Mechanical properties and toughening mechanism of polyurethane epoxy resin composite materials
-
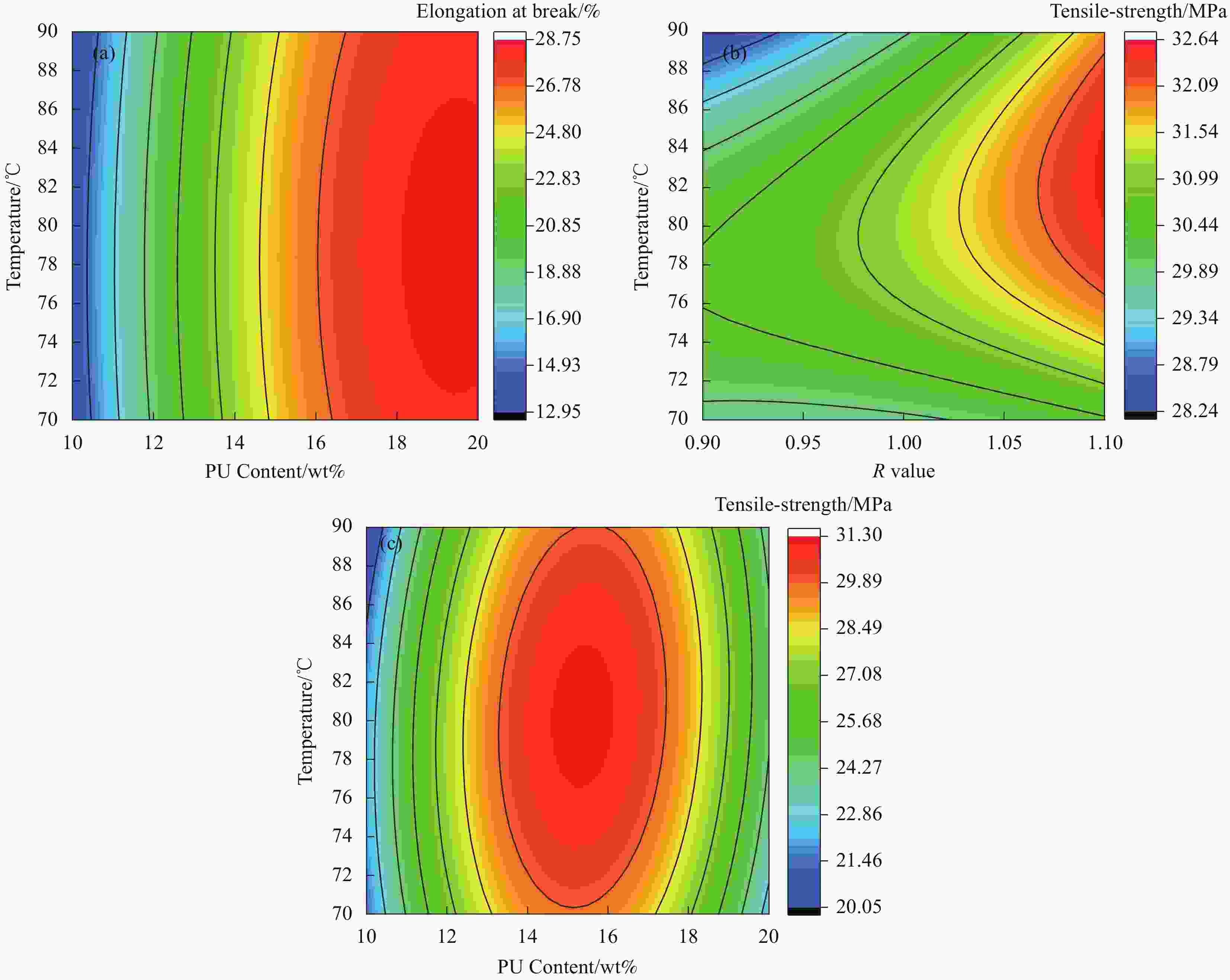
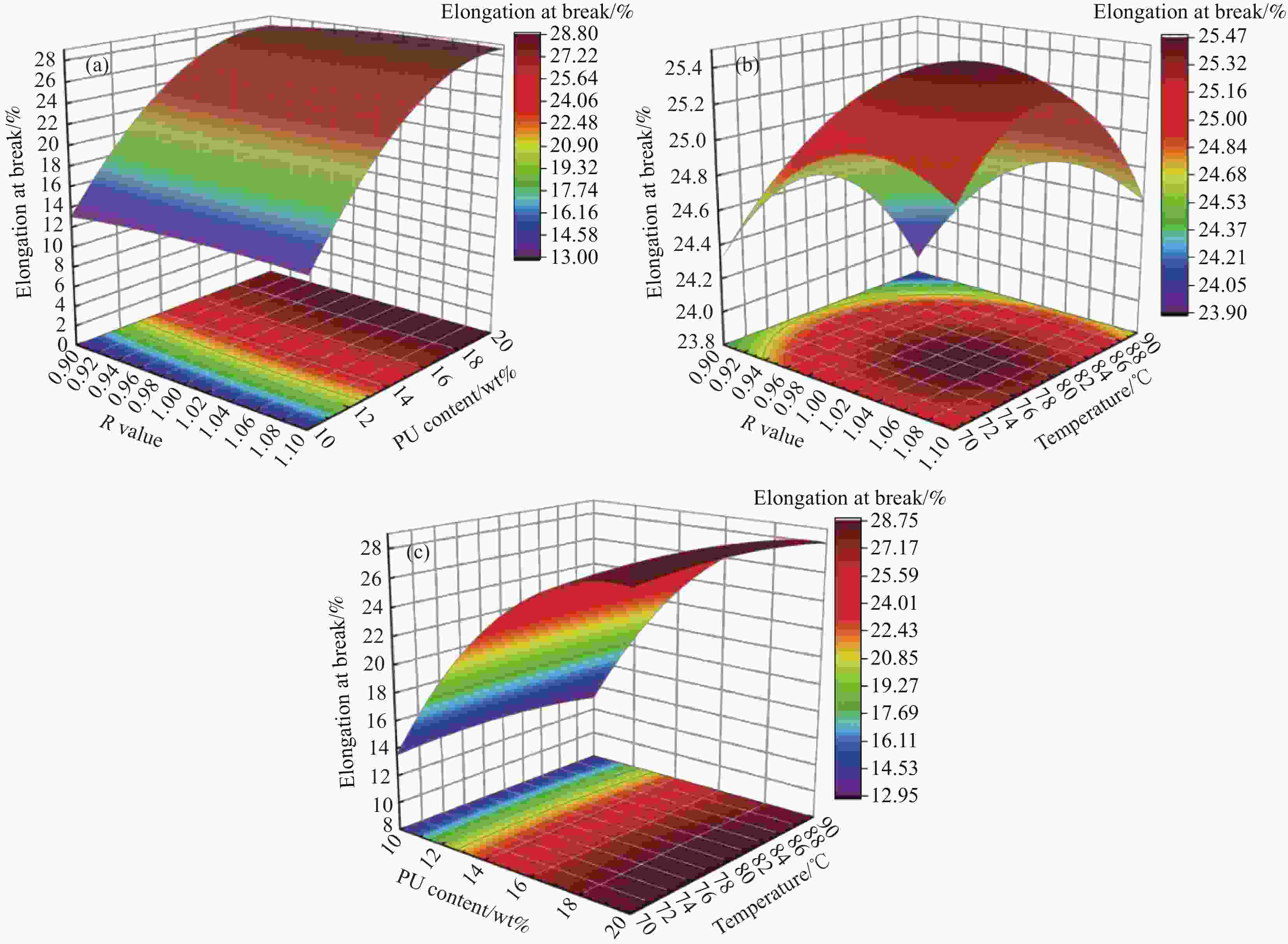
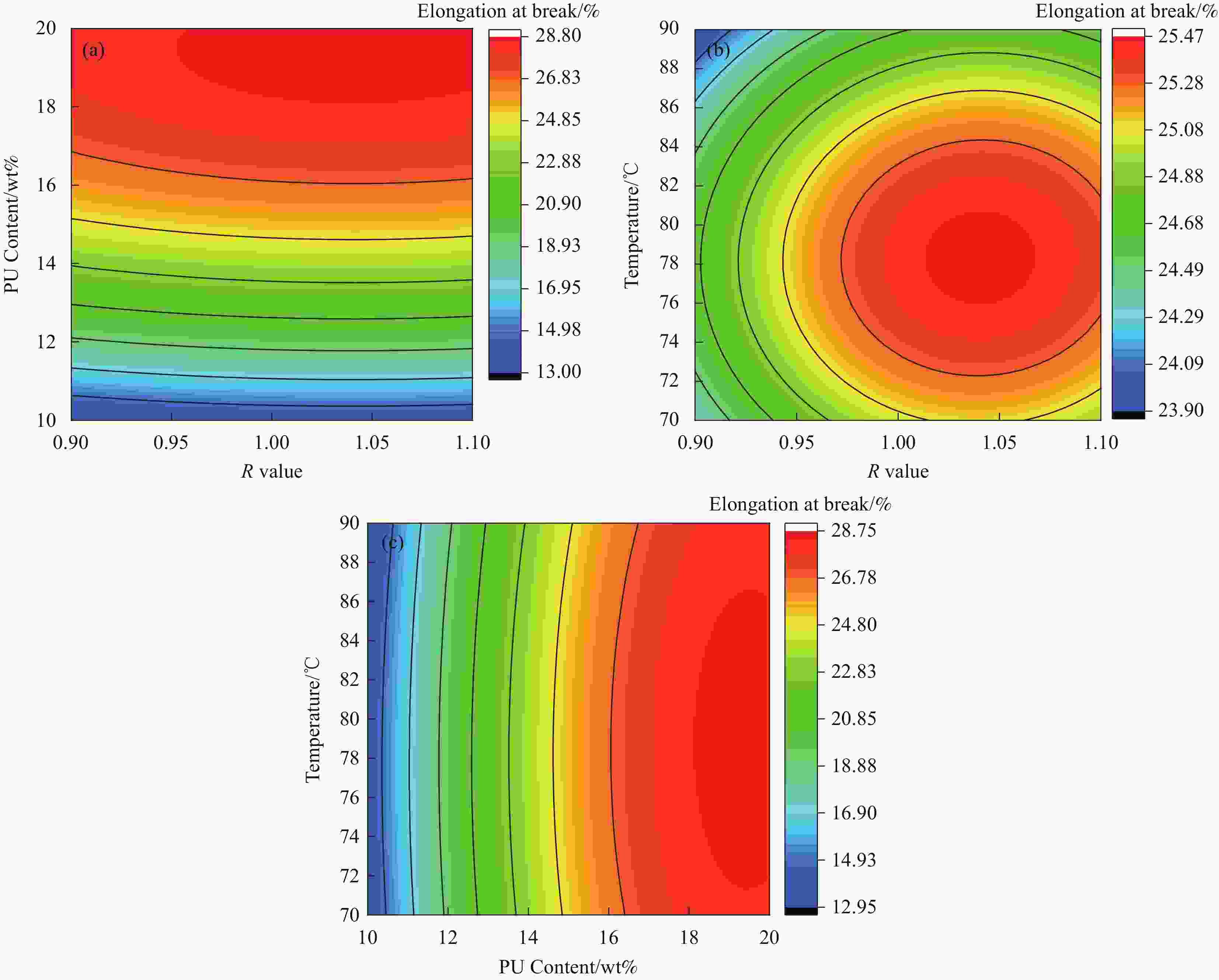
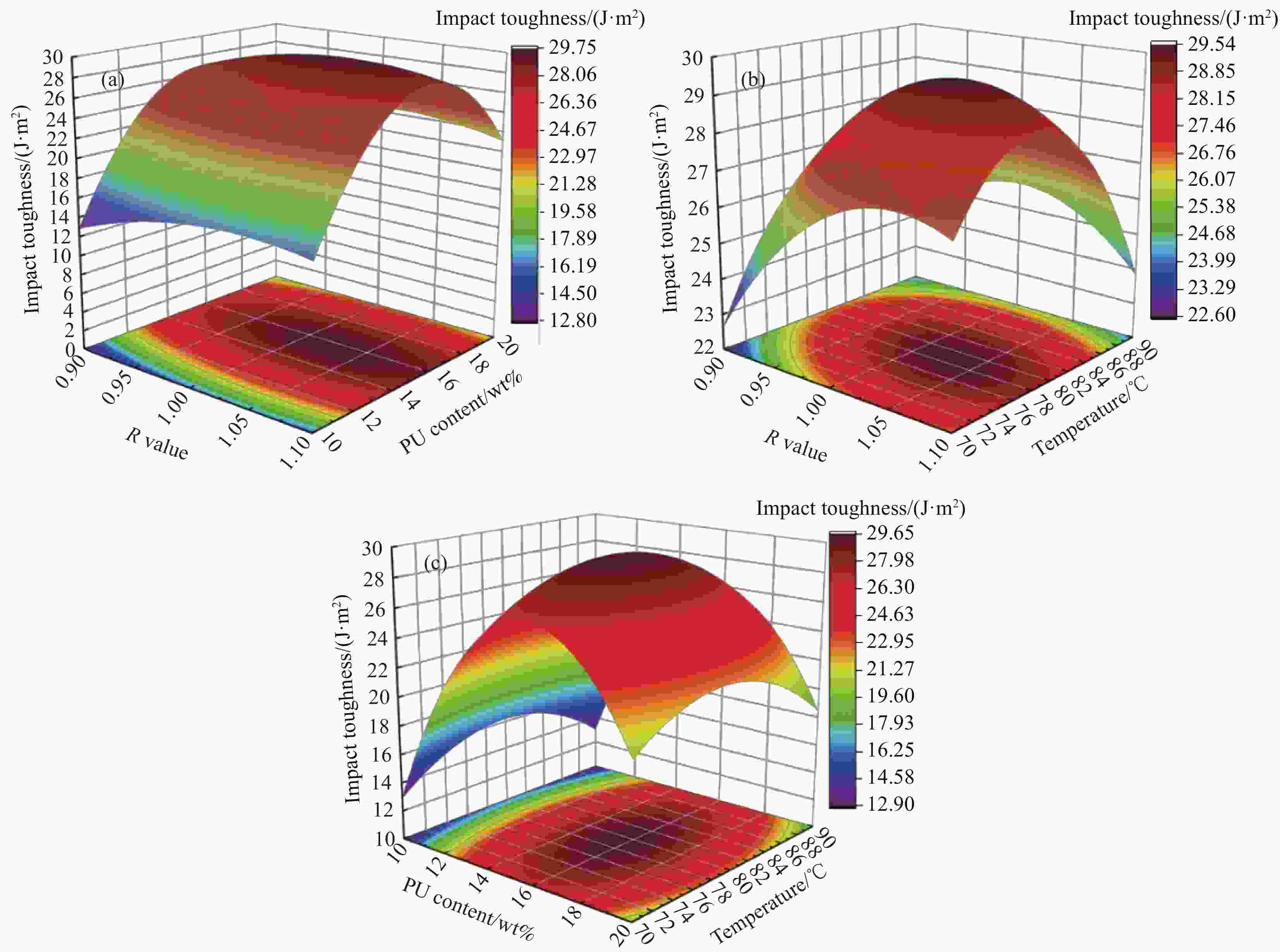
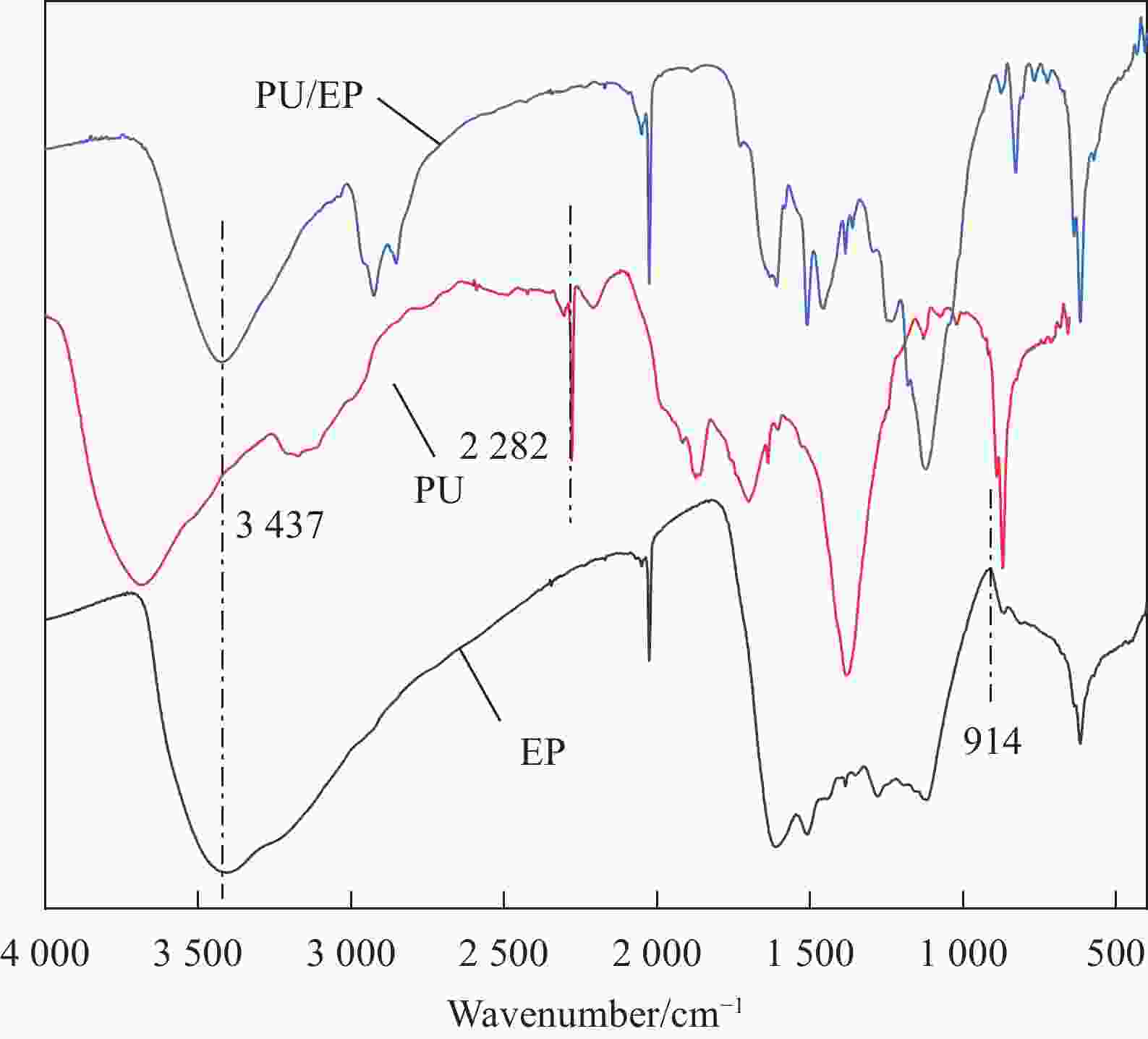
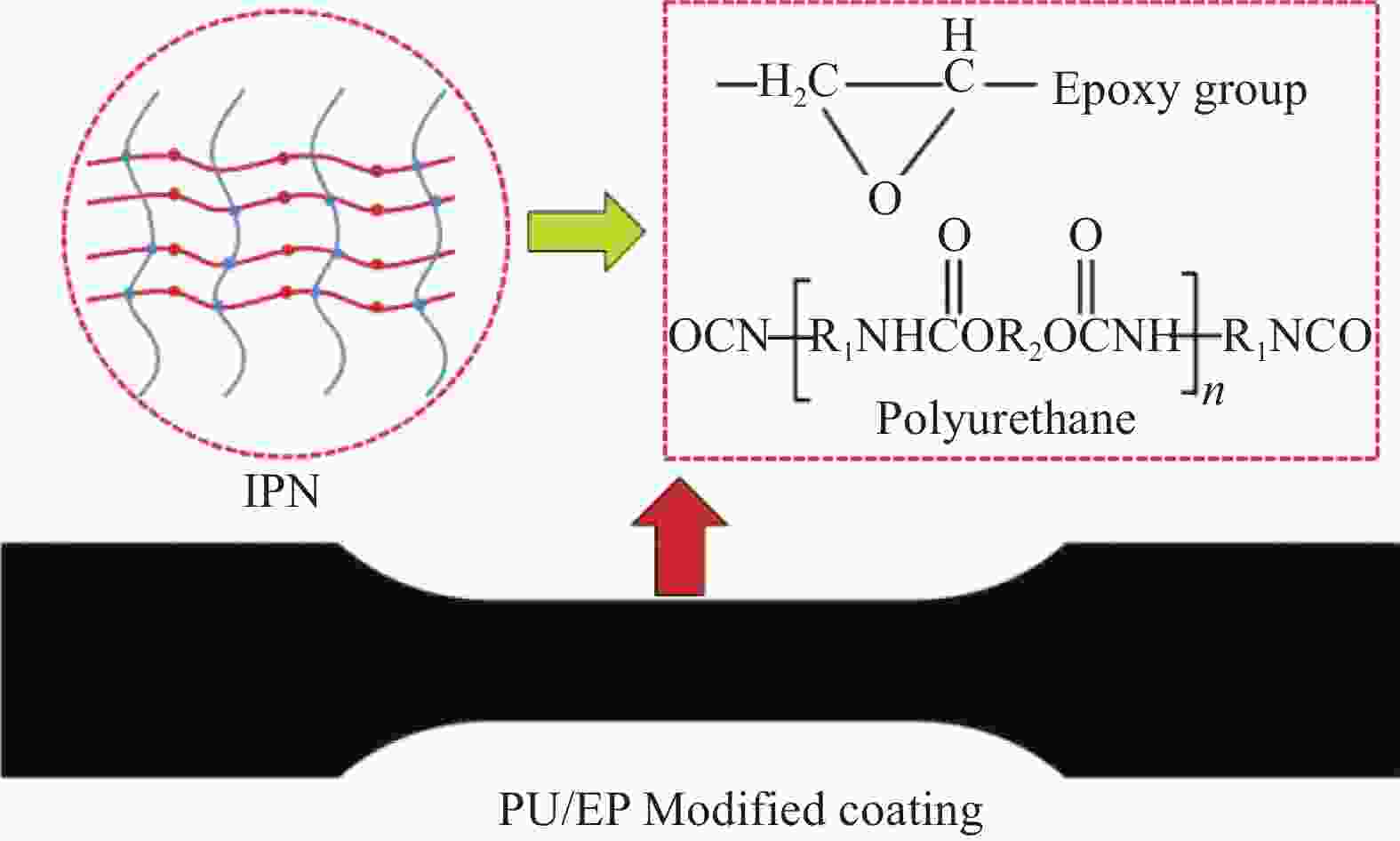
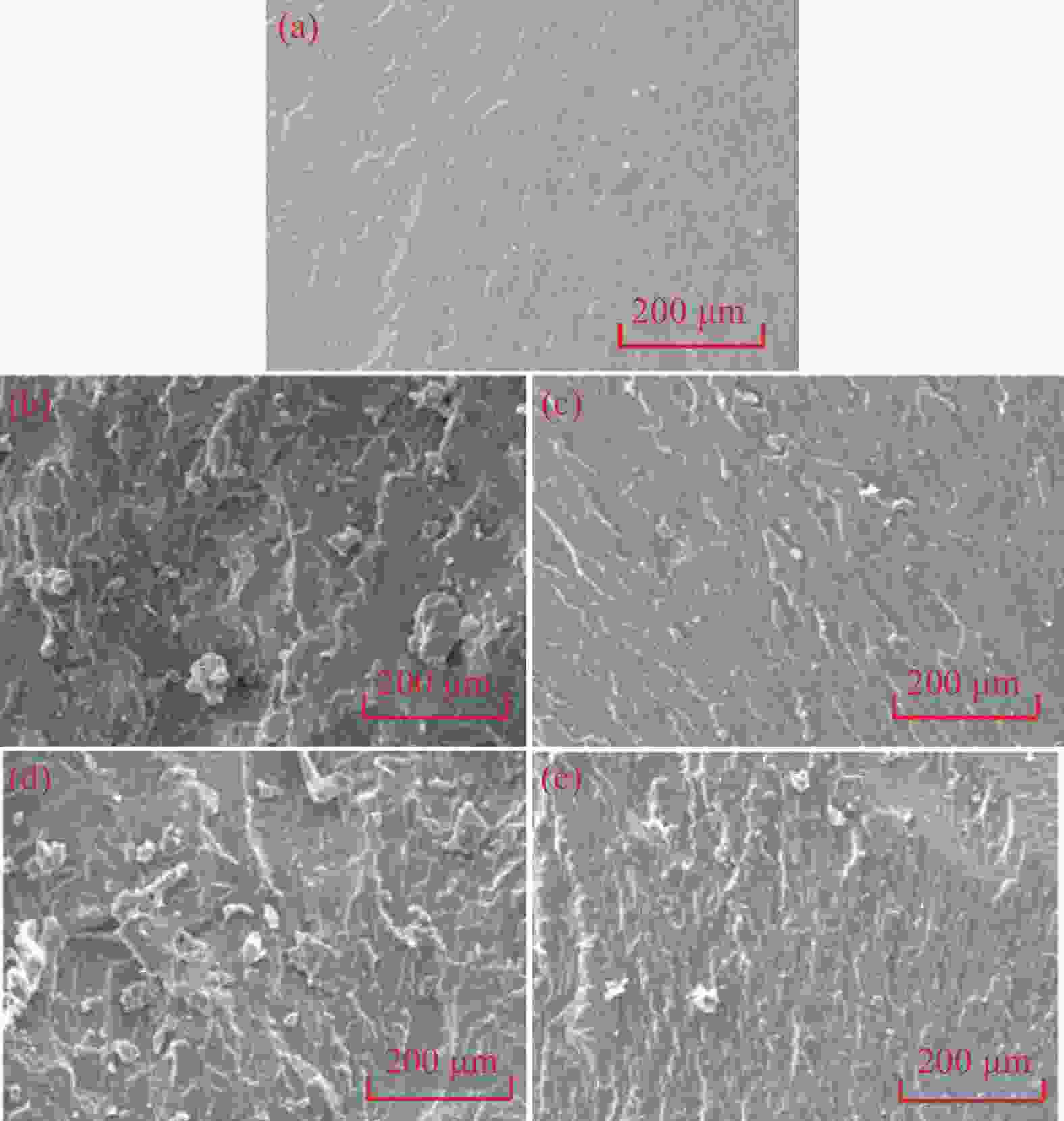
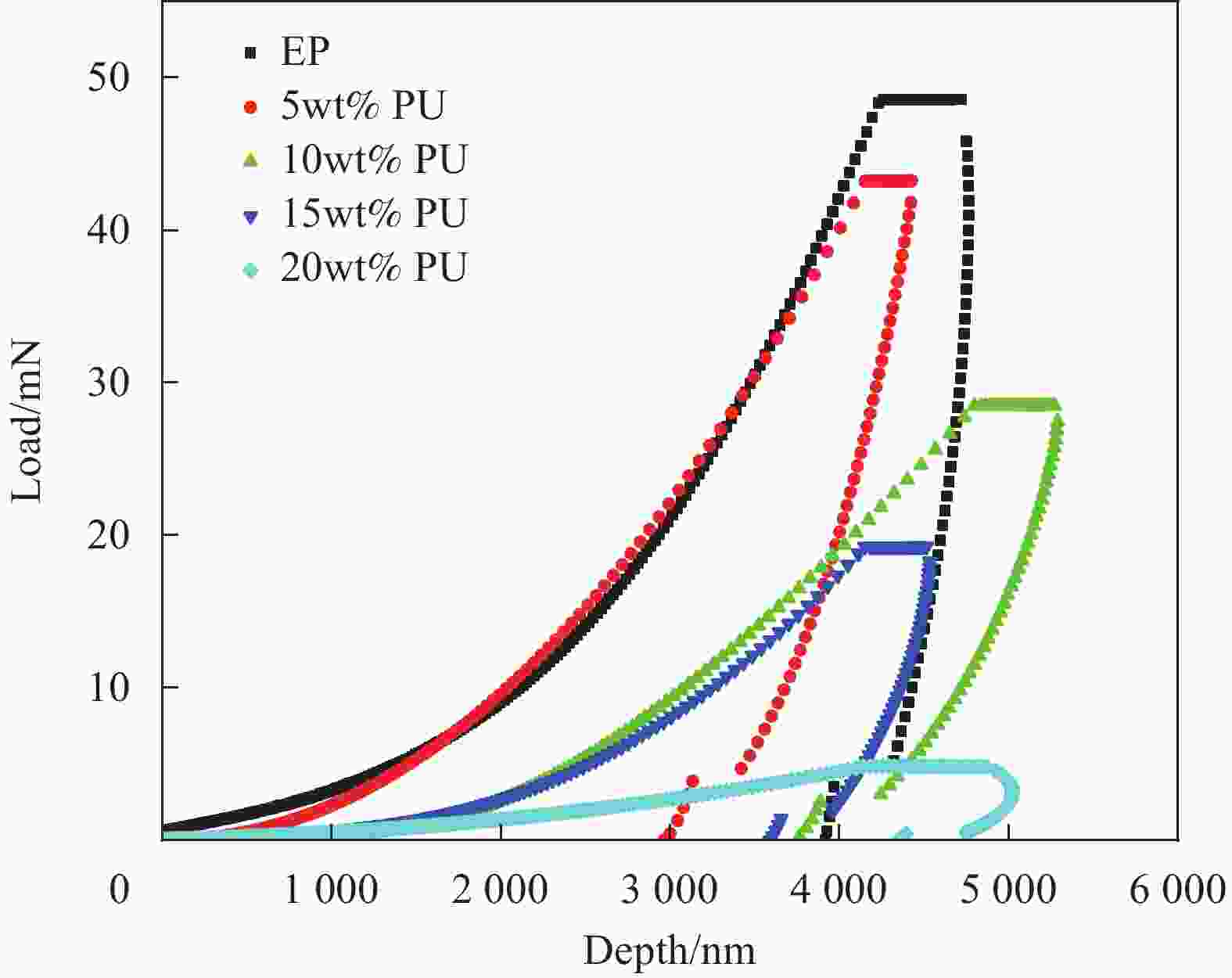
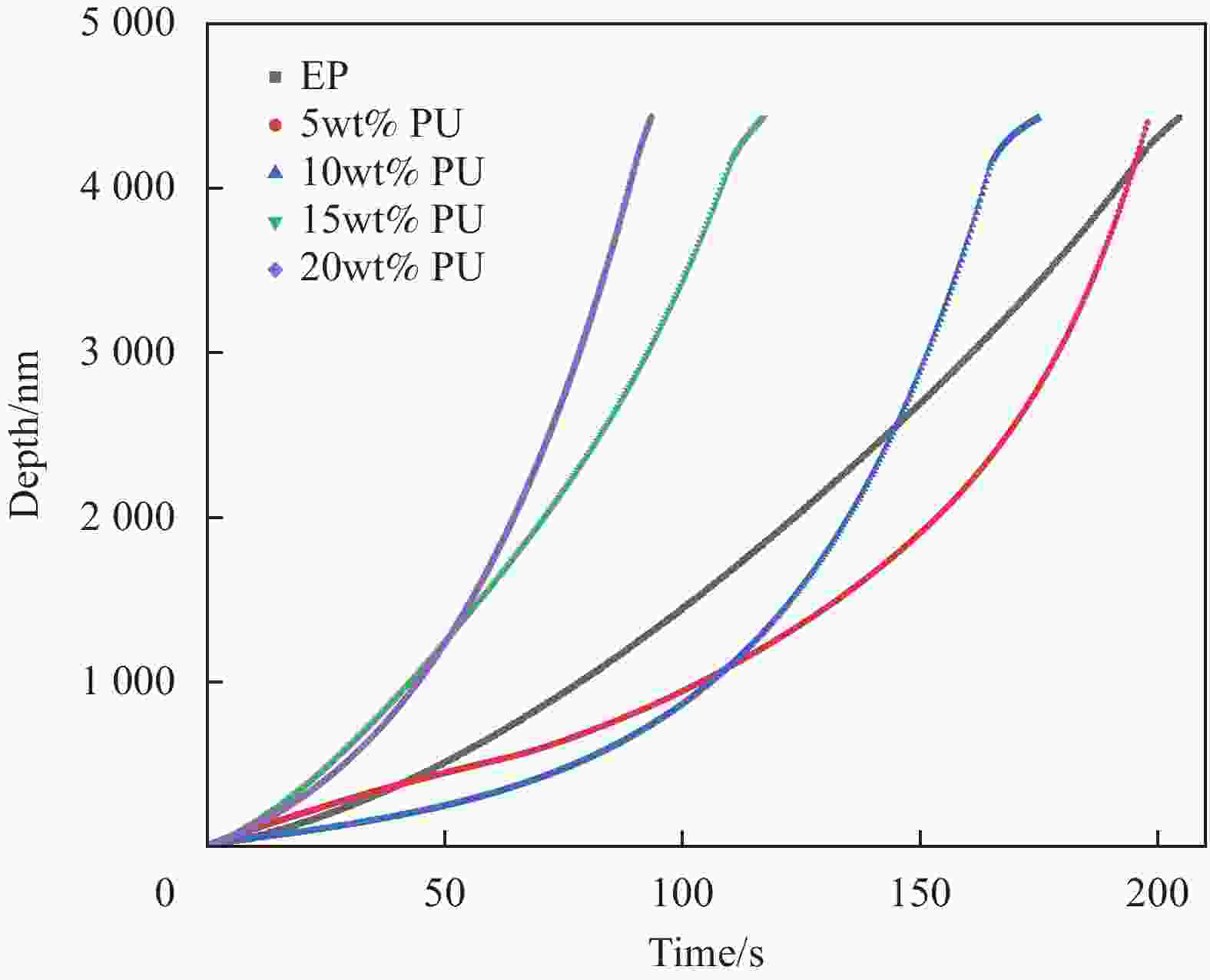
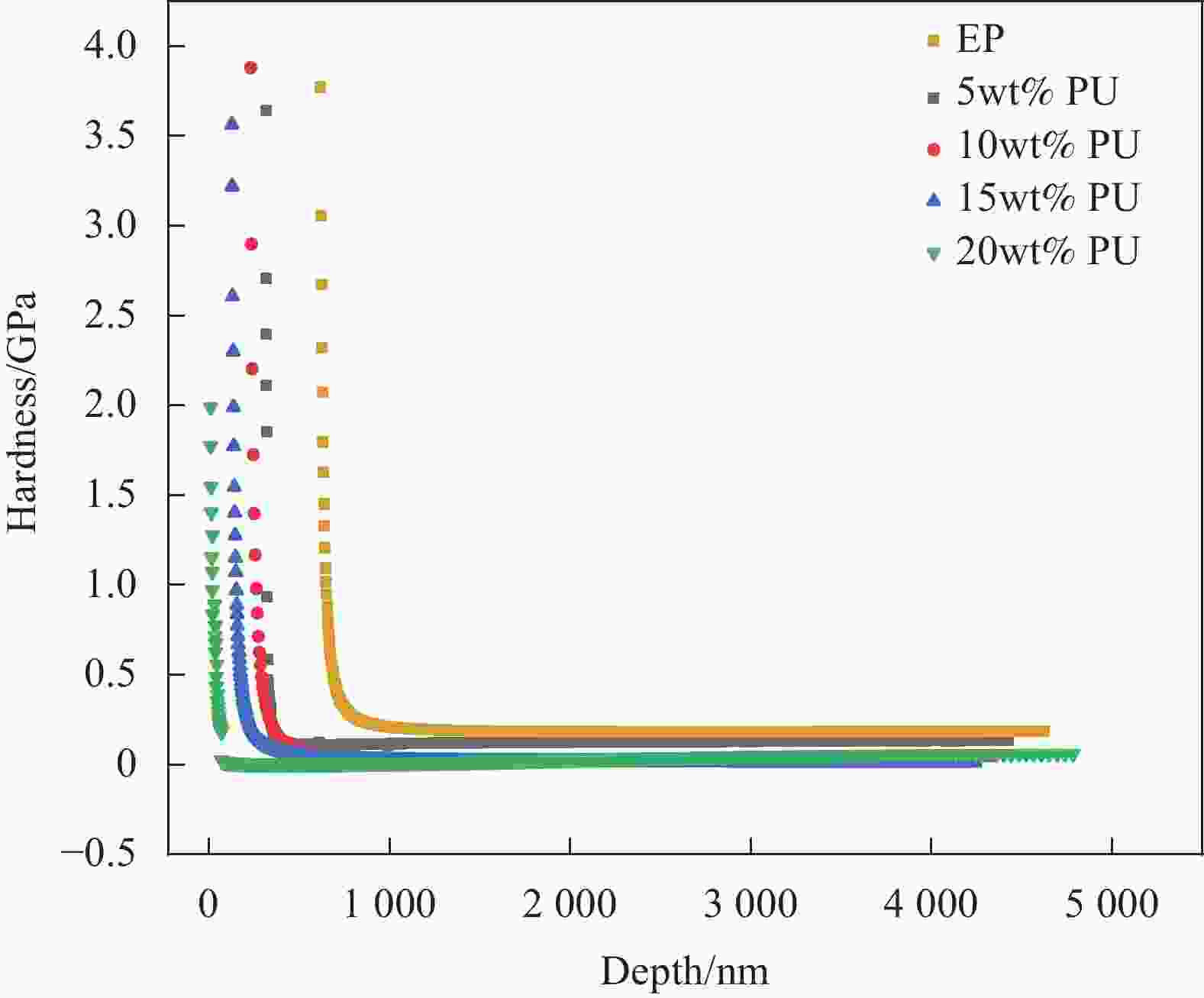
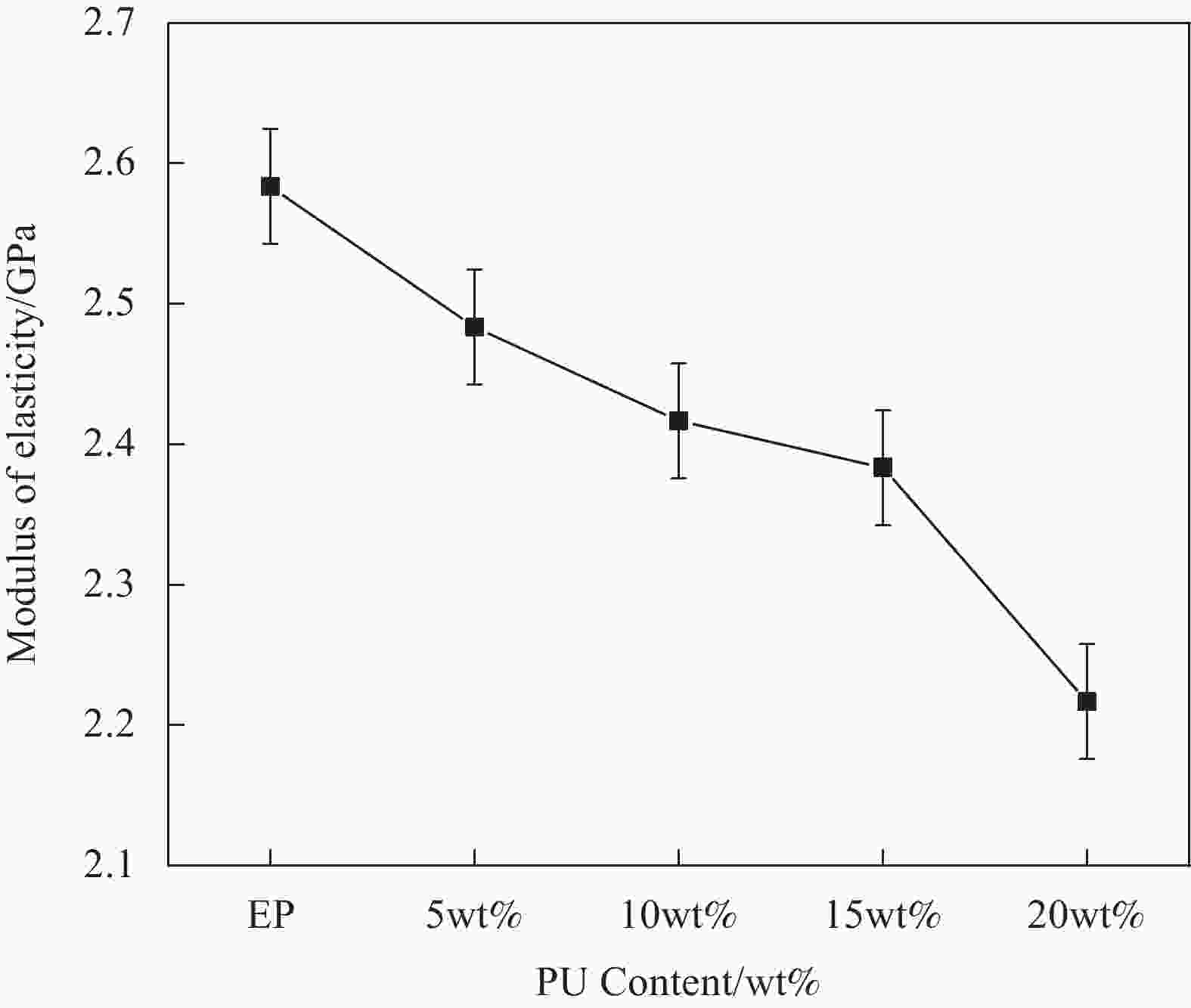
摘要: 环氧树脂材料固化后脆性大、韧性差,表面容易发生老化、龟裂、剥落等问题,难以保护混凝土应对海工环境等复杂的工况。设计、制备了不同体系的聚氨酯/环氧树脂(PU/EP)复合材料,以PU/EP复合材料的拉伸强度、断裂伸长率、冲击韧性作为评价指标进行了正交实验,结合响应面分析法确定了PU/EP复合材料的最佳制备配方为:R值为1、PU掺量为15wt%、制备温度为80℃。研究结果表明:聚氨酯(PU)和EP交联效果良好,PU/EP复合材料的拉伸强度、断裂伸长率、冲击韧性较纯环氧树脂分别提高37.61%、52.21%、47.07%。随着PU掺量的增加,材料中柔性长链段的比例增大,形成二级网络的区域增大,分子间的配位作用以及软连段的增加极大提高了材料的力学性能,并且PU/EP复合材料的硬度和弹性模量有一定程度的降低。Abstract: Epoxy resin materials have high brittleness and poor toughness, and are prone to aging, cracking, and peeling on the surface, making it difficult to protect concrete from complex working conditions such as marine environments. Polyurethane/Epoxy resin (PU/EP) composite materials with different systems were designed, and orthogonal experiments were conducted using the tensile strength, fracture elongation, and impact toughness of PU/EP composite materials as evaluation indicators. The optimal preparation formula for PU/EP composite materials was determined through response surface analysis method, with an R value of 1, a PU content of 15wt%, and a preparation temperature of 80℃. The results showed that the crosslinking effect of PU and EP was good, and the tensile strength, fracture elongation, and impact toughness of PU/EP composite materials were improved by 37.61%, 52.21%, and 47.07% compared to pure epoxy resin, respectively. With the increase of PU content, the proportion of flexible long chain segments in the material increases, and the area forming the secondary network increases. The coordination effect between molecules and the increase of soft connecting segments greatly improved the mechanical properties of the material, and the hardness and elastic modulus of PU/EP composite materials are reduced to a certain extent.
-
Key words:
- Epoxy resin /
- Polyurethane /
- Toughened design /
- Mechanical /
- Toughening mechanism
-
表 1 聚氨酯/环氧树脂(PU/EP)复合材料的正交实验设计表
Table 1. Orthogonal test design table of Polyurethane/Epoxy resin (PU/EP) composite
Group number A Numerical
valueB
Dosage/%C Temperature/
℃1(A1B1C1) 0.8 5 70 2(A1B2C2) 0.8 10 80 3(A1B3C3) 0.8 15 90 4(A1B4C4) 0.8 20 100 5(A2B1C2) 0.9 5 80 6(A2B2C1) 0.9 10 70 7(A2B3C4) 0.9 15 100 8(A2B4C3) 0.9 20 90 9(A3B1C3) 1.0 5 90 10(A3B2C4) 1.0 10 100 11(A3B3C1) 1.0 15 70 12(A3B4C2) 1.0 20 80 13(A4B1C4) 1.1 5 100 14(A4B2C3) 1.1 10 90 15(A4B3C2) 1.1 15 80 16(A4B4C1) 1.1 20 70 表 2 PU/EP复合材料测试结果
Table 2. Test results of PU/EP composite
Group number Tensile strength/MPa Elongation at break/% Impact Strength/(J·m−2) 1(A1B1C1) 22.12 14.30 20.33 2(A1B2C2) 21.08 18.24 21.01 3(A1B3C3) 24.25 20.15 25.15 4(A1B4C4) 20.65 23.22 27.33 5(A2B1C2) 19.85 14.73 17.54 6(A2B2C1) 22.31 15.21 21.23 7(A2B3C4) 24.67 23.45 25.33 8(A2B4C3) 18.23 26.51 25.55 9(A3B1C3) 23.44 14.45 18.44 10(A3B2C4) 25.15 18.72 23.87 11(A3B3C1) 32.35 25.34 30.40 12(A3B4C2) 21.89 26.42 24.43 13(A4B1C4) 22.84 14.16 16.44 14(A4B2C3) 24.54 15.74 20.45 15(A4B3C2) 29.64 20.14 26.88 16(A4B4C1) 21.89 30.41 23.58 表 3 PU/EP复合材料实验设计与力学性能
Table 3. Experimental Design and Results of PU/EP composite
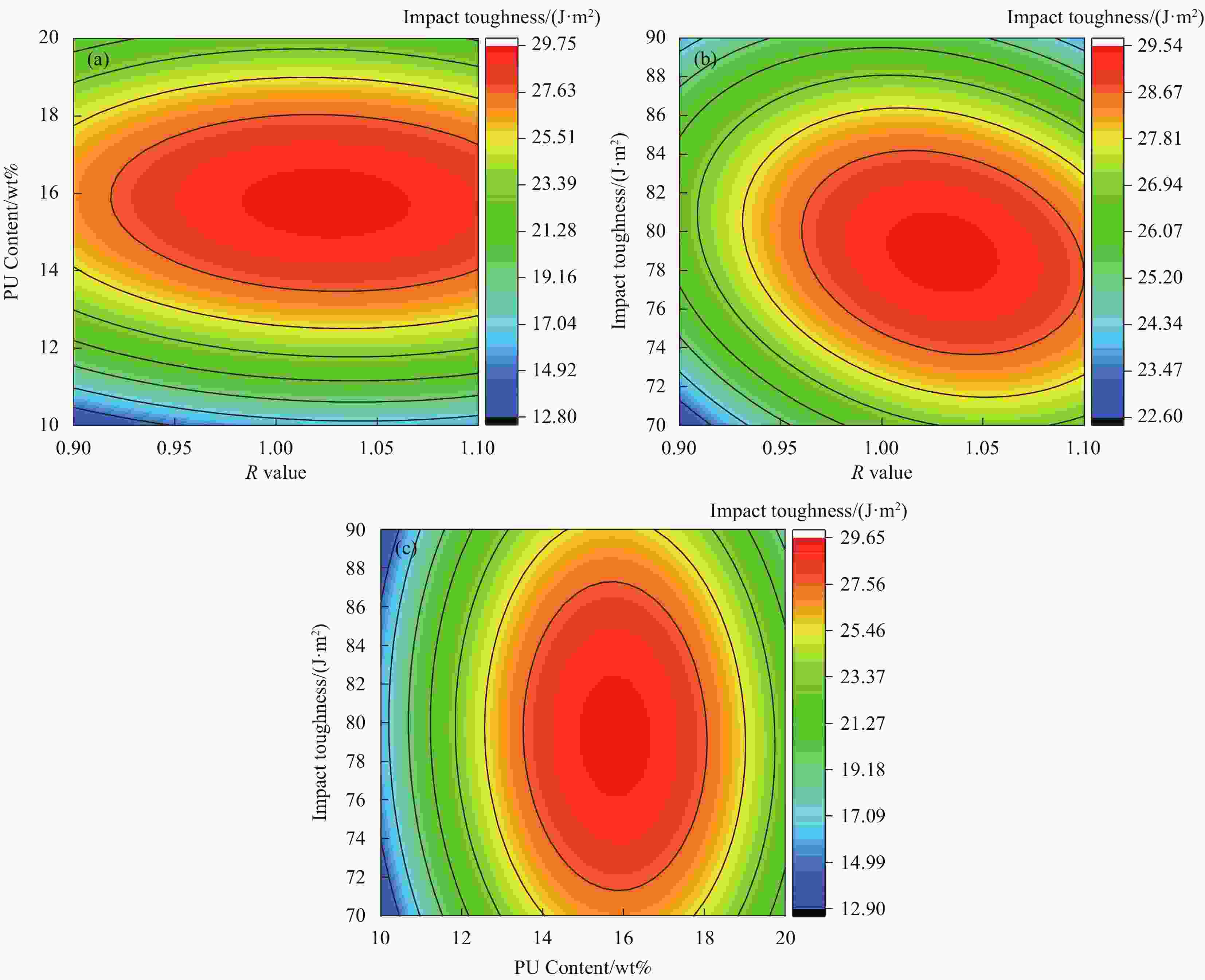
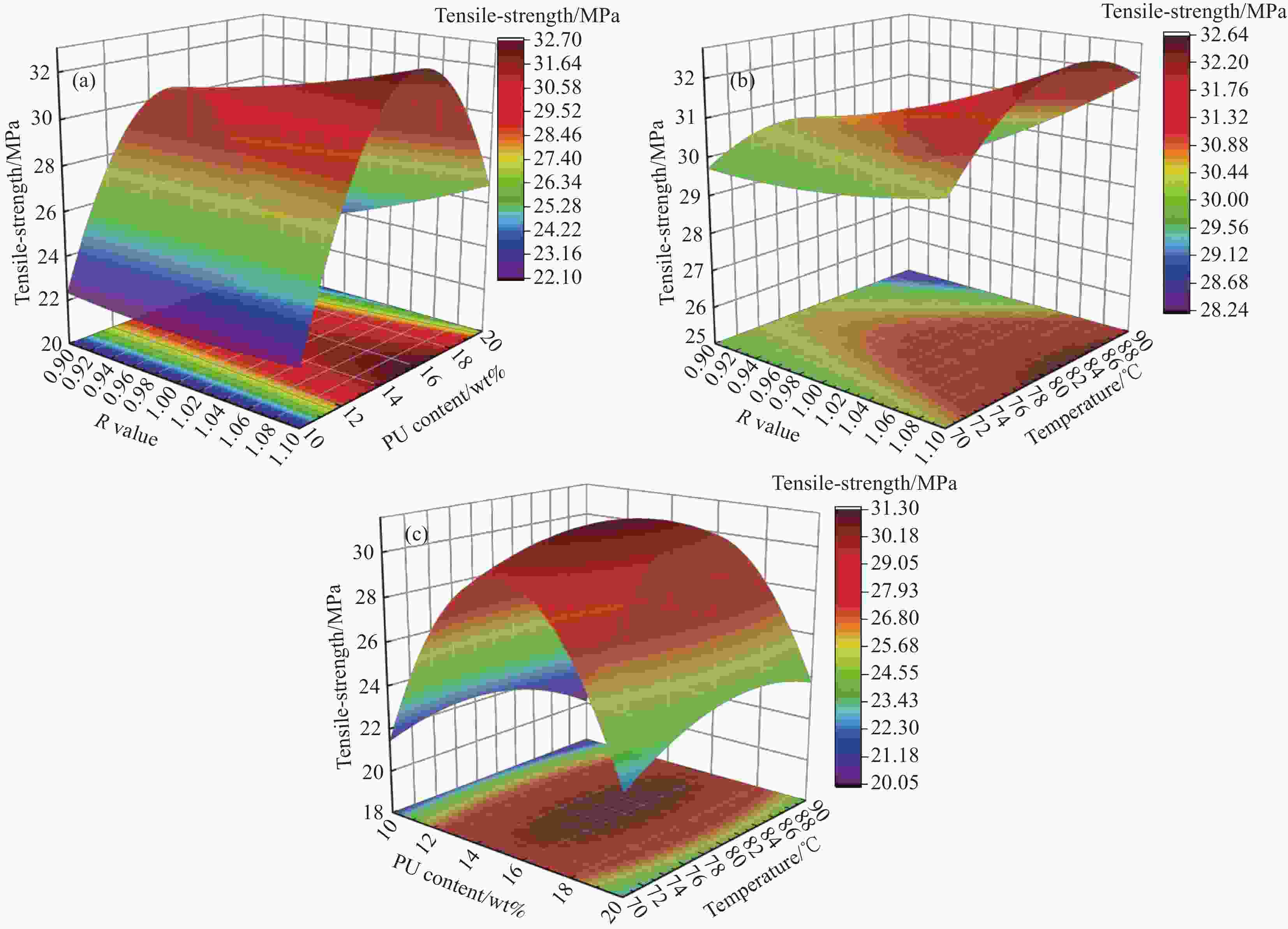
Number R Dosage/wt% Temperature/℃ Tensile strength/MPa Elongation at break/% Impact Strength/(J·m−2) 1 1.0 20 70 21.75 28.04 19.87 2 1.1 15 70 30.50 24.53 27.33 3 1.1 10 80 22.11 14.24 15.53 4 1.1 15 90 31.63 23.88 24.02 5 1.0 20 90 23.53 28.15 18.67 6 0.9 15 70 29.96 25.04 22.43 7 0.9 15 90 28.13 24.32 23.33 8 1.0 15 80 31.14 25.37 28.35 9 1.0 15 80 31.03 25.21 28.87 10 0.9 20 80 22.89 27.42 20.58 11 1.0 15 80 30.76 25.30 29.33 12 1.0 15 80 32.35 26.21 30.40 13 1.0 10 90 20.66 13.21 13.24 14 1.1 20 80 27.23 29.25 20.67 15 0.9 10 80 21.89 12.41 13.24 16 1.0 15 80 30.80 24.87 29.86 17 1.0 10 70 21.61 13.44 12.67 表 4 回归方差分析
Table 4. Analysis of Regression Variance
Source Sum of squares Freedom Mean square F P Model 306.82 9 34.09 73.59 <0.0001 A 9.25 1 9.25 19.96 0.0029 B 10.42 1 10.42 22.49 0.0021 C 0.002113 1 0.002113 0.00456 0.9480 AB 4.24 1 4.24 9.16 0.0192 AC 2.19 1 2.19 4.73 0.0662 BC 1.86 1 1.86 4.02 0.0849 A2 0.24 1 0.24 0.53 0.4915 B2 264.56 1 264.56 571.10 <0.0001 C2 8.27 1 8.27 17.86 0.0039 Residual 3.24 7 0.46 Misfit term 1.54 3 0.51 1.20 0.4169 Error 1.71 4 0.43 Sum 310.06 16 Notes: F-value is the statistic of the F-test; P-value is a constant criterion in hypothesis testing 表 5 回归方差分析(断裂伸长率)
Table 5. Regression analysis of variance (elongation at break)
Source Sum of squares Freedom Mean square F P Model 521.39 9 57.93 104.94 <0.0001 A 0.9180 1 0.9180 1.66 0.2382 B 443.42 1 443.42 803.24 <0.0001 C 0.2775 1 0.2775 0.5027 0.5012 AB 0.00001 1 0.00001 0.00001 1.0000 AC 0.0012 1 0.0012 0.0022 0.9637 BC 0.0289 1 0.0289 0.0524 0.8256 A2 0.7243 1 0.7243 1.31 0.2897 B2 72.42 1 72.42 131.18 <0.0001 C2 1.20 1 1.20 2.18 0.1832 Residual 3.86 7 0.5520 Incoherent orientation 2.88 3 0.9602 3.90 0.1106 Error 0.9837 4 0.2459 Total 525.26 16 表 6 回归方差分析(冲击韧性)
Table 6. Regression analysis of variance (impact toughness)
Source Sum of squares Freedom Mean square F P Model 604.41 9 67.16 109.85 <0.0001 A 7.94 1 7.94 12.99 0.0087 B 78.81 1 78.81 128.91 <0.0001 C 1.16 1 1.16 1.89 0.2116 AB 1.21 1 1.21 1.98 0.2023 AC 4.43 1 4.43 7.25 0.0310 BC 0.7832 1 0.7832 1.28 0.2950 A² 14.35 1 14.35 23.47 0.0019 B² 421.98 1 421.98 690.23 <0.0001 C² 44.16 1 44.16 72.23 <0.0001 Residual 4.28 7 0.6114 Incoherent orientation 1.69 3 0.5623 0.8675 0.5276 Error 2.59 4 0.6482 Total 608.69 16 -
[1] MA Y, ZHANG Y, LIU J, et al. Self-Healing Epoxy Coating Modified by Double-Walled Microcapsules Based Polyurea for Metallic Protection[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2019, 821: 313-320. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.821.313 [2] 马衍轩, 宋晓辉, 于霞, 等. 海工钢筋环氧涂层的多尺度结构设计与防护性能调控研究进展[J/OL][J]. 材料导报, 2023, (24): 1-26.MA Y, SONG X, YU X, et al. Research progress on multi-scale structural design and protective performance control of epoxy coatings for marine steel reinforcement[J]. Material Guide, 2023, (24): 1-26(in Chinese). [3] 袁玉环, 左进霞, 彭聪, 等. 聚氨酯/纳米SiO2改性碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料界面性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(11): 6073-6086.YUAN Y, ZUO J, PENG C, et al. Polyurethane/Nano SiO_ Interface properties of modified carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2023, 40(11): 6073-6086(in Chinese). [4] MAROUF B T, MAI Y W, BAGHERI R, et al. Toughening of Epoxy Nanocomposites: Nano and Hybrid Effects[J]. Polymer Reviews, 2016, 56(1): 70-112. doi: 10.1080/15583724.2015.1086368 [5] NEVES R M, ORNAGHI H L, ZATTERA A J, et al. Toughening Epoxy Resin with Liquid Rubber and Its Hybrid Composites: A Systematic Review[J]. Journal of Polymer Research, 2022, 29(8): 340. doi: 10.1007/s10965-022-03195-z [6] JAYAN J S, SARITHA A, JOSEPH K. Innovative Materials of This Era for Toughening the Epoxy Matrix: A Review[J]. Polymer Composites, 2018, 39(S4): E1959-E1986. [7] MERZ E H, CLAVER G C, BAER M. Studies on Heterogeneous Polymeric Systems[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 1956, 22(101): 325-341. doi: 10.1002/pol.1956.1202210114 [8] AMOS J L. The SPE International Award Address—1973 the Development of Impact Polystyrene–A Review[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 1974, 14(1): 1-11. [9] 李瑜, 邓金飞, 孙昭宜, 等. 端氨基聚硫橡胶增韧改性环氧树脂[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2019, 35(6): 100-104.LI Y, DENG J, SUN Z, et al. Modified epoxy resin toughened by amino terminated polysulfide rubber[J]. Polymer Material Science and Engineering, 2019, 35(6): 100-104(in Chinese). [10] WANG J F, ZHANG X H, JIANG L, et al. Advances in Toughened Polymer Materials by Structured Rubber Particles[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2019, 98: 101160. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2019.101160 [11] GAO Y L, SUN L Y, CHEN P C, et al. A stretch hardening self-assembly strategy inspired by natural rubber for degradable, recyclable and self-repairing polyurethane elastomers, Polymer Degradation and Stability, Volume 215, 2023, 110441, ISSN 0141-3910. [12] D M, TISS L, D J, et al. Protective films on complex substrates of thermoplastic and cellular elastomers: Prospective applications to rubber, nylon and cork, Surface and Coatings Technology, Volume 442, 2022, 128405, ISSN 0257-8972. [13] 姚佳伟, 冯瑞瑄, 牛一凡, 等. 纳米碳材料/热塑性树脂层间增韧热固性树脂基复合材料研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2): 528-543.YAO J, FENG R, NIU Y, et al. Research progress in nanocarbon materials/thermoplastic resin interlayer toughening thermosetting resin based composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2022, 39(2): 528-543 (in Chinese). [14] 李泽宇, 邓夏玲, 韩威, 等. 高韧性和自修复的壳聚糖-聚丙烯酸-MXene导电水凝胶及其压力传感性能[J/OL]. 复合材料学报, 1-102023-12-13]. LI Z, DENG X, HANG W, et al. Chitosan polyacrylic acid MXene conductive hydrogel with high toughness and self-healing and its pressure sensing properties[J/OL]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2022, 39(02): 528-543 (in Chinese). [15] P P, PUGLIA D, AL M, et al. Elastomer/thermoplastic Modified Epoxy Nanocomposites: The Hybrid Effect of 'Micro' and 'Nano' Scale[J]. Materials Science & Engineering R-Reports, 2017, 116: 1-29. [16] CHEN D, LI J, YUAN Y, et al. A new strategy to improve the toughness of epoxy thermosets by introducing the thermoplastic epoxy, Polymer, Volume 240, 2022, 124518, ISSN 0032-3861. [17] 翟乐, 吉海峰, 姚艳梅, 等. 利用聚丙烯酸正丁酯@聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯核/壳结构聚合物增韧氰酸酯树脂[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(4): 705-708.ZHAI Y, JI H, YAO Y, et al. Toughening of cyanate ester resin using poly (n-butyl acrylate) @ poly (methyl methacrylate) core/shell structure polymer[J]. Material Guide, 2019, 33(4): 705-708(in Chinese). [18] SHENG W, MEHMET C, Kali B, et al. The effect of hygrothermal ageing on the delamination of Carbon/epoxy laminates with Core-shell rubber nanoparticle and Micro-fibre thermoplastic veil toughening, Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, Volume 171, 2023, 107576, ISSN 1359-835X. [19] MOUSAVI S R, ESTAJI S, JAVIDI M R, et al. Toughening of Epoxy Resin Systems Using Core-Shell Rubber Particles: A Literature Review[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2021: 1-23. [20] JAWAD M, AQSA A, MUHAMMAD H, et al. Electrophoretic deposition of moringa loaded chitosan coatings on Mg: A study on antibacterial properties and degradation kinetics, Materials Letters, Volume 354, 2024, 135430, ISSN 0167-577X. [21] CHEN S F, Xu Z J, ZHANG D H. Synthesis and Application of Epoxy-ended Hyperbranched Polymers[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 343: 283-302. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.014 [22] SANTIAGO D, SERRA A. Enhancement of Epoxy Thermosets with Hyperbranched and Multiarm Star Polymers: A Review[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(11): 2228. doi: 10.3390/polym14112228 [23] 张雅, 柴春鹏, 罗运军, 等. 超支化聚酯基二茂铁/环氧树脂复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(6): 48-53.ZHANG Y, CAHI C, LUO Y, et al. Preparation and properties of hyperbranched polyester based ferrocene/epoxy resin composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2013, 30(6): 48-53(in Chinese). [24] K D, M D. Network structure formation during crosslinking of organic coating systems, Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 25, Issue 9, 2000, Pages 1215-1260, ISSN 0079-6700. [25] 张代军, 包建文, 钟翔屿, 等. 聚醚砜超细纤维无纺布层间增韧碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料制备与表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(8): 3767-3775.ZHANG D, BAO J, ZHONG X, et al. Preparation and characterization of polyethersulfone ultrafine fiber non-woven fabric interlayer toughened carbon fiber/epoxy resin composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2022, 39(8): 3767-3775(in Chinese). [26] FAROOQ U, TEUWEN J, DRANSFELD C. Toughening of Epoxy Systems with Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN): A Review[J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(9): 1908. doi: 10.3390/polym12091908 [27] LIGON-AUER S C, SCH M, GOR C, et al. Toughening of Photo-Curable Polymer Networks: A Review[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2016, 7(2): 257-286. doi: 10.1039/C5PY01631B [28] CAI M, LIN Q, LI W, et al. Phen@TiO2 modified epoxy resin/polyacrylate IPN composite coating towards wear/corrosion resistance and intelligent self-repairing/diagnosis, Progress in Organic Coatings, Volume 173, 2022, 107207, ISSN 0300-9440. [29] WANG S. , ZHAO H. Low Temperature Nanoindentation: Development and applications[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(4): 407. doi: 10.3390/mi11040407 [30] PHARR G M, OLIVER W C, BROTZEN F R. On the Generality of the Relationship Among Contact Stiffness, Contact Area, and Elastic Modulus During Indentation[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1992, 7(3): 613-617. doi: 10.1557/JMR.1992.0613 -

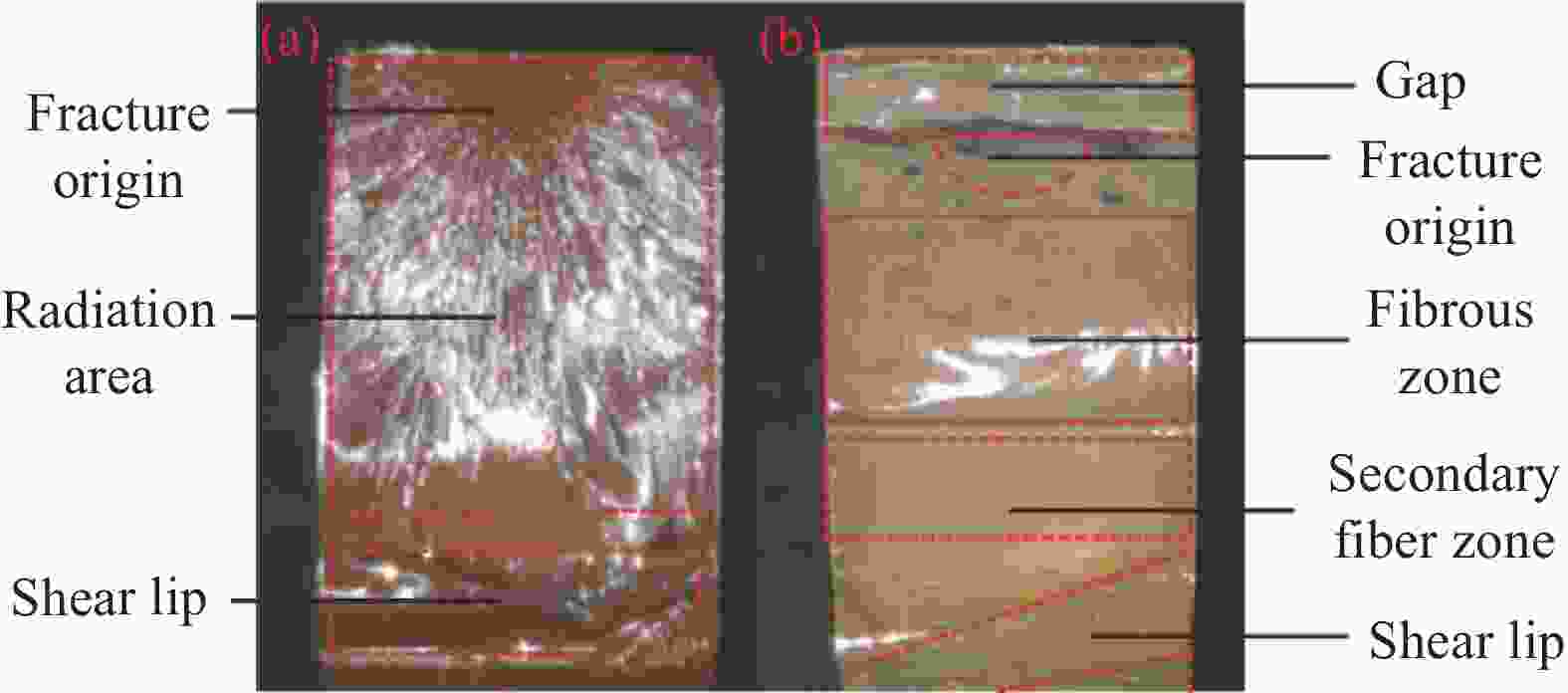
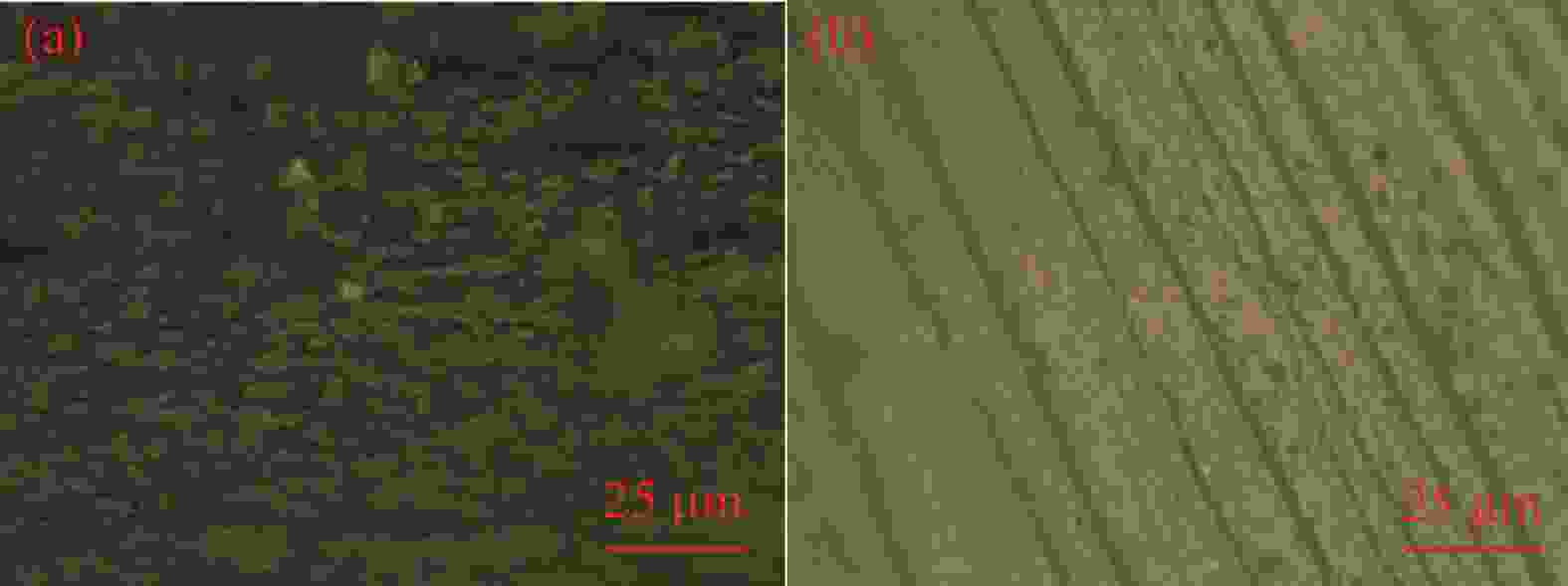
 点击查看大图
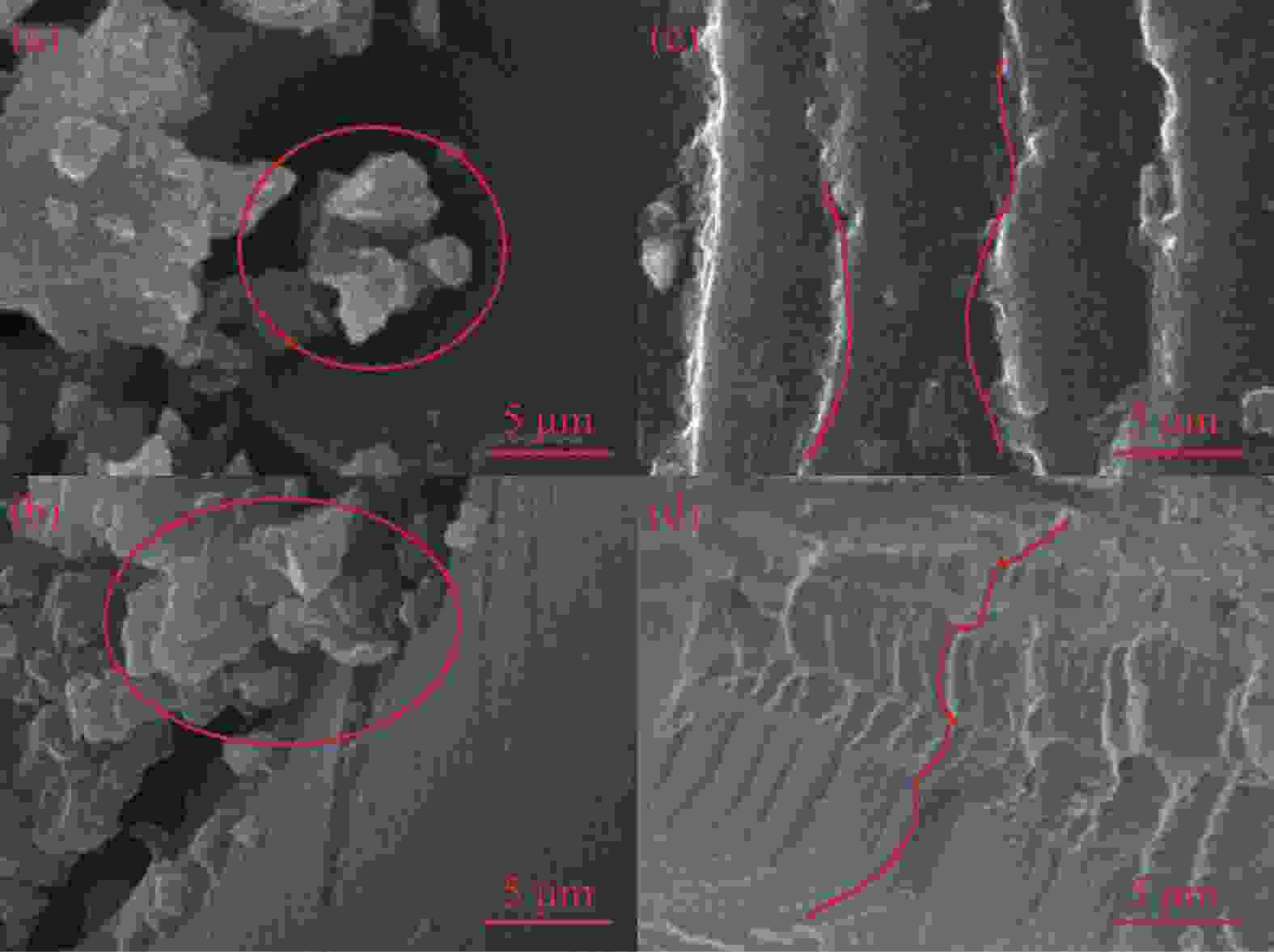
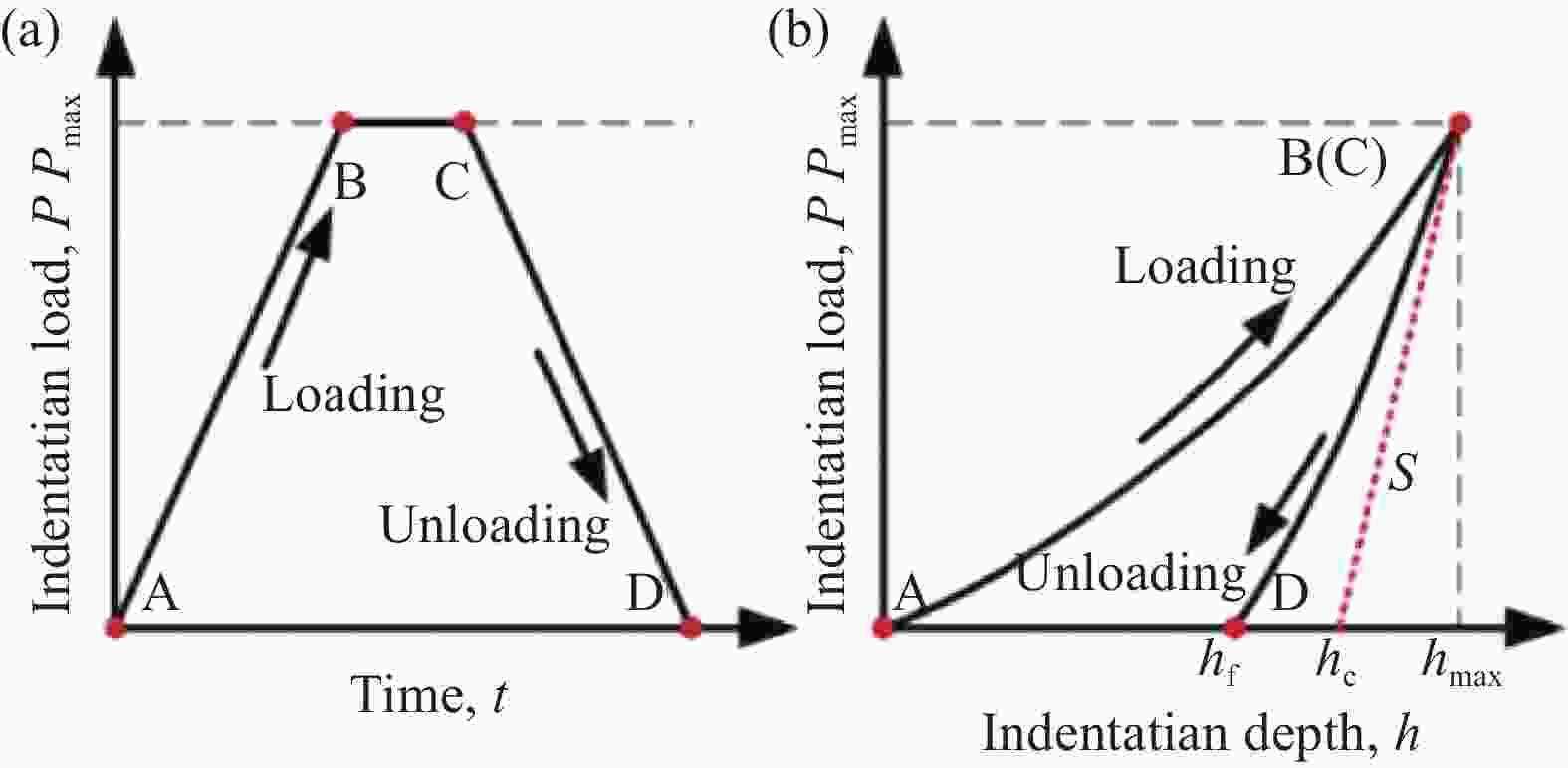
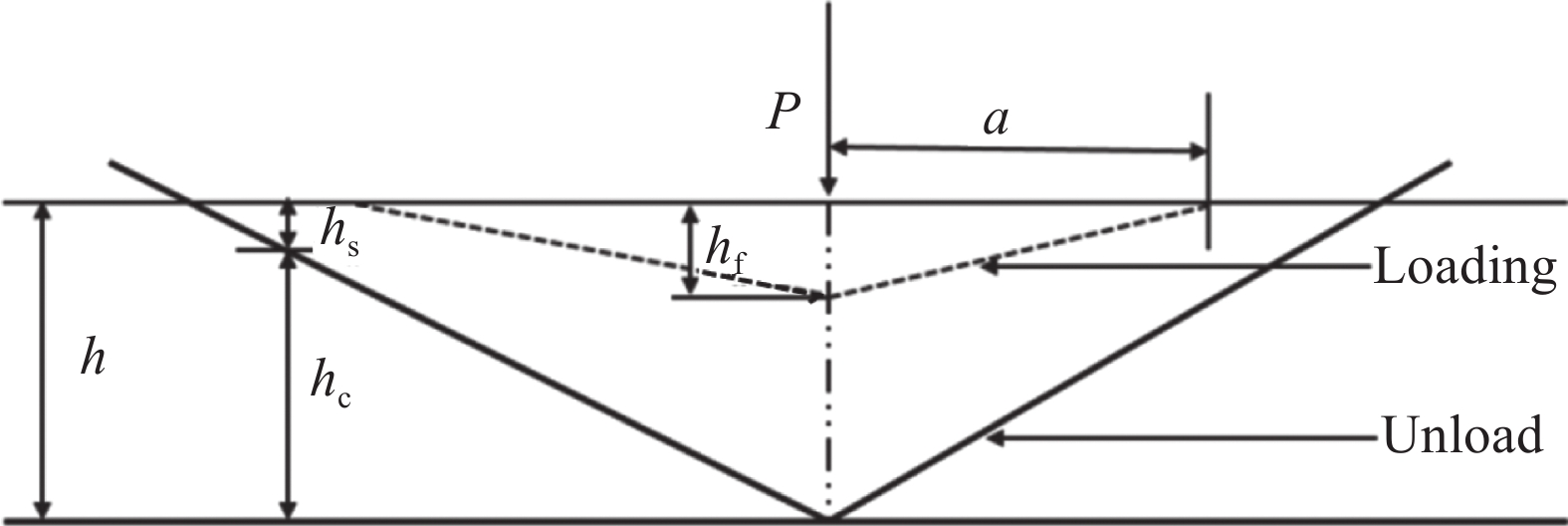
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 52
- HTML全文浏览量: 31
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: