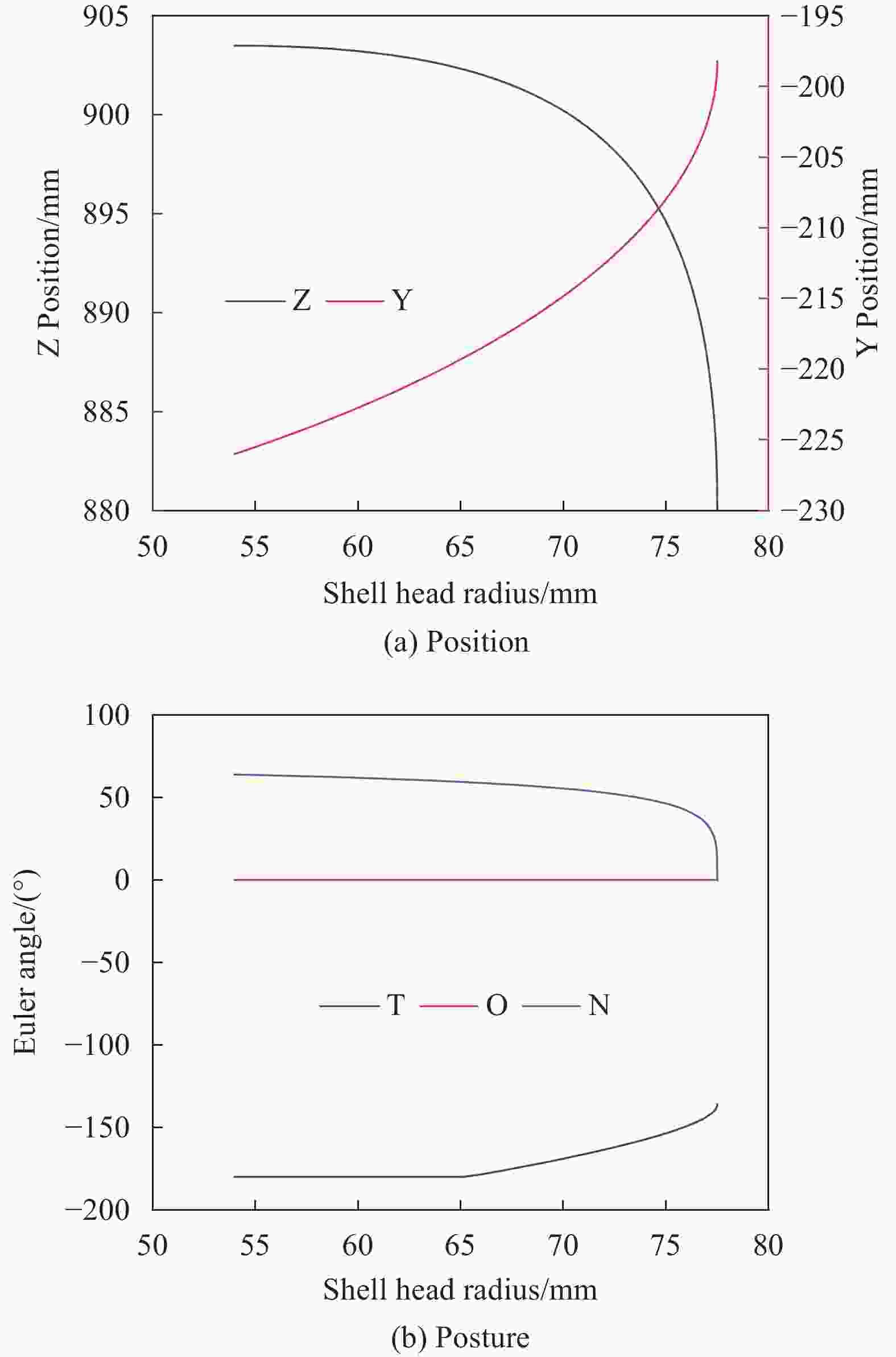
Trajectory planning of in-situ fiber placement for carbon fiber composite shells
-
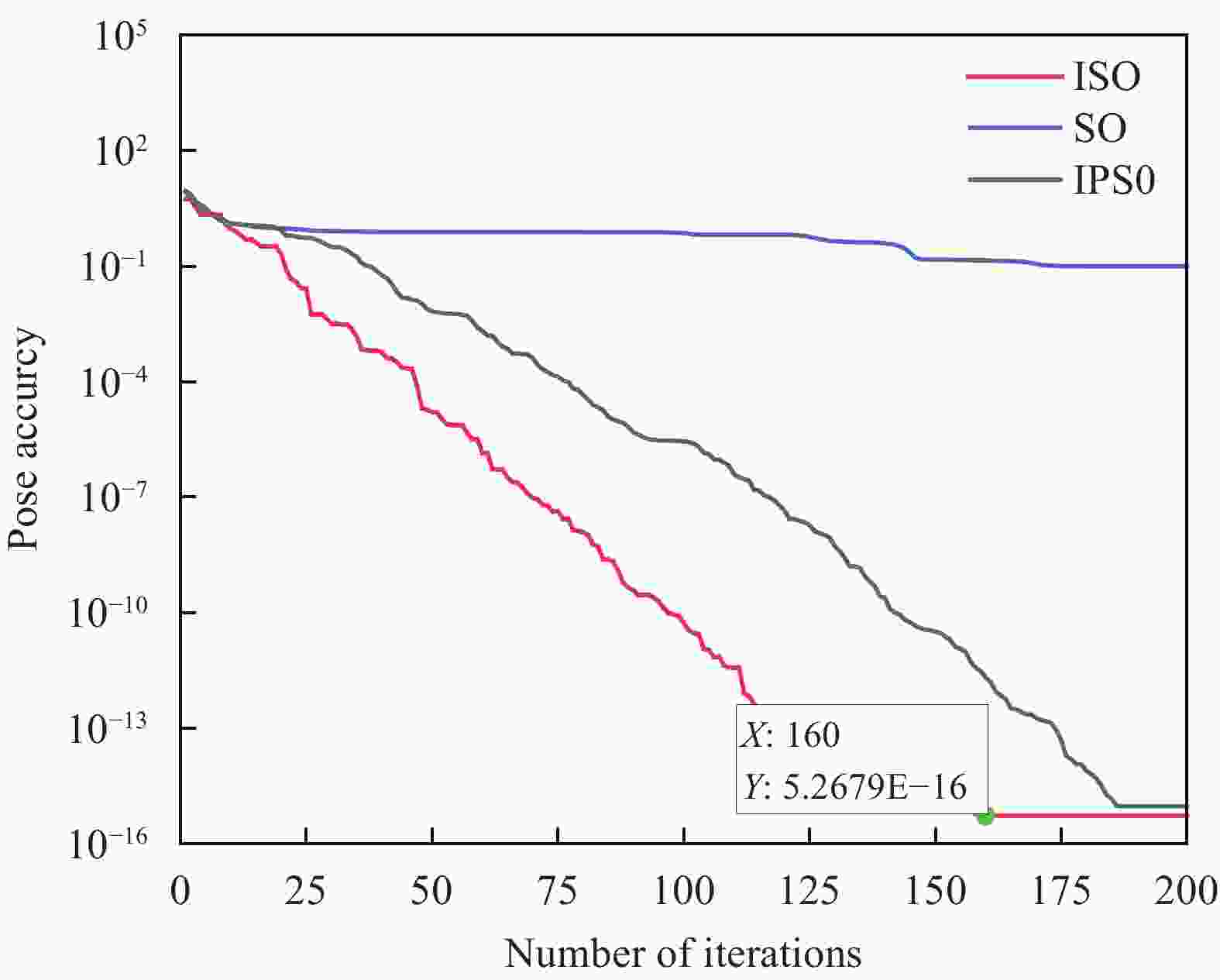
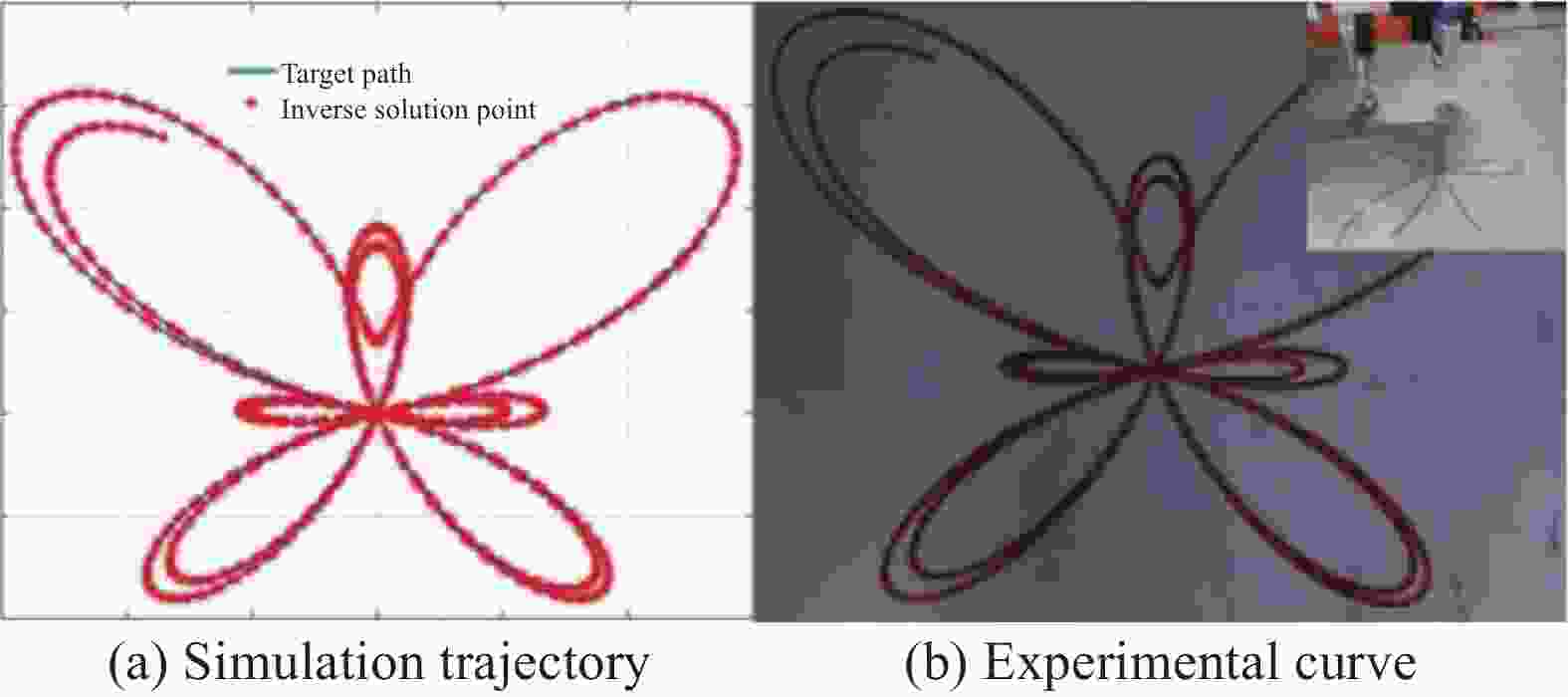
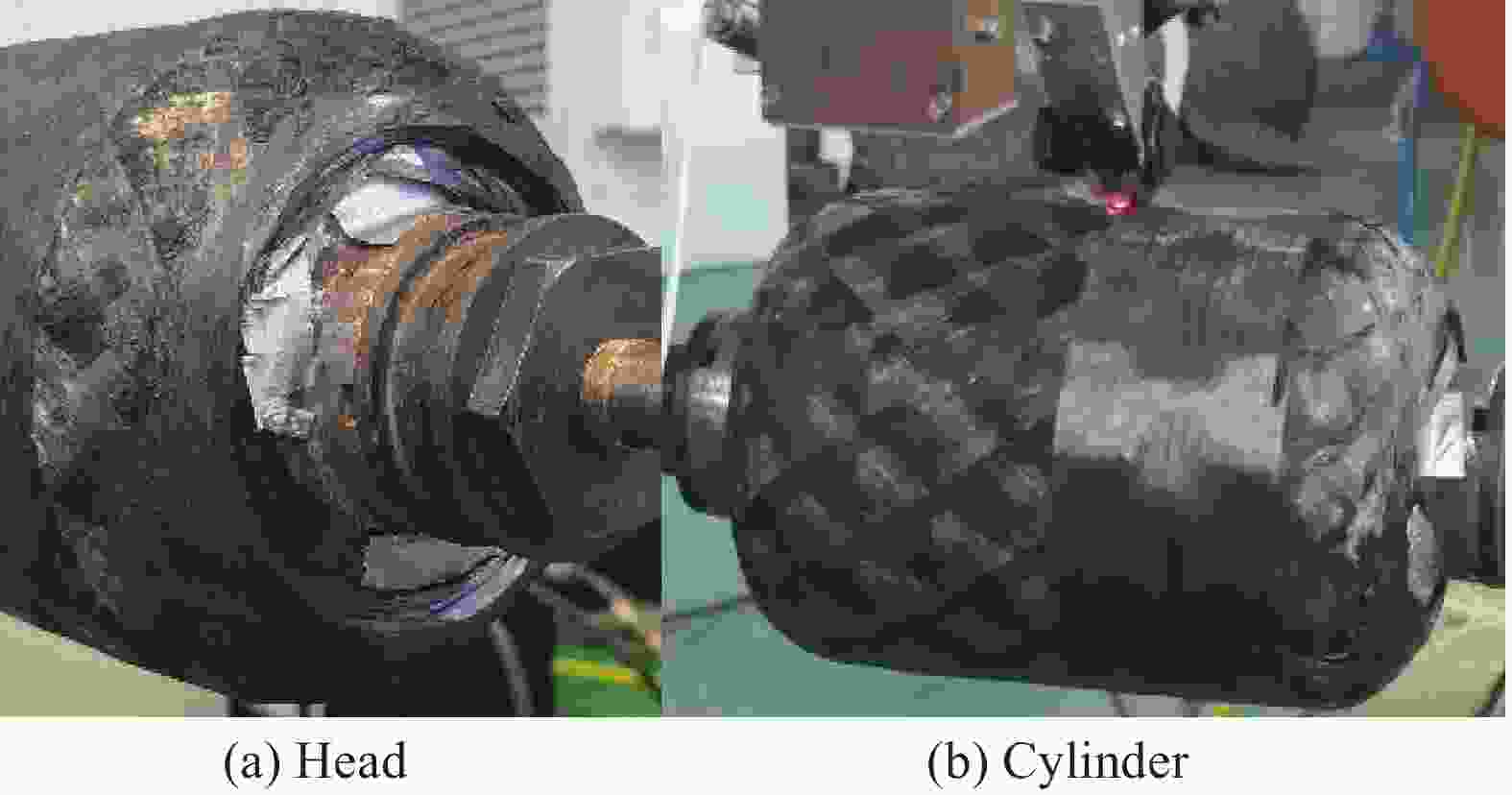
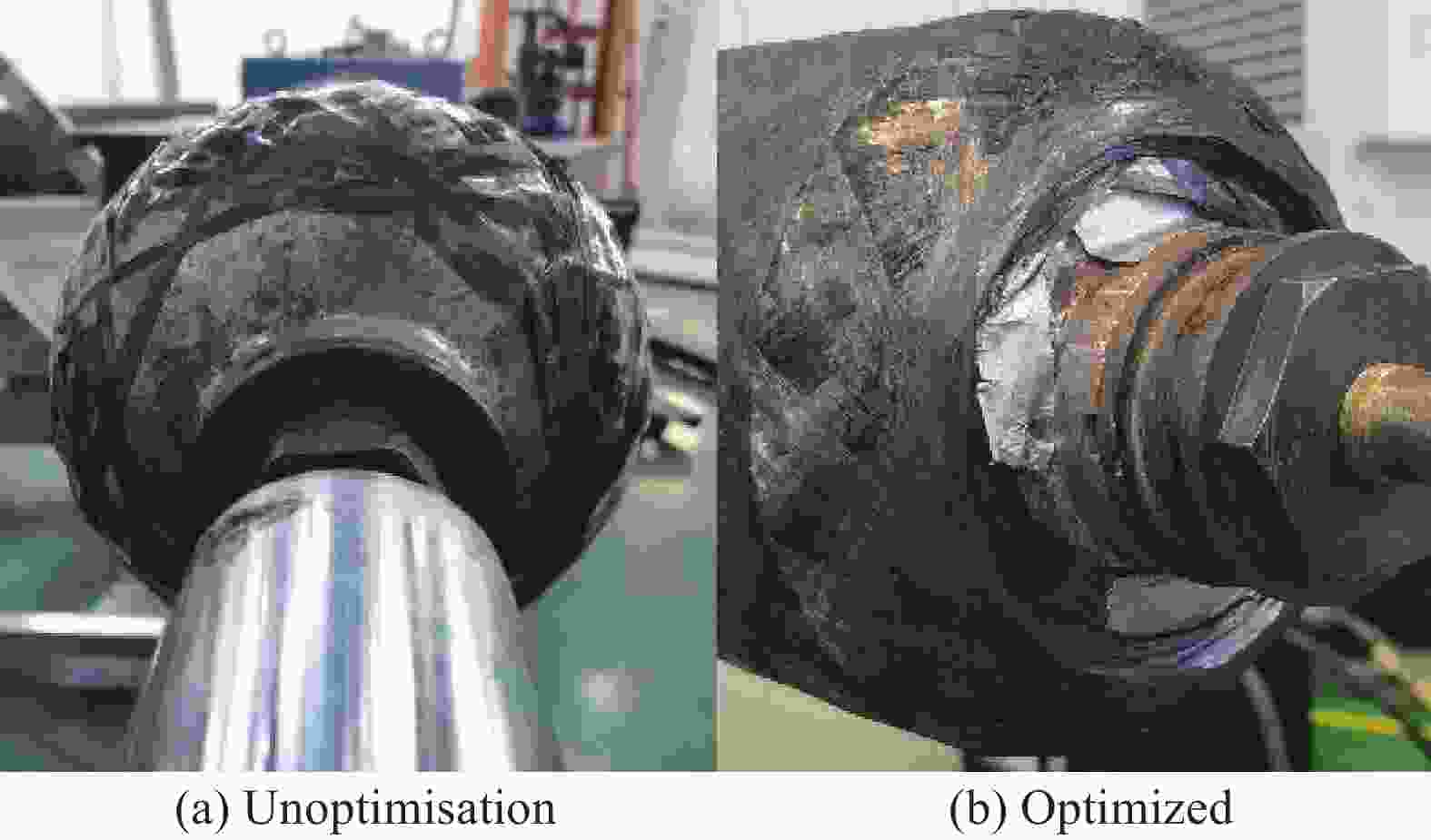
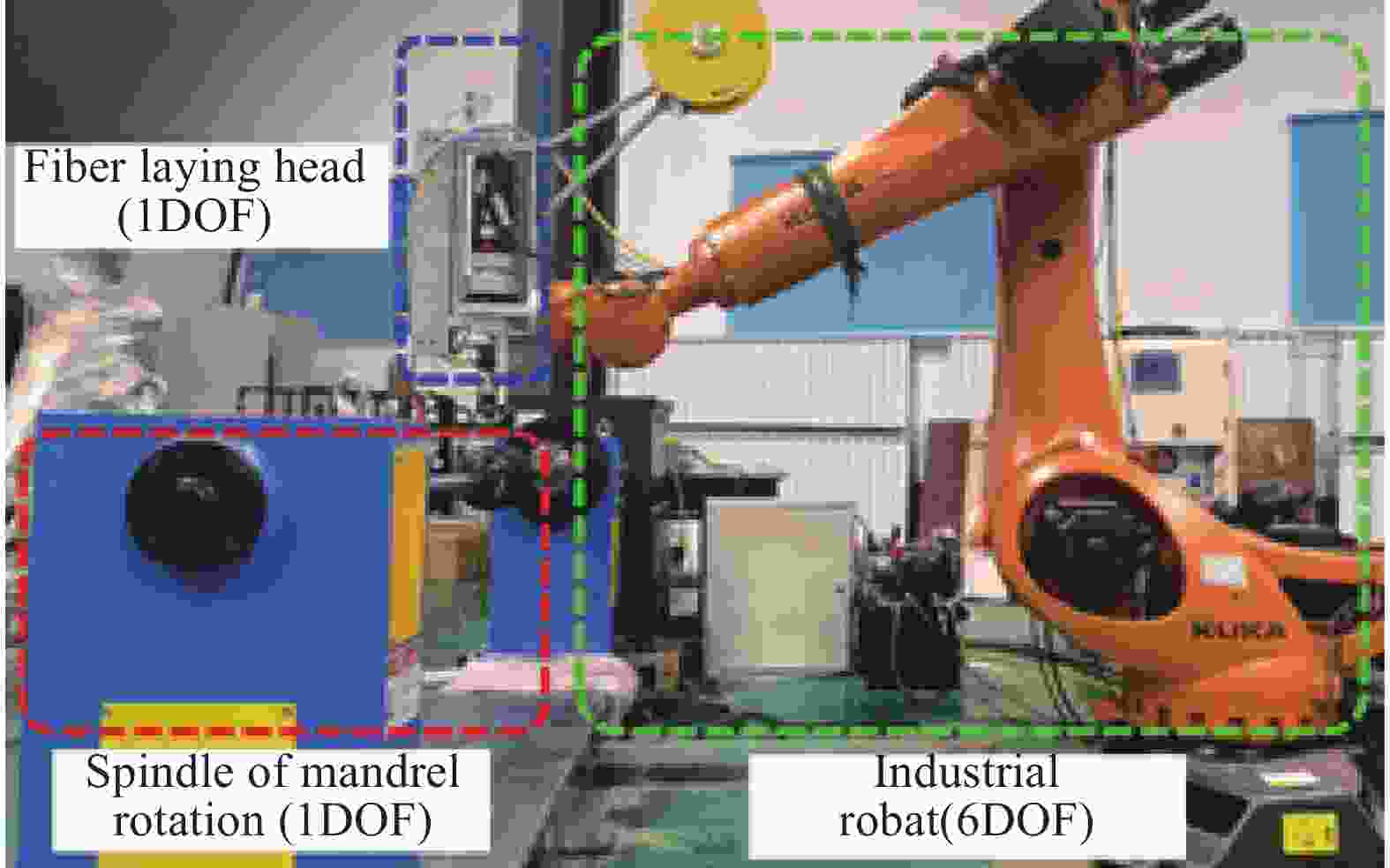
摘要: 针对复合材料壳体封头预浸带铺放原位成型过程中多功能铺放头末端滑移问题,开展对碳纤维复合材料铺放机器人轨迹规划的研究。通过构建预浸带铺放路径模型获取铺放角与中心转角,利用中心转角进行动静坐标转换并运用微分几何解算出铺放位姿,通过改进原始蛇优化算法来提高算法收敛速度与精度并应用于铺放机器人逆运动学,逆解铺放位姿获取铺放机器人前七轴关节角度匹配中心转角实现铺放头末端滑移抑制。进行椭球壳体预浸带铺放原位成型仿真与实验。结果表明,预浸带铺放轨迹规划方法在不等极孔壳体预浸带铺放原位成型实验中没有发生滑移与褶皱现象,铺放位姿精度为10−16;满足预浸带铺放原位成型位姿精度要求,能够应用于实际预浸带铺放原位成型工作。Abstract: To address slippage issues at the end of a multi-function laying head, a prepreg tape laying trajectory planning method for robot placing carbon fiber composite material is proposed. First, laying angles and center angles are obtained based on a prepreg tape laying path model. A differential geometric solution is applied to transition from dynamic to static coordinates based on the center angle, enabling calculation of the paving pose. Second, the convergence speed and calculation accuracy are enhanced by refining the original Snake Optimization Algorithm and incorporating it into the inverse kinematics of the laying robot. Inverse kinematics is employed to obtain the joint angles of the front seven axes of the laying robot from the laying pose. Matching the joint angles to the center angles effectively suppresses slippage at the end of the placement head. Finally, simulations and experiments are conducted on in-situ molding of ellipsoid shell tow laying. The results demonstrate no occurrences of slippage or wrinkles during the in-situ molding experiment involving the laying out of tows for unequal pole hole shells. The laying pose accuracy reaches 10−16, meeting the precision requirements for in-situ molding pose of tow laying, thus making it suitable for practical applications in tow laying in-situ molding work.
-
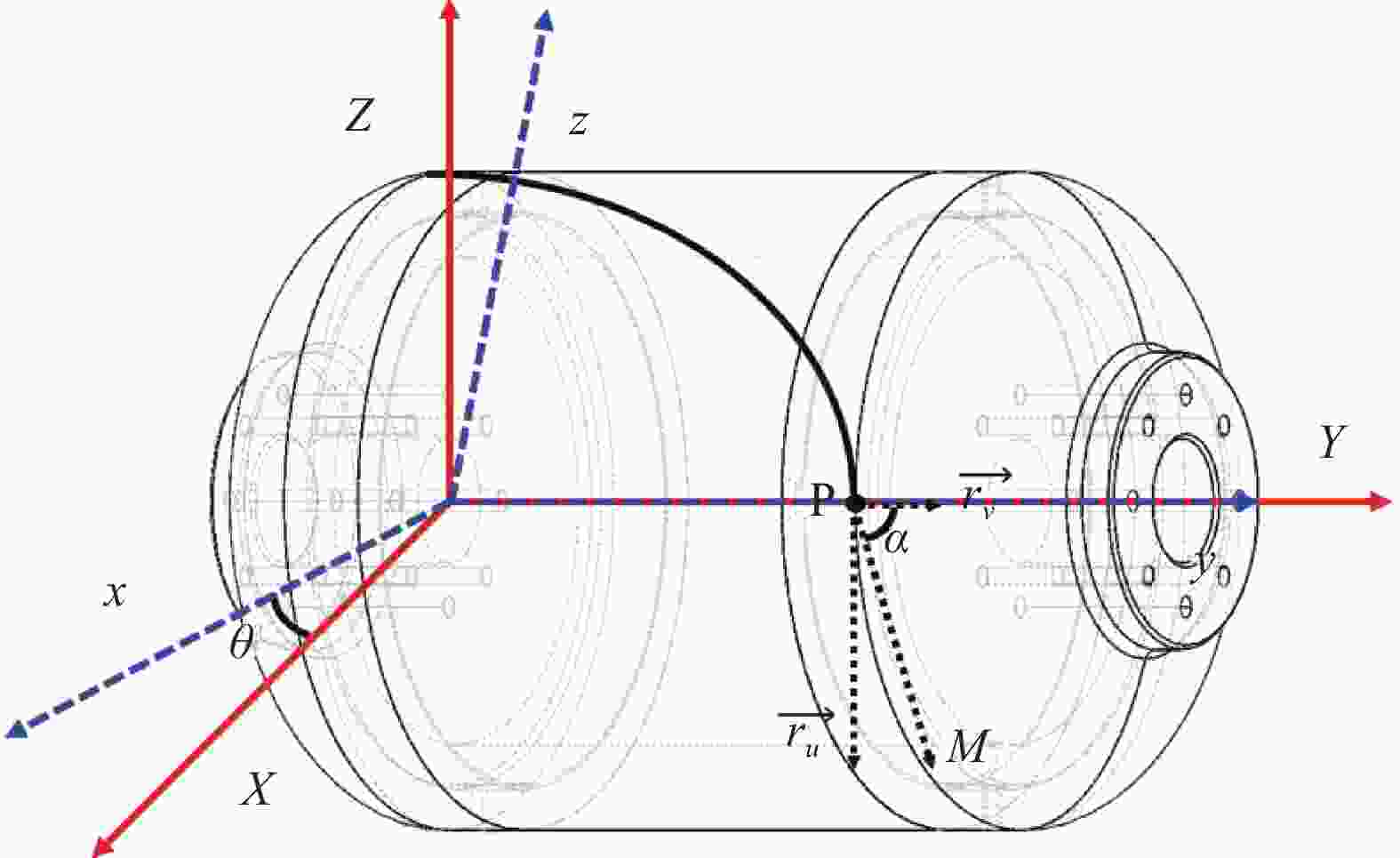
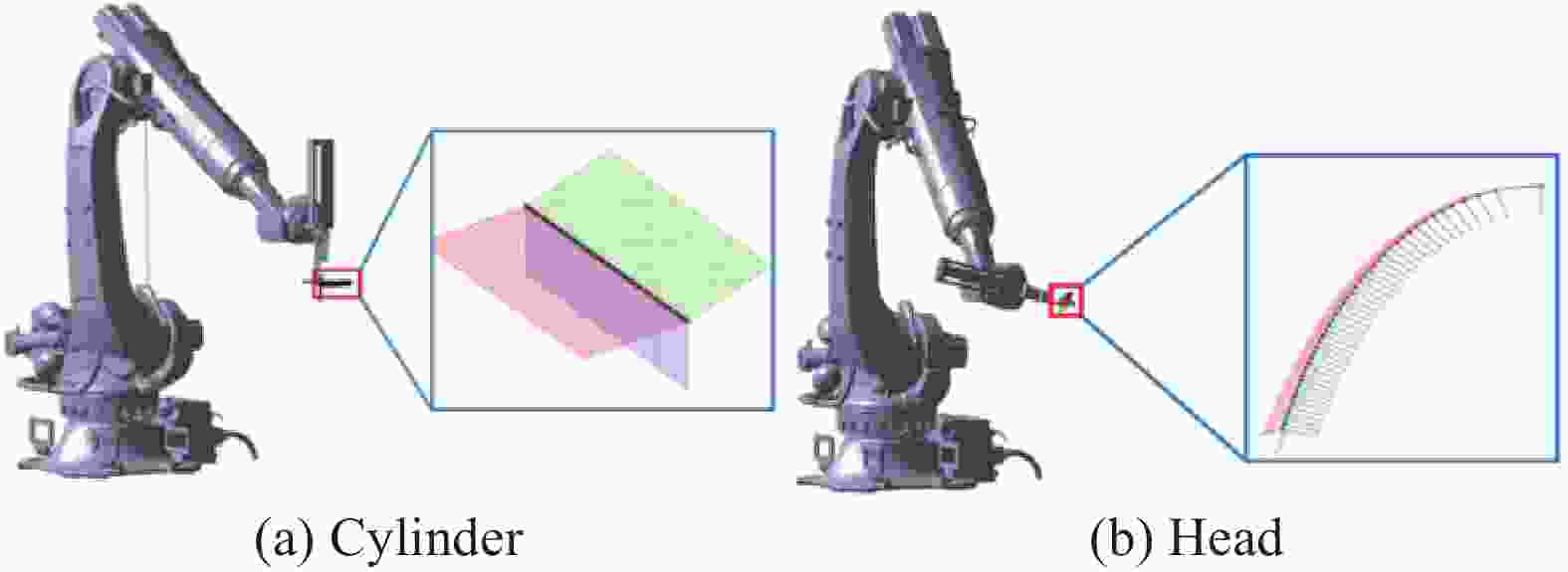
图 3 铺放点轨迹示意图
Figure 3. Schematic of the trajectory of the laying point
PM is the direction of the tangent line to the laying point P, α is the lay angle when laying point P,$ \theta $ is the center angle, $ \overrightarrow{{r}_{u}} $ and $ \overrightarrow{{r}_{x}} $ are the first order partial derivative of the rotary surface of the mandrel
表 1 铺放机器人MDH参数
Table 1. MDH parameters for fiber-placement robot
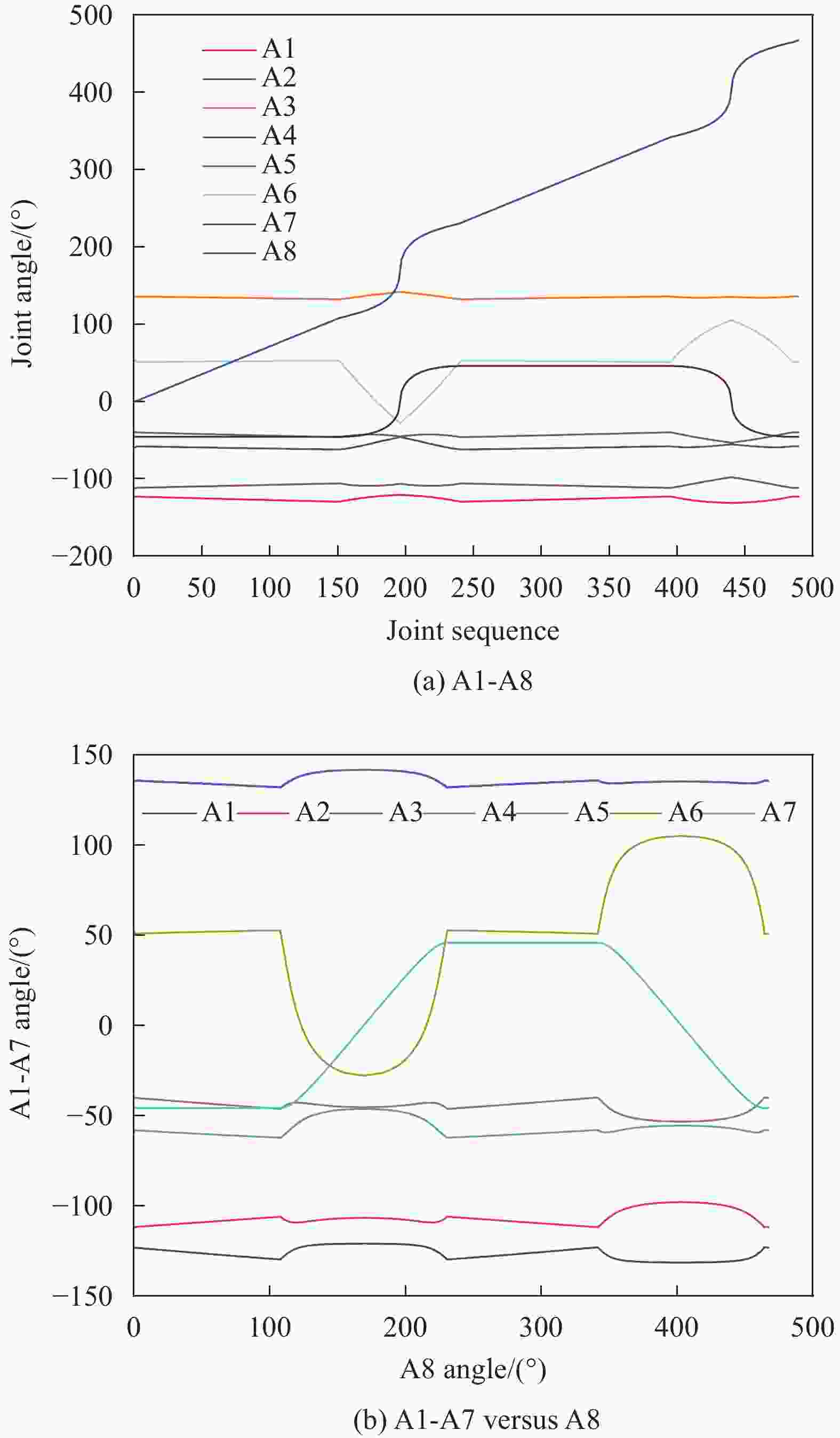
$ i $ $ {a}_{i}/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ $ {\alpha }_{i}/\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d} $ $ {d}_{i}/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ $ {\theta }_{i}/\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d} $ $ offse{t}_{i}/\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d} $ 1 0 $ {\text{π}} $ −645 $ {\theta }_{1} $ 0 2 330 $ {\text{π}} /2 $ 0 $ {\theta }_{2} $ 0 3 1150 0 0 $ {\theta }_{3} $ $ {\text{π}} /2 $ 4 115 $ -{\text{π}} /2 $ 1220 $ {\theta }_{4} $ 0 5 0 $ {\text{π}} /2 $ 0 $ {\theta }_{5} $ 0 6 0 $ -{\text{π}} /2 $ 215 $ {\theta }_{6} $ 0 7 0 $ {\text{π}} /2 $ 0 $ {\theta }_{7} $ 0 Notes: $ i $ is the sequence of fiber-placement robot joints, ai is the length of the fiber-placement robot linkage, $ {\alpha }_{i} $ is the fiber-placement robot linkage angle, $ {d}_{i} $ is the fiber-placement robot linkage bias, $ {\theta }_{i} $ is the fiber-placement robot joint position, and $ offse{t}_{i} $ is the laying robot joint bias. 表 2 不同优化算法求解结果
Table 2. Results of different optimization algorithms
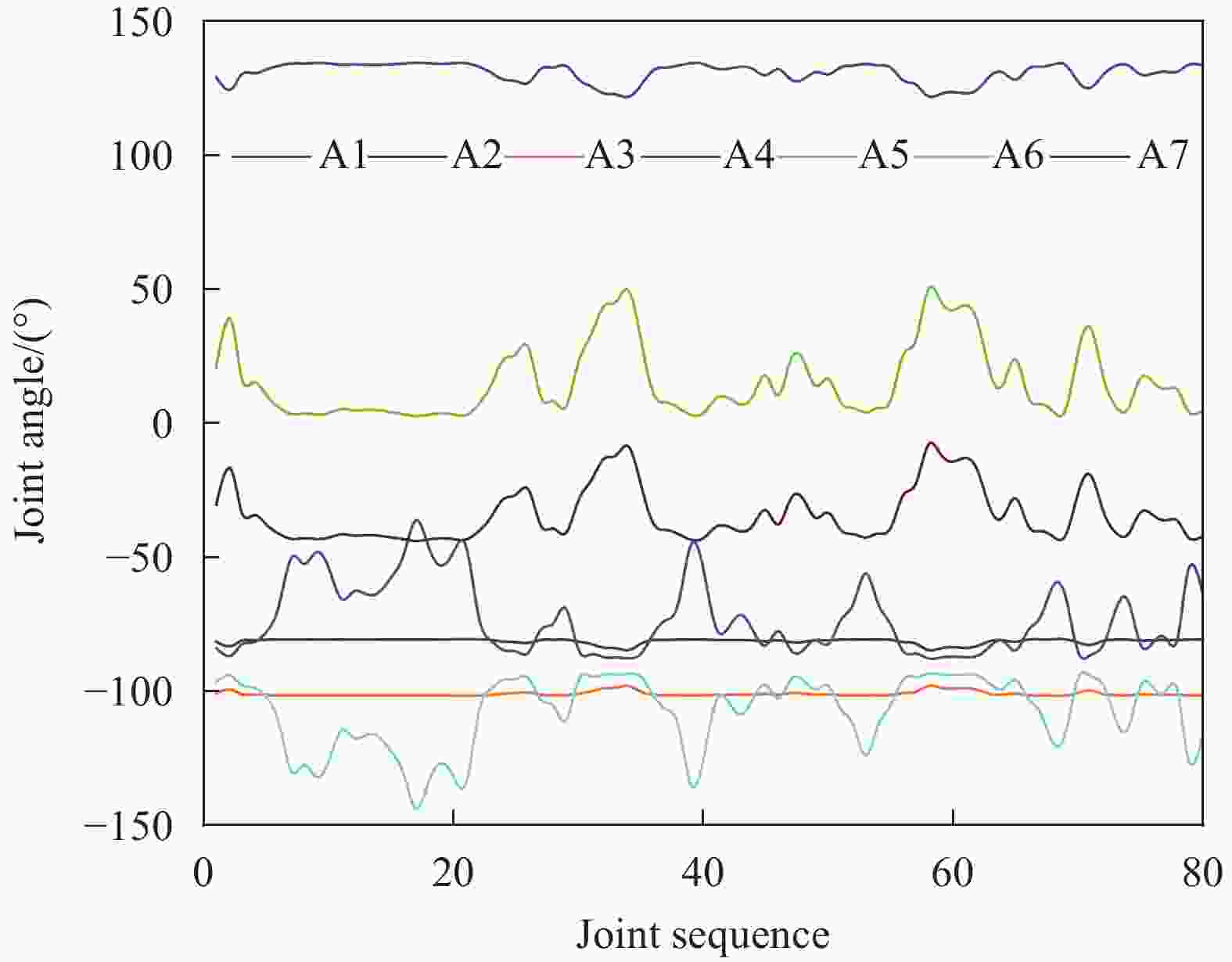
A1 A2 A3 IPSO 81.2 −112.4 −87.5 SO −89.4 −71.8 114.5 ISO −89.5 −87.4 133.9 A4 A5 A6 A7 −53.5 20.1 174.9 42.9 92.3 215.1 29.9 −95.2 33.7 −88.2 −59.4 −18.4 Notes:Improved Swarm Optimisation Algorithm(IPSO), Snake Optimisation Algorithm(SO), Improved Snake Optimisation Algorithm(ISO) -
[1] ALMUSHAIKEH A M, ALASWAD S O, ALSUHYBANI M S, et al Manufacturing of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastics and its recovery of carbon fiber: A review[J]. Polymer Testing, 2023, 122: 108029. [2] CHEN J, FU K, LI Y. Understanding pro-cessing parameter effects for carbon fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites manu-factured by laser-assisted automated fibre placement (AFP)[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2021, 140: 106160. [3] ANDRIANOV A, TOMITA E K, VERAS C A G, et al. A Low-Cost Filament Winding Tech-nology for University Laboratories and Startups[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(5): 1066. [4] DE CARVALHO J, LOSSIE M, VANDEPITTE D, et al. Optimization of filament-wound parts based on non-geodesic winding[J]. Compo-sites Manufacturing, 1995, 6(2): 79-84. [5] ZU L, XU H, WANG H, et al. Design and analysis of filament-wound composite pres-sure vessels based on non-geodesic wind-ing[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 207: 41-52. [6] 郭凯特, 王春, 文立华, 等. 不等开口纤维增强树脂复合材料缠绕壳体非测地线线型设计[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(5): 1189-1199.GUO K, WANG C, WEN L, et al. Winding pattern design of fiber reinforced resin polymer composites winding vessels with unequal polar openings based on non-geodesics[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(5): 1189-1199 (in Chinese). [7] 尤波, 王燕, 许家忠, 等. 干纤维增强橡胶膨胀节缠绕线型设计及仿真[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2016, (10): 15-19.YOU B, WANG Y, XU J, et al. Design and Simulation of Winding Pattern of dry fiber reinforced Rubber Expansion Joint[J]. Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic/Composite Materials, 2016, (10): 15-19(in Chinese). [8] DALIBOR I H, LISBÔA T V, MARCZAK R J, et al. Optimum slippage dependent, non-geodesic fiber path determination for a filament wound composite nozzle[J]. Euro-pean Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids, 2020, 82: 103994. [9] ZAPLANA I, BASANEZ L. A novel closed-form aolution for the inverse kinematics of re-dundant manipulators through workspace analysis[J]. [10] JIN M, LIU Q, WANG B, et al. An Efficient and Accurate Inverse Kinematics for 7-DOF Redundant Manipulators Based on a Hybrid of Analytical and Numerical Method[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 16316-16330. [11] SHIMIZU M, KAKUYA H, YOON W-K, et al. Analytical Inverse Kinematic Computation for 7-DOF Redundant Manipulators With Joint Limits and Its Application to Redun-dancy Resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(5): 1131-1142. [12] OH S-Y, ORIN D, BACH M. An inverse kine-matic solution for kinematically redundant robot manipulators[J]. Journal of Robotic Systems, 1984, 1(3): 235-249. [13] GOLDENBERG A, BENHABIB B, FENTON R. A complete generalized solution to the inverse kinematics of robots[J]. IEEE Journal on Robotics and Automation, 1985, 1(1): 14-20. [14] CHIACCHIO P, CHIAVERINI S, SCIAVICCO L, et al. Closed-Loop Inverse Kinematics Schemes for Constrained Redundant Ma-nipulators with Task Space Augmentation and Task Priority Strategy[J]. The Interna-tional Journal of Robotics Research, 1991, 10(4): 410-425. [15] BAILLIEUL J. KINEMATIC Programming alterna-tives for redundant manipula-tors[C]//Proceedings. 1985 IEEE Interna-tional Conference on Robotics and Automa-tion. St. Louis, MO, USA: Institute of Elec-trical and Electronics Engineers, 1985: 722–728[2023-09-12]. [16] TEVATIA G, SCHAAL S. Inverse kinematics for humanoid robots[C]//Proceedings 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE In-ternational Conference on Robotics and Au-tomation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37065). San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2000: 294–299[2023-09-12]. [17] SIMAS H, DI G R. A Technique Based on Adaptive Extended Jacobians for Improving the Robustness of the Inverse Numerical Kinematics of Redundant Ro-bots[J]. Journal of Mechanisms and Robot-ics, 2019, 11(2): 020913. [18] WANG X, CAO J, LIU X, et al. An Enhanced Step-Size Gaussian Damped Least Squares Method Based on Machine Learning for In-verse Kinematics of Redundant Robots[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 68057-68067. [19] NAKAMURA Y, HANAFUSA H. Inverse Kinemat-ic Solutions With Singularity Robustness for Robot Manipulator Control[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1986, 108(3): 163-171. doi: 10.1115/1.3143764 [20] LIEGEOIS A. Automatic supervisory control of the configuration and behavior of multibody mechanisms[J]. IEEE transactions on systems, man, and cybernetics, 1977, 7(12): 868-871. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1977.4309644 [21] XIE S, SUN L, CHEN G, et al. A Novel Solu-tion to the Inverse Kinematics Problem of General 7R Robots[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 67451-67469. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3184451 [22] REITER A, MULLER A, Gattringer H. On High-er Order Inverse Kinematics Methods in Time-Optimal Trajectory Planning for Kin-ematically Redundant Manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(4): 1681-1690. [23] WOLIŃSKI Ł, WOJTYRA M. A Novel QP-Based Kinematic Redundancy Resolution Method With Joint Constraints Satisfaction[J]. 2022, 10: 41023-41037. [24] GIAMOU M, MARIC F, ROSEN D M, Pere-troukhin V, Roy N, Petrovic I, Kelly J. Convex Iteration for Distance-Geometric Inverse Kinematics[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 1952-1959. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3141763 [25] TRUTMAN P, DIN M S E, HENRION D, et al. Globally Optimal Solution to Inverse Kin-ematics of 7DOF Serial Manipulator[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(3): 6012-6019. [26] SHI J, MAO Y, LI P, et al. Hybrid Mutation Fruit Fly Optimization Al-gorithm for Solving the Inverse Kinematics of a Redundant Robot Manipulator[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 2020: 1-13. [27] YIYANG L, XI J, HONGFEI B, et al. A General Robot Inverse Kinematics Solution Method Based on Improved PSO Algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 32341-32350. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3059714 [28] PENG Y, PENG Z, LAN T. Neural Network Based Inverse Kinematics Solution for 6-R Robot Implement Using R Package Neural-net[C]//2021 5th International Conference on Robotics and Automation Sciences (ICRAS). Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2021: 65–69[2022-07-08]. [29] WAGAA N, KALLEL H, MELLOULI N. Analytical and deep learning approaches for solving the inverse kinematic problem of a high de-grees of freedom robotic arm[J]. Engineer-ing Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 123: 106301. [30] WANG X, LIU X, CHEN L, et al. Deep-learning damped least squares method for inverse kinematics of redundant robots[J]. Measurement, 2021, 171: 108821. [31] KÖKER R, ÇAKAR T. A neuro-genetic-simulated annealing approach to the inverse kinematics solution of robots: a simulation based study[J]. Engineering with Comput-ers, 2016, 32(4): 553-565. doi: 10.1007/s00366-015-0432-z [32] ZHANG L, XIAO N. A novel artificial bee colony algorithm for inverse kinematics calculation of 7-DOF serial manipulators[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(10): 3269-3277. doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2975-y [33] ZENG Z, CHEN Z, SHU G, et al. Optimization of analytical inverse kinematic solution for redundant manipulators using GA-PSO al-gorithm[C]//2018 IEEE Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS). St. Peters-burg: IEEE, 2018: 446–451[2023-05-05]. [34] HASHIM F A, HUSSIEN A G. Snake Optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization algo-rithm[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 242: 108320. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108320 [35] MOHAMMAD N A, MAHLOOJI H. A re-vised particle swarm optimization based discrete Lagrange multipliers method for nonlinear programming problems[J]. Com-puters & Operations Research, 2011, 38(8): 1164-1174. [36] STORN R. Differential Evolution – A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for Global Optimiza-tion over Continuous Spaes[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 1997, 11: 341-359. doi: 10.1023/A:1008202821328 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 54
- HTML全文浏览量: 43
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: