PVDF/MWCNTs-AgNWs@MXene bilayer 3 D networks electromagnetic shielding composite films with highly conductive
-
摘要: 随着通信网络、无线设备以及航空航天的快速发展,电磁波危害日益加剧,因而急需电磁屏蔽性能更优异的复合材料。本文采用MXene (Ti3C2Tx)、银纳米线(AgNWs)和多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)构建了双层的高导电三维(导电率最高为1.4×104 S·m−1)网络电磁屏蔽复合薄膜(Ti3C2Tx MXene基功能复合薄膜)。特别是采取真空辅助抽滤法(VAF)将10 mL AgNWs以及15 mL Ti3C2Tx MXene的水溶液吸附于聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)/MWCNTs复合薄膜之上,制备出的Ti3C2Tx MXene基功能复合薄膜的总电磁干扰屏蔽效能(EMI SET)高达69.0 dB,比商用标准(20 dB)高出245%,其中吸收损耗效能(SEA)占比85.1%。说明Ti3C2Tx MXene基功能复合薄膜主要的电磁损耗机制为吸收损耗,比电磁屏蔽效能(SSEt)最高可达2719.8 dB/(cm−2·g)。这项工作为新型MXene材料在电磁屏蔽复合材料中的应用提供了结构设计和研究思路。
-
关键词:
- Ti3C2Tx MXene /
- AgNWs /
- 复合薄膜 /
- 电磁屏蔽 /
- 吸收损耗
Abstract: With the development of communication networks, wireless devices and aerospace industries. Electromagnetic wave hazards become prevalent. Therefore, it is essential to develop composites with better electromagnetic shielding properties. In this paper, highly conductive three-dimensional (conductivity up to 1.4×104 S·m−1) networked electromagnetic shielding composite films (Ti3C2Tx MXene-based functional composite films) were constructed using MXene (Ti3C2Tx), silver nanowires (AgNWs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) in a bilayer. In particular, the aqueous solutions of 10 mL AgNWs and 15 mL Ti3C2Tx MXene were adsorbed on top of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/MWCNTs composite films by vacuum-assisted filtration (VAF), and the total electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness (EMI SET) of the Ti3C2Tx MXene-based functional composite film was as high as 69.0 dB, which was 245% higher than that of the commercial standard (20 dB), of which the absorption loss effectiveness (SEA) accounted for 85.1%. It is shown that the main electromagnetic loss mechanism of Ti3C2Tx MXene-based functional composite films is absorption loss, with a specific electromagnetic shielding effectiveness (SSE/t) of up to 2719.8 dB/(cm−2·g). This work provides structural design and research ideas for the application of novel MXene materials in electromagnetic shielding composites.-
Key words:
- Ti3C2Tx MXene /
- AgNWs /
- composite films /
- electromagnetic shielding /
- absorption loss
-
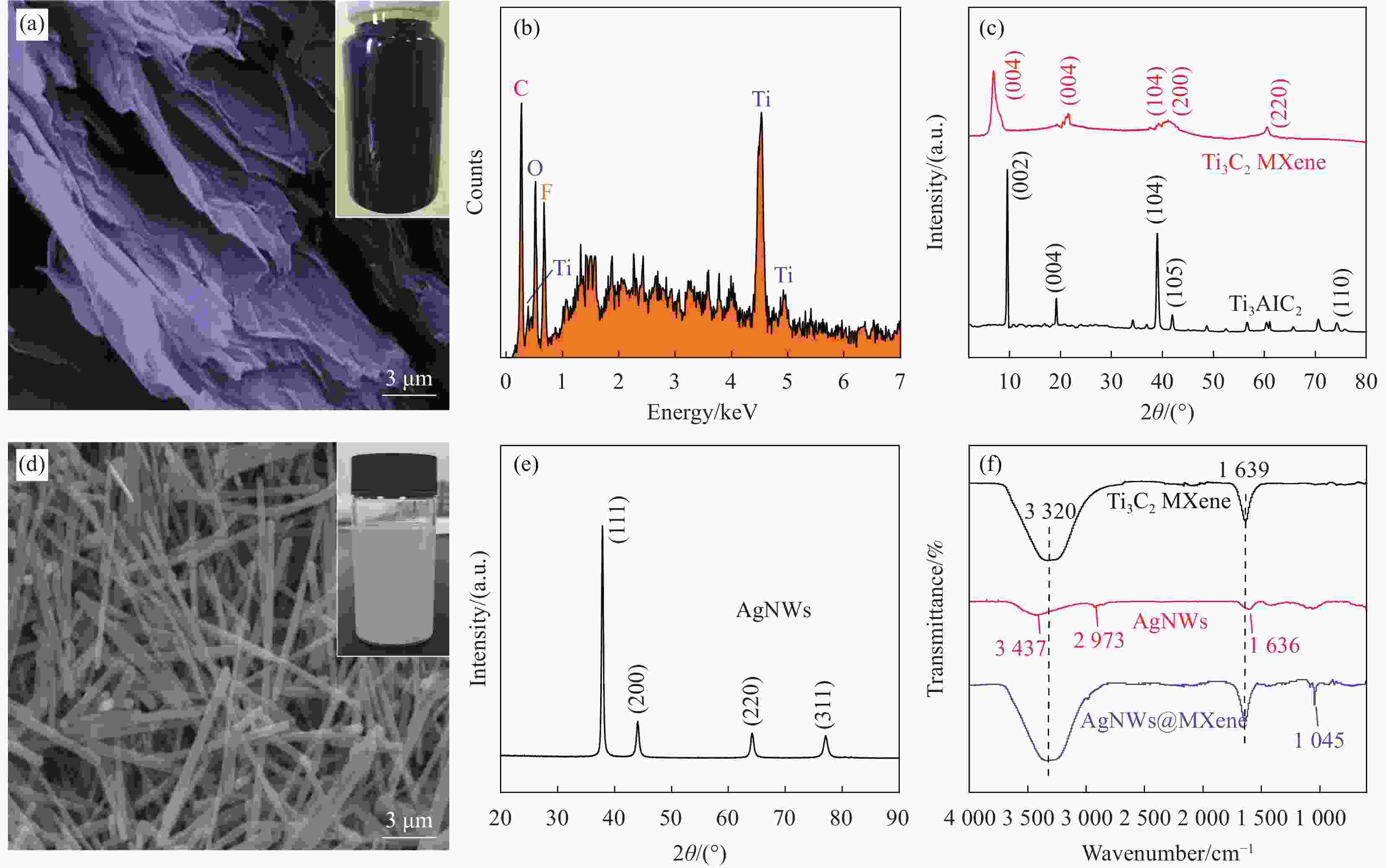
图 2 Ti3C2Tx MXene的SEM图片 (a)和EDS(b)以及Ti3AlC2(刻蚀前)和Ti3C2Tx MXene(刻蚀后)的XRD谱图(c)AgNWs的SEM形貌分析(d)和XRD谱图(e)以及Ti3C2Tx MXene、AgNWs和AgNWs@MXene的FTIR谱图(f)
Figure 2. SEM images of Ti3C2Tx MXene (a) and EDS (b) and XRD spectra of Ti3AlC2 (before etching) and Ti3C2Tx MXene (after etching) (c) SEM morphology analysis (d) and XRD spectra of AgNWs (e) and FTIR spectra ofTi3C2Tx MXene, AgNWs and AgNWs@MXene (f)
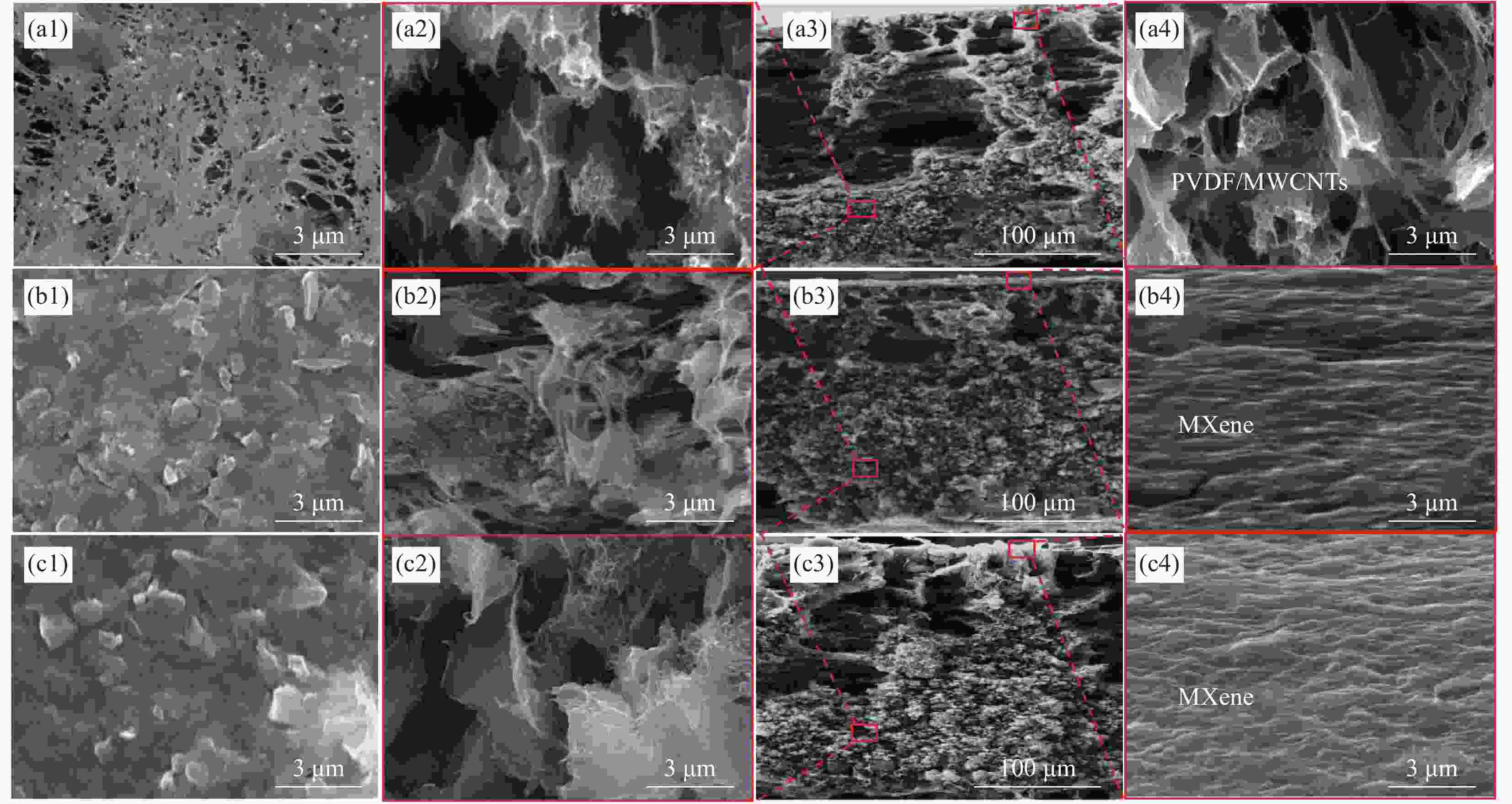
图 3 PVDF/MWCNTs-3 wt%-MXene-X双层复合薄膜的形貌表征(a、b、c分别代表M3-MX-0、M3-MX-10、M3-MX-20;1:表观形貌;2:底层局部放大形貌;3:断面形貌;4:抽滤层局部放大形貌)
Figure 3. Morphological characterisation of PVDF/MWCNTs-3 wt%-MXene-X bilayer composite films(a, b, c represent M3-MX-0, M3-MX-10, M3-MX-20, respectively; 1: apparent appearance; 2: local enlargement of the bottom layer; 3: cross-section appearance; 4: local enlargement of the extraction layer)
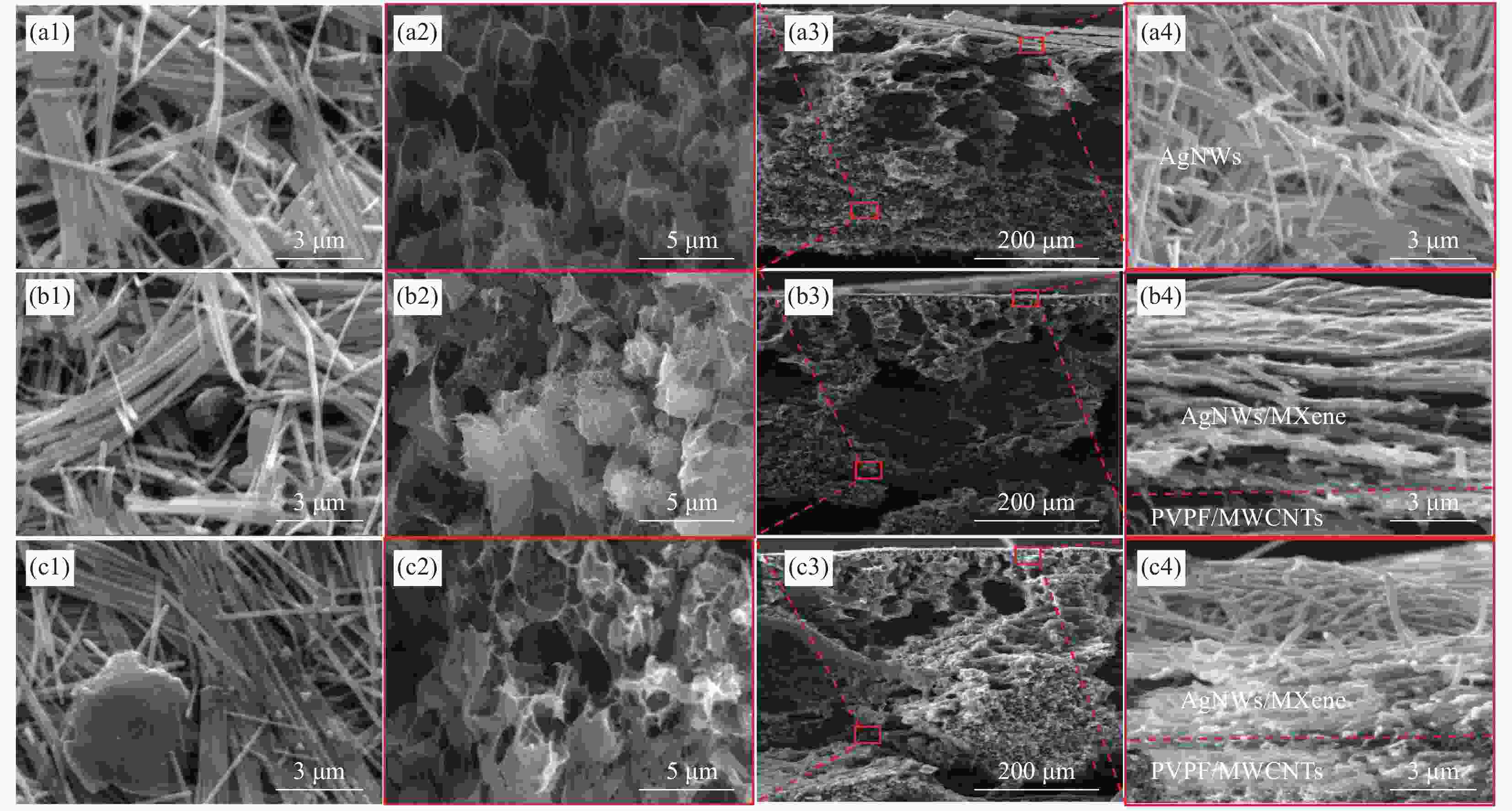
图 4 PVDF/MWCNTs-3 wt%-AgNWs@MXene-X双层复合薄膜的形貌表征(A、B、C分别代表M3-Ag@MX-0、M3-Ag@MX-10、M3-Ag@MX-20;1:表观形貌;2:底层局部放大形貌;3:断面形貌;4:抽滤层局部放大形貌)
Figure 4. Morphological characterisation of PVDF/MWCNTs-3 wt%/AgNWs@MXene-X bilayer composite films (A, B, C represent M3-Ag@MX-0, M3-Ag@MX-10, M3-Ag@MX-20, respectively; 1: apparent appearance; 2: local enlargement of the bottom layer; 3: cross-section appearance; 4: local enlargement of the extraction layer)
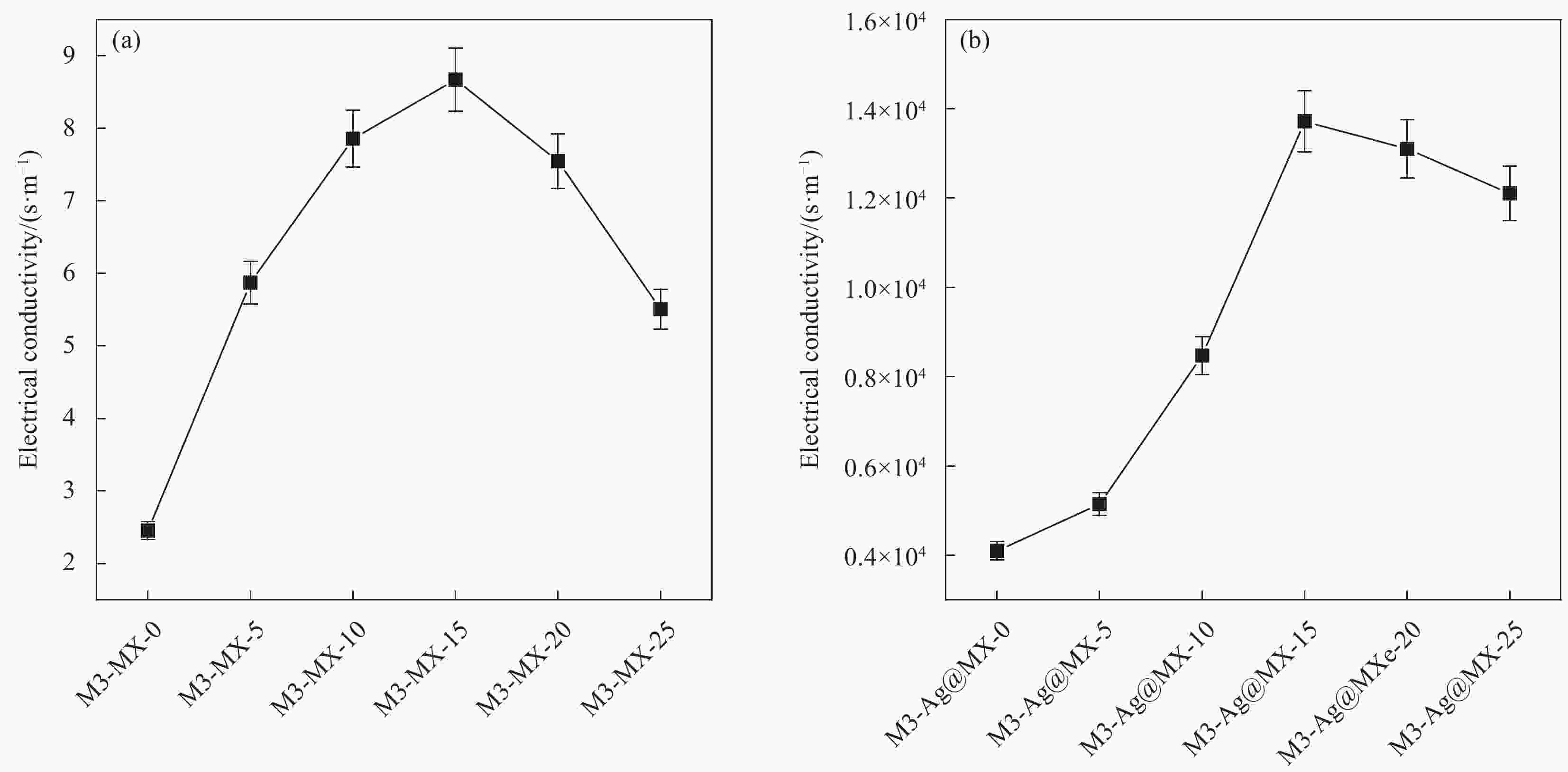
表 1 不同Ti3C2Tx MXene含量的双层复合薄膜的导电性能数据
Table 1. Conductivities of bilayer composite films with different Ti3C2Tx MXene contents
Sample items Thickness/
mmElectrical conductivity/(S·m−1) Conductivity
growth rate/%M3-MX-0 0.57 2.5×100 − M3-MX-5 0.46 5.9×100 57.6 M3-MX-10 0.42 7.9×100 25.3 M3-MX-15 0.39 8.7×100 9.2 M3-MX-20 0.50 7.5×100 −16.0 M3-MX-25 0.44 5.5×100 −36.4 M3-Ag@MX-0 0.51 4.1×103 99.9 M3-Ag@MX-5 0.46 5.1×103 19.6 M3-Ag@MX-10 0.6 8.5×103 40.0 M3-Ag@MX-15 0.47 1.4×104 39.3 M3-Ag@MX-20 0.43 1.3×104 −7.7 M3-Ag@MX-25 0.46 1.2×104 −8.3 表 2 不同Ti3C2Tx MXene含量的双层复合薄膜的电磁屏蔽效能数据
Table 2. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness data of bilayer composite films with different Ti3C2Tx MXene contents
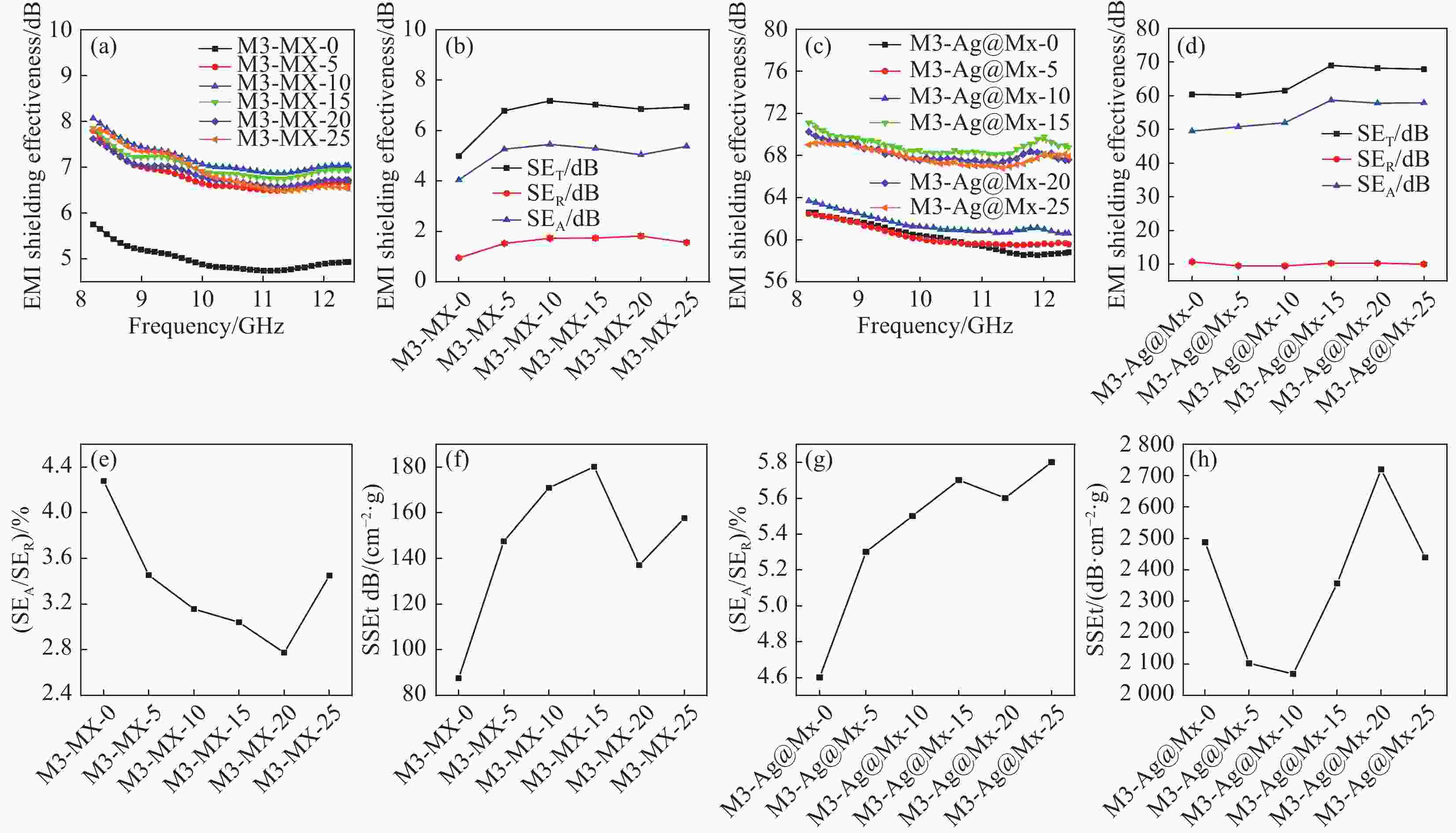
Sample items SET/dB SER/dB SEA/dB SEA/SER/% SSEtdB/(cm−2·g) M3-MX-0 5.0 0.9 4.0 4.3 87.6 M3-MX-5 6.8 1.5 5.3 3.5 147.5 M3-MX-10 7.2 1.7 5.5 3.2 171.0 M3-MX-15 7.0 1.7 5.3 3.0 180.2 M3-MX-20 6.9 1.8 5.0 2.8 137.1 M3-MX-25 6.9 1.6 5.4 3.5 157.7 M3-Ag@MX-0 60.2 9.5 50.8 4.6 2487.7 M3-Ag@MX-5 60.4 10.7 49.5 5.3 2102.2 M3-Ag@MX-10 61.5 9.5 52.0 5.5 2068.3 M3-Ag@MX-15 69.0 10.3 58.7 5.7 2356.6 M3-Ag@MX-20 68.2 10.3 57.8 5.6 2719.8 M3-Ag@MX-25 67.9 10.0 57.9 5.8 2439.4 Notes: The values of SET (dB), SEA (dB), and SER (dB) in the table are the average values obtained at 8.2-12.4 GHz. SEA/SER is the ratio of absorption loss SEA to reflection loss SER. SSEt denotes the ratio of EMI SE. -
[1] SHARMA R, CLOWER W, RADADIA A D, et al. Development of geopolymer composites for EMI shielding from steel industry waste[J]. Journal of Materials Science:Materials in Electronics, 2022, 33(8): 1-15. [2] BATOOL S, BIBI A, F FREZZA, et al. Benefits and hazards of electromagnetic waves, telecommunication, physical and biomedical: a review[J]. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 2019, 23(7): 3121-3128. [3] LI Y M, LI Y R, HU WJ, et al. Designing of an rGO-based heterostructure for highly efficient microwave absorption performance and flame retardancy[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(20): 32600-32610. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.07.227 [4] ZHANG WM, ZHAO B, NI N, et al. High entropy rare earth hexaborides/tetraborides (HE REB6/HE REB4) composite powders with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 87: 155-166. [5] TENG R, SUN JM, NIE YX, et al. An ultra-thin and highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding composite paper with hydrophobic and antibacterial properties[J]. International journal of biological macromolecules, 2023: 127510-127510. [6] LI J T, LI JZ, LI T, et al. Flexible and excellent electromagnetic interference shielding film with porous alternating PVA-derived carbon and graphene layers[J]. iScience, 2023, 26(10): 107975-107975. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107975 [7] DU C L, WAN G P, WU LH, et al. Iron-doped nickel-cobalt bimetallic phosphide nanowire hybrids for solid-state supercapacitors with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of colloid and interface science, 2023, 654(Pt A): 486-494. [8] ZAHID M, ANUM R, SIDDIQUE S, et al. Polyaniline-based nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding applications: A review[J]. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 2023, 36(4): 1717-1761. doi: 10.1177/08927057211022408 [9] WANG Z, FAN J, GUO X, et al. Enhanced permittivity of negative permittivity middle-layer sandwich polymer matrix composites through conductive filling with flake MAX phase ceramics[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(45): 27025-27032. doi: 10.1039/D0RA03493B [10] FARD K H A, GHASEMI R, MOHAMMADI B. Study of EMI-Based Damage Type Identification in a Cracked Metallic Specimen Repaired by a Composite Patch[J]. Russian Journal of Nondestructive Testing, 2020, 56(6): 540-548. doi: 10.1134/S1061830920060054 [11] XIA Y X, GAO W W, GAO C. A Review on Graphene-Based Electromagnetic Functional Materials: Electromagnetic Wave Shielding and Absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(42): 1-36. [12] LUO W, JIANG X, LIU Y, et al. Entropy-Driven Morphology Regulation of MAX Phase Solid Solutions with Enhanced Microwave Absorption and Thermal Insulation Performance[J]. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2023: e2305453-e2305453. [13] YAO Y Y, JIN S H, ZOU H M, et al. Polymer-based lightweight materials for electromagnetic interference shielding: a review[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(11): 1-32. [14] YANG L, CHEN Y H, WANG M, et al. Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing of Novel Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Graphene Nanocomposite with Enhanced Mechanical and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(16): 8066-8077. [15] JIANG D W, MURUGADOSS V, WANG Y, et al. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Polymers and Nanocomposites - A Review[J]. Polymer Reviews, 2019, 59(2): 280-337. doi: 10.1080/15583724.2018.1546737 [16] HSIAO S, MA C M , LIAO W. Lightweight and Flexible Reduced Graphene Oxide/Water-Borne Polyurethane Composites with High Electrical Conductivity and Excellent Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Performance[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2014, 6(13): 10667-10678. [17] HUANG X, TUERSUN Y, LUO P, et al. In-situ reduction of AgNPs on MXene surfaces for synthesis of efficient thermally conductive composites with powerful electromagnetic shielding capabilities[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 677(PB): 132444. [18] XIONG C Y, WANG T X, ZHOU L F, et al. Fabrication of dual-function conductive cellulose-based composites with layered conductive network structures for supercapacitors and electromagnetic shielding[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 472: 144958. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.144958 [19] GAO Q, Yu Z, ZHANG S, et al. Hierarchical structured epoxy/reduced graphene oxide/Ni-chains microcellular composite foam for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Composites Part A, 2023, 170: 107536. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2023.107536 [20] MA Z L, KANG S L, MA J Z, et al. Military and Defense; Studies from Shaanxi University of Science and Technology Update Current Data on Military and Defense (Ultraflexible and Mechanically Strong Double-layered Aramid Nanofiber-Ti3C2Tx Mxene/silver Nanowire Nanocomposite Papers for High-performance )[J]. Defense & Aerospace Week, 2020, 14(7): 8368-8382. [21] QU Y F, LI X, WANG X, et al. Multifunctional AgNWs@MXene/AgNFs electromagnetic shielding composites for flexible and highly integrated advanced electronics[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2022, 230: 109753. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2022.109753 [22] IQBAL A, HASSAN T, GAO Z G, et al. MXene-incorporated 1D/2D nano-carbons for electromagnetic shielding: A review[J]. Carbon, 2023, 203(25): 542-560. [23] CHU Q D, LIN H, MA M, et al. Cellulose Nanofiber/Graphene Nanoplatelet/MXene Nanocomposites for Enhanced Electromagnetic Shielding and High In-Plane Thermal Conductivity[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5(5): 7217-7227. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.2c01126 [24] ZHU L L, MO R, YIN C G, et al. Synergistically Constructed Electromagnetic Network of Magnetic Particle-Decorated Carbon Nanotubes and MXene for Efficient Electromagnetic Shielding[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(50): 56120-56131. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c17696 [25] SHAHZAD F, ALHABEB M, HATTER B C, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes)[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6304): 1137-1140. doi: 10.1126/science.aag2421 [26] XIN W, XI G, CAO W, ET AL. Lightweight and flexible MXene/CNF/silver composite membranes with a brick-like structure and high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding[J]. RSC Advances, 2019: 2046-2069. [27] CHARD K, ZHANG X, CHEN Y J. Recent progress in MXene and graphene based nanocomposites for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 15(10): 104143. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104143 [28] HAN Y X, RUAN K P, GU J W, et al. Janus (BNNS/ANF)-(AgNWs/ANF) thermal conductivity composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(5): 1-9. [29] TAN Y Y, XUE Y, LI K T, et al. PVDF/MWCNTs/RGO@Fe3O4/AgNWs composite film with a bilayer structure for high EMI shielding and electrical conductivity[J]. Polymer Composites, 2023: 1-16. [30] 谭东宸. 基于银纳米管网络的柔性透明电磁屏蔽薄膜 [D]; 大连理工大学, 2022.TAN D C. Flexible and transparent electromagnetic shielding films based on silver nanotube networks [D]; Dalian University of Technology, 2022(in Chinese). [31] JIANG Z Y, ZHAO S Q, CHEN L S, et al. Freestanding "core-shell" AgNWs/metallic hybrid mesh electrodes for a highly efficient transparent electromagnetic interference shielding film[J]. Optics express, 2021, 29(12): 18760-18768. doi: 10.1364/OE.423369 [32] KHOT A C, DONGALE T D, PARK J H, et al. Ti3C2-Based MXene Oxide Nanosheets for Resistive Memory and Synaptic Learning Applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(4): 5216-5227. [33] 李亚萍. 缝型及缝迹对电磁屏蔽服装屏蔽效能的影响 [D]; 中原工学院, 2018.Li Y P. Effect of sewing type and stitching on shielding effectiveness of electromagnetic shielding garments [D]; Zhongyuan Institute of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [34] CHENG C B, JIANG Y L, SUN X, et al. Tunable negative permittivity behavior and electromagnetic shielding performance of silver/silicon nitride metacomposites[J]. Composites Part A, 2020, 130: 105753-105753. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105753 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 178
- HTML全文浏览量: 99
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: