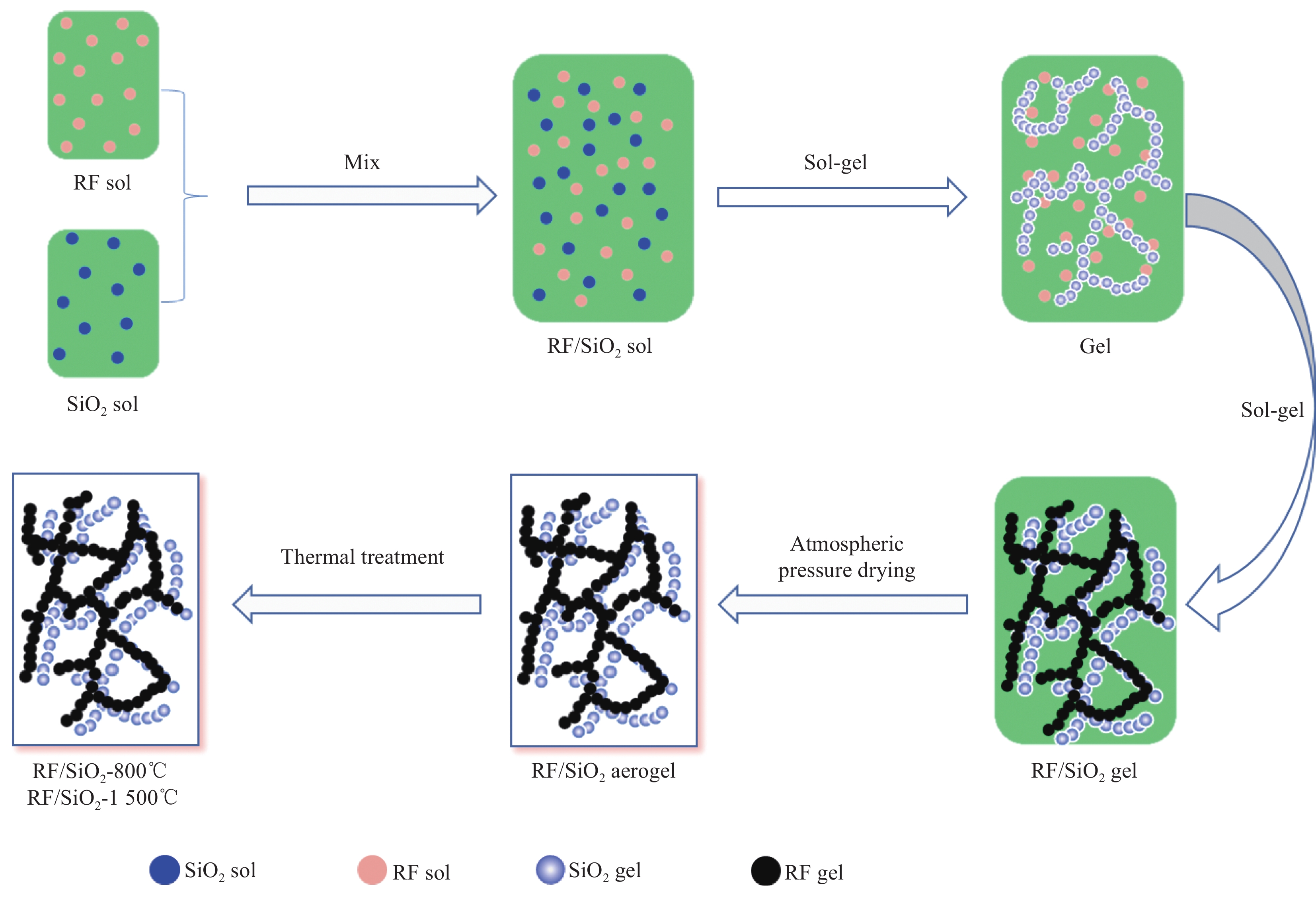
Preparation of resorcinol-formaldehyde enhanced silica aerogels and their absorption properties
-
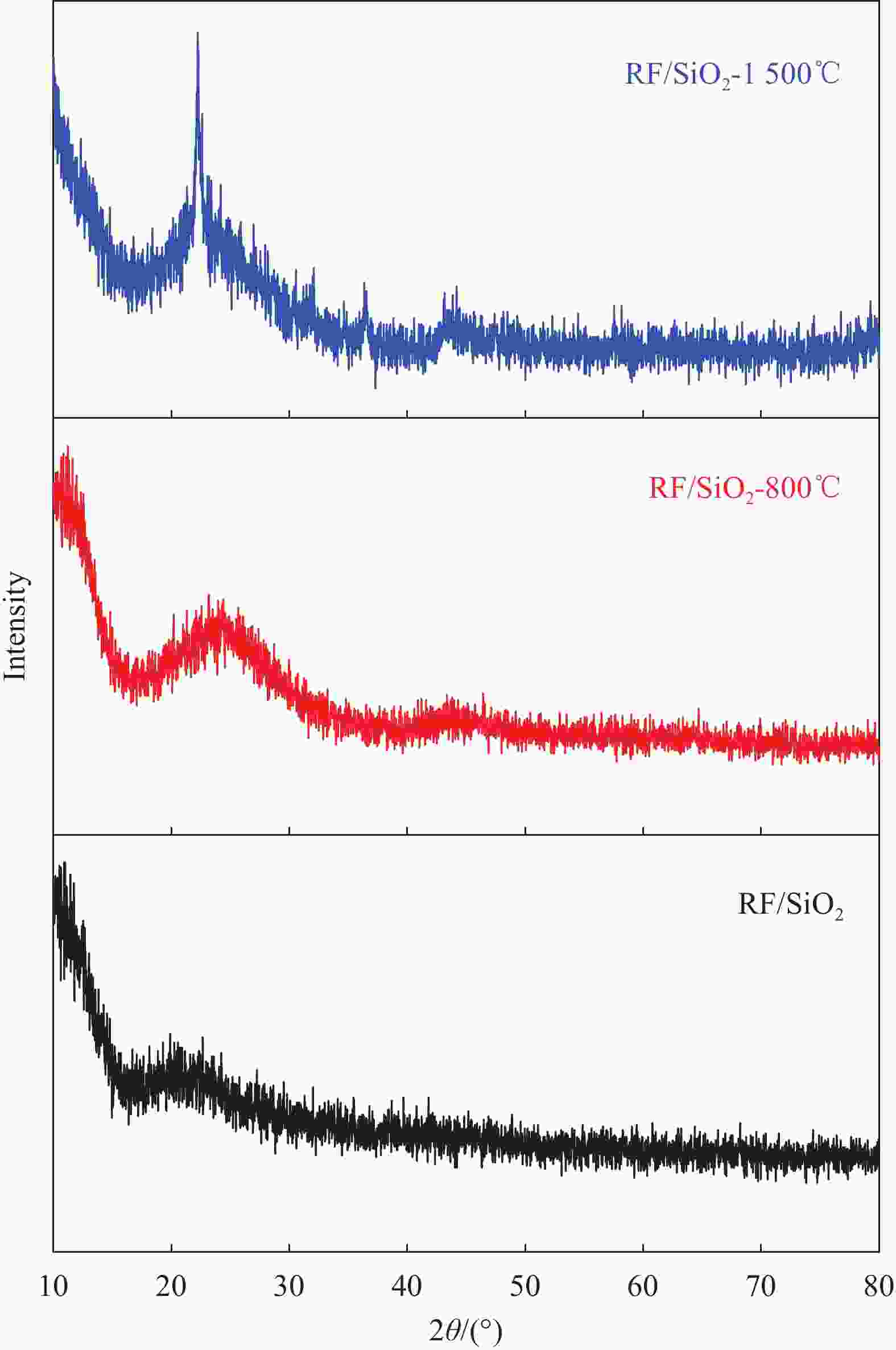
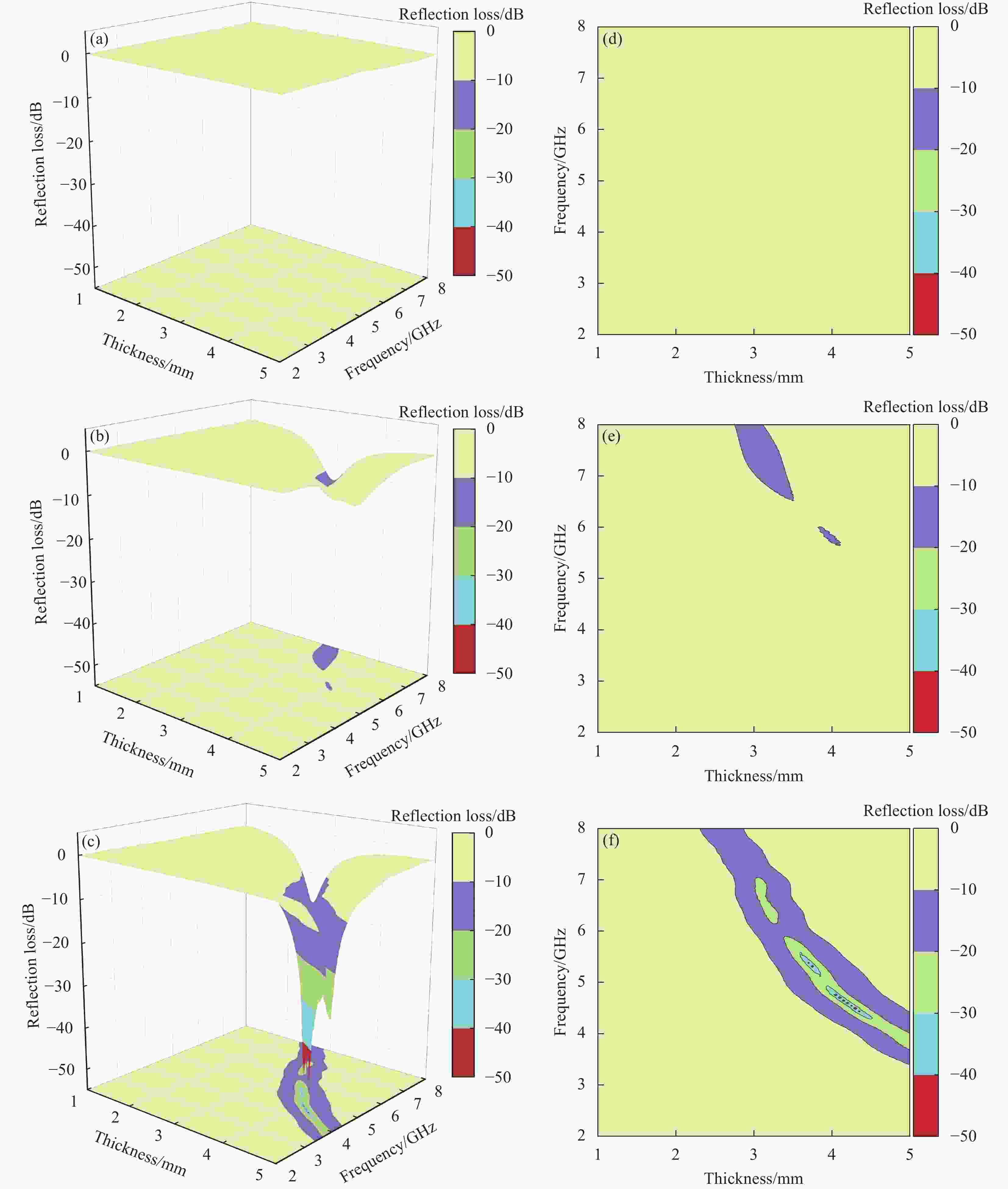
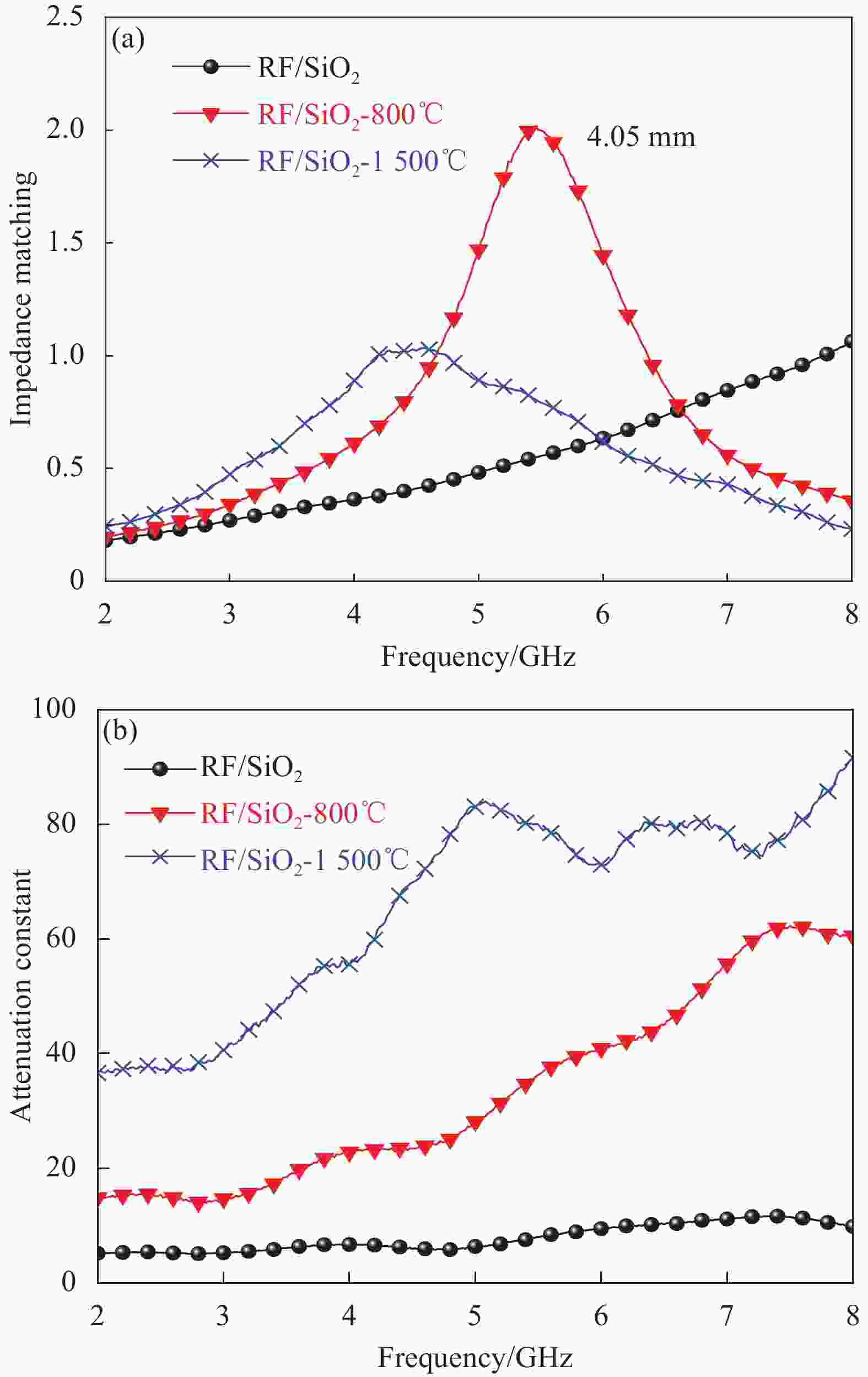
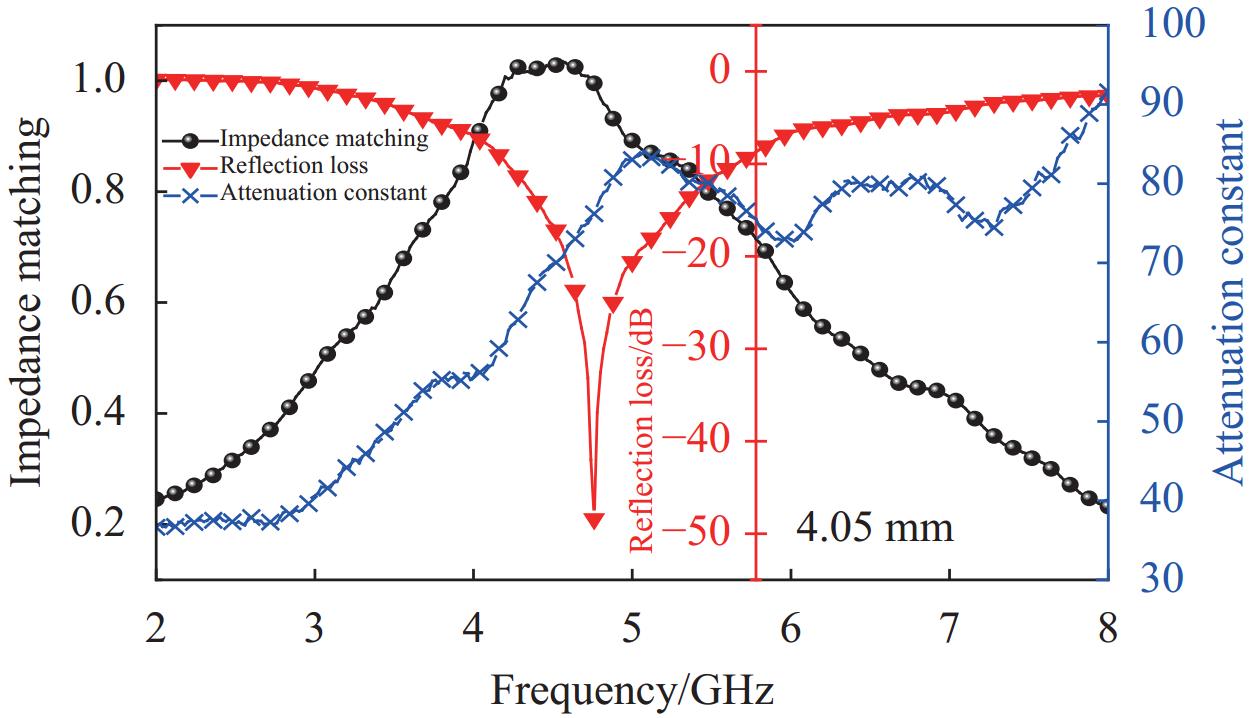
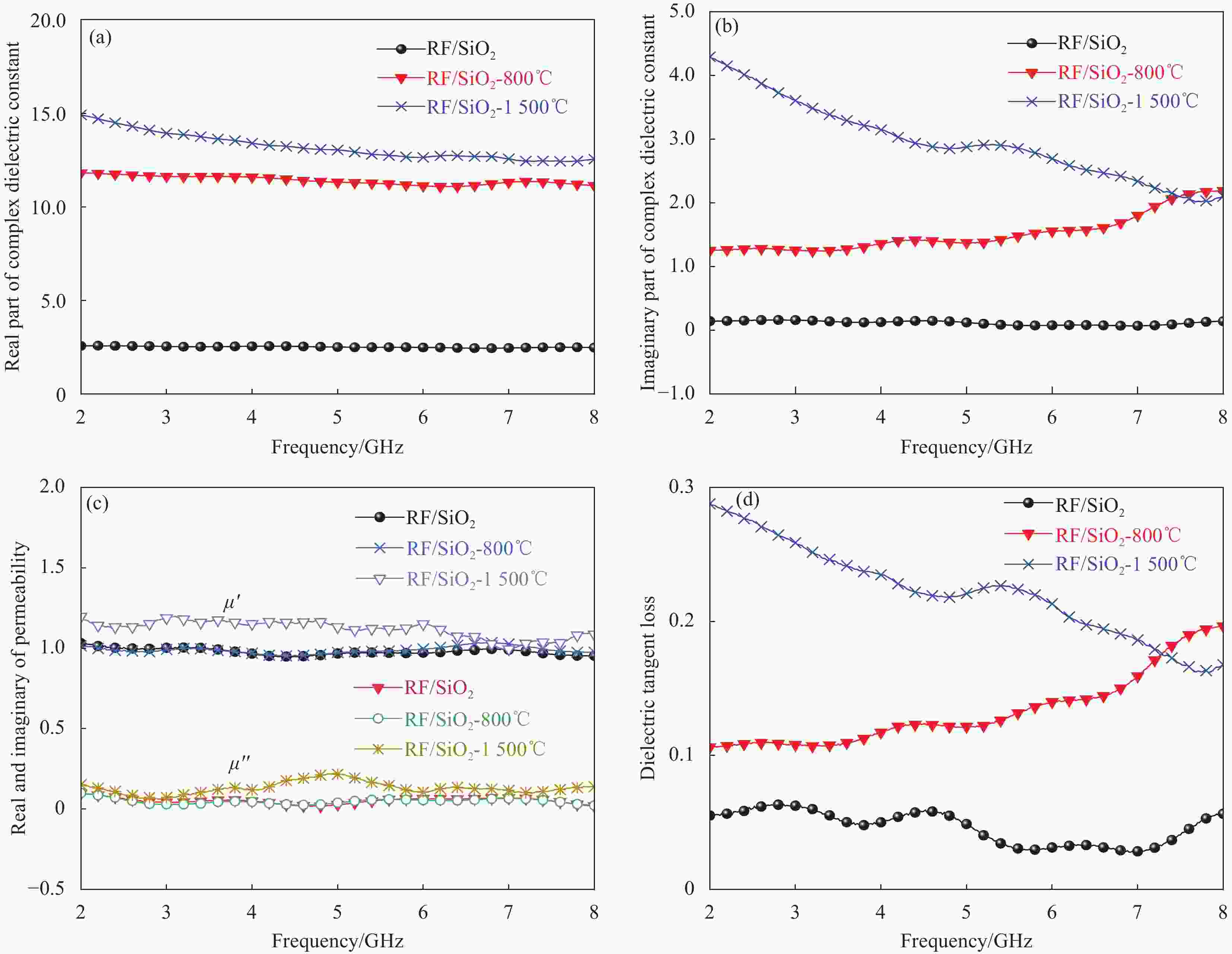
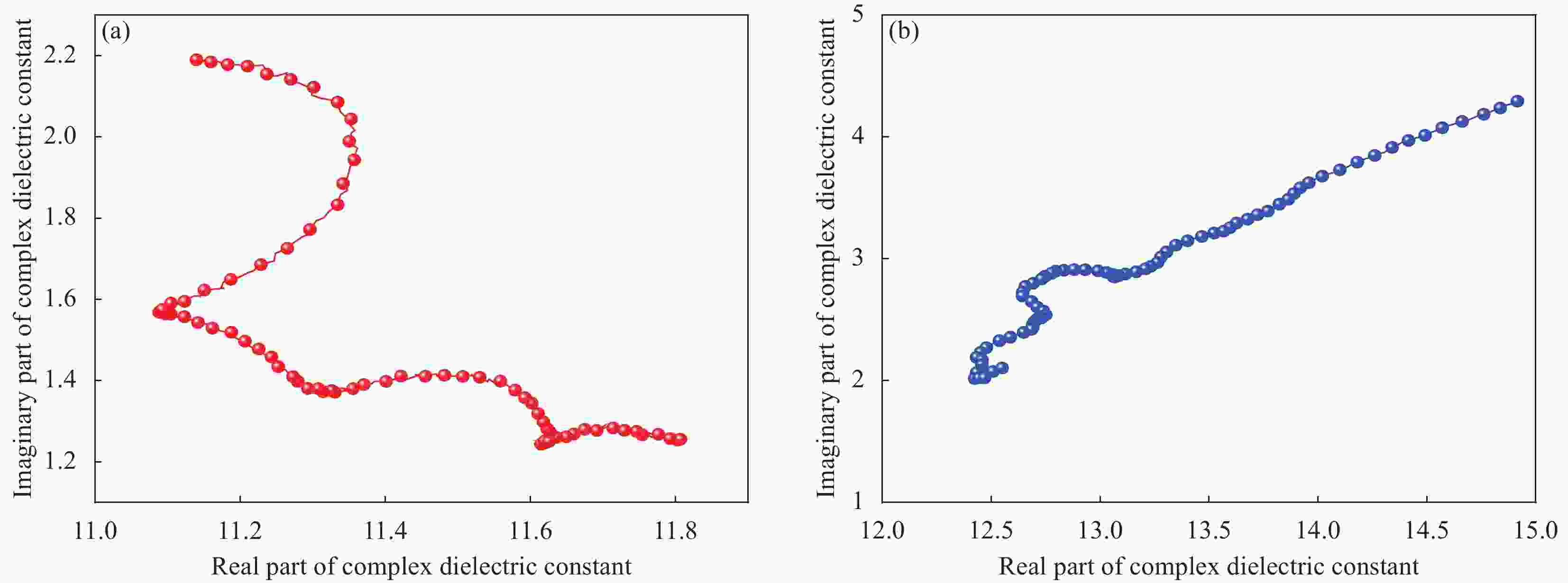
摘要: 为了探究SiO2气凝胶在电磁吸波领域应用的可能性,通过溶胶-凝胶技术引入间苯二酚-甲醛(RF)构建多孔骨架,再结合常压干燥法,成功合成RF/SiO2复合材料,并对RF/SiO2气凝胶进行了热处理,通过SEM、XRD等对热处理后的RF/SiO2气凝胶微观结构和理化性能进行表征,探究了热处理温度对RF/SiO2气凝胶吸波性能的影响规律。结果表明:随热处理温度的增加,吸波性能大幅提升,当热处理温度为1500℃时,RF/SiO2气凝胶在4.05 mm厚度下表现出−48.42 dB的最小反射损耗,当厚度为3.45 mm时有效吸收带宽达到了2.06 GHz,表现出了优异的电磁波吸收性能。该研究为制备高性能吸波材料提供了指导。
-
关键词:
- RF/SiO2气凝胶 /
- 溶胶-凝胶法 /
- 微观结构 /
- 热处理 /
- 吸波性能
Abstract: A composite material of resorcinol-formaldehyde (RF) enhanced silica dioxide aerogel (RF/SiO2) had been successfully synthesized by introducing RF to build a porous framework through the sol-gel technique, followed by ambient pressure drying to explore the possibility of the application of silica dioxide aerogel in electromagnetic microwave absorption. The RF/SiO2 aerogel was then subjected to heat treatment, and its microstructure and physicochemical properties after heat treatment were characterized using SEM, XRD, and other methods. The influence of heat treatment temperature on the microwave absorption performance of RF/SiO2 aerogel was investigated. The results show that the microwave absorption performance of RF/SiO2 aerogel is significantly improved with increasing heat treatment temperature. At a heat treatment temperature of 1500℃, the RF/SiO2 aerogel exhibits a minimum reflection loss of −48.42 dB at a thickness of 4.05 mm. At a thickness of 3.45 mm, the effective absorption bandwidth reaches 2.06 GHz, demonstrating excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. This study provides guidance for the preparation of high-performance microwave-absorbing materials.-
Key words:
- RF/SiO2 aerogel /
- sol-gel method /
- microstructure /
- heat treatment /
- absorbing performance
-
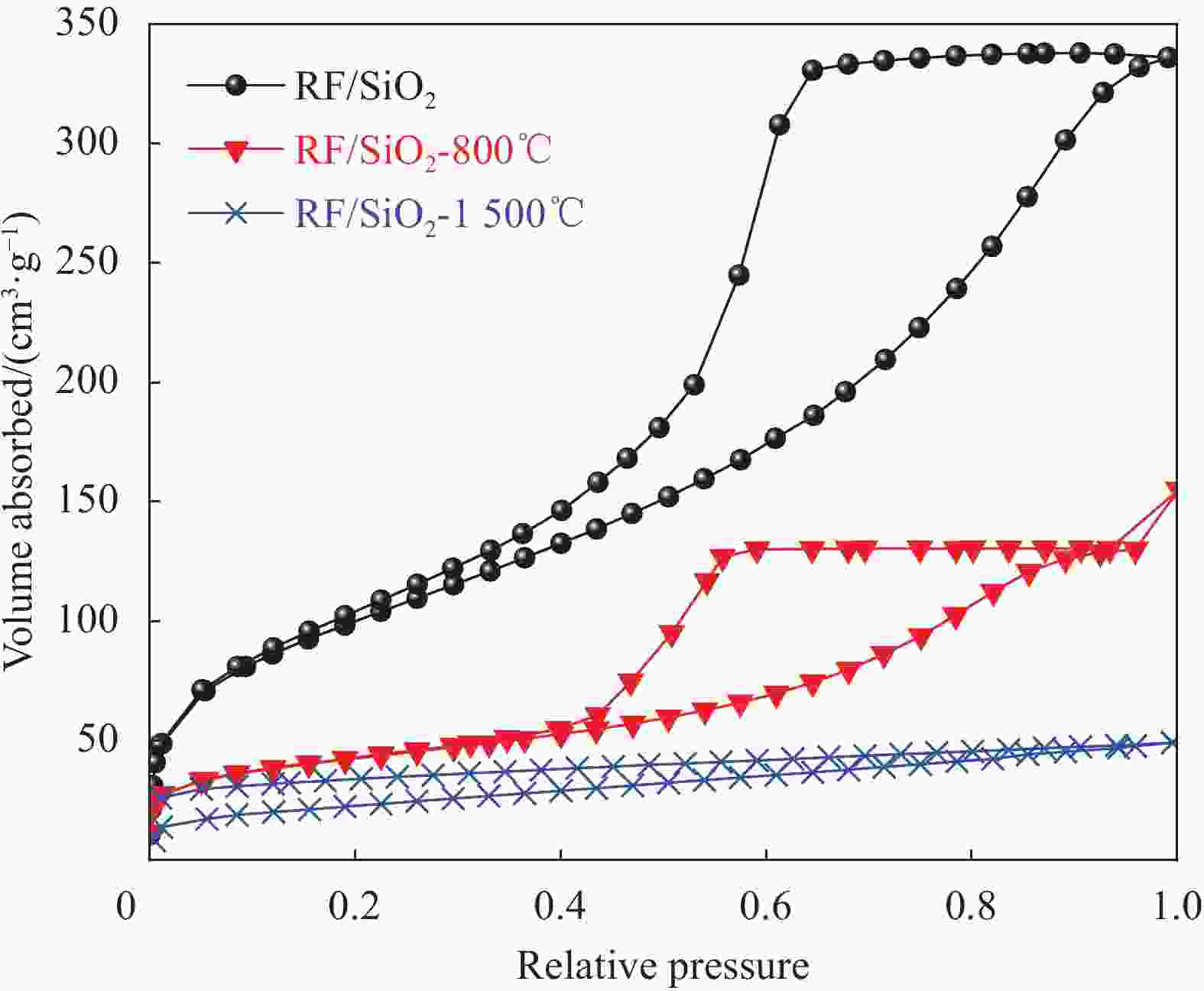
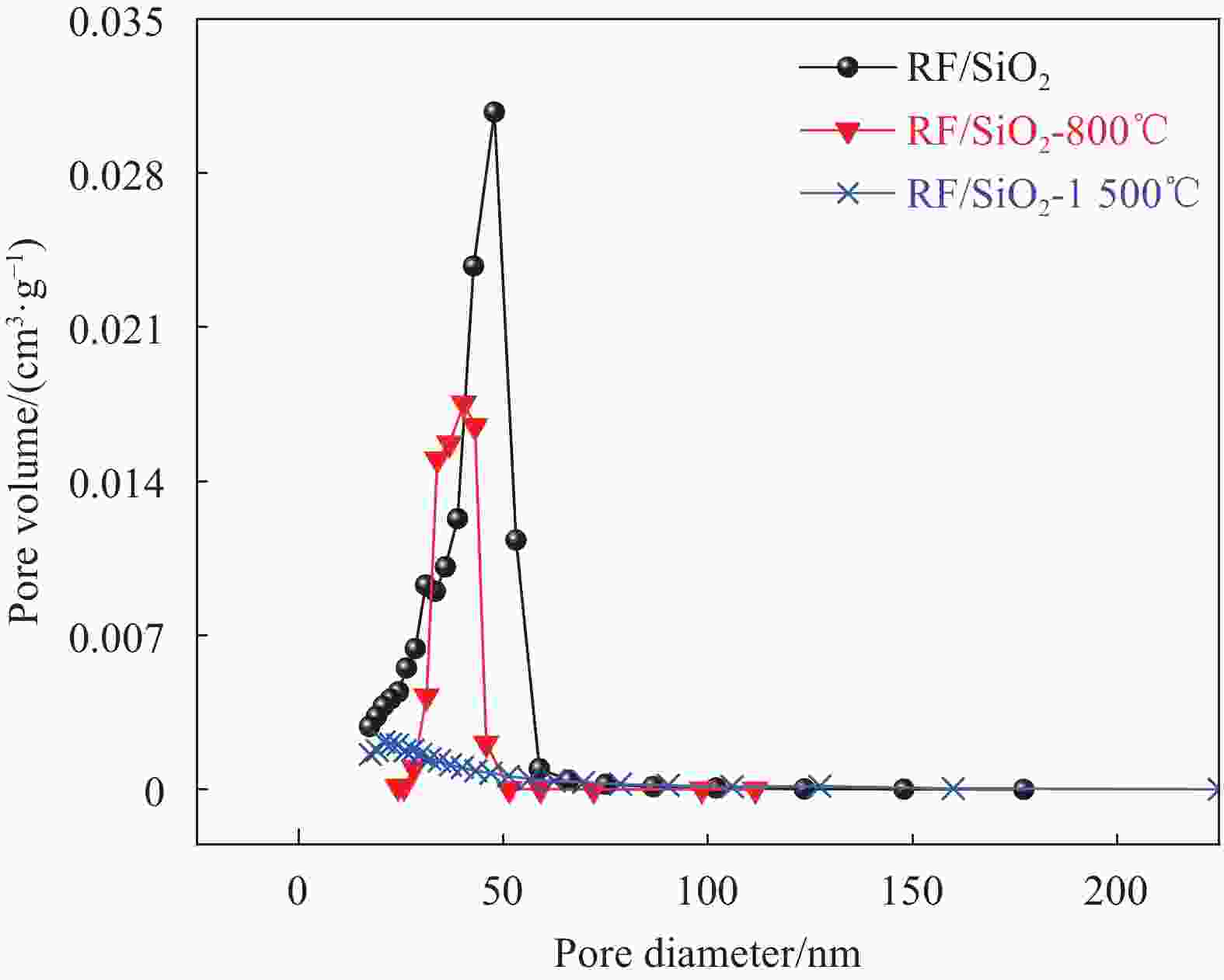
表 1 气凝胶的孔隙结构性质
Table 1. Pore structure properties of aerogels
Sample BET surface
area/(m2·g−1)Pore volume/
(cm3·g−1)RF/SiO2 370 0.50 RF/SiO2-800℃ 152 0.21 RF/SiO2-1500℃ 82 0.08 Note: BET—Brunau-Emmett-Teller. -
[1] SONG L, FAN B, CHEN Y, et al. Multifunctional SiC nanofiber aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(17): 25140-25150. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.174 [2] CHENG Y, XIE Y, MA Y, et al. Optimization of ion/electron channels enabled by multiscale MXene aerogel for integrated self-healable flexible energy storage and electronic skin system[J]. Nano Energy, 2023, 107: 108131. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.108131 [3] LIU J, LIU J, SHI F, et al. A facile pore size controlling strategy to construct rigid/flexible silica aerogels for super heat insulation and VOCs adsorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138196. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138196 [4] CHEN S, SHAO Q, HU L, et al. Hydrophobic and magnetic fabrication of hydroxyethyl cellulose-lignin aerogel through ultrasound enhancement for efficient oil/water separation[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2023, 52: 103503. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.103503 [5] SHAHZADI I, WU Y, LIN H, et al. Yeast biomass ornamented macro-hierarchical chitin nanofiber aerogel for enhanced adsorption of cadmium(II) ions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 453: 131312. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131312 [6] ANDERSON A M, BRUNO B A, SANTOS J, et al. PGM nanoparticle-based alumina aerogels for three-way catalyst applications[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2022, 172: 106547. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2022.106547 [7] WAN Y, WANG J, LI Z. Effect of modified SiO2 aerogel on the properties of inorganic cementing materials[J]. Materials Letters, 2023, 341: 134217. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2023.134217 [8] GAO X, XING Z, LI Z, et al. A review on recent advances in carbon aerogels: Their preparation and use in alkali-metal ion batteries[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2020, 35(5): 486-507. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(20)60504-2 [9] WANG Z, ZHAO H, DAI D, et al. Ultralight, tunable monolithic SiC aerogel for electromagnetic absorption with broad absorption band[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(18): 26416-26424. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.332 [10] TENG X, ZHANG B, YIN L, et al. Facile fabrication of superior Pd and Ce containing SiO2 aerogel composite adsorbents for deep desulfurization of model fuels and aromatics[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2023, 301: 127562. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127562 [11] JIANG D, QIN J, ZHOU X, et al. Improvement of thermal insulation and compressive performance of Al2O3-SiO2 aerogel by doping carbon nanotubes[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(11): 16290-16299. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.02.178 [12] XU M, LIU Z, ZHANG X, et al. Steam reforming of biomass gasification tar over Ni-based catalyst supported by TiO2-SiO2 composite[J]. Fuel, 2023, 343: 127934. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127934 [13] ZHAO Z, LI P, LI Y, et al. Durable thermal fluid super-repellency of elastic fluorine-modified SiO2@sponge composite aerogel[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 140247. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140247 [14] YANG M, YAGN L, CHEN Z, et al. Flexible electrospun strawberry-like structure SiO2 aerogel nanofibers for thermal insulation[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(6): 9165-9172. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.076 [15] WANG Y, CHU C, DUAN C, et al. Thermal insulation of 3D printed complex and miniaturized SiO2 aerogels at medium-high temperatures[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2023, 608: 122251. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122251 [16] YE X, CHEN Z, ZHANG J, et al. SiC network reinforced SiO2 aerogel with improved compressive strength and preeminent microwave absorption at elevated temperatures[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(22): 31497-31505. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.027 [17] MAO B, XIA X, QIN R, et al. Microstructure evolution and microwave absorbing properties of novel double-layered SiC reinforced SiO2 aerogel[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 936: 68314. [18] XIANG Z, HE Q, WANG Y, et al. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of SiC/SiO2 nanocomposites with different special structures[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 599: 153968. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153968 [19] TANG R, WANG H, CHEN Y, et al. Flexible preparation of nanoporous SiO2 aerogel as novel adsorbent for efficient adsorption of Zearalenone[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 109828. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.109828 [20] SAMANTA S, KHILARI S, BHUNIA K, et al. Double-metal-ion-exchanged mesoporous Zeolite as an efficient electrocatalyst for alkaline water oxidation: Synergy between Ni-Cu and their contents in catalytic activity enhancement[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(20): 10725-10736. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b01769 [21] PANG H, DUAN Y, DAI X, et al. The electromagnetic response of composition-regulated honeycomb structural materials used for broadband microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2021, 88: 203-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2021.01.072 [22] MA Y, QUAN B, ZENG Z, et al. Multiple interface-induced evolution of electromagnetic patterns for efficient microwave absorption at low thickness[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 8(7): 1810-1818. doi: 10.1039/D0QI01486A [23] GREEN M, CHEN X. Recent progress of nanomaterials for microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2019, 5(4): 503-541. doi: 10.1016/j.jmat.2019.07.003 [24] LI H, YUAN X, ZHAO P, et al. A synergistic strategy for SiC/C nanofibers@MXene with core-sheath microstructure toward efficient electromagnetic wave absorption and photothermal conversion[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 613: 155998. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155998 [25] CHENG R, WANG Y, DI X, et al. Heterostructure design of MOFs derived Co9S8/FeCoS2/C composite with efficient microwave absorption and waterproof functions[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2022, 129: 15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2022.04.031 [26] LU Z, WANG Y, DI X, et al. Heterostructure design of carbon fiber@graphene@layered double hydroxides synergistic microstructure for lightweight and flexible microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2022, 197: 466-475. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.06.075 -





 下载:
下载: