Influence of multiple process parameters on the friction coefficient of prepregs and machine learning prediction method
-
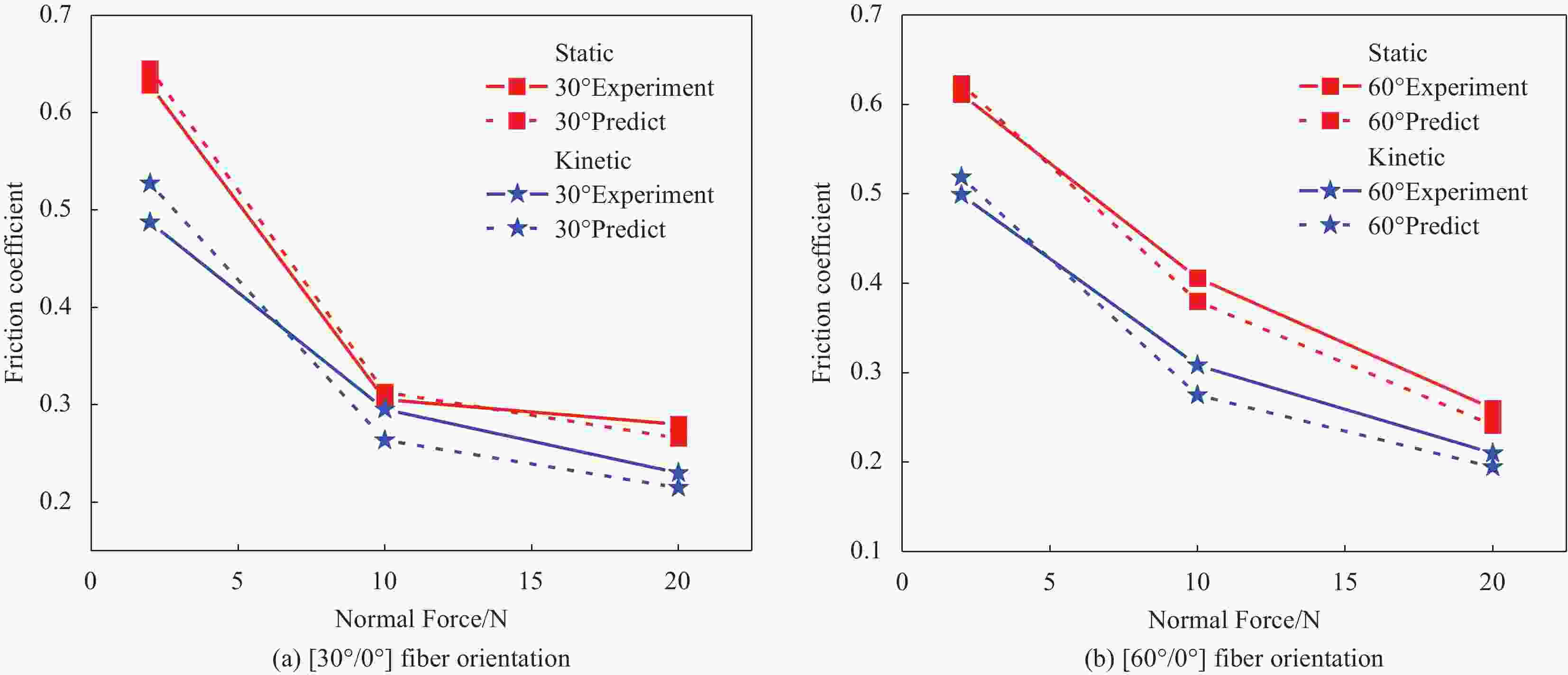
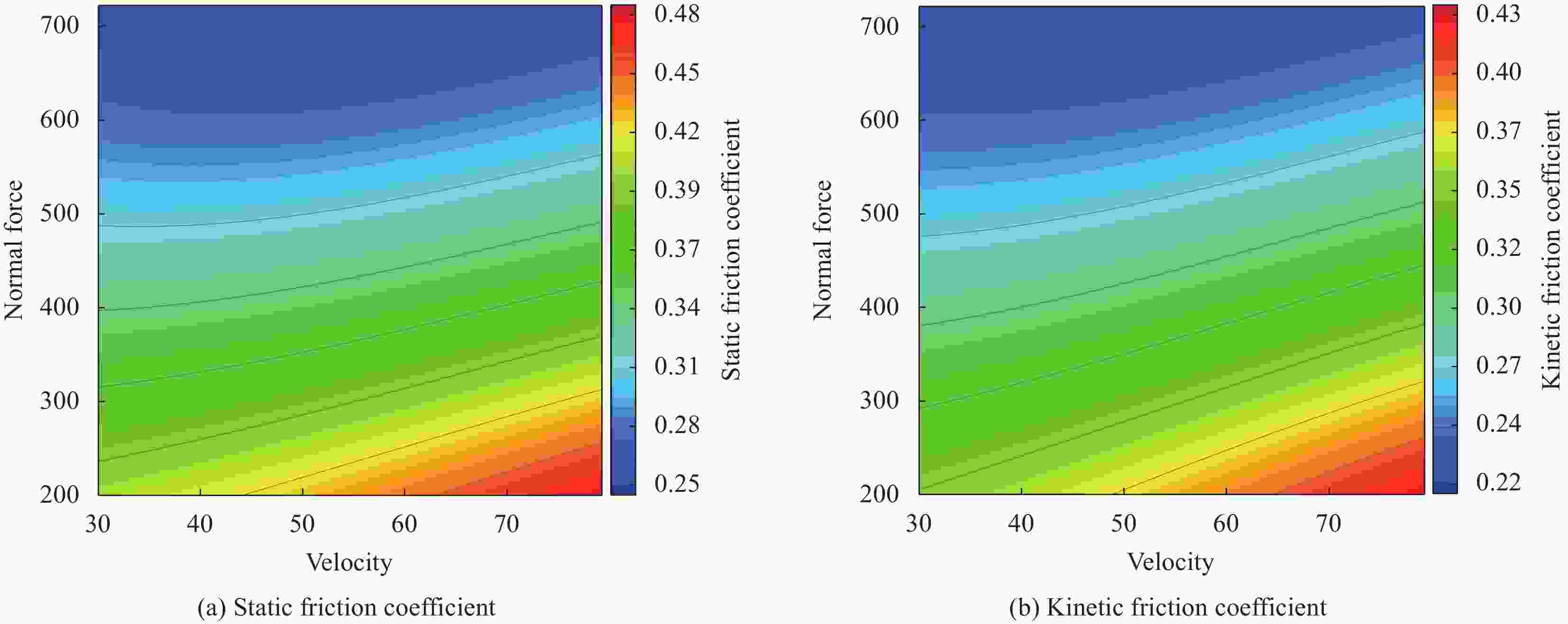
摘要: 在复合材料成型过程中,预浸料/预浸料和预浸料/模具之间的摩擦滑移行为会导致褶皱、孔隙等缺陷,严重影响构件力学性能。然而复杂构件成型过程中预浸料层间摩擦行为影响因素众多,现有理论模型涵盖的工艺参数有限,导致成型工艺仿真精度低,无法满足高质量成型要求。本文设计了面向多工艺参数的碳纤维预浸料摩擦试验方法,研究了速率、法向力、粘度、表面粗糙度、接触材料、纤维方向等工艺参数对摩擦系数的影响规律,以典型纤维方向$ {{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/4}}{{\text{5}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/9}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}} $为例,揭示了不同纤维方向的界面摩擦机理。为实现多工艺参数下摩擦系数的快速、准确预示,建立了基于支持向量回归(SVR)的预浸料摩擦系数预示模型。开展相对纤维方向为$ {\text{[3}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{]}} $和$ {\text{[6}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{]}} $的预浸料/预浸料界面摩擦系数的试验和预测,两者偏差小于7%。Abstract: During the forming process of composites, the friction-sliding behavior between prepreg ply-ply and ply-tool may lead to defects such as wrinkles and pores, which seriously affect the mechanical properties of the components. However, there are many factors affecting the inter-ply friction of the prepreg plies in the forming process of complex components. The existing theoretical models contain insufficient process parameters, resulting in the accuracy of forming process simulation not meeting high-quality forming requirements. In this paper, a friction test method for carbon fiber prepregs was designed for multiple process parameters. The influence of sliding velocity, normal force, viscosity, surface roughness, contact material, and fiber orientation on the friction coefficient were studied. Taking the typical fiber orientations of $ {{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/4}}{{\text{5}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/9}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}} $ as examples, the inter-ply friction mechanism in different fiber orientations was revealed. In order to predict the friction coefficient of prepreg corresponding to multiple process parameters rapidly and accurately, a prediction model for the friction coefficient of prepreg was established using the support vector regression (SVR) method. Taking the prepreg ply-ply friction behavior with relative fiber orientation of $ {\text{[3}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{]}} $ and $ {\text{[6}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{/}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{]}} $ as examples, the experiments and predictions were conducted, and the error was less than 7%.
-
Key words:
- carbon fiber prepreg /
- multiple processing parameters /
- friction /
- machine learning
-
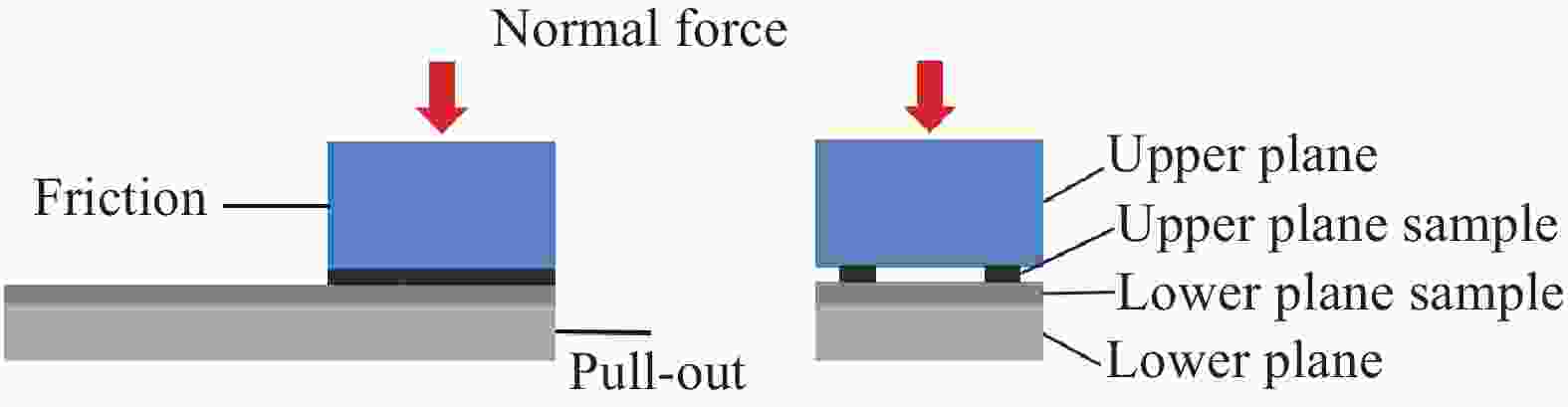
表 1 摩擦试验参数
Table 1. Friction test parameters
Parameter Baseline value Additional values
investigatedSurface roughness Ra12.5 Ra12.5、Ra25 Contact material - Ra12.5 Metal、Sand、Laminate、Gypsum、Prepreg、Rubber Fiber orientation/(°) 0 0、45、90 Sliding velocity/
(mm·min−1)100 30、100、200 Normal force/N 10 2、10、20 Viscosity/
($ {\text{MPa}} \cdot {\text{s}} $)591.8 591.8、895.7 表 2 测试集中不同静摩擦系数预示模型的决定系数${R^2}$和预测误差的方差${S^2}$
Table 2. Coefficient of determination ${R^2}$ and forecast error variance ${S^2}$ for different static friction coefficient prediction models in the test set
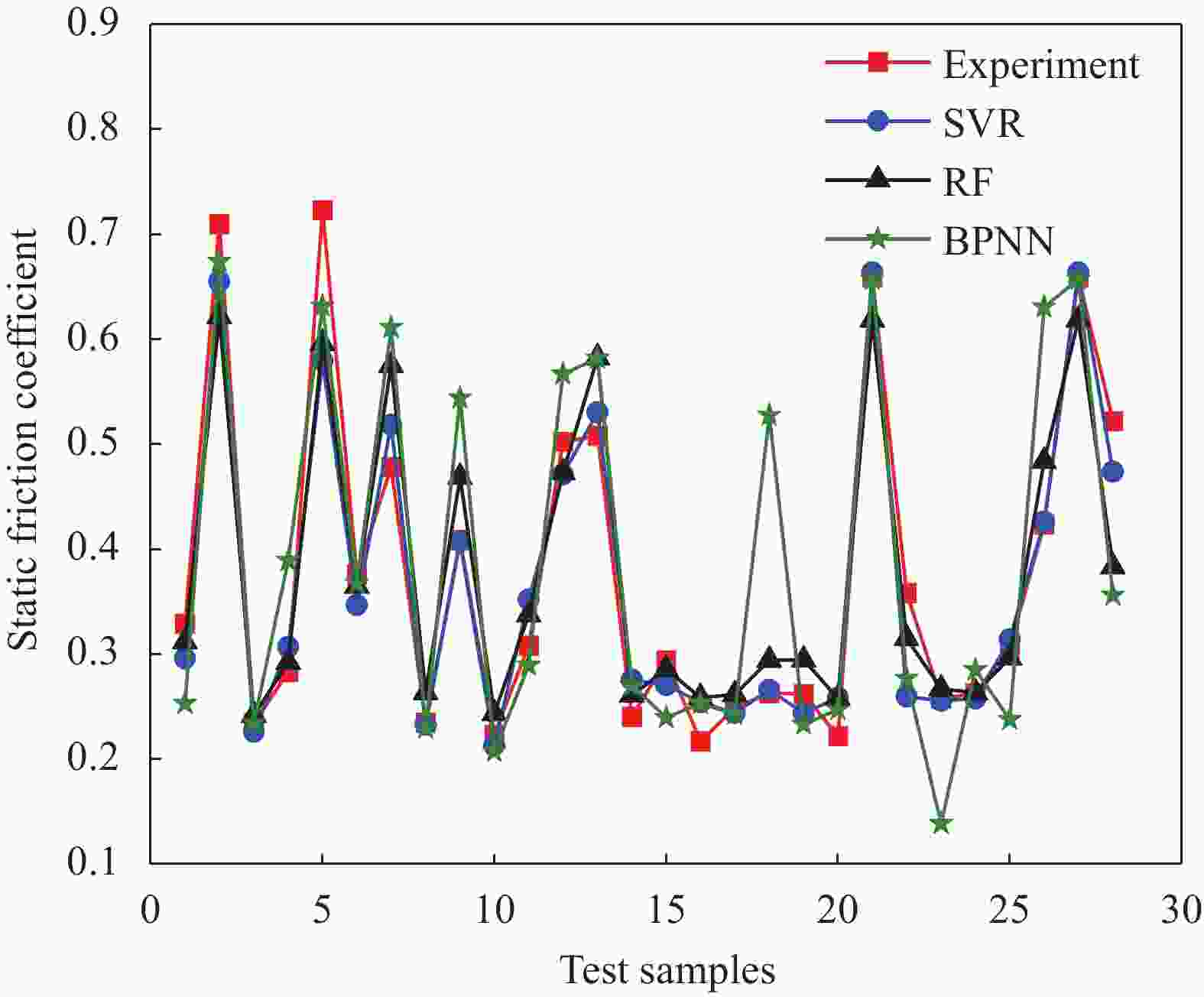
Model ${R^2}$value ${S^2}$value BPNN 0.642 0.0091 RF 0.884 0.0029 SVR 0.930 0.0016 表 3 测试集中不同动摩擦系数预示模型的决定系数${R^2}$和预测误差的方差${S^2}$
Table 3. Coefficient of determination ${R^2}$ and forecast error variance ${S^2}$ for different kinetic friction coefficient prediction models in the test set
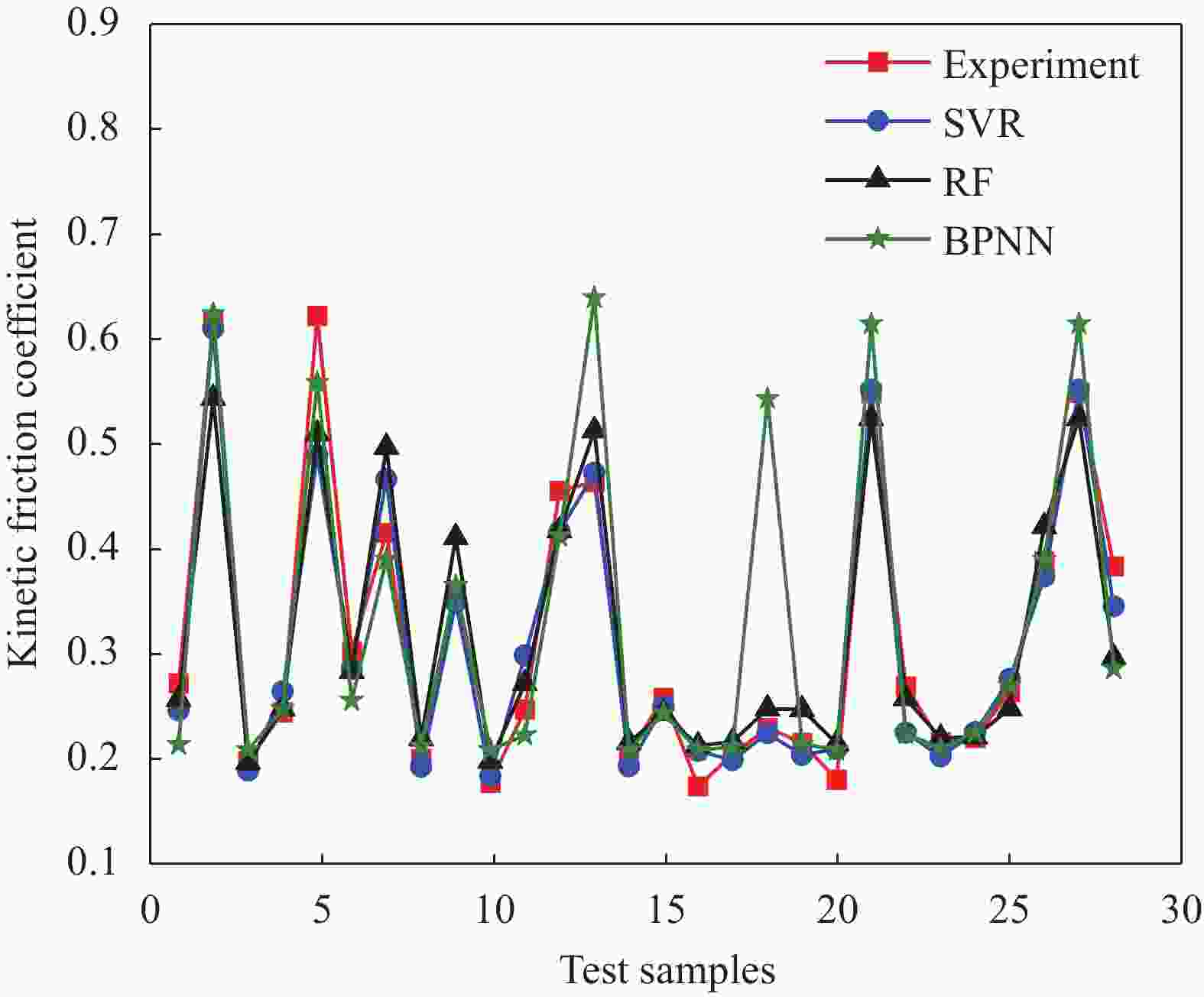
Model ${R^2}$ value ${S^2}$ value BPNN 0.682 0.0062 RF 0.908 0.0018 SVR 0.938 0.0011 -
[1] TEN THIJE R H W, AKKERMAN R, UBBINK M, et al. A lubrication approach to friction in thermoplastic composites forming processes[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2011, 42(8): 950-960. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.03.023 [2] 李哲夫. 航空复合材料热模压预成型缺陷形成机理与仿真预测研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2023.LI Zhefu. Study on the formation mechanism and simulation prediction of defects in the process of hot-press forming for aerospace composites[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2023(in Chinese). [3] 矫维成, 王荣国, 刘文博, 等. 缠绕纤维与芯模表面间滑线系数的测量表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, (3): 191-196.JIAO Weicheng, WANG Rongguo, LIU Wenbo, et al. Measurement of slippage coefficient between fiber and mandrel surface for non-geodesic filament winding[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2012, (3): 191-196(in Chinese). [4] MARTIN C J, SEFERIS J C, WILHELM M A. Frictional resistance of thermoset prepregs and its influence on honeycomb composite processing[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 1996, 27(10): 943-951. doi: 10.1016/1359-835X(96)00037-1 [5] ÅKERMO M, LARBERG Y R, SJÖLANDER J, et al. Influence of interply friction on the forming of stacked UD prepreg[C]. The International Conference on Composite Materials. 2013: 919-928. [6] BENDEMRA H, COMPSTON P, CROTHERS P J. Optimisation study of tapered scarf and stepped-lap joints in composite repair patches[J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 130: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.04.016 [7] LIU S, SINKE J, DRANSFELD C. An inter-ply friction model for thermoset based fibre metal laminate in a hot-pressing process[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2021, 227: 109400. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109400 [8] DUTTA A, HAGNELL M K, ÅKERMO M. Interply friction between unidirectional carbon/epoxy prepreg plies: Influence of fibre orientation[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 166: 107375. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.107375 [9] LARBERG Y R, ÅKERMO M. On the interply friction of different generations of carbon/epoxy prepreg systems[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2011, 42(9): 1067-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.04.010 [10] HALLANDER P, ÅKERMO M, MATTEI C, et al. An experimental study of mechanisms behind wrinkle development during forming of composite laminates[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2013, 50: 54-64. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.03.013 [11] SOSE A T, JOSHI S Y, KUNCHE L K, et al. A review of recent advances and applications of machine learning in tribology[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25(6): 4408-4443. doi: 10.1039/D2CP03692D [12] PATURI U M R, PALAKURTHY S T, REDDY N S. The Role of Machine Learning in Tribology: A Systematic Review[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2023, 30: 1345-1397. doi: 10.1007/s11831-022-09841-5 [13] BAŞ H, KARABACAK Y E. Triboinformatic modeling of the friction force and friction coefficient in a cam-follower contact using machine learning algorithms[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 181: 108336. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108336 [14] WU B, QIN D, HU J, et al. Experimental data mining research on factors influencing friction coefficient of wet clutch[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2021, 143(12): 121802. doi: 10.1115/1.4050140 [15] WANG Q, WANG X, ZHANG X, et al. Tribological properties study and prediction of PTFE composites based on experiments and machine learning[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 188: 108815. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108815 [16] EGALA R, JAGADEESH G V, SETTI S G. Experimental investigation and prediction of tribological behavior of unidirectional short castor oil fiber reinforced epoxy composites[J]. Friction, 2021, 9: 250-272. doi: 10.1007/s40544-019-0332-0 [17] NIRMAL U. Prediction of friction coefficient of treated betelnut fibre reinforced polyester (T-BFRP) composite using artificial neural networks[J]. Tribology International, 2010, 43(8): 1417-1429. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2010.01.013 [18] American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM D 1894 Standard test method for static and kinetic coefficients of friction of plastic film and sheeting[S]. America: American Society for Testing and Materials Standard International, 1998. [19] ZHANG W, ZHOU H, HUANG B, et al. Characterization of tool-ply friction behavior for treated jute/PLA biocomposite prepregs in thermoforming[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2024, 177: 107875. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2023.107875 [20] RASHIDI A, MONTAZERIAN H, YESILCIMEN K, et al. Experimental characterization of the inter-ply shear behavior of dry and prepreg woven fabrics: Significance of mixed lubrication mode during thermoset composites processing[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2020, 129: 105725. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105725 [21] 薛建凯. 一种新型的群智能优化技术的研究与应用: 麻雀搜索算法[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2021.XUE Jiankai. Research and application of a novel swarm intelligence optimization technique: sparrow search algorithm[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2021(in Chinese). -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 50
- HTML全文浏览量: 29
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: