Degradation of oxytetracycline by the in situ hydrogen peroxide-producing photo-Fenton system g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+: Mechanism, degradation pathway and toxicity change analysis
-
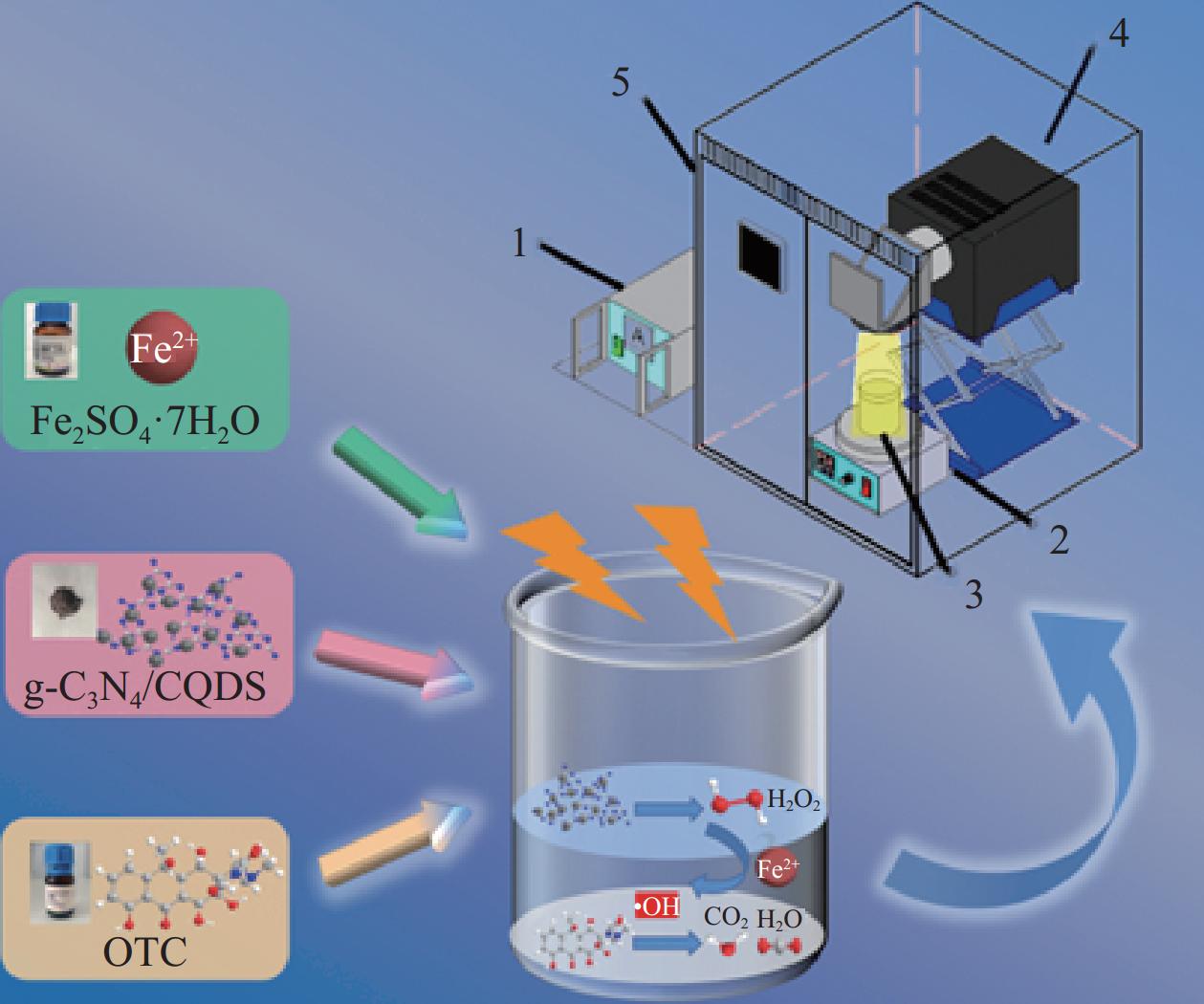
摘要: 芬顿反应是一种通过Fe2+催化H2O2分解生成羟基自由基(•OH)的氧化工艺,因其•OH生成速率快和操作简单等优点被广泛应用于废水中有机污染物的降解,然而存在需要外部加入H2O2和pH适用范围窄的缺陷限制其进一步应用。为解决以上问题,通过外加Fe2+活化复合光催化剂石墨相氮化碳/碳量子点(g-C3N4/CQDs)原位生成的H2O2,构建了g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+光芬顿体系,避免了H2O2在储存和运输过程中的潜在风险,并扩宽了反应的pH值范围。该体系对土霉素(OTC)的降解表现出优异的活性,在g-C3N4/CQDs投加量为120 mg,OTC初始浓度为20 mg·L−1,Fe2+投加量为0.36 mmol·L−1,OTC的初始pH为7时,其降解效率高达97%。基于自由基捕获、•OH的生成变化测定及与H2O2生成过程的对比等实验,证明g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+光芬顿降解OTC优异的活性,主要来源于Fe2+活化原位H2O2产生的•OH活性物种。进一步地,OTC降解的中间产物也通过质谱联用仪检测分析,并推断出OTC被降解的可能路径。此外,通过测量光密度(OD 600)值获得细菌的生长曲线,结果表明随着g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+降解OTC的进行,其反应溶液的毒性是逐渐减小的。最后,与外加H2O2传统芬顿体系降解OTC进行了对比分析,结果表明该光芬顿体系基本能够达到传统芬顿降解OTC的效果,且不受pH值范围的限制,为改善芬顿反应在实际废水处理中的应用提供了新的思路。Abstract: Fenton reaction is an oxidation process that generates hydroxyl radicals (•OH) through the decomposition of H2O2 catalyzed by Fe2+, which is widely used for the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater because of its fast •OH generation rate and simple operation. In this study, the g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ photo-Fenton system was constructed by adding Fe2+ activated composite photocatalyst graphite phase carbon nitride/carbon quantum dots (g-C3N4/CQDs) to generate H2O2 in situ, which avoids the potential risk of H2O2 during storage and transportation, and broadens the pH range of the reaction. The system showed excellent activity for the degradation of oxytetracycline (OTC) with a high degradation efficiency of 97% at a g-C3N4/CQDs dosing of 120 mg, an initial OTC concentration of 20 mg·L−1, an Fe2+ dosing of 0.36 mmol·L−1, and an initial pH of 7 for OTC solution. The excellent activity of g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ photo-Fenton degradation of OTC based on experiments such as radical capture, determination of changes in the generation of •OH and comparison with the H2O2 generation process was demonstrated to be mainly derived from the •OH active species generated by Fe2+ activation of in situ H2O2 production. Further, the intermediate products of OTC degradation were detected and analyzed by mass spectrometry, and the possible degradation paths of OTC were inferred. In addition, by measuring the optical density (OD600) value to obtain the growth curve of bacteria, the results showed that the toxicity of the reaction solution gradually decreased with the degradation of OTC by g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+. Finally, compared with the conventional Fenton system with the addition of H2O2 to degrade OTC, the results showed that the photo-Fenton system can basically achieve the effect of conventional Fenton, and it is not limited by the pH range which provides a new idea for improving the application of Fenton reaction in actual wastewater treatment.
-
Key words:
- photo-Fenton /
- photocatalysis /
- in-situ H2O2 /
- oxytetracycline /
- degradation path /
- toxicity analysis
-
图 3 (a) g-C3N4/CQDs光催化生产H2O2的能力;g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+体系对OTC的降解曲线(b)和降解效率(c)
The reaction conditions is g-C3N4/CQDs 120 mg, initial pH=7; C0—Initial concentration of OTC; C—Concentration of OTC after time t
Figure 3. (a) H2O2 photocatalytic productivity of g-C3N4/CQDs; Degradation curves (b) and degradation rate (c) of OTC by g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ system
图 4 不同g-C3N4/CQDs投加量对g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+体系降解OTC的降解曲线(a)、二级动力学方程(b)、降解效率(c)和不同投加量产H2O2的能力(d)
k—Second order rate constant
Figure 4. Degradation curves (a), second-order kinetic equation (b), degradation rate (c) of OTC with different dosage of g-C3N4/CQDs for g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ system and ability to produce H2O2 in different dosage (d)
图 8 g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+体系对比传统外加H2O2芬顿体系降解OTC的降解曲线(a)、二级动力学方程(b)和降解效率(pH=7,0.36 mmol·L−1 Fe2+,0.17 mmol·L−1 H2O2) (c) ;(d) g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+体系降解OTC的稳定性测试结果
Figure 8. Degradation curves (a), second-order kinetic equation (b) and degradation rate of OTC with g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ system compared with the traditional plus H2O2 Fenton system (pH=7, 0.36 mmol·L−1 Fe2+, 0.17 mmol·L−1 H2O2 ) (c) ; (d) Stability test results of g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ system for degradation of OTC
图 9 不同捕获剂对g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+降解OTC的影响(a)和g-C3N4/CQDs产 H2O2的影响(b);(c) •OH的生成变化测定实验;(d) g-C3N4/CQDs产H2O2、g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+体系•OH生成与OTC降解各时间段效果比例图
AO—Ammonium oxalate; p-BQ—p-benzoquinone; IPA—Isopropyl alcohol
Figure 9. Effects of different trapping agents on OTC degradation in g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ (a) and production of H2O2 in g-C3N4/CQDs (b); (c) Experiment for the determination of changes in the generation of •OH; (d) Proportion of the results of the H2O2 production capacity of g-C3N4/CQDs, the •OH generation capacity and the effect on degrading OTC of g-C3N4/CQDs/Fe2+ in each time period
-
[1] WU S, ZHANG J M, XIA A, et al. Microalgae cultivation for antibiotic oxytetracycline wastewater treatment[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 214: 113850. [2] WANG J S, YI X H, XU X T, et al. Eliminating tetracycline antibiotics matrix via photoactivated sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation process over the immobilized MIL-88A: Batch and continuous experiments[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431(3): 133213. [3] FANG G G, LI J L, ZHANG C, et al. Periodate activated by manganese oxide/biochar composites for antibiotic degradation in aqueous system: Combined effects of active manganese species and biochar[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 300: 118939. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118939 [4] VILLEGAS-GUZMAN P, GIANNAKIS S, RTIMI S, et al. A green solar photo-Fenton process for the elimination of bacteria and micropollutants in municipal wastewater treatment using mineral iron and natural organic acids[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 219: 538-549. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.07.066 [5] LIU Y, ZHAO Y, WANG J L. Fenton/Fenton-like processes with in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for degradation of emerging contaminants: Advances and prospects[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 404: 124191. [6] 于晓丹, 林鑫辰, 冯威, 等. Fe3O4/TiO2@生物碳骨架复合材料的一步法制备及UV-Fenton催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11): 2500-2506. doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180450YU Xiaodan, LIN Xinchen, FENG Wei, et al. One-step preparation and UV-Fenton properties of Fe3O4/TiO2@bio-carbon composities[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2500-2506(in Chinese). doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180450 [7] LIU Y, FAN Q, WANG J L. Zn-Fe-CNTs catalytic in situ generation of H2O2 for Fenton-like degradation of sulfamethoxazole[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 166-176. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.08.016 [8] WANG Y J, SONG H M, CHEN J, et al. A novel solar photo-Fenton system with self-synthesizing H2O2: Enhanced photo-induced catalytic performances and mechanism insights[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 512: 145650. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145650 [9] 张小玉, 曲干, 薛冬萍, 等. 碳基催化剂用于电催化氧还原生产H2O2的研究进展: 策略、计算及实际应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 24-46.ZHANG Xiaoyu, QU Gan, XUE Dongping, et al. Recent process of carbon-based catalysts for the production of H2O2 by electrocatalytic oxygen reduction: Strategies, calculation and practical[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 24-46 (in Chinese). [10] ZHOU L, FENG J R, QIU B C, et al. Ultrathin g-C3N4 nanosheet with hierarchical pores and desirable energy band for highly efficient H2O2 production[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 267: 118396. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118396 [11] 罗一飞, 石建惠, 王辉, 等. pg-C3N4/CQDs复合物可见光下光催化产过氧化氢的性能研究[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2023, 54(2): 235-240.LUO Yifei, SHI Jianhui, WANG Hui, et al. Photocatalytic production of hydrogen peroxide by pg-C3N4/CQDs composite under visible light[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology 2023, 54(2): 235-240(in Chinese). [12] 罗一飞. 磷掺杂和碳量子点负载改性多孔石墨相氮化碳可见光产过氧化氢的性能研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2023.LUO Yifei. Performance of phosphorus-doped and carbon quantum dot-loaded modified porous graphitic phase carbon nitride for hydrogen peroxide production under visible light [D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2023(in Chinese). [13] CLARIZIA L, RUSSO D, DI SOMMA I, et al. Homogeneous photo-Fenton processes at near neutral pH: A review[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 209: 358-371. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.011 [14] TIAN S H, ZHANG J L, CHEN J, et al. Fe2(MoO4)3 as an effective photo-Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of anionic and cationic dyes in a wide pH range[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(37): 13333-13341. [15] JIANG Z Y, WANG L Z, LEI J Y, et al. Photo-Fenton degradation of phenol by CdS/rGO/Fe2+ at natural pH with in situ-generated H2O2[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 241: 367-374. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.049 [16] 孙厚祥, 张立中, 张化冰. 复合材料TiO2/MCM-41光催化降解四环素的研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2023, 43(9): 119-125.SUN Houxiang, ZHANG Lizhong, ZHANG Huabing. Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by composite TiO2/MCM-41[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2023, 43(9): 119-125(in Chinese). [17] YANG S B, GONG Y J, ZHANG J S, et al. Exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as efficient catalysts for hydrogen evolution under visible light[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(17): 2452-2456. doi: 10.1002/adma.201204453 [18] DI J, XIA J X, LI X W, et al. Constructing confined surface carbon defects in ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride for photocatalytic free radical manipulation[J]. Carbon, 2016, 107: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.05.028 [19] TENG Z Y, LYU H Y, WANG C Y, et al. Bandgap engineering of ultrathin graphene-like carbon nitride nanosheets with controllable oxygenous functionalization[J]. Carbon, 2017, 113: 63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.11.030 [20] ZHAO S, ZHAO X. Polyoxometalates-derived metal oxides incorporated into graphitic carbon nitride framework for photocatalytic hydrogen peroxide production under visible light[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 366: 98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2018.08.003 [21] WANG M, JIN C Y, KANG J, et al. CuO/g-C3N4 2D/2D heterojunction photocatalysts as efficient peroxymonosulfate activators under visible light for oxytetracycline degradation: Characterization, efficiency and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 416: 128118. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128118 [22] ZHANG S, ZHAO S R, HUANG S J, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of oxytetracycline under visible light by nanohybrids of CoFe alloy nanoparticles and nitrogen-/sulfur-codoped mesoporous carbon[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 130516. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130516 [23] 王松, 徐立新, 郭庆, 等. 纳米Fe-TiO2可见光下光催化降解罗丹明B[J]. 功能材料, 2023, 54(4): 4150-4156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2023.04.021WANG Song, XU Lixin, GUO Qing, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B by nano Fe-TiO2 under visible light[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2023, 54(4): 4150-4156(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2023.04.021 [24] HU J, LI J, CUI J, et al. Surface oxygen vacancies enriched FeOOH/Bi2MoO6 photocatalysis-Fenton synergy degradation of organic pollutants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121399. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121399 [25] WANG L, ALI J, WANG Z B, et al. Oxygen nanobubbles enhanced photodegradation of oxytetracycline under visible light: Synergistic effect and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124227. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124227 [26] HAN C H, PARK H D, KIM S B, et al. Oxidation of tetracycline and oxytetracycline for the photo-Fenton process: Their transformation products and toxicity assessment[J]. Water Research, 2020, 172: 115514. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115514 [27] 王旭, 陈熙, 徐新阳, 等. CQDs/TiO2复合材料的制备及光催化降解抗生素[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(12): 3876-3885. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022040301WANG Xu, CHEN Xi, XU Xinyang, et al. Preparation of CQDs/TiO2 composites and photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic wastewater[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(12): 3876-3885(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022040301 [28] ZHANG Y, ZHOU M H. A critical review of the application of chelating agents to enable Fenton and Fenton-like reactions at high pH values[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 362: 436-450. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.035 [29] SHI Y H, SUN Y S, JIN J N, et al. Strongly coupled FeOOH nanoparticles/O doped g-C3N4 nanosheets for visible-light-driven effective treatment of oxytetracycline hydrochlorides[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(22): 33722-33735. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.07.318 [30] SHI W L, SUN W, LIU Y N, et al. A self-sufficient photo-Fenton system with coupling in-situ production H2O2 of ultrathin porous g-C3N4 nanosheets and amorphous FeOOH quantum dots[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 436: 129141. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129141 [31] TRAN M L, NGUYEN C H, VAN TRAN T T, et al. One-pot synthesis of bimetallic Pt/nZVI nanocomposites for enhanced removal of oxytetracycline: Roles of morphology changes and Pt catalysis[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2020, 111: 130-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2020.05.001 [32] HUO X Q, YI H, ALMATRAFI E, et al. Insights into Fenton-like oxidation of oxytetracycline mediated by Fe-doped porous g-C3N4 nanomaterials: Synthesis, performance and mechanism[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2023, 10(7): 1828-1841. [33] TANG S F, LI X, ZHANG C, et al. Strengthening decomposition of oxytetracycline in DBD plasma coupling with Fe-Mn oxide-loaded granular activated carbon[J]. Plasma Science & Technology, 2019, 21(2): 90-96. [34] GUSAIN R, KUMAR N, OPOKU F, et al. MoS2 nanosheet/ZnS composites for the visible-light-assisted photocatalytic degradation of oxytetracycline[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(5): 4721-4734. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c00330 [35] GAO S Y, FENG D K, CHEN F, et al. Multi-functional well-dispersed pomegranate-like nanospheres organized by ultrafine ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals for high-efficiency visible-light-Fenton catalytic activities[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 648: 129282. [36] LAI C, MA D S, YI H, et al. Functional partition of Fe and Ti co-doped g-C3N4 for photo-Fenton degradation of oxytetracycline: Performance, mechanism, and DFT study[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 306: 122546. [37] SUN H M, ZHOU T, KANG J N, et al. High-efficient degradation of oxytetracycline by visible photo-Fenton process using MnFe2O4/g-C3N4: Performance and mechanisms[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 299: 121771. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121771 [38] PEREIRA J H O S, VILAR V J P, BORGES M T, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of oxytetracycline using TiO2 under natural and simulated solar radiation[J]. Solar Energy, 2011, 85(11): 2732-2740. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2011.08.012 [39] LIU Y Q, HE X X, FU Y S, et al. Kinetics and mechanism investigation on the destruction of oxytetracycline by UV-254 nm activation of persulfate[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 305: 229-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.11.043 -






 下载:
下载: