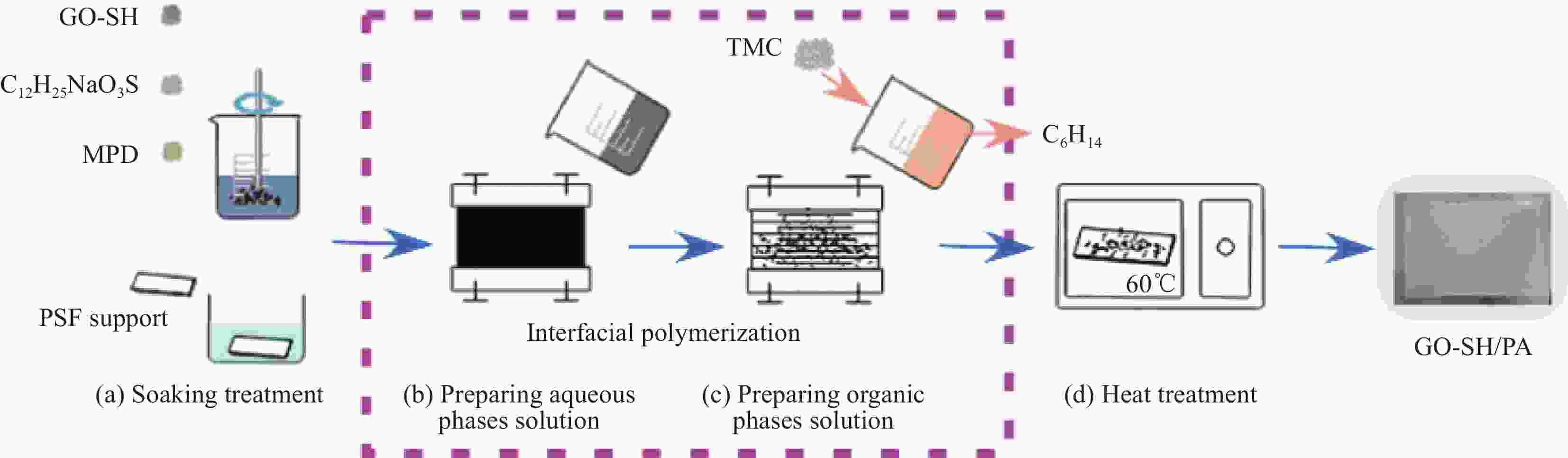
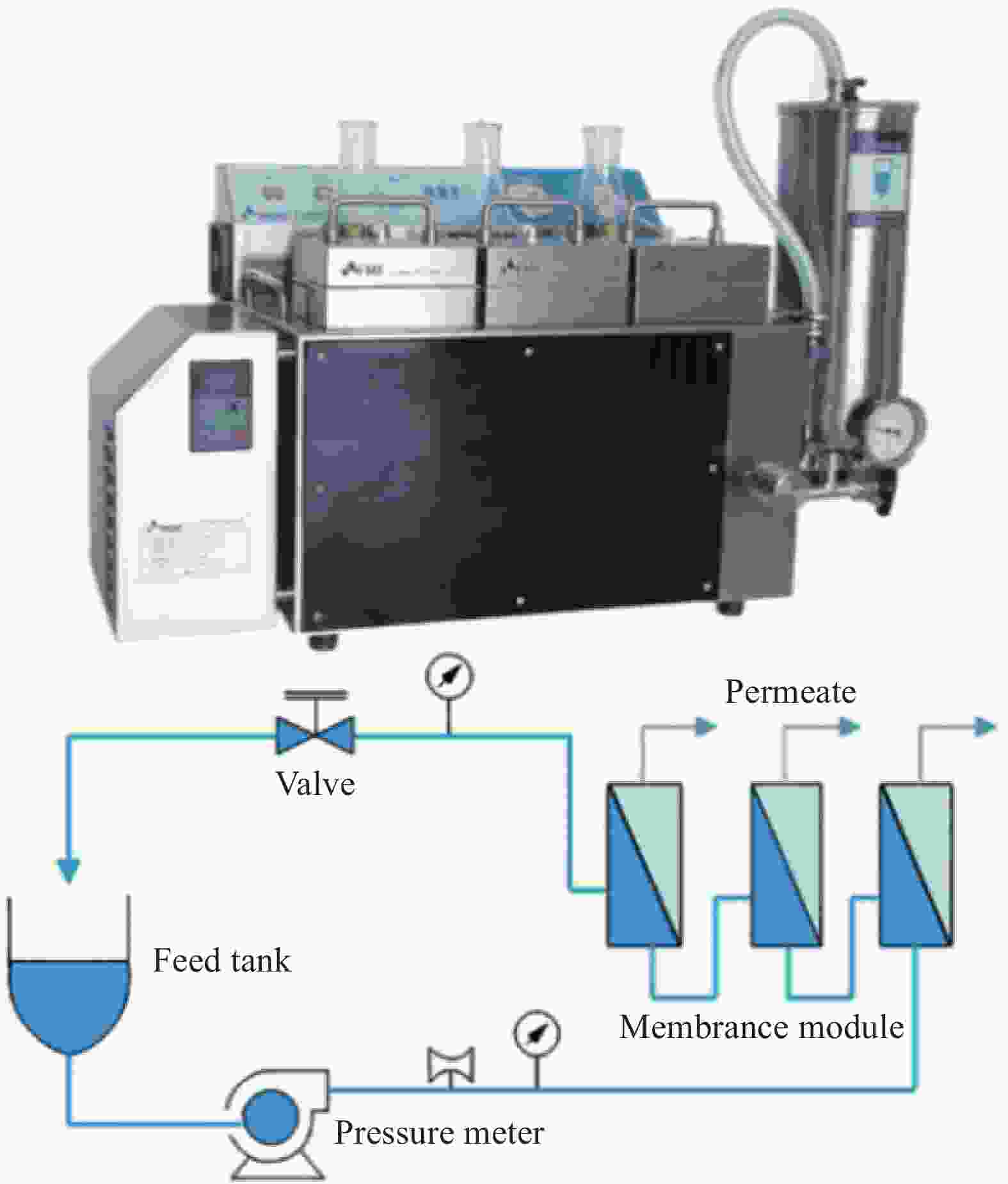
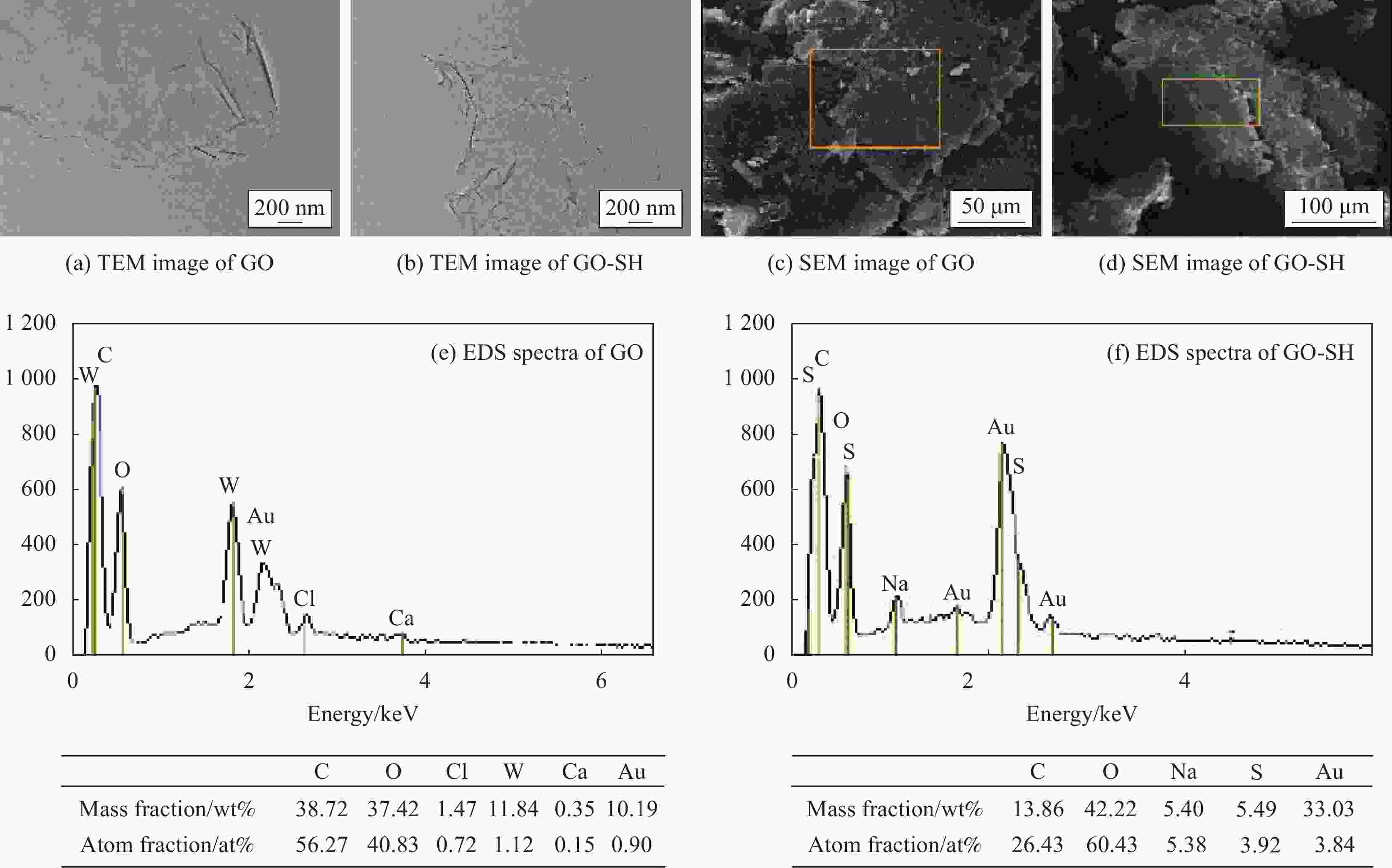
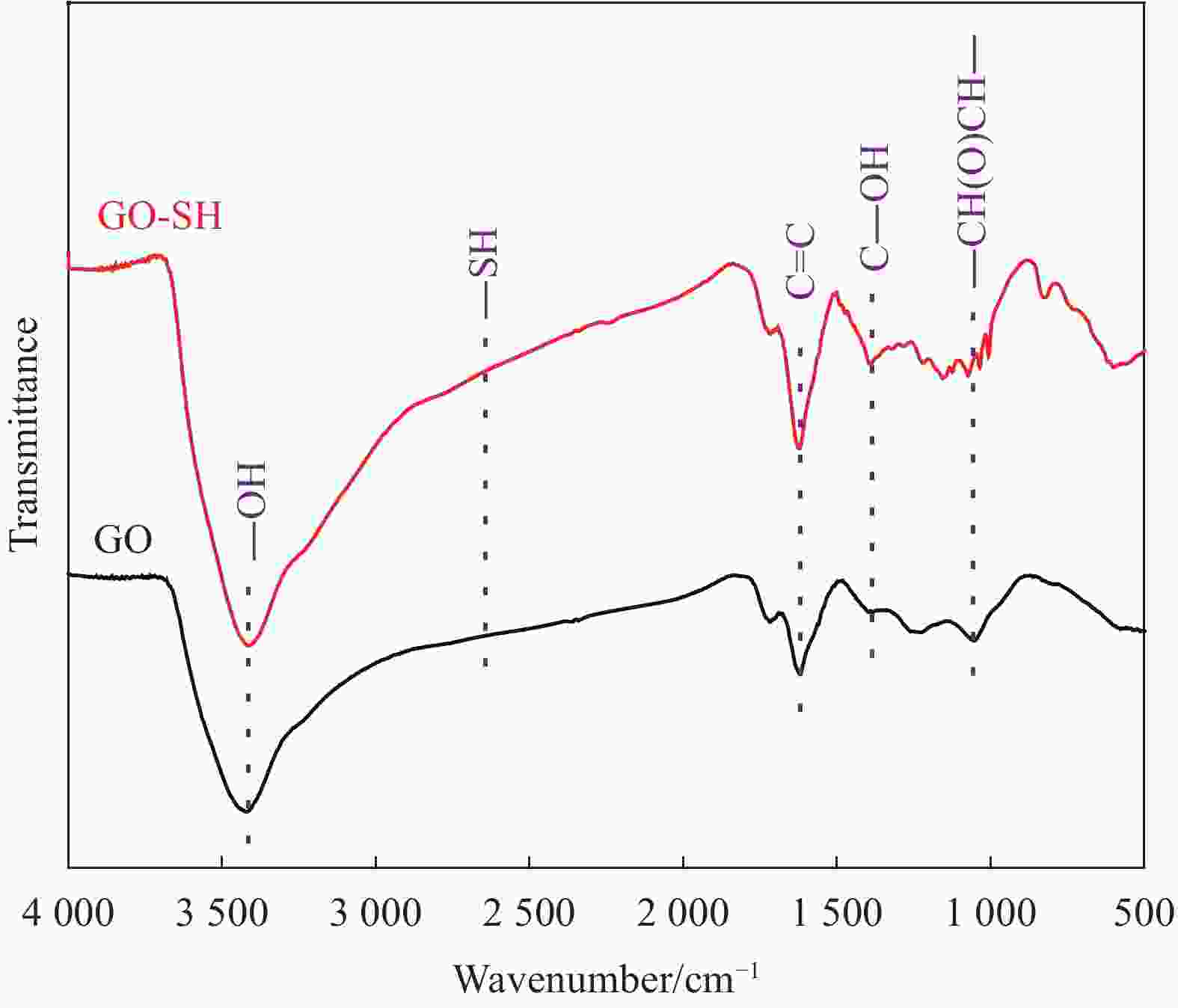
| [1] |
PENATE B, GARCIA-RODRIGUEZ L. Current trends and future prospects in the design of seawater reverse osmosis desalination technology[J]. Desalination,2012,284:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.09.010
|
| [2] |
SAFARPOUR M, KHATAEE A, VATANPOUR V. Thin film nanocomposite reverse osmosis membrane modified by reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 with improved desalination performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2015,489:43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2015.04.010
|
| [3] |
GREENLEE L F, LAWLER D F, FREEMAN B D, et al. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today's challenges[J]. Water Research,2009,43(9):2317-2348. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.010
|
| [4] |
MCGILVERY C M, ABELLAN P, KLOSOWSKI M M, et al. Nanoscale chemical heterogeneity in aromatic polyamide membranes for reverse osmosis applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(17):19890-19902.
|
| [5] |
ALBO J, HAGIWARA H, YANAGISHITA H, et al. Structural characterization of thin-film polyamide reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2014,53(4):1442-1451.
|
| [6] |
席丹, 曹从军, 齐萨仁, 等. 超薄皮层反渗透复合膜制备技术的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020:1-10.XI D, CAO C J, QI S R, et al. Progress in preparation of ultra-thin composite reverse osmosis membrane[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2020:1-10(in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
ANTONY A, CHILCOTT T, COSTER H, et al. In situ structural and functional characterization of reverse osmosis membranes using electrical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2013,425:89-97.
|
| [8] |
JIMENEZ-SOLOMON M F, SONG Q L, JELFS K E, et al. Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization[J]. Nature Materials,2016,15(7):760-767. doi: 10.1038/nmat4638
|
| [9] |
王娇娜, 尹泽芳, 李从举. 静电纺丝复合反渗透膜的改性制备与脱盐性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2):396-402. doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150519WANG Q N, YIN Z F, LI C J. Preparation and desalination performance of composite reverse osmosis membrane based on electrospinning technology[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2016,37(2):396-402(in Chinese). doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150519
|
| [10] |
LI Z H, WANG L, LI Y, et al. Carbon-based functional nanomaterials: Preparation, properties and applications[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,179:10-40. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.04.028
|
| [11] |
KWAK S Y, KIM S, HKIM S S. Hybrid organic/inorganic reverse osmosis (RO) membrane for bactericidal anti-fouling. 1. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2001,35(11):2388-2394.
|
| [12] |
TAKEUCHI K, TAKIZAWA Y, KITAZAWA H, et al. Salt rejection behavior of carbon nanotube-polyamide nanocomposite reverse osmosis membranes in several salt solutions[J]. Desalination,2018,443:165-171. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2018.04.021
|
| [13] |
LEE T H, LEE M Y, LEE H D, et al. Highly porous carbon nanotube/polysulfone nanocomposite supports for high-flux polyamide reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2017,539:441-450. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2017.06.027
|
| [14] |
ABDIKHEIBARI S, LEI W W, DUMEE L F, et al. Novel thin film nanocomposite membranes decorated with few-layered boron nitride nanosheets for simultaneously enhanced water flux and organic fouling resistance[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,488:565-577. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.217
|
| [15] |
ISHII K, IKEDA A, TAKEUCHI T, et al. Silica-based RO membranes for separation of acidic solution[J]. Membranes,2019,9(8):94. doi: 10.3390/membranes9080094
|
| [16] |
DONG H, ZHAO L, ZHANG L, et al. High-flux reverse osmosis membranes incorporated with NaY zeolite nanoparticles for brackish water desalination[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2015,476:373-383. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2014.11.054
|
| [17] |
LI Z Y, WANG L, LI Y, et al. Frontiers in carbon dots: Design, properties and applications[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers,2019,3(12):2571-2601. doi: 10.1039/C9QM00415G
|
| [18] |
ZHANG Y, CHUNG T S. Graphene oxide membranes for nanofiltration[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering,2017,16:9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2017.03.002
|
| [19] |
XIA S, YAO L J, ZHAO Y, et al. Preparation of graphene oxide modified polyamide thin film composite membranes with improved hydrophilicity for natural organic matter removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,280:720-727. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.063
|
| [20] |
YIN J, ZHU G C, DENG B L. Graphene oxide (GO) enhanced polyamide (PA) thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane for water purification[J]. Desalination,2016,379:93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2015.11.001
|
| [21] |
LAI G S, LAU W J, GOH P S, et al. Tailor-made thin film nanocomposite membrane incorporated with graphene oxide using novel interfacial polymerization technique for enhanced water separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,344:524-534. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.116
|
| [22] |
YIN J, KIM E S, YANG J, et al. Fabrication of a novel thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane containing MCM-41 silica nanoparticles (NPs) for water purification[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2012,423:238-246.
|
| [23] |
DONG L Q, FENG Y Y, WANG L, et al. Azobenzene-based solar thermal fuels: Design, properties, and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews,2018,47(19):7339-7368. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00470F
|
| [24] |
LI X Y, ZHOU H H, WU W Q, et al. Studies of heavy metal ion adsorption on chitosan/sulfydryl-functionalized graphene oxide composites[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2015,448:389-397. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.02.039
|
| [25] |
MURUGAN A V, MURALIGANT H T, MANTHIRAM A. Rapid, facile microwave-solvothermal synthesis of graphene nanosheets and their polyaniline nanocomposites for energy strorage[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2009,21(21):5004-5006. doi: 10.1021/cm902413c
|
| [26] |
ZHAO D L, GAO X, CHEN S H, et al. Interaction between U(VI) with sulfhydryl groups functionalized graphene oxides investigated by batch and spectroscopic techniques[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2018,524:129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.04.012
|
| [27] |
FENG X M, HU J Q, CHEN X H, et al. Synthesis and electron transfer property of sulfhydryl-containing multi-walled carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticle heterojunctions[J]. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics,2009,42(4):042001. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/42/4/042001
|
| [28] |
GAO W, MAJUMDER M, ALEMANY L B, et al. Engineered graphite oxide materials for application in water purification[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2011,3(6):1821-1826.
|
| [29] |
谢欣, 张潇, 李蕊含, 等. 反渗透膜微结构的调控及海水脱硼性能的提升[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9):2033-2040. doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190104XIE X, ZHANG X, LI R H, et al. Microstructure regulation of the reverse osmosis membrane to improve the boron removal performance[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2019,40(9):2033-2040(in Chinese). doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190104
|
| [30] |
KIM E S, DENG B L. Fabrication of polyamide thin-film nano-composite (PA-TFN) membrane with hydrophilized ordered mesoporous carbon (H-OMC) for water purifications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2011,375(1-2):46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2011.01.041
|
| [31] |
宋杰, 徐子丹, 周勇, 等. 表面改性纳米二氧化钛-芳香聚酰胺复合反渗透膜的制备与表征[J]. 水处理技术, 2013, 39(6):24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.06.007SONG J, XU Z D, ZHOU Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of surface-modified nano-TiO2/aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2013,39(6):24-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.06.007
|
| [32] |
LIU M H, YU S C, TAO J, et al. Preparation, structure characteristics and separation properties of thin-film composite polyamide-urethane seawater reverse osmosis membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2008,325(2):947-956. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2008.09.033
|
| [33] |
YU S C, LIU M H, LUE Z H, et al. Aromatic-cycloaliphatic polyamide thin-film composite membrane with improved chlorine resistance prepared from m-phenylenediamine-4-methyl and cyclohexane-1, 3, 5-tricarbonyl chloride[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2009,344(1-2):155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2009.07.046
|
| [34] |
YAN W T, SHI M Q, WANG Z, et al. Confined growth of skin layer for high performance reverse osmosis membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2019,585:208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.05.033
|
| [35] |
XU J, YAN H, ZHANG Y, et al. The morphology of fully-aromatic polyamide separation layer and its relationship with separation performance of TFC membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2017,541:174-188. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2017.06.057
|
| [36] |
YIN C, ZHANG Y J, CHEN Z, et al. Correlation between the pore resistance and water flux of the cellulose acetate membrane[J]. Environmental Science-Water Research & Technology,2017,3(6):1037-1041.
|
| [37] |
WANG X, FANG D F, HSIAO B S, et al. Nanofiltration membranes based on thin-film nanofibrous composites[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2014,469:188-197. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2014.06.049
|
| [38] |
FORNASIERO F, PARK H G, HOLT J K, et al. Ion exclusion by sub-2-nm carbon nanotube pores[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2008,105(45):17250-17255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710437105
|
| [39] |
HOLT J K, PARK H G, WANG Y M, et al. Fast mass transport through sub-2-nanometer carbon nanotubes[J]. Science,2006,312(5776):1034-1037. doi: 10.1126/science.1126298
|
| [40] |
LI L X, LEE R. Purification of produced water by ceramic membranes: material screening, process design and economics[J]. Separation Science and Technology,2009,44(15):3455-3484. doi: 10.1080/01496390903253395
|
| [41] |
WANG X Y, LI Q Q, ZHANG J F, et al. Novel thin-film reverse osmosis membrane with MXene Ti3C2Tx embedded in polyamide to enhance the water flux, anti-fouling and chlorine resistance for water desalination[J]. Jounal of Membrane Science,2020,603:118036. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118036
|
| [42] |
DAVID C T, GROSSMAN J C. Water desalination across nanoporous graphene[J]. Nano Letters,2012,12(7):3602-3608. doi: 10.1021/nl3012853
|
| [43] |
GEISE G M, PAUL D R, FREEMAN B D. Fundamental water and salt transport properties of polymeric materials[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2014,39(1):1-42. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.07.001
|
| [44] |
ROH I J, GREENBERG A R, KHARE V P. Synthesis and characterization of interfacially polymerized polyamide thin films[J]. Desalination,2006,191(1-3):279-290. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2006.03.004
|






 下载:
下载: