Research progress of MXenes for second near-infrared window photothermal diagnosis and therpay of tumors
-
摘要: 由近红外二区(NIR-II,1000-1350 nm)光触发光热剂进行光热治疗是一种新兴的肿瘤治疗方式,具有良好的应用前景。过渡金属碳化物、氮化物或碳氮化合物(MXenes)具有超薄层状结构、独特的电子性质、比表面积大、光热转换效率高、良好的亲水性以及易于表面功能化等优点,可作为一类具有优良性质的光热剂应用于NIR-Ⅱ 区肿瘤光热治疗。本文介绍了NIR-II区光热治疗的优势,概括了MXenes的光热性能和MXenes胶体溶液稳定性,重点总结了MXenes在NIR-Ⅱ区肿瘤光热诊疗的研究进展,并阐述了该领域未来发展所面临的挑战和机遇。Abstract: Photothermal tumor therapy with second near-infrared (NIR-II, 1000-1350 nm) phototriggered photothermal agents is a promising emerging method of tumor therapy. Transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitridges compounds (MXenes) have advantages such as ultra-thin layered structure, unique electronic properties, large specific surface area, high photothermal conversion efficiency, good hydrophilicity, and easy surface functionalization, making them suitable as photothermal agents for tumor photothermal therapy. This review introduces the advantages of NIR-Ⅱ photothermal therapy, summarizes the photothermal performance of MXenes and the stability of MXenes colloidal solution. At the same time, the research progress of MXenes in NIR-Ⅱ tumor photothermal therapy was discussed, and the challenges and opportunities faced in the future development of this field were elaborated.
-
Key words:
- MXenes /
- tumor /
- photothermal diagnosis and therapy /
- NIR-II /
- combined therapy
-
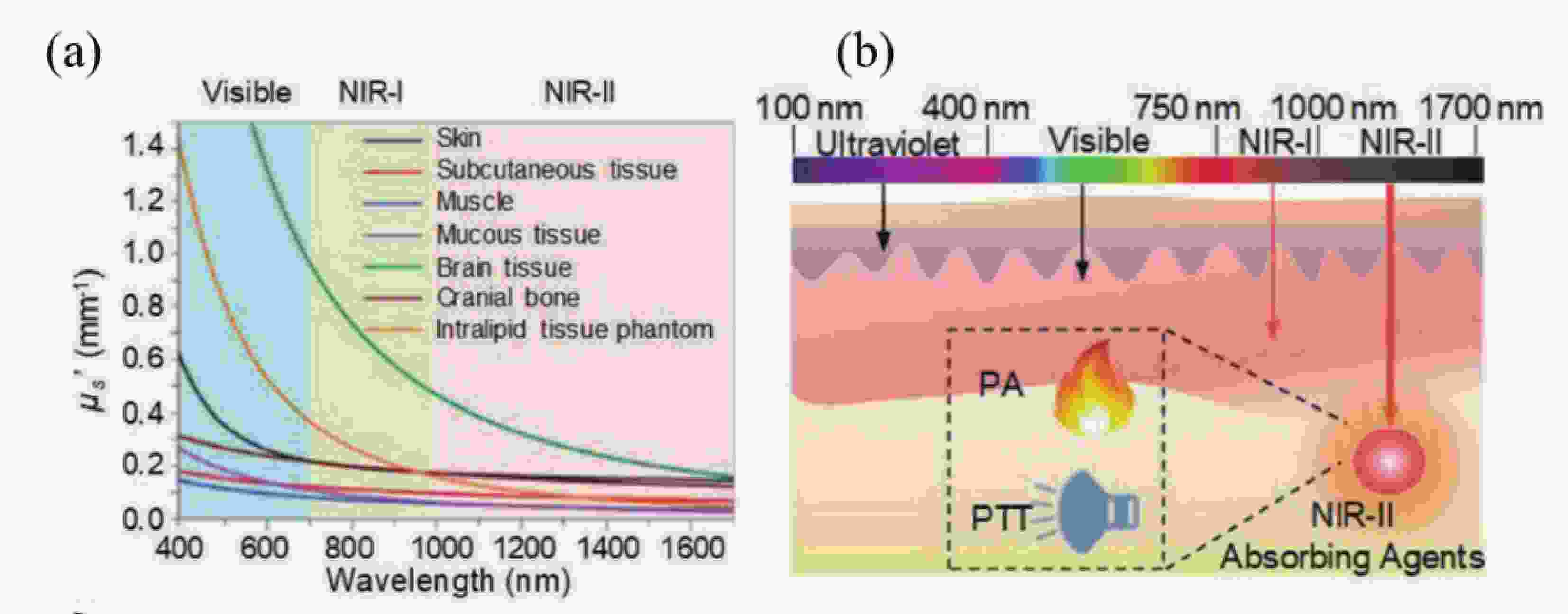
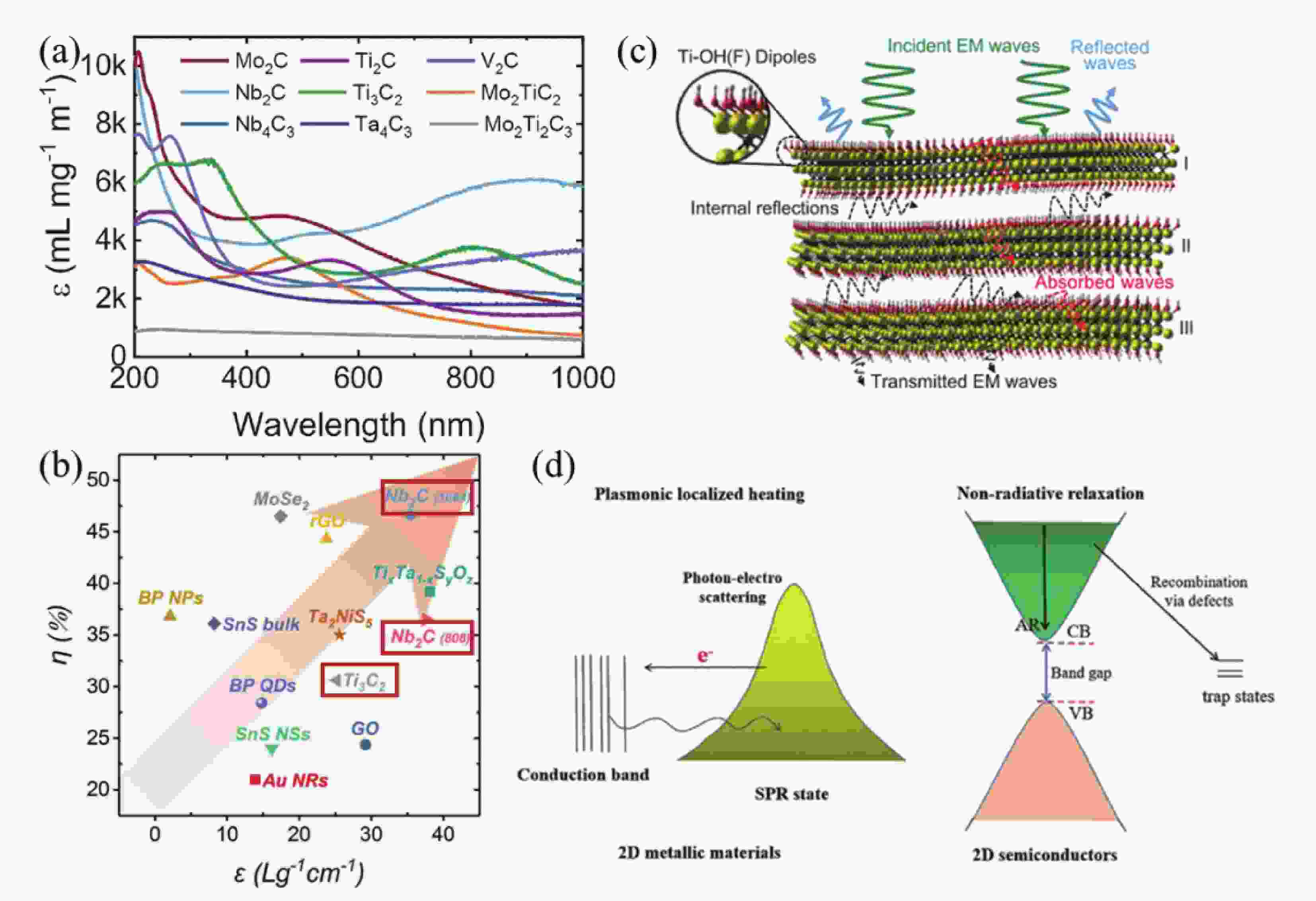
图 3 光热转换机制。(a) MXenes的紫外-可见-近红外吸收图[25]. (b)常见2D无机纳米材料的光热性能参数,包括消光系数(ε)和光热转换效率(η)[32];(c)电磁干扰屏蔽机制示意图[38];(d) 2D金属材料和半导体材料的光热转换机制示意图[14]。
Figure 3. Photothermal conversion mechanism. (a) UV-vis-NIR optical extinction properties of MXenes[25]. (b) The photothermal performance parameters of various 2D inorganic nanomaterials, including mass extinction coefficient (ε) and photothermal conversion efficiency (η) [26]; (c) Schematic diagram of electromagnetic interference shielding mechanism [38] ; (d) Typical photothermal conversion mechanisms of 2D metallic materials and 2D semiconductors[14].
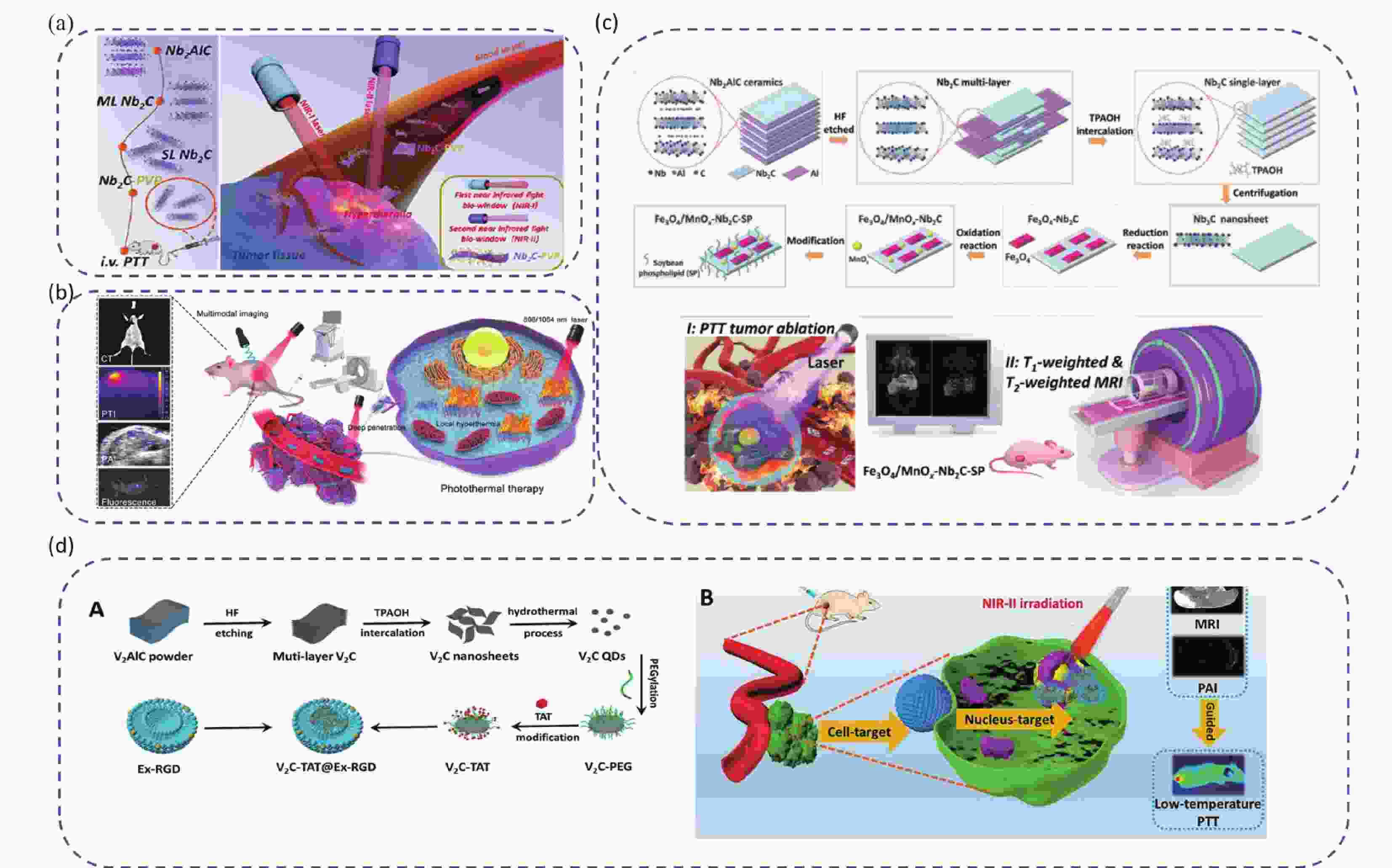
图 5 (a) Nb2C-PVP用于NIR-I和NIR-II区肿瘤PTT示意图[27];(b) W1.33C-BSA诊疗示意图[31];(c) Fe3O4/MnOx-Nb2C制备及用于肿瘤诊疗示意图[59];(d) V2C-TAT@Ex-RGD制备及双重靶向PTT诊疗示意图[30]。
Figure 5. (a) Schematic illustration of Nb2C-PVP for in vivo photothermal tumor ablation in NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows[27]; (b) Schematic illustration of 2D W1.33C-BSA for multimodal-imaging-guidedcancer treatment[31]; (c) Schematic illustration of the synthetic process of Fe3O4/MnOx–Nb2C–SP for in vivo imaging-guided photothermal ablation of breast cancer[59]; (d) Schematic diagram of the synthetic process of V2C-TAT@Ex-RGD for in vivo dual-target PTT diagnosis and treatment[30].
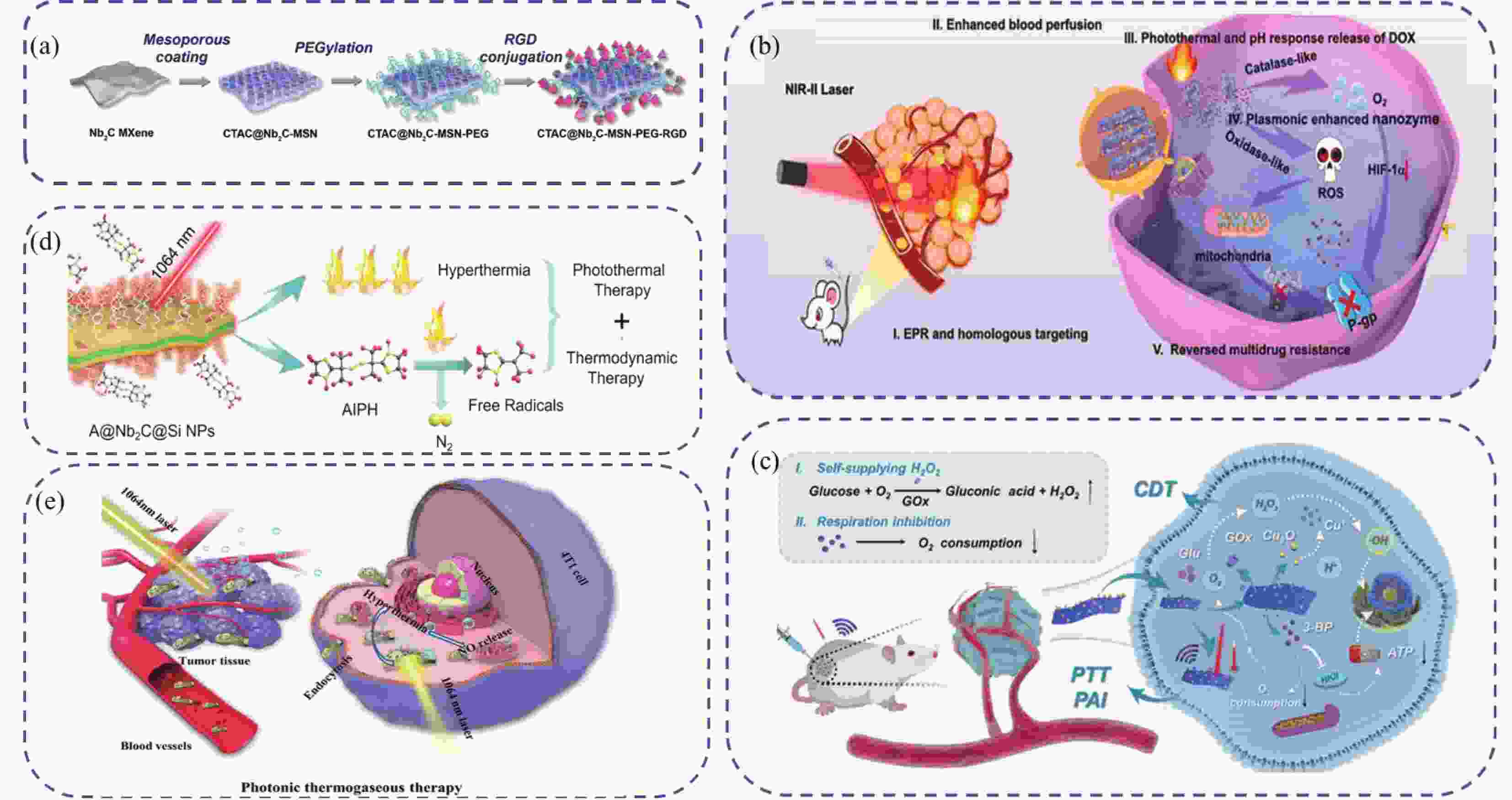
图 6 (a) CTAC@Nb2C-MSN制备过程示意图[63];(b) Nb2C-Pt-DOX@M体内治疗机制示意图[65];(c) 3-BP@MCG PTT/CDT体内治疗机制示意图[8];(d) AIPH@Nb2C@mSiO2治疗机制示意图[72];(e) Nb2C–MSNs–SNO体内治疗机制示意图[74]。
Figure 6. (a) The schematic diagram of the synthetic process of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN[63]; (b) The schematic diagram of treatment mechanism of Nb2C-Pt-DOX@M in vivo[65]; (c) The schematic diagram of treatment mechanism of 3-BP@MCG NSs PTT/CDT in vivo in vivo[8]; (d) The schematic diagram of treatment mechanism of AIPH@Nb2C@mSiO2[72]; (e) The schematic diagram of treatment mechanism of Nb2C–MSNs–SNO in vivo[74].
表 1 MXenes在NIR-Ⅱ PTT中的应用
Table 1. Application of MXenes in NIR-Ⅱ PTT
MAX Materials Therapeutic modes Power (W/cm2) PTCE (%) Ref. Ti3AlC2 Ti3C2@Au PTT/RT/CTI/PAI 0.75 39.60 [75] Ti3C2-Cu-PEG PTT/PDT/CDT 1.0 47.84 [70] Ti3C2Tx-Pt-PEG PTT/CDT/PAI 0.75 31.78 [68] Ti3C2@TiO2-x-PEG PTT/SDT/PAI 0.80 35.80 [76] Ti3C2/CA4@PLEL PTT/CHT 1.0 41.40 [77] HH-Ti3C2-PEG PTT/SDT/PAI 1.0 49.60 [78] Ti3C2/TiO2-PVP HJs PTT/PDT 0.6 44.98 [9] 3-BP@Ti3C2/Cu2O/GOX PTT/CDT/PAI 1.0 53.39 [8] CD@Ti3C2Tx HJs PTT/SDT 1.0 64.50 [79] Nb2AlC Nb2C-PVP PTT/PAI 0.8 46.65 [27] Nb2C-Ox-PVP PTT/SDT 1.0 - [73] PVP/Nb2C MNs PTT 1.0 32.89 [62] Nb2C/zein PTT 1.0 - [61] CTAC@Nb2C-MSN-PEG-RGD PTT/CHT/PAI 1.5 28.60 [63] Nb2C@PDA-R837@RBC PTT/IT 1.5 27.60 [28] Nb2C-MSNs-SNO PTT/GT/PAI 1.0 39.09 [74] NPD@M(Nb2C) PTT/CDT/CHT 0.5 51.00 [65] Nb2C/Au/anti-TNFα-PVP PTT 0.75 - [80] Fe3O4/MnOx-Nb2C-SP PTT/MRI 1.5 30.90 [59] AIPH@Nb2C@Si PTT/TDT/PAI 1.0 27.03 [72] Nb2C-IO-CaO2-PVP PTT/ CDT 1.0 45.65 [64] Mo2Ga2C Mo2C-PVA PTT 1.0 43.30 [29] (W2/3Y1/3)2AlC W1.33C-BSA PTT/CHT /PTI/PAI/FLI 1.25 49.30 [31] Ti3AlCN Ti3CN-BSA PTT 1.0 32.10 [58] V2AlC V2C-TAT@Ex-RGD(QDs) PTT/PAI/MRI 0.96 45.05 [30] Ti2AlN Ti2N-SP(QDs) PTT/PAI 1.0 45.51 [60] Notes: CA4,Combretastatin A4; PLEL, poly(D,L-lactide)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(D,L-lactide); HJs, Heterojunctions; Gox, Glucose Oxidase; CDs, Carbon Dots;Nb2C-Ox,in-situ self-oxidized Nb2C MXenes; MNs, Microneedles; CTAC, Cetanecyltrimethylammonium chloride; RGD, Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic; MSN, Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles; PDA, polydopamine; RBC, Red Blood Cell; RSNO, S-nitrosothiol; NPD@M, biomimetic photoinduced plasmonic assembly; TNF-α,tumor necrosis factor-α; PVP, Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone; SP, Soybean phospholipid;AIPH,2,2′-azobis[2-(2-imidazolin-2-yl)propane] dihydrochloride; IO, Iron Oxide; PVA, Polyvinyl Alcohol; BSA, Bovine Serum Albumin; Ex, Engineered exosomes; TAT, TAT peptides; QDs, Quantum Dots.
PTT, Photothermal therapy; PDT, Photodynamic therapy; CDT, Chemodynamic therapy; SDT, Sonodynamic therapy; CHT, Chemotherapy; IT, Immunotherapy; TDT, Thermodynamic therapy; RT, Radio Therapy; GT, Gas therapy; PAI, Photoacoustic Imaging; CTI, Computed tomography imaging; PTI, Photothermal imaging; FLI, Fluorescence imaging; MRI, Magnetic resonance imaging. -
[1] HUANG, H, WEI, CHEN, Y, Two-dimensional biomaterials: Material science, biological effect and biomedical engineering applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews 2021, 50 (20): 11381-11485. [2] NAGUIB, M, KURTOGLU, M, PRESSER, V, et al. , Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2[J]. Advanced Materials 2011, 23 (37): 4248-4253. [3] NAGUIB, M, MASHTALIR, O, CARLE, J, et al. , Two-dimensional transition metal carbides[J]. ACS Nano 2012, 6 (2): 1322-1331. [4] POGORIELOV, M, SMYRNOVA, K, KYRYLENKO, S, et al. , MXenes-a new class of two-dimensional materials: Structure, properties and potential applications[J]. Nanomaterials 2021, 11 (12): 3412. [5] HUANG, H, DONG, C, FENG, W, et al. , Biomedical engineering of two-dimensional MXenes[J]. Advanced drug delivery reviews 2022, 184: 114178. [6] IRAVANI, S, VARMA, R S, MXenes in cancer nanotheranostics[J]. Nanomaterials 2022, 12 (19): 3360. [7] SHAO, J D, XIE, H H, HUANG, H, et al. , Biodegradable black phosphorus-based nanospheres for in vivo photothermal cancer therapy[J]. Nature Communications 2016, 7 (1): 12967. [8] WANG, Z, LI, H, SHE, W, et al. , 3-bromopyruvate-loaded Ti3C2 MXene/Cu2O nanosheets for photoacoustic imaging-guided and hypoxia-relieving enhanced photothermal/chemodynamic therapy[J]. Analytical Chemistry 2023, 95 (2): 1710-1720. [9] ZHU, H, ZHANG, X Q, WANG, Q S, et al. , In situ assembled titanium carbide-based heterojunctions for the synergistic enhancement of NIR-II photothermal/photodynamic therapy against breast cancer[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2022, 10 (48): 10083-10096. [10] GAO, W, ZHANG, W H, YU, H P, et al. , 3D CNT/MXene microspheres for combined photothermal/photodynamic/chemo for cancer treatment[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2022, 10: 996177. [11] ZAMHURI, A, LIM, G P, MA, N L, et al. , MXene in the lens of biomedical engineering: Synthesis, applications and future outlook[J]. Biomedical Engineering Online 2021, 20 (1): 33. [12] JIANG, Y Y, LI, J C, ZHEN, X, et al. , Dual-peak absorbing semiconducting copolymer nanoparticles for first and second near-infrared window photothermal therapy: A comparative study[J]. Advanced Materials 2018, 30 (14): 5980-5987. [13] LYU, Y, LI, J, PU, K, Second near-infrared absorbing agents for photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy[J]. Small Methods 2019, 3 (11): 1900553. [14] AN, D, FU, J Y, ZHANG, B, et al. , NIR-II responsive inorganic 2D nanomaterials for cancer photothermal therapy: Recent advances and future challenges[J]. Advanced Functional Materials 2021, 31 (32): 2101625. [15] LIN, H, WANG, X G, YU, L D, et al. , Two-dimensional ultrathin MXene ceramic nanosheets for photothermal conversion[J]. Nano Letters 2017, 17 (1): 384-391. [16] LU, B B, ZHU, Z Y, MA, B Y, et al. , 2D MXene nanomaterials for versatile biomedical applications: Current trends and future prospects[J]. Small 2021, 17 (46): 2100946. [17] LIU, Y J, BHATTARAI, P, DAI, Z F, et al. , Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer[J]. Chemical Society Reviews 2019, 48 (7): 2053-2108. [18] XU, Y, WANG, Y, AN, J, et al. , 2D-ultrathin MXene DOXjade platform for iron chelation chemo-photothermal therapy[J]. Bioactive Materials 2022, 14: 76-85. [19] LIANG, R J, LI, Y S, HUO, M F, et al. , Triggering sequential catalytic fenton reaction on 2D MXenes for hyperthermia-augmented synergistic nanocatalytic cancer therapy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2019, 11 (46): 42917-42931. [20] SHI, T, HUANG, C, LI, Y, et al. , NIR-II phototherapy agents with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for tumor imaging and therapy[J]. Biomaterials 2022, 285: 121535. [21] LI, Z, ZHANG, C, ZHANG, X, et al. , NIR-II functional materials for photoacoustic theranostics[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2022, 33 (1): 67-86. [22] DAI, H, WANG, X, SHAO, J, et al. , NIR-II organic nanotheranostics for precision oncotherapy[J]. Small 2021, 17 (44): 2102646. [23] JIANG, S, HUANG, K, QU, J, et al. , Cancer nanotheranostics in the second near-infrared window[J]. View 2021, 2 (1): 20200075. [24] XU, C, PU, K Y, Second near-infrared photothermal materials for combinational nanotheranostics[J]. Chemical Society Reviews 2021, 50 (2): 1111-1137. [25] MALESKI, K, SHUCK, C E, FAFARMAN, A T, et al. , The broad chromatic range of two-dimensional transition metal carbides[J]. Advanced Optical Materials 2021, 9 (4): 2001563. [26] LIN, H, CHEN, Y, SHI, J L, Insights into 2D MXenes for versatile biomedical applications: Current advances and challenges ahead[J]. Advanced Science 2018, 5 (10): 1800518. [27] LIN, H, GAO, S S, DAI, C, et al. , A two-dimensional biodegradable niobium carbide (MXene) for photothermal tumor eradication in NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2017, 139 (45): 16235-16247. [28] LU, Y, ZHANG, X G, HOU, X Q, et al. , Functionalized 2D Nb2C nanosheets for primary and recurrent cancer photothermal/immune-therapy in the NIR-II biowindow[J]. Nanoscale 2021, 13 (42): 17822-17836. [29] FENG, W, WANG, R, ZHOU, Y, et al. , Ultrathin molybdenum carbide mxene with fast biodegradability for highly efficient theory-oriented photonic tumor hyperthermia[J]. Advanced Functional Materials 2019, 29 (22): 1942-1957. [30] CAO, Y, WU, T, ZHANG, K, et al. , Engineered exosome-mediated near-infrared-II region V2C quantum dot delivery for nucleus-target low-temperature photothermal therapy[J]. ACS Nano 2019, 13 (2): 1499-1510. [31] ZHOU, B, YIN, H, DONG, C, et al. , Biodegradable and excretable 2D W1.33C i-MXene with vacancy ordering for theory-oriented cancer nanotheranostics in near-infrared biowindow[J]. Advanced Science 2021, 8 (24): 2101043. [32] XU, D X, LI, Z D, LI, L S, et al. , Insights into the photothermal conversion of 2D MXene nanomaterials: Synthesis, mechanism, and applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials 2020, 30 (47): 2000712. [33] ZHAO, J, XUE, S, JI, R, et al. , Localized surface plasmon resonance for enhanced electrocatalysis[J]. Chemical Society Reviews 2021, 50 (21): 12070-12097. [34] AN, D, FU, J, ZHANG, B, et al. , NIR-II responsive inorganic 2D nanomaterials for cancer photothermal therapy: Recent advances and future challenges[J]. Advanced Functional Materials 2021, 31 (32): 2101625. [35] ZHANG, L, OUDENG, G, WEN, F Q, et al. , Recent advances in near-infrared-II hollow nanoplatforms for photothermal-based cancer treatment[J]. Biomaterials Research 2022, 26 (1): 61. [36] FAN, X Q, LIU, L, JIN, X, et al. , MXene Ti3C2Tx for phase change composite with superior photothermal storage capability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2019, 7 (23): 14319-14327. [37] LIU, G, ZOU, J, TANG, Q, et al. , Surface modified Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets for tumor targeting photothermal/photodynamic/chemo synergistic therapy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2017, 9 (46): 40077-40086. [38] KUMAR, P, Ultrathin 2D nanomaterials for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces 2019, 6 (24): 1901454. [39] SHAHZAD, F, ALHABEB, M, HATTER, C B, et al. , Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes)[J]. Science 2016, 353 (6304): 1137-1140. [40] JIANG, J Z, BAI, S S, ZOU, J, et al. , Improving stability MXenes[J]. Nano Research 2022, 15 (7): 6551-6567. [41] PALISAITIS, J, PERSSON, I, HALIM, J, et al. , On the structural stability of MXene and the role of transition metal adatoms[J]. Nanoscale 2018, 10 (23): 10850-10855. [42] ZHANG, J Z, KONG, N, HEGH, D, et al. , Freezing titanium carbide aqueous dispersions for ultra-long-term storage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2020, 12 (30): 34032-34040. [43] PENG, C, YANG, X, LI, Y, et al. , Hybrids of two-dimensional Ti3C2 and TiO2 exposing facets toward enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2016, 8 (9): 6051-6060. [44] DONG, L M, YE, C, ZHENG, L L, et al. , Two-dimensional metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes): Preparation, property, and applications in cancer therapy[J]. Nanophotonics 2020, 9 (8): 2125-2145. [45] ZHANG, C J, PINILLA, S, MCEYOY, N, et al. , Oxidation stability of colloidal two-dimensional titanium carbides (MXenes)[J]. Chemistry of Materials 2017, 29 (11): 4848-4856. [46] HUANG, S, MOCHALIN, V N, Hydrolysis of 2D transition-metal carbides (MXenes) in colloidal solutions[J]. Inorganic Chemistry 2019, 58 (3): 1958-1966. [47] HUANG, S, MOCHALIN, V N, Understanding chemistry of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and carbonitrides (MXenes) with gas analysis[J]. ACS Nano 2020, 14 (8): 10251-10257. [48] ZHAO, X, VASHISTH, A, PREHN, E, et al. , Antioxidants unlock shelf-stable Ti3C2Tx (MXene) nanosheet dispersions[J]. Matter 2019, 1 (2): 513-526. [49] PENG, J, CHENG, H, LIU, J, et al. , Superhydrophobic MXene-based fabric with electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal management ability for flexible sensors[J]. Advanced Fiber Materials 2023. [50] WANG, X Y, WANG, Z Y, QIU, J S, Stabilizing MXene by hydration chemistry in aqueous solution[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2021, 60 (51): 26587-26591. [51] MALESKI, K, MOCHALIN, V N, GOGOTSI, Y, Dispersions of two-dimensional titanium carbide MXene in organic solvents[J]. Chemistry of Materials 2017, 29 (4): 1632-1640. [52] CHAE, Y, KIM, S J, CHO, S Y, et al. , An investigation into the factors governing the oxidation of two-dimensional Ti3C2 MXene[J]. Nanoscale 2019, 11 (17): 8387-8393. [53] MATHIS, T S, MALESKI, K, GOAD, A, et al. , Modified max phase synthesis for environmentally stable and highly conductive Ti3C2 MXene[J]. ACS Nano 2021, 15 (4): 6420-6429. [54] CHENG, L, WANG, X, GONG, F, et al. , 2D nanomaterials for cancer theranostic applications[J]. Advanced Materials 2020, 32 (13): 1902333. [55] HUANG, Z, CUI, X, LI, S, et al. , Two-dimensional MXene-based materials for photothermal therapy[J]. Nanophotonics 2020, 9 (8): 2233-2249. [56] HU, J J, CHENG, Y J, ZHANG, X Z, Recent advances in nanomaterials for enhanced photothermal therapy of tumors[J]. Nanoscale 2018, 10 (48): 22657-22672. [57] HUANG, K, LI, Z J, LIN, J, et al. , Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for biomedical applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews 2018, 47 (14): 5109-5124. [58] ZHU, Y H, TANG, X F, LIU, Q, et al. , Metallic carbonitride MXene based photonic hyperthermia for tumor therapy[J]. Small 2022, 18 (22): 2200646. [59] LIU, Z, ZHAO, M L, YU, L D, et al. , Redox chemistry-enabled stepwise surface dual nanoparticle engineering of 2D MXenes for tumor-sensitive T-1 and T-2 MRI-guided photonic breast-cancer hyperthermia in the NIR-II biowindow[J]. Biomaterials Science 2022, 10 (6): 1562-1574. [60] SHAO, J D, ZHANG, J, JIANG, C, et al. , Biodegradable titanium nitride MXene quantum dots for cancer phototheranostics in NIR-I/II biowindows[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 400: 126009. [61] ZHOU, B, PU, Y, LIN, H, et al. , In situphase-changeable 2D MXene/zein bio-injection for shear wave elastography-guided tumor ablation in NIR-II bio-window[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2020, 8 (24): 5257-5266. [62] LIN, S Y, LIN, H, YANG, M, et al. , A two-dimensional MXene potentiates a therapeutic microneedle patch for photonic implantable medicine in the second NIR biowindow[J]. Nanoscale 2020, 12 (18): 10265-10276. [63] HAN, X X, JING, X X, YANG, D Y, et al. , Therapeutic mesopore construction on 2D Nb2C MXenes for targeted and enhanced chemo-photothermal cancer therapy in NIR-II biowindow[J]. Theranostics 2018, 8 (16): 4491-4508. [64] GAO, S S, LU, X Y, ZHU, P, et al. , Self-evolved hydrogen peroxide boosts photothermal-promoted tumor-specific nanocatalytic therapy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2019, 7 (22): 3599-3609. [65] HAO, Z N, LI, Y F, LIU, X Y, et al. , Enhancing biocatalysis of a MXene-based biomimetic plasmonic assembly for targeted cancer treatments in NIR-II biowindow[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 425: 130639. [66] WANG, A, MAO, Q, ZHAO, M, et al. , pH/Reduction dual stimuli-triggered self-assembly of NIR theranostic probes for enhanced dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy of tumors[J]. Analytical Chemistry 2020, 92 (24): 16113-16121. [67] SUN, R, ZHANG, Y Q, GAO, Y J, et al. , A tumor-targetable NIR probe with photoaffinity crosslinking characteristics for enhanced imaging-guided cancer phototherapy[J]. Chemical Science 2023, 14 (9): 2369-2378. [68] ZHU, Y, WANG, Z, ZHAO, R, et al. , Pt decorated Ti3C2Tx MXene with NIR-II light amplified nanozyme catalytic activity for efficient phototheranostics[J]. ACS Nano 2022, 16 (2): 3105-3118. [69] GONG, F, YANG, N, WANG, X, et al. , Tumor microenvironment-responsive intelligent nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics[J]. Nano Today 2020, 32: 100851. [70] ZHANG, Y, LI, S, FANG, X, et al. , Copper decorated Ti3C2 nanosystem with NIR-II-induced gsh-depletion and reactive oxygen species generation for efficient nanodynamic therapy[J]. Nanophotonics 2022, 11 (22): 5189-5204. [71] HU, H, FENG, W, QIAN, X, et al. , Emerging nanomedicine-enabled/enhanced nanodynamic therapies beyond traditional photodynamics[J]. Advanced Materials 2021, 33 (12): 2005062. [72] XIANG, H J, LIN, H, YU, L D, et al. , Hypoxia-irrelevant photonic thermodynamic cancer nanomedicine[J]. ACS Nano 2019, 13 (2): 2223-2235. [73] XU, J, CHEN, L, DING, S, et al. , Self-generated schottky barriers in niobium carbide MXene nanocatalysts for theory-oriented sonocatalytic and NIR-II photonic hyperthermia tumor therapy[J]. Nano Today 2023, 48: 101750. [74] YIN, H, GUAN, X, LIN, H, et al. , Nanomedicine-enabled photonic thermogaseous cancer therapy[J]. Advanced Science 2020, 7 (2): 1901954. [75] TANG, W T, DONG, Z L, ZHANG, R, et al. , Multifunctional two-dimensional core-shell MXene@gold nanocomposites for enhanced photo-radio combined therapy in the second biological window[J]. ACS Nano 2019, 13 (1): 284-294. [76] ZHANG, D, LIU, H, YOUNIS, M R, et al. , In situ TiO2-x decoration of titanium carbide MXene for photo/sono-responsive antitumor theranostics[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20 (1): 53. [77] TAO, N, LIU, Y, WU, Y, et al. , Minimally invasive antitumor therapy using biodegradable nanocomposite micellar hydrogel with functionalities of NIR-II photothermal ablation and vascular disruption[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials 2020, 3 (7): 4531-4542. [78] LI, G Q, ZHONG, X Y, WANG, X W, et al. , Titanium carbide nanosheets with defect structure for photothermal-enhanced sonodynamic therapy[J]. Bioactive Materials 2022, 8: 409-419. [79] GENG, B, XU, S, SHEN, L, et al. , Multifunctional carbon dot/MXene heterojunctions for alleviation of tumor hypoxia and enhanced sonodynamic therapy[J]. Carbon 2021, 179: 493-504. [80] KONG, F L, FANG, C, ZHANG, Y, et al. , Abundance and metabolism disruptions of intratumoral microbiota by chemical and physical actions unfreeze tumor treatment resistance[J]. Advanced Science 2022, 9 (7): 2105523. [81] CHAO, M, DI, P, YUAN, Y, et al. , Flexible breathable photothermal-therapy epidermic sensor with MXene for ultrasensitive wearable human-machine interaction[J]. Nano Energy 2023, 108: 108201. -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 91
- HTML全文浏览量: 69
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: