Research progress on energy absorption mechanism and damage mode of fiber reinforced resin based bulletproof composites
-
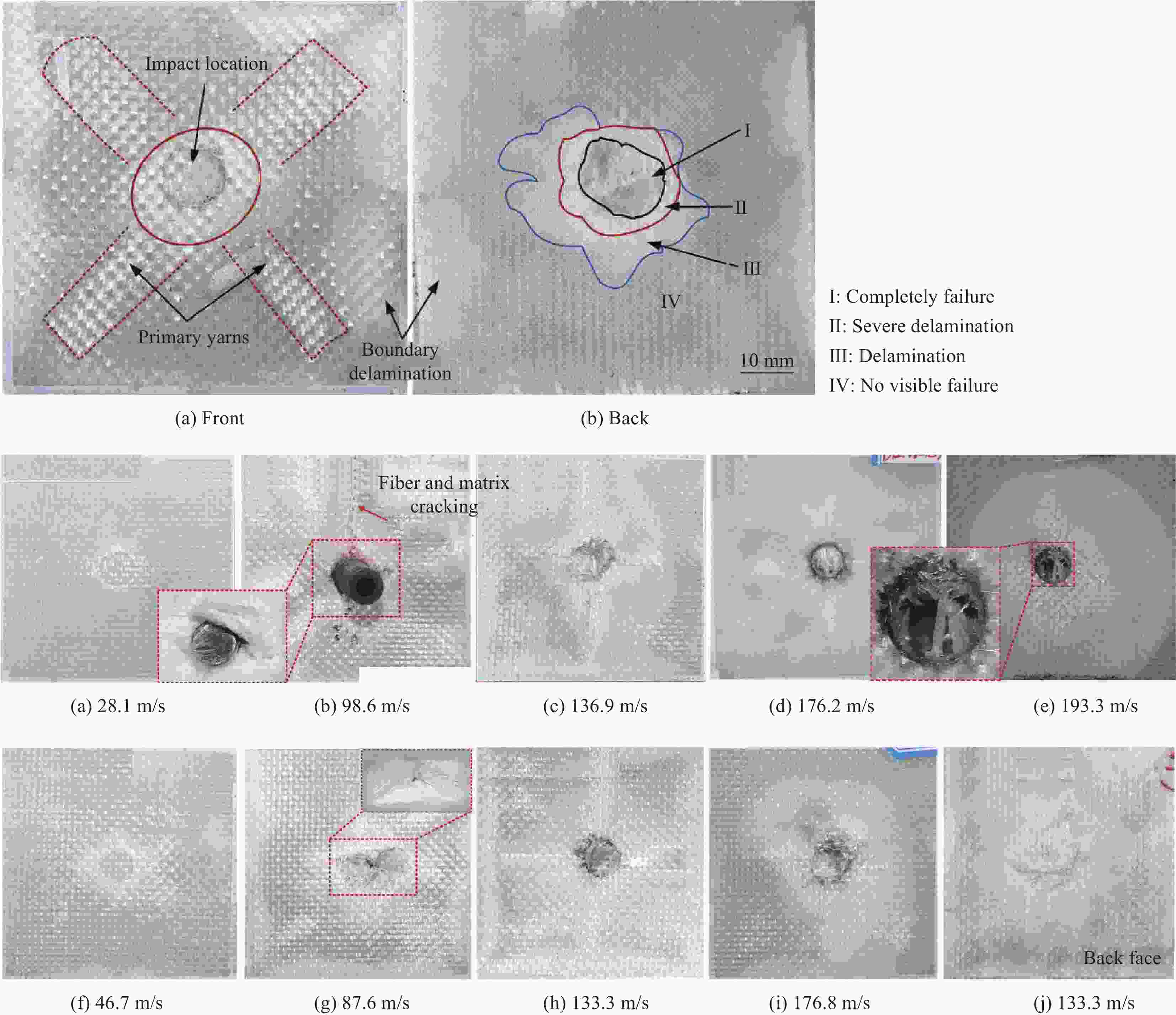
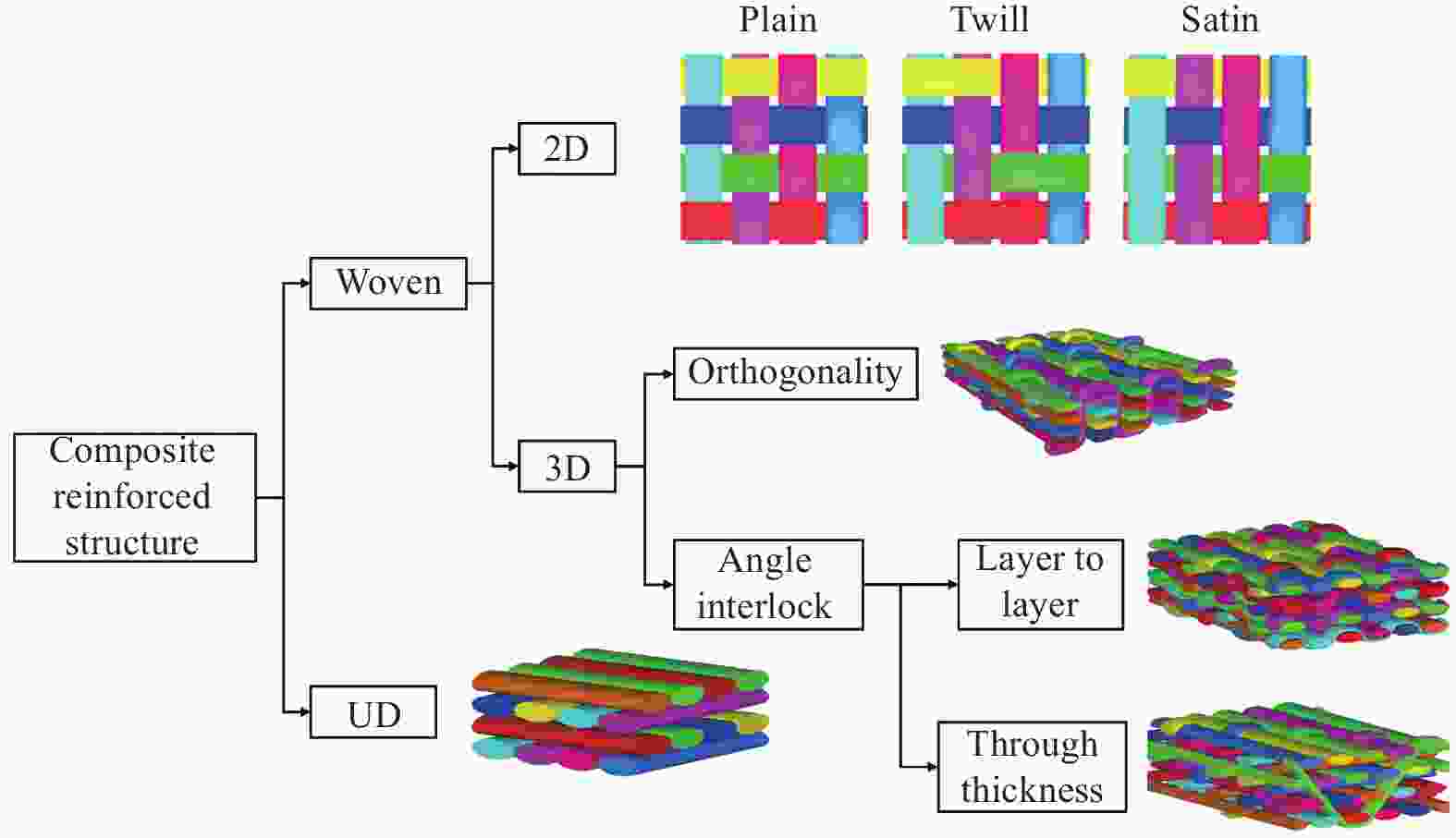
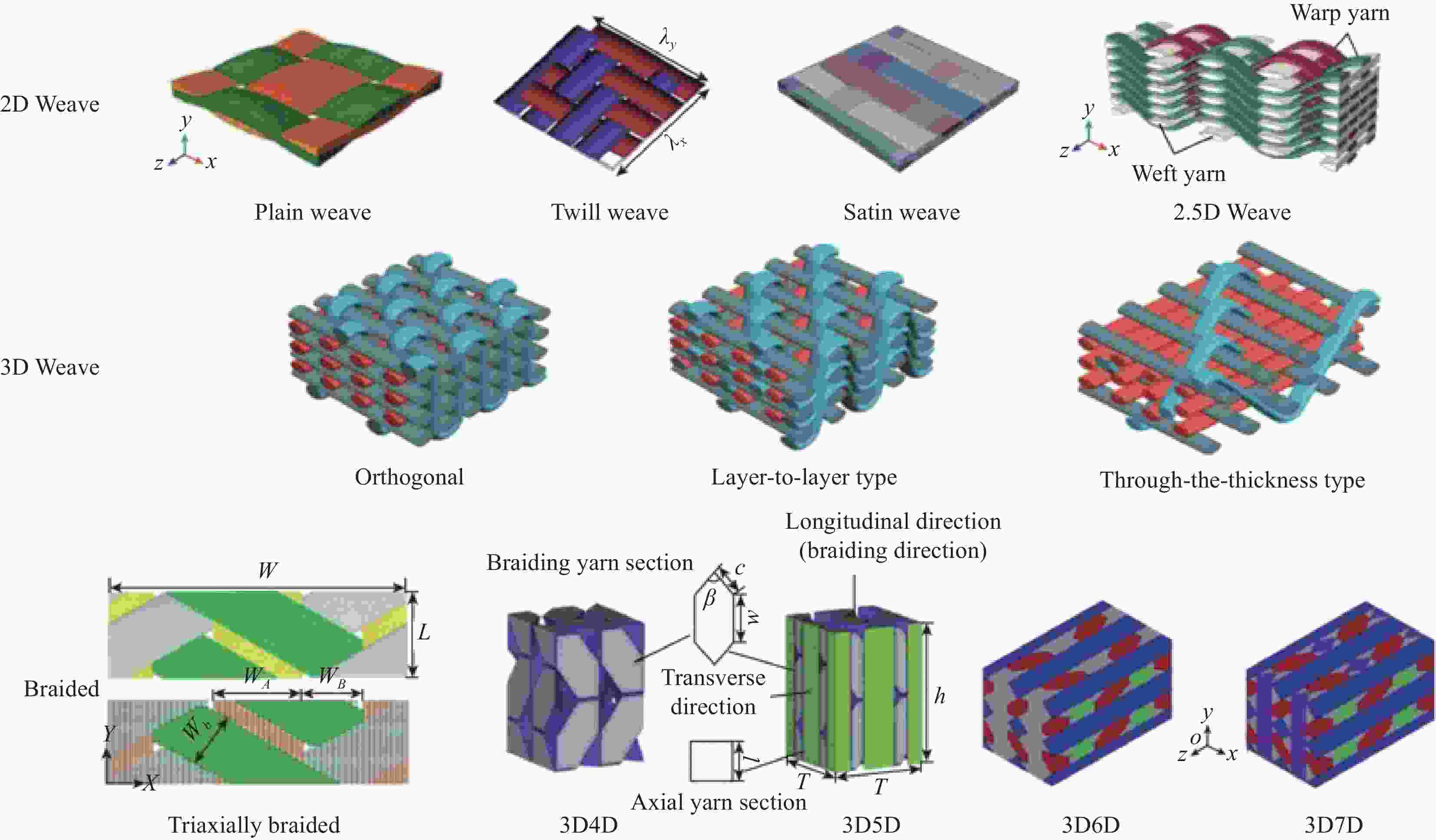
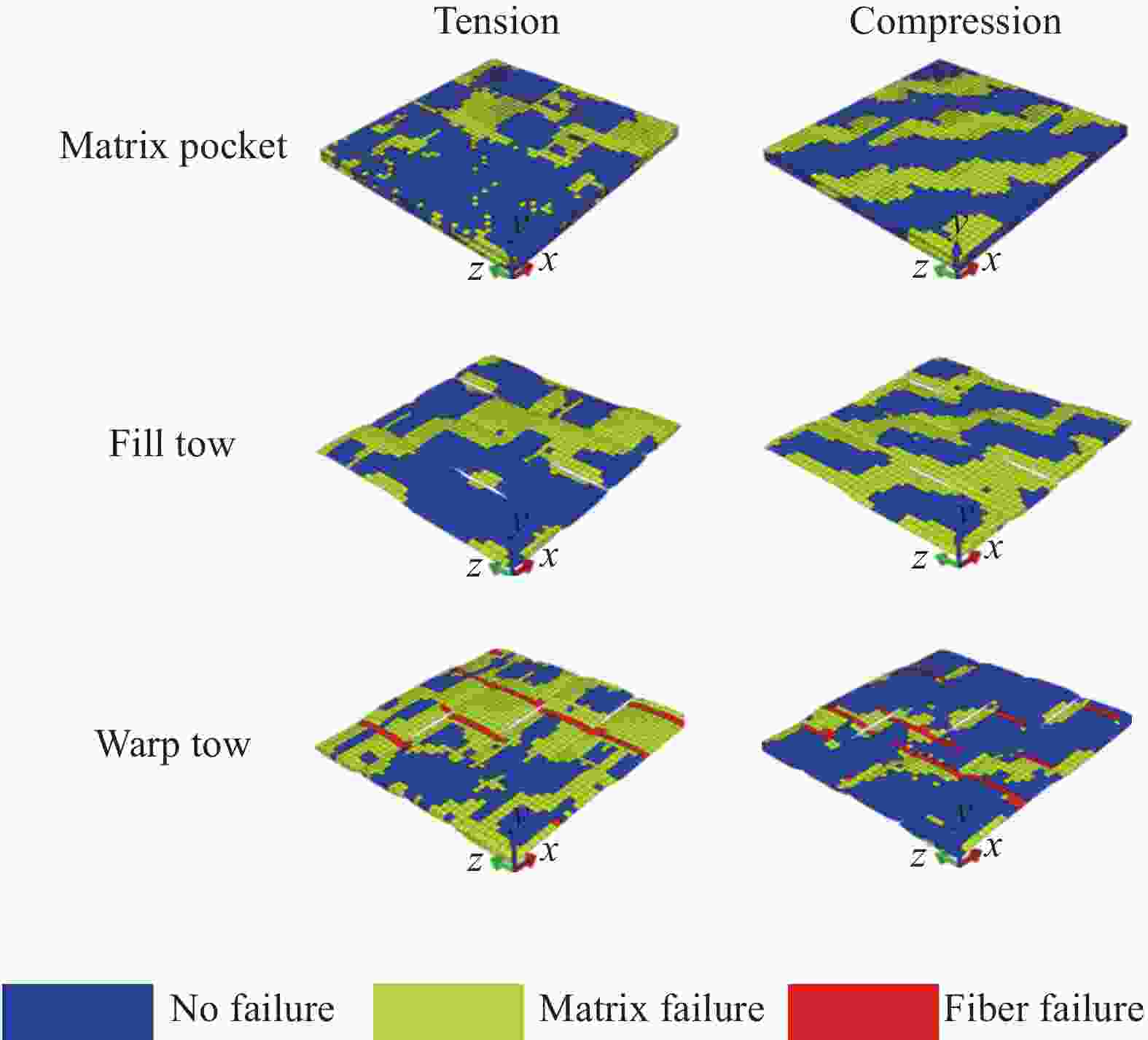
摘要: 本文对纤维增强树脂基复合材料在抗冲击领域的吸能机制及损伤模式进行了综述。首先,介绍了纤维增强复合材料在弹道防护、航空航天等领域的应用,对比了超高分子量聚乙烯(UHMWPE)纤维、芳纶纤维、碳纤维等高性能纤维的优缺点;其次,以各种纤维增强树脂基复合材料的弹道实验及理论模拟为基础,分析了防弹复合材料的吸能机制和损伤模式,发现拉伸变形是复合材料的主要吸能方式,分层破坏是其主要损伤模式;最后,总结了纤维编织结构的分类、特点及其对复合材料防弹性能的影响并对纤维增强树脂基复合材料的发展前景进行了展望。
-
关键词:
- 纤维增强树脂基复合材料 /
- 弹道响应 /
- 吸能机制 /
- 损伤模式 /
- 编织结构
Abstract: This article reviews the energy absorption mechanism and damage modes of fiber reinforced resin matrix composites in the field of impact resistance. Firstly, the applications of fiber reinforced composites in the fields of ballistic protection and aerospace are introduced. In addition, the advantages and disadvantages of high-performance fibers such as ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber (UHMWPE), aramid fibers and carbon fibers are compared. Secondly, based on ballistic experiments and theoretical simulations of various fiber reinforced resin matrix composites, the energy absorption mechanism and damage mode of bulletproof composites are analyzed. It is found that tensile deformation is the main energy absorption mode of composites, and delamination is its main damage mode. Finally, the classification and characteristics of fabric structures and their influence on the ballistic performance of composites are summarized and the development prospect of fiber reinforced resin matrix composites is prospected. -
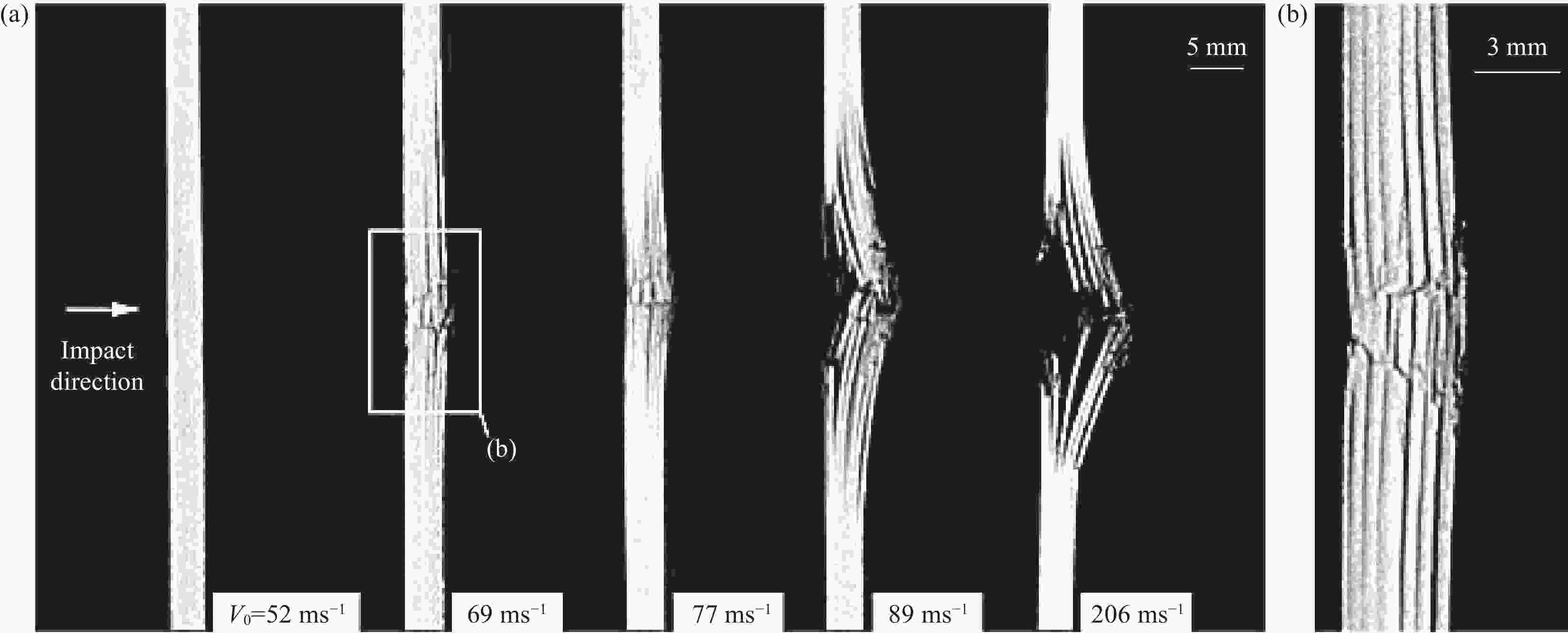
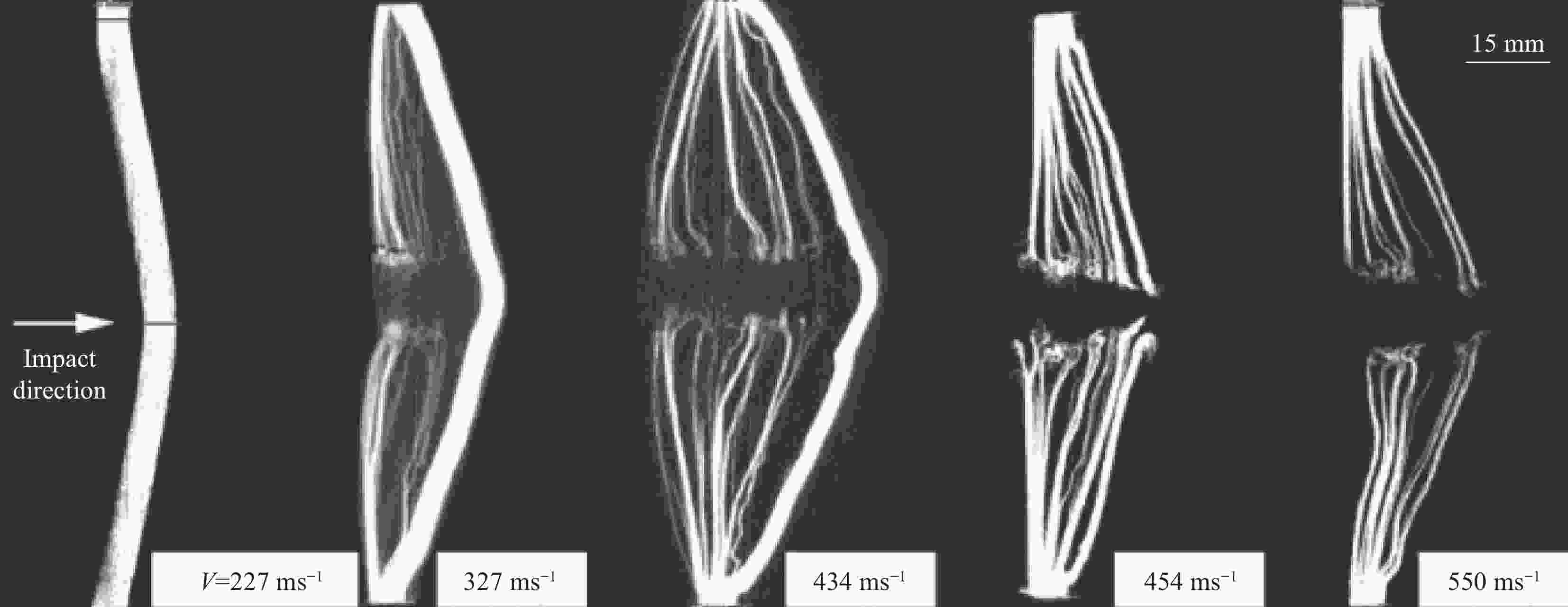
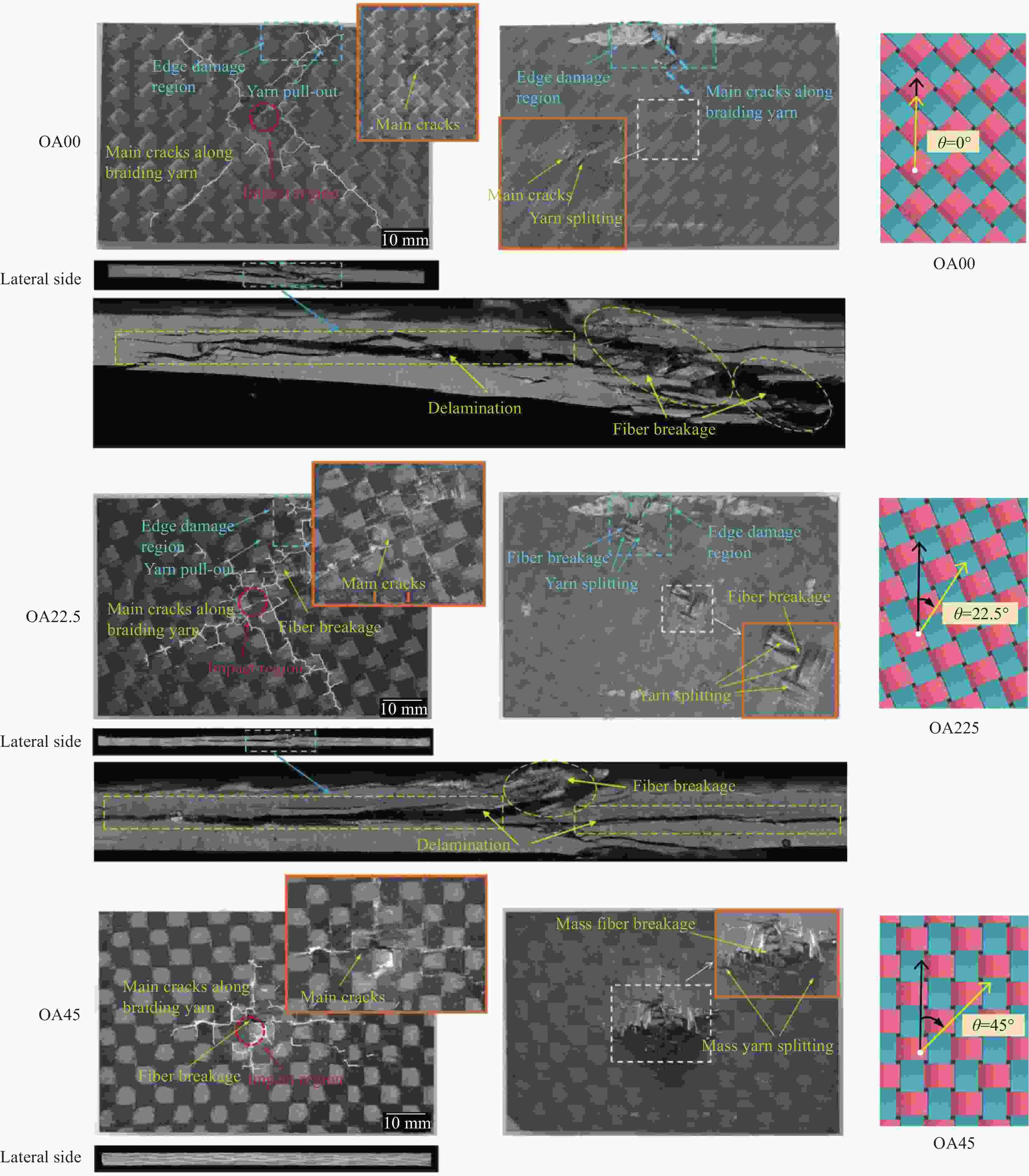
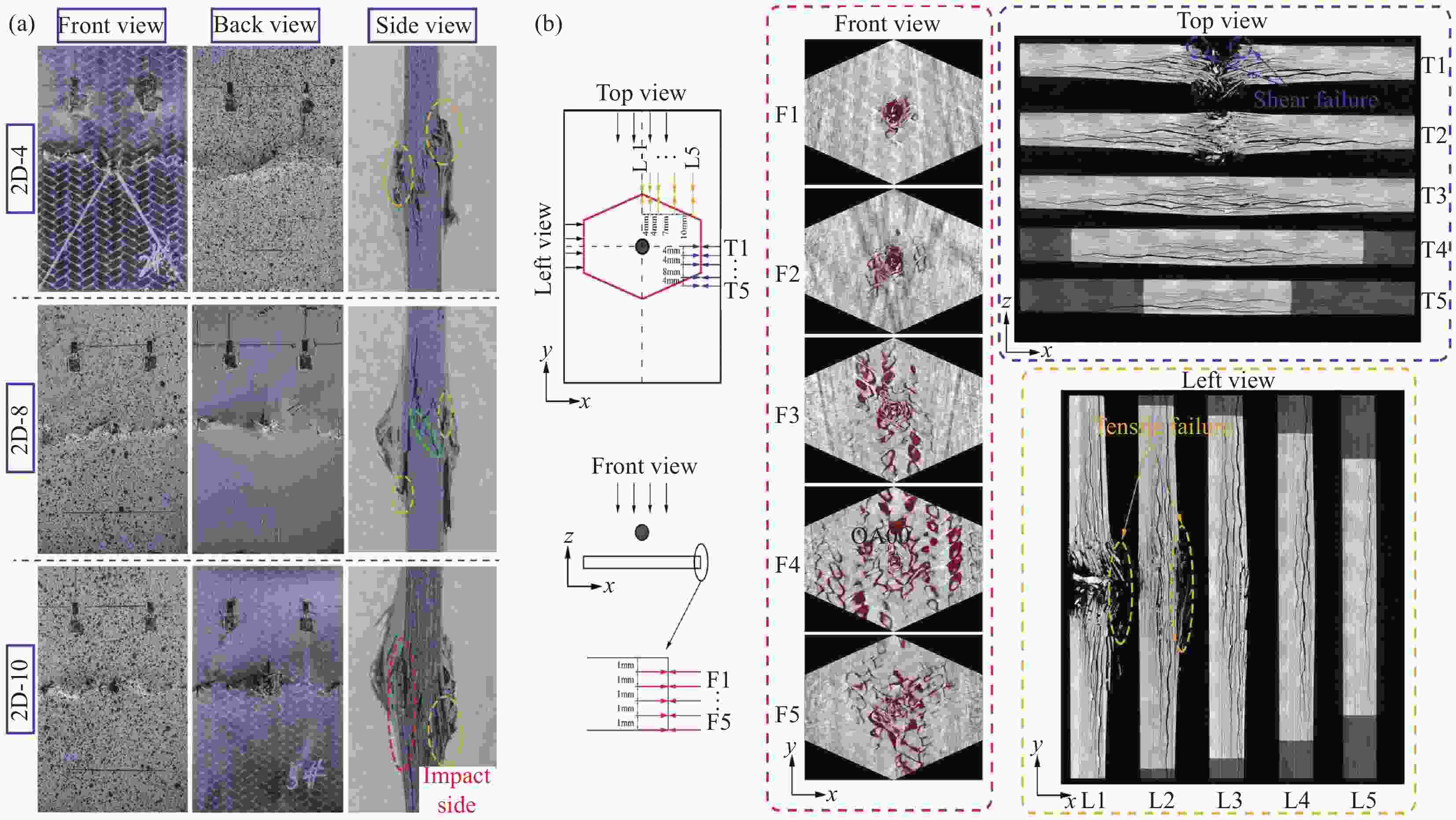
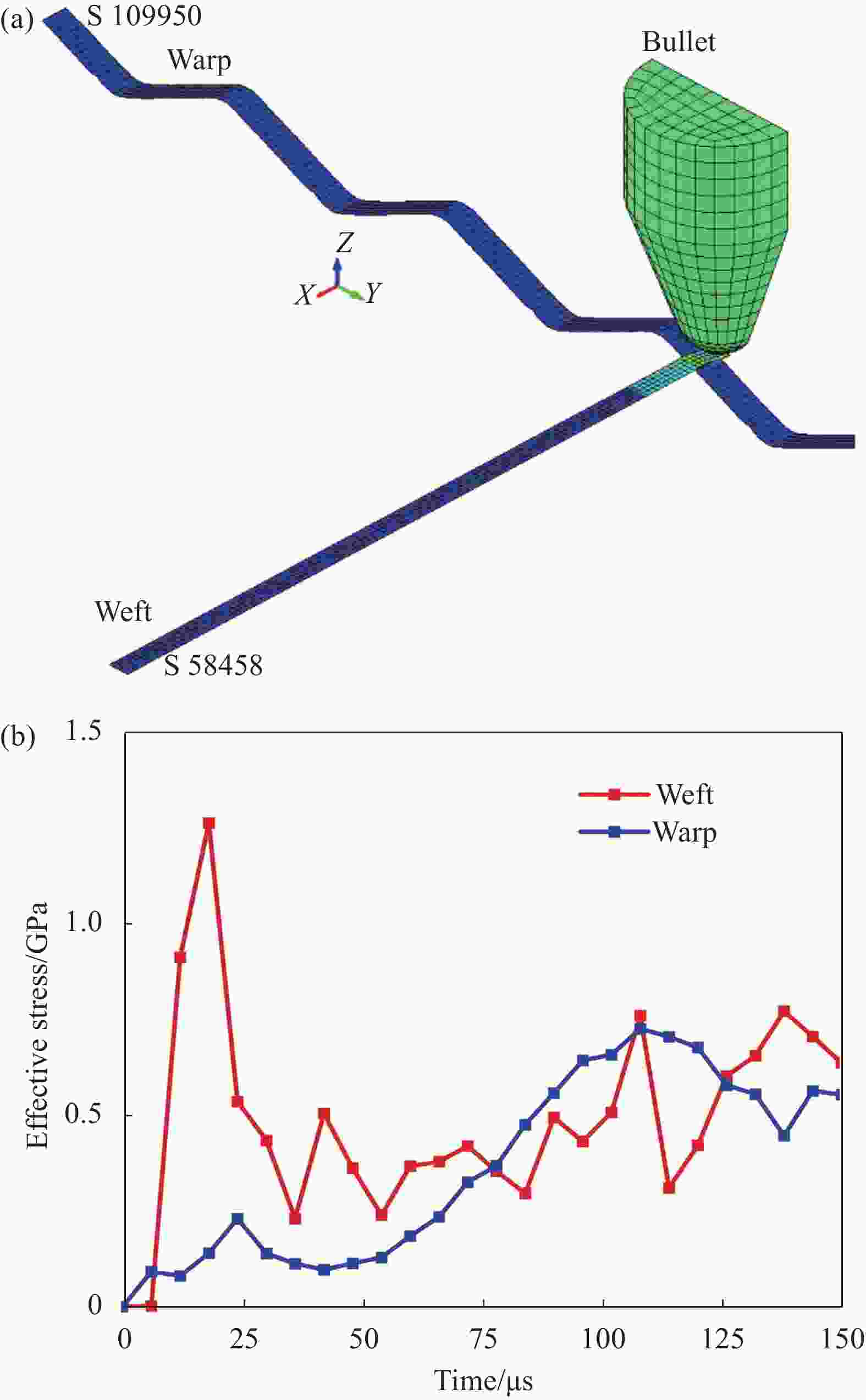
图 1 弹道极限实验纤维断裂形貌(12.7 mm FSP以1346 m/s的速度撞击35 mm厚的靶板): (a)正面; (b)距正面9 mm; (c)距正面18 mm;(d)背面[34]
Figure 1. Fiber fracture morphology from ballistic limit tests (35 mm thick target impacted by 12.7 mm FSP at 1346 m/s). Images taken: (a) at the front face; (b) 9 mm from the front face; (c) 18 mm from the front face; and (d) at the back face [34]
-
[1] 滕凌虹. 陶瓷/纤维复合装甲抗侵彻性能研究及仿真模拟[D]. 天津工业大学, 2021.TENG Linghong. Ceramic/penetration resistance of fiber composite armor [D]. Tiangong University, 2021. (in Chinese). [2] ZHANG Y, DONG H, LIANG K, et al. Impact simulation and ballistic analysis of B4C composite armour based on target plate tests[J]. CERAMICS INTERNATIONAL, 2021, 47(7): 10035-10049. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.150 [3] 王亚进, 王陶, 王良模, 等. 陶瓷/芳纶纤维复合靶板防弹性能研究及结构改进[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 47(2): 74-80.WANG Yajin, WANG Tao, WANG Liangmo, et al. Ballistic performance and structural improvement of an aramid fiber/ceramic composite target[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 47(2): 74-80(in Chinese). [4] CHEN J, ZENG Y, LIANG X, et al. Lightweight Design and Experimental Study of Ceramic Composite Armor[J]. Processes, 2022, 10(6): 1056. doi: 10.3390/pr10061056 [5] 秦刚, 邹顺睿, 蒋龙飞, 等. 碳化硅纤维增韧碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展综述[J]. 陶瓷学报, 2023, 44(3): 389-407.QinGang, ZouShunrui, JiangLongfei, et al. Research Progress of Silicon Carbide Fiber Reinforced Silicon Carbide Ceramic Matrix Composites [J] Journal of Ceramics, 2023, 44(3): 389-407. (in Chinese). [6] MA Y, WANG J, ZHAO G, et al. New insights into the damage assessment and energy dissipation weight mechanisms of ceramic/fiber laminated composites under ballistic impact[J]. CERAMICS INTERNATIONAL, 2023, 49(13): 21966-21977. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.04.021 [7] 王得盼, 梁森, 周越松, 等 . 短切碳纤维增强氧化铝复相陶瓷力学性能及抗冲击性能研究[J]. 复合材料科学与工程,2023 , (6 ):12 -16 .WANG Depan, LIANG Sen, ZHOU Yesong, et al . Study on mechanical properties and impact resistance of short carbon fiber reinforced alumina composite ceramics.[J]. Composite materials science and engineering,2023 , (6 ):12 -16 (in Chinese)..[8] 贾文星, 贾子琪, 田国峰, 等. 聚酰亚胺/超高分子量聚乙烯纤维混杂增强复合材料防弹性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(7): 3921-3927.JIA Wenxing, JIA Ziqi, TIAN Guofeng, et al. Bulletproof performance of polyimide/UHMWPE fiber hybrid reinforced composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(7): 3921-3927 (in Chinese). [9] 付杰, 李伟萍, 黄献聪, 等. 新型超高分子量聚乙烯防弹膜材料研究进展[J]. 纺织高校基础科学学报, 2021, 34(4): 1-9.FU Jie, LI Weiping, HUANG Xiangcong, et al. Research progress of new UHMWPE bullet-proof film materials[J]. Basic Science Journal of Textile Universities, 2021, 34(4): 1-9(in Chinese). [10] WANG Z, ZHANG H, DONG Y, et al. Ballistic performance and protection mechanism of aramid fabric modified with polyethylene and graphene[J]. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL SCIENCES, 2023, 237: 107772. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107772 [11] LEI X, XIAO K, WU X, et al. Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Several High-Performance Single Fibers[J]. MATERIALS, 2021, 14(13): 3574. doi: 10.3390/ma14133574 [12] XIAO K, ZHANG P, HU D, et al. Micron-Thick Interlocked Carbon Nanotube Films with Excellent Impact Resistance via Micro-Ballistic Impact[J]. SMALL, 2023[2023-09-06]. [13] WANG M, ZHONG L, CAO H, et al. Research on Bending and Ballistic Performance of Three-Dimensional Ply-to-Ply Angle Interlock Kevlar/EP Armor Material[J]. MATERIALS, 2022, 15(19): 6994. doi: 10.3390/ma15196994 [14] 肖露. 混杂热固性树脂基防弹复合材料的制备及侵彻机理研究[D]. 浙江理工大学, 2013.XIAO Lu. A Study on the Preparation and Ballistic Penetration Properties of Hybrided Thermosetting Resin Bulletproof Composite[D]. Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2013 (in Chinese). [15] Recent advances in the development of aerospace materials[J]. Original Article, 2019. [16] KULKARNI S G, GAO X L, HORNER S E, et al. Ballistic helmets – Their design, materials, and performance against traumatic brain injury[J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 101: 313-331. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.02.014 [17] LEMSTRA P J. Chapter 1: High-performance polyethylene fibers[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research, 2022, 5(2): 49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.aiepr.2022.03.001 [18] 肖文莹, 郭万涛, 李想. 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维增强防弹复合材料研究进展[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2019, 34(2): 131-138.XIAO Wenying, GUO Wantao, LI Xiang. The Progress of UHMWPE Fiber-Reinforced Ballistic Composites[J]. Material development and application, 2019, 34(2): 131-138(in Chinese). [19] 董彬, 魏汝斌, 王小伟, 等. 高性能有机纤维在防弹复合材料领域应用研究现状[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2023, (1): 116-123.DONG Bin, WEI Rubin, WANG Xiaowei, et al. Review of high performance organ fibers in ballistic composite fields[J]. Composite materials science and engineering, 2023, (1): 116-123 (in Chinese). [20] WANG R H, LI F Q, WANG X C, et al. Research on dynamic response of pbo fiber-reinforced composite under high-speed penetration[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2020, 1507(8): 082040. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1507/8/082040 [21] ZHU J Q, GU Z P, LIU Z P, et al. Silicone rubber matrix composites with shear thickening fluid microcapsules realizing intelligent adaptation to impact loadings[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2022, 247: 110312. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110312 [22] 焦亚男, 何业茂, 周庆, 等. 纤维增强树脂基复合材料防弹性能影响因素及破坏机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(9): 1960-1972.JIAO Yana, HE Yemao, ZHOU Qing, et al. Influence factors on ballistic performance and failure mechanism of fiber reinforced resin matrix composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(9): 1960-1972(in Chinese). [23] KARAHAN M, JABBAR A, KARAHAN N. Ballistic impact behavior of the aramid and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 2015, 34(1): 37-48. doi: 10.1177/0731684414562223 [24] HASSANPOUR ROUDBENEH F, LIAGHAT G, SABOURI H, et al. Experimental investigation of impact loading on honeycomb sandwich panels filled with foam[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2019, 24(2): 199-210. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2018.1426233 [25] MUDRIC T, GIACOMUZZO C, FRANCESCONI A, et al. Experimental Investigation of the Ballistic Response of Composite Panels Coupled with a Self-Healing Polymeric Layer[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2016, 29(6): 04016047. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000628 [26] TARFAOUI M, AKESBI S. A finite element model of mechanical properties of plain weave[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2001, 187-188: 439-448. [27] LIM C T, SHIM V P W, NG Y H. Finite-element modeling of the ballistic impact of fabric armor[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(1): 13-31. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00031-3 [28] KARAHAN M, JABBAR A, KARAHAN N. Ballistic impact behavior of the aramid and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 2015, 34(1): 37-48. doi: 10.1177/0731684414562223 [29] HASSANPOUR ROUDBENEH F, LIAGHAT G, SABOURI H, et al. Experimental investigation of impact loading on honeycomb sandwich panels filled with foam[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2019, 24(2): 199-210. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2018.1426233 [30] MUDRIC T, GIACOMUZZO C, FRANCESCONI A, et al. Experimental Investigation of the Ballistic Response of Composite Panels Coupled with a Self-Healing Polymeric Layer[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2016, 29(6): 04016047. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000628 [31] HA-MINH C, IMAD A, BOUSSU F, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of a 3D woven fabric subjected to a ballistic impact[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 88: 91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.08.011 [32] S. S MORYE, P. J HINE, R. A DUCKETT, et al. Modelling of the energy absorption by polymer composites upon ballistic impact[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2000, 60(14): 2631-2642. [33] LANGSTON T. An analytical model for the ballistic performance of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 179: 245-257. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.07.074 [34] NGUYEN L H, RYAN S, CIMPOERU S J, et al. The effect of target thickness on the ballistic performance of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene composite[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 75: 174-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.07.008 [35] ROYLANCE D, WILDE A, TOCCI G. Ballistic Impact of Textile Structures[J]. Textile Research Journal, 1973, 43(1): 34-41. doi: 10.1177/004051757304300105 [36] 左向春, 王瑞岭, 刘腾龙, 等. 防弹无纬布复合材料的现状[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2010, (5): 81-83.ZUO Xiangchun, WANG Ruiling, LIU Tenglong, et al. Current status of bulletproof weft less fabric composites[J]. Fiberglass/composite materials, 2010, (5): 81-83(in Chinese). [37] FIGUCIA F, WILLIAMS C, KIRKWOOD B, et al. Mechanisms of Improved Ballistic Fabric Performance[J]. mechanisms of improved ballistic fabric performance, 1982[2023-12-23]. [38] LEE B L, WALSH T F, WON S T, et al. Penetration Failure Mechanisms of Armor-Grade Fiber Composites under Impact[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2001, 35(18): 1605-1633. doi: 10.1106/YRBH-JGT9-U6PT-L555 [39] 胡晓兰, 王东, 石毓锬, 等. 用于人体防护装甲的纤维复合材料的研究[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2000, (2): 40-44.HU Xiaolan, Wang Dong, SHI Yutan, et al. Study on fiber composite materials for human body protective armor[J]. Fiber Composites, 2000, (2): 40-44(in Chinese). [40] 孟祥吉, 李彬彬. 基于拉丁超立方方法的复合材料结构吸能性能研究[J]. 中国科技纵横, 2022, (09): 000.MENG Xiangji, LI Binbin. Study on energy absorption properties of composite structures based on Latin Study on energy absorption properties of composite structures based on Latin Hypercube method[J]. China Science & Technology Panorama Magazine, 2022, (09): 000(in Chinese). [41] KARTHIKEYAN K, RUSSELL B P, FLECK N A, et al. The effect of shear strength on the ballistic response of laminated composite plates[J]. European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids, 2013, 42: 35-53. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2013.04.002 [42] YU B, KARTHIKEYAN K, DESHPANDE V S, et al. Perforation resistance of CFRP beams to quasi-static and ballistic loading: The role of matrix strength[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 108: 389-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.04.002 [43] B. G. LIU, H. N. G. WADLEY, V. S. DESHPANDE. Failure mechanism maps for ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibre composite beams impacted by blunt projectiles[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2019, 178-179: 180-198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2019.07.001 [44] LOGANATHAN T M, SULTAN M T H, GOBALAKRISHNAN M K, et al. Ballistic impact response of laminated hybrid composite materials[M]//Mechanical and Physical Testing of Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites. Elsevier, 2019: 171-191[2023-10-14]. [45] RAZALI N, SULTAN M T H, JAWAID M. Impact damage analysis of hybrid composite materials[M]//Durability and Life Prediction in Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites. Elsevier, 2019: 121-132[2023-10-14]. [46] KATZ S, GROSSMAN E, GOUZMAN I, et al. Response of composite materials to hypervelocity impact[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(12): 1606-1611. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.07.032 [47] LEIGH PHOENIX S, PORWAL P K. A new membrane model for the ballistic impact response and V50 performance of multi-ply fibrous systems[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2003, 40(24): 6723-6765. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(03)00329-9 [48] CHEESEMAN B A, BOGETTI T A. Ballistic impact into fabric and compliant composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures, 2003, 61(1-2): 161-173. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(03)00029-1 [49] WOODWARD R L, EGGLESTONE G T, BAXTER B J, et al. Resistance to penetration and compression of fibre-reinforced composite materials[J]. Composites Engineering, 1994, 4(3): 329-341. doi: 10.1016/0961-9526(94)90083-3 [50] ATTWOOD J P, KHADERI S N, KARTHIKEYAN K, et al. The out-of-plane compressive response of Dyneema ® composites[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2014, 70: 200-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2014.05.017 [51] KAZEMI M E, MEDEAU V, MENCATTELLI L, et al. Novel zone-based hybrid laminate structures for high-velocity impact (HVI) in carbon fibre-reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2023, 241: 110148. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.110148 [52] KUMAR S, DURGA SHANKAR GUPTA, SINGH I, et al. Behavior of Kevlar/Epoxy Composite Plates Under Ballistic Impact[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 2010, 29(13): 2048-2064. doi: 10.1177/0731684409343727 [53] GREENHALGH E S, BLOODWORTH V M, IANNUCCI L, et al. Fractographic observations on Dyneema® composites under ballistic impact[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2013, 44: 51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.08.012 [54] O’MASTA M R, CRAYTON D H, DESHPANDE V S, et al. Mechanisms of penetration in polyethylene reinforced cross-ply laminates[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 86: 249-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.08.012 [55] ATTWOOD J P, RUSSELL B P, WADLEY H N G, et al. Mechanisms of the penetration of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composite beams[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 93: 153-165. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.02.010 [56] 何业茂, 焦亚男, 周庆, 等. 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维/水性聚氨酯复合材料层压板抗软钢芯弹侵彻性能及其损伤机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(5): 1455-1467.HE Yemao, JIAO Yanan, ZHOU Qing, et al. Ballistic performance of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber/waterborne polyurethane composite laminate against mild-steel core projectile and its damage mechanism[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(5): 14551467(in Chinese). [57] YANG X chen, JIA N. Hygrothermal effect on high-velocity impact resistance of woven composites[J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(5): 823-833. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.03.028 [58] 梁子青, 周庆, 邱冠雄, 等. 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维防弹复合材料的研究[J]. 天津工业大学学报, 2003, (2): 6-9.LIANG Ziqing, ZHOU Qing, QIU Guanxiong, et al. Study on ultra high molecular weight polyethylene fiber bulletproof composite[J]. Journal of Tianjin Polytechnic University, 2003, (2): 6-9(in Chinese). [59] PAN Z, WU Z, XIONG J. High-speed infrared imaging and mesostructural analysis of localized temperature rise in damage and failure behavior of 3-D braided carbon/epoxy composite subjected to high strain-rate compression[J]. Polymer Testing, 2019, 80: 106151. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.106151 [60] CHEN Z, WANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Failure mechanism of thermo-mechanical coupling of 3D braided composites with different thickness under high strain-rate punch shear loading[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 279: 114826. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114826 [61] PAN Z, SUN B, SHIM V P W, et al. Transient heat generation and thermo-mechanical response of epoxy resin under adiabatic impact compressions[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 95: 874-889. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.12.072 [62] WANG S, WEN L, XIAO J, et al. Influence of strain rate and temperature on mechanical properties of carbon woven-ply PPS thermoplastic laminates under dynamic compression[J]. Polymer Testing, 2020, 89: 106725. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106725 [63] MEOLA C, BOCCARDI S, CARLOMAGNO G M, et al. Impact damaging of composites through online monitoring and non-destructive evaluation with infrared thermography[J]. NDT & E International, 2017, 85: 34-42. [64] LI Y, YANG Z wei, ZHU J tang, et al. Investigation on the damage evolution in the impacted composite material based on active infrared thermography[J]. NDT & E International, 2016, 83: 114-122. [65] TUO H, LU Z, MA X, et al. Damage and failure mechanism of thin composite laminates under low-velocity impact and compression-after-impact loading conditions[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 163: 642-654. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.006 [66] LIANG Z, LEE H K, SUARIS W. Micromechanics-based constitutive modeling for unidirectional laminated composites[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2006, 43(18-19): 5674-5689. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2005.08.020 [67] 廉志军, 王芳, 刘娜, 等. 国产对位芳纶油剂产品开发及应用性能评价[J]. 合成纤维, 2023, 52(9): 25-27+37.LIAN Zhijun, WANG Fang, LIU Na, et al. Development and application performance evaluation of domestic para-aramid oil agent[J] Synthetic Fibre, 2023, 52(9): 25-27+37. (in Chinese). [68] BAJYA M, MAJUMDAR A, BUTOLA B S, et al. Ballistic performance and failure modes of woven and unidirectional fabric based soft armour panels[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 255: 112941. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112941 [69] 官威, 李文晓, 戴瑛, 等. 纺织复合材料预制体变形研究综述[J]. 航空制造技术, 2021, 64(1/2): 22-37.GUAN Wei, LI Wenxiao, DAIYing, et al. Areview of study on deformation of textile composite preforms[J]. Aeronautical ManufacturingTechnology, 2021, 64(1/2): 22-37(in Chinese). [70] HEARLE J W S. The structural mechanics of fibers[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part C:Polymer Symposia, 2007, 20(1): 215-251. [71] PAN Z, GU B, SUN B. Thermo-mechanical behaviors of 3-D braided composite material subject to high strain rate compressions under different temperatures[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2016, 23(4): 385-401. doi: 10.1080/15376494.2014.981619 [72] 李献鑫, 孙颖, 陈利, 等. 立体织物在二氧化硅基复合材料方面的应用前景[J]. 纺织学报, 2013, 34(1): 143-150.LI Xianxin, SUN Ying, CHEN Li, et al. The application prospect of three-dimensional fabric in silica matrix composites[J]. Textile Journal, 2013, 34(1): 143-150(in Chinese). [73] 杨小利, 王钧. 三维织物及复合材料的发展与应用[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 1997, (4): 27-28+31.YANG Xiaoli, Wang Jun. Development and application of three-dimensional fabric and composite materials[J]. Fiberglass/composite materials, 1997, (4): 27-28+31(in Chinese). [74] KARAHAN M. Comparison of Ballistic Performance and Energy Absorption Capabilities of Woven and Unidirectional Aramid Fabrics[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2008, 78(8): 718-730. doi: 10.1177/0040517508090487 [75] KARAHAN M. Comparison of Ballistic Performance and Energy Absorption Capabilities of Woven and Unidirectional Aramid Fabrics[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2008, 78(8): 718-730. doi: 10.1177/0040517508090487 [76] 周庆, 何业茂, 刘婷. 对位芳香族聚酰胺纤维/环氧树脂复合材料防弹性能及其破坏机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(10): 2235-2246.ZHOU Qing, HE Yemao, LIU Ting. Ballistic properties and destruction mechanism of para-aromatic polyamide fiber/epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(10): 2235-2246(in Chinese). [77] ĆWIK T K, IANNUCCI L, CURTIS P, et al. Investigation of the ballistic performance of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene composite panels[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 149: 197-212. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.11.009 [78] LU J, ZHU P, JI Q, et al. Experimental Study of In-plane Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fibre Woven Composite at Different Strain Rates[J]. Polymers and Polymer Composites, 2017, 25(4): 289-298. doi: 10.1177/096739111702500406 [79] YOKOYAMA T. Impact Compressive Failure of a Unidirectional Carbon/Epoxy Laminated Composite in Three Principal Material Directions[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2012, 706-709: 799-804. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.706-709.799 [80] REIS V L, OPELT C V, CÂNDIDO G M, et al. Effect of fiber orientation on the compressive response of plain weave carbon fiber/epoxy composites submitted to high strain rates[J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 203: 952-959. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.06.016 [81] XIE W, ZHANG W, KUANG N, et al. Experimental investigation of normal and oblique impacts on CFRPs by high velocity steel sphere[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2016, 99: 483-493. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.06.020 [82] WEGST U G K, BAI H, SAIZ E, et al. Bioinspired structural materials[J]. Nature Materials, 2015, 14(1): 23-36. doi: 10.1038/nmat4089 [83] CANTWELL W J, MORTON J. The impact resistance of composite materials — a review[J]. Composites, 1991, 22(5): 347-362. doi: 10.1016/0010-4361(91)90549-V [84] 孔春凤, 田伟, 翁浦莹, 等. 高性能纤维层叠复合材料的抗冲击性能研究[J]. 浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 35(3): 367-371.KONG Chunfeng, TIAN Wei, WENG Puying, et al. Study on impact resistance of high performance fiber laminated composites[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (Natural Science Edition) 2016, 35(3): 367-371. (in Chinese). [85] NAIK N K, SHRIRAO P. Composite structures under ballistic impact[J]. Composite Structures, 2004, 66(1-4): 579-590. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.05.006 [86] XIE Y chen, ZHANG H, ZHU W, et al. Effects of textile structure and projectile geometry on ballistic performance of UHMWPE textiles[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 279: 114785. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114785 [87] 潘文革, 矫桂琼, 熊伟, 等. 二维编织层压板湿热环境下冲击后压缩性能的实验研究[J]. 航空材料学报, 2005, (4): 40-44.PAN Wenge, JIAO Guiqiong, XIONG Wei, et al. Experimental study on compressive properties of two dimensional braided laminates after impact in hot and humid environment[J]. Journal of aeronautical materials, 2005, (4): 40-44(in Chinese). [88] YANFEI YANG, XIAOGANG CHEN. Influence of fabric architecture on energy absorption efficiency of soft armour panel under ballistic impact[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 224: 111015. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111015 [89] WU Z, HUANG L, PAN Z, et al. Effect of off-axial angle on the low-velocity impact performance of braided laminates[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2022, 216: 106967. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106967 [90] ZHU X, CHEN W, LIU L, et al. Experimental investigation on high-velocity impact damage and compression after impact behavior of 2D and 3D textile composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 303: 116256. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116256 [91] HARLOW D G, PHOENIX S L. The Chain-of-Bundles Probability Model for the Strength of Fibrous Materials II: A Numerical Study of Convergence[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1978, 12(3): 314-334. doi: 10.1177/002199837801200308 [92] KO F. Tensile Strength and Modulus of a Three-Dimensional Braid Composite[M]//WHITNEY J. Composite Materials: Testing and Design (Seventh Conference). 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959: ASTM International, 1986: 392-392-12[2023-10-13]. [93] 张莉. 三维纺织复合材料新结构的探讨[D]. 天津工业大学, 2006.ZHANG Li. Discussion on new structure of three-dimensional textile composites[D]. Tianjin Polytechnic University, 2006. (in Chinese). [94] MACANDER A, CRANE R, CAMPONESCHI E. Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Multidimensionally (X-D) Braided Composite Materials[M]//WHITNEY J. Composite Materials: Testing and Design (Seventh Conference). 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959: ASTM International, 1986: 422-422-22[2023-10-27]. [95] SHIVAKUMAR K N, EMEHEL T C, SADLER R L. Compression strength and failure mechanisms of 3-D textile composites[C]//36th Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. New Orleans, LA, U. S. A. : American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1995[2023-10-13]. [96] KALIDINDI S R, ABUSAFIEH A. Longitudinal and Transverse Moduli and Strengths of Low Angle 3-D Braided Composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1996, 30(8): 885-905. doi: 10.1177/002199839603000802 [97] YAN S, ZHAO J, LU X, et al. An experimental investigation on the low-velocity impact behavior of 3D five-directional braided composites: LOW-VELOCITY IMPACT BEHAVIOR OF 3D FIVE-DIRECTIONAL COMPOSITES[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2014, 25(12): 1386-1390. doi: 10.1002/pat.3360 [98] MIRAVETE A, BIELSA J M, CHIMINELLI A, et al. 3D mesomechanical analysis of three-axial braided composite materials[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2006, 66(15): 2954-2964. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.02.015 [99] HU M, LIU S, ZHANG J, et al. Multiple transverse impact damage behaviors of 3-D-braided composite beams under room and high temperatures[J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2020, 29(5): 715-747. doi: 10.1177/1056789519867434 [100] 严实, 郭留雨, 赵金阳, 等. 三维五向编织复合材料低速冲击及冲击后压缩性能实验研究[J]. 材料工程, 2017, 45(12): 65-70.YAN Shi, GUO Liuyu, ZHAO Jinyang, et al. Experimental study on low-speed impact and post-impact compression properties of three-dimensional five-direction braided composites[J]. Materials Engineering, 2017, 45(12): 65-70(in Chinese). [101] YAN S, ZHAO J, LU X, et al. An experimental investigation on the low-velocity impact behavior of 3D five-directional braided composites: LOW-VELOCITY IMPACT BEHAVIOR OF 3D FIVE-DIRECTIONAL COMPOSITES[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2014, 25(12): 1386-1390. doi: 10.1002/pat.3360 [102] 严实, 赵金阳, 陆夏美, 等. 基于声发射技术的三维编织复合材料低速冲击损伤分析[J]. 材料工程, 2014, (7): 92-97.YAN Shi, ZHAO Jinyang, LU Xamei, et al. Low speed impact damage analysis of three-dimensional braided composites based on acoustic emission technology[J]. Materials Engineering, 2014, (7): 92-97(in Chinese). [103] LI Y, GAN X, GU B, et al. Dynamic responses and damage evolutions of four-step three-dimensional braided composites subjected to high strain rate punch shear loading[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2016, 50(12): 1635-1650. doi: 10.1177/0021998315595114 [104] TANG G, YAN Y, CHEN X, et al. Dynamic damage and fracture mechanism of three-dimensional braided carbon fiberrepoxy resin composites[J]. 2001. [105] LI D sen, LU Z xing, JIANG N, et al. High strain rate behavior and failure mechanism of three-dimensional five-directional carbon/phenolic braided composites under transverse compression[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2011, 42(2): 309-317. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2010.11.011 [106] LI D sen, LU Z xing, FANG D ning. Longitudinal compressive behavior and failure mechanism of three-dimensional five-directional carbon/phenolic braided composites at high strain rates[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2009, 526(1-2): 134-139. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.07.009 [107] CHEN Z, YUE C, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanical response and failure mechanism of three-dimensional braided composites under various strain-rate loadings by experimental and simulation research: a review[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2022, 92(1-2): 296-314. doi: 10.1177/00405175211030629 [108] 朱丹, 张青菊, 刘胜凯. 三维编织和角联锁复合材料的高速冲击响应[J]. 现代纺织技术, 2023, 31(2): 101-106.ZHU Dan, ZHANG Qingju, LIU Shengkai. High speed impact response of three-dimensional braided and angular interlocking composites[J]. Advanced Textile Technology, 2023, 31(2): 101-106(in Chinese). [109] 熊健, 杜昀桐, 杨雯, 等. 轻质复合材料夹芯结构设计及力学性能最新进展[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(6): 749-760.XIONG Jian, DU Yuntong, YANG Wen, et al. Research Progress on Design and Mechanical Properties of Lightweight Composite Sandwich Structures[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(6): 749-760(in Chinese). [110] CHEN J , LI E , LIU W , et al. Sustainable composites with ultrahigh energy absorption from beverage cans and polyurethane foam[J]. Composites science and technology, 2023. [111] XUE Z, HUTCHINSON J W. A comparative study of impulse-resistant metal sandwich plates[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(10): 1283-1305. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2003.08.007 [112] SHIN K B, LEE J Y, CHO S H. An experimental study of low-velocity impact responses of sandwich panels for Korean low floor bus[J]. Composite Structures, 2008, 84(3): 228-240. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.08.002 [113] WU Y, LIU Q, FU J, et al. Dynamic crash responses of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP panels[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2017, 121: 122-133. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.03.030 [114] ZHANG D, JIANG D, FEI Q, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on indentation and energy absorption of a honeycomb sandwich panel under low-velocity impact[J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2016, 117-118: 21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.finel.2016.04.003 [115] ZHANG C, TAN K T. Low-velocity impact response and compression after impact behavior of tubular composite sandwich structures[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2020, 193: 108026. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108026 [116] WANG B, ZHANG G, WANG S, et al. High Velocity Impact Response of Composite Lattice Core Sandwich Structures[J]. Applied Composite Materials, 2014, 21(2): 377-389. doi: 10.1007/s10443-013-9345-4 [117] FINNEGAN K, KOOISTRA G, WADLEY H N G, et al. The compressive response of carbon fiber composite pyramidal truss sandwich cores[J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2007, 98(12): 1264-1272. doi: 10.3139/146.101594 [118] LIU P F, LI X K. Explicit finite element analysis of failure behaviors of thermoplastic composites under transverse tension and shear[J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 192: 131-142. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.037 [119] FERREIRA L M, GRACIANI E, PARÍS F. Three dimensional finite element study of the behaviour and failure mechanism of non-crimp fabric composites under in-plane compression[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 149: 106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.04.022 [120] JIN L, SUN B, GU B. Finite element simulation of three-dimensional angle-interlock woven fabric undergoing ballistic impact[J]. Journal of the Textile Institute, 2011, 102(11): 982-993. doi: 10.1080/00405000.2010.529279 [121] LI Y, ZHANG W, GIDEON R K, et al. Finite element analyses on punch shear behaviors of three-dimensional braided composites at microstructure level[J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2017, 26(7): 968-988. doi: 10.1177/1056789516639744 [122] WANG B, FANG G, LIU S, et al. Progressive damage analysis of 3D braided composites using FFT-based method[J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 192: 255-263. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.040 [123] BAHMANI A, LI G, WILLETT T L, et al. Three-dimensional microscopic assessment of randomly distributed representative volume elements for high fiber volume fraction unidirectional composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 192: 153-164. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.075 [124] MA L, SHEN C, ZHANG A, et al. Virtual tests of elastodynamic response of natural fiber-reinforced orthotropic plates[J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 192: 264-273. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.093 [125] LI Y, YAN S, YAN Y, et al. Modelling of the compressive behavior of 3D braided tubular composites by a novel unit cell[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 287: 115303. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115303 [126] 钱逸星, 杨振宇, 卢子兴. 纺织复合材料力学性能数值模拟方法研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2022, 65(16): 135-151.QIAN Yixing, YANG Zhenyu, LU Zixing. Research progress on numerical simulation of mechanical properties of textile composites[J]. AeronauticalManufacturingTechnology, 2022, 65(16): 135-151(in Chinese). [127] GEREKE T, CHERIF C. A review of numerical models for 3D woven composite reinforcements[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 209: 60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.10.085 [128] SHERBURN M, LONG A, JONES A, et al. Prediction of textile geometry using an energy minimization approach[J]. Journal of Industrial Textiles, 2012, 41(4): 345-369. doi: 10.1177/1528083711420747 [129] CAI Y, ZHAO Z, TIE Y, et al. Size-dependency of the transverse-tensile failure behavior for triaxially braided composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2021, 206: 108672. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108672 [130] WANG L, WU J, CHEN C, et al. Progressive failure analysis of 2D woven composites at the meso-micro scale[J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 178: 395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.07.023 [131] ZHAO Q, WANG W, LIU Y, et al. Multiscale modeling framework to predict the low-velocity impact and compression after impact behaviors of plain woven CFRP composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 299: 116090. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116090 [132] 张超. 二维三轴编织复合材料渐进损伤行为的细观有限元模拟研究[C]//第三届中国国际复合材料科技大会摘要集-分会场41-45. 中国复合材料学会、杭州市人民政府, 2017: 62023-10-24]. ZHANG Chao. Microscopic finite element simulation of progressive damage behavior of two-dimensional triaxial braided composites[C]. 2017: 6. (in Chinese). [133] 谭焕成, 许善迎, 黄雄, 等. 三维四向编织复合材料宏观有限元模型冲击损伤仿真及试验验证[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(5): 1139-1148.TAN Huancheng, XU Shanying, HUANG Xiong, et al. Macro-scale finite element model for impact damage simulation and experimental verification of three-dimensional four-directional braided composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2018, 35(5): 1139-1148(in Chinese). [134] 练军. 动力有限元在三维编织复合材料弹道冲击性能研究中的应用[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2006, (2): 14-17.LIAN Jun. Application of dynamic finite element in the study of ballistic impact properties of three-dimensional braided composites[J]. Fiberglass/composite materials, 2006, (2): 14-17(in Chinese). [135] WEI Q, YANG D, GU B, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation on 3D angle interlock woven fabric under ballistic impact[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 266: 113778. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113778 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 122
- HTML全文浏览量: 44
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: