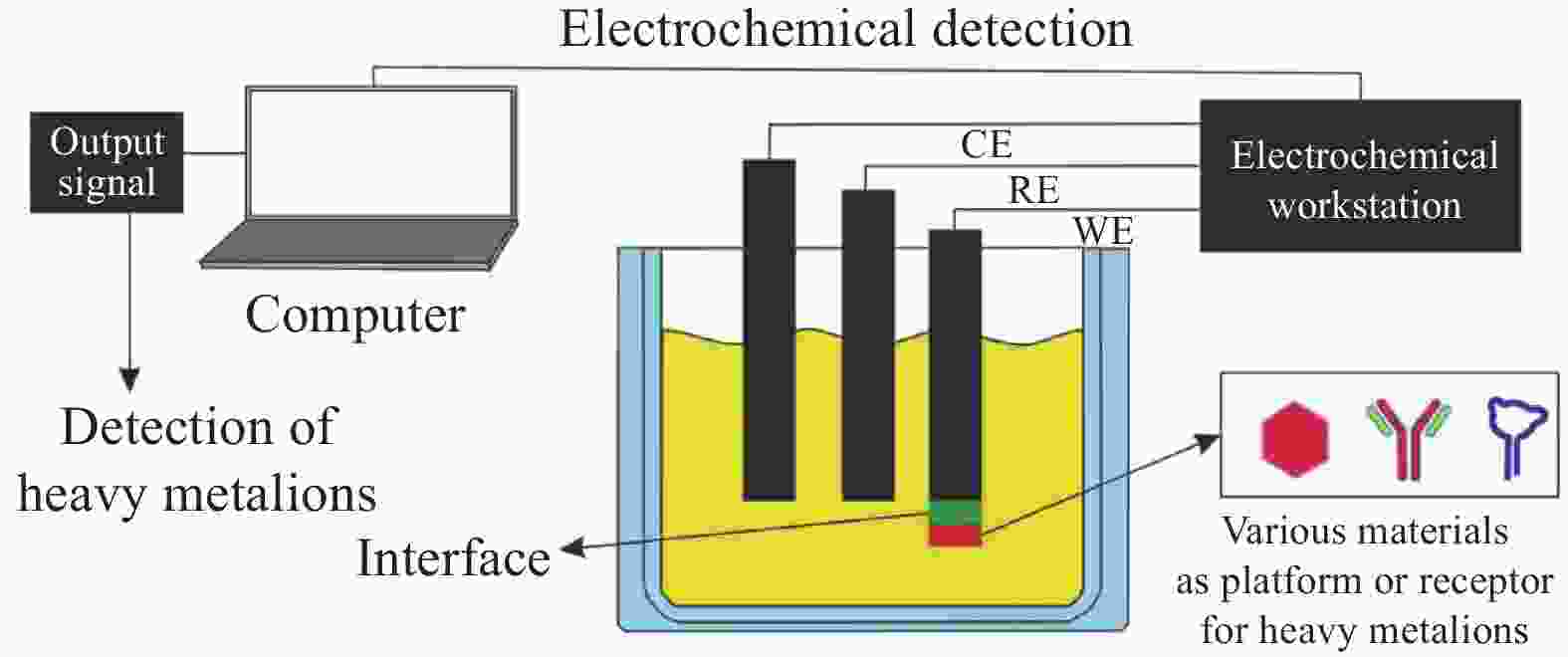
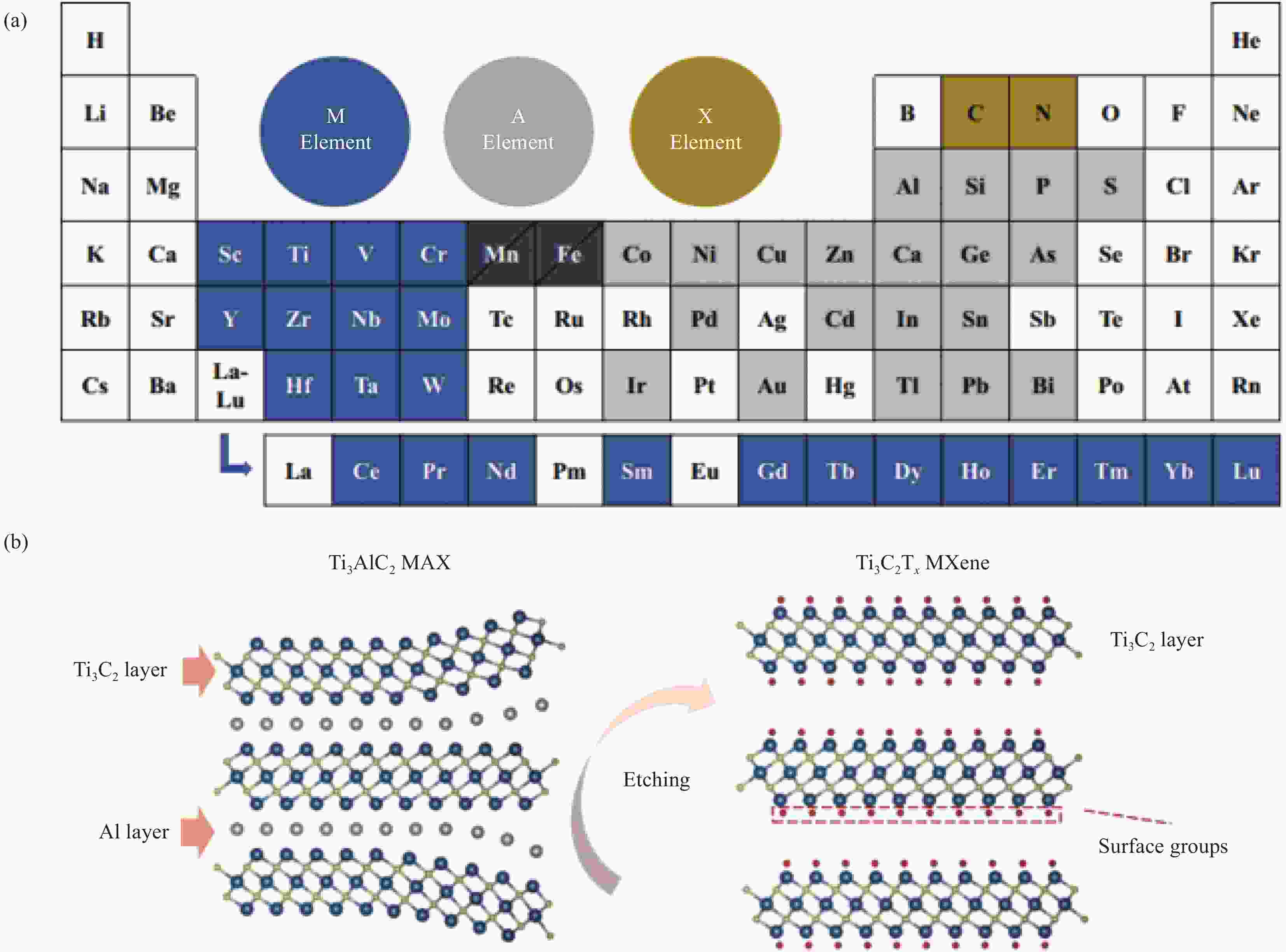
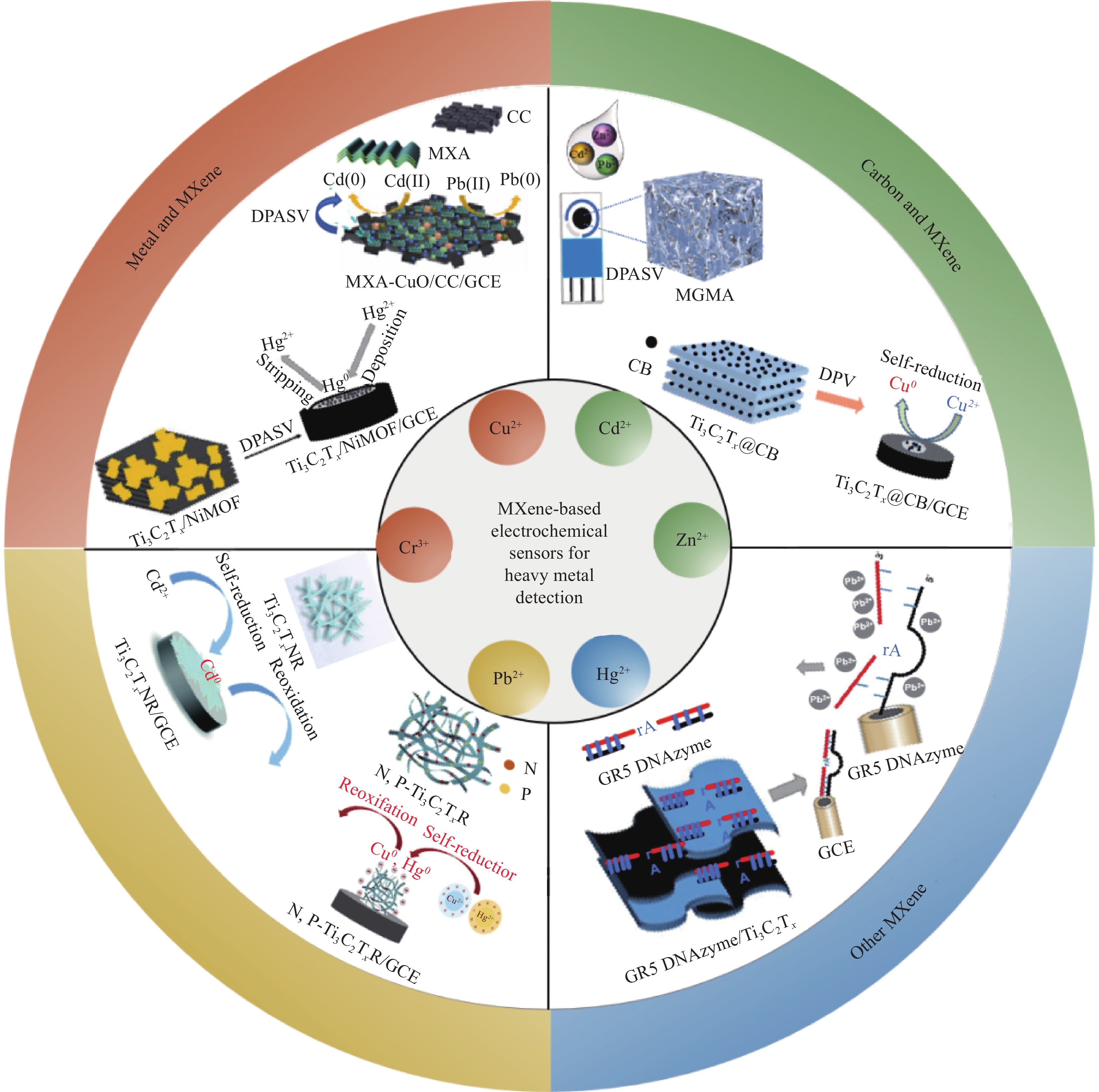
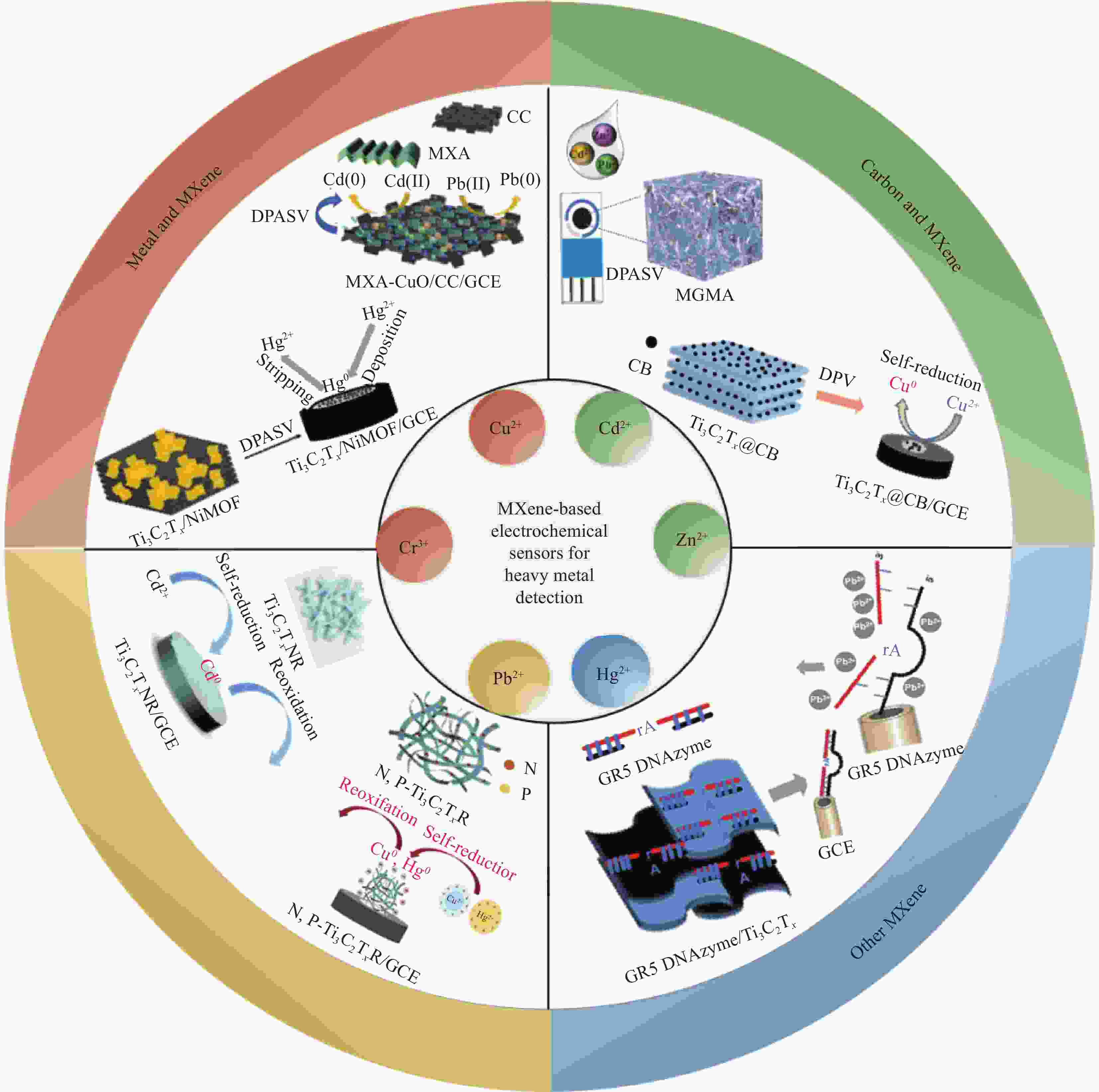
Research progress of MXene materials in the application of heavy metal electrochemical detection
-
摘要: 检测重金属污染已成为风险防控、农业绿色发展、食品安全及生态保护等领域重要的技术保障。目前有许多方法来检测重金属离子,其中电化学检测法对重金属离子的检测具有灵敏度高,分析速度快,可同时对多种金属离子进行检测等优点,成为了重金属快速检测领域的研究热点。MXene是具有类石墨烯结构的过渡金属碳/氮化物材料,它具备良好的亲水性、导电性和丰富可调节的终端基团。本文综述了MXenes在电化学检测重金属离子领域的研究进展:对重金属污染物的来源、危害和检测方法进行了简述;其次,概述MXene的合成方法,并重点综述了近年来MXene电化学检测重金属的研究进展,及其传感机理和检测性能分析;最后,讨论了MXene材料在电化学检测重金属领域面临的挑战和展望。Abstract: Detecting heavy metal pollution has become an essential technical guarantee in risk prevention and control, agricultural green development, food safety, and ecological protection. At present, there are many technologies to detect heavy metal ions, among which electrochemical detection methods have the advantages of high sensitivity, fast analysis, and simultaneous detection of a variety of metal ions, which have become a research area in the field of rapid detection of heavy metals. MXene is a transition metal-carbon/nitride material with a graphene-like structure with good hydrophilicity, electrical conductivity, and rich adjustable surface terminations. The focus of this study is the research progress of MXenes in the electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions. The sources, hazards, and detection methods of heavy metal contaminants are briefly described. Secondly, the synthesis methods of MXene are summarized, and the research progress of MXene in the electrochemical detection of heavy metals in recent years is reviewed, including the sensing mechanism and detection performance analysis. Finally, the challenges and prospects of MXene materials in the electrochemical detection of heavy metals are discussed.
-
Key words:
- Heavy metal /
- MXene /
- electrochemical sensors /
- detect /
- food safety
-
图 4 (a) Ti3C2TxNRs(Ti3C2Tx MXene纳米带)的制备原理图(上)和Cd2+的电化学传感(下);(b) N,P-Ti3C2TxR( N and P co-doped Ti3C2Tx MXenes 纳米带)的制备及Cu2+和Hg2+的电化学传感原理图[46, 47]
Figure 4. (a) Preparation schematic diagram of Ti3C2TxNRs(Ti3C2Tx MXene nanoribbons) (top) and electrochemical sensing of Cd2+ (bottom); (b) Preparation of N,P-Ti3C2TxR( N and P co-doped Ti3C2Tx MXenes nanoribbons) and electrochemical sensing schematic diagram of Cu2+ and Hg2+[46, 47]
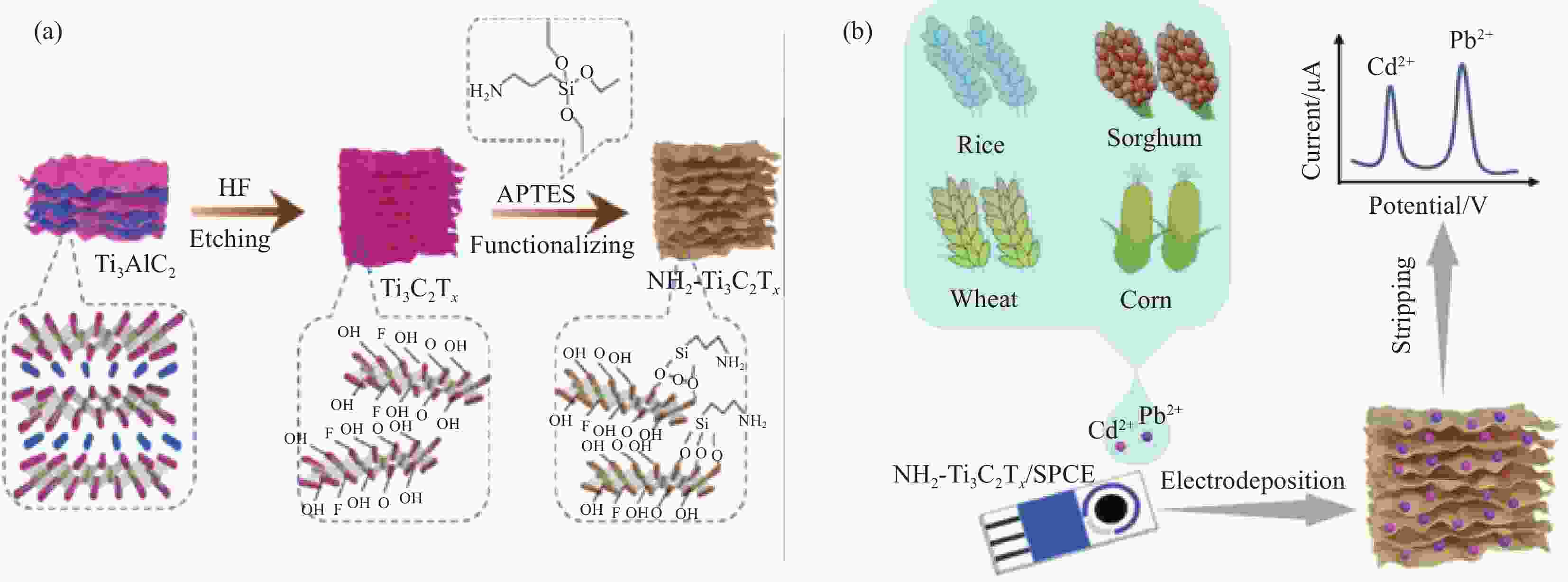
图 6 (a) NH2-Ti3C2Tx(氨基官能化多层碳化钛)制备工艺示意图;(b) NH2-Ti3C2Tx/SPE(丝网印刷电极)测定食品样品中Cd2+和Pb2+的示意图[50]
Figure 6. (a) Schematic diagram of NH2-Ti3C2Tx(amino-functionalized multilayer titanium carbide) preparation process; (b) Schematic diagram of NH2-Ti3C2Tx/SPE(screen printed electrode) determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ in food samples[50]
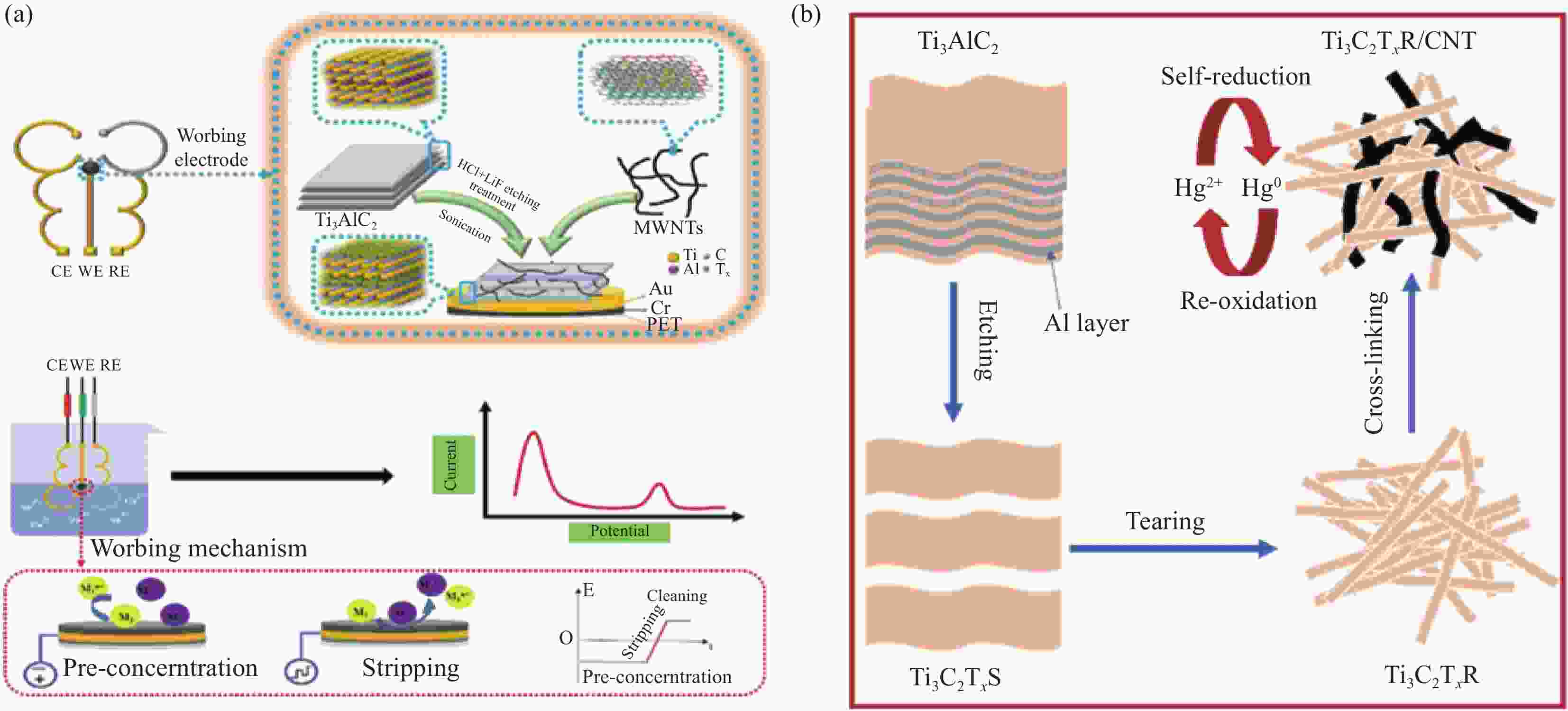
图 8 (a)柔性Ti3C2Tx/MWNTs(multiwalled carbon Nanotubes)/Au/PET电极的制备及重金属检测示意图;(b)制备Ti3C2TxR/CNT( Ti3C2Tx MXenes 纳米带/碳纳米管)及ASV检测汞的示意图[58, 59]
Figure 8. (a) Preparation of flexible Ti3C2Tx/MWNTs(multiwalled carbon Nanotubes)/Au/PET electrode and schematic diagram of heavy metal detection; (b) Schematic diagram of preparation of Ti3C2TxR/CNT( Ti3C2Tx MXenes nanoribbons/carbon nanotube) and ASV detection of mercury[58, 59]
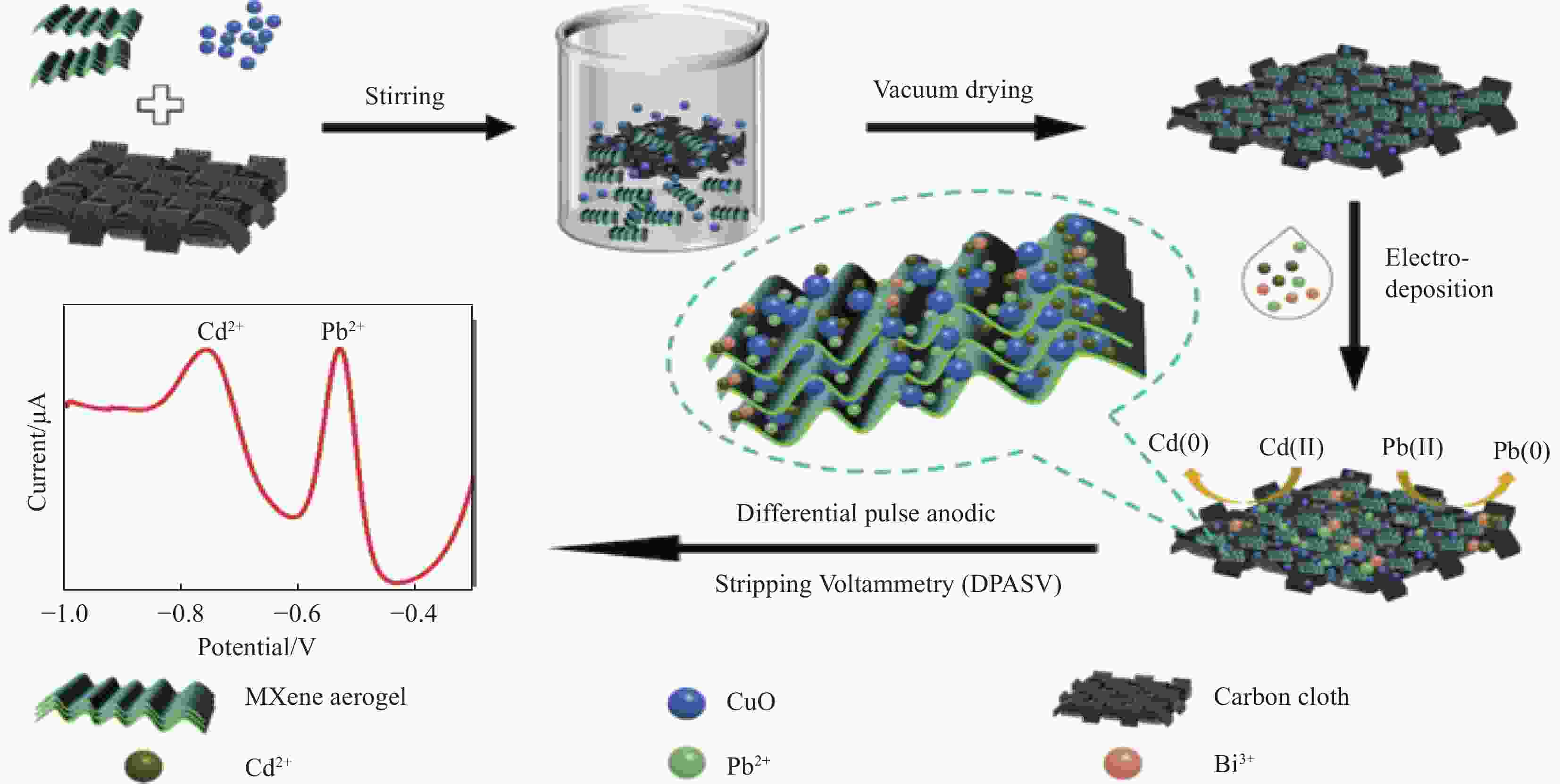
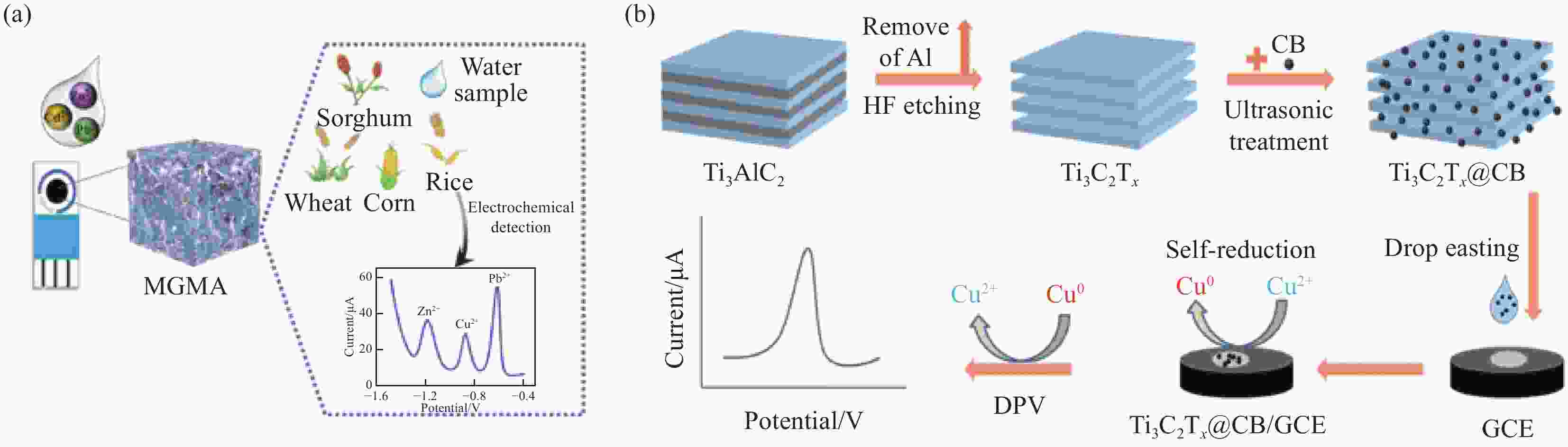
图 9 (a)三维MGMA/SPCE (三聚氰胺掺杂氧化石墨烯/MXene复合气凝胶 )示意图及环境样品中Zn2+、Cd2+和Pb2+检测;(b)Ti3C2Tx@CB的合成及Cu2+的电化学传感示意图[26, 60]
Figure 9. (a)Schematic diagram of three-dimensional MGMA/SPCE (melamine-doped graphene oxide/MXene composite aerogel ) and detection of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ in environmental samples;(b) Synthesis of Ti3C2Tx@CB and electrochemical sensing of Cu2+[26, 60]
图 10 (a) Ti3C2@N-C/GCE(Ti3C2-MXene异质结构/玻碳电极)制造及重金属检测应用示意图;(b) Cd2+和Pb2+测定的传感机制以及氮与重金属之间的相互作用[27]
Figure 10. (a) Schematic diagram of Ti3C2@N-C/GCE(Ti3C2-MXene heterostructure/glassy carbon electrode) manufacturing and HMI detection applications; (b) Sensing mechanisms for Cd2+ and Pb2+ assays and nitrogen and HMI interactions[27]
Heavy metal Source Adverse effects on the body National standards Pb Mining and smelting of heavy metal
ore, battery manufacturingKidney and nervous system damage, as well as mental retardation and cancer Fresh vegetables and fruits do not exceed 0.1 mg/kg cereals, legumes
and nuts do not exceed 0.2 mg/kg,
and meat products do not exceed 0.3 mg/kgCd Lead-zinc ore, as well as non-ferrous metal smelting and electroplating Deformation of intramuscular atrophy joints, unbearable bone pain, inability to sleep, pathological fractures, and death Fresh vegetables, fruits and eggs do
not exceed 0.05 mg/kg, cereals, fish
and meat do not exceed 0.1 mg/kgHg Fuel combustion, mining, smelting,
waste incineration, fertilization, pesticides, domestic wasteCauses damage to the kidneys, brain, reproductive and respiratory systems Eggs and meat do not exceed 0.05 mg/kg, vegetables and dairy products do not exceed 0.01 mg/kg,
and cereals do not exceed 0.02 mg/kgAs Industrial wastewater from mining, metallurgy, chemical industry, chemical pharmaceutical, pesticide production, textile, glass, tanning and other sectors It can cause skin cancer, lung cancer, bladder cancer and liver cancer Raw milk and oil do not exceed 0.1 mg/kg, cereals, vegetables, meat, condiments and chocolate do not exceed 0.5 mg/kg Materials Metal ions LOD/(nmol·L−1) Analytical performance Glutathione-functionalized gold/multi-walled
carbon nanotubesPb2+ 10 Rice phloem sap Multiwalled carbon nanotube-based ion-imprinted
polymerCd2+ 30 Water Polyglycine-modified graphene paste electrode Hg2+, Pb2+ 6600, 800 Water and biological samples Reduced graphene oxide/zinc oxide nanoparticles-ethylenediaminetetraaceticacid Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ 6810, 2510, 5610, 1010 Water Ti3C2Tx MXene//carbon black Cu2+ 4.6 Water Ti3C2-MXene heterostructure Cd2+, Pb2+ 2.55, 1.10 Water -
[1] MALIK L A, BASHIR A, QUREASHI A, et al. Detection and removal of heavy metal ions: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2019, 17(4): 1495-1521. doi: 10.1007/s10311-019-00891-z [2] JIN M, YUAN H, LIU B, et al. Review of the distribution and detection methods of heavy metals in the environment[J]. Analytical Methods, 2020, 12(48): 5747-5766. doi: 10.1039/D0AY01577F [3] JI W B, YAP S H K, PANWAR N, et al. Detection of low-concentration heavy metal ions using optical microfiber sensor[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2016, 237: 142-149. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.053 [4] BANSOD B, KUMAR T, THAKUR R, et al. A review on various electrochemical techniques for heavy metal ions detection with different sensing platforms[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2017, 94: 443-455. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.031 [5] KEMPAHANUMAKKAGARI S, DEEP A, KIM K-H, et al. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for arsenic - A review[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2017, 95: 106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.04.013 [6] ZHANG Y, WANG L, ZHANG N, et al. Adsorptive environmental applications of MXene nanomaterials: a review[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(36): 19895-19905. doi: 10.1039/C8RA03077D [7] DING Q, LI C, WANG H, et al. Electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions in water[J]. Chemical Communications, 2021, 57(59): 7215-7231. doi: 10.1039/D1CC00983D [8] MOHANADAS D, ROHANI R, SULAIMAN Y, et al. Heavy metal detection in water using MXene and its composites: A review[J]. Materials Today Sustainability, 2023, 22: 100411. doi: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100411 [9] WU X, MA P, SUN Y, et al. Application of MXene in Electrochemical Sensors: A Review[J]. Electroanalysis, 2021, 33(8): 1827-1851. doi: 10.1002/elan.202100192 [10] SONG Y, GAO S, YUAN X, et al. Two-compartment membrane electrochemical remediation of heavy metals from an aged electroplating-contaminated soil: A comparative study of anodic and cathodic processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 423: 127235. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127235 [11] HU X, HU Y, XU G, et al. Green synthesis of a magnetic β-cyclodextrin polymer for rapid removal of organic micro-pollutants and heavy metals from dyeing wastewater[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 180: 108796. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108796 [12] LIN Y, JIAO Y, ZHAO M, et al. Ecological Restoration of Wetland Polluted by Heavy Metals in Xiangtan Manganese Mine Area[J]. Processes2021, 9(10), 1702. [13] ZHANG Y, SONG B, ZHOU Z. Pollution assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from lead – Zinc mining areas of south China[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(2): 109320. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.109320 [14] CHEN R, HAN L, LIU Z, et al. Assessment of Soil-Heavy Metal Pollution and the Health Risks in a Mining Area from Southern Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Toxics, 2022, 10(7): 385. doi: 10.3390/toxics10070385 [15] KIM H K, JANG T I, KIM S M, et al. Impact of domestic wastewater irrigation on heavy metal contamination in soil and vegetables[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(5): 2377-2383 doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3581-2 [16] YANG X, CHENG B, GAO Y, et al. Heavy metal contamination assessment and probabilistic health risks in soil and maize near coal mines[J]. Frontiers in Public Health, 2022, 10. [17] FENG Z, ZHU H, DENG Q, et al. Environmental pollution induced by heavy metal(loid)s from pig farming[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(3): 103. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7300-2 [18] 食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量 [Z]. 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会;国家市场监督管理总局. 2022: 2024National food safety standard Limit of contaminants in food [Z]. National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China; State Administration for Market Regulation. 2022: 2024(in Chinese). [19] 马麟莉, 李树旺, 程亚萍. 食品中重金属污染的危害[J]. 食品安全导刊, 2022, (3): 181-183.MA Linli, LI Shuwang, CHENG Yaping. Hazards of heavy metal pollutants in food[J]. Food Safety Guide, 2022, (3): 181-183(in Chinese). [20] GUMPU M B, SETHURAMAN S, KRISHNAN U M, et al. A review on detection of heavy metal ions in water – An electrochemical approach[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2015, 213: 515-533. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.02.122 [21] MENG R, ZHU Q, LONG T, et al. The innovative and accurate detection of heavy metals in foods: A critical review on electrochemical sensors[J]. Food Control, 2023, 150: 109743. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.109743 [22] IIJIMA S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon[J]. Nature, 1991, 354(6348): 56-58. doi: 10.1038/354056a0 [23] ARAVIND A, MATHEW B. Tailoring of nanostructured material as an electrochemical sensor and sorbent for toxic Cd(II) ions from various real samples[J]. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 2018, 9(1): 22. doi: 10.1186/s40543-018-0153-1 [24] RARIL C, MANJUNATHA J G. Fabrication of novel polymer-modified graphene-based electrochemical sensor for the determination of mercury and lead ions in water and biological samples[J]. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 2020, 11(1): 3. doi: 10.1186/s40543-019-0194-0 [25] ERçARıKCı E, ALANYALıOĞLU M. Dual-Functional Graphene-Based Flexible Material for Membrane Filtration and Electrochemical Sensing of Heavy Metal Ions[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(3): 2468-2475. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3021988 [26] XIA Y, MA Y, WU Y, et al.[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2021, 188(11): 377. [27] ZHANG X, AN D, BI Z, et al. Ti3C2-MXene@N-doped carbon heterostructure-based electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2022, 911: 116239. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116239 [28] LIN Z, SHAO H, XU K, et al. MXenes as High-Rate Electrodes for Energy Storage[J]. Trends in Chemistry, 2020, 2(7): 654-664. doi: 10.1016/j.trechm.2020.04.010 [29] HARRIS K J, BUGNET M, NAGUIB M, et al. Direct Measurement of Surface Termination Groups and Their Connectivity in the 2D MXene V2CTx Using NMR Spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(24): 13713-13720. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03038 [30] KAMYSBAYEV V, FILATOV A S, HU H, et al. Covalent surface modifications and superconductivity of two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6506): 979-983. doi: 10.1126/science.aba8311 [31] JIANG Q, LEI Y, LIANG H, et al. Review of MXene electrochemical microsupercapacitors[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 27: 78-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.01.018 [32] HART J L, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, LANG A C, et al. Control of MXenes’ electronic properties through termination and intercalation[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 522. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08169-8 [33] NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals: Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2 (Adv. Mater. 37/2011)[J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(37): 4248-4253. doi: 10.1002/adma.201102306 [34] HONG L-F, GUO R-T, YUAN Y, et al. Recent progress of two-dimensional MXenes in photocatalytic applications: a review[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2020, 18: 100521. doi: 10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100521 [35] ZHOU C, ZHAO X, XIONG Y, et al. A review of etching methods of MXene and applications of MXene conductive hydrogels[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2022, 167: 111063. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111063 [36] WEI Y, ZHANG P, SOOMRO R A, et al. Advances in the Synthesis of 2D MXenes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(39): 2103148. doi: 10.1002/adma.202103148 [37] ZHANG T, PAN L, TANG H, et al. Synthesis of two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene using HCl+LiF etchant: Enhanced exfoliation and delamination[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 695: 818-826. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.10.127 [38] GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA M R, ZHAO M-Q, et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance[J]. Nature, 2014, 516(7529): 78-81. doi: 10.1038/nature13970 [39] HALIM J, LUKATSKAYA M R, COOK K M, et al. Transparent Conductive Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide Epitaxial Thin Films[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(7): 2374-2381. doi: 10.1021/cm500641a [40] WU J, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Highly safe and ionothermal synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene with expanded interlayer spacing for enhanced lithium storage[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 47: 203-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.11.029 [41] QIAN A, SEO J Y, SHI H, et al. Surface Functional Groups and Electrochemical Behavior in Dimethyl Sulfoxide-Delaminated Ti3C2Tx MXene[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(21): 3719-3723. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201801759 [42] XU J, PENG T, ZHANG Q, et al. Intercalation Effects on the Electrochemical Properties of Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanosheets for High-Performance Supercapacitors[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5(7): 8794-8803. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.2c00632 [43] ZHANG L, HUANG D, ZHAO P, et al. Highly efficient methylene blue removal by TMAOH delaminated Ti3C2Tx MXene suspension and the mechanistic aspect[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 288: 120718. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120718 [44] DRISCOLL N, RICHARDSON A G, MALESKI K, et al. Two-Dimensional Ti3C2 MXene for High-Resolution Neural Interfaces[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(10): 10419-10429. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b06014 [45] ZHU X L, LIU B C, HOU H J, et al. Alkaline intercalation of Ti3C2 MXene for simultaneous electrochemical detection of Cd(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Hg(II)[J]. ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA, 2017, 248: 46-57. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.084 [46] YI Y, MA Y, AI F, et al. Novel methodology for anodic stripping voltammetric sensing of heavy-metal ions using Ti3C2Tx nanoribbons[J]. Chemical Communications, 2021, 57(63): 7790-7793. doi: 10.1039/D1CC02560K [47] XIA Y, ZHAO Y, AI F, et al. N and P co-doped MXenes nanoribbons for electrodeposition-free stripping analysis of Cu(II) and Hg(II)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 425: 127974. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127974 [48] ZHU X, LIU B, HOU H, et al. Alkaline intercalation of Ti3C2 MXene for simultaneous electrochemical detection of Cd(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Hg(II)[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 248: 46-57. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.084 [49] BAGHERI S, CHILCOTT R, LUO S, et al. Bifunctional Amine- and Thiol-Modified Ti3C2Tx MXene for Trace Detection of Heavy Metals[J]. Langmuir, 2022, 38(42): 12924-12934. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c02058 [50] CHEN Y, ZHAO P, HU Z, et al. Amino-functionalized multilayer Ti3C2Tx enabled electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ in food samples[J]. Food Chemistry, 2023, 402: 134269. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134269 [51] SAWAN S, MAALOUF R, ERRACHID A, et al. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in the voltammetric detection of heavy metals: A review[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 131: 116014. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.116014 [52] LU Z, DAI W, LIN X, et al. Facile one-step fabrication of a novel 3D honeycomb-like bismuth nanoparticles decorated N-doped carbon nanosheet frameworks: Ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 266: 94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.01.188 [53] ZHU X, LIU B, LI L, et al. A micromilled microgrid sensor with delaminated MXene-bismuth nanocomposite assembly for simultaneous electrochemical detection of lead(II), cadmium(II) and zinc(II)[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2019, 186(12): 776. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3837-3 [54] HE Y, MA L, ZHOU L, et al. Preparation and Application of Bismuth/MXene Nano-Composite as Electrochemical Sensor for Heavy Metal Ions Detection [J] 2020, 10(5). [55] WEN L, DONG J, YANG H, et al. A novel electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of Cd2+ and Pb2+ by MXene aerogel-CuO/carbon cloth flexible electrode based on oxygen vacancy and bismuth film[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 851: 158325. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158325 [56] WANG X, BAI X, WANG W, et al. TiO2/Ni–NC Hybrid Derived from Ti3C2TX/NiMOF for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensing of Mercury Ions[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2023, 170(3): 037519. doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/acc362 [57] LIU T, ZHOU R, WU K, et al. Colorimetric method transforms into highly sensitive homogeneous voltammetric sensing strategy for mercury ion based on mercury-stimulated Ti3C2Tx MXene nanoribbons@gold nanozyme activity[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2023, 1250: 340975. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.340975 [58] HUI X, SHARIFUZZAMAN M, SHARMA S, et al. High-Performance Flexible Electrochemical Heavy Metal Sensor Based on Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Ti3C2Tx/MWNTs Nanocomposites for Noninvasive Detection of Copper and Zinc Ions in Human Biofluids[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(43): 48928-48937. [59] XIA Y, LI J, ZHU G, et al. Innovative strategy based on novel Ti3C2Tx MXenes nanoribbons/carbon nanotubes hybrids for anodic stripping voltammetry sensing of mercury ion[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2022, 355: 131247. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.131247 [60] CHEN Y, ZHAO P, LIANG Y, et al. A sensitive electrochemical sensor based on 3D porous melamine-doped rGO/MXene composite aerogel for the detection of heavy metal ions in the environment[J]. Talanta, 2023, 256: 124294. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124294 [61] ZHANG Z, KARIMI-MALEH H. In situ synthesis of label-free electrochemical aptasensor-based sandwich-like AuNPs/PPy/Ti3C2Tx for ultrasensitive detection of lead ions as hazardous pollutants in environmental fluids[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 324: 138302. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138302 [62] LIU Y, QIU R, ZHANG Z, et al. Label-free electrochemical biosensor based on GR5 DNAzyme/Ti3C2Tx Mxenes for Pb2+ detection[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2022, 905: 115979 doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115979 -





 下载:
下载: