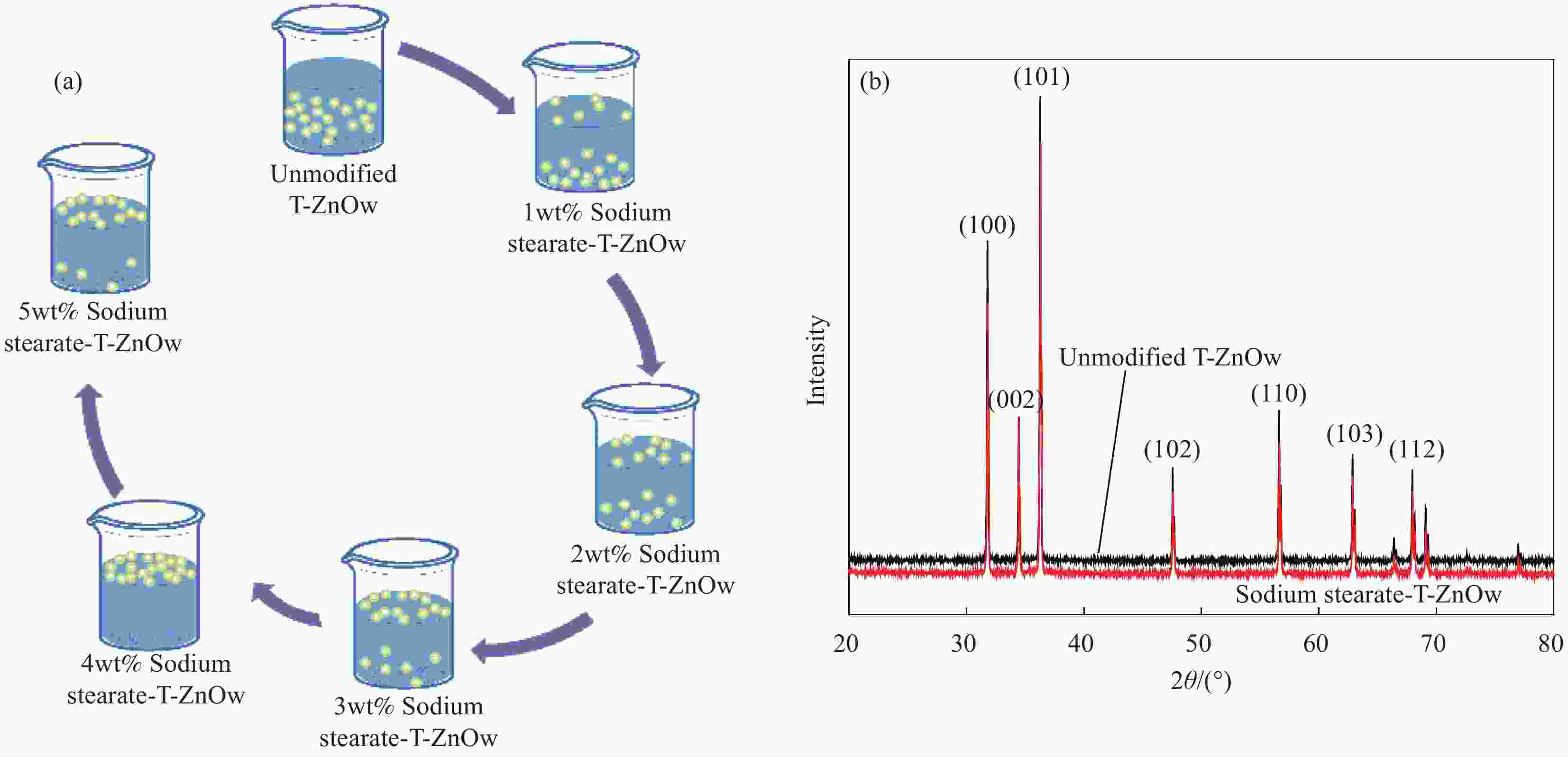
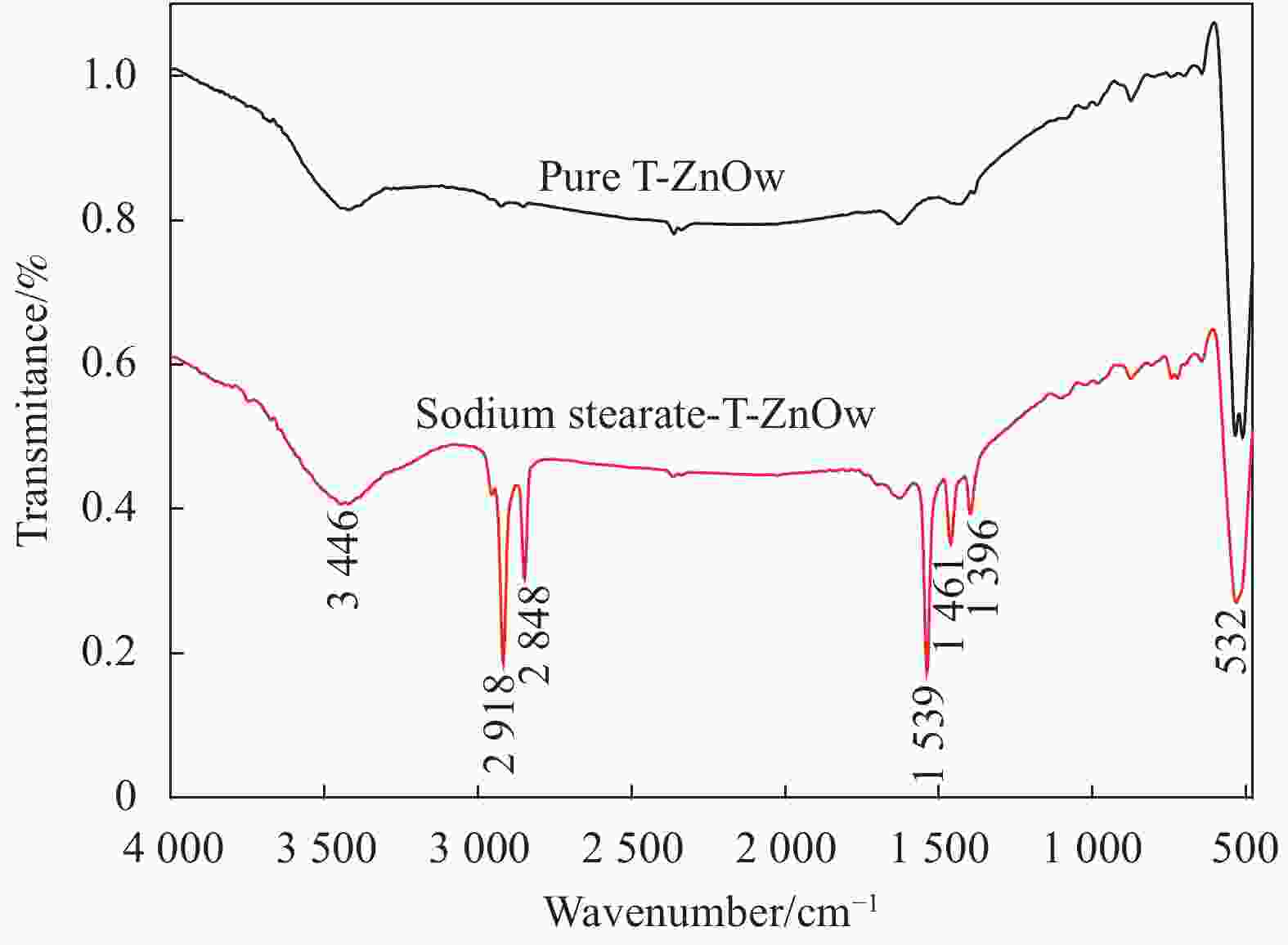
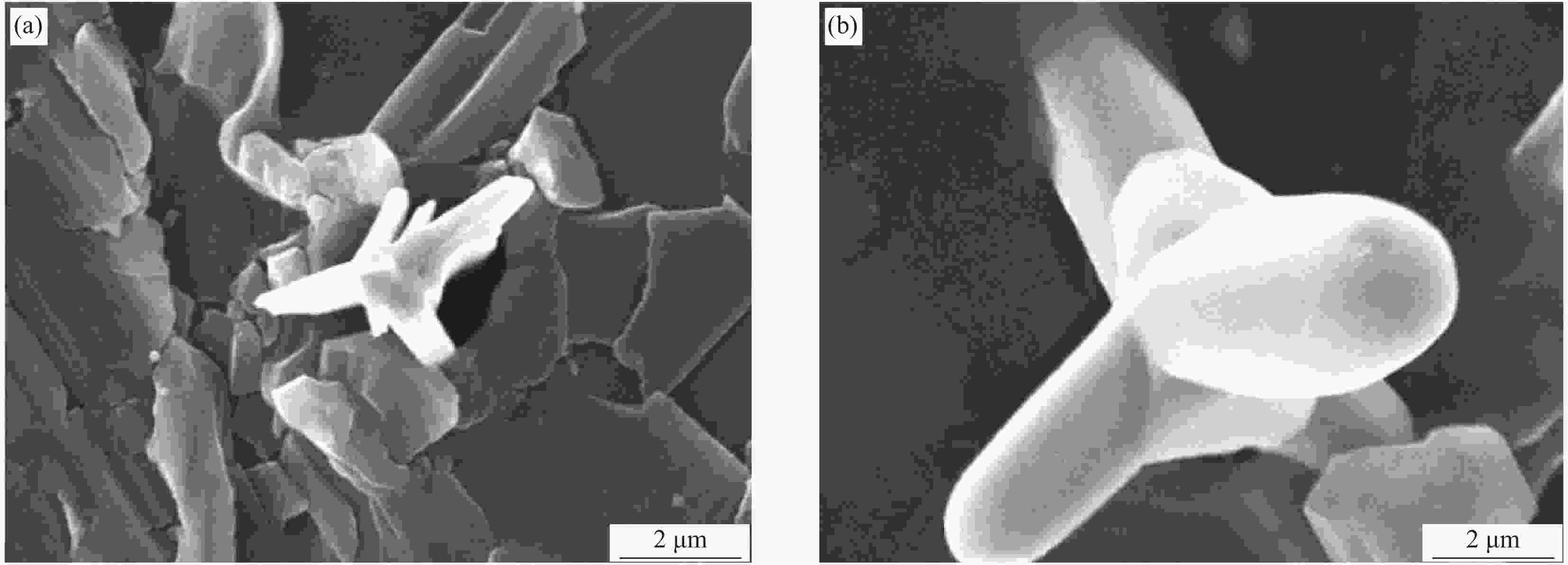
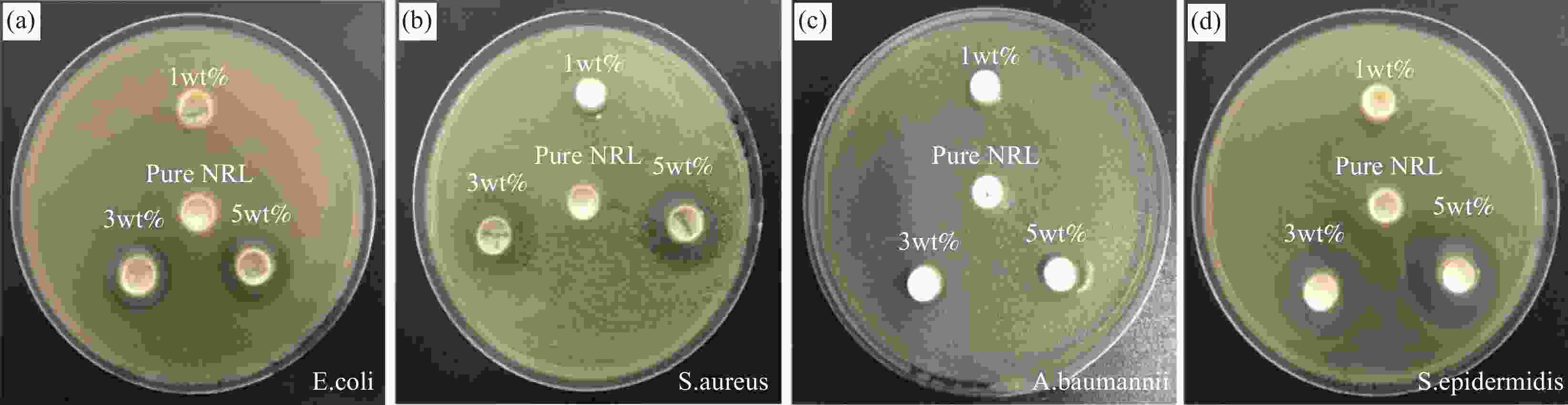
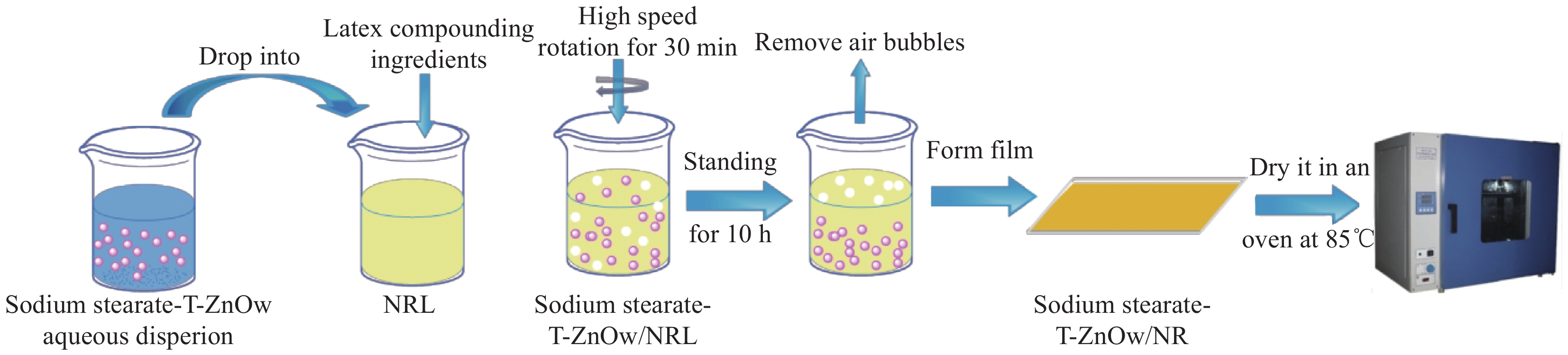
Preparation of tetra-needle-like zinc oxide whiskers/natural rubber antibacterial medical composites
-
摘要: 将硬脂酸钠改性四针状氧化锌晶须(Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw)超声分散液引入天然胶乳(NRL)基体中,制备了绿色环保的Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/橡胶(NR)抗菌医用复合材料。系统研究了Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR复合材料的综合力学性能、抗菌性能和热稳定性能。结果表明:当Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw含量达3wt%时,Sodium sterate-T-ZnOw/NR复合材料的综合力学性能,相比纯胶,邵尔A硬度,300%定伸应力,拉伸强度,撕裂强度,断裂伸长率,提高了8.6%、25.4%、20.3%、25.6%、6.4%。此时,复合材料的热稳定性能也达到了最大值,相比纯胶,复合材料的起始热降解温度(T0)和终止热降解温度(Tf)分别比纯胶的T0和Tf提高了21.2℃和5.9℃。当Sodiumstearate-T-ZnOw含量超过3wt%时,其能在天然胶乳中充分发挥抑制大肠杆菌、金葡萄球菌、鲍曼不动杆菌、表皮葡萄球菌生长的能力,它可以进入细菌细胞,导致细胞壁被破坏,细胞内成分泄漏,细胞死亡。Abstract: The sodium stearate-tetra-needle-like zinc oxide whiskers (T-ZnOw)/natural rubber (NR) antibacterial medical composites were prepared by introducing the sodium stearate-T-ZnOw ultrasonic dispersion into natural rubber latex (NRL) matrix. The comprehensive mechanical properties, antibacterial properties and thermal stability properties of the composites were systematically studied. The results show that when sodium stearate-T-ZnOw loading of 3wt%, the mechanical properties and thermal stability properties of the composites achieve optimum results. Compared with the pure NR, the shore a hardness, modulus at 300%, tensile strength, tear strength and elongation at break of composites are increased by 8.6%, 25.4%, 20.3%, 25.6% and 6.4%, respectively; The initial thermal degradation temperature (T0) and the termination thermal degradation temperature (Tf) of the composites are increased by 21.2℃ and 5.9℃. When the content of sodium stearate-T-ZnOw exceeds 3wt%, it can inhibit the growth of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter baumannii and Staphylococcus epidermidis in natural rubber latex. It can enter bacterial cells, resulting in cell wall damage, cell leakage, cell death.
-
表 1 硬脂酸钠(Sodium stearate)-四针状氧化锌晶须(T-ZnOw)与橡胶(NR)的配比
Table 1. Ratio of sodium stearate-tetra-needle-like zinc oxide whiskers (T-ZnOw) and natural rubber (NR)
Sample NR/wt% T-ZnOw/wt% Pure NR 100 0 1wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 100 1 2wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 100 2 3wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 100 3 4wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 100 4 5wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 100 5 Note: Pure NR has been added with curing agent. 表 2 T-ZnOw的活化指数
Table 2. Activation index of T-ZnOw
Mass fraction of sodium
stearate-T-ZnOw/wt%0 1 2 3 4 5 Activation index of
sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/%8.9 23.5 45.7 76.9 100 87.9 表 3 T-ZnOw/NR复合材料的综合力学性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of T-ZnOw/NR composites
Sample Shore A hardness/(°) Modulusat
300%/MPaTensile
strength/MPaTearStrength/
(kN·m−1)Elongationat
break/%Pure NR 35±1 1.42±0.06 23.47±0.54 28.24±0.33 823±10 1wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 36±1 1.51±0.05 28.08±1.08 31.37±0.65 839±8 2wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 37±1 1.64±0.07 31.13±0.75 33.76±0.54 856±7 3wt% Unmodified -T-ZnOw/NR 36±1 1.65±0.04 28.23±0.37 31.67±0.56 855±7 3wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 38±1 1.78±0.03 32.39±1.03 35.48±0.71 879±9 4wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 38±0 1.68±0.06 32.17±0.76 33.95±0.65 866±10 5wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 37±1 1.55±0.04 30.75±0.65 32.65±0.45 854±8 表 4 24 h后纯NRL和Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、鲍曼不动杆菌和表皮葡萄球菌的抑菌圈大小
Table 4. Inhibition zone diameter of the pure NRL and sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR against E.coil, S.aureus, A.baumannii and S.epidermidis after 24h
Sample Inhibition zone diameter/mm E.coli S.aureus A.baumannii S.epidermidis Pure NRL 0 0 0 0 1wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NRL 12.8 17.1 0 8.2 3wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NRL 17.6 20.8 8.7 22.6 5wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NRL 18.3 24.3 13.7 26.4 Notes: E.coli—Escherichia coli; S.aureus—Staphylococcus aureus; A.baumannii—Acineto bacterbaumannii; S.epidermidis—Staphylococcus epidermidis. 表 5 Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR复合材料在热降解中的特征温度
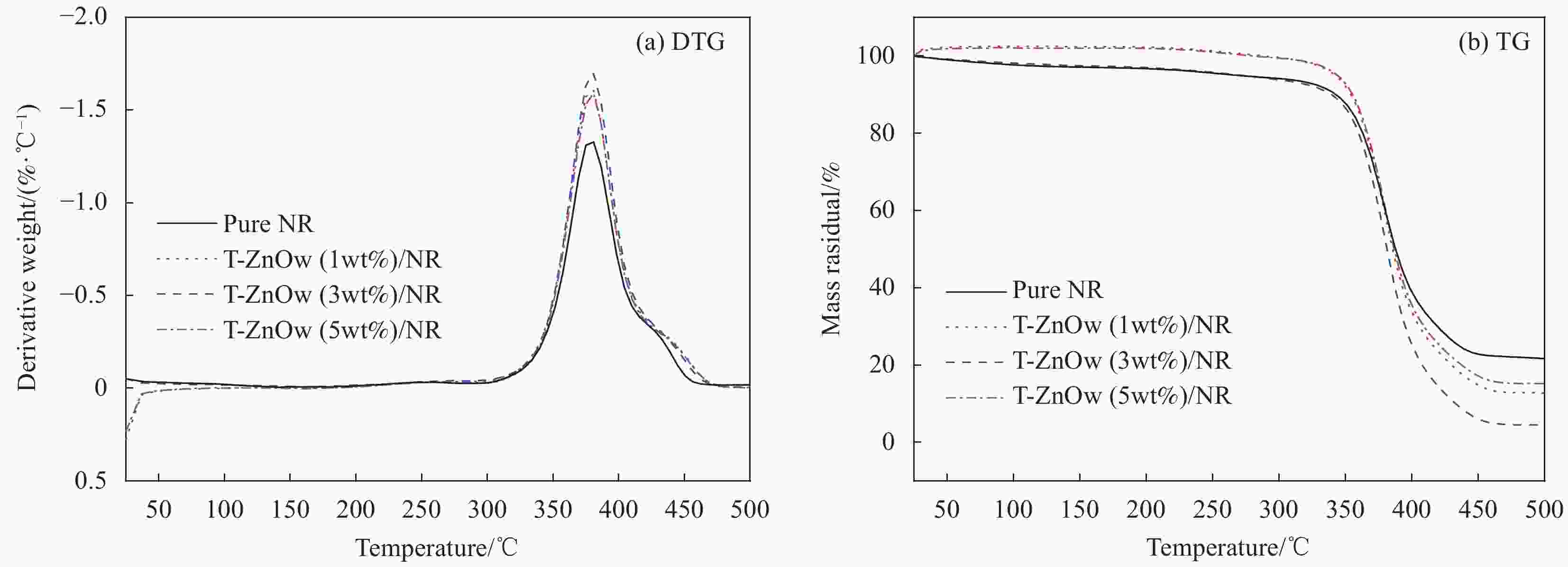
Table 5. Characteristic temperature of sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR in N2 atmosphere
Sample T0/℃ Tp/℃ Tf/℃ Pure NR 317.5 379.5 444.5 1wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 328.6 379.5 445.8 3wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 339.7 380.3 450.4 5wt% Sodium stearate-T-ZnOw/NR 334.3 380.0 442.1 Notes: T0—Initial thermal degradation temperature; Tp—Maximum thermal degradation temperature; Tf—Termination of thermal degradation temperature. -
[1] PENG Z, KONG L, LI S, et al. Self-assembled natural rubber/silica nanocomposites: Its preparation and characterization[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2007,67:3130-3139. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.04.016 [2] YAN N, WU J K, ZHAN Y H, et al. Carbon nanotubes/carbon black synergistic reinforced natural rubber compo-sites[J]. Plastics, Rubber and Composites,2009,38:290-296. doi: 10.1179/146580109X12473409436580 [3] CHEN X, HU Z, ZHANG F, et al. Natural rubber/tetra-needle-like zinc oxide whisker composites: Their preparation and characterization[J]. Journal of Polymer Engineering,2018,38:1-8. doi: 10.1515/polyeng-2016-0366 [4] FAIBUNCHAN P, PICHAIYUT S, CHUEANGCHAYAPHAN W, et al. Influence type of natural rubber on properties of green biodegradable thermoplastic natural rubber based on poly (butylene succinate)[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2019,30:1010-1026. doi: 10.1002/pat.4534 [5] ZHOU Y, KOSUGI K, YAMAMOTO Y, et al. Effect of non-rubber components on the mechanical properties of natural rubber[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2016,28:159-165. [6] LI C P, FENG C F, PENG Z, et al. Ammonium-assisted green fabriacation of graphene/natural rubber latex composite[J]. Polymer Composites,2013,34:88-95. doi: 10.1002/pc.22380 [7] SANTOS R J D, AGOSTINI D L D S, CABRERA F C et al. Sugarcane bagasse ash: new filler to natural rubber composite[J]. Polímeros,2014,24:646-653. doi: 10.1590/0104-1428.1547 [8] 姜国飞, 李旭飞, 刘芳, 等. 纳米ZnO-氧化石墨烯及ZnO-氧化石墨烯/水性聚氨酯复合涂层的抗菌性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7):1930-1938.JIANG G F, LI X F, LIU F, et al. Antibacterial properties of nano ZnO-graphene oxide and ZnO-graphene oxide/waterborne polyurethane composite coating[J]. Acta Matriae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(7):1930-1938(in Chinese). [9] 王德松, 张艳艳, 安静, 等. Ag/低分子量壳聚糖复合胶乳的制备及抗菌性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(5):1250-1257.WANG D S, ZHANG Y Y, AN J, et al. Preparation of Ag/low molecular weight chitosan composite colloids and their antibacterial activities[J]. Acta Matriae Compositae Sinica,2014,31(5):1250-1257(in Chinese). [10] 王静. 一种细菌纤维素/姜黄素复合材料的制备及表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7):1897-1902.WANG J. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose/curcumin composites[J]. Acta Matriae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(7):1897-1902(in Chinese). [11] CHAWLA K, CHAUHAN A P S, PANDEY A. Influence of different grades of furnace carbon blacks on curing kinetics and reinforcement of natural rubber composites[J]. Plastics, Rubber and Composites,2016,45:1-8. doi: 10.1080/14658011.2015.1110956 [12] PRASERTSRI S, RATTANASOM N. Fumed and precipitated silica reinforced natural rubber composites prepared from latex system: Mechanical and dynamic properties[J]. Polymer Testing,2012,31:593-605. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.03.003 [13] SOMARATNE M C W, LIYVANAGE N M V K, WALPALAGE S. Contribution of hydrogen and/or covalent bonds on reinforcement of natural rubber latex films with surface modified silica[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2014,131:40380-40387. [14] FAN X, ZHANG H, WANG J, et al. Influence of annealing temperature on field emission from tetrapod-shaped ZnO-whisker films obtained by screen printing[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,2010,13:400-404. doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2011.05.012 [15] FAN X, ZHAO L, ZHOU Z, et al. Impact of Al doping on microstructure and optical characteristics of tetrapod-like zinc oxide whiskers[J]. Physica B Condensed Matter,2010,405:2538-2541. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2010.03.026 [16] ZHOU Z, CHU L, HU S. Microwave absorption behaviors of tetra needle like ZnO whiskers[J]. Materials Science & Engineering B,2006,126:93-96. [17] GUO Z, XIONG J, YANG M, et al. Microstructure and properties of tetrapod-like ZnO whiskers reinforced Al matrix composite[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds,2008,461:342-345. [18] RATHNAYAK W, ISMAIL H, BAHARIN A, et al. Enhancement of the antibacterial activity of natural rubber latex foam by the incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2014,131:1-15. [19] PAN X, PENG L, LIU Y, et al. Highly antibacterial and toughened polystyrene composites with silver nanoparticles modified tetrapod-like zinc oxide whiskers[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2014,131(20):1366-1373. [20] PALMELA C, CHEVARIN C, XU Z, et al. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases,2018,67:574-587. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314903 [21] LINDEN D S V D, SHORT D, DITTMANN A, et al. Synergistic effects of ovine-derived cathelicidins and other antimicrobials against Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Staphylococcus aureus 1056 MRSA[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2009,31(8):1265-1267. doi: 10.1007/s10529-009-0010-9 [22] KIM J B, JUNG W H, RYU J M. Identification of a fibrinolytic enzyme by Bacillus vallismortis and its potential as a bacteriolytic enzyme against Streptococcus mutans[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2007,29(4):605-610. doi: 10.1007/s10529-006-9284-3 [23] 刘立华, 栾震, 陈梦玉, 等. 氢氧化铝阻燃剂的表面改性及在软质聚氯乙烯中的应用研究[J]. 首都师范大学学报, 2019, 40(2):37-41.LIU L H, LUAN Z, CHEN M Y, et al. Surface modification of aluminum hydroxide asflame retardant and its application in soft PVC[J]. Journal of Capital Normal University,2019,40(2):37-41(in Chinese). [24] 李丽匣, 韩跃新, 陶世杰. 碳酸钙晶须表面改性研究[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2008(5):4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7524.2008.05.002LI L X, HAN Y X, TAO S J. Research on surface modification of calcium carbonate whiskers[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing,2008(5):4-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7524.2008.05.002 [25] 周扬波, 古菊, 贾德民. 纳米碳酸钙的表面改性及其在橡胶中的应用[J]. 特种橡胶制品, 2004(3):54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4030.2004.03.018ZHOU Y B, GU J, JIA D M. Surface modification of nano-calcium carbonate and its application to rubber[J]. Special Purpose Rubber Products,2004(3):54-58(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4030.2004.03.018 [26] 姜玉芝, 韩跃新, 印万忠, 等. 碱式硫酸镁晶须表面改性研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2008, 4:60-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2008.05.016JIANG Y Z, HAN Y X, YIN W Z, et al. Study on surface modification of basic magnesium sulfate whiskers[J]. Metal Mine,2008,4:60-63(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2008.05.016 [27] 孙明赫, 孙秋菊, 代丽, 等. 碳酸钙和硼酸铝晶须的表面处理研究[J]. 沈阳师范大学学报, 2011, 29(3):417-420.SUN M H, SUN Q J, DAI L, et al. Surface modification of calcium carbonate whiskers and aluminum borate whiskers[J]. Journal of Shenyang Normal University,2011,29(3):417-420(in Chinese). [28] 童柯锋, 杨小波, 杨冬冬, 等. 硬脂酸改性氢氧化镁分散性能的研究[J]. 盐业与化工, 2013, 42(11):32-38.TONG K F, YANG X B, YANG D D, et al. Research on dispersing performance of magnesium hydroxide modified by stearic acid[J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry,2013,42(11):32-38(in Chinese). [29] 杨统林, 赵中华, 肖建军, 等. 硬脂酸改性纳米氧化铝的工艺[J]. 南昌大学学报, 2018, 40(1):8-12.YANG T L, ZHAO Z H, XIAO J J, et al. Surface modification process of nano-Al2O3 with stearic acid[J]. Journal of Nanchang University,2018,40(1):8-12(in Chinese). [30] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性压入硬度试验方法 第1部分: 邵氏硬度计法: GB/T 531—2008[S]. 北京: 国家标准出版社, 2008.Stadardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of in-dentation hardness-Part 1: Duromerer method: GB/T 531-2008[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008 (in Chinese). [31] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶拉伸应力应变性能的测定: GB/T 528—2009[S]. 北京: 国家标准出版社, 2009.Stadardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of stress-strain: GB/T 528—2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009 (in Chinese). [32] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶拉伸应力应变性能的测定: GB/T 529—2008[S]. 北京: 国家标准出版社, 2008.Stadardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of tear stress-strain: GB/T 529—2008 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008 (in Chinese). [33] 武志富, 李素娟. 氢氧化锌和氧化锌的红外光谱特征[J]. 光谱实验室, 2012, 29(4):2172-2175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2012.04.052WU Z F, LI S J. Infrared spectra characteristics of zinc hydroxide and zinc oxide[J]. Chinese Journal Spectroscopy Laboratory,2012,29(4):2172-2175(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2012.04.052 [34] 王晓梅, 郑涛, 马琳, 等. 荞麦七提取物的体外抑菌活性研究[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2015, 32(5):40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2015.05.010WANG X M, ZHENG T, MA L, et al. Optimization of extract process of total flavonoids from blueberry leaves by ultrasonic method[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering,2015,32(5):40-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2015.05.010 [35] 宋庆平, 丁纯梅. 壳聚糖Ag微球配合物抑菌性能的研究[J]. 安徽工程科技学院学报, 2010, 25(1):5-7.SONG Q P, DING C M. Study on antibacterial properties of microsphere-chitosan silver complex[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Technology and Science,2010,25(1):5-7(in Chinese). [36] 杨婧, 林宇星, 刘莘轶, 等. 利用Mariannaea sp. HJ菌株胞内提取物合成纳米银及其抗菌特性研究[J]. 微生物学报, 2020, 60(4):749-758.YANG J, LIN Y X, LIU X Y, et al. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by the cell-free extracts of Mariannaea sp. HJ and their antimicrobial characteristics research[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2020,60(4):749-758(in Chinese). [37] 项荣, 丁栋博, 范亮亮, 等. 氧化锌的抗菌机制及其安全性研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(3):470-475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.03.023XIANG R, DING D B, FAN L L, et al. Antibacterial mechanism and safety of zinc oxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2014,18(3):470-475(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.03.023 [38] BHADRA P, MITRA M K, DAS G C, et al. Interaction of chitosan capped ZnO nanorods with Escherichia coli[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2011,31(5):929-937. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2011.02.015 [39] RAGHUPATHI K R, KOODALI R T, MANNA A C. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles[J]. Langmuir,2011,27(7):4020-4028. doi: 10.1021/la104825u [40] ZHANG L, DING Y, POVEY M, et al. ZnO nanofluids-A potential antibacterial agent[J]. Progress in Natural Science,2008,18(8):939-944. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.01.026 [41] AMNA T, HASSAN M S, BARAKAT N A M, et al. Antibacterial activity and interaction mechanism of electrospun zinc-doped titania nanofibers[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2012,93(2):743-751. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3459-0 [42] WAHAB R, KIM Y S, MISHRA A, et al. Formation of ZnO micro-flowers prepared via solution process and their antibacterial activity[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters,2010,5(10):1675-1681. doi: 10.1007/s11671-010-9694-y [43] 马建中, 惠爱平, 刘俊莉. 纳米ZnO抗菌材料的研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2014, 45(24):24001-24007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.24.001MA J Z, HUI A P, LIU J L. Research progress on antibacterial materials of nano-ZnO[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2014,45(24):24001-24007(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.24.001 [44] LI Y, ZHANG W, NIU J, et al. Mechanism of photogenerated reactive oxygen species and correlation with the antibacterial properties of engineered metal-oxide nanoparticles[J]. ACS Nano,2012,6(6):5164-5173. doi: 10.1021/nn300934k [45] XIA T, KOVOCHICH M, LIONG M, et al. Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nano-particles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties[J]. ACS Nano,2008,2(10):2121-2134. doi: 10.1021/nn800511k [46] ABDULRAHMAN S H H, CHANDRASEKAEAN K, SEEMAISAMY S, et al. Impact of alkaline metal ions Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ on the structural, optical, thermal and antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by the coprecipitation method[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2013,1:5956-5962. [47] ANSARI S A, KHAN M M, ANSARI M O, et al. Biogenic synthesis, photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance of Ag-ZnO Nanocomposite[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2013,117:27023-27030. doi: 10.1021/jp410063p [48] 胡占江, 赵忠, 王雪梅. 纳米氧化锌抗菌性能及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(3):527-530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2012.03.033HU Z J, ZHAO Z, WANG X M. Antibacterial properties and mechanism of nano-zinc oxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2012,16(3):527-530(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2012.03.033 [49] 陈晰, 何慧卿, 简璐璐, 等. 碱式硫酸镁晶须/橡胶基复合材料的制备[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11):3137-3145.CHEN X, HE H Q, JIAN L L, et al. Preparation and characterization of magnesium oxysulfate whiskers/natural rubber composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(11):3137-3145(in Chinese). [50] CHEN X, QIU T. Natural rubber composites reinforced with basic magnesium oxysulfate whiskers: Processing and ultraviolet resistance/flame retardant properties[J]. Polymer Testing,2020,81:106271. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.106271 -





 下载:
下载: