Impact damage repair and performance of carbon fiber reinforced poly aryl ether ketone composites
-
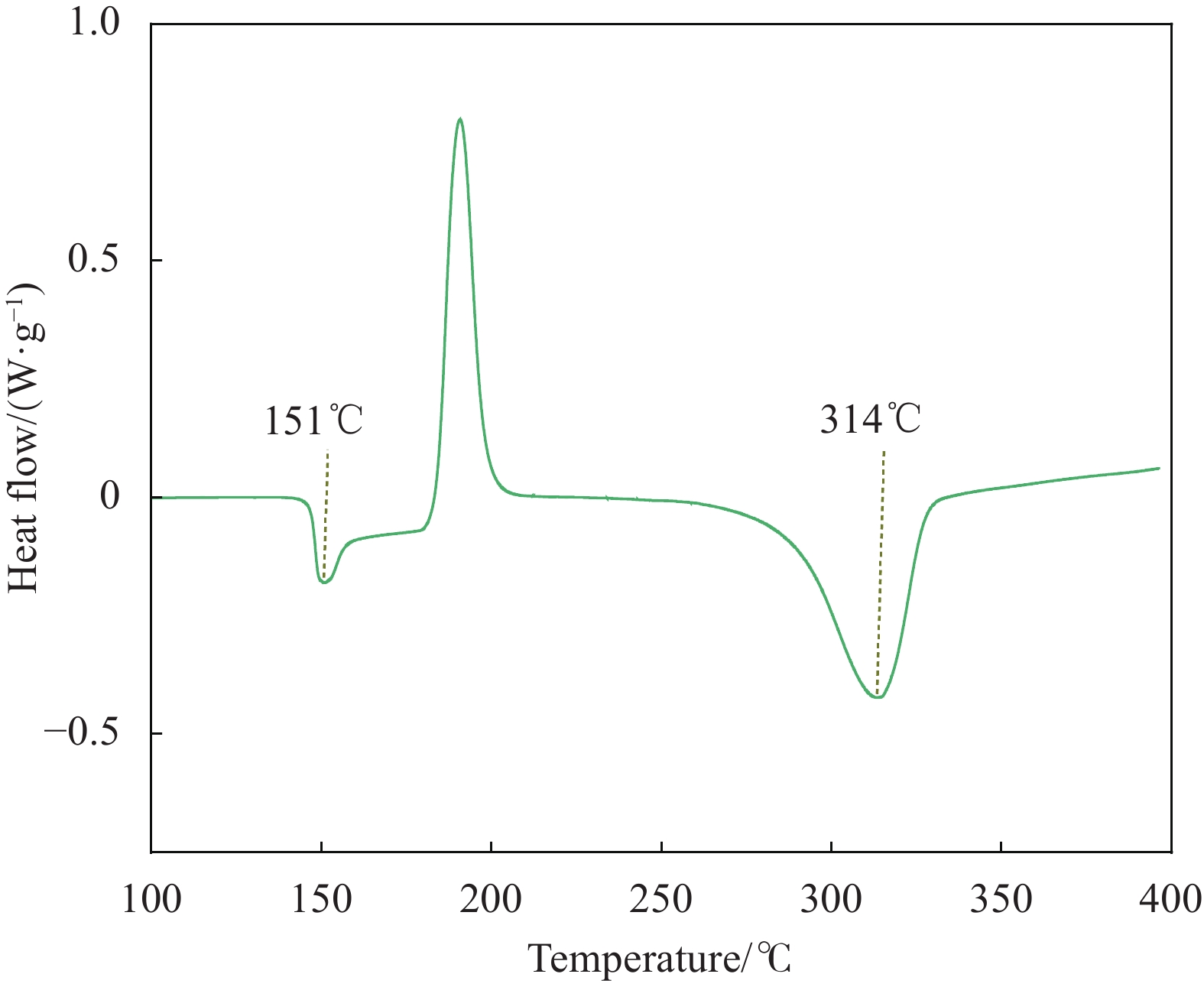
摘要: 针对国产T300级碳纤维增强高性能聚芳醚酮树脂预浸料(SCF35/PAEK-L)制备的热塑性复合材料,采用热压工艺修复不同冲击能量作用下产生的冲击损伤,以压缩强度评价复合材料冲击损伤修复的效果,并利用Micro-CT研究复合材料修复前、后的微观形貌。结果显示:复合材料的冲击损伤修复效果受到热压修复工艺的影响,随着修复温度的提高复合材料的压缩强度呈现先增加后降低的趋势,较低的修复温度及较高的修复压力与较高的修复温度及较低的修复压力能够得到相近的压缩强度;同时,复合材料的修复效果与冲击损伤程度具有相关性,随着冲击损伤程度的提高,复合材料修复后的压缩强度逐渐降低,标准能量冲击的复合材料修复后,其修复后压缩强度恢复到无损伤状态压缩强度的~70%,为~417 MPa,复合材料出现穿透损伤后,其修复后压缩强度恢复到56%,为~334 MPa。Abstract: For the thermoplastic composites prepared by domestic T300 grade carbon fiber reinforced high performance poly aryl ether ketone resin prepreg (SCF35/PAEK-L), the impact damages generated by different impact energies were repaired by hot pressing process. The compressive strength was used to evaluate the repair effect of composite impact damage, and Micro-CT was utilized to study the microscopic morphology of composites before and after repair. The results show that the impact damage repair effect of the composite is affected by the hot pressing repair process, and the compression strength of the composite shows a trend of increasing and then decreasing as the repair temperature increases. The lower repair temperature and higher repair pressure are able to obtain similar compression strength with higher repair temperature and lower repair pressure. The repair effect of the composite material is influenced by the degree of impact damage, and the compressive strength of the composite material after repair gradually decreases as the degree of impact damage increases. The repaired compressive strength of the composites with standard energy impact recoveres to ~70% of the compression strength in the undamaged state, which is ~417 MPa, and when the composite material has penetration damage, its compressive strength after repair recovers to 56%, which is ~334 MPa.
-
图 5 SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料不同修复温度下的压缩强度
Figure 5. Compression strength of SCF35/PAEK-L composites at different repair temperatures
CAI—Compression strength of SCF35/PAEK-L composite after impact; CAR—Compression strength of SCF35/PAEK-L composite after repair; CNI—Compression strength of SCF35/PAEK-L composite with no impact damage
图 10 SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料不同修复压力下的内部质量:(a) 320℃,1 MPa;(b) 320℃,2 MPa;(c) 320℃,3 MPa;(d) 340℃,1 MPa;(e) 340℃,2 MPa;(f) 340℃,3 MPa
Figure 10. Internal quality of SCF35/PAEK-L composite at different repair pressures: (a) 320℃, 1 MPa; (b) 320℃, 2 MPa; (c) 320℃, 3 MPa;(d) 340℃, 1 MPa; (e) 340℃, 2 MPa; (f) 340℃, 3 MPa
表 1 碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮树脂(SCF35/PAEK-L)预浸带参数及其复合材料基本性能
Table 1. Parameters of carbon fiber reinforced poly aryl ether ketone resin (SCF35/PAEK-L) prepreg andits basic composite properties
Prepreg FAW/
(g∙m−2)FC/
vol%RC/
wt%Tensile properties (0°) Compression properties (0°) Flexural properties (0°) Strength/
MPaModulus/
GPaStrength/
MPaModulus/
GPaStrength/
MPaModulus/
GPaSCF35/PAEK-L 145±5 52±3 40±2 1730 119 1140 116 1400 117 Notes:FAW—Fiber areal mass of SCF35/PAEK-L prepreg; FC—Fiber content by volume of SCF35/PAEK-L prepreg; RC—Resin content by mass of SCF35/PAEK-L prepreg. 表 2 SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料压缩强度恢复率
Table 2. Compression strength recovery of SCF35/PAEK-L composites
Repair
parameterCompression strength
after repair/MPaRecovery rate/% 300℃, 2 MPa 353±12 (30 J) 59 320℃, 1 MPa 403±13 (30 J) 68 320℃, 2 MPa 415±15 (30 J) 70 320℃, 3 MPa 420±15 (30 J) 71 417±10 (30 J) 70 340℃, 1 MPa 402±7.6 (50 J) 68 334±12.6 (70 J) 56 340℃, 2 MPa 407±7.5 (30 J) 68 340℃, 3 MPa 391±13.5 (30 J) 66 -
[1] LIU H B, LIU J, DING Y Z, et al. The behaviour of thermoplastic and thermoset carbon fibre composites subjected to low-velocity and high-velocity impact[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(33): 15741-15768. doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-05133-0 [2] JOGUR G, NAWAZ KHAN A, DAS A, et al. Impact properties of thermoplastic composites[J]. Textile Progress, 2018, 50(3): 109-183. doi: 10.1080/00405167.2018.1563369 [3] 谌广昌, 姚佳楠, 张金栋, 等. 高性能热塑性复合材料在直升机结构上的应用与展望[J]. 航空材料学报, 2019, 39(5): 24-33. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2019.000035CHEN Guangchang, YAO Jianan, ZHANG Jindong, et al. Application and prospect of high performance thermoplastic composites in helicopter structure[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2019, 39(5): 24-33(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2019.000035 [4] 见雪珍, 杨洋, 袁协尧, 等. 商用客机连续纤维增强热塑性复合材料的现状及其发展趋势[J]. 上海塑料, 2015(2): 17-22.JIAN Xuezhen, YANG Yang, YUAN Xieyao, et al. Status and development trend of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites in commercial aircraft[J]. Shanghai Plastics, 2015(2): 17-22(in Chinese). [5] 郭云竹. 热塑性复合材料研究及其在航空领域中的应用[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2016, 33(3): 20-23.GUO Yunzhu. Research on thermoplastic composites and its application in the field of aviation[J]. Fiber Composites, 2016, 33(3): 20-23(in Chinese). [6] 罗云烽, 姚佳楠. 高性能热塑性复合材料在民用航空领域中的应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2021, 64(16): 93-102. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2021.16.093LUO Yunfeng, YAO Jianan. Applications of high performance thermoplastic composites in civil aviation[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 64(16): 93-102(in Chinese). doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2021.16.093 [7] 王兴刚, 于洋, 李树茂, 等. 先进热塑性树脂基复合材料在航天航空上的应用[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2011, 28(2): 44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2011.02.011WANG Xinggang, YU Yang, LI Shumao, et al. The research on fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite[J]. Fiber Composites, 2011, 28(2): 44-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2011.02.011 [8] 肇研, 刘寒松. 连续纤维增强高性能热塑性树脂基复合材料的制备与应用[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(8): 49-61. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.000209ZHAO Yan, LIU Hansong. Preparation and application of continuous fiber reinforced high-performance thermoplastic resin matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2020, 48(8): 49-61(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.000209 [9] LAGACE P A, WILLIAMSON J E, WILSON TSANG P H, et al. A preliminary proposition for a test method to measure (impact) damage resistance[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 1993, 12(5): 584-601. doi: 10.1177/073168449301200508 [10] BYERS B A. Behavior of damaged graphite/epoxy laminates under compression loading: NASA-CR-159293[R]. Seattle: Boeing Commercial Airplane Co., 1980. [11] 杜龙, 万建平. 复合材料损伤及结构修理技术[J]. 教练机, 2012, 10(4): 60-68.DU Long, WAN Jianping. Damage in composite materials and repair technique of composite structures[J]. Trainer, 2012, 10(4): 60-68(in Chinese). [12] 王长越, 邢素丽. 冲击损伤下航空复合材料修复技术研究进展[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2017(12): 91-98.WANG Changyue, XING Suli. A review of repair techniques for aviation composite materials under impact damage[J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2017(12): 91-98(in Chinese). [13] 刘岩松, 张子健, 宋晓晨, 等. 复合材料结构修理技术探究[J]. 航空维修与工程, 2018(11): 76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0989.2018.11.029LIU Yansong, ZHANG Zijian, SONG Xiaochen, et al. Research on repair technology of composite material structure[J]. Aviation Maintenance & Engineering, 2018(11): 76-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0989.2018.11.029 [14] ORSATELLI J B, PAROISSIEN E, LACHAUD F, et al. Bonded flush repairs for aerospace composite structures: A review on modelling strategies and application to repairs optimization, reliability and durability[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 304: 116338. [15] IREMAN T, RANVIK T, ERIKSSON I. On damage development in mechanically fastened composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures, 2000, 49(2): 151-171. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(99)00130-0 [16] KATNAM K B, DA SILVA L F M, YOUNG T M. Bonded repair of composite aircraft structures: A review of scientific challenges and opportunities[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2013, 61: 26-42. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2013.03.003 [17] REIS J P, DE MOURA M, SAMBORSKI S. Thermoplastic composites and their promising applications in joining and repair composites structures: A review[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(24): 5832. doi: 10.3390/ma13245832 [18] BARROETA ROBLES J, DUBÉ M, HUBERT P, et al. Repair of thermoplastic composites: An overview[J]. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science, 2022, 8(2): 68-96. [19] REYES G, SHARMA U. Modeling and damage repair of woven thermoplastic composites subjected to low velocity impact[J]. Composite Structures, 2010, 92(2): 523-531. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.08.038 [20] TARPANI J R, CANTO R B, SARACURA R G M, et al. Compression after impact and fatigue of reconsolidated fiber-reinforced thermoplastic matrix solid composite laminate[J]. Procedia Materials Science, 2014, 3: 485-492. doi: 10.1016/j.mspro.2014.06.081 [21] SLATTERY P G, MCCARTHY C T, O'HIGGINS R M. Assessment of residual strength of repaired solid laminate composite materials through mechanical testing[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 147: 122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.03.036 [22] 顾洋洋, 张金栋, 刘刚, 等. 聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂熔体黏度及冲击能量对其复合材料冲击损伤行为的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(10): 5641-5653. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20221228.003GU Yangyang, ZHANG Jindong, LIU Gang, et al. Effect of melt viscosity and impact energy of poly aryl ether ketone (PAEK) resins on the impact damage behavior of their composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(10): 5641-5653. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20221228.003 [23] GE T, ROBBINS M O, PERAHIA D, et al. Healing of polymer interfaces: Interfacial dynamics, entanglements, and strength[J]. Physical Review E, 2014, 90(1): 012602. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.90.012602 [24] MANTELL S C, SPRINGER G S. Manufacturing process models for thermoplastic composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1992, 26(16): 2348-2377. doi: 10.1177/002199839202601602 [25] MIKOS A G, PEPPAS N A. Polymer chain entanglements and brittle fracture: 2. Autohesion of linear polymers[J]. Polymer, 1989, 30(1): 84-91. doi: 10.1016/0032-3861(89)90387-X [26] AGEORGES C, YE L, HOU M. Advances in fusion bonding techniques for joining thermoplastic matrix composites: A review[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2001, 32(6): 839-857. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(00)00166-4 [27] ASTM. Standard test method for measuring the damage resistance of a fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event: ASTM D7136/D7136M—20[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2020. [28] ASTM. Standard test method for compressive residual strength properties of damaged polymer matrix composite laminates: ASTM D7137/D7137M—17[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2017. [29] ASTM. Standard test method for compressive properties of polymer matrix composite materials using a combined loading compression (CLC) test fixture: ASTM D6641/D6641M—14[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2014. [30] KHAN T, IRFAN M S, CANTWELL W J, et al. Crack healing in infusible thermoplastic composite laminates[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 156: 106896. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106896 -






 下载:
下载: