Preparation and Properties of thin-wall flame-retardant polycarbonate materials with low heat release and smoke
-
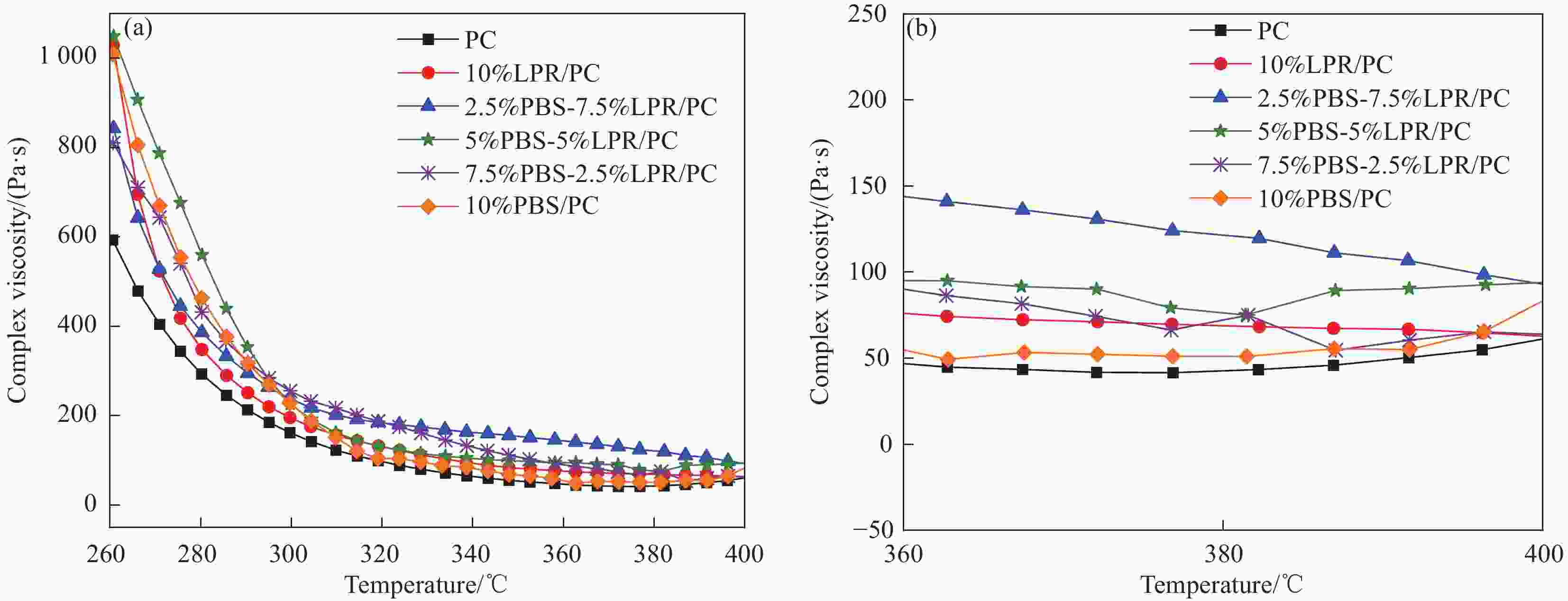
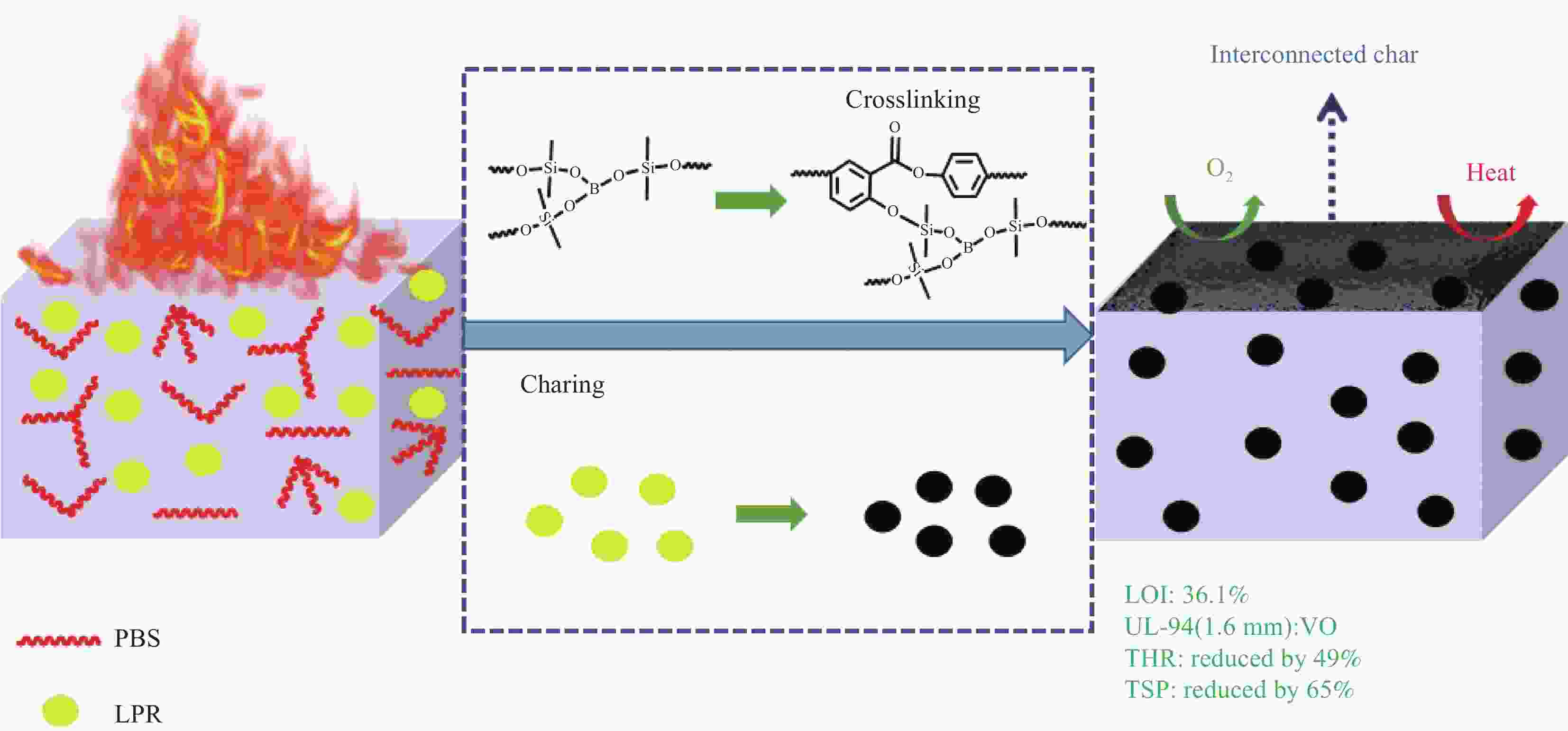
摘要: 兼具低烟低热和薄壁阻燃的无卤无氟聚碳酸酯(PC)的制备是该领域面临的一个挑战。以八甲基环四硅氧烷和硼酸为原料,通过缩聚反应制备了一种聚硼硅氧烷(PBS)阻燃剂,将其与硼酚醛树脂(LPR)复配制备了PBS-LPR/PC复合材料。结果表明,在PBS和LPR总添加量为10 wt%,质量比3∶1时,在PC中表现出最佳的协同阻燃效果,1.6 mm厚的PC样品能够通过UL-94垂直燃烧测试的V-0级别。与PC相比,该样品的峰值放热率(pHRR)、峰值产烟率(pSPR)、总热释放(THR)和总烟生成(TSP)分别降低了76%、64%、49%和65%。阻燃机制研究表明PBS和PC的交联成炭以及LPR的原位成炭是阻燃性能提高的主要原因。7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC的缺口冲击强度是PC的2.3倍,材料表现出高韧的特性。Abstract: The preparation of halogen-free and fluorine-free thin-wall flame-retardant polycarbonate (PC) with low smoke and heat release was a challenge in the field. Polyborosiloxane (PBS) flame retardant wasprepared by polycondensation reaction between octamethyl cyclotetrasiloxane and boric acid, and then compounded with boron-phenolic resin (LPR) to prepare PBS-LPR/PC composites. The results show that whenthe total amount of PBS and LPR is 10 wt% and the mass ratio is 3∶1, the best flame-retardant effect is shown in PC, the 1.6 mm thick PC sample can pass UL-94 V-0 rating. Compared with that of pure PC, the peak heat release rate (pHRR), the peak smoke production rate (pSPR), the total heat release (THR)and the total smoke production (TSP) of sample reduces by 76%, 64%, 49% and 65%, respectively. The investigation on flame-retardant mechanism show that LPR decrease the viscosity of PCcomposites first and then increase, which confirms the generation of cross-linking reaction. The notched ipact strength of 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC is 2.3 times that of PC, which makes the material show high toughness.
-
Key words:
- Polycarbonate /
- borosiloxane /
- phenolic resin /
- thin-walled flame retardant /
- low smoke and low heat
-
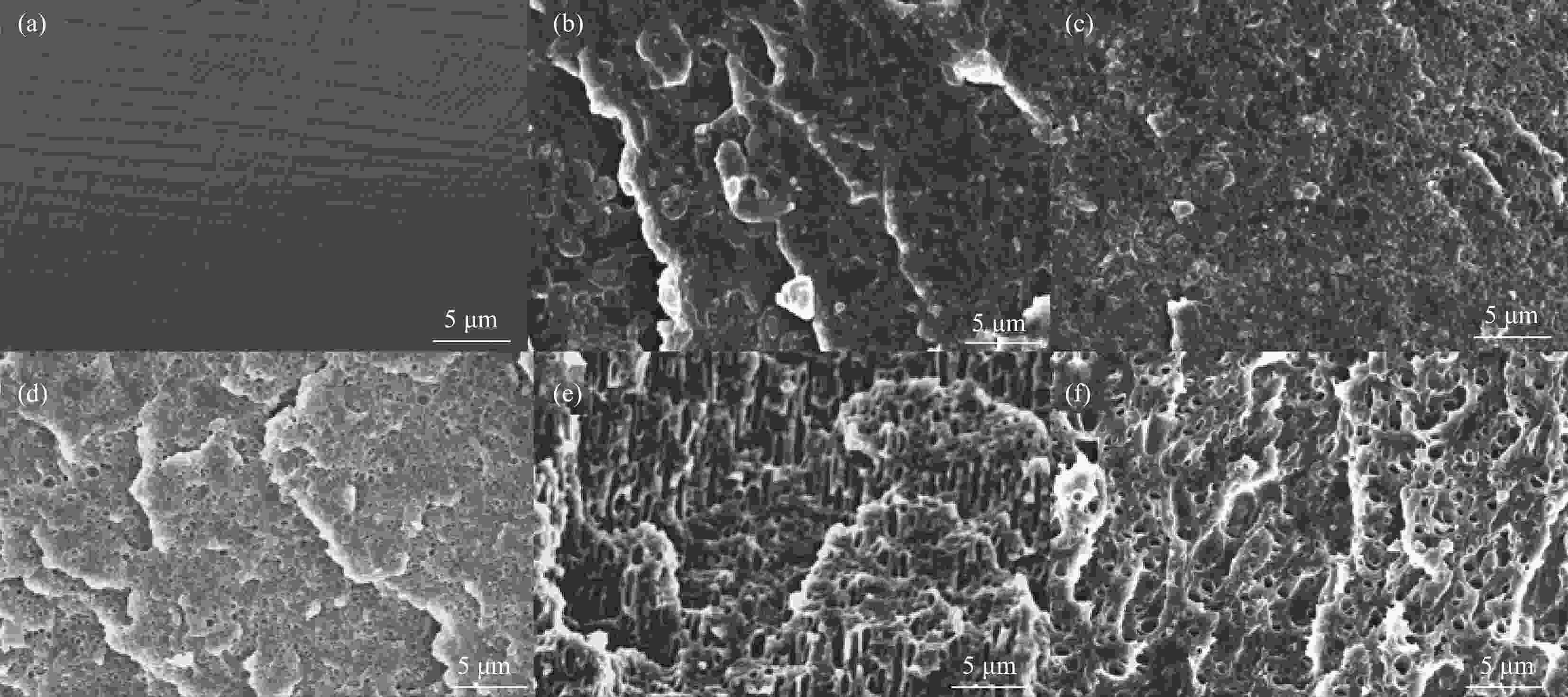
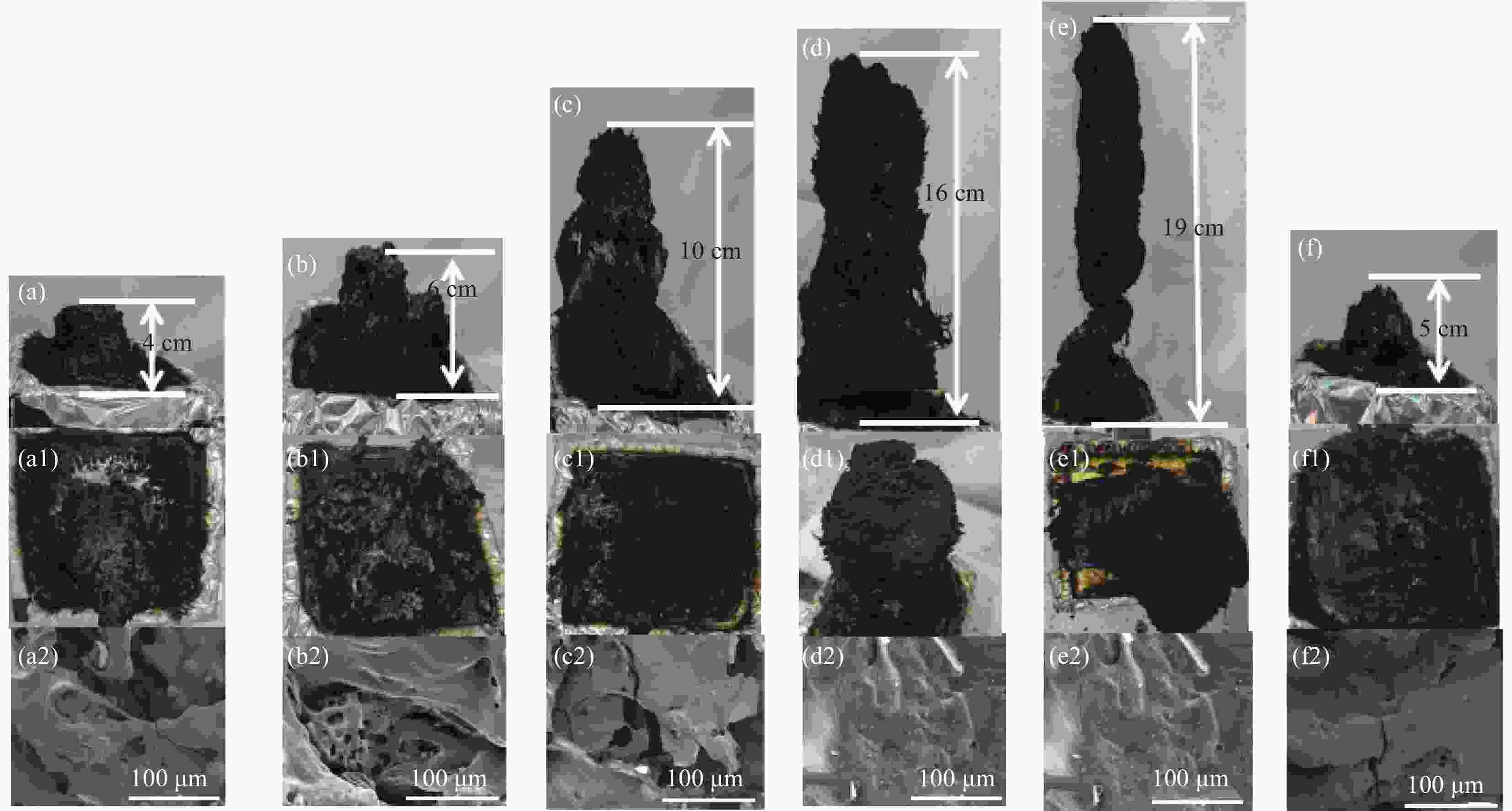
图 4 PC(a), 10%LPR/PC(b), 2.5%PBS-7.5%LPR/PC(c), 5%PBS-5%LPR/PC(d), 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC(e), 10%PBS/PC(f)复合材料锥形量热测试后残炭的数码照片,SEM照片和EDS分析;a,a1表示顶部和侧面残炭形貌,a2表示SEM照片
Figure 4. Morphologies、SEM images and EDS analysis of char residues from PC(a), 10%LPR/PC(b), 2.5%PBS-7.5%LPR/PC(c), 5%PBS-5%LPR/PC(d), 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC(e), 10%PBS/PC(f)composites of digital photos,SEM photos and EDS analysis after the cone calorimeter;a,a1 represent the top and side Morphologies,a2 indicates the SEM images
表 1 PBS-LPR/PC复合材料的组成
Table 1. Composition of PC and PBS-LPR/PC composites
Samples PC /wt% PBS/wt% LPR /wt% PC 100.0 0.0 0.0 10%LPR/PC 90.0 0.0 10.0 2.5%PBS-7.5%LPR/PC 90.0 2.5 7.5 5%PBS-5%LPR/PC 90.0 5.0 5.0 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC 90.0 7.5 2.5 10%PBS/PC 90.0 10.0 0 Notes: LPR−Phenolic Resin; PC—Polycarbonate. 表 2 PC和PBS-LPR/PC复合材料在氮气气氛下的热稳定性数据
Table 2. Thermal stability data of PC and PBS-LPR/PC composites in nitrogen atmosphere
Samples T5% /℃ Tmax /℃ Residue /% PC 476 521 24.0 PBS 219 407 2.8 LPR 148 573 69.7 10%LPR/PC 452 517 28.3 2.5%PBS-7.5%LPR/PC 445 515 27.5 5%PBS-5%LPR/PC 408 516 26.4 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC 378 512 24.3 10%PBS/PC 394 512 24.4 Notes: T5%−5% decomposition temperature in the first; Tmax−Maximum decomposition temperature 表 3 PC和PBS-LPR/PC复合材料的LOI和UL-94数据
Table 3. LOI and UL-94 data of PC and PBS-LPR/PC composites
Sample LOI /% UL-94/ (1.6 mm) t1 /s t2 /s Dripping Rating PC 27.2 19.5±2.2 4.6±1.7 Yes V-2 10%LPR/PC 28.8 18.6±16.5 0.9±0.2 Yes V-2 2.5%PBS-7.5%LPR/PC 35.8 27.2±22.1 24.8±21.0 Yes NR 5%PBS-5%LPR/PC 32.1 6.2±4.2 2.6±1.9 No V-0 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC 36.1 4.9±2.7 1.7±1.1 No V-0 10%PBS/PC 32.9 3.1±1.1 5.6±5.6 Yes V-2 Notes: t1−Self-extinguishing time after the first ignition;t2−Self-extinguishing time after the second ignition. 表 4 PC及PBS-LPR/PC复合材料的锥形量热测试数据
Table 4. Data of cone calorimeter for PC and PBS-LPR/PC composites
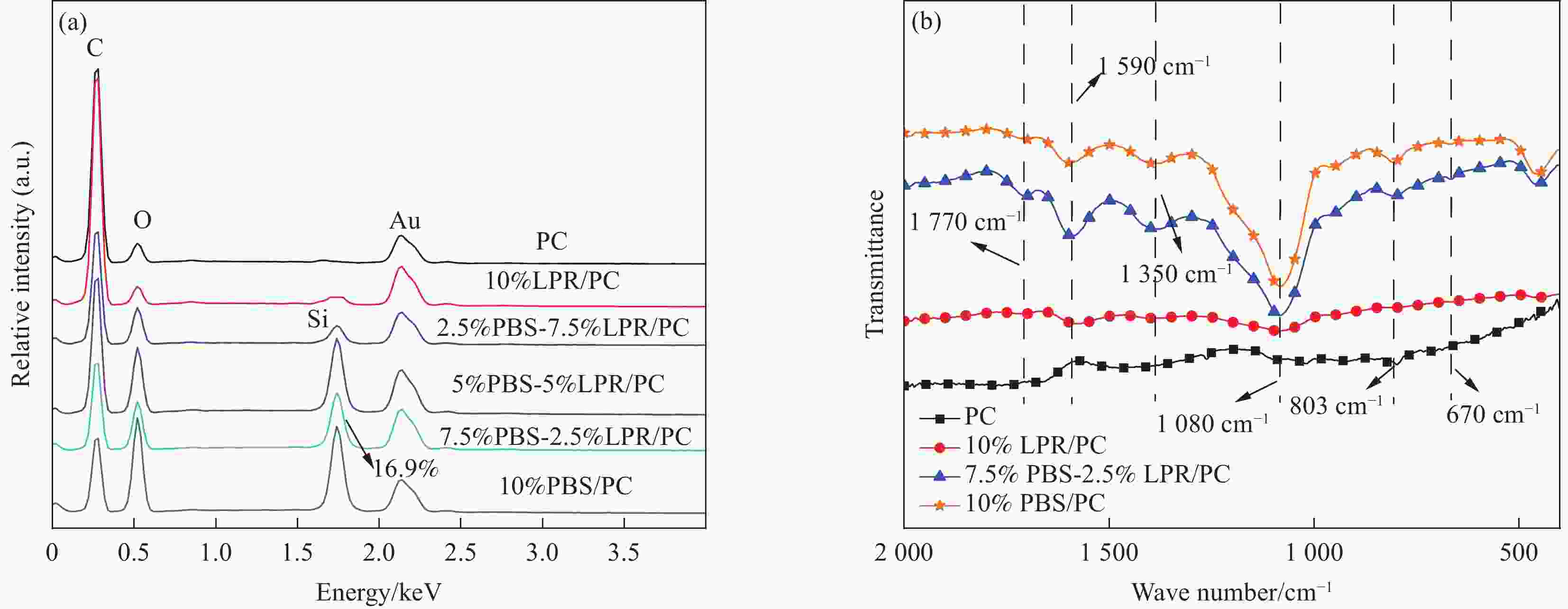
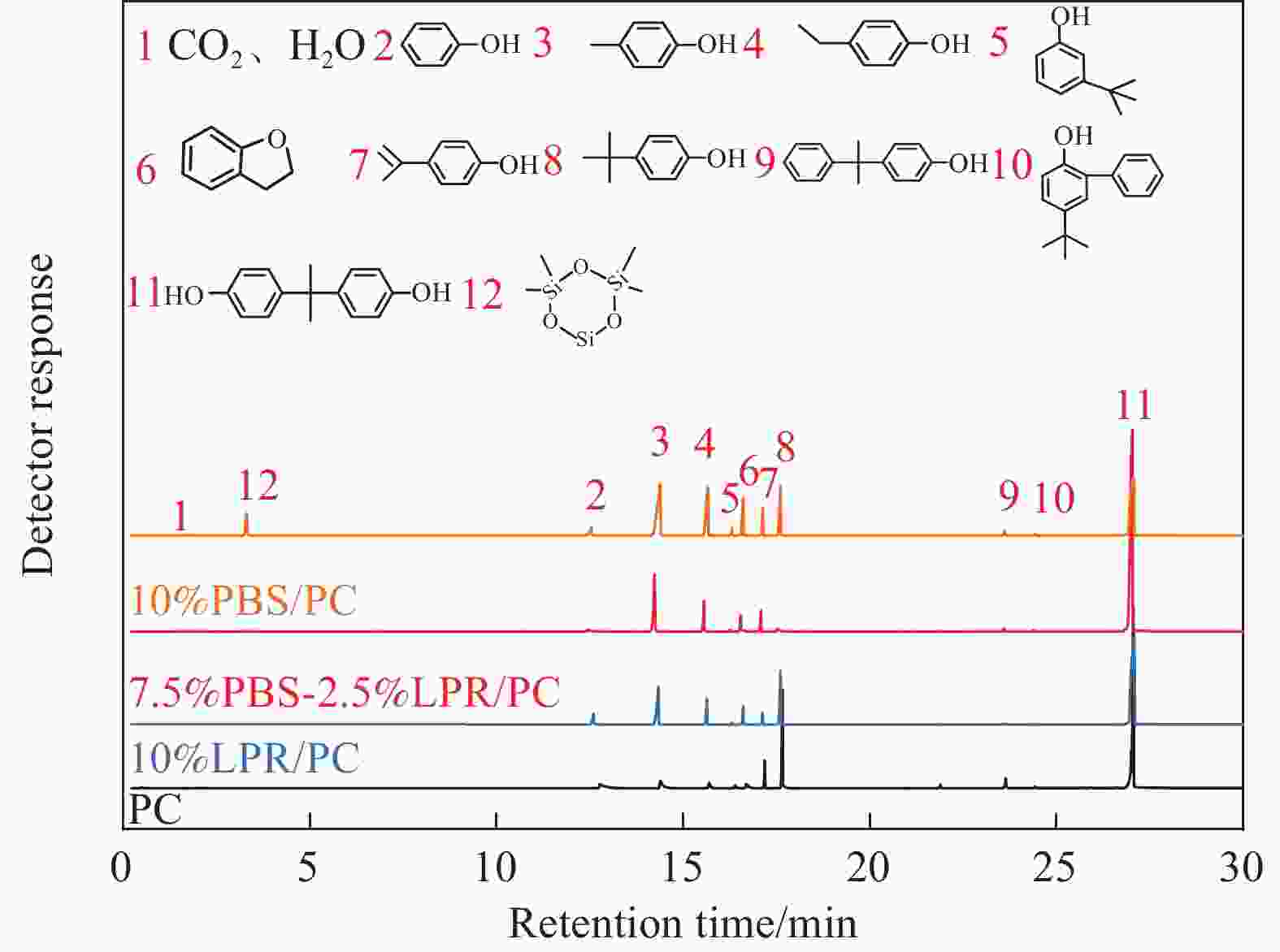
Samples PC 10%LPR/PC 2.5%PBS-7.5%LPR/PC 5%PBS-5%LPR/PC 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC 10%PBS/PC TTI /s 138 115 129 107 135 114 pHRR/(kW·m−2) 590 218 153 149 139 212 THR/(MJ·m−2) 65.9 49.2 43.1 40.7 33.4 51.8 pSPR/(m2·s−1) 0.22 0.10 0.07 0.08 0.08 0.07 TSP/m2 16.8 18.2 10.7 8.4 5.9 9.7 MARHE/(kW·m−2) 172 109 65 67 54 93 FPI/(m2·s·kW−1) 0.223 0.528 0.843 0.718 0.969 0.538 CHR/% 19.1 21.6 38.1 32.8 30.0 18.4 Notes: TTI−Time to ignition; pHRR−Peak heat release rate; THR−Total heat release at 600 s; pSPR−Peak smoke production rate; TSP−Total smoke production at 600 s; MARHE−Maximum average heat release rate; FPI−Fire performance index; CHR−Char residue. 表 5 GC/MS测定PC及其复合材料主要降解产物组成
Table 5. The composition of the main degradation products from PC and its composites obtained by GC/MS measurements.
Number Structure PC 10%LPR/PC 7.5%PBS-2.5%LPR/PC 10%PBS/PC 1 CO2、H2O 0.7 0.6 1.04 0.5 2 
5.8 3.1 1.26 2.3 3 
5.6 13.6 11.6 24.6 4 
2.6 5.2 4.1 6.2 5 
3.6 0 2.6 0.9 7 
4.1 10.7 1.3 3.7 8 
17.9 2.0 0 9.3 Monophenolics 40.3 35.2 21.9 47.5 11 
56.1 61.1 72.3 31.9 6 
0.5 3.2 4.8 6.3 9 
2.8 0.3 0.4 0.7 10 
0.1 0.2 0.2 0.4 12 
0 0 0.4 5.2 -
[1] LIU Z, MA M, GE B, et al. Toward flame-retardant, transparency, and high mechanical property of polycarbonate based on low addition of linear polyborosiloxane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 474: 145799. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145799 [2] YU R H, LIU J, GAO D D, et al. Striking effect of nanosized carbon black modified by grafting sodium sulfonate on improving the flame retardancy of polycarbonate[J]. Composites Communications, 2020, 20: 100359. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2020.100359 [3] LIU S M, YANG Y, JIANG Z J, Synergistic flame retardant effect of poly(ethersulfones) and polysiloxane on polycarbonate[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 124(6): 4502-4511. [4] DING Z, WANG S, GE J, et al. Flame-retardant epoxy resin: synergistic effect between aluminum diethylphosphinate and piperazine pyrophosphate[J]. Iranian Polymer Journal, 2023: 1-11. [5] NI P, FANG Y, QIAN L, et al. Flame-retardant behavior of a phosphorus/silicon compound onpolycarbonate[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2017, 135: 45815-45822. [6] WANG S, YANG X, LI Z, et al. Novel eco-friendly maleopimaric acid based polysiloxane flame retardant and application in rigid polyurethanefoam[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2020, 198: 108272. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108272 [7] WANG Z, QIU Y, LIU A, et al. Micro-crosslinking of phosphaphenanthrene/siloxane molecule initiate aggregation flame retardant and tougheningenhancement effectson its polycarbonate composite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 466: 143169. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.143169 [8] 刘春雷, 刘颖, 吴大鸣. 无卤阻燃聚碳酸酯薄壁材料[J]. 塑料, 2010, 39(6): 63-65.LIU Chunlei, LIU Ying, WU Daming. Halogen-free flame retardant polycarbonate thin-walled material[J]. Plastic, 2010, 39(6): 63-65(in Chinese). [9] HUANG H, SHI Y, LV G, et al. Flameresistance and aging mechanism of flame retardant polycarbonate sheet containing linear phenolic resin charring agent[J]. PolymerDegradation and Stability, 2015, 122: 139-145. [10] 岑茵, 吴俊, 王培涛, 等. 薄壁阻燃聚碳酸酯的研究[J]. 塑料工业, 2018, 46(4): 142-146.CEN Yin, WU Jun, WANG Peitao, et al. The study of thin wall flame retardant polycarbonate[J]. Plastic industry, 2018, 46(4): 142-146(in Chinese). [11] ZHU Y, YU R H, WANG S D, et al. Unexpected core-shell char from polycarbonate/polyborosiloxane composites and its application in improving flame retardancy[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 136742. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136742 [12] WAN Y, YU S, JIANG S, et al. Microscopicpyrolysis mechanism on the octyphenylsiloxane flame retarded polycarbonate by reactive molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 158: 105274. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105274 [13] TANG T, CHEN X, CHEN H, et al. Catalyzing carbonization of polypropylene itself by supported nickel catalyst during combustion of polypropylene/clay nanocomposite for improving fire retardancy[J]. Chemistry of materials, 2005, 17(11): 2799-2802. doi: 10.1021/cm047771c [14] TANG T, CHEN X, MENG X, et al. Synthesis of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by catalytic combustion of polypropylene[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2005, 117(10): 1541-1544. doi: 10.1002/ange.200461506 [15] 王旭, 梁西良. 耐高温酚醛树脂研究进展[J]. 化学与粘合, 2022, 44(2): 162-164.WANG Xu, LIANG Xiliang. The research progress of high temperature-resistant phenolic resin[J]. Chemistry and adhesion, 2022, 44(2): 162-164(in Chinese). [16] 王许云, 张军, 张峰, 等. 应用锥形量热法评价聚合物复合材料热释放速率[J]. 复合材料学报, 2004, (3): 162-166.WANG Xuyun, ZHANG Jun, ZHANG Feng, et al. The use of cone-shaped heat method evaluationpolymer composite material thermal release rate[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2004, (3): 162-166(in Chinese). [17] ZHANG L, ZHANG Y, WANG L, et al. Phenolic resin modified by boron-siliconwithhigh charyield[J]. Polymer Testing, 2019, 73: 208-213. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.11.033 [18] 李文洋. 硼酚醛树脂基复合材料用胶黏剂制备及性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2023.LI Wenyang. Bonoline-based resin base compositematerials are prepared and performance research for adhesives[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Architecture, 2023(in Chinese). [19] YANG R, CHEN L, ZHANG W Q, et al. Insitu reinforced and flame-retarded polycarbonate by a novel phosphorus-containingthermotropic liquidcrystalline copolyester[J]. Polymer, 2011, 52(18): 4150-4157. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2011.06.047 [20] 高纳川, 高雪雨, 闫莉, 等. 多功能阻燃增韧剂对聚碳酸酯阻燃和力学性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41.GAO Nachuan, GAO Xueyu, YAN Li, et al. Effect of Multifunctional Flame Retardant Toughenerson the Flame Re-tardant and Mechanical Properties of Polycarbonates[J]. Acta Materiae CompositaeSinica, 2024, 41(in Chinese). [21] CHEN D, ZHANG Y, HE J, et al. Making polycarbonate flame retardant: Flame retardant selection and calorimetric analyses[J]. Polymer Testing, 2023, 117: 107876. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2022.107876 [22] 何吉来, 金小涵, 宁淑慧, 等. 氮硫硅协效阻燃剂的合成及在聚碳酸酯中的应用[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2021, 37(7): 87-94.HE Jilai, JIN Xiaohan, NING Shuhui, et al. The synthesis of nitrogen-sulfur-silicon synergistic flameretardant and the application in polycarbonate[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2021, 37(7): 87-94(in Chinese). [23] JANG B N, WILKIE C A. A TGA/FTIR andmass spectral study on the thermal degradation ofbisphenol A polycarbonate[J]. Polymer Degradationand Stability, 2004, 86(3): 419-430. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.05.009 [24] YANG S, LV G, LIU Y, et al. Synergism of polysiloxane and zinc borate flame retardant polycarbonate[J]. Polymer degradation and stability, 2013, 98(12): 2795-2800. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.10.017 [25] CHEN W, LIU P, CHENG Y, et al. Flame retardancy mechanisms of melaminecyanurate in combination with aluminum diethylphosphinate in epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2019, 136(12): 47223 doi: 10.1002/app.47223 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 44
- HTML全文浏览量: 22
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: