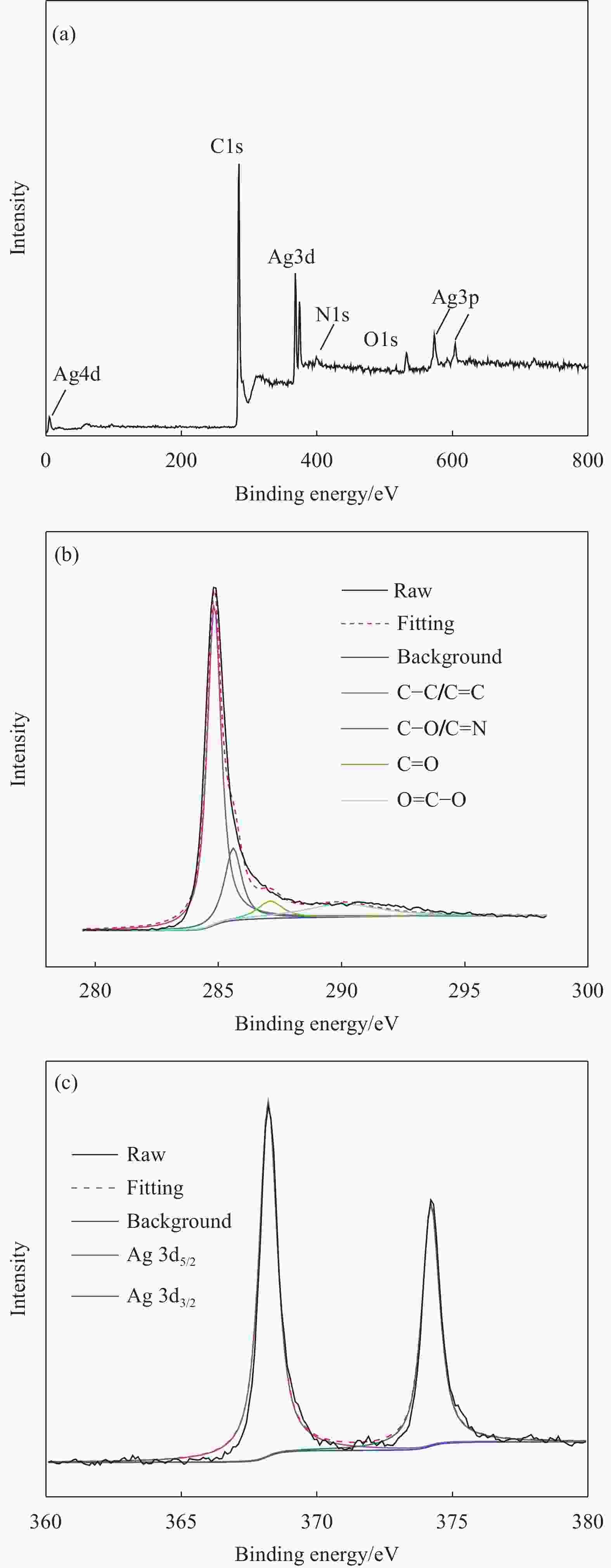
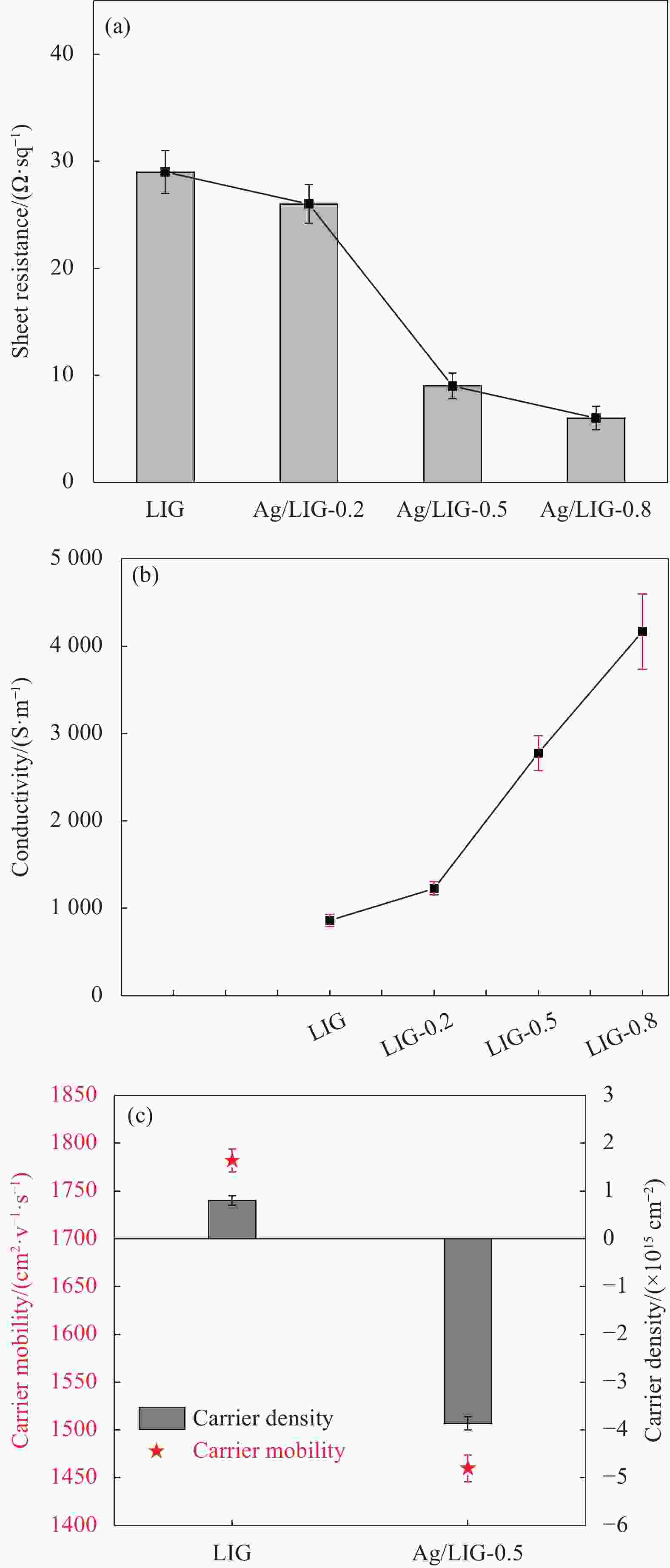
In-situ modification of laser-induced graphene with silver nanoparticles and its electronic conductivity modulation
-
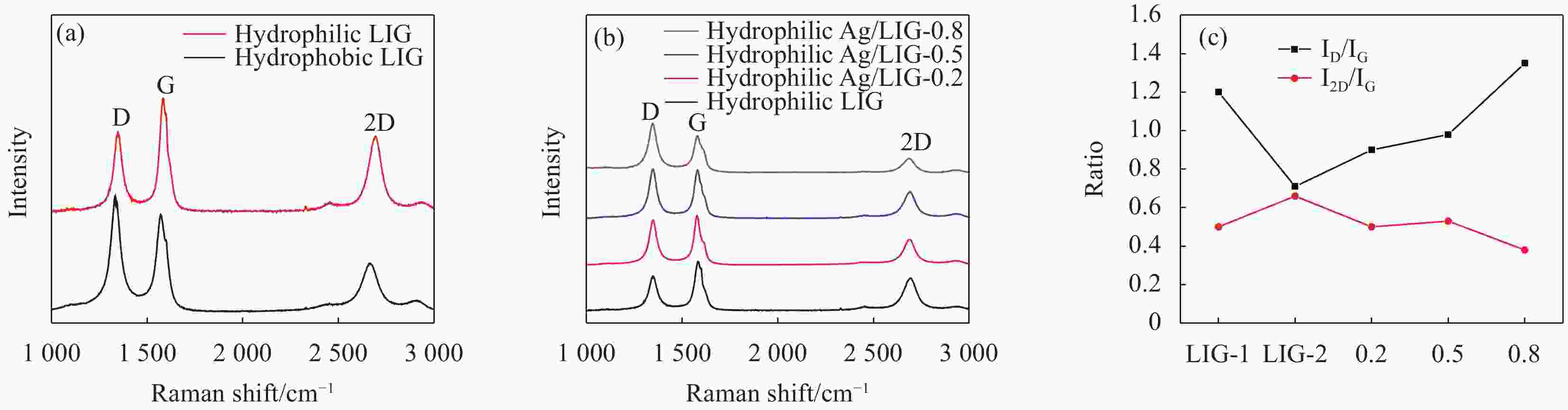
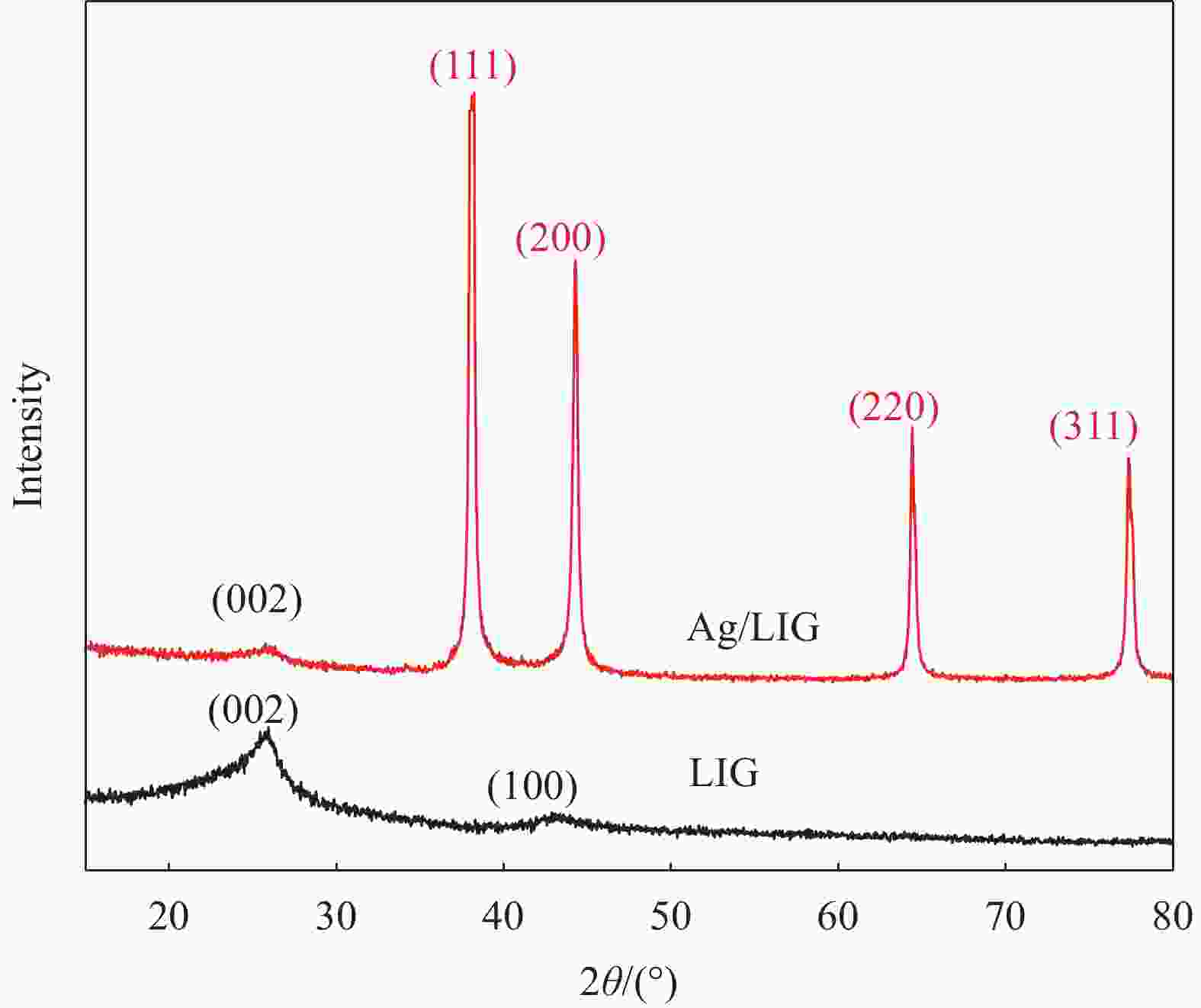
摘要: 随着高频通信技术的快速发展,由电磁波造成的电磁干扰问题日益严重,亟需开发针对5G频段的电磁屏蔽材料。以两次激光诱导法直接在固体材料上快速制备了银纳米颗粒/多孔石墨烯柔性复合薄膜:首次激光制备的亲水性激光诱导石墨(LIG)能够高效吸附AgNO3溶液,二次激光照射实现了银纳米粒子在多孔石墨烯上的原位生成和均匀负载。进一步研究了不同AgNO3浓度对所制得Ag/LIG材料的微观形貌、结构性质和导电特性的影响。结果表明,当AgNO3浓度为0.5 mol/L时,复合薄膜中银纳米颗粒保持小尺寸的同时分散性最好,其展现出2788 S/m的高电导率;同时,材料屏蔽效能从LIG的18-26 dB增加到复合材料的36-40 dB。在26 GHz频段处,Ag/LIG的屏蔽效能达到38 dB,经200次弯曲循环后效能保有率在90%以上。Abstract: With the rapid development of high-frequency communication technology, electromagnetic interference (EMI) issue has been increasing. Hence, EMI shielding materials for the 5G frequency band are in high demand. Here, a two-step laser-induced strategy was developed to rapidly prepare silver nanoparticles/porous graphene flexible composite in a solid-phase synthesis process. AgNO3 solution can be efficiently adsorbed by hydrophilic laser-induced graphene (LIG) obtained by the first laser irradiation with tuned parameters, which provides favorable conditions for the abundant and homogeneous loading of Ag nanoparticles on LIG after in-situ the second laser irradiation. Furthermore, the microstructures, structural properties and electronic conductivity of the prepared Ag/LIG composites with different AgNO3 additive concentrations are detailedly analyzed. As a result, with a 0.5 mol/L AgNO3 additive concentration, Ag nanoparticles in the composite film maintain small size while exhibiting the best dispersion, exhibiting a high conductivity of 2788 S/m. In the 18-27 GHz frequency band, the EMI shielding effectiveness increases from 18-26 dB of LIG to 36-40 dB of composite materials. The EMI shielding effectiveness of Ag/LIG-0.5 at the 26 GHz reaches 38 dB with an over 90% shielding effectiveness retention rate after 200 bending cycles.
-
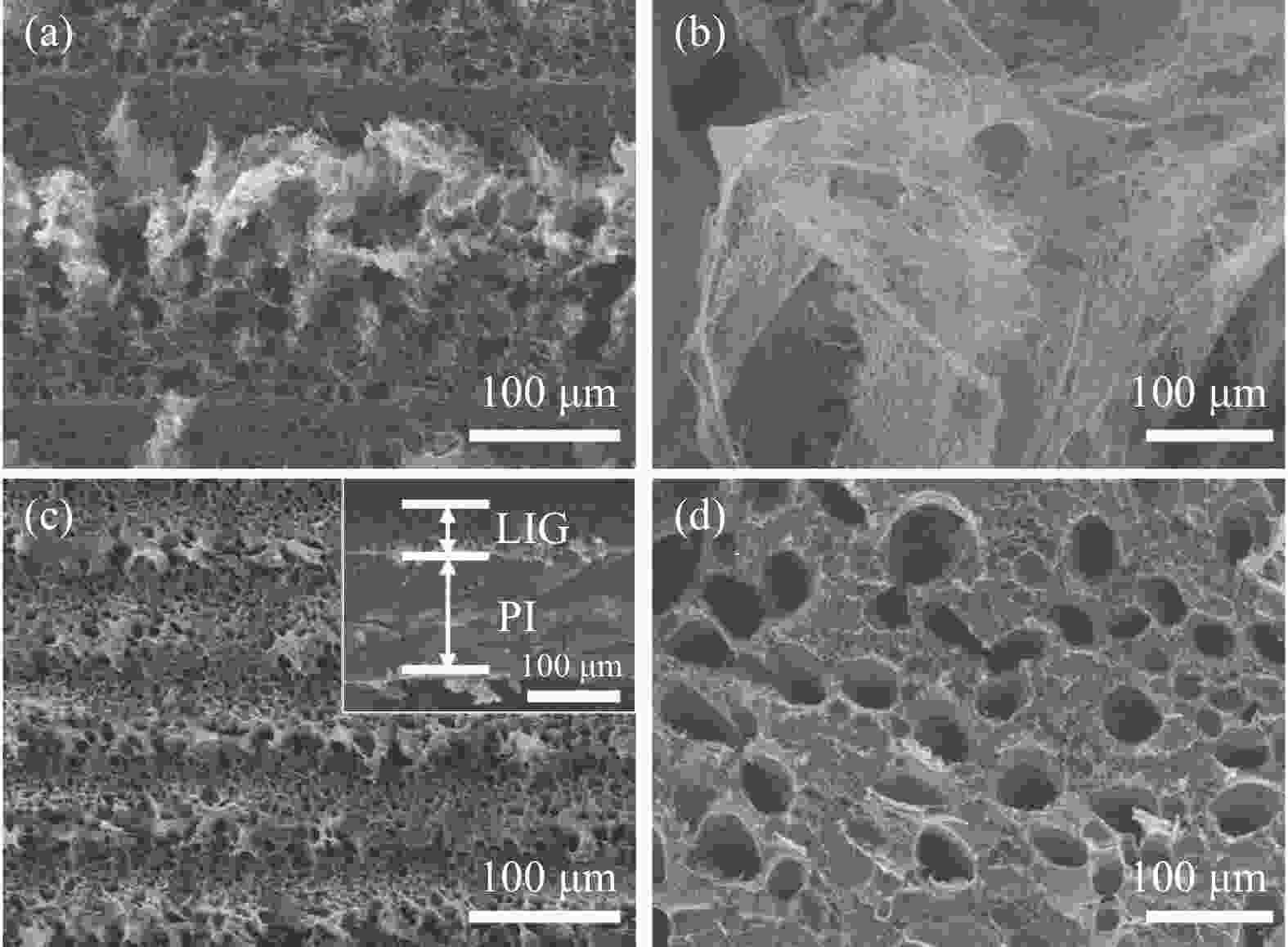
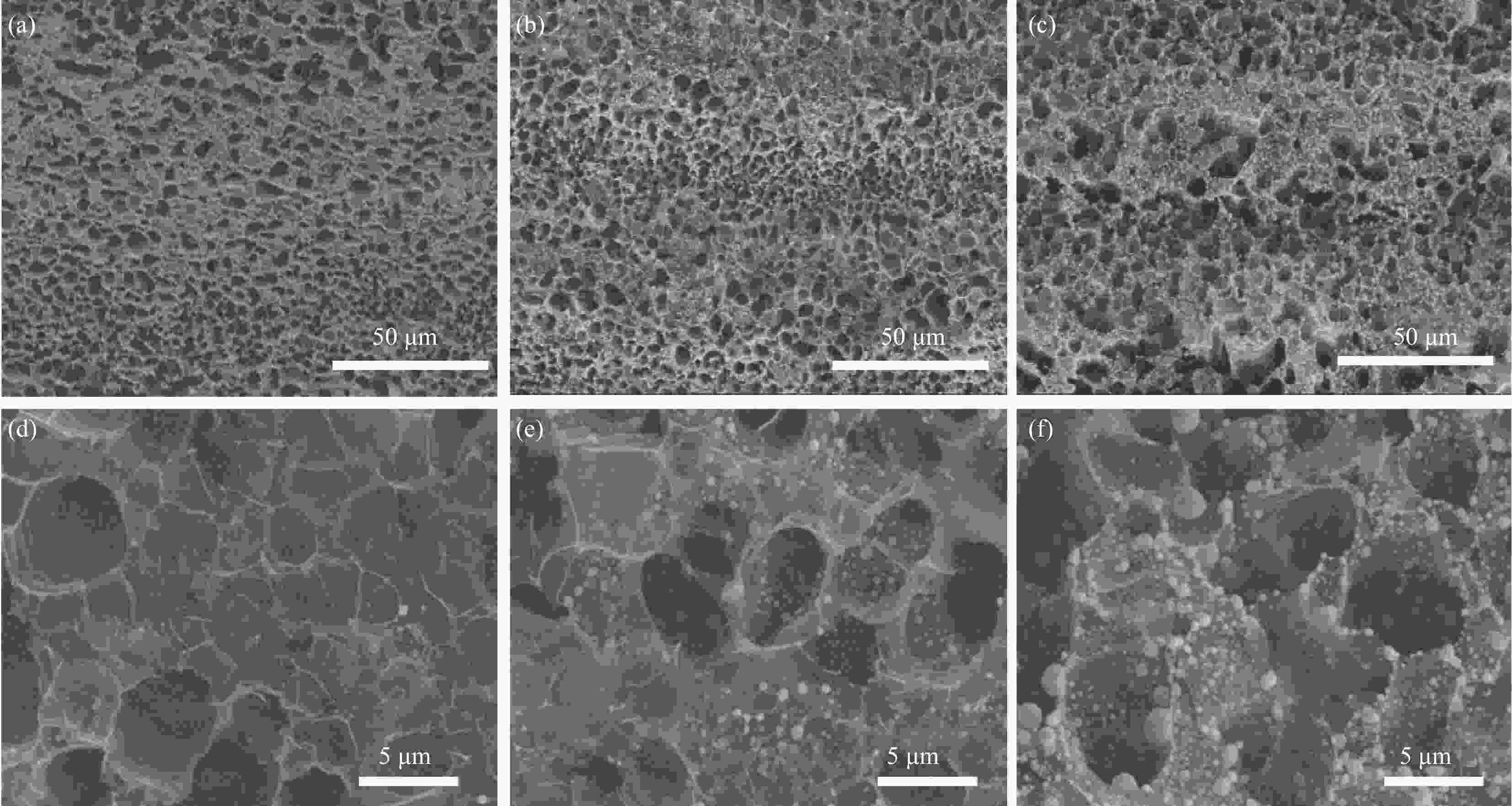
图 10 (a)不同AgNO3浓度制备的Ag/LIG复合材料及商用屏蔽膜的EMI SET;(b) LIG和Ag/LIG-0.5样品的SEA和SER对比;(c、d)不同AgNO3浓度制备的Ag/LIG复合材料在26 GHz频段的SET、SEA和SER(c)以及反射、吸收和透射系数(R、A和T)(d);(e)Ag/LIG-0.5复合薄膜在反复弯曲和超声处理后26 GHz处的屏蔽效能(f)二次激光照射前后LIG和Ag/LIG-0.5的实物图及薄膜的柔性展示(插图为Ag/LIG的水接触角)。
Figure 10. (a) EMI SET of Ag/LIG prepared with different AgNO3 concentrations and commercial film; (b) Comparison of SEA and SER of LIG and Ag/LIG-0.5 samples; (c, d) SET, SEA, and SER (c), R, A, and T coefficients (d) of Ag/LIG with different AgNO3 concentrations at the 26 GHz frequency band; (e) EMI SE of Ag/LIG-0.5 composite film at 26 GHz after bending or ultrasound; (f) The digital photograph of LIG and Ag/LIG-0.5 before and after secondary laser irradiation, as well as the flexibility of the film (The inset shows the water contact angle of Ag/LIG).
-
[1] WANG B, JI Y, MU C, et al. Well-controlled Core-shell structures based on Fe3O4 nanospheres coated by polyaniline for highly efficient microwave absorption[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 591: 153176. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153176 [2] YU J, GU W, ZHAO H, et al. Lightweight, flexible and freestanding PVA/PEDOT: PSS/Ag NWs film for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Science China Materials, 2021, 64(7): 1723-1732. doi: 10.1007/s40843-020-1557-3 [3] GUO D, HUO Y, MU C, et al. Flexible aramid nanofiber/Ag nanowires/graphene nanosheets composite films with sandwich structure for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 923: 166401. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166401 [4] 瞿明城, 张礼颖, 周剑锋, 等. 碳纳米管改性CF/PEEK复合材料的力学与电磁屏蔽性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(07): 3251-3261.QU Mingcheng, ZHANG Liying, ZHOU Jianfeng, et al. Effect of carbon nanotube reinforcement on the mechanical and EMI shielding properties of CF/PEEK composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(07): 3251-3261(in Chinese). [5] 张明伟, 曲冠达, 庞梦瑶, 等. 电磁屏蔽机理及涂敷/结构型吸波复合材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(Z1): 62-70.ZHANG Mingwei, QU Guanda, PANG Mengyao, et al. Research Progress of Electromagnetic Shielding Mechanism and Coated/Structural Absorbing Composite Materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(Z1): 62-70(in Chinese). [6] AMARO A, SUAREZ A, TAMBURRANO A, et al. EMI Shielding Effectiveness Study for Innovative Carbon Nanotube Materials in the 5G Frequency Region[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2023, 65(1): 177-185. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2022.3209708 [7] HAN G, MA Z, ZHOU B, et al. Cellulose-based Ni-decorated graphene magnetic film for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 583: 571-578. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.072 [8] JAN R, HABIB A, AKRAM M A, et al. Flexible, thin films of graphene–polymer composites for EMI shielding[J]. Materials Research Express, 2017, 4(3): 035605. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/aa6351 [9] JUNG M, LEE Y-S, HONG S-G, et al. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Dispersion, mechanical properties, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding effectiveness (SE)[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2020, 131: 106017. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2020.106017 [10] ESWARAIAH V, SANKARANARAYANAN V, RAMAPRABHU S. Functionalized Graphene-PVDF Foam Composites for EMI Shielding[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2011, 296(10): 894-898. doi: 10.1002/mame.201100035 [11] RAJAVEL K, HU Y, ZHU P, et al. MXene/metal oxides-Ag ternary nanostructures for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 399: 125791. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125791 [12] 丁雪, 王建才, 叶志国, 等. 高性能石墨烯电磁屏蔽材料的研究进展[J/OL][J]. 功能材料, 2023, 54(3): 03001-03009.DING Xue, WANG Jiancai, YE Zhiguo, et al. Research progress of high-performance graphene electromagnetic shielding materials[J]. Journal of Functional Material, 2023, 54(3): 03001-03009(in Chinese). [13] YIN C, TAO C-A, CAI F, et al. Effects of activation temperature on the deoxygenation, specific surface area and supercapacitor performance of graphene[J]. Carbon, 2016, 109: 558-565. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.08.053 [14] SHEN B, ZHAI W, ZHENG W. Ultrathin Flexible Graphene Film: An Excellent Thermal Conducting Material with Efficient EMI Shielding[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(28): 4542-4548. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201400079 [15] SRIVASTAVA S K, MANNA K. Recent advancements in the electromagnetic interference shielding performance of nanostructured materials and their nanocomposites: a review[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(14): 7431-7496. doi: 10.1039/D1TA09522F [16] WANG M, TANG X-H, CAI J-H, et al. Construction, mechanism and prospective of conductive polymer composites with multiple interfaces for electromagnetic interference shielding: A review[J]. Carbon, 2021, 177: 377-402. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.02.047 [17] YE R, JAMES D K, TOUR J M. Laser-Induced Graphene: From Discovery to Translation[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(1): 1803621. doi: 10.1002/adma.201803621 [18] SONG Y, LI N, HAN S, et al. Macro-Sized All-Graphene 3D Structures via Layer-by-Layer Covalent Growth for Micro-to-Macro Inheritable Electrical Performances[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023: 2305191. [19] XU Y, FEI Q, PAGE M, et al. Laser-induced graphene for bioelectronics and soft actuators[J]. Nano Research, 2021, 14: 3033-3050. doi: 10.1007/s12274-021-3441-9 [20] SHEN Y, LIN Z, WEI J, et al. Facile synthesis of ultra-lightweight silver/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) coated carbonized-melamine foams with high electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness and high absorption coefficient[J]. Carbon, 2022, 186: 9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.09.068 [21] CHEN L, LI N, YU X, et al. A general way to manipulate electrical conductivity of graphene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 462: 142139. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.142139 [22] Peng M. , Qin F. Clarification of basic concepts for electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2021, 130: 225108. doi: 10.1063/5.0075019 [23] DONG Y, RISMILLER S C, LIN J. Molecular dynamic simulation of layered graphene clusters formation from polyimides under extreme conditions[J]. Carbon, 2016, 104: 47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.03.050 [24] LIN J, PENG Z, LIU Y, et al. Laser-induced porous graphene films from commercial polymers[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 5714. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6714 [25] DUY L X, PENG Z, LI Y, et al. Laser-induced graphene fibers[J]. Carbon, 2018, 126: 472-479. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.10.036 [26] NASSER J, LIN J, ZHANG L, et al. Laser induced graphene printing of spatially controlled super-hydrophobic/hydrophilic surfaces[J]. Carbon, 2020, 162: 570-578. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.03.002 [27] WANG Y, WANG G, HE M, et al. Multifunctional Laser-Induced Graphene Papers with Combined Defocusing and Grafting Processes for Patternable and Continuously Tunable Wettability from Superlyophilicity to Superlyophobicity[J]. Small, 2021, 17(42): 2103322. doi: 10.1002/smll.202103322 [28] SONG W-L, CAO M-S, QIAO B-B, et al. Nano-scale and micron-scale manganese dioxide vs corresponding paraffin composites for electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2014, 51: 277-286. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.12.042 [29] ZHAO G, WANG F, ZHANG Y, et al. High-performance hydrogen peroxide micro-sensors based on laser-induced fabrication of graphene@Ag electrodes[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 150565. [30] 崔梦雅, 黄婷, 肖荣诗. 基于纳米颗粒热效应的飞秒激光高效直写金属铜微结构[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 8(49): 0802015.CUI Mengya, HUANG Ting, XIAO Rongshi. Femtosecond Laser Direct Writing of Copper Microstructures with High Efficiency via Thermal Effect of Nanoparticles[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 8(49): 0802015(in Chinese). [31] SHEN H, LIU J, PAN P, et al. One-step synthesis of nanosilver embedding laser-induced graphene for H2O2 sensor[J]. Synthetic Metals, 2023, 293: 117235. doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2022.117235 [32] DONG Z, PENG Y, TAN Z, et al. Simultaneously enhanced electrical conductivity and strength in Cu/graphene/Cu sandwiched nanofilm[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2020, 187: 296-300. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.06.051 [33] 马来鹏, 任文才, 成会明. 表面电荷转移掺杂石墨烯的研究进展[J]. 物理化学学报, 2022, 38(1): 2012080MA Laipeng, REN Wencai, CHENG Huiming. Progress in Surface Charge Transfer Doping of Graphene[J]. Acta Physco-Chimica Sinica, 2022, 38(1): 2012080(in Chinese). [34] RYU S H, PARK B, HAN Y K, et al. Electromagnetic wave shielding flexible films with near-zero reflection in the 5G frequency band[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(8): 4446-4455. doi: 10.1039/D1TA10065C -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 104
- HTML全文浏览量: 119
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: