Construction of a synergistic photothermic/chemotherapeutic nanosystem for anti-tumor and study of its drug controlled release behavior
-
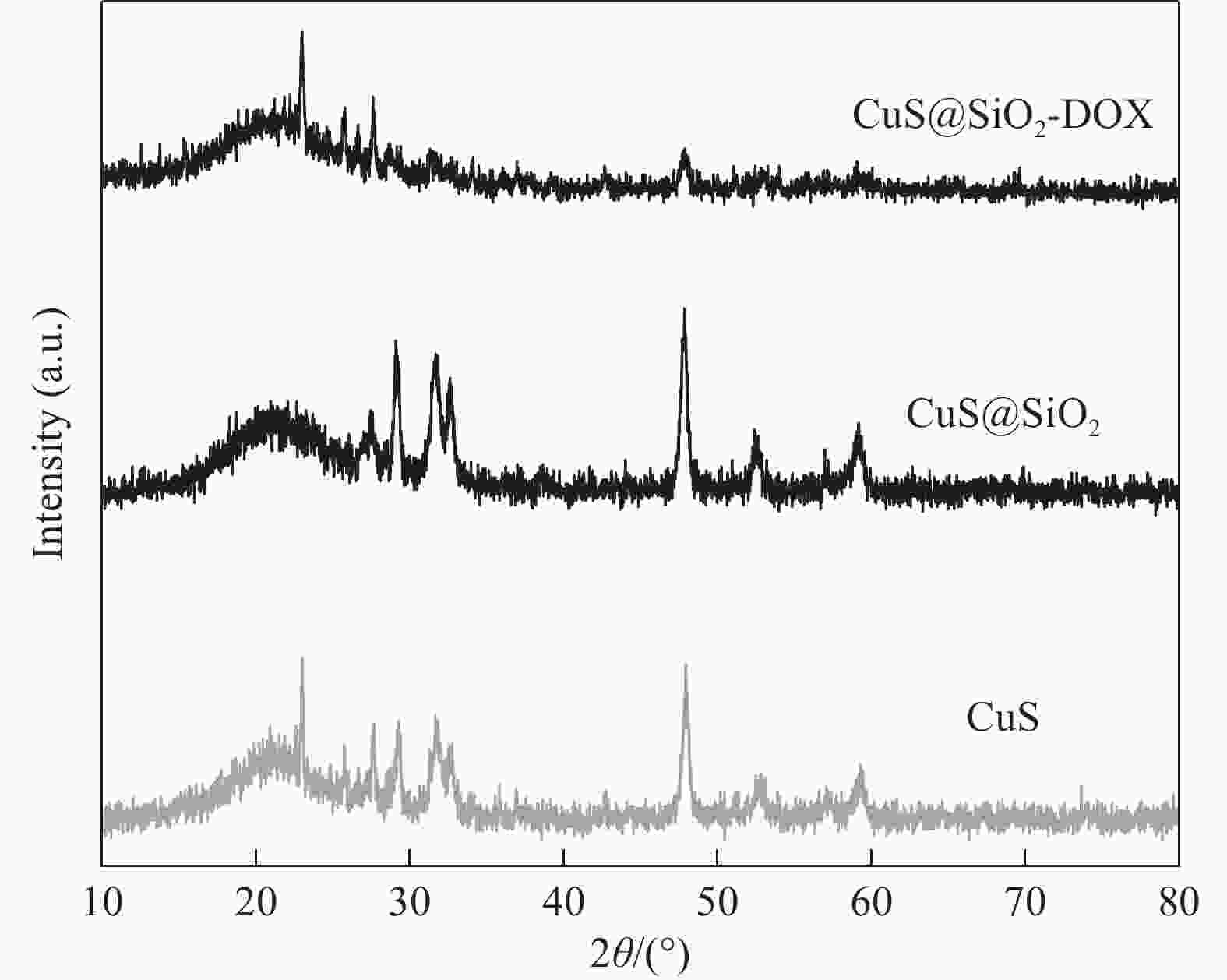
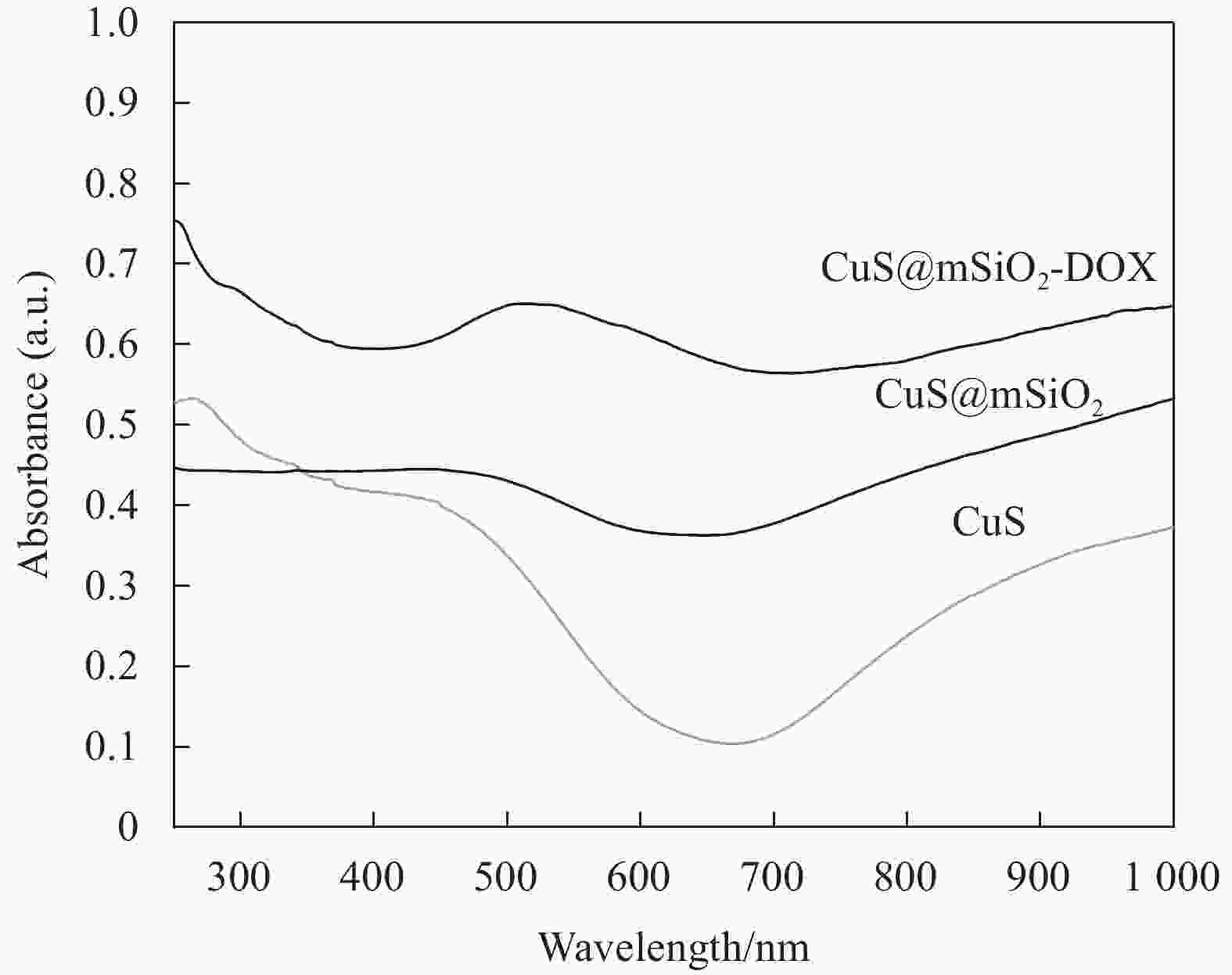
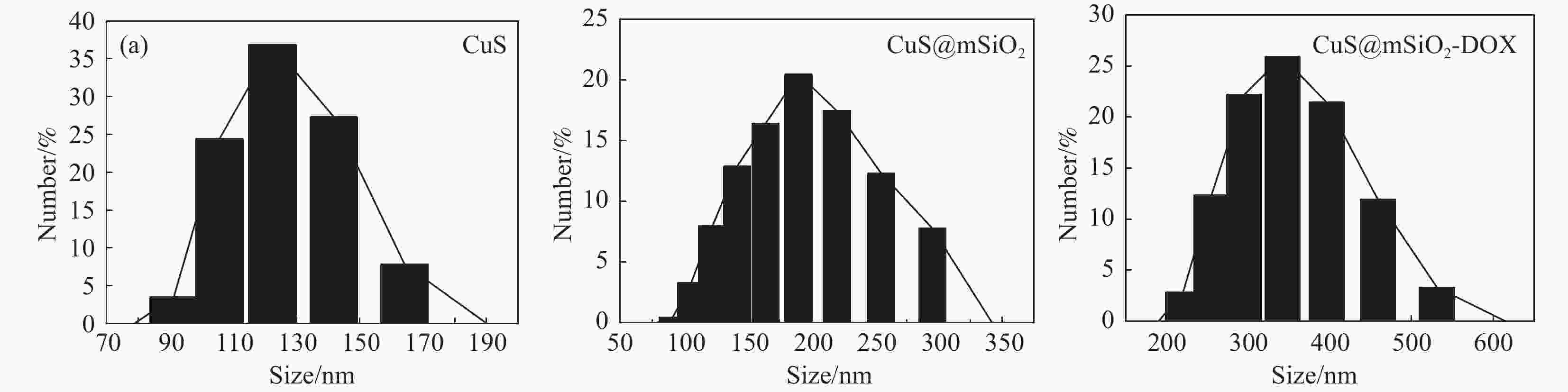
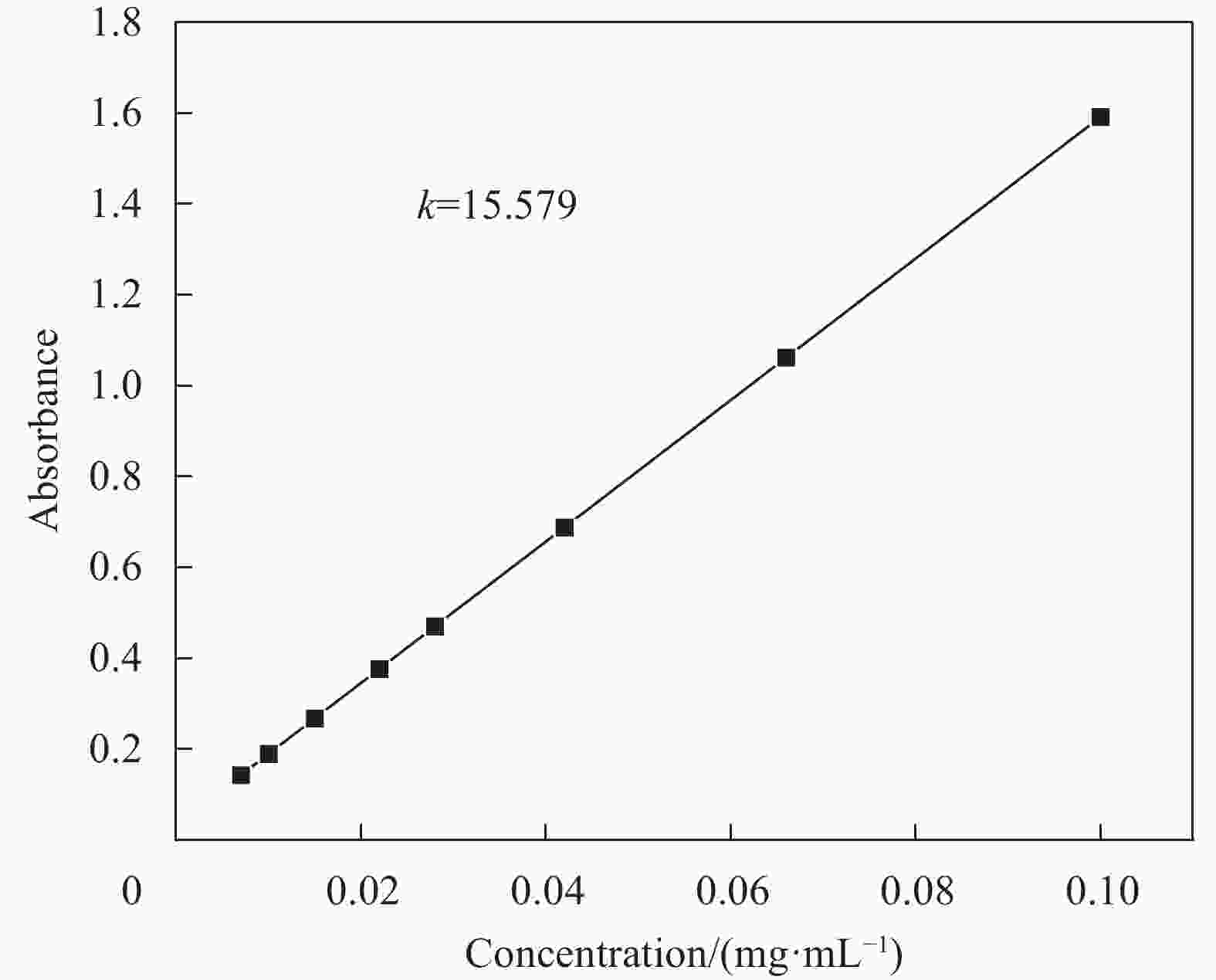
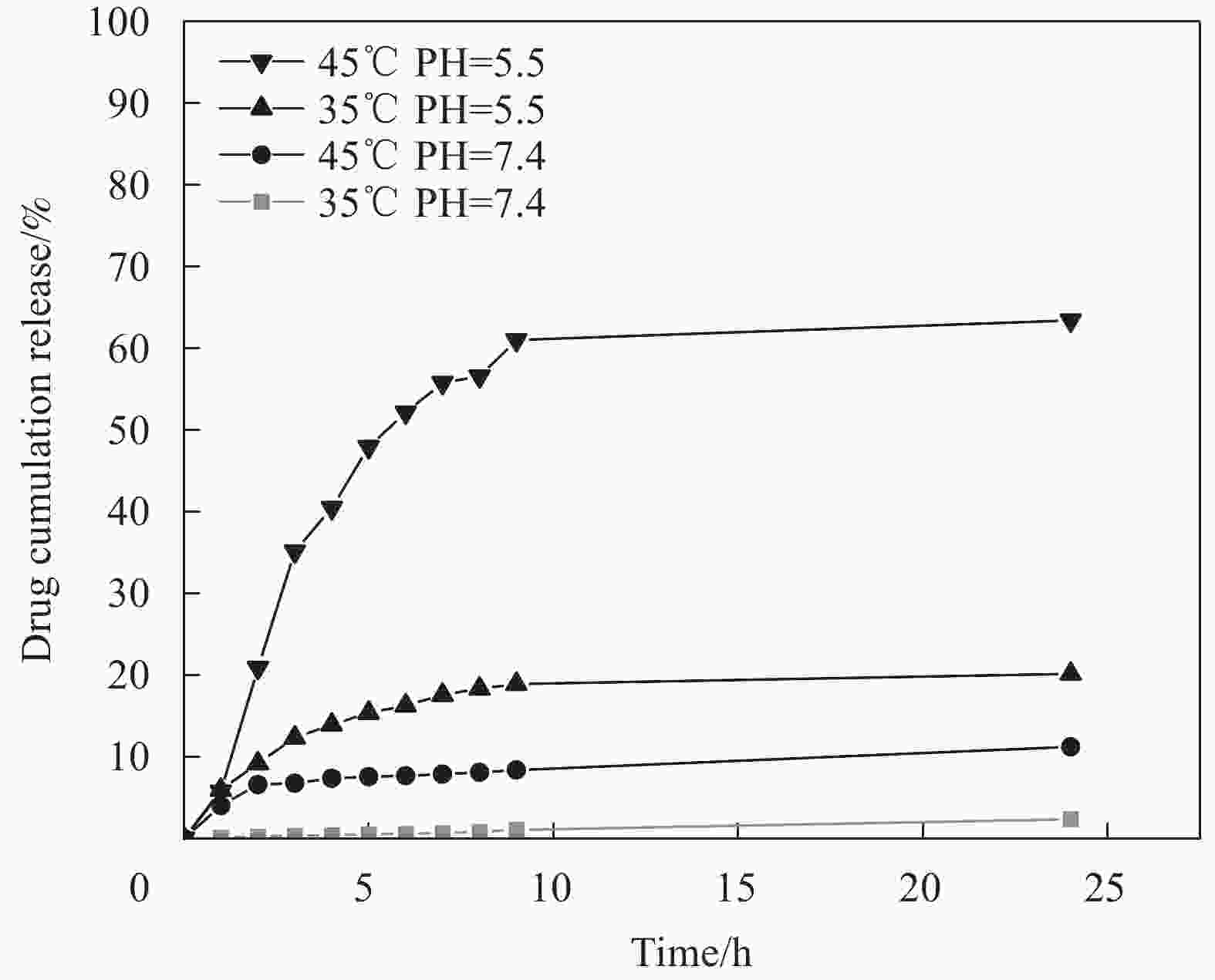
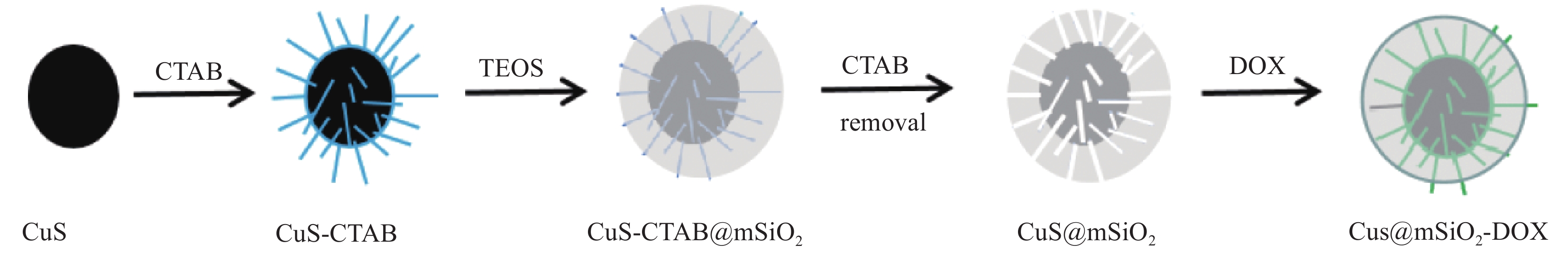
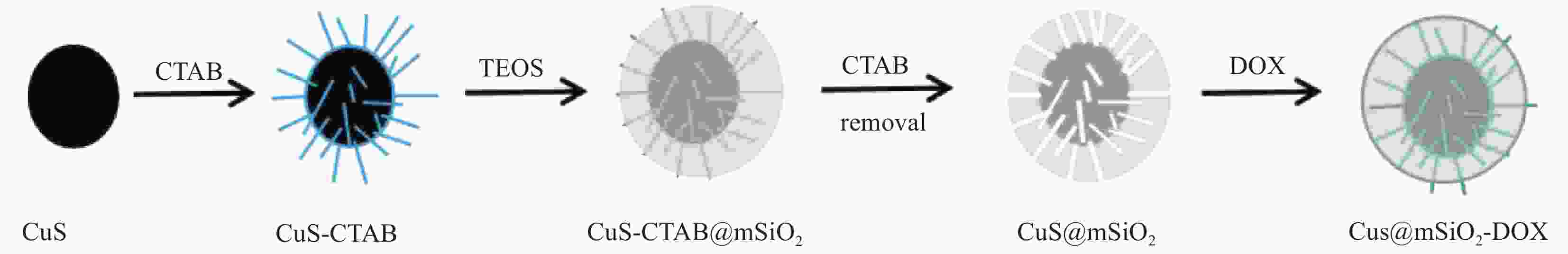
摘要: 传统治疗肿瘤的方式包括手术、放疗和化疗。手术治疗创伤大、易复发,放疗周期过长,尽管化疗被认为是消灭肿瘤细胞的首选但其存在着明显的毒副作用,长期化疗会严重影响患者的生存质量。因而,设计一种响应性功能载体实现抗肿瘤药物的高效运输及协同抑瘤在临床上具有广阔的前景。本研究以CuS为光热剂,采用溶剂热及去模板法在CuS表面包被上介孔二氧化硅(mSiO2),借助mSiO2的大比表面积制备出高负载盐酸阿霉素(DOX)的纳米药物体系(CuS@mSiO2-DOX)。XRD、UV-Vis、SEM、TEM及DLS结果证实成功的合成了颗粒尺寸约为300-400 nm的CuS@mSiO2-DOX纳米体系,且DOX的负载效率可高达99.76%。CuS@mSiO2-DOX在pH=5.5、t=45℃的条件下24 h时药物释放率达到63.44%,相比正常生理环境(pH=7.4、t=35℃)释放率提高了近20倍,呈现出明显的pH及温度响应释放特性。对纳米载药体系CuS@mSiO2的光热性能及体外细胞毒性进行了测试,结果显示CuS@mSiO2 表现出良好的光热稳定性、光热转换效率达到31.67%,且对正常的人肝细胞(HL-7702)呈低毒性。CuS@mSiO2纳米体系具有较好的生物相容性、良好的光热转换及载药性能,吸附DOX后体系表现出优异的pH及激光响应型药物控释性能,在联合光热-化疗协同抗肿瘤领域有望得到广泛应用。Abstract: Traditional methods of cancer treatment include surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. The surgical treatment is highly traumatic and easy to recur, while the period of radiotherapy is too long. Although chemotherapy is considered as the first choice to destroy tumor cells, it has obvious toxic and side effects, and the long-term chemotherapy can seriously affect the quality of the patients’ life. In this study, CuS was selected as a photothermal agent, and mesoporous silica (mSiO2) was coated on the surface of CuS using the solvothermal and template removal methods. With the aid of the large specific surface area of mSiO2, a highly doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) loaded nanodrug system was prepared (CuS@mSiO2-DOX). XRD, UV-Vis, SEM, TEM, and DLS results jointly confirm that the CuS@mSiO2-DOX nanosystem with a particle size of approximately 300-400 nm is successfully synthesized, and the loading efficiency of DOX in this system can reach up to 99.76%. The 24 h-drug release rate of CuS@mSiO2-DOX reaches 63.44% under the conditions of pH=5.5 and t=45℃, which is nearly 20 times higher than that under the normal physiological environment (pH=7.4 and t=35℃), indicating that the CuS@mSiO2-DOX nanosystem possesses obvious pH and temperature responsive release characteristics. In addition, the photothermal performance and in-vitro cytotoxicity of the CuS@mSiO2 nanodrug delivery system was tested, and the results show that CuS@mSiO2 exhibits a good photothermal stability with a photothermal conversion efficiency of 31.67%, and which also reveals low toxicity to normal human liver cells (HL-7702). CuS@mSiO2 nanosystem has good biocompatibility, outstanding photothermal conversion and drug loading properties, and after DOX adsorption, the system exhibits excellent pH and laser responsive drug controlled release performance, which is expected to be widely used in the field of combining the photothermal-chemotherapy to synergistically resist tumor.
-
Key words:
- biomedical materials /
- tumor /
- nanosystems /
- photo-thermal /
- chemotherapy /
- drug controlled release /
- mesoporous silica /
- CuS
-
图 4 (a)CuS纳米颗粒形貌;(b)CuS@mSiO2纳米颗粒形貌;(c)CuS@mSiO2-DOX纳米颗粒形貌;(d)CuS纳米颗粒TEM明场像,右上方嵌入图为CuS颗粒内部的高分辨像;(e)CuS@mSiO2纳米颗粒的TEM明场像;(f)CuS@mSiO2-DOX 纳米颗粒的TEM明场像
Figure 4. Surface morphological images of (a) CuS NPs, (b) CuS@mSiO2 NPs and (c) CuS@mSiO2-DOX NPs; (d) TEM bright field image of CuS NPs, the inset in the upper right corner is the high resolution image inside a typical CuS NP, and TEM bright-field images of (e) CuS@mSiO2 NPs and (f) CuS@mSiO2-DOX NPs
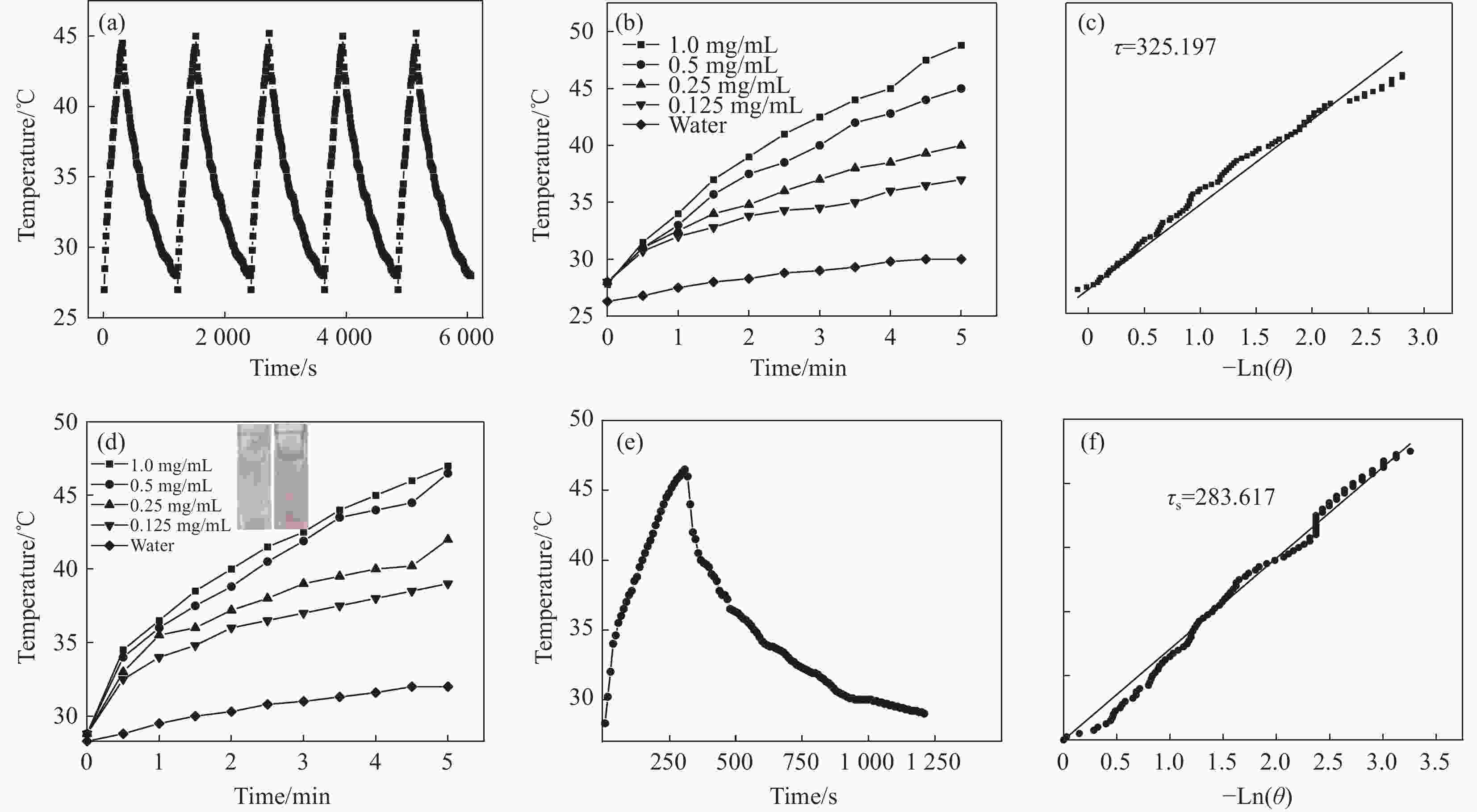
图 9 (a)0.5 mg·ml−1 CuS@mSiO2激光(808 nm, 1.5 W·cm−2)照射5 min、冷却15 min循环5次的温度变化曲线;(b)不同浓度的CuS@mSiO2纳米体系溶液在激光(808 nm, 1.5 W·cm−2)照射下的温度变化曲线;(c)从图a得到的时间常数τs;(d)不同浓度的CuS@mSiO2-DOX纳米体系溶液在激光(808 nm, 1.5 W·cm−2)照射下的温度变化曲线及激光照射前后CuS@mSiO2-DOX纳米体系溶液颜色变化插图;(e)0.5 mg·ml−1 CuS@mSiO2-DOX激光(808 nm, 1.5 W·cm−2)照射5 min,冷却15 min温度变化曲线;(f)从图e得到的时间常数τs
Figure 9. (a) Temperature change curve of 0.5 mg·ml−1 CuS@mSiO2 under laser (808 nm,1.5 W·cm−2) irradiation for 5 min and cooled for 15 min for 5 cycles; (b) Temperature change curves of different concentrations of CuS@mSiO2 solutions under laser (808 nm,1.5 W·cm−2) irradiation; (c) The time constant τs obtained from (a); (d) Temperature change curves of different concentrations of CuS@mSiO2-DOX solutions under laser (808 nm,1.5 W·cm−2) irradiation and the inset shows color change of CuS@mSiO2-DOX solutions before and after laser irradiation; (e) Temperature change curve of 0.5 mg·ml−1 CuS@mSiO2-DOX under laser (808 nm,1.5 W·cm−2) irradiation for 5 min and cooled for 15 min; (f) The time constant τs obtained from (e)
-
[1] 马书丽, 李悦, 尚靖, 等. 光热联合免疫抗肿瘤治疗的研究进展[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2023, 40(6): 792-798.MA Shuli, LI Yue, SHANG Jin, et al. Research progress of photothermal combined immunotherapy against tumor[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2023, 40(6): 792-798(in Chinese). [2] 王晓驰, 景亚, 张光辉, 等. 磁性碳纳米管的制备及其在肿瘤细胞光热疗与磁共振成像中的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(12): 6548-6556.WANG Xiaochi, JING Ya, ZHANG Guanghui, et al. Preparation of magnetic carbon nanotubes and their application in tumor cell photo-thermal therapy and magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(12): 6548-6556(in Chinese). [3] 李鑫, 王冯瑞, 丁超, 等. 太白七药抗肿瘤研究进展[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2022, 41(2): 38-48.LI Xin, WANG Fengrui, DING Chao, et al. Review on antitumor activities of Taibai qi medicines[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2022, 41(2): 38-48(in Chinese). [4] 齐雅平, 高宁, 卢晓明, 等. Flash放射治疗技术研究进展[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2022, 38(1): 146-149.QI Yaping, GAO Ning, LU Xiaoming, et al. Research progresses of Flash radiotherapy technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging Technology, 2022, 38(1): 146-149(in Chinese). [5] 贾斐, 杜传超, 毛天立, 等. 纳米载体共递送基因和化疗药物用于肿瘤治疗的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(17): 25-33.JIA Pei, DU Chuangchao, MAO Tianli, et al. Progress in the use of nanocarriers for co-delivery of genes and chemotherapeutic agents for cancer therapy[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(17): 25-33(in Chinese). [6] OHTA S, GLANCY D, CHAN W C W. DNA-controlled dynamic colloidal nanoparticle systems for mediating cellular interaction[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6275): 841-845. doi: 10.1126/science.aad4925 [7] KAWEETEERAWAT C, CHANG C H, ROY K R, et al. Cu nanoparticles have different impacts in Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus brevis than their microsized and ionic analogues[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(7): 7215-7225. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b02021 [8] BIAN W Q, WANG Y K, PAN Z X, et al. Review of functionalized nanomaterials for photothermal therapy of cancers[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(11): 11353-11385. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c01903 [9] WANG F, WANG Y C, DOU S, et al. Doxorubicin-tethered responsive gold nanoparticles facilitate intracellular drug delivery for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer cells[J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(5): 3679-3692. doi: 10.1021/nn200007z [10] ZENG J F, SHI D J, GU Y L, et al. Injectable and near-infrared-responsive hydrogels encapsulating dopamine-stabilized gold nanorods with long photothermal activity controlled for tumor therapy[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2019, 20(9): 3375-3384. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00600 [11] LI L, LIU H, BIAN J X, et al. Ag/Pd bimetal nanozyme with enhanced catalytic and photothermal effects for ROS/hyperthermia/chemotherapy triple-modality antitumor therapy[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125438. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125438 [12] DONG K, LIU Z H, LI Z, et al. Hydrophobic anticancer drug delivery by a 980 nm laser-driven photothermal vehicle for efficient synergistic therapy of cancer cells in vivo[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(32): 4452-4458. doi: 10.1002/adma.201301232 [13] OVERCHUK M, WEERSINK R A, WILSON B C, et al. Photodynamic and photothermal therapies: Synergy opportunities for nanomedicine[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(9): 7979-8003. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c00891 [14] PENG S, CHEN H. Biocompatible CuS-based nanoplatforms for efficient photothermal therapy and chemotherapy in vivo[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2018, 14(5): 1843. [15] ZHANG M Y, LIU X J, LUO Q, et al. Tumor environment responsive degradable CuS@mSiO2@MnO2/DOX for MRI guided synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy and chemodynamic therapy[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 389: 124450. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124450 [16] CHEN G S, LENG X, LUO J Y, et al. In vitro toxicity study of a porous iron(III) metal-organic framework[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(7): 1211. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071211 [17] MUSTAFA R A, RAN M X, WANG Y H, et al. A pH/temperature responsive nanocomposite for chemo-photothermal synergistic cancer therapy[J]. Smart Materials in Medicine, 2023, 4: 199-211. doi: 10.1016/j.smaim.2022.09.004 [18] 赵婧, 崔潞, 李映璐, 等. 壳聚糖复合纳米载药体系的构建及其释药性能[J]. 纺织高校基础科学学报, 2022, 35(3): 45-55.ZHAO Qian, CUI Lu, LI Yinglu, et al. Construction and controlled release properties of chitosan-based composite nano drug delivery system[J]. Basic Sciences Journal of Textile Universities, 2022, 35(3): 45-55(in Chinese). [19] 王锦, 白波, 罗钰, 等. 纳米金刚石/酵母-壳聚糖复合微球的制备及光热控释性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(3): 1676-1685. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220616.001WANG Jin, BAI Bo, LUO Yu, et al. Preparation and photo-thermal controlled release properties of nanodiamond/yeast-chitosan composite microspheres[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(3): 1676-1685(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220616.001 [20] MUTO R, SUZUKI Y, SHIMIZU H, et al. Recurrent cerebrovascular complications under enzyme replacement therapy in a patient with fabry disease on peritoneal dialysis[J]. Internal Medicine, 2023, 62(4): 565-569. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0185-22 [21] PAYDAYESH A, SOLTANI S, SH DADKHAH A. Preparation and evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels with zinc oxide nanoparticles as a drug controlled release agent for a hydrophilic drug[J]. Journal of Polymer Engineering, 2023, 43(7): 584-593. doi: 10.1515/polyeng-2023-0011 [22] FENG K, XU Z T, WANG Y H, et al. Renal-clearable porous hollow copper iron oxide nanoparticles for trimodal chemodynamic-photothermal-chemo anti-tumor therapy[J]. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(7): 3188-3198. doi: 10.1039/D2NR06224K [23] ZHANG K, ZHANG J M, YANG A L. Photoheating effects of CuS@PEI GQDs nanoshells under near-infrared laser and sunlight irradiation[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2023, 23(3): 1697-1708. [24] MUTALIK C, OKORO G, KRISNAWATI D I, et al. Copper sulfide with morphology-dependent photodynamic and photothermal antibacterial activities[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 607(2): 1825-1835. [25] HE J, AI L S, LIU X, et al. Plasmonic CuS nanodisk assembly based composite nanocapsules for NIR-laser-driven synergistic chemo-photothermal cancer therapy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2018, 6(7): 1035-1043. doi: 10.1039/C7TB02772A [26] TRUJILLO-CASARREAL J D, MORALES-JIMÉNEZ J I, RODRÍGUEZ-GONZÁLEZ V. Mesoporous CuS/SiO2 as a sulfamethoxazole loading carrier against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2023, 603: 122128. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2022.122128 [27] BAO Y N, XIE X L, LU L L, et al. NiFe-layered double hydroxide nanoparticle for co-delivery of DOX and siRNA to overcome multidrug resistance in MCF-7/ADR cells[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023, 87: 104829. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104829 [28] DEMIN A M, VAKHRUSHEV A V, VALOVA M S, et al. Features of doxorubicin adsorption on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles coated with SiO2 or SiO2/aminopropylsilane[J]. Mendeleev Communications, 2023, 33(2): 160-163. doi: 10.1016/j.mencom.2023.02.004 [29] 张文君, 赵雪莹, 吕江维, 等. 中空有序介孔有机硅的研究进展: 制备及在肿瘤治疗中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1192-1202. doi: 10.15541/jim20220435ZHANG Wenjun, ZHAO Xueying, LYU Jiangwei, et al. Progresses on hollow periodic mesoporous organosilicas: Preparation and application in tumor therapy[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1192-1202(in chinese). doi: 10.15541/jim20220435 [30] LI Z H, QIAN K, OZIOMA-UDOCHUKWU A, et al. A Smart glutathione and H2O2 dual-responsive signal inversion magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent for tumor diagnosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 49(8): 21141-21150. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(21)60111-1 [31] ADHIKARI C, MISHRA A, NAYAK D, et al. Drug delivery system composed of mesoporous silica and hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres for chemotherapeutic drug delivery[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2018, 45: 303-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2018.03.020 [32] 任晶, 闫锦慧, 张安懿, 等. pH调控Y型分子筛负载阿霉素纳米药物制备及与MM-231细胞的作用[J]. 无机化学学报, 2022, 38(1): 93-102 doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2022.019REN Jing, YUAN Jinhui, ZHANG Anyi, et al. pH regulated nanomedicine based on Y-Type molecular sieve loading doxorubicin: preparation and interaction with MM-231 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2022, 38(1): 93-102(in chinese). doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2022.019 [33] DUKHOPELNYKOV E V, BLYZNIUK Y N, SKURATOVSKA A A, et al. Interaction of doxorubicin delivered by superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with DNA[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2022, 219: 112815. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112815 [34] HAN Q Q, WANG X, QIU L, et al. Gelatinase responsive nanogel for antibacterial phototherapy and wound healing[J]. Gels, 2022, 8(7): 397. doi: 10.3390/gels8070397 [35] GAO F L, JIANG L T, ZHANG J E, et al. Near-infrared light-responsive nanosystem with prolonged circulation and enhanced penetration for increased photothermal and photodynamic therapy[J]. ACS Materials Letters, 2023, 5(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.2c00707 [36] LI Z L, HU Y, CHANG M L, et al. Highly porous PEGylated Bi2S3 nano-urchins as a versatile platform for in vivo triple-modal imaging, photothermal therapy and drug delivery[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(35): 16005-16016. doi: 10.1039/C6NR03398A [37] BAO T, YIN W Y, ZHENG X P, et al. One-pot synthesis of PEGylated plasmonic MoO3-x hollow nanospheres for photoacoustic imaging guided chemo-photothermal combinational therapy of cancer[J]. Biomaterials, 2016, 76: 11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.10.048 -





 下载:
下载: