Research progress of preparation of Janus micro/nano fibers prepared by electrospinning
-
摘要: 为进一步深入研究静电纺丝技术及Janus微纳米纤维的可控制备,使具有非均质结构特点的Janus纤维材料在多功能复合材料领域得到更广泛的应用。近年来,随着静电纺丝技术的不断发展,Janus纤维的纺制工艺逐渐从纺丝装置拓展、纺丝参数优化以提高纤维并行率,逐渐向纤维形貌多样化、结构多级化及组成多相化的导向性设计方向发展,以推动Janus纤维在多功能复合材料领域的快速发展。本文综述了基于静电纺丝技术所制备的并轴及同轴结构的Janus微纳米纤维,比较说明了不同结构Janus微纳米纤维的制备方法、形成机制及结构调控等方面的研究进展及成果,并进一步表明了静电纺丝技术在实现Janus纤维微纳米尺度导向性结构控制方面具有广泛的应用潜力。Abstract: In order to further study the electrospinning technology and the controllable preparation of Janus micro/ nano fibers, Janus fibers materials with heterogeneous structure characteristics have been more widely used in the field of multi-functional materials. In recent years, with the continuous development of electrospinning technology, the spinning process of Janus fiber has gradually expanded from spinning device, spinning parameter optimization to improve fiber parallelism rate, and gradually developed to the guided design direction of fiber morphology diversification, structure multiphase and composition multiphase, in order to promote the rapid development of Janus fiber in the field of multi-functional materials. In this paper, the co-axial and coaxial-structure Janus micro/nano fibers prepared by electrospinning technology and other fiber structures derived from them are reviewed. The research progress and achievements in the preparation methods, formation mechanism and structural regulation of Janus fibers with different morphologies and structures are compared. It is further demonstrated that electrospinning technology has wide application potential in realizing micro- and nano-scale oriented structure control of Janus fibers.
-
Key words:
- electrospinning /
- Janus fibers /
- fiber structure /
- mechanism /
- electrospinning device
-
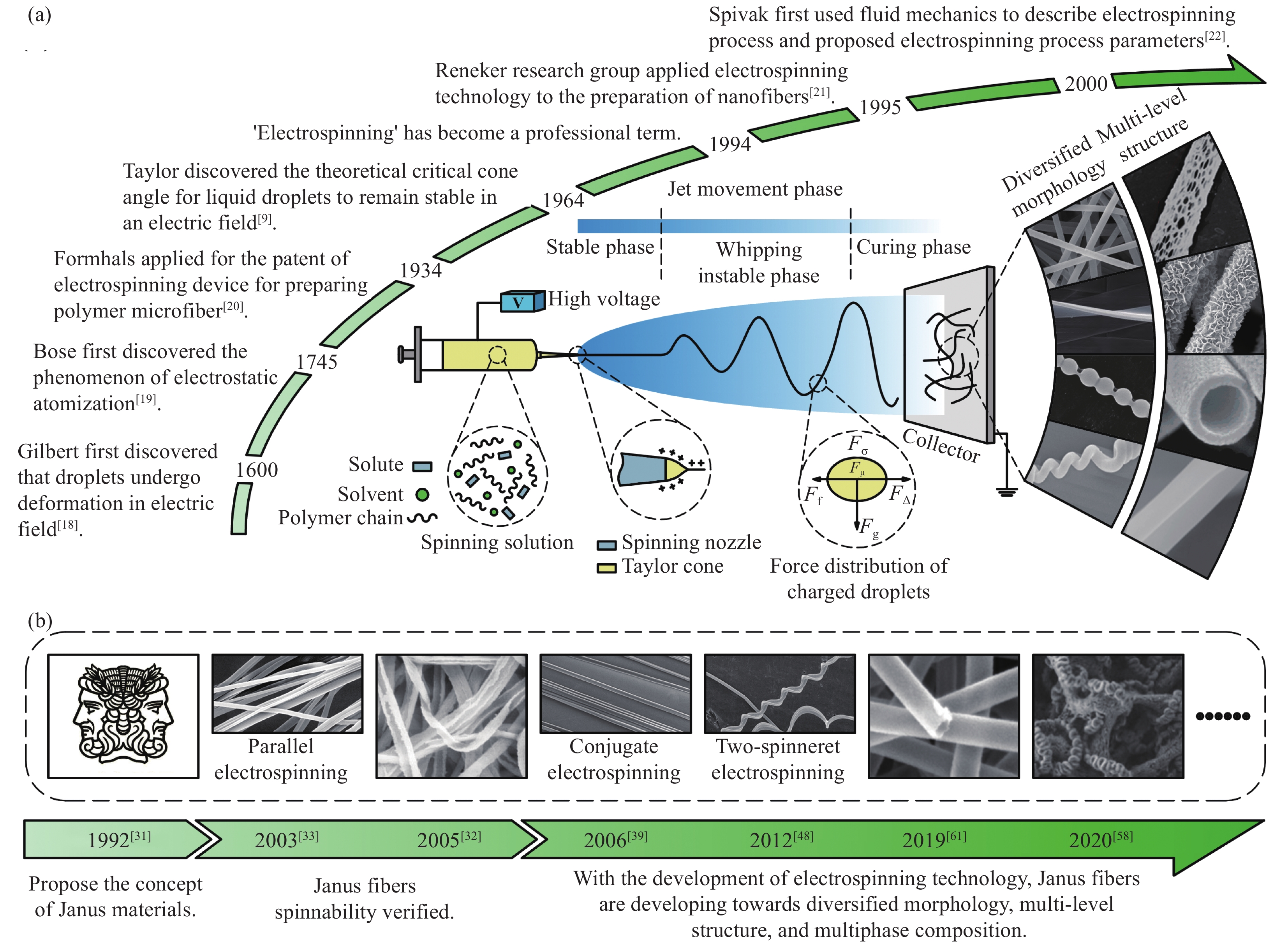
图 1 (a) 静电纺丝技术的发展[9, 18-22];(b) 静电纺丝技术制备Janus纤维的发展[31-33, 39, 48, 58, 61]
Fg—Gravity; Ff—Air resistance; Fσ—Surface tension; Fμ—Viscoelasticity; FΔ—Coulomb combined force; V—Voltage
Figure 1. (a) Development of electrospinning technology[9, 18-22]; (b) Development of Janus fibers preparation by electrospinning technology[31-33, 39, 48, 58, 61]
图 2 ((a)~(f))复合Taylor锥及Janus纤维形成机制;((g), (h))反转电场纺丝法装置示意图及Janus纤维SEM图像;((i)~(k))共轭电纺法装置示意图及Janus纤维SEM图像
PVP—Polyvinyl pyrrolidone; Fγ—Molecular force; Fe, F'e—Intermolecular repulsion; F'c—Charge repulsion; F'μ—Adhesion between spinning fluids; Fc—Electrostatic repulsive force; PMMA—Polymethyl methacrylate; PANI—Polyaniline; Tb(TTA)3(TTPO)2—Terbium complex; TPU—Thermoplastic polyurethane; PLGA—Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
Figure 2. ((a)-(f)) Formation mechanism diagram of composite Taylor cone and Janus fibers; ((g), (h)) Schematic illustrations of reverse electric field electrospinning device and SEM image of Janus fibers; ((i)-(k)) Schematic illustrations of conjugate electrospinning device and SEM images of Janus fibers
图 3 ((a), (b)) 热塑性聚氨酯(TPU)//聚酰亚胺(PI) Janus螺旋纤维SEM图像及荧光照片[47];(c) 双喷头纺丝法装置示意图;(d) 热塑性聚酯弹性体(HSPET)//聚对苯二甲酸丙二醇酯(PTT) Janus螺旋纤维SEM图像[49]
Figure 3. ((a), (b)) SEM and fluorescence images of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)//polyimide (PI) Janus helical fibers[47]; (c) Schematic illustrations of two-spinneret electrospinning device; (d) SEM image of thermoplastic polyester elastomer (HSPET)//polyethylene terephthalate (PTT) Janus helical fibers[49]
图 4 (a) 偏轴共纺法装置示意图及[肉桂酸(FA)/聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)]//[FA/玉米醇溶蛋白(zein)] Janus纤维TEM图像[51];(b) 单轴电纺法装置示意图及聚己内酯(PCL)//[纳米Ag粒子(AgNP)/PVP] Janus纤维TEM图像[52]
Figure 4. (a) Schematic illustrations of off-axisl electrospinning device and TEM image of [cinnamic acid (FA)/polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP)]//[FA/zein] Janus nanofibers[51]; (b) Schematic illustrations of single-axis electrospinning device and TEM image of polycaprolactone (PCL)//[Ag nanoparticles (AgNP)/PVP] Janus nanofibers[52]
图 5 (a) Janus带状纤维形成机制;(b) [铽有机配合物(Tb(BA)3phen)/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)]//[聚苯胺(PANI)/Fe3O4/PMMA] Janus纤维光学显微镜图像[57]
NPs—Nanoparticles
Figure 5. (a) Formation mechanism diagram of Janus ribbon fibers; (b) Optical microscope image of [terbium complexes (Tb(BA)3phen)/polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)]//[polyaniline (PANI)/Fe3O4/PMMA] Janus fibers[57]
图 6 ((a), (b)) [聚环氧乙烷(PEO)/PCL]//PCL Janus纤维SEM及荧光照片[59];((c), (d)) 聚乳酸(PLA)//聚乙烯醇(PVA) Janus纤维SEM及荧光照片[61]
Figure 6. ((a), (b)) SEM and fluorescence images of [polyethylene oxide (PEO)/PCL]//PCL Janus fibers[59]; ((c), (d)) SEM and fluorescence images of polylactic acid (PLA)//polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) Janus fibers[61]
图 9 (a) Janus膜结构示意图; ((b~(e)) 不同结构Janus膜SEM图像及光学显微镜图像
PNM—Polyacrylonitrile fiber membrane; CNT—Carbon nanotubes; MCP—Modified polyurethane composite nanofiber membrane; MP—Coated polyurethane composite nanofiber membrane; Tb(BA)3phen—Terbium complex
Figure 9. (a) Schematic diagram of Janus membrane structure; ((b)-(e)) SEM and optical microscope images of different structures of Janus membrane
-
[1] CHO I, LEE K W. Morphology of latex particles formed by poly(methyl methacrylate)-seeded emulsion polymerization of styrene[J]. Applied Polymer Science, 1985, 30(5): 1903-1926. doi: 10.1002/app.1985.070300510 [2] HWANG S, LAHANN J. Differentially degradable Janus particles for controlled release applications[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2012, 33(14): 1178-1183. doi: 10.1002/marc.201200054 [3] SAFAIE N, FERRIER R C. Janus nanoparticle synthesis: Overview, recent developments, and applications[J]. Journal Applied Physics, 2020, 127: 170902. doi: 10.1063/5.0003329 [4] ZHAO B, ZHOU H, LIU C Y, et al. Fabrication and directed assembly of magnetic Janus rods[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 40(8): 6541-6545. doi: 10.1039/C6NJ00825A [5] CHEN Y Q, LIANG Y, WANG L, et al. Preparation and applications of freestanding Janus nanosheets[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(36): 15151-15176. doi: 10.1039/D1NR04284J [6] ZHAO C X, JIAN X X, ZHANG X, et al. Rapid capture and photocatalytic inactivation of target cells from whole blood by rotating Janus nanotubes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(36): 12972-12981. [7] WANG M L, YU D G, BLIGH S W A. Progress in preparing electrospun Janus fibers and their applications[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2023, 31: 101766. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2023.101766 [8] LI M, LU K J, WANG L J, et al. Janus membranes with asymmetric wettability via a layer-by-layer coating strategy for robust membrane distillation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 603: 118031. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118031 [9] TAYLOR G. Disintegration of water droplets in and electric field[J]. Proceedins of the Royal Society A, 1964, 280: 383-397. [10] LIU Z Q, RAMAKRISHNA S, LIU X L. Electrospinning and emerging healthcare and medicine possibilities[J]. APL Bioengineering, 2020, 4(3): 030901. doi: 10.1063/5.0012309 [11] BHUSHANI J A, ANANDHARAMAKRISHNAN C. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food based applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2014, 38(1): 21-33. [12] SUN G R, SUN L Q, XIE H M, et al. Electrospinning of nanofibers for energy applications[J]. Nanomaterials, 2016, 6(7): 129-158. doi: 10.3390/nano6070129 [13] 许景钫, 熊昆, 柯爌琼, 等. 多级结构电纺纳米纤维在环境催化领域的应用[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11): 3617-3626. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072104XU Jingfang, XIONG Kun, KE Kuangqiong, et al. Application of hierarchical structure electrospinning nanofibers in the environmental catalysis[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(11): 3617-3626(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072104 [14] ZHOU Y J, LIU Y N, ZHANG M X, et al. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for air filtration: A review[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(7): 1077. doi: 10.3390/nano12071077 [15] 韩正意, 赵欣, 徐晓冬. 静电纺丝纳米纤维在吸附分离领域的应用进展[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(32): 242-246.HAN Zhengyi, ZHAO Xin, XU Xiaodong. Application progress of electrospun nanofibers in adsorption and separation[J]. Materials Reports, 2018, 32(32): 242-246(in Chinese). [16] CUI Y, XU K Z, ZHU B, et al. Synthesis of niobium nitride porous nanofibers with excellent microwave absorption properties via reduction nitridation of electrospinning precursor nanofibers with ammonia gas[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 907: 164453. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164453 [17] CHEN L, YU Q W, PAN C Y, et al. Chemiresistive gas sensors based on electrospun semiconductor metal oxides: A review[J]. Talanta, 2022, 246: 123527. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123527 [18] LAURICELLA M, SUCCI S, ZUSSMAN E, et al. Models of polymer solutions in electrified jets and solution blowing[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2020, 92(3): 035004. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.92.035004 [19] BOSE G M. Recherches sur la cause et sur la véritable théorie de l'électricité[M]. France: Wittenberg, 1745. [20] FORMHALS A. Process and apparatus for preparing artificial threads: US patent, 1975504A[P]. 1934-10-02. [21] RENEKER D H, CHUN I. Nanometre diameter fibers of polymer, produced by electrospinning[J]. Nanotechnology, 1996, 7(3): 216-223. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/7/3/009 [22] SPIVAK A F, DZENIS Y A, RENEKER D H. Model of steady state jet in the electrospinning process[J]. Mechanical & Materials Engineering, 2000, 27(1): 37-42. [23] 刘思彤. 静电纺丝技术制备稀土钨酸盐低维纳米材料与表征[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2015.LIU Sitong. Electrospinning fabrication and characterization of rare earth tungstate low-dimensional nanomaterials[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2015(in Chinese). [24] 吕喆, 董相廷, 王进贤. 静电纺丝制备Eu3+/SiO2复合纳米带及其发光性能研究[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2022, 58(8): 22-26.LYU Zhe, DONG Xiangting, WANG Jinxian. Fabrication and luminescent properties of Eu3+/SiO2 nanoribbons by electrospinning[J]. China Ceramics, 2022, 58(8): 22-26(in Chinese). [25] JIN Y, YANG D Y, KANG D Y, et al. Fabrication of necklace-like structures via electrospinning[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(2): 1186-1190. doi: 10.1021/la902313t [26] CHEN S L, HOU H Q, HU P, et al. Polymeric nanosprings by bicomponent electrospinning[J]. Macromolecular Materials Engineering, 2009, 294(4): 265-271. doi: 10.1002/mame.200800342 [27] ZHAO J H, SI N, XU L, et al. Experimental and theoretical study on the electrospinning nanoporous fibers process[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 170: 294-302. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.12.054 [28] LAI F L, MIAO Y E, HUANG Y P, et al. Flexible hybrid membranes of NiCo2O4-doped carbon nanofiber@MnO2 core-sheath nanostructures for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(24): 13442-13450. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b02739 [29] LI D, XIA Y N. Direct fabrication of eomposite and eeramic hollow nanofibers by electrospinning[J]. Nano Letters, 2004, 4(5): 933-938. doi: 10.1021/nl049590f [30] SUN F, QI H N, XIE Y R, et al. Flexible self-supporting bifunctional [TiO2/C]//[Bi2WO6/C] carbon-based Janus nanofiber heterojunction photocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution and degradation of organic pollutant[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 830: 154673. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154673 [31] DE GENNES P G. Soft matter[J]. Science, 1992, 256(5056): 495-497. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5056.495 [32] LIN T, WANG H X, WANG X G. Self-crimping bicomponent nanofibers electrospun from polyacrylonitrile and elastomeric polyurethane[J]. Advanced Materials, 2005, 17(22): 2699-2703. doi: 10.1002/adma.200500901 [33] GUPTA P, WILKES G L. Some investigations on the fiber formation by utilizing a side-by-side bicomponent electrospinning approach[J]. Polymer, 2003, 44(20): 6353-6359. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(03)00616-5 [34] CAI M, HE H W, ZHANG X, et al. Efficient synthesis of PVDF/PI side-by-side bicomponent nanofiber membrane with enhanced mechanical strength and good thermal stability[J]. Nanomaterials, 2019, 9(1): 39-50. [35] ZHOU X J, MA Q L, DONG X T, et al. Magnetism and white-light-emission bifunctionality simultaneously assembled into flexible Janus nanofiber via electrospinning[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2015, 50(24): 7884-7895. doi: 10.1007/s10853-015-9313-5 [36] YU D G, YANG C, JIN M, et al. Medicated Janus fibers fabricated using a Teflon-coated side-by-side spinneret[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2016, 138: 110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.11.055 [37] XIANG Q, MA Y M, YU D G, et al. Electrospinning using a Teflon-coated spinneret[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 284: 889-893. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.08.030 [38] LEE J Y, MOON S J, HAN Y B, et al. Facile fabrication of anisotropic multicompartmental microfibers using charge reversal electrohydrodynamic co-jetting[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2022, 43(1): 2100560. doi: 10.1002/marc.202100560 [39] DOSHI J, RENEKER D H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 1995, 35(2-3): 151-160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3886(95)00041-8 [40] PAN H, LI L M, HU L, et al. Continuous aligned polymer fibers produced by a modified electrospinning method[J]. Polymer, 2006, 47(14): 4901-4904. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2006.05.012 [41] TIAN J, MA Q L, YU W S, et al. Preparation of Janus microfibers with magnetic and fluorescence functionality via conjugate electro-spinning[J]. Materials & Design, 2019, 170: 107701. [42] TIAN J, MA Q L, YU W S, et al. High pairing rate Janus-structured microfibers and array: High-efficiency conjugate electrospinning fabrication, structure analysis and coinstantaneous multifunctionality of anisotropic conduction, magnetism and enhanced red fluorescence[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(19): 10679-10692. doi: 10.1039/C9RA01147A [43] 胡小赛, 沈勇, 王黎明, 等. 吸波材料结构、性能及应用研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2015, 44(9): 1741-1746. doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.2015.09.043HU Xiaosai, SHEN Yong, WANG Liming, et al. Study on the structure, properties and application of microwave absorbing materials[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2015, 44(9): 1741-1746(in Chinese). doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.2015.09.043 [44] RAGHUBANSHI H, DIKIO E D, NAIDOO E B. The properties and applications of helical carbon fibers and related materials: A review[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2016, 44: 23-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2016.08.023 [45] SIM H J, JANG Y, KIM H, et al. Self-helical fiber for glucose-responsive artificial muscle[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(18): 20228-20233. [46] TENG D F, ZENG Y C. Effect of co-electrospinning system on morphology and oil adsorption of helical nanofibers[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2022, 92(21-22): 4244-4259. [47] 蔡明. 并列双组分纳米纤维膜的制备及其性能研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2019.CAI Ming. The preparation and characteristics of side-by-side bicomponent nanofiber membranes[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2019(in Chinese). [48] WU H H, BIAN F G, GONG R H, et al. Effects of electric field and polymer structure on the formation of helical nanofibers via coelectrospinning[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(39): 9585-9590. [49] LI C J, WANG J N, ZHANG B F. Direct formation of "artificial wool" nanofiber via two-spinneret electrospinning[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 123(5): 2992-2995. doi: 10.1002/app.34944 [50] SUN Z, ZUSSMAN E, YARIN A L, et al. Compound core-shell polymer nanofibers by co-electrospinning[J]. Advanced Materials, 2003, 15(22): 1929-1932. doi: 10.1002/adma.200305136 [51] WANG M L, LI D, LI J, et al. Electrospun Janus zein-PVP nanofibers provide a two-stage controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 196: 109075. [52] LI R, CHENG Z Q, YU X B, et al. Preparation of antibacterial PCL/PVP-AgNP Janus nanofibers by uniaxial electrospinning[J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 254: 206-209. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.07.075 [53] PAN Z W, DAI Z R, WANG Z L. Nanobelts of semiconducting oxides[J]. Science, 2001, 291(5510): 1947-1949. doi: 10.1126/science.1058120 [54] KOOMBHONGSE S, LIU W X, RENEKER D H. Flat polymer ribbons and other shapes by electrospinning[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, Part B: Polymer Physics, 2001, 39(21): 2598-2606. [55] TOPUZ F, UYAR T. Electrospinning of gelatin with tunable fiber morphology from round to flat/ribbon[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2017, 80: 371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.06.001 [56] YIN D D, MA Q L, DONG X T, et al. Single flexible Janus nanobelts to realize tunable and enhanced simultaneous photoluminescent, electrical, and magnetic trifunctionality[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2015, 80(3): 568-575. doi: 10.1002/cplu.201402334 [57] MA Q L, WANG J X, DONG X T, et al. Flexible Janus nanoribbons array: A new strategy to achieve excellent electrically conductive anisotropy, magnetism, and photoluminescence[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(16): 2436-2443. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201500348 [58] TIAN J, MA Q L, YU W S, et al. An electrospun flexible Janus nanoribbon array endowed with simultaneously tuned trifunctionality of electrically conductive anisotropy, photoluminescence and magnetism[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 41(22): 13983-13992. doi: 10.1039/C7NJ03090H [59] SU Y C, TASKIN M B, DONG M D, et al. A biocompatible artificial tendril with a spontaneous 3D Janus multi-helix-perversion configuration[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2020, 4(7): 2149-2156. doi: 10.1039/D0QM00125B [60] MANZ A, FETTINGER J C, VERPOORTE E, et al. Micromachining of monocrystalline silicon and glass for chemical analysis systems A look into next century's technology or just a fashionable craze[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 1991, 10(5): 144-149. doi: 10.1016/0165-9936(91)85116-9 [61] ZHOU G L, YANG G, LI X L, et al. Hydrophobic/hydrophilic cooperative Janus branched polymer fibers with controllable length and density of nanobranches[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2018, 303(5): 1800006. doi: 10.1002/mame.201800006 [62] LIU H Y, HAN C H, SHAO C L, et al. ZnO/ZnFe2O4 Janus hollow nanofibers with magnetic separability for photocatalytic degradation of water-soluble organic dyes[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2019, 2(8): 4879-4890. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b00838 [63] CHEN X, PU J, HU X H, et al. Janus hollow nanofiber with bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for rechargeable Zn-air battery[J]. Small, 2022, 18(16): 2200578. doi: 10.1002/smll.202200578 [64] WANG X S, WANG W H, ZHANG J Q, et al. Carbon sustained SnO2-Bi2O3 hollow nanofibers as Janus catalyst for high-efficiency CO2 electroreduction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 131867. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131867 [65] XI X, MA Q L, DONG X T, et al. Peculiarly structured Janus nanofibers display synchronous and tuned trifunctionality of enhanced luminescence, electrical conduction, and superparamagnetism[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2018, 83(3): 108-116. doi: 10.1002/cplu.201800030 [66] YANG X L, TIAN J, QI H N, et al. Electrospun aeolotropic electrically conductive neoteric janus nanostrips array functionalized by enhancive up-conversion luminescence and magnetism[J]. Material Today Communications, 2020, 24: 101035. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101035 [67] WANG M L, GE R L, ZHAO P, et al. Exploring wettability difference-driven wetting by utilizing electrospun chimeric Janus microfiber comprising cellulose acetate and polyvinylpyrrolidone[J]. Materials & Design, 2023, 226: 111652. [68] LIU H, WANG H B, LU X H, et al. Electrospun structural nanohybrids combining three composites for fast helicide delivery[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2022, 5(2): 1017-1029. doi: 10.1007/s42114-022-00478-3 [69] KIDOAKI S, KWON I, MATSUDA T. Mesoscopic spatial designs of nano- and microfiber meshes for tissue-engineering matrix and scaffold based on newly devised multilayering and mixing electrospinning techniques[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(1): 37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.01.063 [70] YAN X H, WANG Y X, HUANG Z Z, et al. Janus polyacrylonitrile/carbon nanotube nanofiber membranes for oil/water separation[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023, 6(6): 4511-4521. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c00006 [71] TANG Y, YAN J, WANG J J, et al. MXene based flexible Janus nanofibrous membrane composite for unidirectional water transportation[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2023, 239: 110032. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.110032 [72] HOU L L, WANG N, MAN X K, et al. An interpenetrating Janus membrane for high rectification ratio liquid unidirectional penetration[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(4): 4124-4132. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b08753 [73] HU R J, WANG N, HOU L L, et al. A bioinspired hybrid membrane with wettability and topology anisotropy for highly efficient fog collection[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(1): 124-132. doi: 10.1039/C8TA10615K [74] QI H N, MA Q L, XIE Y R, et al. Electrospun polyfunctional conductive anisotropic Janus-shaped film, derivative 3D Janus tube and 3D plus 2D complete flag-shaped structures[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(19): 6565-6576. doi: 10.1039/D0TC00366B -






 下载:
下载: