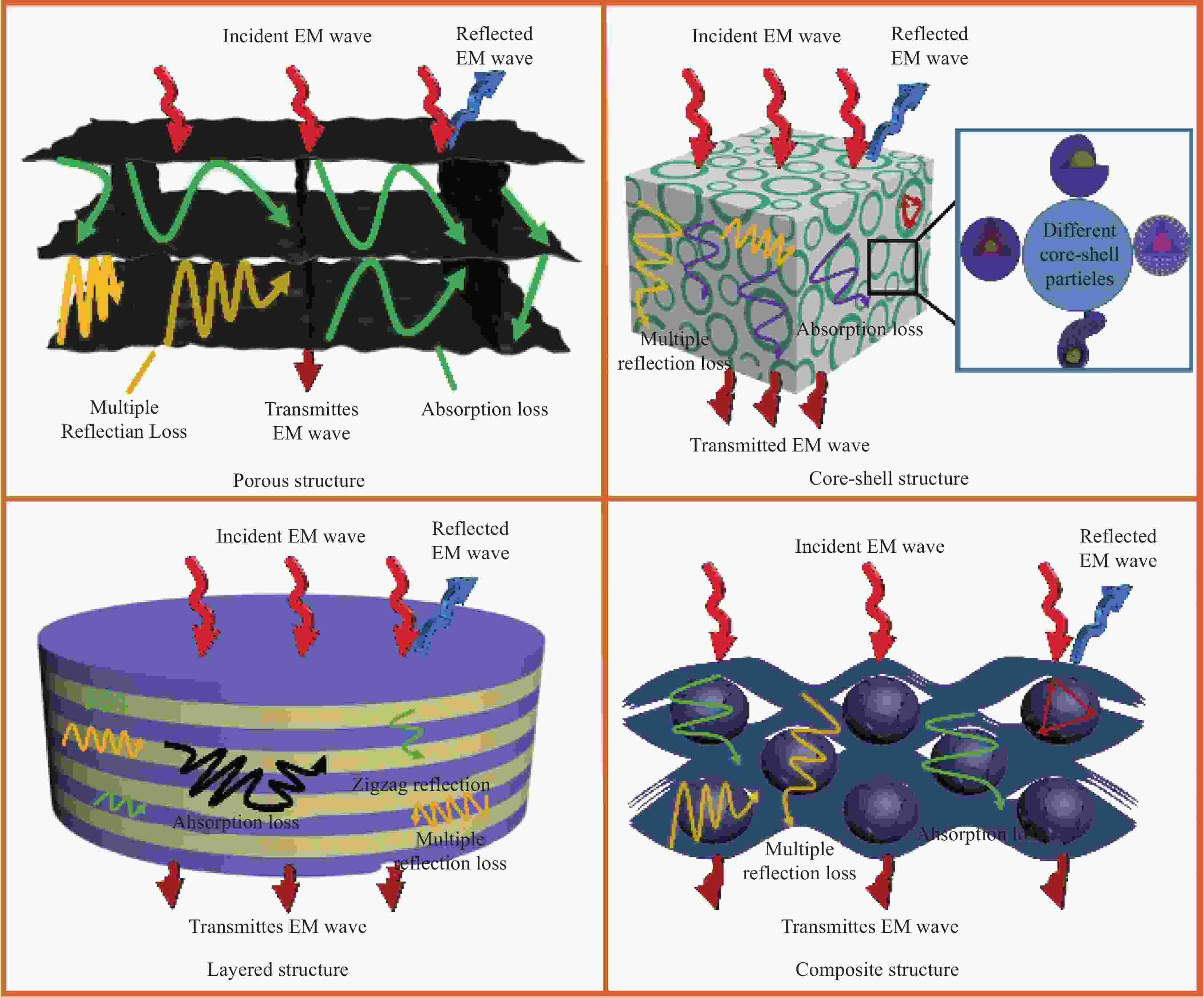
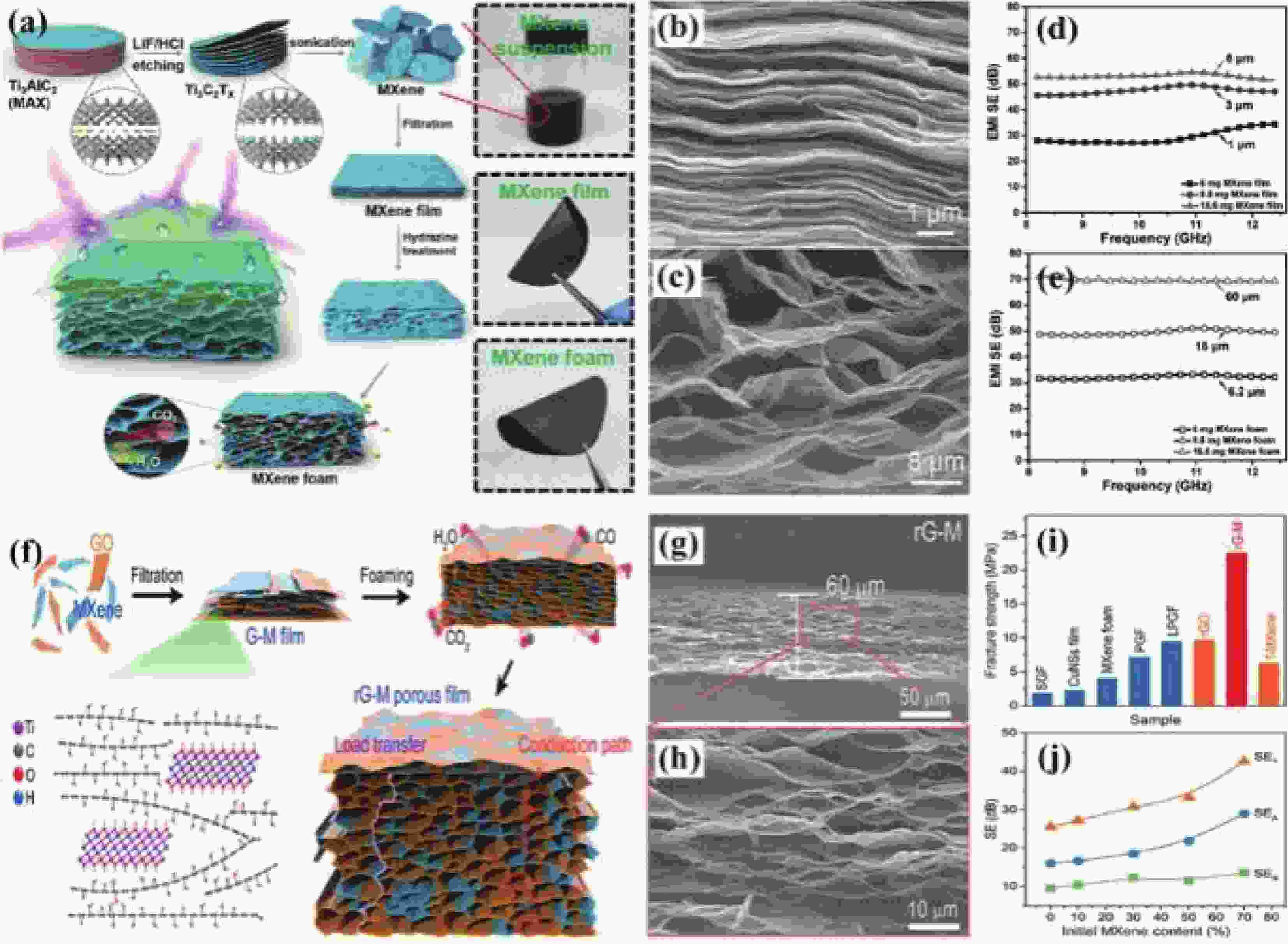
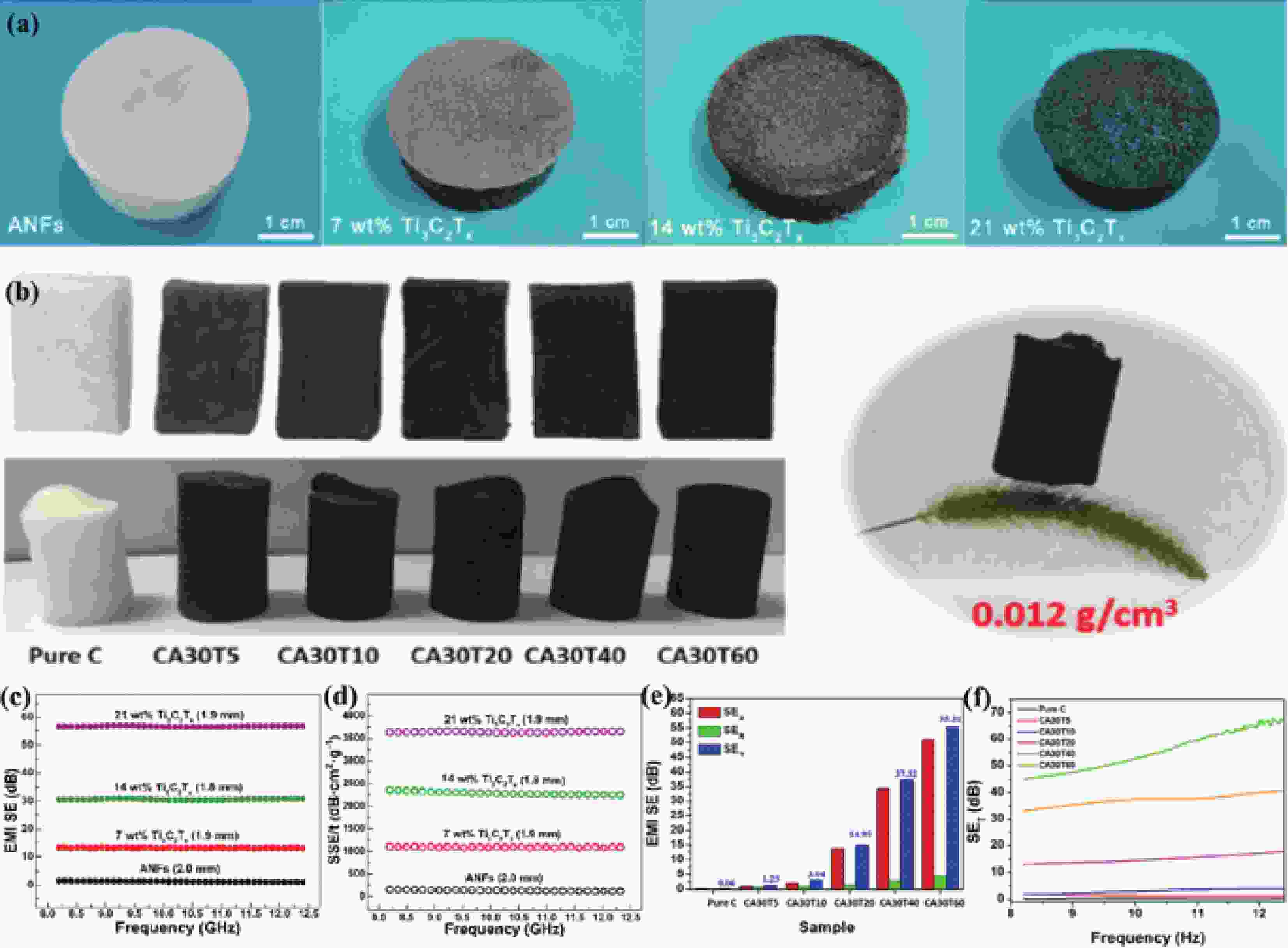
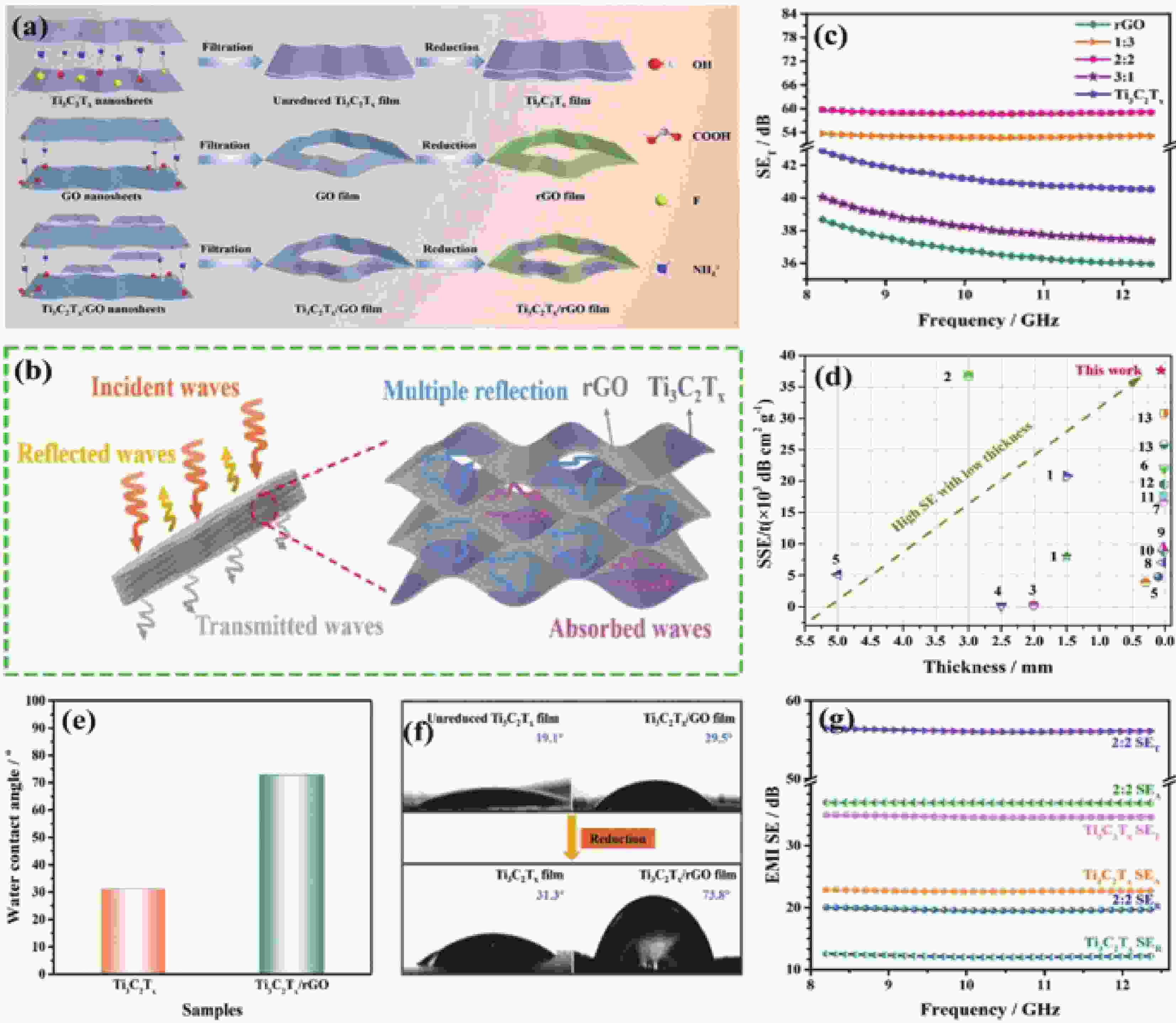
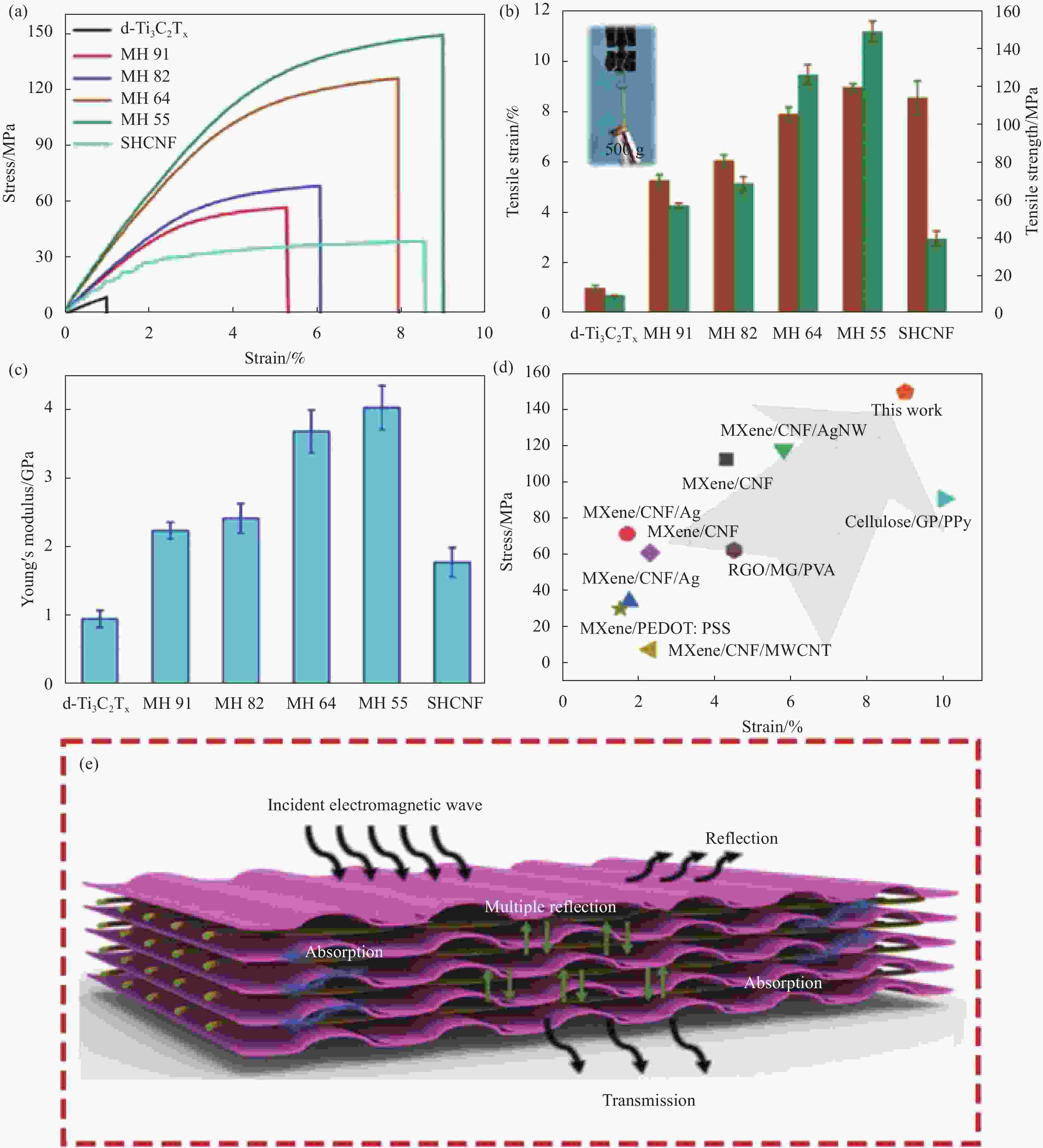
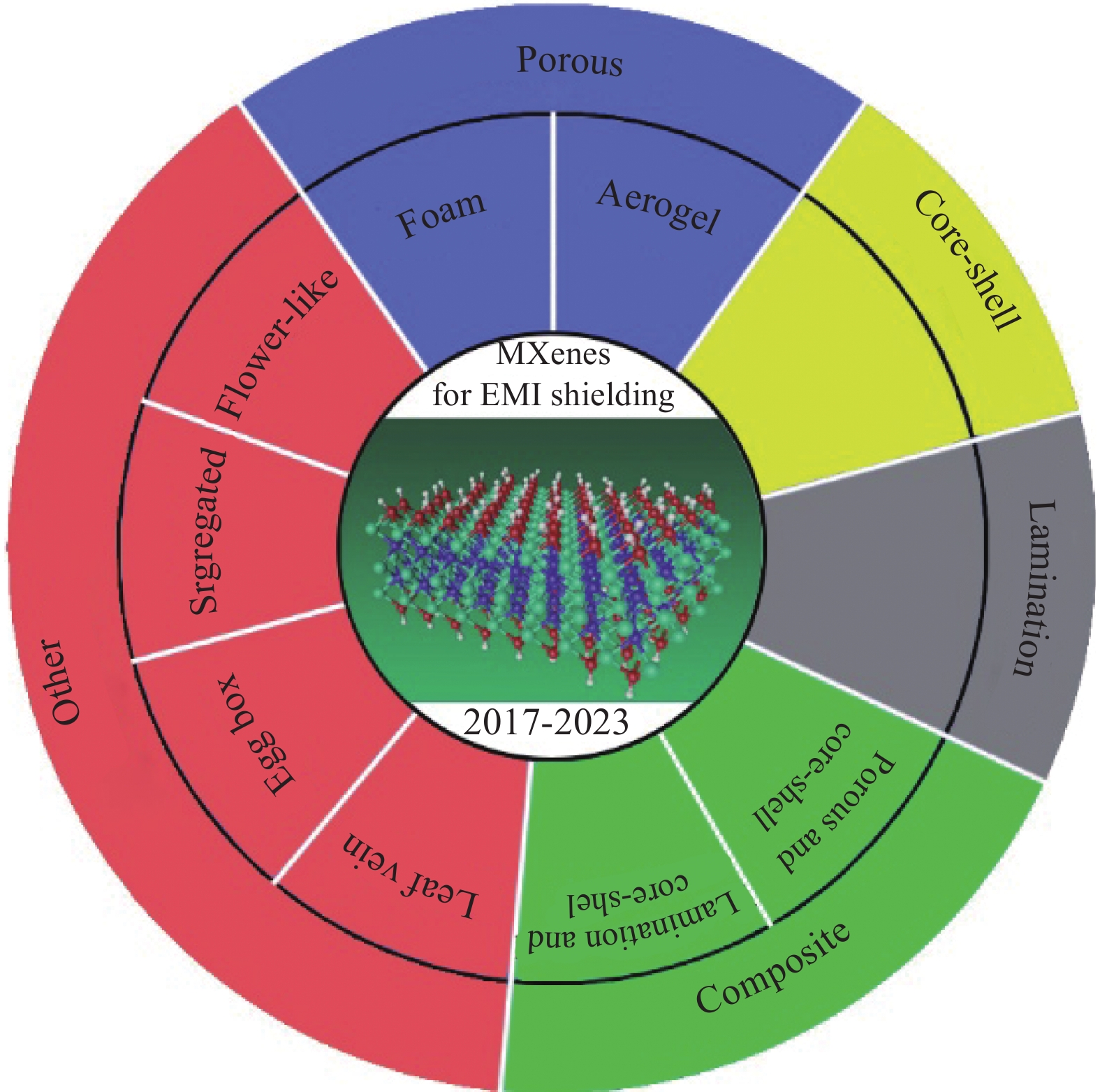
| [1] |
AZARKAMAN A, ABDOLLAHI E, SAFAEI M. The level of awareness of the citizens of Kohgiluyeh and Boyer Ahmad, Ardabil, Bushehr and Hamadan provinces about the laws and harms of electromagnetic waves and radio radiation[J]. Political Sociology of Iran, 2021, 3(4): 3475-3492.
|
| [2] |
杨新兴, 李世莲, 尉鹏, 等. 环境中的电磁波污染及其危害[J]. 前沿科学, 2014, 8(01): 13-26.Yang Xinxing, Li Shilian, Wei Peng, et al. Electromagnetic wave pollution in the environment and its harm[J]. Journal of Cutting-edge Science, 2014, 8(01): 13-26 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
THANKAPPAN M, RIFà-POUS H, GARRIGUES C. Multi-channel man-in-the-middle attacks against protected wi-fi networks: A state of the art review[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022: 118401.
|
| [4] |
ONGEL K, GUMRAL N, OZGUNER F. The potential effects of electromagnetic field: a review[J]. Cell Membranes and Free Radical Research, 2009, 1(3): 85-89.
|
| [5] |
MOON J-H. Health effects of electromagnetic fields on children[J]. Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics, 2020, 63(11): 422-428. doi: 10.3345/cep.2019.01494
|
| [6] |
MERCOLA J. EMF* D: 5G, Wi-Fi & cell phones: Hidden harms and how to protect yourself [M]. Hay House, Inc, 2020.
|
| [7] |
WONGKASEM N. Electromagnetic pollution alert: Microwave radiation and absorption in human organs and tissues[J]. Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine, 2021, 40(2): 236-253. doi: 10.1080/15368378.2021.1874976
|
| [8] |
SHEN J-E. Analysis of the harm of electromagnetic wave pollution and its protection strategies; proceedings of the 2020 Cross Strait Radio Science & Wireless Technology Conference (CSRSWTC), F, 2020 [C]. IEEE.
|
| [9] |
CHEN M, ZHANG L, DUAN S, et al. Highly conductive and flexible polymer composites with improved mechanical and electromagnetic interference shielding performances[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(7): 3796-3803. doi: 10.1039/C3NR06092F
|
| [10] |
CHAUDHARY A, KUMARI S, KUMAR R, et al. Lightweight and easily foldable MCMB-MWCNTs composite paper with exceptional electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(16): 10600-10608.
|
| [11] |
JAMADADE S, JADHAV S V, PURI V. Electromagnetic reflection, shielding and conductivity of polypyrrole thin film electropolymerized in P-Tulensulfonic acid[J]. Journal of Non-crystalline Solids, 2011, 357(3): 1177-1181. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.11.022
|
| [12] |
LIANG C, SONG P, MA A, et al. Highly oriented three-dimensional structures of Fe3O4 decorated CNTs/reduced graphene oxide foam/epoxy nanocomposites against electromagnetic pollution[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2019, 181: 107683. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107683
|
| [13] |
THOMASSIN J-M, PAGNOULLE C, BEDNARZ L, et al. Foams of polycaprolactone/MWNT nanocomposites for efficient EMI reduction[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2008, 18(7): 792-796. doi: 10.1039/b709864b
|
| [14] |
HAN M, YIN X, DUAN W, et al. Hierarchical graphene/SiC nanowire networks in polymer-derived ceramics with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing capability[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(11): 2695-2703. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.04.003
|
| [15] |
PAN H, YIN X, XUE J, et al. In-situ synthesis of hierarchically porous and polycrystalline carbon nanowires with excellent microwave absorption performance[J]. Carbon, 2016, 107: 36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.05.045
|
| [16] |
WANG G, HAO L, ZHANG X, et al. Flexible and transparent silver nanowires/biopolymer film for high-efficient electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 607: 89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.08.190
|
| [17] |
JIA L, DING X, SUN J, et al. A controllable gradient structure of hydrophobic composite fabric constructed by silver nanowires and polyvinylidene fluoride microspheres for electromagnetic interference shielding with low reflection[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 156: 106884. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106884
|
| [18] |
FU M, JIAO Q, ZHAO Y. Preparation of NiFe2 O4 nanorod–graphene composites via an ionic liquid assisted one-step hydrothermal approach and their microwave absorbing properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(18): 5577-5586. doi: 10.1039/c3ta10402h
|
| [19] |
WU G, CHENG Y, REN Y, et al. Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@ C nanorod-carbon sphere composite and its application as microwave absorbing material[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 652: 346-350. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.08.236
|
| [20] |
GUPTA S, CHANG C, LAI C-H, et al. Hybrid composite mats composed of amorphous carbon, zinc oxide nanorods and nickel zinc ferrite for tunable electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 164: 447-457. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.060
|
| [21] |
AL-ASBAHI B A, QAID S M H, EL-SHAMY A G. Flexible conductive nanocomposite PEDOT: PSS/Te nanorod films for superior electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding: A new exploration[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2021, 100: 233-247. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2021.05.019
|
| [22] |
AL NAIM A F, IBRAHIM S S, EL-SHAMY A G. A new class of electromagnetic shields based on carbon dots adorning Te nanorods embedded into PEDOT: PSS for protection from electromagnetic (EM) pollutions[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2021, 161: 106509. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106509
|
| [23] |
ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, JIANG X, ZHANG H, et al. Perspectives on solution processing of two-dimensional MXenes[J]. Materials Today, 2021, 48: 214-240. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2021.02.010
|
| [24] |
SHI X, ZHANG R, RUAN K, et al. Improvement of thermal conductivities and simulation model for glass fabrics reinforced epoxy laminated composites via introducing hetero-structured BNN-30@ BNNS fillers[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 82: 239-249.
|
| [25] |
ZHU Y, BAI B, DING E, et al. Enhanced elec tromagnetic interference shielding performance of geopolymer nanocomposites by incorporating carbon nanotubes with controllable silica shell[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(8): 11103-11110. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.330
|
| [26] |
HE Q-M, TAO J-R, YANG Y, et al. Electric-magnetic-dielectric synergism and Salisbury screen effect in laminated polymer composites with multiwall carbon nanotube, nickel, and antimony trioxide for enhancing electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 156: 106901. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106901
|
| [27] |
GAO J, DING Q, YAN P, et al. Highly improved microwave absorbing and mechanical properties in cold sintered ZnO by incorporating graphene oxide[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(3): 993-1000. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.10.053
|
| [28] |
WANG J, WANG Q, WANG W, et al. Hollow Ni/C microsphere@ graphene foam with dual-spatial and porous structure on the microwave absorbing performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 873: 159811. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159811
|
| [29] |
XU F, ZHANG S, WANG G, et al. Lightweight Low-Frequency Sound-Absorbing Composites of Graphene Network Reinforced by Honeycomb Structure[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2021, 8(16): 2100183. doi: 10.1002/admi.202100183
|
| [30] |
HONG J-Y, SOHN E-H, PARK S, et al. Highly-efficient and recyclable oil absorbing performance of functionalized graphene aerogel[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 269: 229-235. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.066
|
| [31] |
LIU J, ZHANG L, WU H. Electromagnetic wave-absorbing performance of carbons, carbides, oxides, ferrites and sulfides: review and perspective[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2021, 54(20): 203001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/abe26d
|
| [32] |
PRASAD J, SINGH A K, GAHLOT A P S, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding properties of hierarchical core-shell palladium-doped MoS2/CNT nanohybrid materials[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(19): 27586-27597. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.06.183
|
| [33] |
PRASAD J, SINGH A K, TOMAR M, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of micro-flower like morphology aluminum-doped MoS2/rGO nanohybrids for high efficient electromagnetic wave shielding materials[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(11): 15648-15660. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.135
|
| [34] |
HORMOZI N, ESMAEILI A. Synthesis and correction of albumin magnetic nanoparticles with organic compounds for absorbing and releasing doxorubicin hydrochloride[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces, 2019, 182: 110368. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110368
|
| [35] |
MAJID F, ALI M D, ATA S, et al. Fe3O4/graphene oxide/Fe4 [Fe (CN) 6] 3 nanocomposite for high performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(8): 11587-11595. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.291
|
| [36] |
LIU H, WU S, YOU C, et al. Fe3O4 nanoparticles decorated flexible carbon foam for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(13): 19452-19459. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.246
|
| [37] |
VERMA S, DWIVEDI U, CHATURVEDI K, et al. Progress of 2D MXenes based composites for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding applications: a review[J]. Synthetic Metals, 2022, 287: 117095. doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2022.117095
|
| [38] |
RAAGULAN K, KIM B M, CHAI K Y. Recent advancement of electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of two dimensional (2D) MXene and graphene aerogel composites[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(4): 702. doi: 10.3390/nano10040702
|
| [39] |
FEI Y, LIANG M, ZHOU T, et al. Unique carbon nanofiber@ Co/C aerogel derived bacterial cellulose embedded zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Carbon, 2020, 167: 575-584. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.06.013
|
| [40] |
MEI H, ZHAO X, GUI X, et al. SiC encapsulated Fe@ CNT ultra-high absorptive shielding material for high temperature resistant EMI shielding[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14): 17144-17151. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.268
|
| [41] |
IQBAL A, SAMBYAL P, KOO C M. 2D MXenes for electromagnetic shielding: a review[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(47): 2000883. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000883
|
| [42] |
WXX W C Y, MAO S C. Progress in research on lightweight graphene-based EMI shielding materials[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2016, 44: 109-118.
|
| [43] |
WEI H, ZHANG Z, HUSSAIN G, et al. Techniques to enhance magnetic permeability in microwave absorbing materials[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2020, 19: 100596. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100596
|
| [44] |
HU S, LI S, XU W, et al. Rapid preparation, thermal stability and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of two-dimensional Ti3C2 MXene[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(16): 19902-19909. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.246
|
| [45] |
ZHOU A, LIU Y, LI S, et al. From structural ceramics to 2D materials with multi-applications: A review on the development from MAX phases to MXenes[J]. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021: 1-49.
|
| [46] |
RONCHI R M, ARANTES J T, SANTOS S F. Synthesis, structure, properties and applications of MXenes: Current status and perspectives[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(15): 18167-18188. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.114
|
| [47] |
LIU J, ZHANG H B, SUN R, et al. Hydrophobic, flexible, and lightweight MXene foams for high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(38): 1702367. doi: 10.1002/adma.201702367
|
| [48] |
CHEN Q, FAN B, ZHANG Q, et al. Design of 3D lightweight Ti3C2Tx MXene porous film with graded holes for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding performance[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(10): 14578-14586. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.01.351
|
| [49] |
WANG Y, QI Q, YIN G, et al. Flexible, ultralight, and mechanically robust waterborne polyurethane/Ti3C2Tx MXene/nickel ferrite hybrid aerogels for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(18): 21831-21843.
|
| [50] |
HOJJATI-NAJAFABADI A, MANSOORIANFAR M, LIANG T, et al. Magnetic-MXene-based nanocomposites for water and wastewater treatment: A review[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 47: 102696. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102696
|
| [51] |
HE Z, HUANG D, YUE G, et al. Ca2+ induced 3D porous MXene gel for continuous removal of phosphate and uranium[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 570: 150804. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150804
|
| [52] |
ZHANG Y, XU M-K, WANG Z, et al. Strong and conductive reduced graphene oxide-MXene porous films for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(6): 4916-4924. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4311-9
|
| [53] |
LU Z, JIA F, ZHUO L, et al. Micro-porous MXene/Aramid nanofibers hybrid aerogel with reversible compression and efficient EMI shielding performance[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2021, 217: 108853. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108853
|
| [54] |
ZHANG Y, YU J, LU J, et al. Facile construction of 2D MXene (Ti3C2Tx) based aerogels with effective fire-resistance and electromagnetic interference shielding performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 870: 159442. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159442
|
| [55] |
ZHANG Y, RUAN K, SHI X, et al. Ti3C2Tx/rGO porous composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding performances[J]. Carbon, 2021, 175: 271-280. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.12.084
|
| [56] |
YUE Y, LIU N, MA Y, et al. Highly self-healable 3D microsupercapacitor with MXene–graphene composite aerogel[J]. Acs Nano, 2018, 12(5): 4224-4232. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07528
|
| [57] |
SAMBYAL P, IQBAL A, HONG J, et al. Ultralight and Mechanically Robust Ti₃C₂Tₓ Hybrid Aerogel Reinforced by Carbon Nanotubes for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(41): 38046-38054.
|
| [58] |
MA Z, KANG S, MA J, et al. Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber–Ti3C2Tx mxene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Acs Nano, 2020, 14(7): 8368-8382. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02401
|
| [59] |
WANG S, LI D, MENG W, et al. Scalable, superelastic, and superhydrophobic MXene/silver nanowire/melamine hybrid sponges for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10(13): 5336-5344. doi: 10.1039/D2TC00516F
|
| [60] |
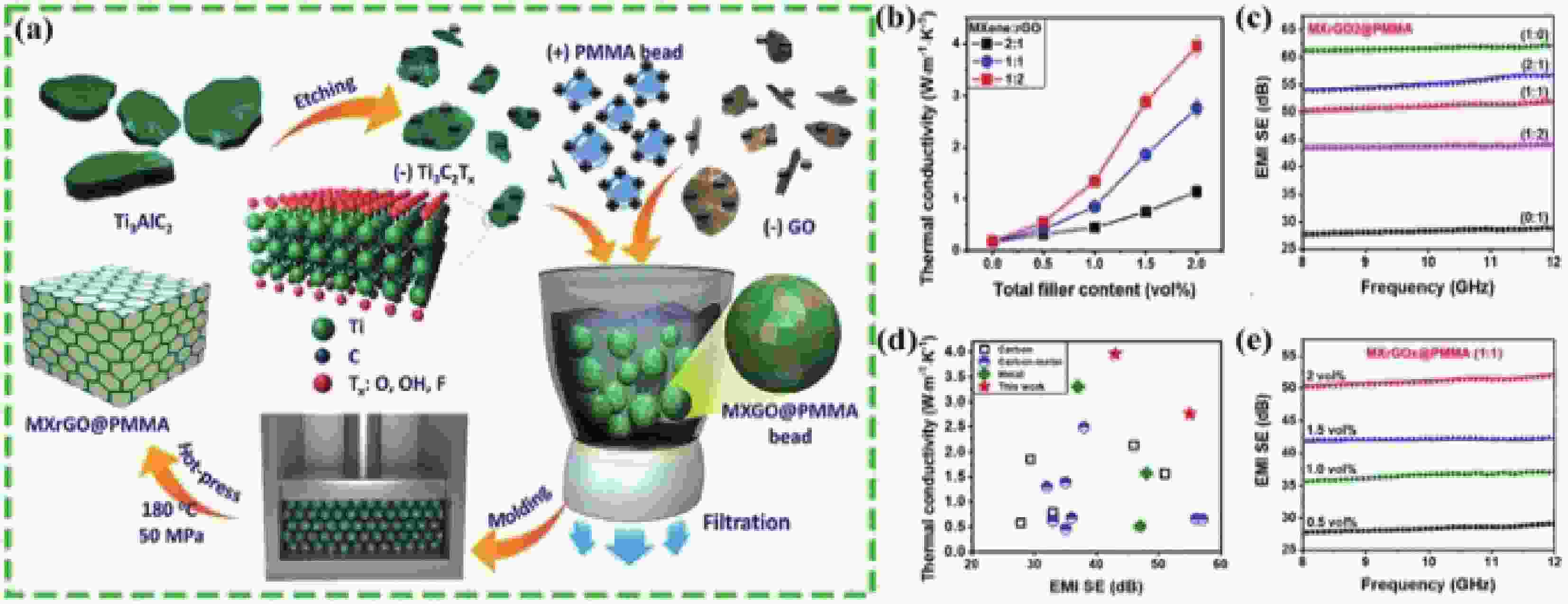
VU M C, MANI D, KIM J-B, et al. Hybrid shell of MXene and reduced graphene oxide assembled on PMMA bead core towards tunable thermoconductive and EMI shielding nanocomposites[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2021, 149: 106574. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106574
|
| [61] |
LI C, NI X, LEI Y, et al. Plasmolysis-inspired yolk–shell hydrogel-core@ void@ MXene-shell microspheres with strong electromagnetic interference shielding performance[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(47): 26839-26851. doi: 10.1039/D1TA08788F
|
| [62] |
CHEN X, JIANG J, YANG G, et al. Bioinspired wood-like coaxial fibers based on MXene@ graphene oxide with superior mechanical and electrical properties[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(41): 21325-21333. doi: 10.1039/D0NR04928J
|
| [63] |
LIU L-X, CHEN W, ZHANG H-B, et al. Tough and electrically conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene–based core–shell fibers for high–performance electromagnetic interference shielding and heating application[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 133074. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133074
|
| [64] |
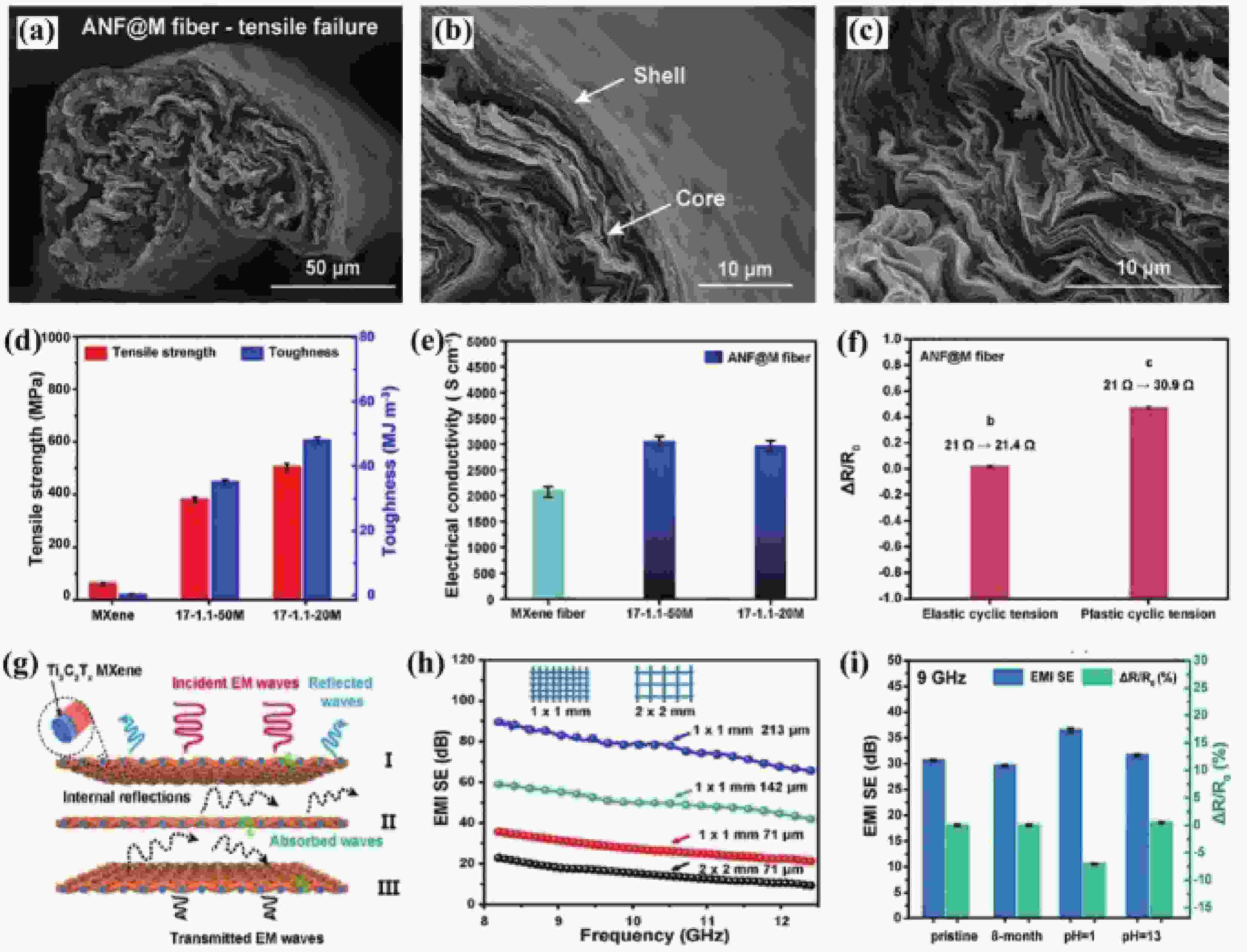
LIU L-X, CHEN W, ZHANG H-B, et al. Super-tough and environmentally stable aramid. Nanofiber@ MXene coaxial fibers with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency[J]. Nano-micro letters, 2022, 14(1): 111. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00853-1
|
| [65] |
ZHANG Y, WANG L, ZHANG J, et al. Fabrication and investigation on the ultra-thin and flexible Ti3C2Tx/co-doped polyaniline electromagnetic interference shielding composite films[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2019, 183: 107833. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107833
|
| [66] |
CUI C, XIANG C, GENG L, et al. Flexible and ultrathin electrospun regenerate cellulose nanofibers and d-Ti3C2Tx (MXene) composite film for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 788: 1246-1255. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.294
|
| [67] |
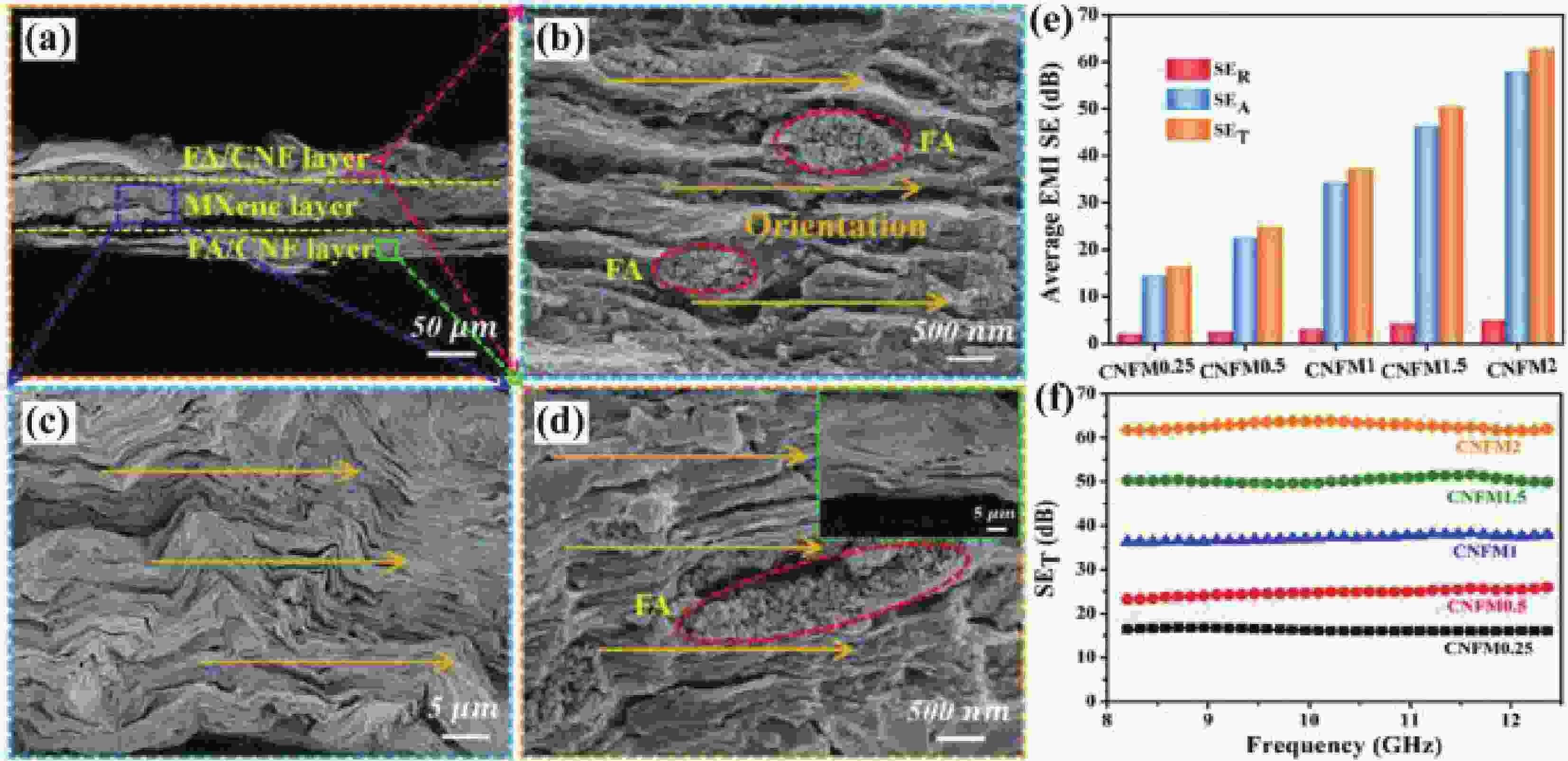
XIN W, XI G-Q, CAO W-T, et al. Lightweight and flexible MXene/CNF/silver composite membranes with a brick-like structure and high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(51): 29636-29644. doi: 10.1039/C9RA06399D
|
| [68] |
LIU R, MIAO M, LI Y, et al. Ultrathin biomimetic polymeric Ti3C2Tx MXene composite films for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(51): 44787-44795.
|
| [69] |
ZHANG Y, CHENG W, TIAN W, et al. Nacre-inspired tunable electromagnetic interference shielding sandwich films with superior mechanical and fire-resistant protective performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(5): 6371-6382.
|
| [70] |
ZHOU B, ZHANG Z, LI Y, et al. Flexible, robust, and multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding film with alternating cellulose nanofiber and MXene layers[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(4): 4895-4905.
|
| [71] |
JIN X, WANG J, DAI L, et al. Flame-retardant poly (vinyl alcohol)/MXene multilayered films with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal conductive performances[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122475. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122475
|
| [72] |
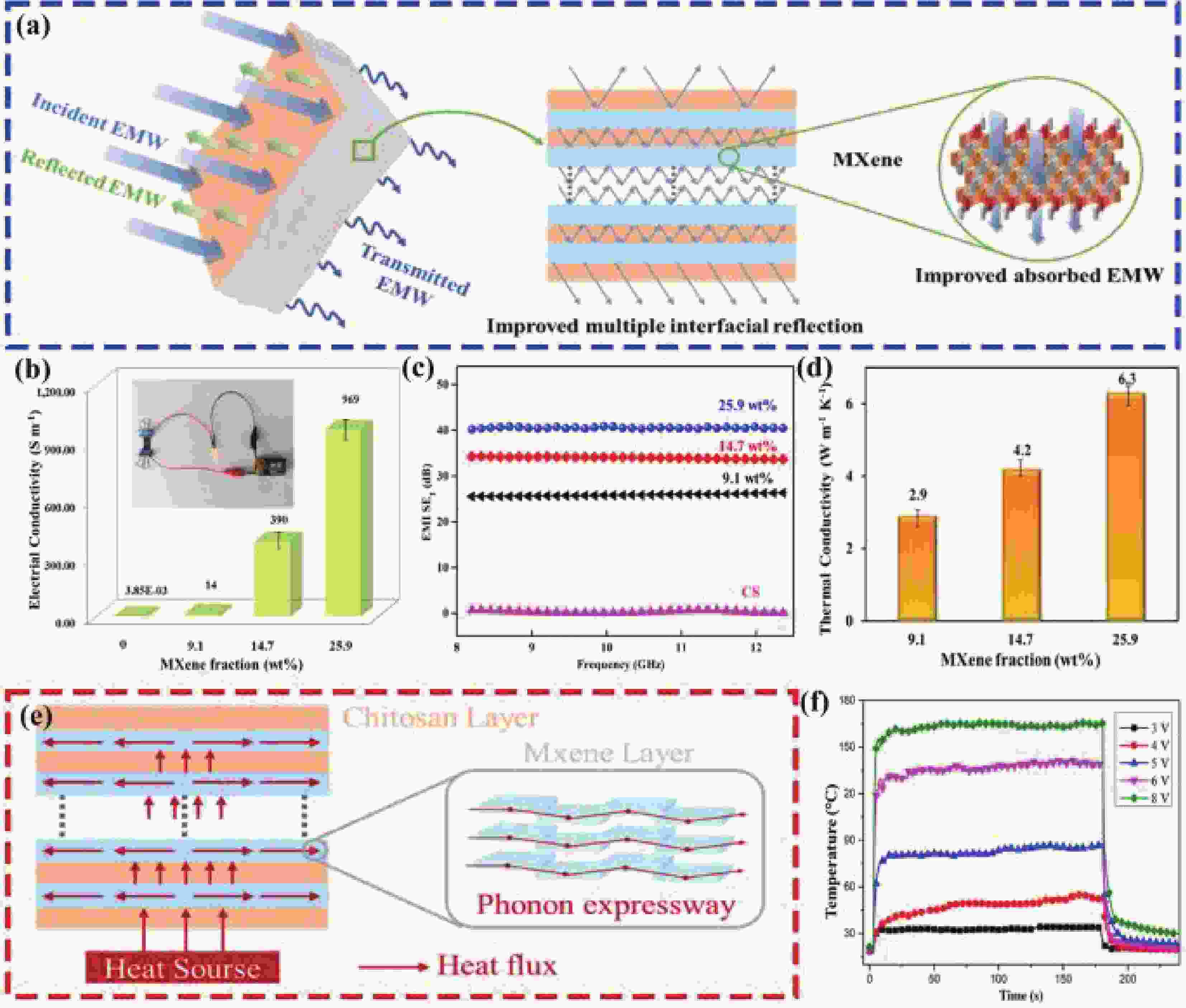
TAN Z, ZHAO H, SUN F, et al. Fabrication of Chitosan/MXene multilayered film based on layer-by-layer assembly: Toward enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal management capacity[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 155: 106809. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106809
|
| [73] |
CAO W-T, CHEN F-F, ZHU Y-J, et al. Binary strengthening and toughening of MXene/cellulose nanofiber composite paper with nacre-inspired structure and superior electromagnetic interference shielding properties[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(5): 4583-4593. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b00997
|
| [74] |
LI L, ZHANG M, ZHANG X, et al. New Ti3C2 aerogel as promising negative electrode materials for asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 364: 234-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.08.029
|
| [75] |
MICHELI D, MORLES R B, MARCHETTI M, et al. Broadband electromagnetic characterization of carbon foam to metal contact[J]. Carbon, 2014, 68: 149-158. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.10.074
|
| [76] |
ZHANG Y, HUANG Y, ZHANG T, et al. Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(12): 2049-2053. doi: 10.1002/adma.201405788
|
| [77] |
SONG W-L, CAO M-S, LU M-M, et al. Flexible graphene/polymer composite films in sandwich structures for effective electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Carbon, 2014, 66: 67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.08.043
|
| [78] |
LE K Y, VILLARUZ A E, ZHENG Y, et al. Role of phenol-soluble modulins in Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation and infection of indwelling medical devices[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2019, 431(16): 3015-3027. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.03.030
|
| [79] |
ZHOU Z, SONG Q, HUANG B, et al. Facile fabrication of densely packed Ti3C2 MXene/nanocellulose composite films for enhancing electromagnetic interference shielding and electro-/photothermal performance[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(7): 12405-12417. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c04526
|
| [80] |
ZHAO S, ZHANG H-B, LUO J-Q, et al. Highly electrically conductive three-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene/reduced graphene oxide hybrid aerogels with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding performances[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(11): 11193-11202. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05739
|
| [81] |
GUO Z, REN P, WANG J, et al. Multifunctional sandwich-structured magnetic-electric composite films with Joule heating capacities toward absorption-dominant electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2022, 236: 109836. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109836
|
| [82] |
WANG Z, CHENG Z, XIE L, et al. Flexible and lightweight Ti3C2Tx MXene/Fe3O4@ PANI composite films for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(4): 5747-5757. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.161
|
| [83] |
HU S, LI S, XU W, et al. Core@ shell and sandwich-like Ti3C2Tx@ Ni particles with enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding performance[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(21): 29995-30004. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.174
|
| [84] |
TIAN W, VAHIDMOHAMMADI A, WANG Z, et al. Layer-by-layer self-assembly of pillared two-dimensional multilayers[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2558. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10631-0
|
| [85] |
WANG Y, PENG H-K, LI T-T, et al. MXene-coated conductive composite film with ultrathin, flexible, self-cleaning for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 412: 128681. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128681
|
| [86] |
LI Y, CHEN Y, LIU Y, et al. Holocellulose nanofibrils assisted exfoliation to prepare MXene-based composite film with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding performance[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 274: 118652. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118652
|
| [87] |
XIANG Z, WANG X, ZHANG X, et al. Self-assembly of nano/microstructured 2D Ti3CNTx MXene-based composites for electromagnetic pollution elimination and Joule energy conversion application[J]. Carbon, 2022, 189: 305-318. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.12.075
|
| [88] |
LUO J-Q, ZHAO S, ZHANG H-B, et al. Flexible, stretchable and electrically conductive MXene/natural rubber nanocomposite films for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2019, 182: 107754. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107754
|
| [89] |
SUN R, ZHANG H B, LIU J, et al. Highly conductive transition metal carbide/carbonitride (MXene)@ polystyrene nanocomposites fabricated by electrostatic assembly for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(45): 1702807. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201702807
|
| [90] |
XU M-K, LIU J, ZHANG H-B, et al. Electrically conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene/polypropylene nanocomposites with an ultralow percolation threshold for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(11): 4342-4350.
|
| [91] |
WU Z, YANG Z, JIN C, et al. Accurately Engineering 2 D/2D/0D Heterojunction In Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanoarchitectures for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and Shielding[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(4): 5866-5876.
|
| [92] |
QIAN K, ZHOU Q, WU H, et al. Carbonized cellulose microsphere@ void@ MXene composite films with egg-box structure for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2021, 141: 106229. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.106229
|
| [93] |
LIU L X, CHEN W, ZHANG H B, et al. Flexible and multifunctional silk textiles with biomimetic leaf-like MXene/silver nanowire nanostructures for electromagnetic interference shielding, humidity monitoring, and self-derived hydrophobicity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(44): 1905197. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201905197
|
| [94] |
IQBAL A, SAMBYAL P, KOO C M. 2D MXenes for electromagnetic shielding: a review[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(47): 2000883. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000883
|





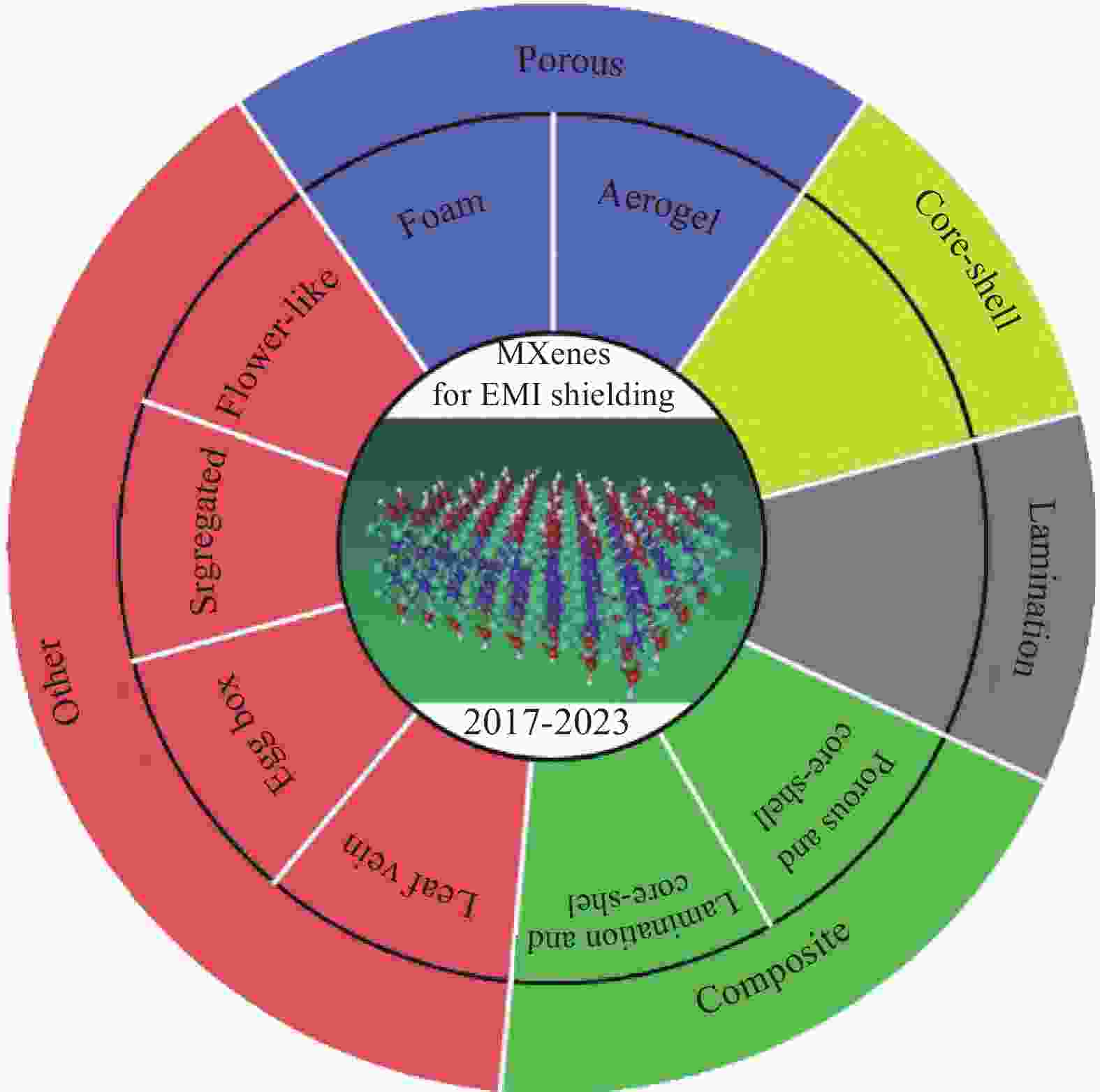
 下载:
下载: