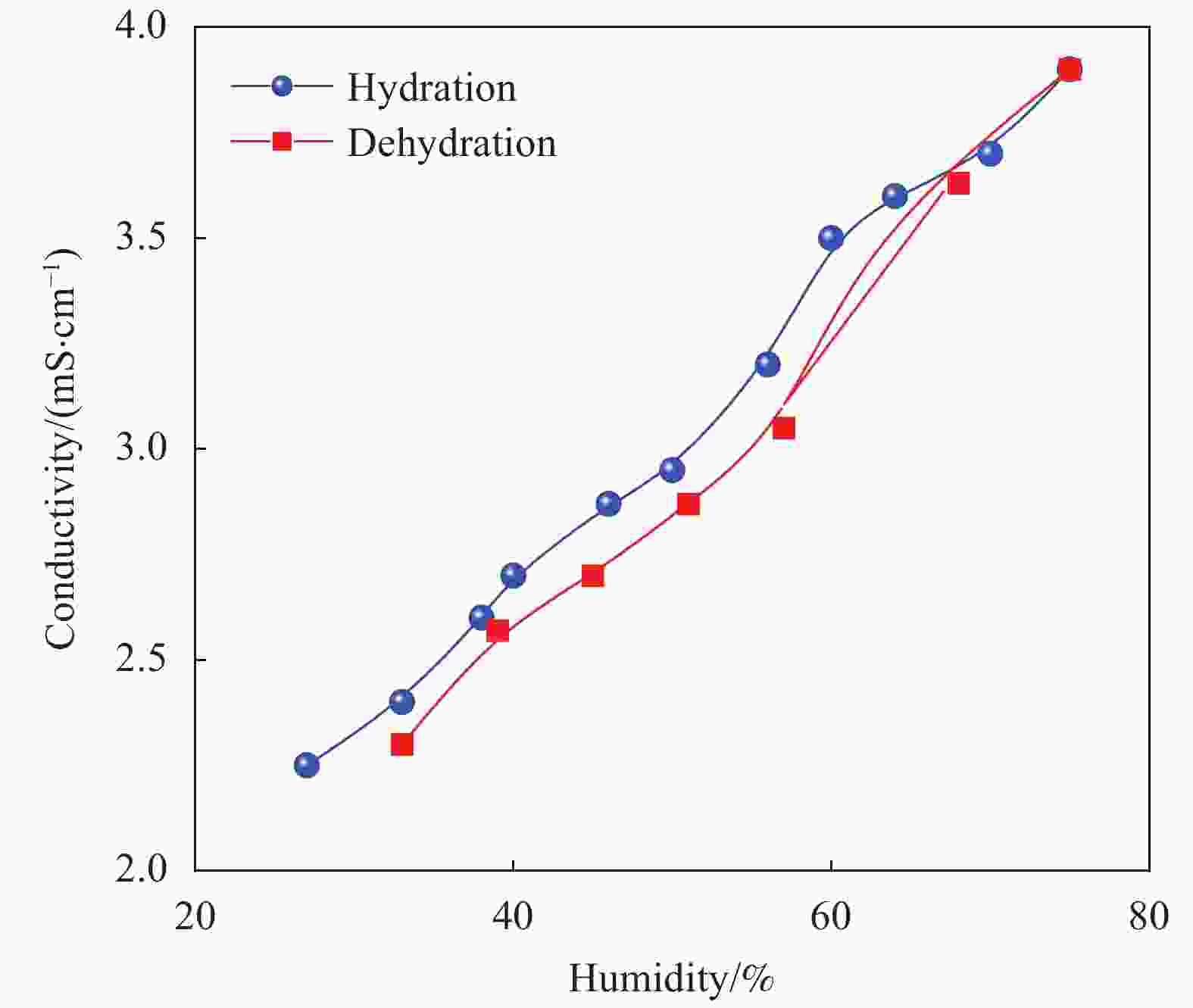
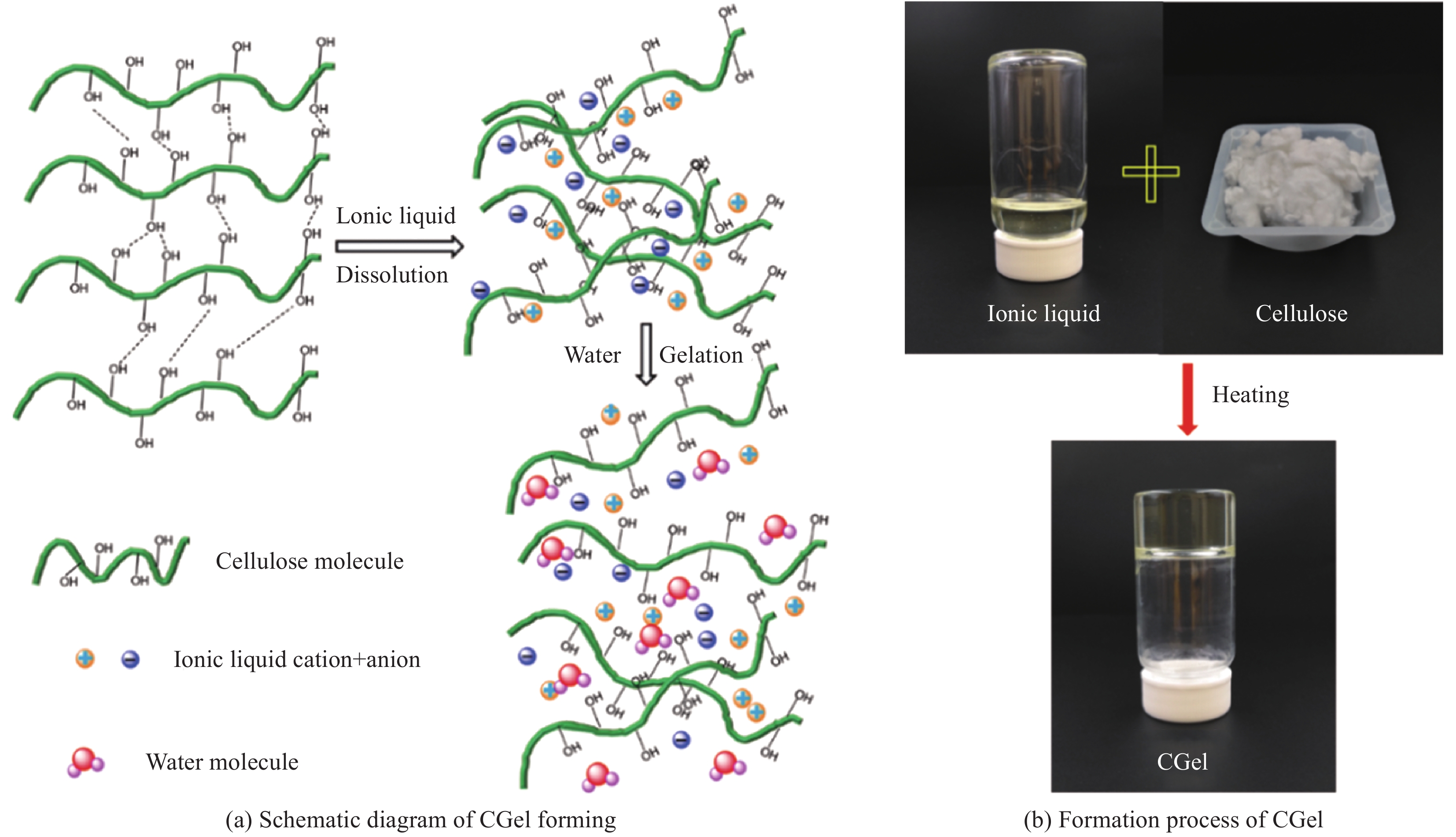
| [1] |
王晓园, 杨晓泉. 新型Ph敏感性壳聚糖/明胶水凝胶的制备及其性能[J]. 化工进展, 2009, 28(10):1781-1786.WANG Xiaoyuan, YANG Xiaoquan. Preparation and properties of a novel Ph-sensitive chitosan/gelatin hydrogel[J]. Progress in Chemical Industry,2009,28(10):1781-1786(in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
ZHANG M C, GUO R, CHEN K, et al. Microribbons composed of directionally self-assembled nanoflakes as highly stretchable ionic neural electrodes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America,2020,117(26):14667-14675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2003079117
|
| [3] |
ZHOU Y, DONG X X, MI Y Y, et al. Hydrogel smart windows[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2020,8(20):10007-10025. doi: 10.1039/D0TA00849D
|
| [4] |
黄翠萍, 黎杉珊, 漆天乐, 等. 金-铂纳米颗粒/石墨烯-纤维素微纤维复合电极材料的制备与电化学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(7):2274-2283.HUANG Cuiping, LI Shanshan, QI Tianle, et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of gold-platinum nanoparticles/ graphene-cellulose microfiber composite electrodes[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(7):2274-2283(in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
李华, 李靖靖, 王焕锋. 多孔Co3O4纳米纤维用于锂-空气电池高性能正极催化剂[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(7):2305-2312.LI Hua, LI Jingjing, WANG Huanfeng. Porous Co3O4 nano-fibers applied as an efficient cathode catalyst for Li-air batteries[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(7):2305-2312(in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
ZHANG S, ZHOU Z T, ZHONG J J, et al. Body-integrated, enzyme-triggered degradable, silk-based mechanical sensors for customized health/fitness monitoring and in Situ treatment[J]. Advanced Science,2020,7(13):1903802. doi: 10.1002/advs.201903802
|
| [7] |
王露一, 单国荣. 聚环氧乙烷对PMAPS/PAM双网络水凝胶结构和性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2012(8):2642-2647.WANG Luyi, SHAN Guorong. The effect of polyethylene oxide on structure and properties of PMAPS/PAM double network hydrogel[J]. CIESC Journal,2012(8):2642-2647(in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
ZHAO D, ZHU Y, CHENG W, et al. A dynamic gel with reversible and tunable topological networks and performances[J]. Matter,2020,2(2):390-403. doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2019.10.020
|
| [9] |
赵莉, 杜蘅, 刘虎, 等. 纳米SiO2微球在PMMA凝胶聚合物电解质中的尺寸效应及其在全固态电致变色器件中的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(5):1446-1454.ZHAO Li, DU Heng, LIU Hu, et al. Size effect of nano-SiO2 microspheresin PMMA gel polymer electrolyte and its application in all-solid-state electrochromic devices[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(5):1446-1454(in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
杨润苗, 董观秀, 赵德建, 等. 基于偶氮苯的超分子凝胶材料的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2015, 34(6):1661-1671.YANG Runmiao, DONG Guanxiu, ZHAO Dejian, et al. Research progress of supramolecular gelmaterials based on azobenzene[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2015,34(6):1661-1671(in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
CUI C, FU Q, MENG L, et al. Recent progress in natural biopolymers conductive hydrogels for flexible wearable sensors and energy devices: Materials, structures and performance[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials,2020,4(1):85-121.
|
| [12] |
刘壮, 谢锐, 巨晓洁, 等. 具有快速响应特性的环境响应型智能水凝胶的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(1): 202-208.LIU Zhuang, XIE Rui, JU Xiaojie, et al. Research progress of environmentally responsive smart hydrogels with fast response characteristics[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2016, 67(1): 202-208(in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
佘小红, 杜娟, 朱雯莉. 高强度聚苯胺-聚丙烯酸/聚丙烯酰胺导电水凝胶的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(4):1223-1230.SHE Xiaohong, DU Juan, ZHU Wenli. Preparation and properties of strong PANI-PAA/PAM conductive hydrogel[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(4):1223-1230(in Chinese).
|
| [14] |
WANG Y, ZHANG L N, LU A. Highly stretchable, transparent cellulose/PVA composite hydrogel for multiple sensing and triboelectric nanogenerators[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2020,8(28):13935-13941. doi: 10.1039/D0TA02010A
|
| [15] |
CHEN G, WANG G, TAN X, et al. Integrated dynamic wet spinning of core-sheath hydrogel fibers for optical-to-brain/tissue communications[J]. National Science Review,2020,8(9):neaa209.
|
| [16] |
LEE Y, SONG W J, JUNG Y, et al. Ionic spiderwebs[J]. Science Robotics,2020,5(44):eaaz5405.
|
| [17] |
HE K, LIU Z Y, WAN C J, et al. An on-skin electrode with anti-epidermal-surface-lipid function based on a zwitterionic polymer brush[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(24):e2001130. doi: 10.1002/adma.202001130
|
| [18] |
PEI X J, ZHANG H, ZHOU Y, et al. Stretchable, self-healing and tissue-adhesive zwitterionic hydrogels as strain sensors for wireless monitoring of organ motions[J]. Materials Horizons,2020,7(7):1872-1882. doi: 10.1039/D0MH00361A
|
| [19] |
JU M, WU B H, SUN S T, et al. Redox-active iron-citrate complex regulated robust coating-free hydrogel microfiber net with high environmental tolerance and sensitivity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(14):1910387.
|
| [20] |
CAO L, WU H, HE X Y, et al. Flexible, transparent ion-conducting membranes from two-dimensional nanoclays of intrinsic conductivity[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2019,7(44):25657-25664. doi: 10.1039/C9TA09140H
|
| [21] |
CHO K G, KIM H S, JANG S S, et al. Optimizing electrochemically active surfaces of carbonaceous electrodes for ionogel based supercapacitors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(30):2002053.
|
| [22] |
WANG Y L, LI B, SARMAN S, et al. Microstructural and dynamical heterogeneities in ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Reviews,2020,120(13):5798-5877. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00693
|
| [23] |
QIU Z G, WANG Y B, ZHOU W H, et al. Ionic skin with biomimetic dielectric layer templated from calathea zebrine leaf[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28(37):1802343.
|
| [24] |
QU X X, NIU W W, WANG R, et al. Solid-state and liquid-free elastomeric ionic conductors with autonomous self-healing ability[J]. Materials Horizons,2020,7(11):2994-3004.
|
| [25] |
YING B B, WU Q Y, LI J Y, et al. An ambient-stable and stretchable ionic skin with multimodal sensation[J]. Materials Horizons,2020,7(2):477-488. doi: 10.1039/C9MH00715F
|
| [26] |
SUN J Y, KEPLINGER C, WHITESIDES G M, et al. Ionic skin[J]. Advanced Materials,2014,26(45):7608-7614. doi: 10.1002/adma.201403441
|
| [27] |
DANG C, WANG M, YU J, et al. Transparent, highly stretchable, rehealable, sensing, and fully recyclable ionic conductors fabricated by one-step polymerization based on a small biological molecule[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2019,29(30):1902467.
|
| [28] |
YE Y H, ZHANG Y F, CHEN Y, et al. Cellulose nanofibrils enhanced, strong, stretchable, freezing-tolerant ionic conductive organohydrogel for multi-functional sensors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(35):2003430.
|
| [29] |
姜跃平, 李如燕, 孙可伟, 等. 柠檬酸交联纤维素凝胶材料的制备与性能表征[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(7):1796-1802.JIANG Yueping, LI Ruyan, SUN Kewei, et al. Preparation and characterization of citric acid cross-linked cellulose gel material[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2014,33(7):1796-1802(in Chinese).
|
| [30] |
周可可, 唐亚丽, 卢立新, 等. 氧化纳米纤维素增强再生纤维素全纤维素复合薄膜的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(7):1657-1666.ZHOU Keke, TANG Yali, LU lixin, et al. Preparation and properties of oxidized nanocellulose reinforced regenerated cellulose whole cellulose composite film[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(7):1657-1666(in Chinese).
|





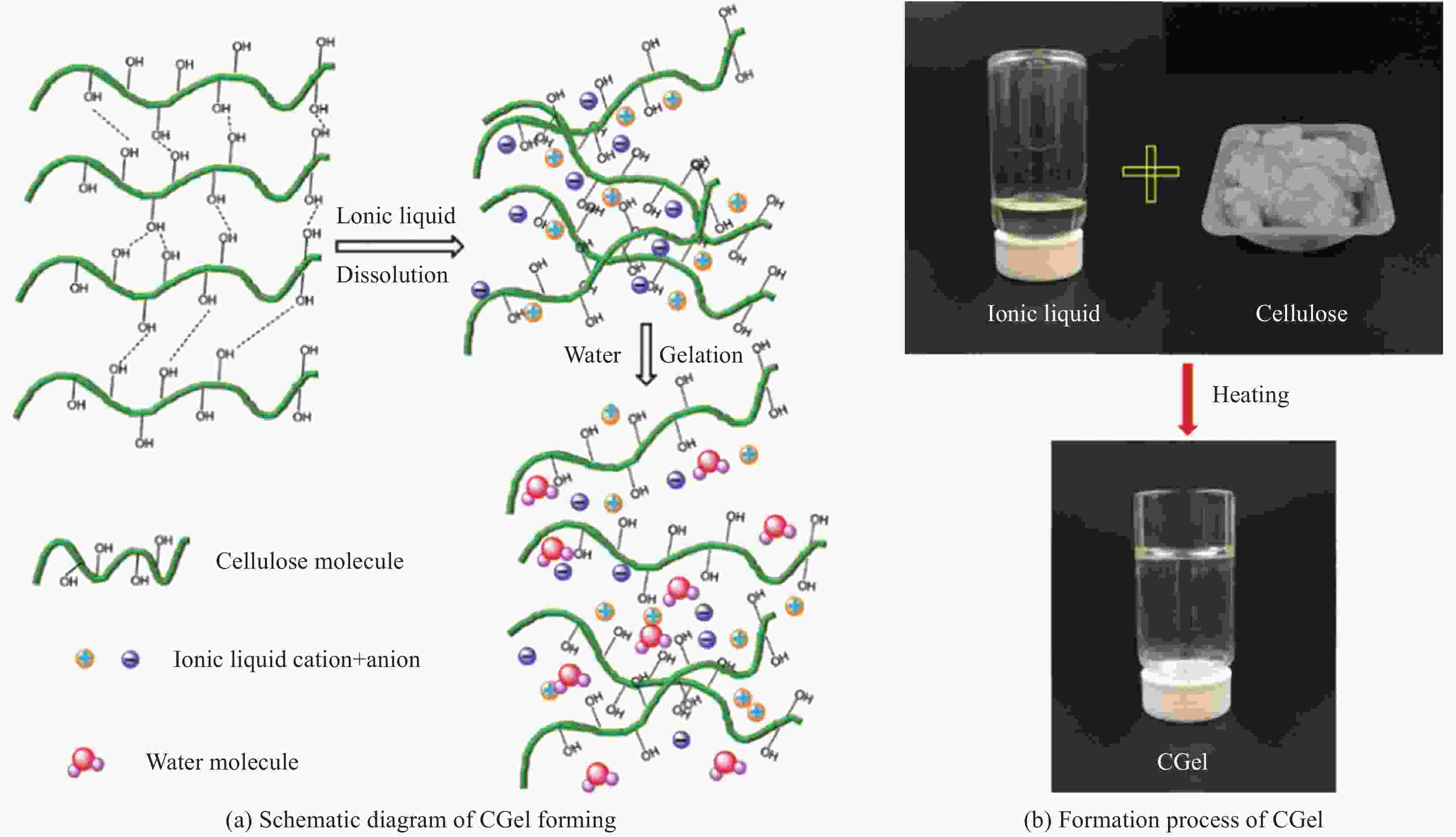
 下载:
下载: