Microstructure and properties investigation of B4C/Al composite materialsfabricated by selective laser melting
-
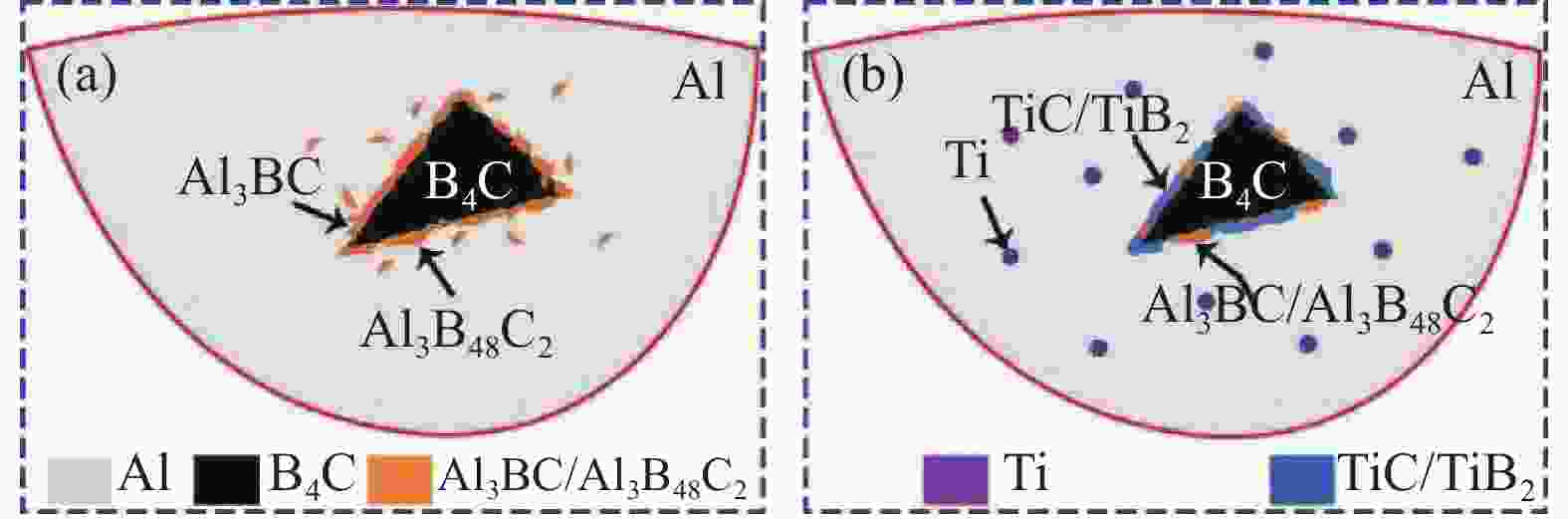
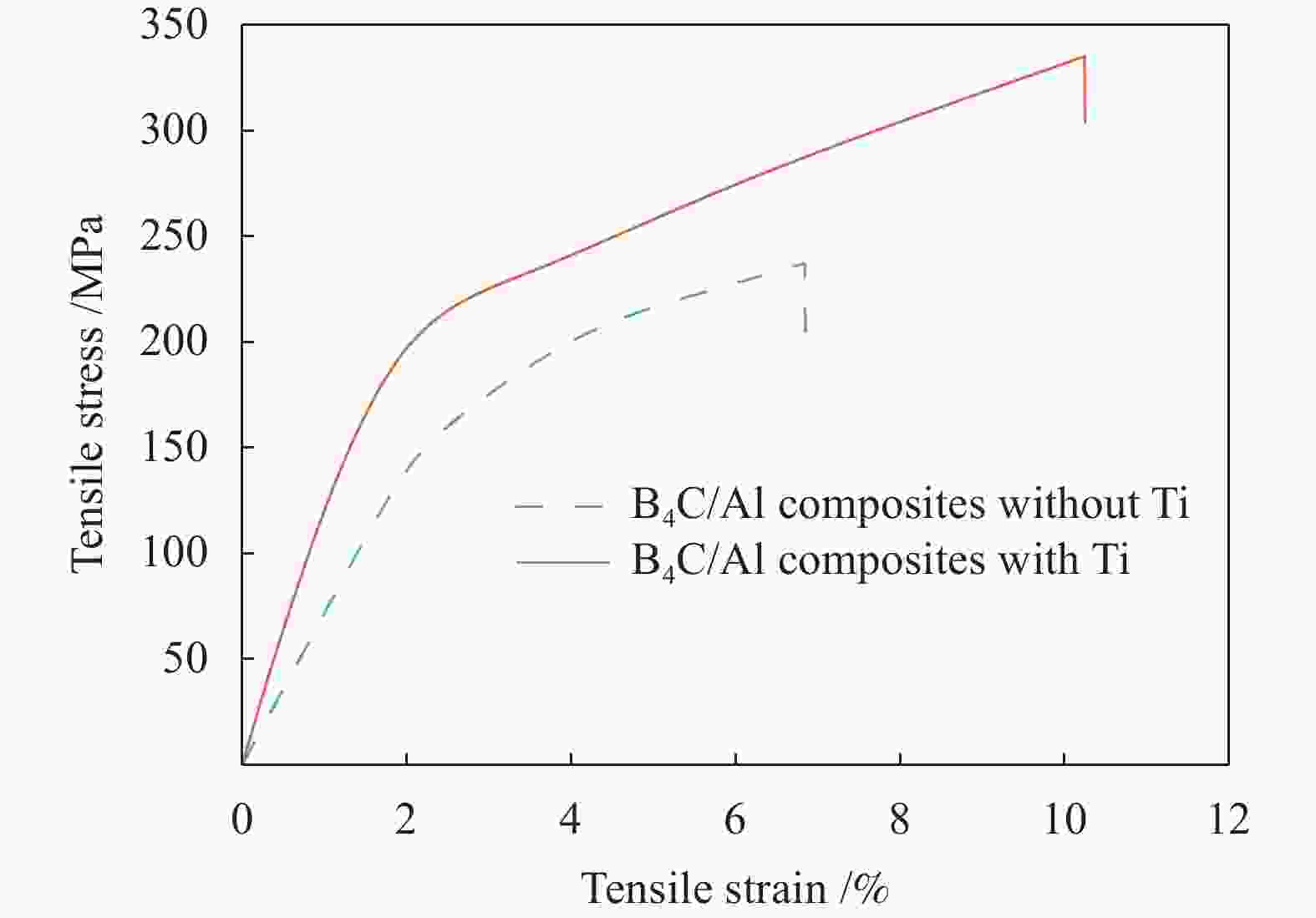
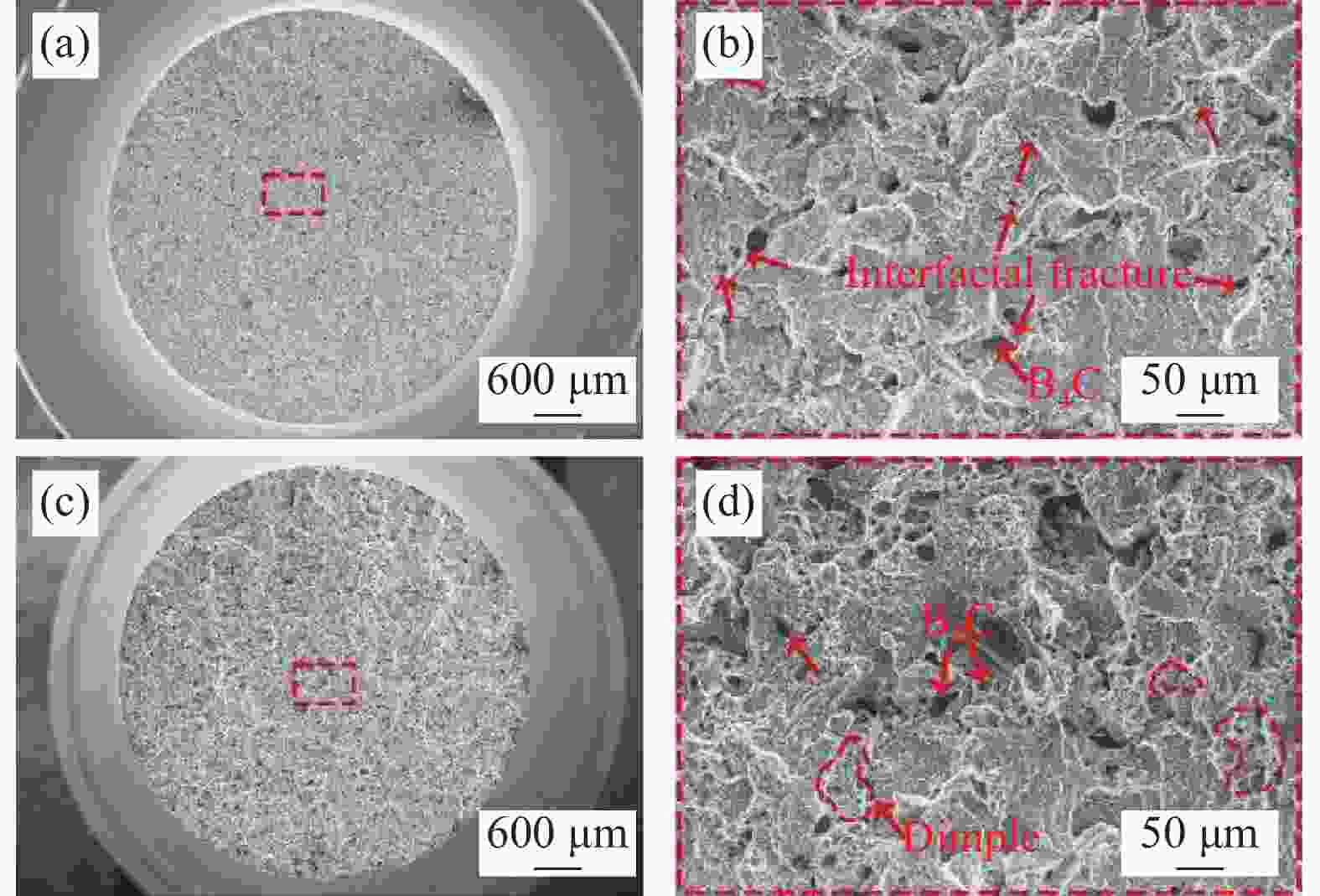
摘要: 为了解决B4C/Al复合材料制备过程中B4C颗粒分布不均、团聚及易与Al基体发生剧烈反应的问题。本文采用选区激光熔化法制备了B4C/Al复合材料,研究了激光功率和Ti元素对B4C/Al复合材料微观组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明,B4C/Al复合材料的致密度随激光功率的增大先增大后减少,激光功率240 W时致密度达到最大为94.1%;制备过程中B4C颗粒易与Al基体发生界面反应并且随激光功率增大而增大,形成界面产物Al3BC和Al3B48C2脆性相和微裂纹,导致界面结合性能降低;加Ti的B4C/Al复合材料的致密度提高到95.2%,形成的界面产物TiC和TiB2能有效抑制界面反应,界面清晰完整结合性能高,复合材料抗拉强度和伸长率分别提高41%、49.3%,拉伸断裂方式由脆性断裂转变为韧性断裂。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of uneven distribution of B4C particles, agglomeration and violent reaction with Al matrix during the preparation of B4C/Al composites. In this paper, B4C/Al composites were prepared by selective laser melting method. The effects of laser power and Ti elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of B4C/Al composites were studied. The results show that the density of B4C/Al composites increases first and then decreases with the increase of laser power, and reaches the maximum density of 94.1% at 240 W. During the preparation process, B4C particles are prone to interfacial reaction with Al matrix and increase with the increase of laser power, resulting in brittle phases and micro-cracks of Al3BC and Al3B48C2, resulting in decreased interfacial bonding properties. The density of B4C/Al composite with Ti increased to 95.2%, the resulting interface products TiC and TiB2 could effectively inhibit the interface reaction, and the interface was clear and complete with high bonding properties. The tensile strength and elongation of the composite were increased by 41% and 49.3%, respectively, and the tensile fracture mode changed from brittle fracture to ductile fracture.
-
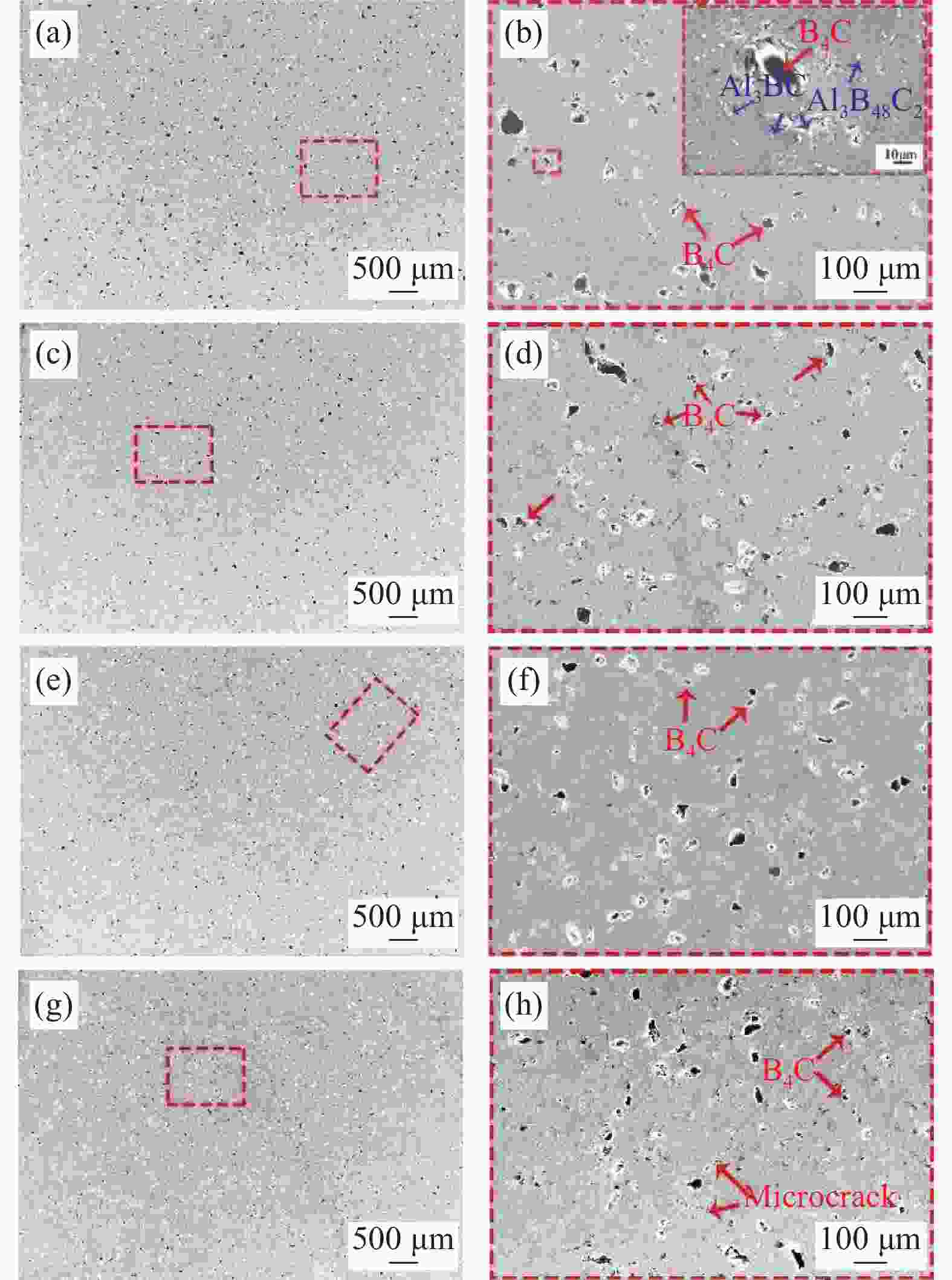
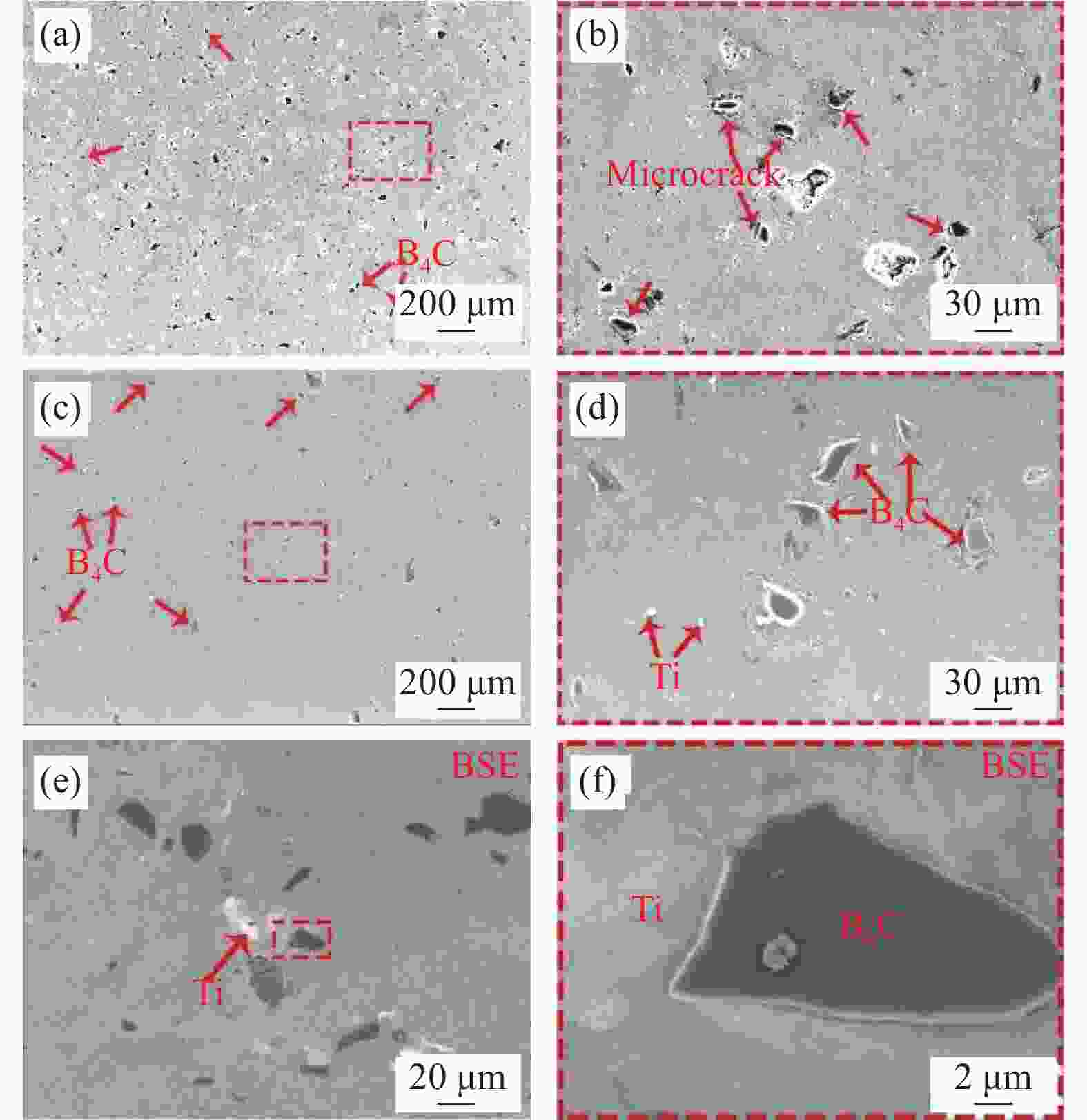
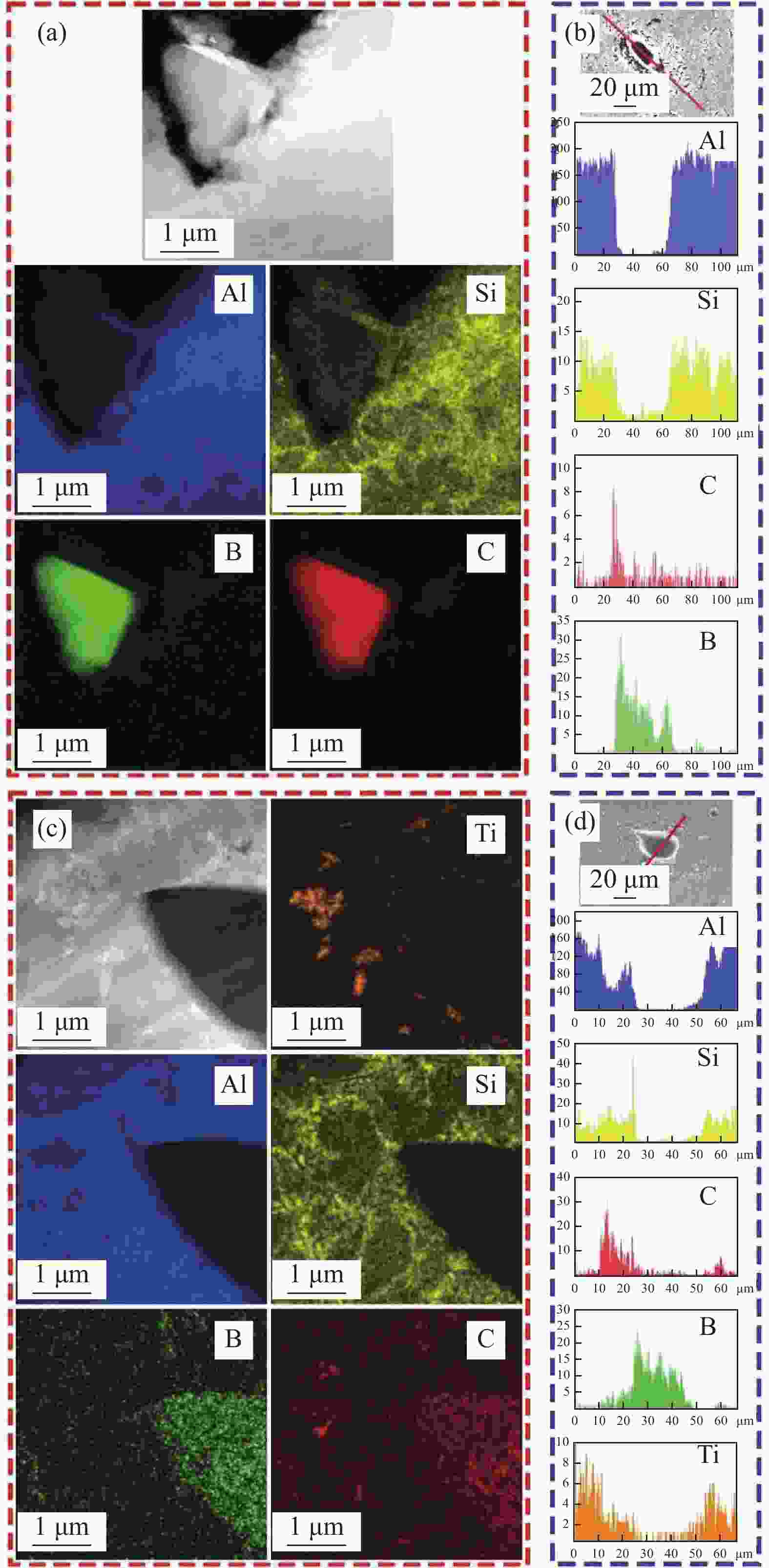
图 5 (a)无Ti复合材料OM图像及致密度;(b)含Ti复合材料OM图像及致密度;(c)无Ti时B4C/Al界面微结构TEM图像;(d)含Ti时B4C/Al界面微结构TEM图像;(e)含Ti复合材料的HRTEM图像;(f) 含Ti复合材料的SAED图像
Figure 5. (a) OM image and density of composites without Ti; (b) OM image and density of composites containing Ti; (c) TEM images of as-prepared B4C/Al interface microstructure without Ti; (d) TEM images of as-prepared B4C/Al interface microstructure with Ti; (e) HRTEM images of composites with Ti; (f) SAED images of composites with Ti
表 1 铝合金AlSi10 Mg的化学成分(wt%)
Table 1. Chemical composition of AlSi10 Mg (wt%)
Element Al Si Mg Zn Cu Ni Fe Ti Mn O Content Bal 9.87 0.34 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 0.86 <0.01 <0.01 0.051 表 2 SLM制备B4C/Al复合材料的工艺参数
Table 2. Process parameters of B4C/Al composites prepared by SLM
B4C/Al (Ti+B4C)/Al Processing parameters Parameter values Parameter values Laser power /W 220、240、260、280 240 Scanning speed/(mm·s−1) 1200 1200 Scanning spacing /mm 0.17 0.17 Layer thickness /mm 0.03 0.03 表 3 B4C/Al复合材料的力学性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of as-prepared B4C/Al composites
-
[1] SHARMA D K, SHARMA M, UPADHYAY G. Boron carbide (B4C) reinforced aluminum matrix composites (AMCs)[J]. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 2019, 9(1): 2194-2203. doi: 10.35940/ijitee.A4766.119119 [2] LEMINE A S, FAYYAZ O, YUSUF M, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum matrix composites with bimodal-sized hybrid NbC-B4C reinforcements[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 33: 104512. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104512 [3] 杨涛, 刘润爱, 王文先, 等. 热轧高含量B4C颗粒增强Al基复合材料的成形性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(7): 2234-2243.YANG Tao, LIU Runai, WANG Wenxian, et al. Formability of high content B4C particle reinforced Al matrix composites by hot rolling[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(7): 2234-2243(in Chinese). [4] NIRALA A, SOREN S, KUMAR N, et al. A comprehensive review on mechanical properties of Al-B4C stir casting fabricated composite[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 21(3): 1432-1435. [5] CHEN X G, HARK R. Developments of Al-30%B4C metal matrix composites for neutron absorber material[J]. TMS Annual Meeting, 2008: 3-9. [6] WANG Z X, LI Q L, ZHENG J Y, et al. Improving Al wettability on B4C by transition metal doping: A combined DFT and experiment study[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(9): 2345-2351. [7] GUO W B, HU Q Y, XIAO P, et al. Effect of Ti element on the interfacial reactions and micro-structures of the Al-B4C composites fabricated by the stir-casting method[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 584: 152619. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152619 [8] GUO H, ZHANG Z W, ZHANG Y, et al. Improving the mechanical properties of B4C/Al composites by solid-state interfacial reaction[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 829: 154521. [9] 李明川, 蒋立异, 刘婷婷, 等. 碳纳米管对激光选区熔化成形Al基复合材料的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7): 1889-1896. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20171108.004LI Mingchuan, JIANG Liyi, LIU Tingting, et al. Effect of carbon nanotubes on Al matrix composites fabricated by selected laser melting[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2018, 35(7): 1889-1896(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20171108.004 [10] CHEN Y, SONG S Q, ZHU S, et al. Selective laser remelting of in-situ Al2O3 particles reinforced AlSi10Mg matrix composite: Densification, microstructure and microhardness[J]. Vacuum, 2021, 191: 110365. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110365 [11] 宋亢, 坚增运, 王渭中, 等. SLM成形10%SiC颗粒增强铝基复合材料的工艺优化及性能[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(S2): 1376-1380.SONG Kang, JIAN Zengyun, WANG Weizhong, et al. Proper ties and process optimization of 10%SiCp/AlSi10Mg composites by SLM[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(S2): 1376-1380(in Chinese). [12] ZHANG D Y, YI D H, WU X P, et al. SiC reinforced AlSi10Mg composites fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 894: 162365. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162365 [13] 章敏立, 吴一, 廉清, 等. 激光选区熔化成形原位自生TiB2/Al-Si复合材料的微观组织和力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11): 3114-3121.ZHANG Minli, WU Yi, LIAN Qing, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of in situ TiB2/Al-Si composite fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2018, 35(11): 3114-3121(in Chinese). [14] XUE G, KE L D, ZHU H H, et al. Influence of processing parameters on selective laser melted SiCp/AlSi10Mg composites: Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 764: 138155. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.138155 [15] ANANDKUMAR R, ALMEIDA A, COLAÇO R, et al. Microstructure and wear studies of laser clad Al-Si/SiC(p) composite coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(24): 9497-9505. [16] VIALA J C, BOUIX J, GONZALEZ G, et al. Chemical reactivity of aluminium with boron carbide[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1997, 32(17): 4559-4573. doi: 10.1023/A:1018625402103 [17] WU H Y, ZHANG S C, GAO M X, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multi-carbides/(Al, Si) composites derived from porous B4C preforms by reactive melt infiltration[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 551: 200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.05.008 [18] WANG L Z, WANG S, WU J J. Experimental investigation on densification behavior and surface roughness of AlSi10Mg powders produced by selective laser melting[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2017, 96: 88-96. [19] ZHANG Z, FORTIN K, CHARETTE A, et al. Effect of titanium on microstructure and fluidity of Al–B4C composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2011, 46(9): 3176-3185. [20] 郭文波, 胡启耀, 肖鹏. 界面反应产物对 B4C/Al 复合材料颗粒润湿性及界面强度的影响机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(6): 2941-2948.GUO Wenbo, HU Qiyao, XIAO Peng. Effect of interfacial reaction products on the wettability and interfacial strength of B4C/Al composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(6): 2941-2948(in Chinese) [21] AZIMI H, NOUROUZI S, JAMAATI R. Effects of Ti particles and T6 heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 alloy fabricated by compocasting[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2021, 818: 141443. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141443 [22] YI J C, ZHANG X W, RAO J H, et al. In-situ chemical reaction mechanism and non-equilibrium microstructural evolution of (TiB2+TiC)/AlSi10Mg composites prepared by SLM-CS processing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 857: 157553. [23] ZHANG L, PANG S P, GU W H, et al. Interface regulation mechanism of Ti doping on B4C/Al composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(4): 6113-6118. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.10.109 [24] YI J C, ZHANG X W, LIU G Z, et al. Microstructure and dynamic microhardness of additively manufactured (TiB2+TiC)/AlSi10Mg composites with AlSi10Mg and B4C coated Ti powder[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 939: 168718. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.168718 [25] GU D D, MEINERS W, WISSENBACH K, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of metallic components: Materials, processes and mechanisms[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2012, 57(3): 133-164. doi: 10.1179/1743280411Y.0000000014 [26] ARSLAN G, KARA F, TURAN S. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of reactive infiltrated boron carbide–aluminium composites[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2003, 23(8): 1243-1255. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(02)00304-7 [27] 叶大伦, 胡建华. 实用无机物热力学数据手册[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002.YE Dalun, HU Jianhua. Practical inorganic thermodynamic data handbook[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002(in Chinese). [28] WANG M L, CHEN D, CHEN Z, et al. Mechanical properties of in-situ TiB2/A356 composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 590: 246-254. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.10.021 [29] 韩静, 吕俊霞, 王晋, 等. 选区激光熔化AlSi10Mg合金不同温度原位拉伸变形行为及断裂机理研究[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2022, 30(6): 10-19.HAN Jing, LYU Junxia, WANG Jin, et al. In-situ investigation of deformation behavior and fracture mechanism of selective laser melting AlSi10Mg alloy at different temperatures[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2022, 30(6): 10-19(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: