Two-dimensional MXene supported MoO3/Ni-NiO heterostructures for high-performance hydrogen evolution reaction at alkaline condition
-
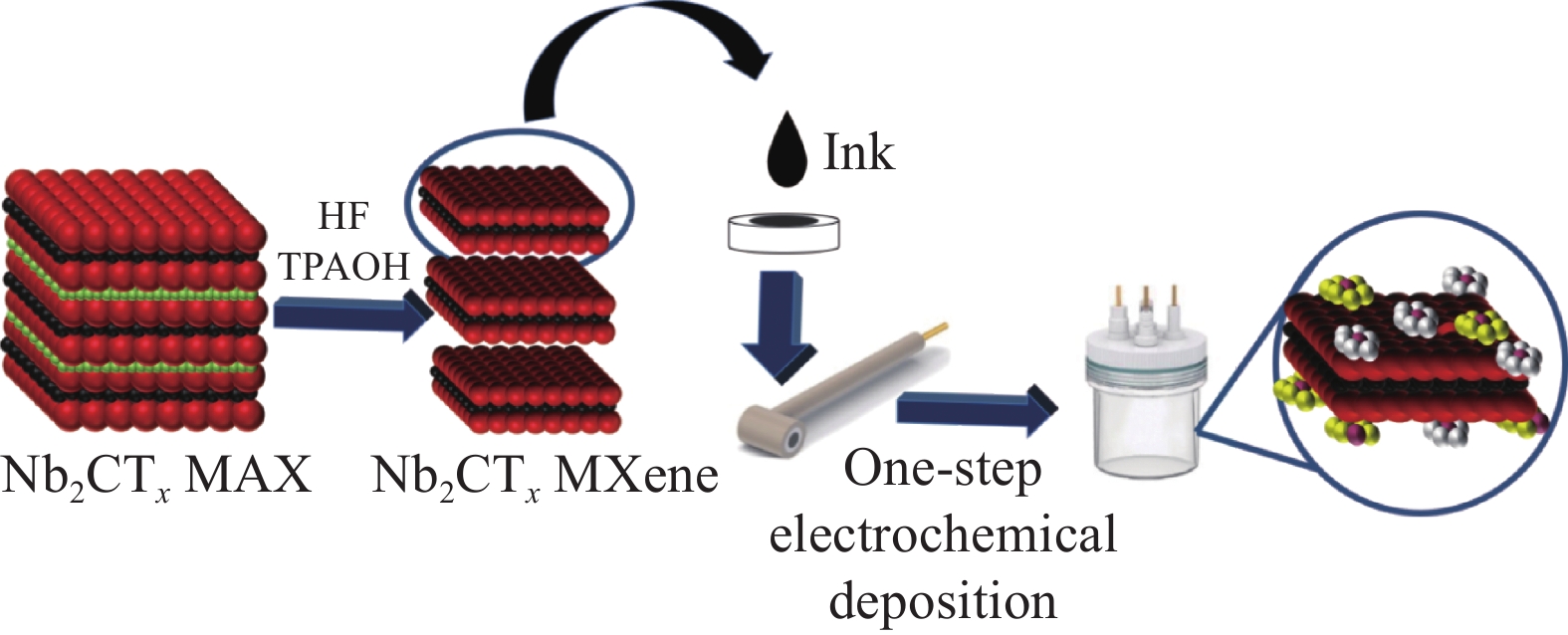
摘要: 氢能作为低碳和零碳能源,是未来国家能源体系的重要组成部分,开发高效、低廉的碱性析氢(HER)电催化剂对于氢能的大规模制备和利用具有重要的意义。本文以二维Nb2CTx MXene为载体,通过一步电化学共沉积法在其表面负载MoO3/Ni-NiO异质结构,得到具有优异电催化HER性能的MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx催化材料。采用XRD、SEM和TEM等手段对MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx的表面形貌和结构进行表征,发现通过一步电化学共沉积法成功地将MoO3/Ni-NiO异质结构紧密负载于Nb2CTx MXene纳米片表面。在1.0 mol/L KOH电解质中测试其HER性能,在10 mA·cm−2和100 mA·cm−2的电流密度时,MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx表现出较低的过电压,分别为8 mV和201 mV,Tafel斜率为51 mV·dec−1;并且在电流密度分别为10 mA·cm−2和50 mA·cm−2下连续电解产氢20 h,活性几乎保持不变,具有优异的碱性HER稳定性。此外,本文还采用工况电化学阻抗谱对不同催化电极材料在过电压从0~220 mV (vs 可逆氢电极(RHE))进行HER工况表征,结果表明MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx可有效促进水解离过程和活性氢吸附过程,从而提高HER活性。
-
关键词:
- 二维Nb2CTx MXene /
- MoO3/Ni-NiO异质结 /
- 电催化 /
- 碱性条件 /
- 析氢反应
Abstract: As a low- and zero-carbon energy source, hydrogen energy is an important part of the future national energy system. The development of an efficient and inexpensive alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) electrocatalyst is of great significance for the large-scale preparation and utilization of hydrogen energy. In this paper, the MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx was prepared by one-step co-electrodeposition method to loaded MoO3/Ni-NiO heterostructure on two-dimensional Nb2CTx MXene, and the obtained MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx exhibited excellent HER performance. The XRD, SEM and TEM were conducted to analyze the surface morphology and structure of the catalysts. Results demonstrate that the MoO3/Ni-NiO heterostructure were successfully electrodeposited on the surface of Nb2CTx MXene nanosheets. The results of HER tests in 1.0 mol/L KOH electrolyte show that the MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx at current densities of 10 and 100 mA·cm−2 has small overpotentials of 8 and 201 mV, respectively, and Tafel plot is 51 mV·dec−1. The MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx also has good catalytic stability with almost no detectable activity decay after 20 h HER test at current densities of 10 and 50 mA·cm−2, respectively. Besides, the operando electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements were used to estimate electrocatalytic HER kinetics of different catalysts at overpotential from 0 to 220 mV (vs reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE)), which indicating the MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx can effectively promote hydrolysis dissociation process and active hydrogen adsorption process, thus improving HER activity. -
图 2 (a) 碳纸(CP)基体上负载MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx、Ni/Nb2CTx、NiO/ Nb2CTx和Nb2CTx MXene的XRD图谱对比;((b), (c)) MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx不同放大倍数下的SEM图像;(d) MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx的EDS 图谱;((e)~(g)) MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx不同放大倍数下的TEM图像
Figure 2. (a) XRD patterns of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx, Ni/Nb2CTx, NiO/ Nb2CTx and Nb2CTx MXene loaded on carbon papers (CP); ((b), (c)) Different magnifications SEM images of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx; (d) EDS mapping images of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx; ((e)-(g)) Different magnifications TEM images of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx
图 3 MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx的XPS图谱;(a) MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx的XPS全谱图;(b) Nb2CTx MXene的Nb3d 图谱;(c) MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx和MoO3/Nb2CTx的Mo3d图谱对比;(d) MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx和Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx的Ni2p图谱对比
Figure 3. XPS spectra of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx: (a) Survey of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx; (b) Nb3d of of Nb2CTx MXene; (c) Comparison of Mo3d for MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx and MoO3/Nb2CTx; (d) Comparison of Ni2p for MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx and Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx
图 4 不同催化电极材料在1.0 mol/L KOH电解质中析氢反应(HER)性能:(a) 线性扫描伏安(LSV)曲线;(b) Tafel斜率对比;(c) 电化学活性面积(ECSA)对比;(d) EIS谱图对比;(e) MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx在不同电流密度下稳定性
η10—10 mA·cm−2 current density; η100—100 mA·cm−2 current density; j—Current density; Rs—Internal resistance of solution; C—Capacitance; R0—Electrode resistance; Z'—Real part of impedance; Z''—Imaginary part of impedance
Figure 4. Electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) performance of different catalytic electrodes in 1.0 mol/L KOH: (a) Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves; (b) Tafel patterns; (c) Comparison of electrochemical active surface area (ECSA); (d) Nyquist plots of EIS; (e) Stability of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx at different current densities
表 1 MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx与最近报道的代表性电催化剂的HER性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of electrochemical HER performance of MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx with recently reported representative electrocatalysts
No. Electrocatalyst Electrolyte η10/
mVTafel slop/
(mV·dec−1)Ref. 1 MoO3/Ni-NiO/Nb2CTx 1.0 mol/L KOH 8 51 This work 2 Nitrogen-rich Ag@Ti3C2Tx MXene 1.0 mol/L KOH 153 137.9 [29] 3 IrCo@basal plane-porous titanium carbide MXene 1.0 mol/L KOH 220 60 [30] 4 MoS2@Mo2CTx nanohybrids 1.0 mol/L KOH 176 207 [31] 5 Ru-MoS2/carbon cloth 1.0 mol/L KOH 41 114 [32] 6 Ru-MoO2 nanocomposites 1.0 mol/L KOH 29 44 [33] 7 NiCoP grains@Ti3C2Tx MXene 1.0 mol/L KOH 71 77.3 [24] 8 P-CoFe-LDH@MXene/NF 1.0 mol/L KOH 85 53.19 [34] 9 Co-doped β-Mo2C 1.0 mol/L KOH 141 62 [35] 10 TiO2@CoCH 1.0 mol/L KOH 99 80 [36] Notes:LDH—Layered double hydroxide; NF—Nickel foam;β-Mo2C—Porous molybdenum carbide;CoCH—Cobalt carbonate hydroxide. -
[1] KUMAR A, BUI V Q, LEE J S, et al. Moving beyond bimetallic-alloy to single-atom dimer atomic-interface for all-pH hydrogen evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 6766. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27145-3 [2] DAI J, ZHU Y L, CHEN Y, et al. Hydrogen spillover in complex oxide multifunctional sites improves acidic hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 1189. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28843-2 [3] 吴诗德, 张桂伟, 黄思光, 等. Ni-NiO/N-C的制备及其电解水析氢性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(4): 1667-1677.WU Shide, ZHANG Guiwei, HUANG Siguang, et al. Preparation of Ni-NiO/N-C electrocatalyst and its performance for water splitting into hydrogen[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(4): 1667-1677(in Chinese). [4] WANG Y Q, ZHAO L L, MA J Z, et al. Confined interface transformation of metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient oxygen evolution reactions[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(9): 3830-3841. [5] YU H Z, ZHU S Q, HAO Y S, et al. Modulating local interfacial bonding environment of heterostructures for energy-saving hydrogen production at high current densities[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(12): 2212811. [6] LI M, WANG X, LIU K, et al. Ce-induced differentiated regulation of Co sites via gradient orbital coupling for bifunctional water-splitting reactions[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(30): 2301162. [7] JIANG B W, YANG T, WANG T T, et al. Edge stimulated hydrogen evolution reaction on monodispersed MXene quantum dots[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 442: 136119. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136119 [8] WU Y C, WEI W, YU R H, et al. Anchoring sub-nanometer Pt clusters on crumpled paper-like MXene enables high hydrogen evolution mass activity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(17): 2110910. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202110910 [9] 赖嘉俊, 李潇潇, 曾传旺, 等. 富氧空位铁基复合材料的制备及其电催化析氢性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(5): 2827-2835.LAI Jiajun, LI Xiaoxiao, ZENG Chuanwang, et al. Preparation and electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of iron-based composites with rich oxygen vacancies[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(5): 2827-2835(in Chinese). [10] SUBBARAMAN R, TRIPKOVIC D, STRMCNIK D, et al. Enhancing hydrogen evolution activity in water splitting by tailoring Li+-Ni(OH)2-Pt interfaces[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6060): 1256-1260. doi: 10.1126/science.1211934 [11] ZHENG Y, JIAO Y, VASILEFF A, et al. The hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solution: From theory, single crystal models, to practical electrocatalysts[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(26): 7568-7579. [12] 李创, 王宇, 候利强, 等. 多孔碳负载钌单原子和钌纳米团簇催化剂用于高效析氢反应[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(4): 2155-2168.LI Chuang, WANG Yu, HOU Liqiang, et al. Porous carbon supported ruthenium single atom and ruthenium nanoclusters catalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(4): 2155-2168(in Chinese). [13] KIM J, JUNG H, JUNG S M, et al. Tailoring binding abilities by incorporating oxophilic transition metals on 3D nanostructured Ni arrays for accelerated alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(3): 1399-1408. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c10661 [14] SUBBARAMAN R, TRIPKOVIC D, CHANG K C, et al. Trends in activity for the water electrolyser reactions on 3d M (Ni, Co, Fe, Mn) hydr(oxy)oxide catalysts[J]. Nature Materials, 2012, 11: 550-557. [15] LIU X, NI K, NIU C J, et al. Upraising the O2p orbital by integrating Ni with MoO2 for accelerating hydrogen evolution kinetics[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(3): 2275-2285. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b04817 [16] MAO B G, SUN P P, JIANG Y, et al. Identifying the transfer kinetics of adsorbed hydroxyl as a descriptor of alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 132(35): 15232-15237. [17] NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2[J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(37): 4248-4253. doi: 10.1002/adma.201102306 [18] LIU A M, LIANG X Y, REN X F, et al. Recent progress in MXene-based materials: Potential high-performance electrocatalysts[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(38): 2003437. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202003437 [19] VAHIDMOHAMMADI A, ROSEN J, GOGOTSI Y. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes)[J]. Science, 2021, 372: 6547. [20] CHU K, LUO Y J, SHEN P, et al. Unveiling the synergy of O-vacancy and heterostructure over MoO3−x/MXene for N2 electroreduction to NH3[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(3): 2103022. doi: 10.1002/aenm.202103022 [21] CHU K, LI X C, LI Q Q, et al. Synergistic enhancement of electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction over boron nitride quantum dots decorated Nb2CT x-MXene[J]. Small, 2021, 17(40): e2102363. [22] LI X C, LUO Y J, LI Q Q, et al. Constructing an electron-rich interface over an Sb/Nb2CT x-MXene heterojunction for enhanced electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(29): 15955-15962. doi: 10.1039/D1TA03662A [23] YAN Y, ZHANG R Z, YU Y D, et al. Interfacial optimization of PtNi octahedrons@Ti3C2 MXene with enhanced alkaline hydrogen evolution activity and stability[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 291: 120100. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120100 [24] NIU H J, YAN Y, JIANG S S, et al. Interfaces decrease the alkaline hydrogen-evolution kinetics energy barrier on NiCoP/Ti3C2T x MXene[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(7): 11049-11058. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c03711 [25] LI X P, WANG Y, WANG J J, et al. Sequential electrodeposition of bifunctional catalytically active structures in MoO3/Ni-NiO composite electrocatalysts for selective hydrogen and oxygen evolution[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(39): 2003414. [26] XU D, PAN Y, ZHU L K, et al. Simple coordination complex-derived Ni NP anchored N-doped porous carbons with high performance for reduction of nitroarenes[J]. CrystEngComm, 2017, 19(44): 6612-6619. doi: 10.1039/C7CE01571B [27] ZHANG S J, ZHUO H, LI S Q, et al. Effects of surface functionalization of MXene-based nanocatalysts on hydrogen evolution reaction performance[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 368: 187-195. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.02.002 [28] LI M X, ZHU Y, WANG H Y, et al. Ni strongly coupled with Mo2C encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers as robust bifunctional catalyst for overall water splitting[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(10): 1803185. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201803185 [29] YUAN Z Y, WANG L L, CAO J M, et al. Ultraviolet-assisted construction of nitrogen-rich Ag@Ti3C2T x MXene for highly efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis and supercapacitor[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2020, 7(23): 2001449. doi: 10.1002/admi.202001449 [30] LE T A, TRAN N Q, HONG Y, et al. Porosity-engineering of MXene as a support material for a highly efficient electrocatalyst toward overall water splitting[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(5): 945-955. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201903222 [31] REN J, ZONG H, SUN Y Y, et al. 2D organ-like molybdenum carbide (MXene) coupled with MoS2 nanoflowers enhances the catalytic activity in the hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. CrystEngComm, 2020, 22(8): 1395-1403. doi: 10.1039/C9CE01777A [32] WANG D W, LI Q, HAN C, et al. Single-atom ruthenium based catalyst for enhanced hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 249: 91-97. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.02.059 [33] JIANG P, YANG Y, SHI R H, et al. Pt-like electrocatalytic behavior of Ru-MoO2 nanocomposites for the hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(11): 5475-5485. doi: 10.1039/C6TA09994G [34] DENG L Q, ZHANG K, SHI D, et al. Rational design of Schottky heterojunction with modulating surface electron density for high-performance overall water splitting[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 299: 120660. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120660 [35] MA Y F, CHEN M, GENG H B, et al. Synergistically tuning electronic structure of porous β-Mo2C spheres by Co doping and Mo-vacancies defect engineering for optimizing hydrogen evolution reaction activity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(19): 2000561. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000561 [36] YUAN L, LIU S, XU S C, et al. Modulation of volmer step for efficient alkaline water splitting implemented by titanium oxide promoting surface reconstruction of cobalt carbonate hydroxide[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 82: 105732. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105732 [37] XIAO Z H, HUANG Y C, DONG C L, et al. Operando identification of the dynamic behavior of oxygen vacancy-rich Co3O4 for oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(28): 12087-12095. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c00257 [38] LI J Y, LIU H X, GOU W Y, et al. Ethylene-glycol ligand environment facilitates highly efficient hydrogen evolution of Pt/CoP through proton concentration and hydrogen spillover[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(7): 2298-2304. -






 下载:
下载: