Dynamic mechanical properties of novel star-rhombic negative Poisson's ratio honeycomb structure
-
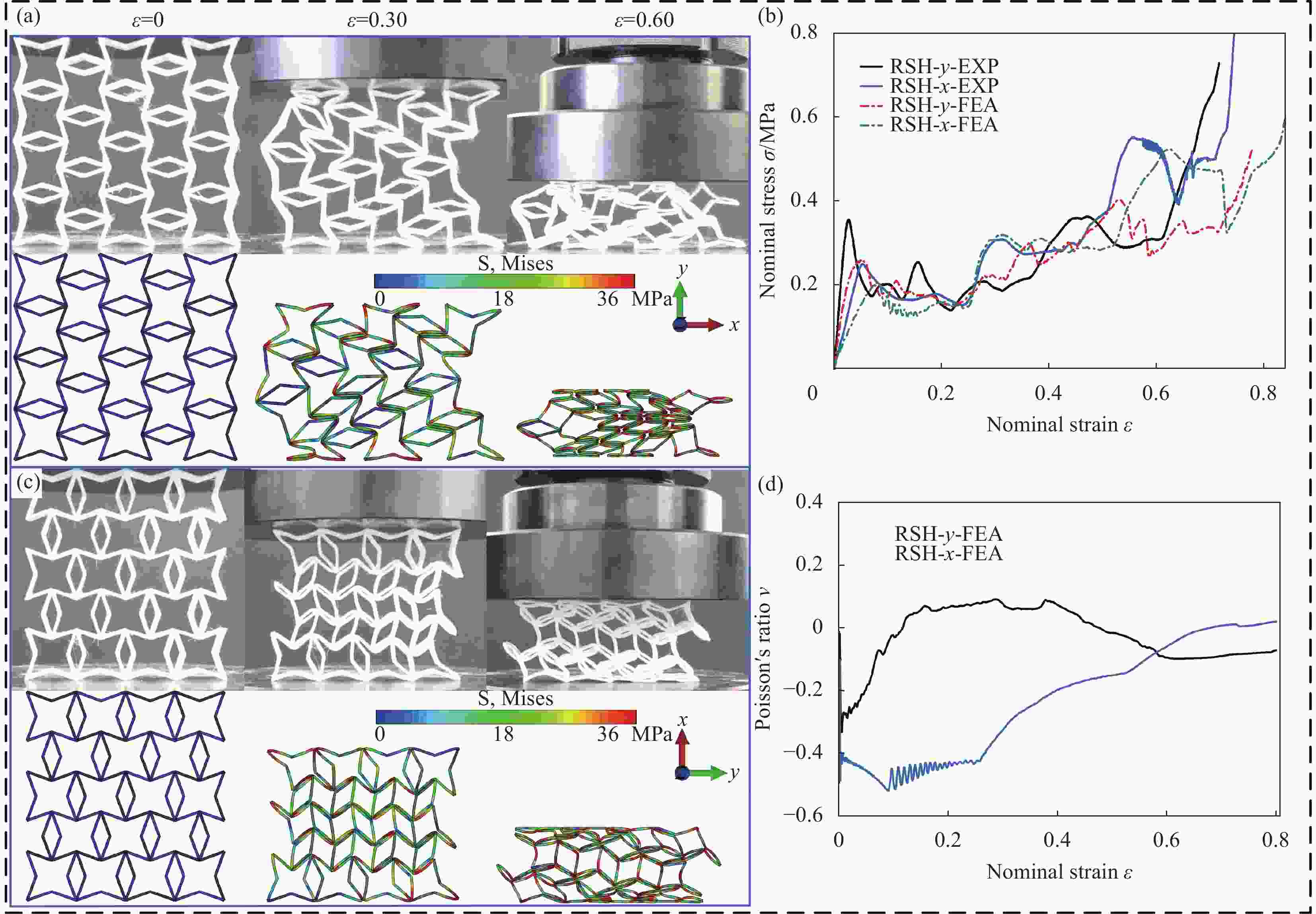
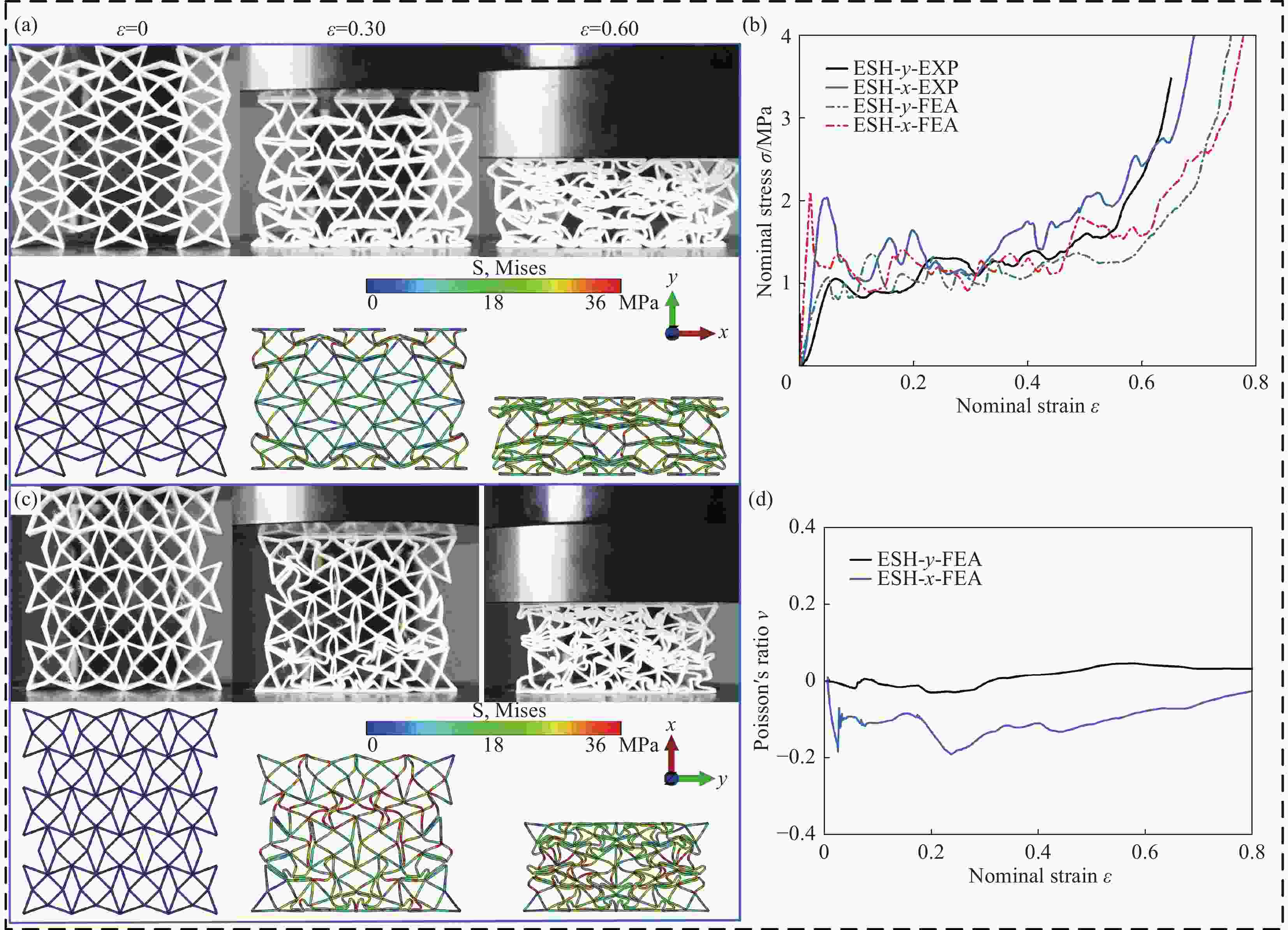
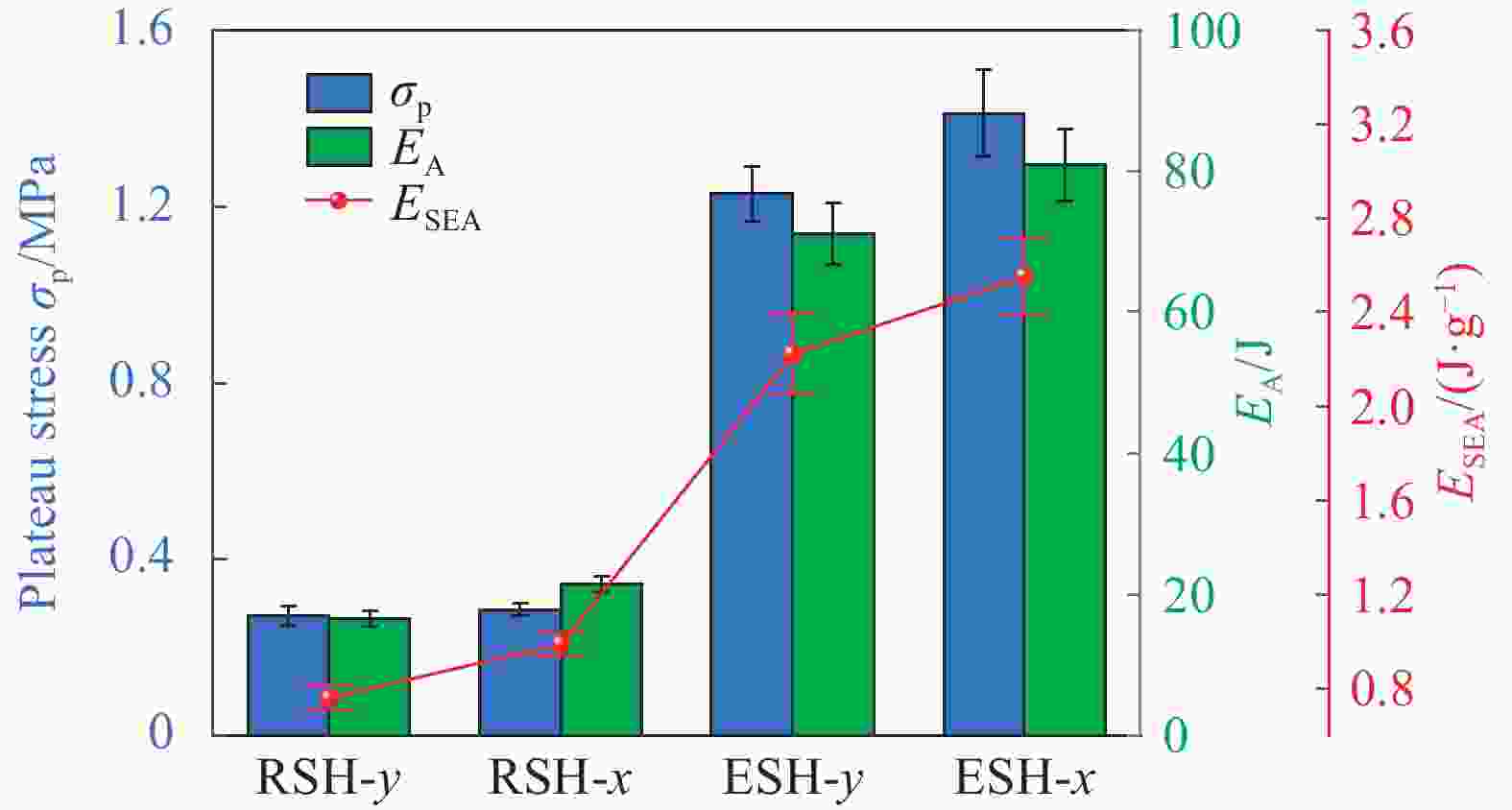
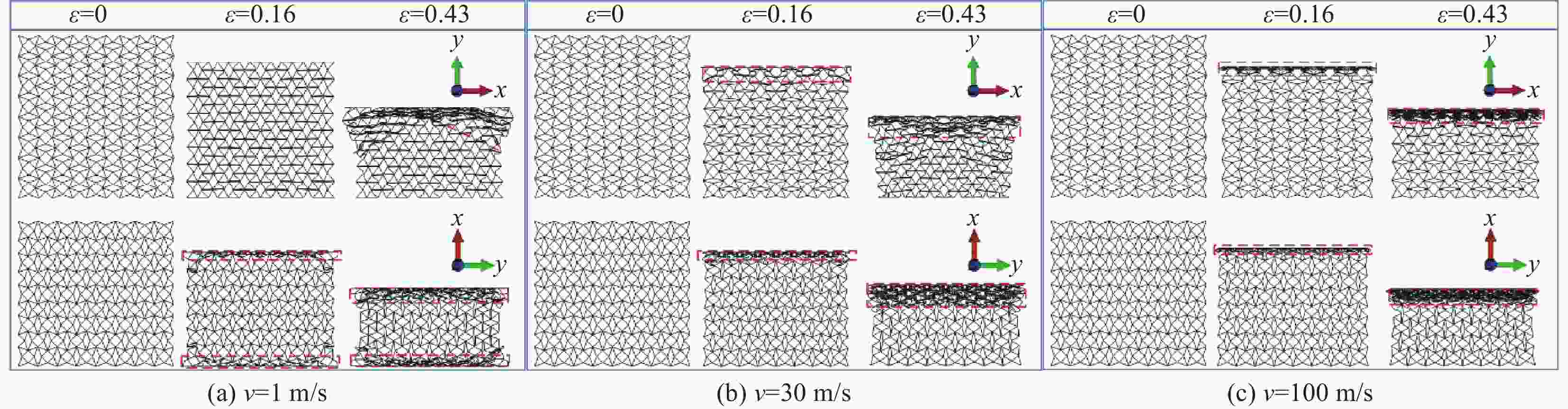
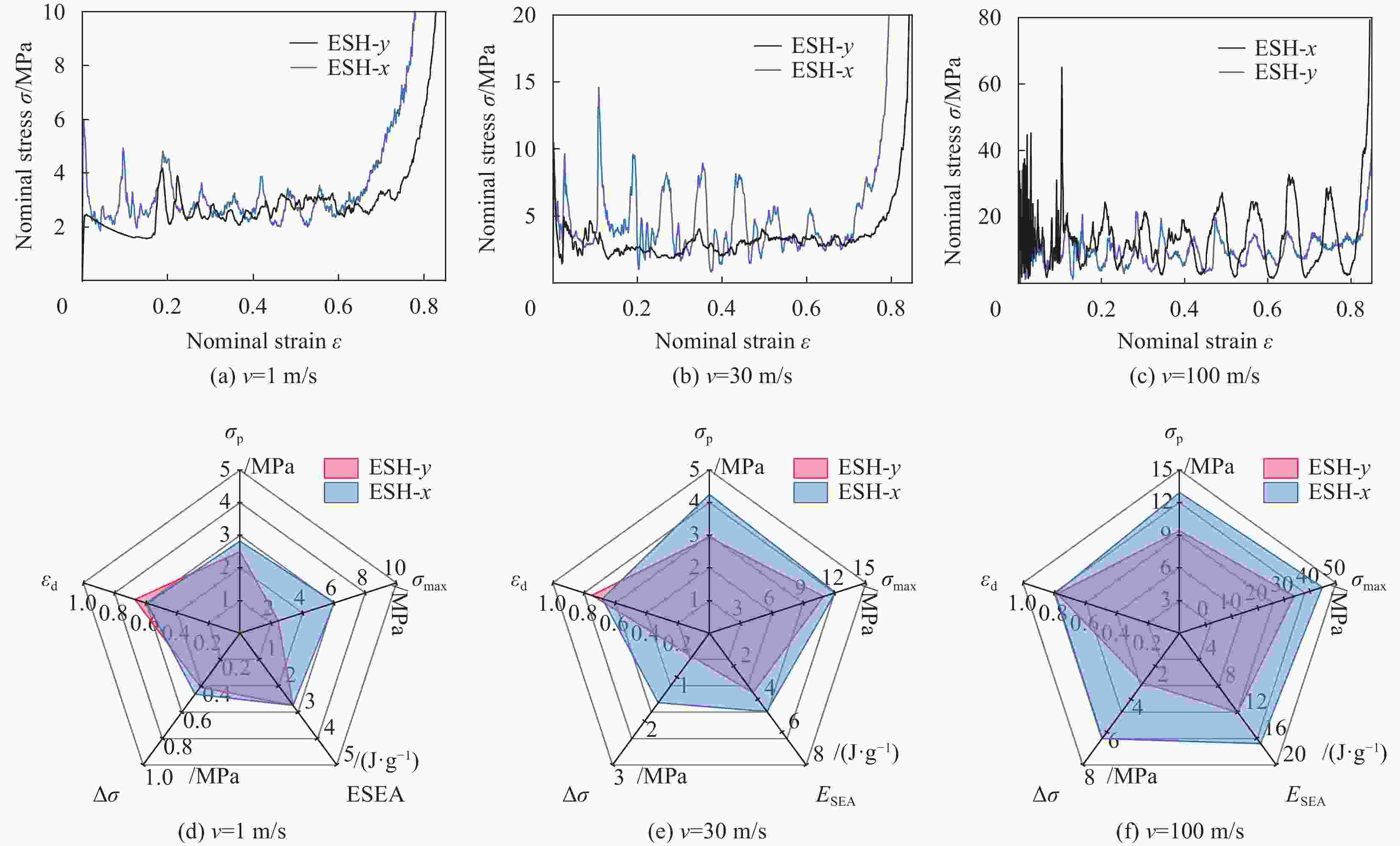
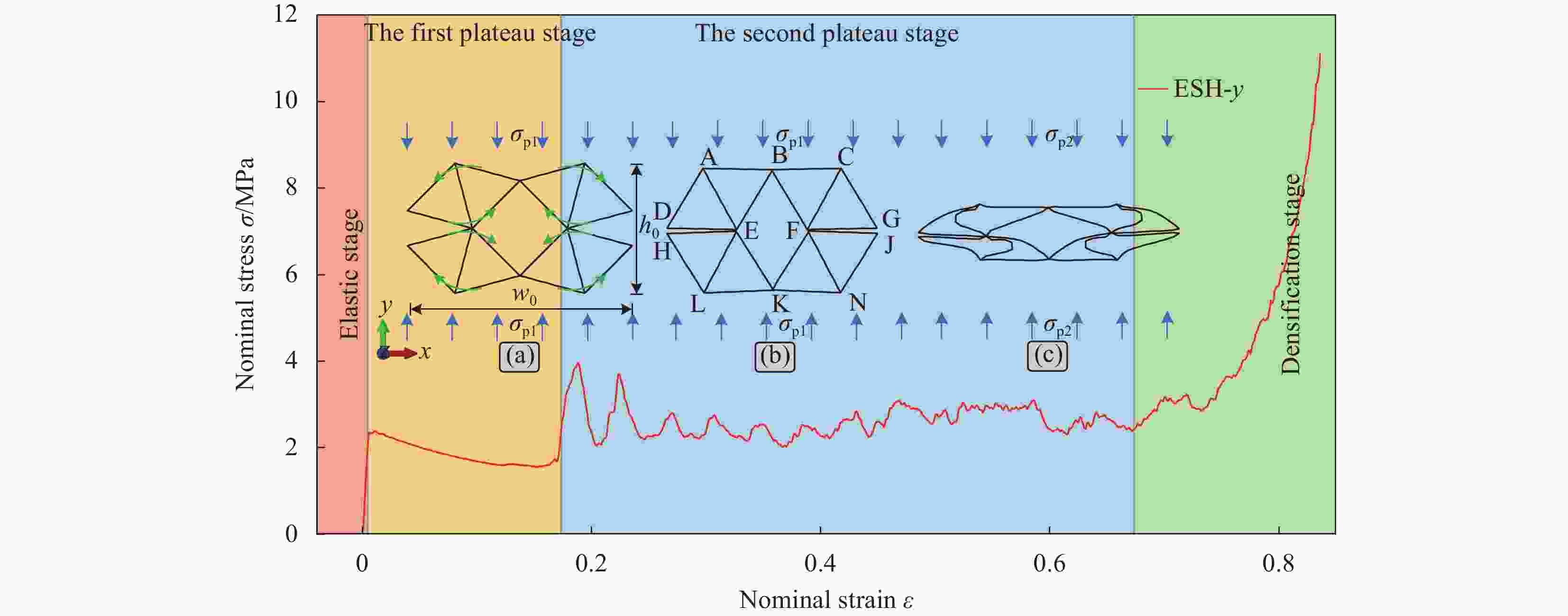
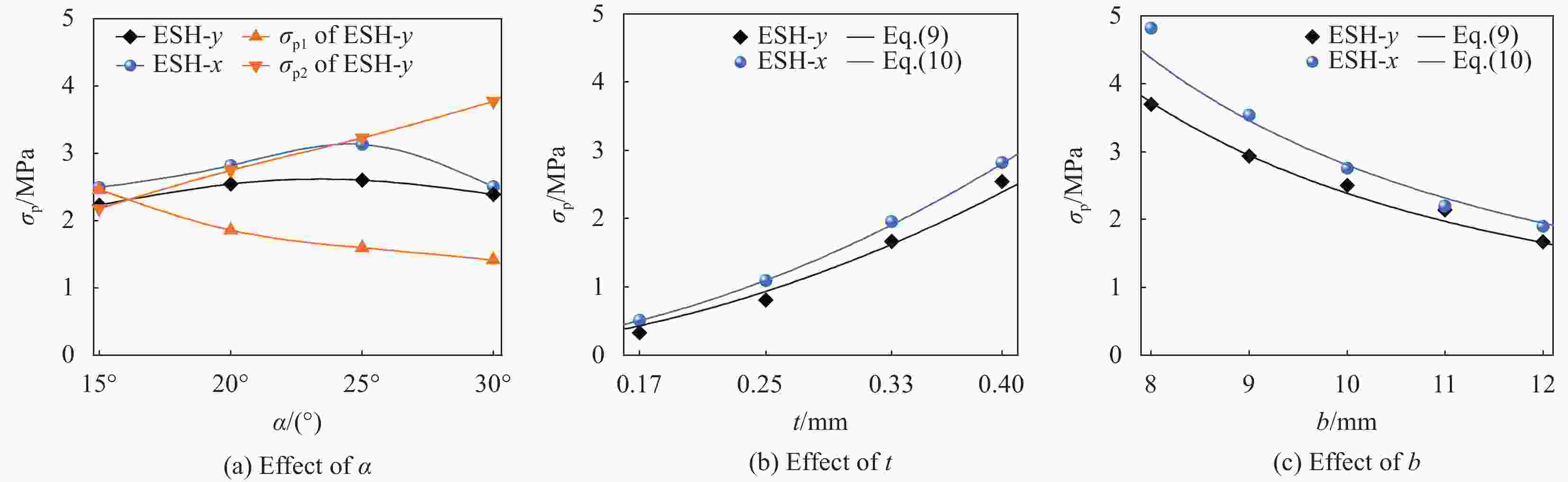
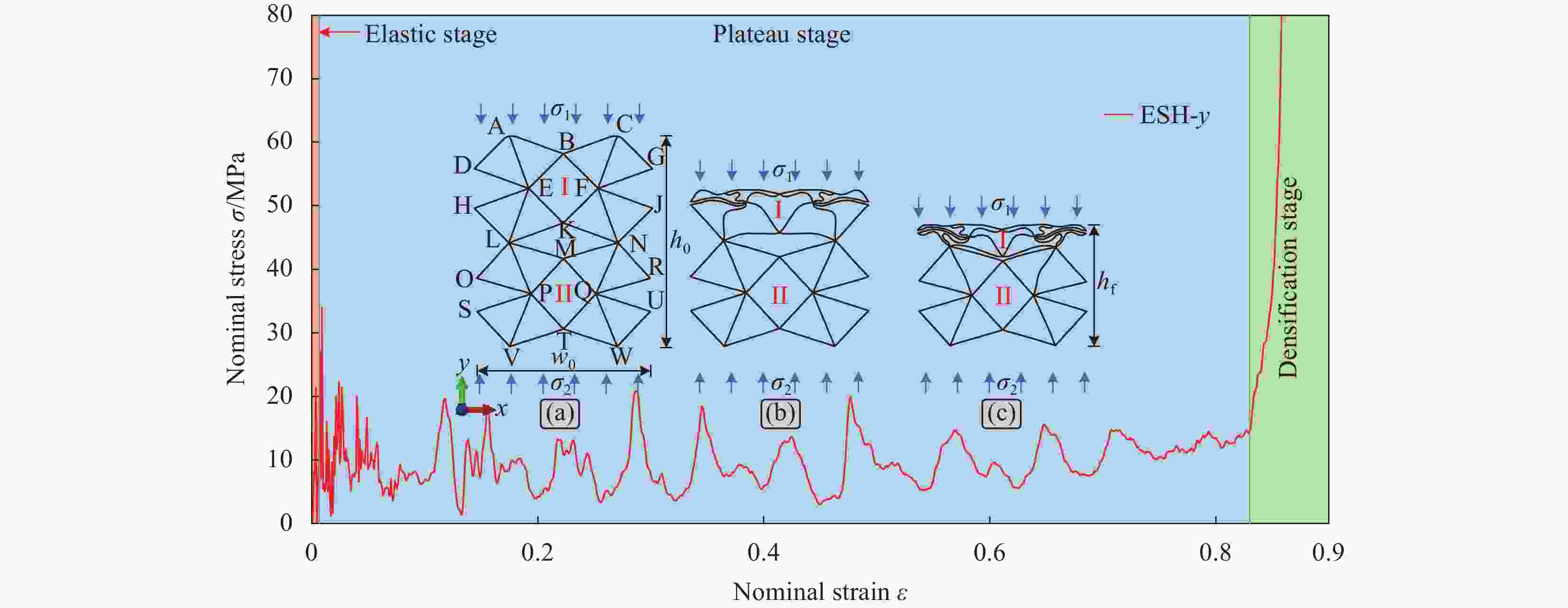
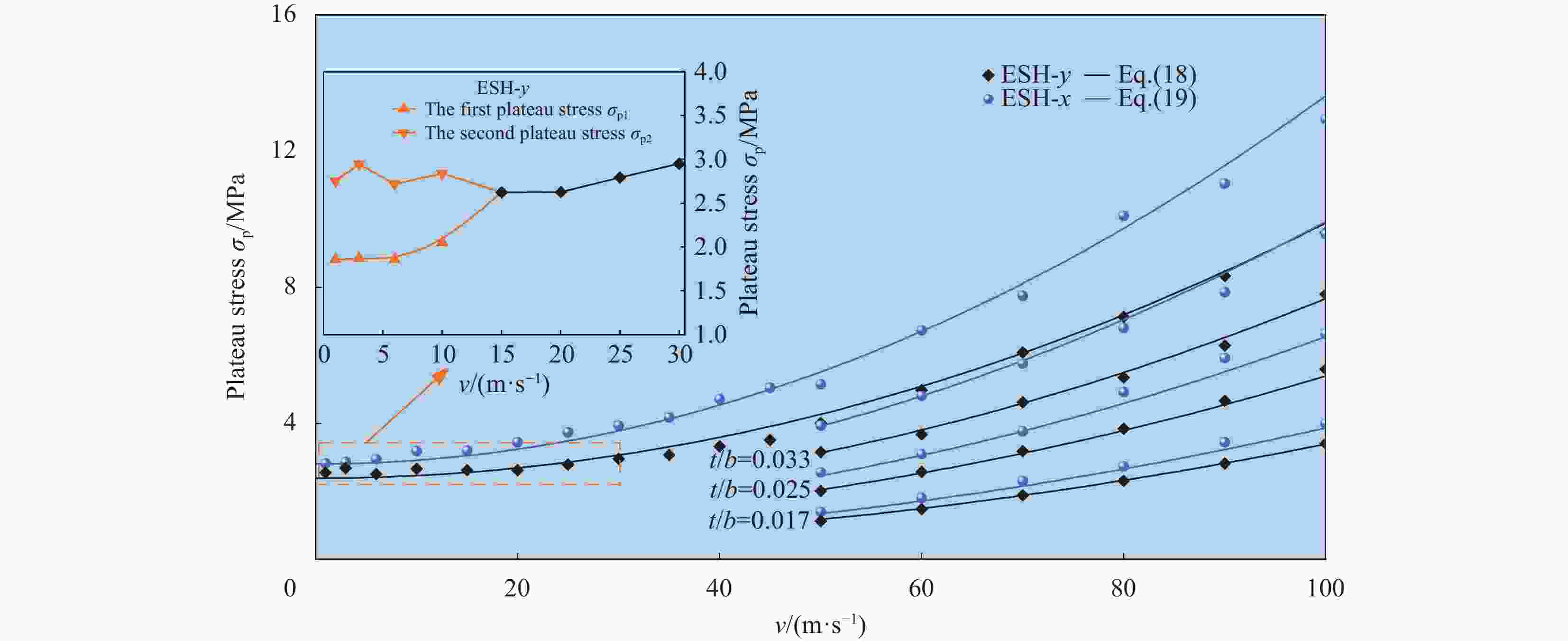
摘要: 为进一步提高蜂窝结构的抗冲击性能和能量吸收能力,通过周期性阵列传统星形胞元和星-菱形胞元,本文构建了内凹星形蜂窝结构(Reentrant star-shaped honeycomb structures, RSH)和新型的面内增强星-菱形蜂窝结构(Enhanced star-rhombic honeycomb structures, ESH)。通过实验和有限元模拟,系统地研究了ESH在不同加载方向的面内力学响应和吸能特性。与RSH相比,准静态压缩下ESH的负泊松比特性减弱,但吸能能力显著提高。此外,结合微拓扑胞元的变形特征,揭示了低速冲击时ESH-y的应力-应变响应呈现双平台特征的变形机制,并讨论了结构参数α、t和b对平台应力的影响规律。基于高速冲击下ESH的周期性逐层坍塌变形特征和动量定理,给出了不同加载方向高速平台应力的理论解,理论结果与有限元结果吻合较好。该研究可为创新设计具有更优力学性能的新型负泊松比结构提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 星-菱形负泊松比结构 /
- 平台应力 /
- 面内增强 /
- 冲击响应 /
- 能量吸收
Abstract: In order to further improve the crushing resistance and energy-absorbing capacity of the honeycomb structure, by periodically arraying typical star-shaped and star-rhombic cells, the reentrant star-shaped honeycomb structures (RSH) and the novel in-plane enhanced star-rhombic honeycomb structures (ESH) were constructed in this paper. The in-plane mechanical response and energy absorption characteristics of ESH under different loading directions were systematically investigated through experiments and finite element (FE) simulations. Compared with RSH, the negative Poisson's ratio characteristics of ESH under quasi-static compression are weakened, but the energy-absorbing capacities are significantly improved. In addition, by combining the deformation features of micro-topological cells, the deformation mechanism that the stress-strain response of ESH-y exhibits a double-plateau characteristic at low velocities of crushing is revealed, and the influence of the structural parameters α, t, and b on the plateau stresses is discussed. Based on the periodic layer-by-layer collapse deformation features of ESH under high-velocity crushing and the momentum theorem, the theoretical solutions of the high-velocity plateau stress in different loading directions are obtained, and theoretical results are in good agreement with FE results. This study can provide a reference for the innovative design of novel negative Poisson's ratio structures with better mechanical properties. -
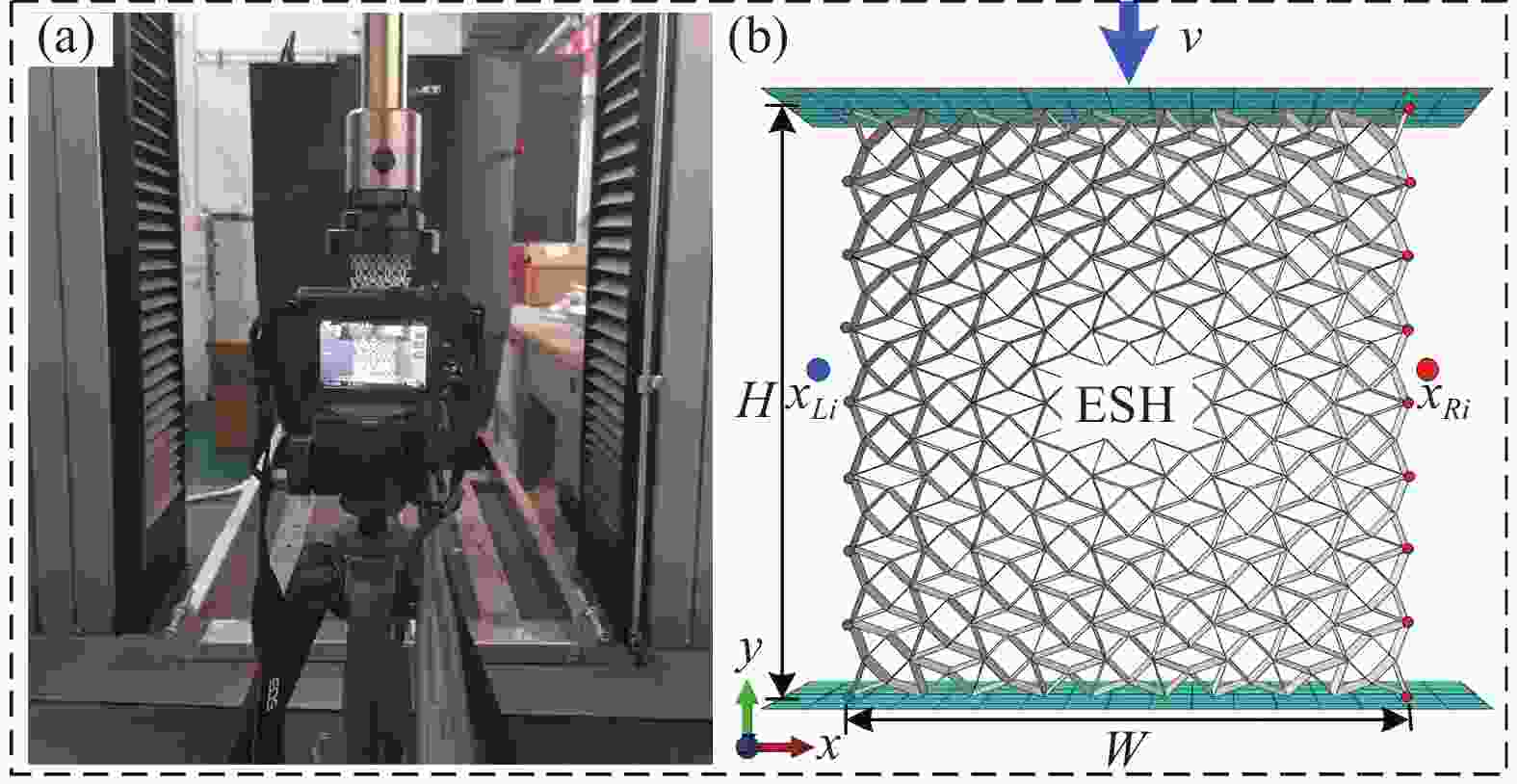
表 1 实验试样的几何参数
Table 1. Geometric parameters of experimental specimens
RSH-y RSH-x ESH-y ESH-x α/(°) 20 20 20 20 t/mm 1 1 1 1 b/mm 20 20 20 20 W/mm 85.89 80.53 85.58 80.34 H/mm 80.47 85.77 80.44 85.60 d/mm 15.19 15.31 15.48 15.47 m/g 21.75 22.05 31.65 31.70 $\bar \rho $ 0.17 0.17 0.24 0.24 Notes: α—Reentrant angle; t—Wall thickness; b—Cell length; W—Width of specimen; H—Height of specimen; d—Out-of-plane depth; m—Mass of specimen; $\bar \rho $—Relative density. 表 2 基体材料属性
Table 2. Material properties of the matrix material
Matrix material PLA Aluminum alloy[1] Young's modulus Es/GPa 2.04±0.04 68.2 Density ρs/(kg·m−3) 1240 2700 Yield stress σys/MPa 30.42±2.21 80 Poisson's ratio ν 0.3 0.3 Note: PLA—Polylactic acid. -
[1] WANG H, LU Z, YANG Z, et al. A novel re-entrant auxetic honeycomb with enhanced in-plane impact resistance[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 208: 758-770. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.10.024 [2] ZHOU S, LIU H, MA J, et al. Deformation behaviors and energy absorption characteristics of a hollow re-entrant auxetic lattice metamaterial[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2023, 142: 108583. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2023.108583 [3] QI C, JIANG F, YANG S. Advanced honeycomb designs for improving mechanical properties: A review[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2021, 227: 109393. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109393 [4] GUO H, ZHANG J. Expansion of sandwich tubes with metal foam core under axial compression[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2023, 90(5): 051008. doi: 10.1115/1.4056686 [5] 刘浩, 周宏元, 王小娟, 等. 泡沫混凝土填充旋转薄壁多胞方管负泊松比结构面内压缩性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(2): 841-859.LIU Hao, ZHOU Hongyuan, WANG Xiaojuan, et al. In-plane compression properties of negative Poisson's ratio structure of rotating thin-walled multi-cell square tubes with foam concrete filler[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(2): 841-859(in Chinese). [6] MA LH, WEI T, RAO W, et al. 4D printed chiral metamaterials with negative swelling behavior[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2023, 32(1): 015014. doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/aca84d [7] ZHOU X, JING L. Large deflection response of sandwich beams with layered-gradient foam cores subjected to low-velocity impact[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 172: 104429. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104429 [8] ZHANG XC, LIU NN, AN CC, et al. Dynamic crushing behaviors and enhanced energy absorption of bio-inspired hierarchical honeycombs with different topologies[J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 22: 99-111. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.11.013 [9] ZHANG J, LU G, YOU Z. Large deformation and energy absorption of additively manufactured auxetic materials and structures: A review[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2020, 201: 108340. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108340 [10] 任鑫, 张相玉, 谢亿民. 负泊松比材料和结构的研究进展[J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(3): 656-687.Ren Xin, Zhang Xiangyu, Xie Yimin. Research progress in auxetic materials and structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(3): 656-687(in Chinese). [11] ZHANG XC, SHEN ZF, WU HX, et al. In-plane dynamic crushing behaviors of joint-based hierarchical honeycombs with different topologies[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials, 2021, 23(8): 4218-4251. [12] ZHANG X, WANG J, SUN Q, et al. Mechanical design and analysis of bio-inspired reentrant negative Poisson’s ratio metamaterials with rigid-flexible distinction[J]. International Journal of Smart and Nano Materials. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475411.2023.2246928 [13] QI C, JIANG F, REMENNIKOV A, et al. Quasi-static crushing behavior of novel re-entrant circular auxetic honeycombs[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2020, 197: 108117. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108117 [14] ZOU Z, XU F, NIU X, et al. In-plane crashing behavior and energy absorption of re-entrant honeycomb reinforced by arched ribs[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 325: 117615. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.117615 [15] ZHANG X, HAO H, TIAN R, et al. Quasi-static compression and dynamic crushing behaviors of novel hybrid re-entrant auxetic metamaterials with enhanced energy-absorption[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 288: 115399. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115399 [16] ZHANG W, WANG H, LOU X, et al. On in-plane crushing behavior of a combined re-entrant double-arrow honeycomb[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 194: 111303. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111303 [17] 冯学凯, 王宝珍, 巫绪涛, 等. 新型节圆正弦蜂窝面内压缩力学性能研究[J]. 力学学报, 2023, 55(9): 1910-1920.Feng Xuekai, Wang Baozhen, Wu Xutao, et al. In-plane compression behavior of sinusoidal honeycomb with circular nodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2023, 55(9): 1910-1920(in Chinese). [18] 韩会龙, 张新春, 王鹏. 负泊松比蜂窝材料的动力学响应及能量吸收特性[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(1): 47-57HAN Huilong, ZHANG Xinchun, WANG Peng. Dynamic responses and energy absorption properties of honeycombs with negative Poisson’s ratio[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(1): 47-57(in Chinese). [19] WEI L, ZHAO X, YU Q, et al. In-plane compression behaviors of the auxetic star honeycomb: Experimental and numerical simulation[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 115: 106797. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.106797 [20] LU H, WANG X, CHEN T. In-plane dynamics crushing of a combined auxetic honeycomb with negative Poisson's ratio and enhanced energy absorption[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 160: 107366. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107366 [21] LANG J P, HAN D, ZHANG X G, et al. A star-shaped tubular structure with multiple-directional auxetic effect[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 193: 111247. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111247 [22] DING H, GUO H, SUN P, et al. In-plane dynamic crushing of a novel hybrid auxetic honeycomb with enhanced energy absorption[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2023.https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2023.2 204082 [23] LI N, LIU SZ, WU XN, et al. Mechanical characteristics of a novel rotating star-rhombic auxetic structure with multi-plateau stages[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 191: 111081. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111081 [24] LIU JY, LIU HT. Energy absorption characteristics and stability of novel bionic negative Poisson’s ratio honeycomb under oblique compression[J]. Engineering Structures, 2022, 267: 114682. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.114682 [25] WU HX, ZHANG XC, LIU Y. In-plane crushing behavior of density graded cross-circular honeycombs with zero Poisson's ratio[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 151: 106767. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106767 [26] LIU K, CAO XF, ZHANG P, et al. Dynamic mechanical performances of enhanced anti-tetra-chiral structure with rolled cross-section ligaments under impact loading[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 166: 104204. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104204 [27] 罗伟洪, 何婉青, 吴文军, 等. 不同速度下负泊松比弧形结构的变形行为[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(11): 75-87.LUO Weihong, HE Wanqing, WU Wenjun, et al. Deformation behavior of curved structures with negative Poisson’s ratio under diverse loading velocities[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(11): 75-87(in Chinese). [28] WEI L, ZHAO X, YU Q, et al. A novel star auxetic honeycomb with enhanced in-plane crushing strength[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 149: 106623. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106623 [29] YANG X, XI X, PAN Q, et al. In-plane dynamic crushing of a novel circular-celled honeycomb nested with petal-shaped mesostructure[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 226: 111219. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111219 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 42
- HTML全文浏览量: 37
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: