Research progress on multiaxial fatigue of continuous fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite
-
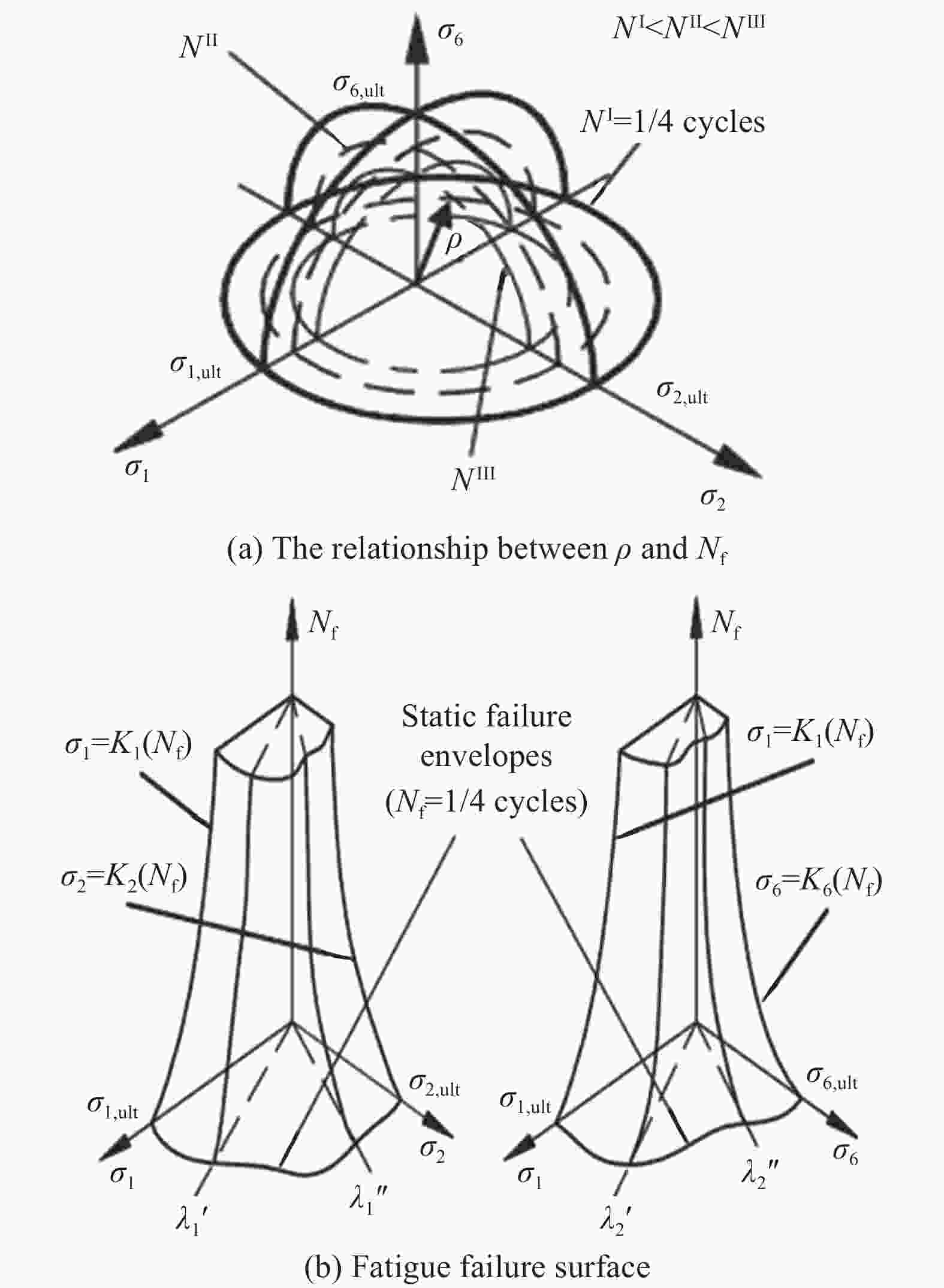
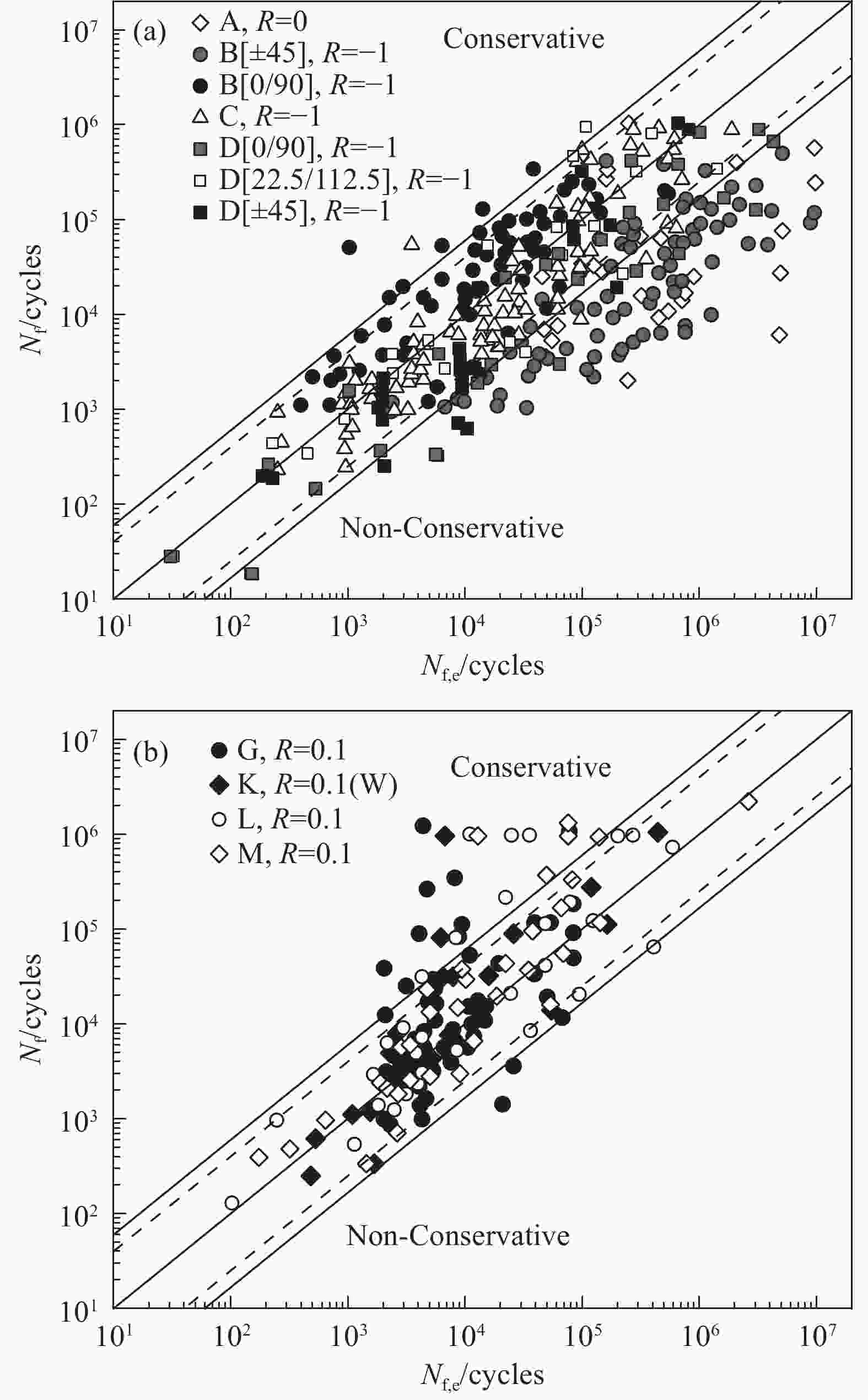
摘要: 目前连续纤维增强聚合物基体复合材料在航空航天等领域具有广泛应用,其在使用过程中会处于复杂的多轴应力状态,且载荷形式大多为疲劳载荷,因而有必要对复合材料多轴疲劳问题进行研究。目前对于复合材料多轴疲劳的研究主要分为三方面:不同试样的多轴疲劳行为研究;多轴疲劳行为影响因素;多轴疲劳寿命预测方法。其中复合材料多轴疲劳试验研究可按试样形式分为管状试样、十字型试样以及板状试样多轴疲劳试验,以十字型和管状试样试验最为常见。讨论了多轴疲劳载荷下堆叠顺序、多轴度、载荷加载方式等因素对复合材料多轴疲劳强度的影响。对于复合材料双轴疲劳寿命预测方法,主要分为唯象模型与非经典模型,这与单轴疲劳寿命预测方法存在类似之处,但并未考虑双轴疲劳载荷下的损伤演化以及控制最终失效的损伤机制。本文概述了纤维增强复合材料的多轴疲劳研究进展,对多轴疲劳的三个方面进行了详细介绍,通过对现有研究结果的总结与分析,提出了复合材料多轴疲劳后续研究的展望。Abstract: Currently, continuous fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite find extensive applications in aerospace and various other industries. These materials undergo intricate multiaxial stress states during usage, with a predominant presence of fatigue loads. Consequently, delving into the multiaxial fatigue study of composite materials becomes imperative. Research on the multiaxial fatigue of composite materials is presently categorized into three primary domains: exploration of multiaxial fatigue behavior across different specimens, identification of factors influencing such behavior, and the development of multiaxial fatigue life prediction methods. The investigation into multiaxial fatigue testing of composite materials encompasses tube-shaped, cross-shaped, and plate-shaped specimens. Among these, cross-shaped and tube-shaped specimen tests are the most prevalent. The impact of factors such as stacking sequence, multiaxial degree, and load loading methods on the multiaxial fatigue strength of composite materials under varying multiaxial fatigue loading conditions are discussed in this article. Concerning the prediction of biaxial fatigue life in composite materials, available methods predominantly consist of phenomenological models and non-classical models. While akin to uniaxial fatigue life prediction methods, these models overlook damage evolution under biaxial fatigue loads and the damage mechanisms controlling final failure. A comprehensive overview of the progress in researching multiaxial fatigue of fiber-reinforced composite materials is furnished, and an in-depth introduction is provided for the three dimensions of multiaxial fatigue. Through the synthesis and analysis of existing research findings, prospective directions for future research on multiaxial fatigue in composite materials are discussed.
-
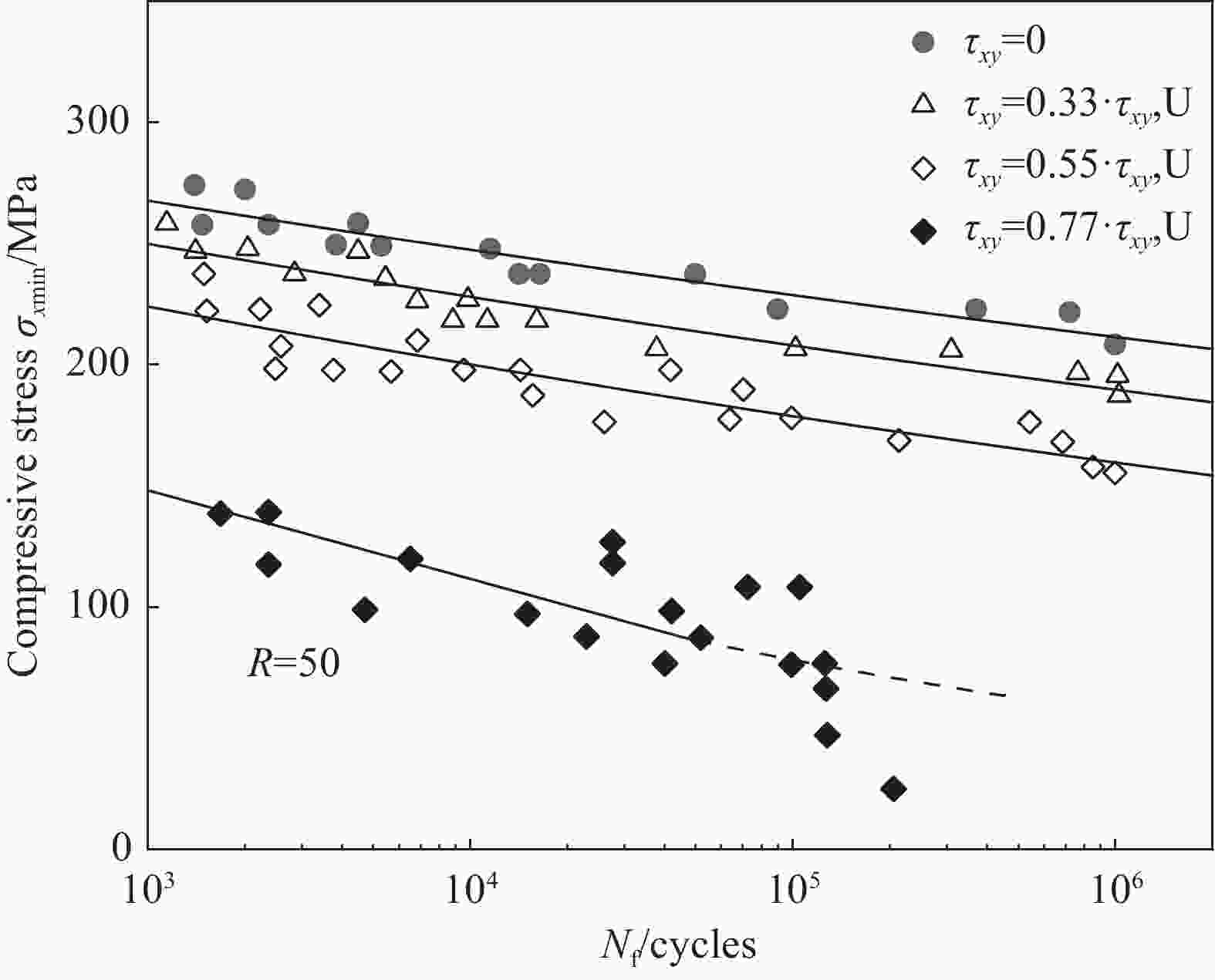
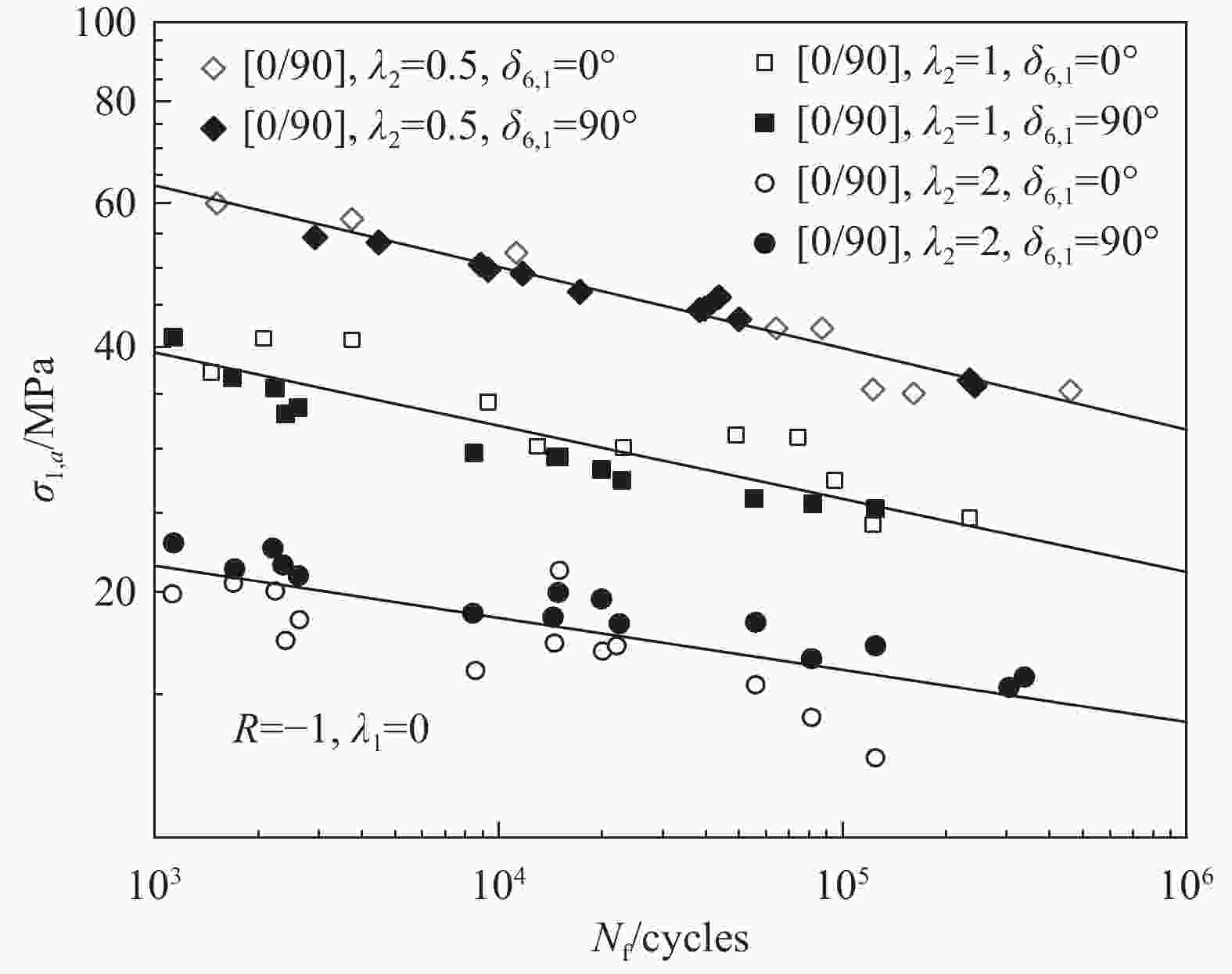
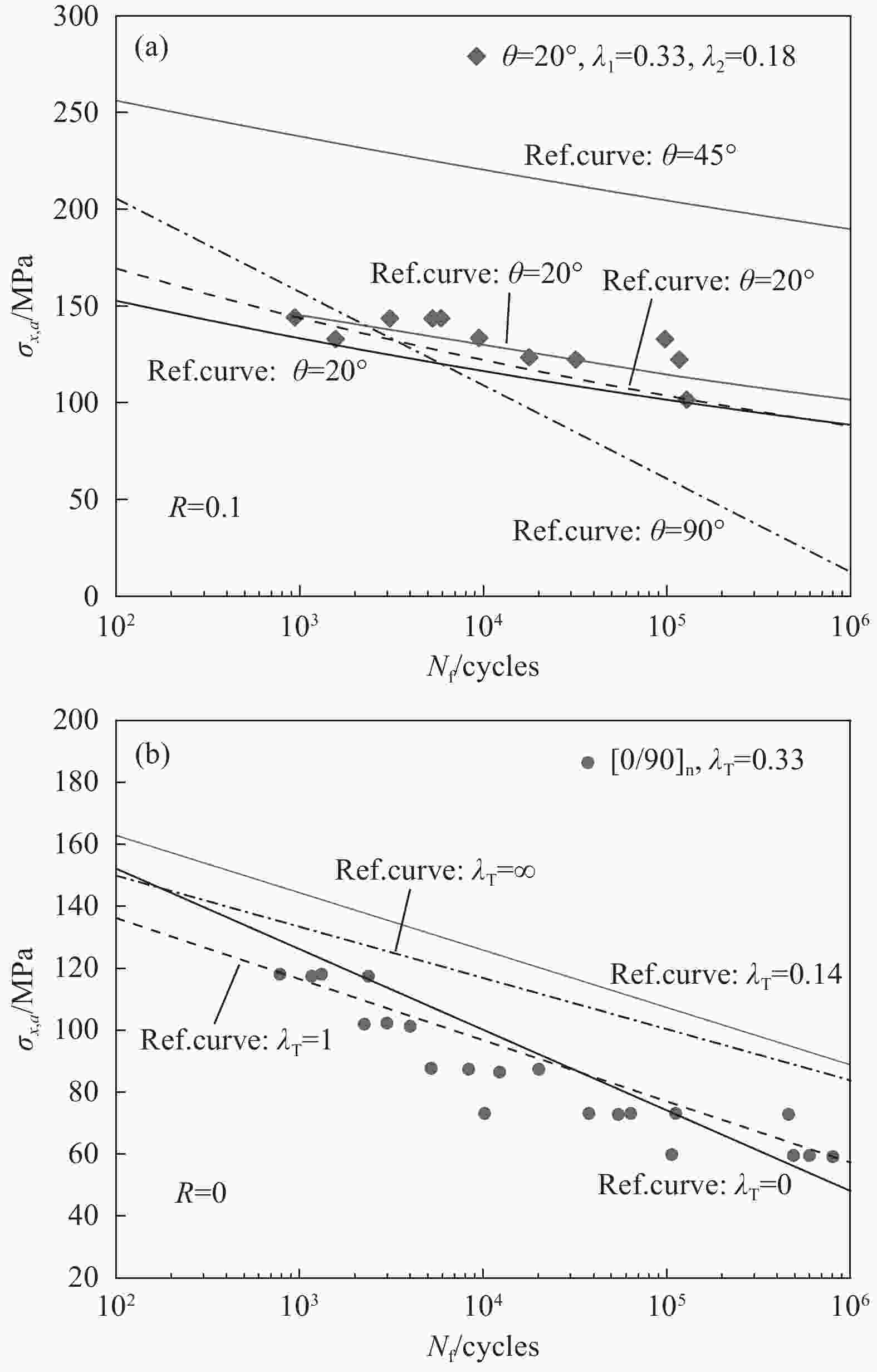
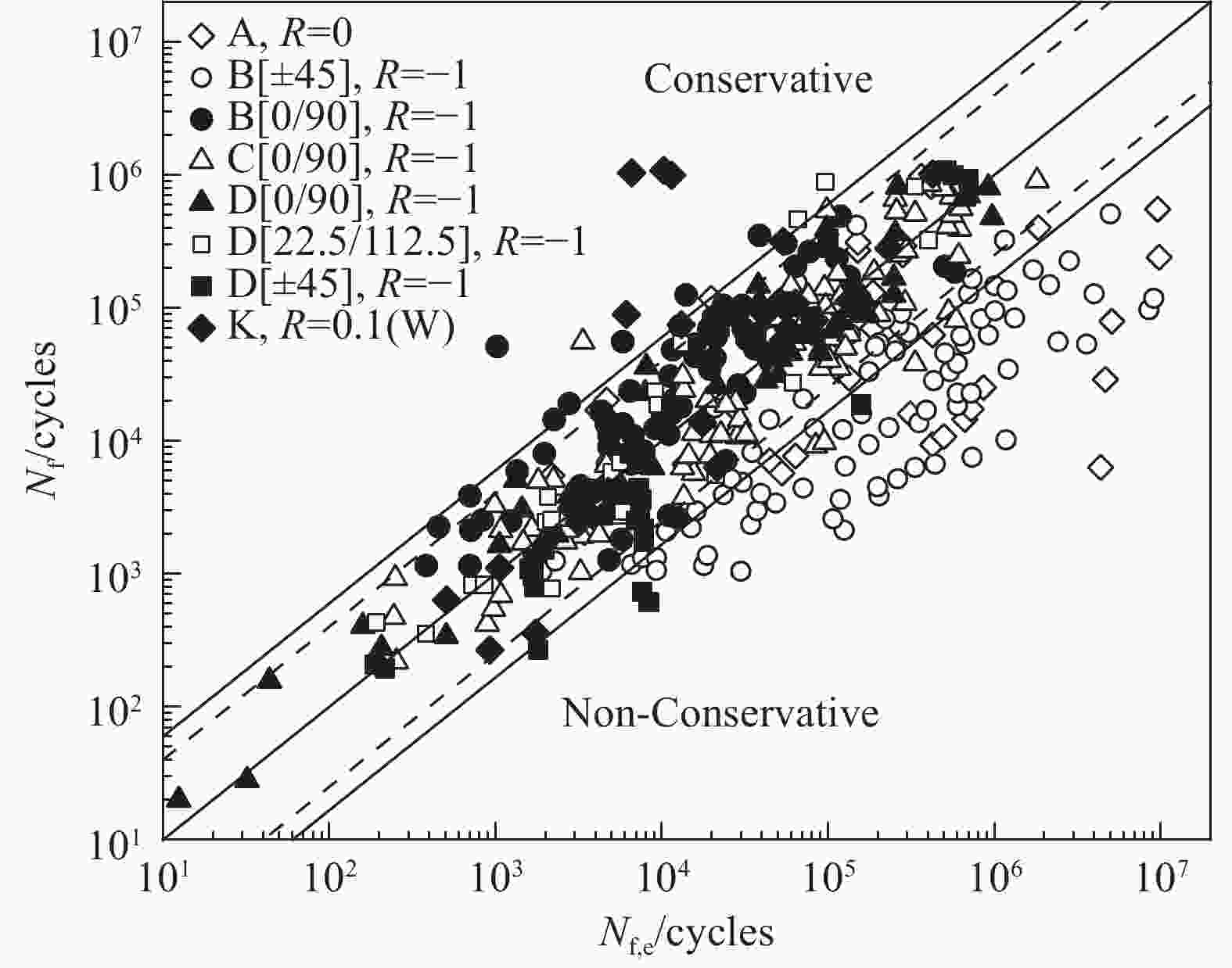
表 1 FRP多轴疲劳试验研究
Table 1. Research on Multiaxial Fatigue Testing of FRP
Specimen shape Test materials Load type Factors affecting fatigue failure Tubular
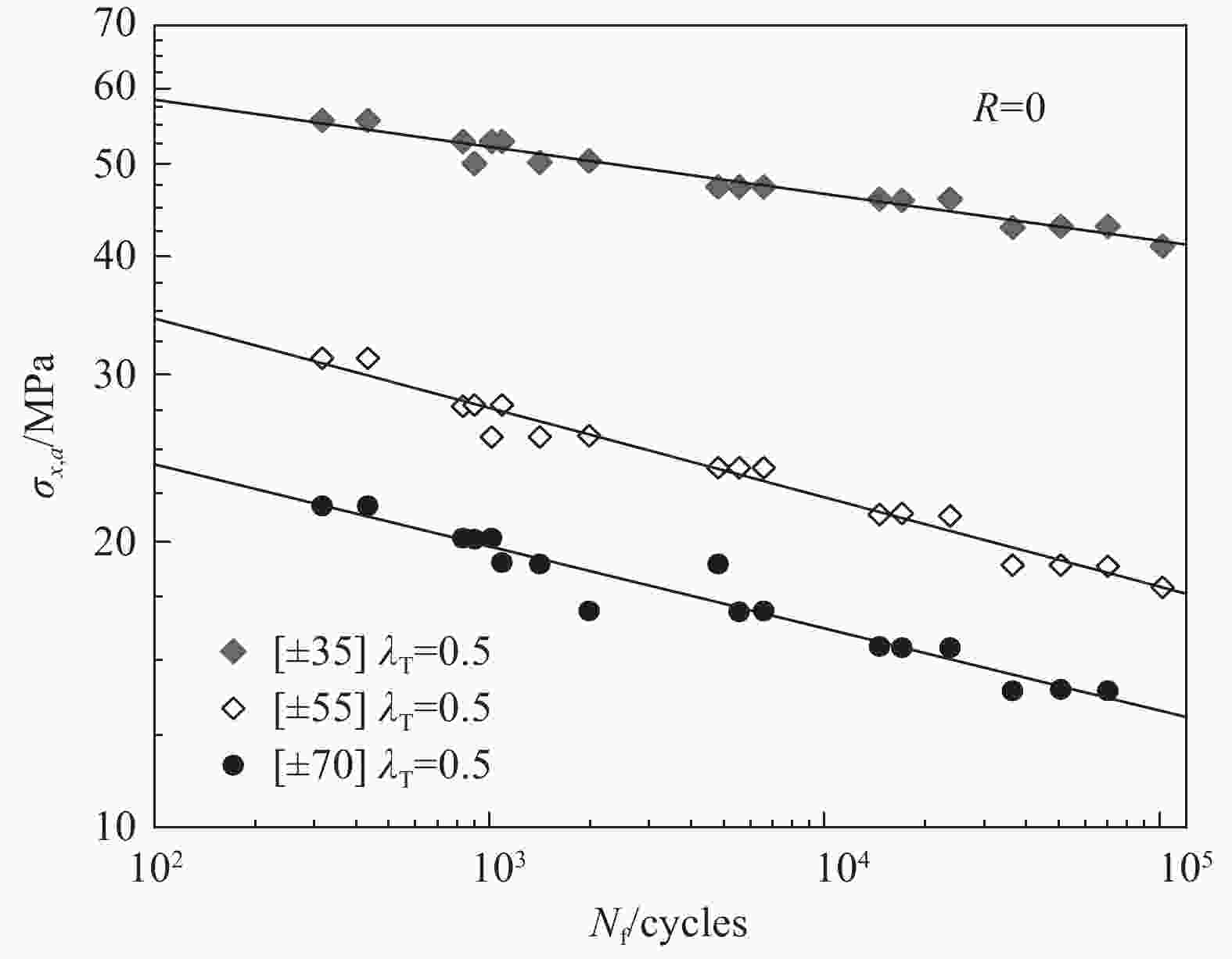
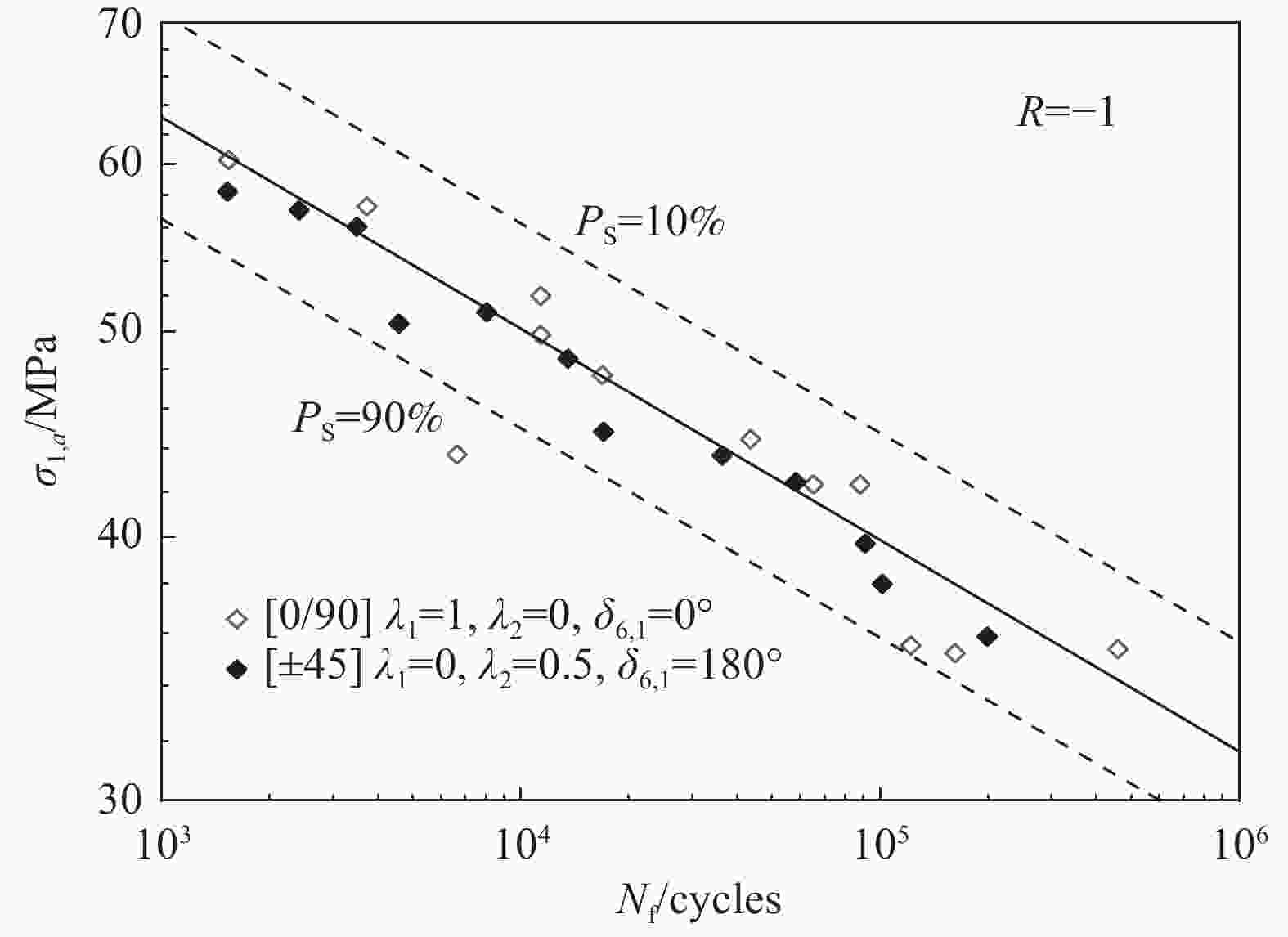
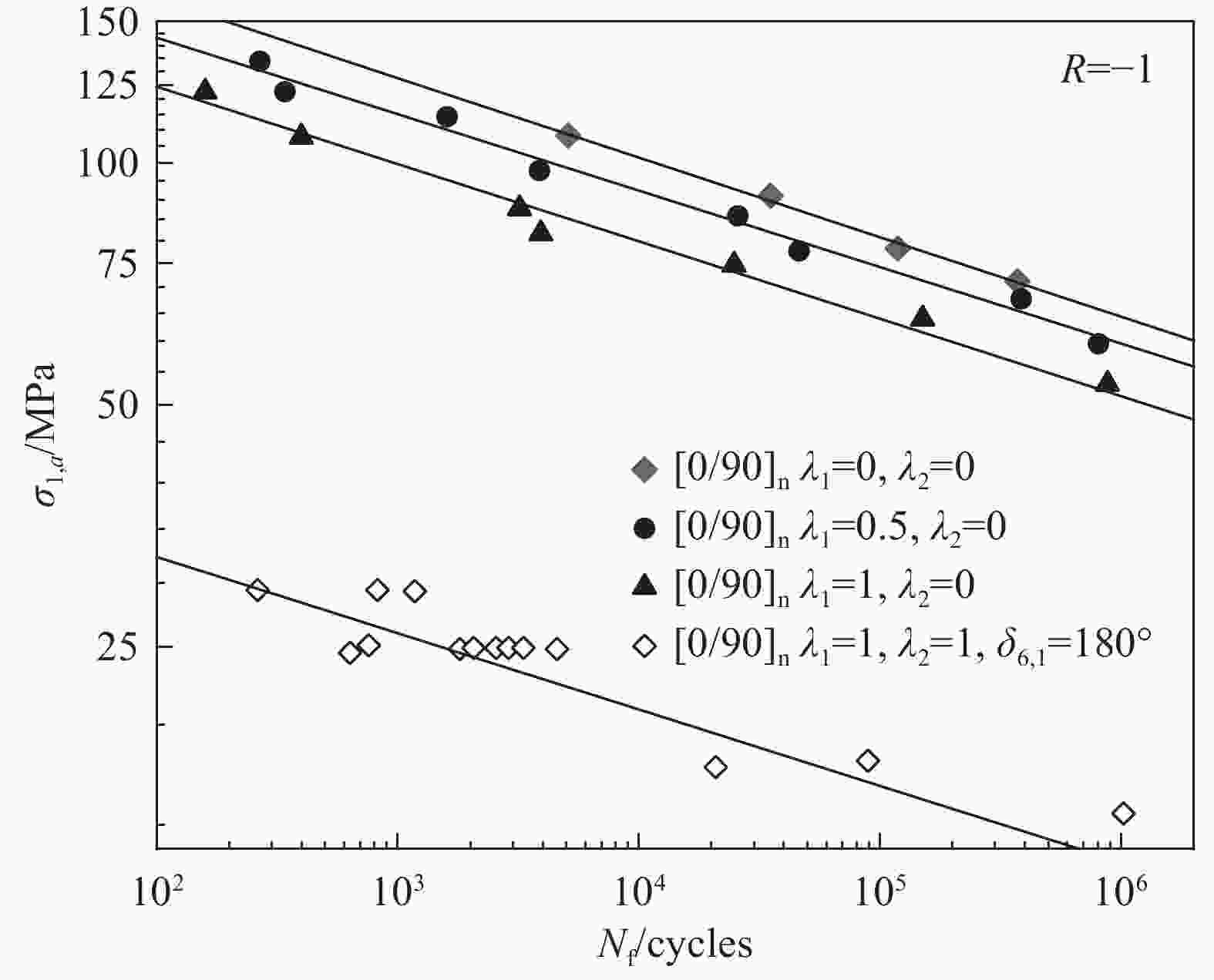
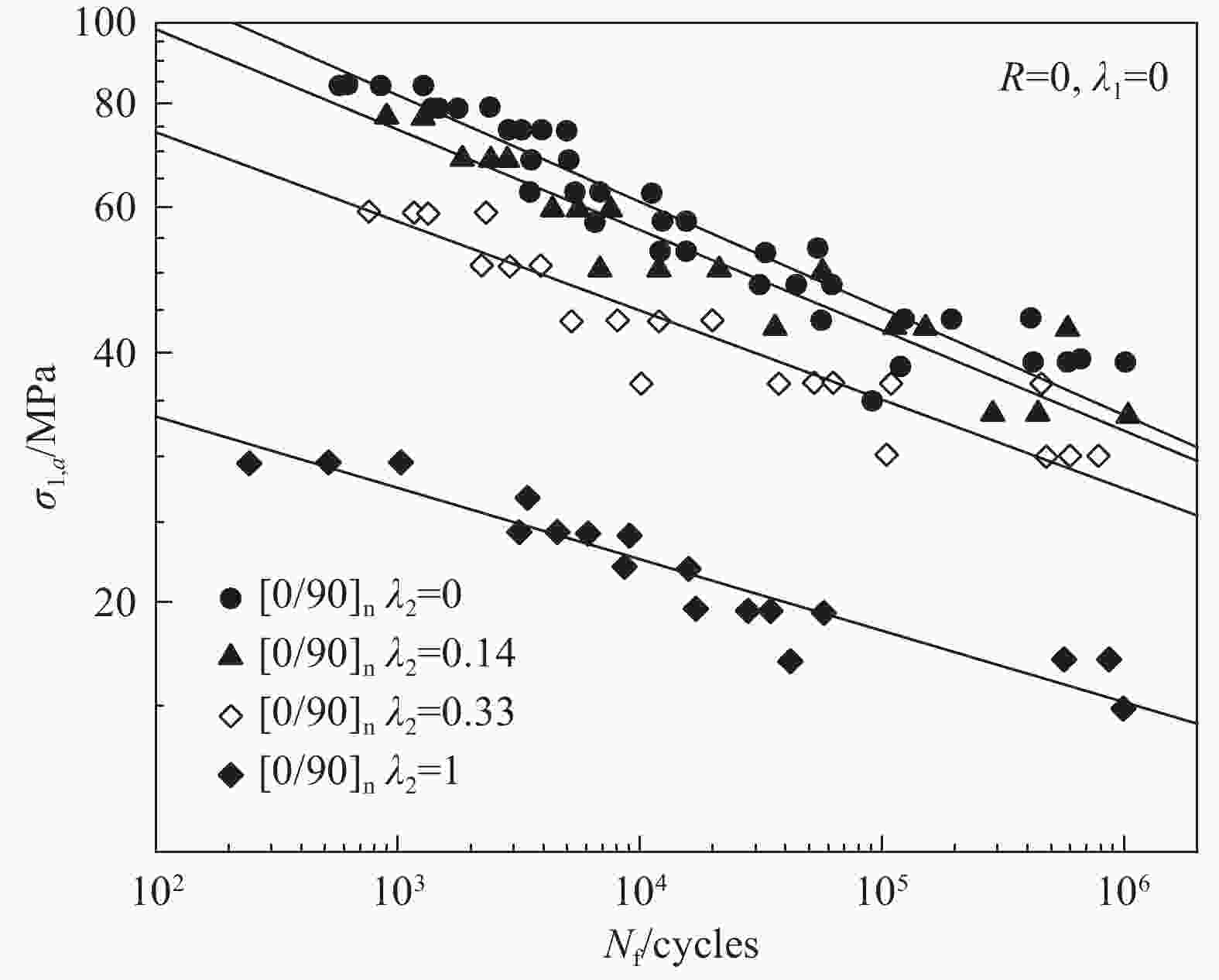
specimenPlain weave GFRP[14, 19, 23] Tension/compression-torsion Off-axis angle[27]、Biaxial ratio[27, 38-40]、Notch[39] 3D Knitting GFRP[15] Tension/compression-torsion Biaxial ratio[15] Laminate GFRP[16, 17, 20] [22] Tension-torsion Off-axis angle[22]、Biaxial ratio[37]、Test loading method[37] Laminate AFRP[21] Tension/compression-torsion Biaxial ratio[21]、Test loading method[44] Laminate CFRP[11] Tension-torsion Biaxial ratio[11]、Test loading method[11] Cross shaped specimen Laminate GFRP[28] Tension-tension Stress concentration[28]、Test loading method[45] Laminate CFRP[29-31] Tension-tension Biaxial ratio[30]、Test loading method[31]、Notch[49] Flat specimen Laminate GFRP[32] Bending-bending Biaxial ratio[32] Laminate CFRP[34] Tension-bending Biaxial ratio[34] -
[1] 沈观林等. 复合材料力学[M]. 清华大学出版社, 2006.SHEN GUANLIN et al. Mechanics of Composite Materials[M]. Tsinghua University Press, 2006(in Chinese). [2] 吴良义. 先进复合材料的应用扩展: 航空、航天和民用航空先进复合材料应用技术和市场预测[J]. 化工新型材料, 2012, 40(01): 4-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2012.01.002WU LIANGYI. Application Expansion of Ad vanced Composite Materials: Application Technology and Market Forecast of Advanced Composite Materials in Aviation, Aerospace, and Civil Aviation[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2012, 40(01): 4-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2012.01.002 [3] 蔡菊生. 先进复合材料在航空航天领域的应用[J]. 合成材料老化与应用, 2018, 47(06): 94-97.CAI JUSHENG. The application of advanced com- posite materials in the aerospace field[J]. Aging and Application of Synthetic Materials, 2018, 47(06): 94-97(in Chinese). [4] WENG J, MENG T, WEN W, et al. Multiaxial fatigue life prediction of composite laminates[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(12): 227-237. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.06.016 [5] EL KADI H, ELLYIN F. Effect of stress ratio on the fatigue of unidirectional glass fibre/epoxy composite laminae[J]. Composites, 1994, 25(10): 917-924. doi: 10.1016/0010-4361(94)90107-4 [6] KAWAI M, YAJIMA S, HACHINOHE A, et al. Off-Axis Fatigue Behavior of Unidirectional Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites at Room and High Temperatures[J]. Journal of composite materials, 2001, 35(7): 545-576. doi: 10.1177/002199801772662073 [7] KAWAI M, TANIGUCHI T. Off-axis fatigue behavior of plain weave carbon/epoxy fabric laminates at room and high temperatures and its mechanical modeling[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2006, 37(2): 243-256. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.07.003 [8] QUARESIMIN M, CARRARO P A, MIKKELSEN L P, et al. Damage evolution under cyclic multiaxial stress state: A comparative analysis between glass/epoxy laminates and tubes[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2014, 61: 282-290. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.01.056 [9] 杜文军, 王卫国, 何敏, 等. 某压气机轮盘低循环疲劳寿命研究[J]. 燃气涡轮试验与研究, 2009, 22(3): 23-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2620.2009.03.005DU WENJUN, WANG WEIGUO, HE MIN, et al. Re search on Low Cycle Fatigue Life of a Compressor Disk[J]. Gas Turbine Testing and Research, 2009, 22(3): 23-27(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2620.2009.03.005 [10] 王相平, 周柏卓, 杨晓光. 多轴疲劳理论在航空发动机零部件寿命预测中的应用[J]. 沈阳航空工业学院学报, 2004, 21(4): 1-4.WANG XIANGPING, ZHOU BAIZHUO, YANG XIAOGUANG. The Application of Multiaxial Fatigue Theory in Life Prediction of Aircraft Engine Components[J]. Journal of Shenyang Institute of Aeronautics and Technology, 2004, 21(4): 1-4(in Chinese). [11] 翁晶萌. 复合材料多轴疲劳行为与寿命预测模型及方法研究[D]. 南京航空航天大学航空宇航推进理论与工程, 2019.WENG JINGMENG. Research on Multiaxial Fatigue Behavior and Life Prediction Models and Methods for Composite Materials[D]. Aerospace Propulsion Theory and Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019(in Chinese). [12] FOUND MS. Review of the multiaxial fatigue test-ing of fiber reinforced plastics. In: Multi-axi-al fa-tigue. ASTM STP 853;1985. pp. 381-95. [13] CHEN A S, MATTHEWS F L. A review of multiaxial/biaxial loading tests for composite materials[J]. Composites, 1993, 24(5): 395-406. doi: 10.1016/0010-4361(93)90247-6 [14] FUJ T, AMIJIMA S, LIN F, et al. Study on Strength and Nonlinear Stress-Strain Response of Plain Woven Glass Fiber Laminates under Biaxial Loading[J]. Journal of composite materials, 1992, 26(17): 2493-2510. doi: 10.1177/002199839202601702 [15] GUDE M, HUFENBACH W, KOCH I. Damage evolution of novel 3D textile-reinforced composites under fatigue loading conditions[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2010, 70(1): 186-192. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.10.010 [16] ELLYIN F, MARTENS M. Biaxial fatigue behaviour of a multidirectional filament-wound glass-fiber/epoxy pipe[J]. Composites science and technology, 2001, 61(4): 491-502. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00215-3 [17] SCHMIDT F, RHEINFURTH M, PROTZ R, et al. Monitoring of multiaxial fatigue damage evolution in impacted composite tubes using non-destructive evaluation[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2012, 43(3): 537-546. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.12.002 [18] QUARESIMIN M, SUSMEL L, TALREJA R. Fatigue behaviour and life assessment of composite laminates under multiaxial loadings[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2010, 32(1): 2-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2009.02.012 [19] LIMONOV VA, RAZIN AF, MIKEL' SONS MYA. Strength and fatigue limit of fabric base com-po-sites under com-bined static shear and cyclic com-pressive stresses. Mech Compos Mater 1992;28(3): 229-36. [20] QUARESIMIN M, CARRARO P A. Damage initiation and evolution in glass/epoxy tubes subjected to combined tension–torsion fatigue loading[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2014, 63: 25-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2014.01.002 [21] ANDERSON YA, LIMONOV VA, TAMUZH VP, PEREVOZCHIKOV VG. Fatigue of laminated com-po-sites with various reinforcement systems. 2. Planar stress state and calculation model. Mech Compos Mater 1990;25(4): 442-9. [22] QI D, CHENG G. Fatigue behavior of filament-wound glass fiber reinforced epoxy composite tubes under tension/torsion biaxial loading[J]. Polymer Composites, 2007, 28(1): 116-123. doi: 10.1002/pc.20275 [23] FUJII T, LIN F, MORITA Y. Fatigue Behavior of Plain Woven Glass-Fabric Laminates under Tension/Torsion Combined Loading : Effect of Shear Stress and Cyclic Condition on Fatigue Failure[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers Series A, 1994, 60(571): 650-657. [24] LECOMPTE D, SMITS A, SOL H, et al. Mixed numerical–experimental technique for orthotropic parameter identification using biaxial tensile tests on cruciform specimens[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44(5): 1643-1656. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2006.06.050 [25] SMITS A, VAN HEMELRIJCK D, PHILIPPIDIS T P, et al. Design of a cruciform specimen for biaxial testing of fibre reinforced composite laminates[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2006, 66(7-8): 964-975. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.08.011 [26] LAMKANFI E, VAN PAEPEGEM W, DEGRIECK J, MA-KRIS A, RAMAULT C, VAN HEMEL-RIJCK D. Optimization of a cruciform composite specimen under biaxial loading by means of evo-lutionary algorithms. In: Proceedings of ICCM17; July 2009. Edinburgh, UK. [27] SMITH EW P K. Biaxial fatigue of glass-fiber reinforced composite. Part 1: fatigue and fracture behavior[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2008, 39(3): 505-512. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2007.03.005 [28] LAMKANFI E, VAN PAEPEGEM W, DEGRIECK J, et al. Strain distribution in cruciform specimens subjected to biaxial loading conditions. Part 2: Influence of geometrical discontinuities[J]. Polymer Testing, 2010, 29(1): 132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2009.10.002 [29] SERNA MORENO M C, MARTÍNEZ VICENTE J L, LÓPEZ CELA J J. Failure strain and stress fields of a chopped glass-reinforced polyester under biaxial loading[J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 103: 27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.03.019 [30] 蔡登安, 周光明, 曹然, 等. 双轴载荷下复合材料十字型试样几何形状对中心测试区系数的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(04): 1138-1144.CAI DENG'AN, ZHOU GUANGMING, CAO RAN, et al. The influence of the geometric shape of composite cross shaped specimens on the coefficient of the central test zone under biaxial loading[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2015, 32(04): 1138-1144(in Chinese). [31] 徐传奇. 复合材料双轴强度与疲劳寿命研究[D]. 南京航空航天大学航空宇航推进理论与工程, 2020.XU CHUANQI. Research on biaxial strength and fatigue life of composite materials[D]. Aerospace Propulsion Theory and Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020(in Chinese). [32] IRWIN, L. H. , DUNLAP, W. A. AND COMPTON, P. V. ' Uni-axial, biaxial and fatigue properties of pol-yester fibre glass' ASTM STP 546(American Society for Testing and Materials, 1974) pp 395-418. [33] TSANGARAKIS, N. AND PEPI, M. S. ' Biaxial flexing of a fiber rein-forced aluminum composite'J Compo-site Mater 24(1990) pp 770-785. [34] 温班宁, 李少林, 石多奇, 等. 复合材料高低周复合疲劳试验技术[J]. 航空动力学报, 2023: 1-7.WEN BANNING, LI SHAOLIN, SHI DUOQI, etc. High low cycle composite fatigue testing technology for composite materials[J]. Journal of Aerodynamics, 2023: 1-7(in Chinese). [35] KWON H J, JAR P Y B, XIA Z. Characterization of Bi-axial fatigue resistance of polymer plates[J]. Journal of materials science, 2005, 40(4): 965-972. doi: 10.1007/s10853-005-6515-2 [36] QIAO Y, DELEO A A, SALVIATO M. A study on the multi-axial fatigue failure behavior of notched composite laminates[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2019, 127: 105640. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105640 [37] ABOUL WAFA MN H A E A. Combined bending torsional fatigue of woven rowing GRP[J]. Composites, 1997, 10(4): 215-222. [38] AMIJIMA S, FUJII T, HAMAGUCHI M. Static and fatigue tests of a woven glass fabric composite under biaxial tension-torsion loading[J]. Composites, 1991, 22(4): 281-289. doi: 10.1016/0010-4361(91)90003-Y [39] FUJII T S T O K. Fatigue notch sensitivity of glass woven fabric composite having a circular hole under tension torsion biaxial loading[J]. Compos Mater, 1994, 28(3): 234-251. doi: 10.1177/002199839402800303 [40] KAWAKAMI H F T M Y. Fatigue degradation and life prediction of glass fabricpolymer composite under tension torsion biaxial loadings[J]. 1996. [41] PEREVOZCHIKOV VG L V P V. Static and fatigue strength of unidirectional composites under the combined effect of shear stress and transverse tension-compression stresses[J]. Mech Compos Mater, 1989, 24(5): 638-644. doi: 10.1007/BF00608850 [42] TAMIAKI M, FUJII T, KAWAKAMI H. Effect of loading path on fatigue degradation and stress-strain response of glass fabric composites under tension/torsion biaxial cyclic loading[R]. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, NY (United States), 1998. [43] INOUE A F T K H. Effect of Loading Path on Mechanical Response of a Glass Fabric Composite at Low Cyclic Fatigue under Tension Torsion Biaxial Loading[J]. Reinf Plast Compos, 2000, 19(2): 111-123. doi: 10.1177/073168440001900202 [44] ANDERSON YAA L V T V. Effect of phase asynchronism on the fatigue resistance of laminated fiber composites in a plane stress state[J]. Mech Compos Mater, 1992, 27(5): 521-529. doi: 10.1007/BF00613476 [45] SKINNER T, DATTA S, CHATTOPADHYAY A, et al. Fatigue damage behavior in carbon fiber polymer composites under biaxial loading[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 174: 106942. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106942 [46] FRANCIS PH W D S D. Biaxial fatigue loading of notched composites[J]. 1977, 11: 488-501. [47] TAKEMURA K F T. Fracture mechanics evaluation of progressive fatigue damage in a circular-hole-notched GRP composite under combined tension/torsion loading[J]. Compos Sci Technol, 1994, 52: 527-534. doi: 10.1016/0266-3538(94)90035-3 [48] TAKEMURA K F T. Fatigue strength and damage progression in a circular-holenotched GRP composite under combined tension/torsion loading[J]. Compos Sci Technol 1994, 1994, 52: 519-526. [49] JONES DL P P L H. Effect of biaxial loads on the static and fatigue properties of composite materials. In: Multiaxial fatigue[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1985, 59(13): 2025-2035. [50] SCHMIDT F, RHEINFURTH M, HORST P, et al. Multiaxial fatigue behaviour of GFRP with evenly distributed or accumulated voids monitored by various NDT methodologies[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2012, 43: 207-216. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2012.03.013 [51] LUA J, XIAO J, CUI X, et al. Multiaxial Fatigue Damage Assessment of Repaired Composite Cruciform Specimens Using Stress Ratio Dependent Fatigue Damage Accumulation Model[C]//AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum. 2022: 0531. [52] KAMALOO A, JABBARI M, TOOSKI M Y, et al. Optimization of thickness and delamination growth in composite laminates under multi-axial fatigue loading using NSGA-II[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 174: 106936. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106936 [53] NAIRN J A, HU S. The initiation and growth of delaminations induced by matrix microcracks in laminated composites[J]. International journal of fracture, 1992, 57(1): 1-24. doi: 10.1007/BF00013005 [54] SKINNER T D, DATTA S, CHATTOPADHYAY A, et al. Biaxial fatigue damage in quasi isotropic laminates[C]//AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum. 2020: 0475. [55] SKINNER T, DATTA S, CHATTOPADHYAY A, et al. Fatigue damage behavior in carbon fiber polymer composites under biaxial loading[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 174: 106942. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106942 [56] QUARESIMIN M, CARRARO P A. Damage accumulation under multiaxial fatigue loading[M]//Modeling Damage, Fatigue and Failure of Composite Materials. Woodhead Publishing, 2016: 61-83. [57] GUO R, LI C, NIU Y, et al. The fatigue performances of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites – A review[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 21: 4773-4789. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.11.053 [58] KOCH I G M. Multiaxial fatigue of a unidirectional ply: an experimental top-down approach[M]. Woodhead Publishing, 2017. [59] CARRARO P A Q M. Modeling the crack initiation in unidirectional laminates under multiaxial fatigue loading[M]. Woodhead Publishing, 2018. [60] WENG J, WEN W, ZHANG H. Multiaxial fatigue life prediction of composite materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2017, 30(3): 1012-1020. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2017.03.019 [61] LAUNAY A, MAITOURNAM M H, MARCO Y, et al. Multiaxial fatigue models for short glass fibre reinforced polyamide. Part II: Fatigue life estimation[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2013, 47: 390-406. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2012.09.015 [62] TALREJA R. Multi-scale modeling in damage mechanics of composite materials[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2006, 41(20): 6800-6812. doi: 10.1007/s10853-006-0210-9 [63] FAWAZ Z, ELLYIN F. Fatigue Failure Model for Fibre-Reinforced Materials under General Loading Conditions[J]. Journal of composite materials, 1994, 28(15): 1432-1451. doi: 10.1177/002199839402801503 [64] AWERBUCH J H H. Off-axis fatigue of graphite/epoxy composites. In: Fatigue of fibrous composite materials[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 1981, 35(7-8): 955-963. [65] KAWAKAMI H, FUJII T J, MORITA Y. Fatigue Degradation and Life Prediction of Glass Fabric Polymer Composite under Tension/Torsion Biaxial Loadings[J]. Journal of reinforced plastics and composites, 1996, 15(2): 183-195. doi: 10.1177/073168449601500204 [66] LABOSSIÈRE P, NEALE K W. A general strength theory for orthotropic fiber-reinforced composite laminae[J]. Polymer composites, 1988, 9(5): 306-317. doi: 10.1002/pc.750090503 [67] PERREUX D, JOSEPH E. The effect of frequency on the fatigue performance of filament-wound pipes under biaxial loading: Experimental results and damage model[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1997, 57(3): 353-364. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(96)00155-8 [68] FERRY L, PERREUX D, VARCHON D, et al. Fatigue behaviour of composite bars subjected to bending and torsion[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1999, 59(4): 575-582. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(98)00103-1 [69] ADDEN S, HORST P. Damage propagation in non-crimp fabrics under bi-axial static and fatigue loading[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2006, 66(5): 626-633. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.07.034 [70] EL-ASSAL A M, KHASHABA U A. Fatigue analysis of unidirectional GFRP composites under combined bending and torsional loads[J]. Composite Structures, 2007, 79(4): 599-605. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2006.02.026 [71] GUDE M, HUFENBACH W, KOCH I, et al. Fatigue failure criteria and degradation rules for composites under multiaxial loadings[J]. Mechanics of composite materials, 2006, 42(5): 443-450. doi: 10.1007/s11029-006-0054-z [72] SMITH EW P K. Biaxial fatigue of a glass-fibre reinforced composite. Part2: failure criteria for fatigue and fracture[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1989, 32(1): 17-28. [73] SMITH EW P K. Biaxial fatigue of a glass-fibre reinforced composite. Part2: failure criteria for fatigue and fracture[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1989, 32(1): 17-28. [74] PETERMANN J, PLUMTREE A. A unified fatigue failure criterion for unidirectional laminates[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2001, 32(1): 107-118. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(00)00099-3 [75] 戚东涛, 程光旭, 段权, 等. 基于临界平面法的复合材料多轴疲劳损伤参量研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2003, 37(11): 1182-1185.QI DONGTAO, CHENG GUANGXU, DUAN QUAN, et al Research on Multiaxial Fatigue Damage Parameters of Composite Materials Based on Critical Plane Method[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2003, 37 (11): 1182-1185(in Chinese). [76] COLOMBO C, VERGANI L. Multi-axial fatigue life estimation of unidirectional GFRP composite[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2011, 33(8): 1032-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2011.01.001 [77] GŁOWACKA K, ŁAGODA T. Application of multiaxial fatigue criterion in critical plane to determine lifetime of composite laminates[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2023, 292: 109644. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2023.109644 [78] M H. Physics-based methodology for predicting ply cracking and laminate failure in symmetric composite laminates under multiaxial loading condition[M]. Woodhead Publishing, 2021. [79] VASSILOPOULOS A, GEORGOPOULOS E, KELLER T. Comparison of genetic programming with conventional methods for fatigue life modeling of FRP composite materials[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2008, 30(9): 1634-1645. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.11.007 [80] VASSILOPOULOS A P, KELLER T. Modeling of the fa-tigue life of adhesively-bonded FRP joints with genetic programming[C]//17th Interna-tional Con-ference on Composite Materials (ICCM17), Edin-burgh, UK. 2009: 27-31. [81] VASSILOPOULOS A, GEORGOPOULOS E, DIONYSOPOULOS V. Artificial neural networks in spectrum fatigue life prediction of composite materials[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2007, 29(1): 20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2006.03.004 [82] VASSILOPOULOS A P, BEDI R. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system in modelling fatigue life of multidirectional composite laminates[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2008, 43(4): 1086-1093. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2008.02.028 [83] ELEFTHEROGLOU N, ZAROUCHAS D, BENEDICTUS R. An adaptive probabilistic data-driven methodology for prognosis of the fatigue life of composite structures[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 245: 112386. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112386 [84] KUMAR C H, SWAMY R P. Fatigue life prediction of glass fiber reinforced epoxy composites using artificial neural networks[J]. Composites Communications, 2021, 26: 100812. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2021.100812 [85] XU X, WANG G, YAN H, et al. Deep-learning-enhanced digital twinning of complex composite structures and real-time mechanical interaction[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2023, 241: 110139. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.110139 [86] MACHELLO C, BAZLI M, RAJABIPOUR A, et al. Using machine learning to predict the long-term performance of fibre-reinforced polymer structures: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 408: 133692. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133692 [87] FERNÁNDEZ J, CHIACHÍO M, CHIACHÍO J, et al. Uncertainty quantification in Neural Networks by Approximate Bayesian Computation: Application to fatigue in composite materials[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 107: 104511. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104511 [88] QUARESIMIN M, CARRARO P A. On the investigation of the biaxial fatigue behaviour of unidirectional composites[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2013, 54: 200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.05.014 [89] CARRARO P A, QUARESIMIN M. A damage based model for crack initiation in unidirectional composites under multiaxial cyclic loading[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2014, 99: 154-163. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.05.012 [90] 吴涛, 姚卫星, 黄杰. 纤维增强树脂基复合材料超高周疲劳研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(6): 210-218.WU TAO, YAO WEIXING, HUANG JIE. Research pro gress on ultra-high cycle fatigue of fiber-reinforced resin matrix composites[J]. Material Introduction, 2022, 36(6): 210-218(in Chinese). -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 163
- HTML全文浏览量: 73
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: