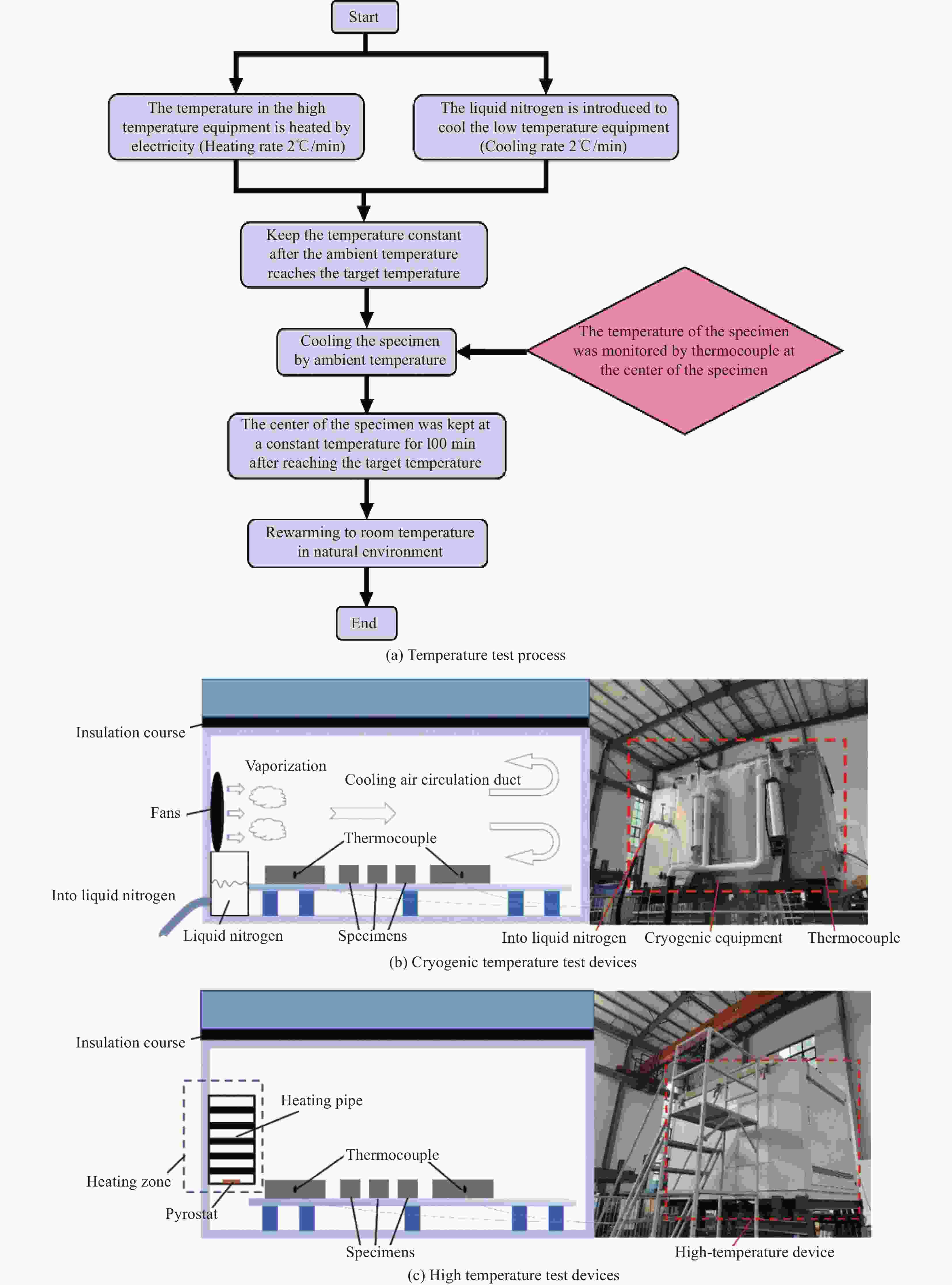
Study on mechanical properties of ultra-high toughness cementitious composites after medium-high temperature and low temperature
-
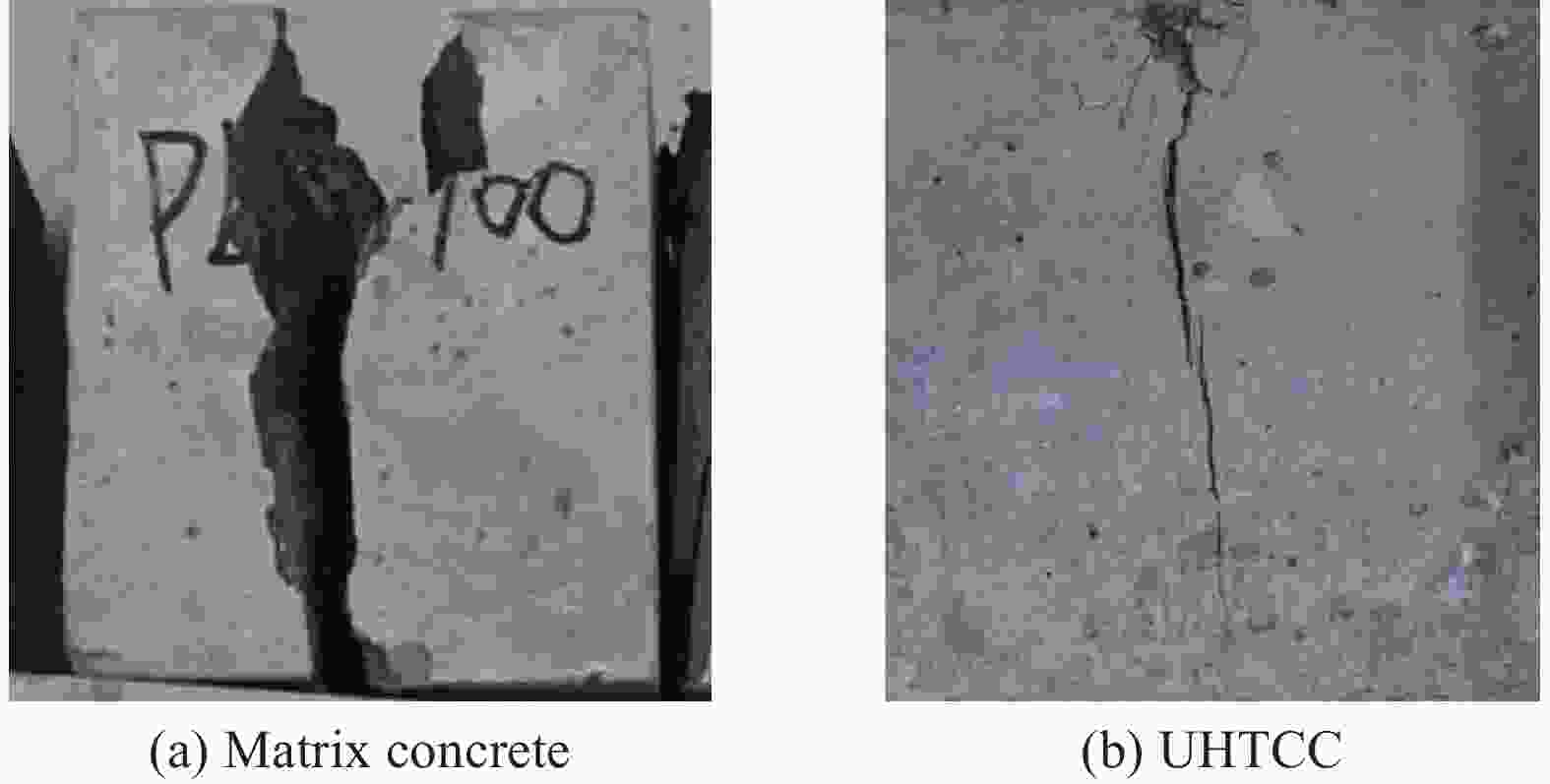
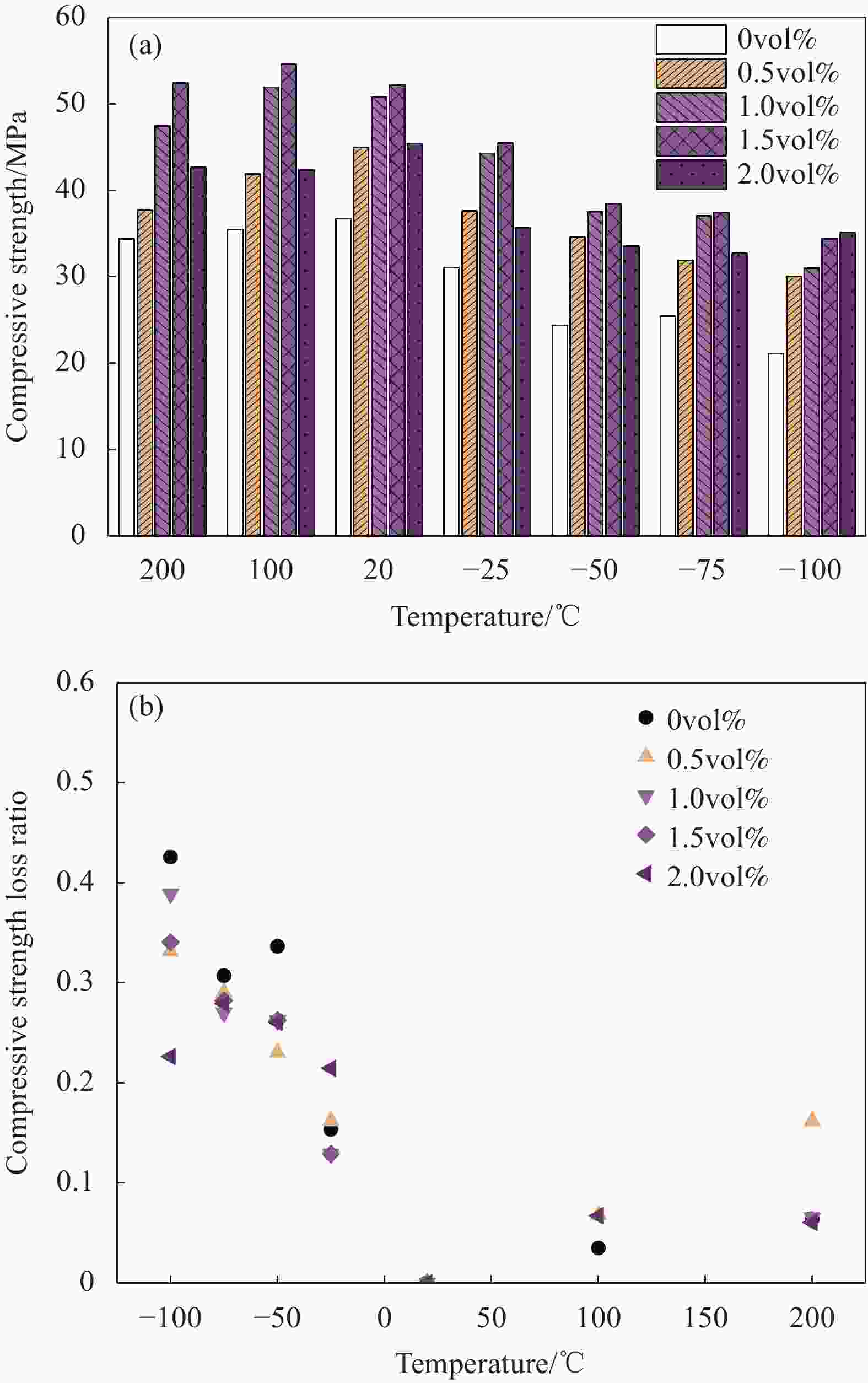
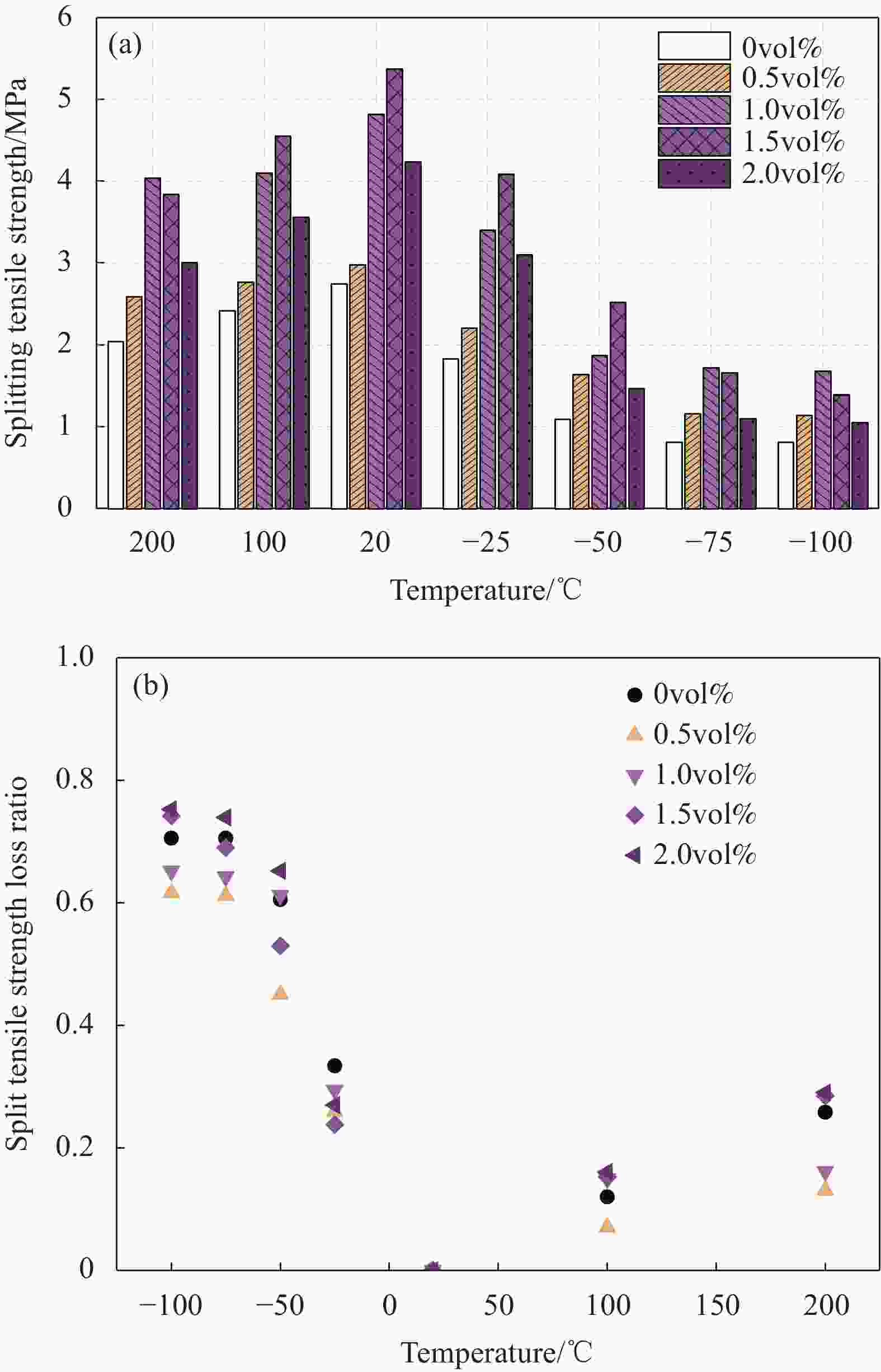
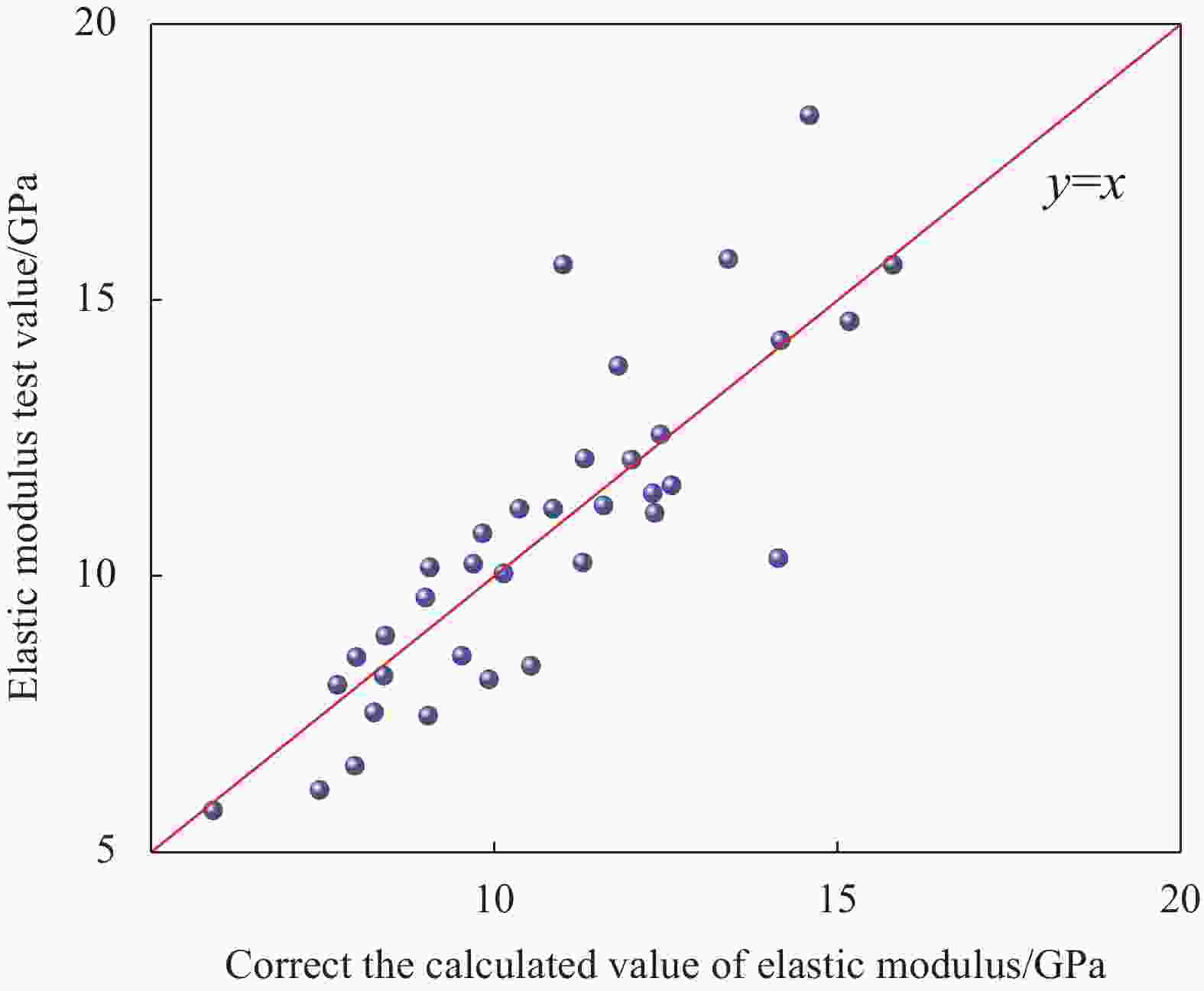
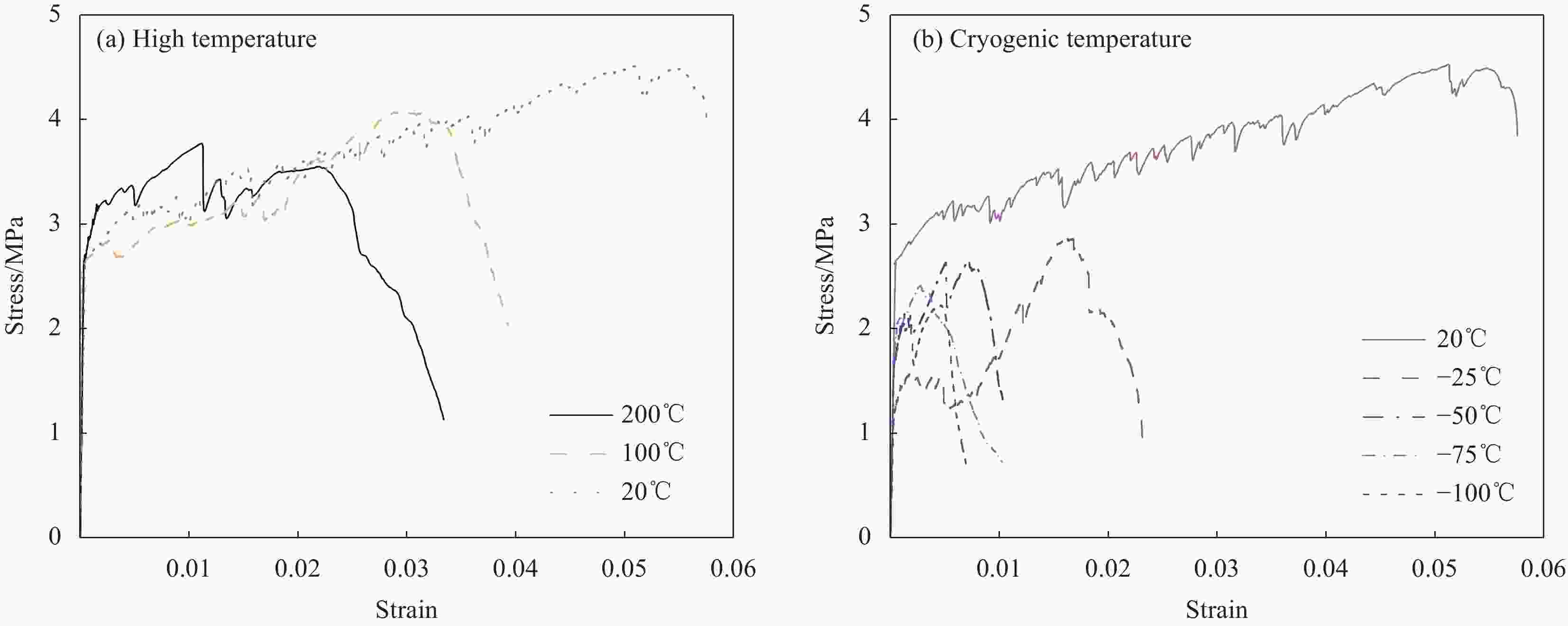
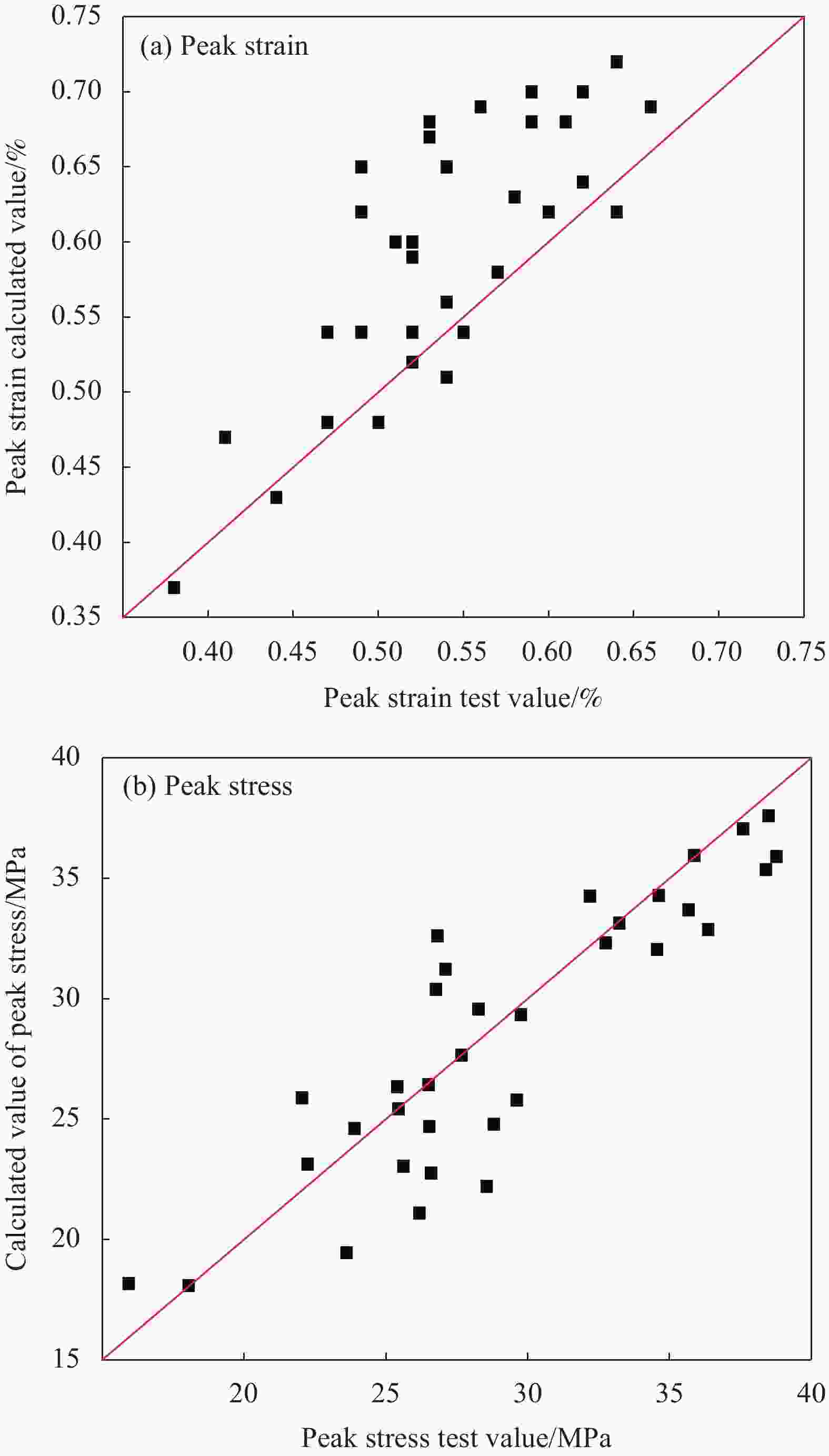
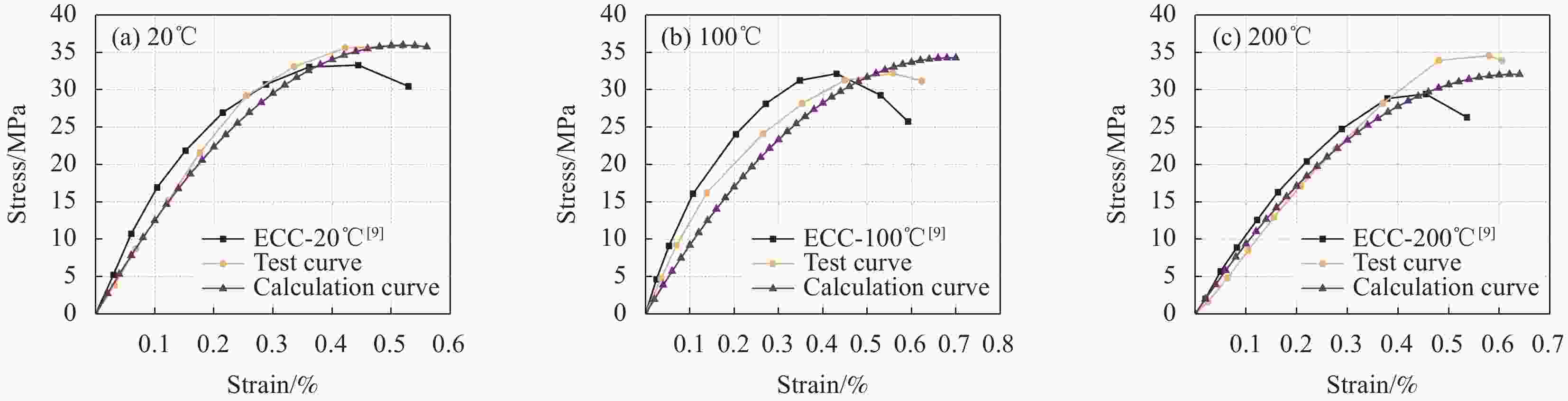
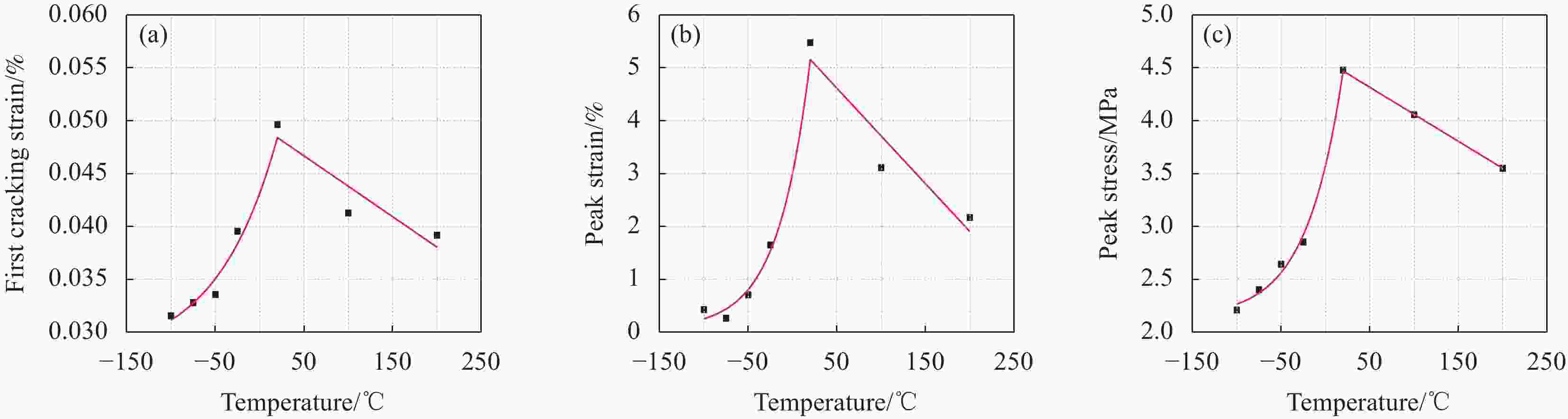
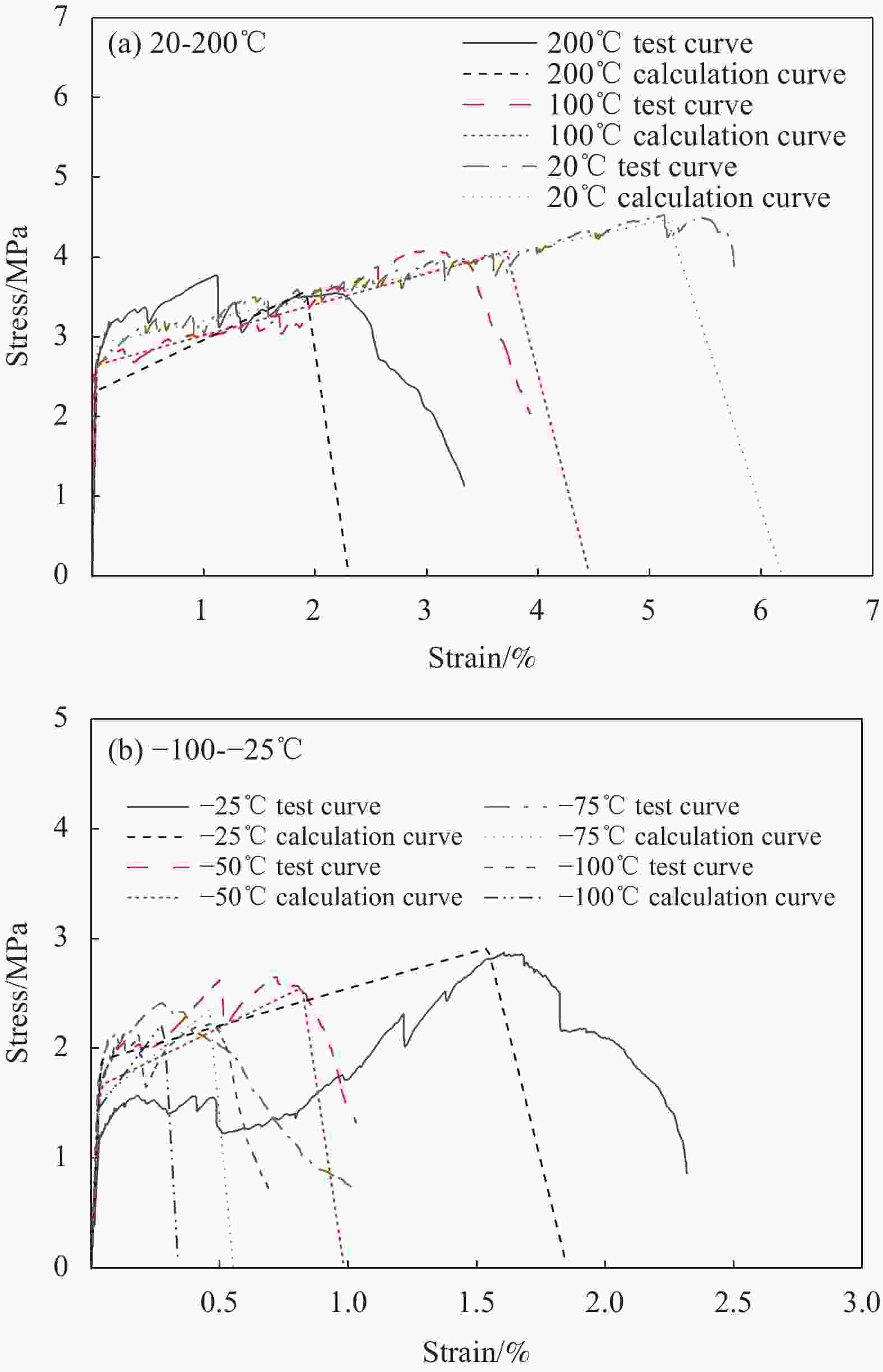
摘要: 为研究超高韧性水泥基复合材料(UHTCC)在200~−100℃温度作用后的力学性能,设计了不同纤维体积掺量的UHTCC,经中高温和低温作用后进行基本力学性能试验,通过UHTCC强度和变形等参数评价了中高温和低温作用后UHTCC的力学性能。结果表明:纤维的掺入能有效改善基体的脆性,提升材料的韧性;同时温度作用导致材料内部出现初始缺陷,对UHTCC的力学性能有明显的影响,且低温作用的影响要明显高于高温作用,当温度降低至−100℃时,UHTCC强度最大降低约75%,变形最大降低约92%,但温度作用未对UHTCC的泊松比产生明显影响。在此基础上提出了中高温及低温作用后UHTCC轴压和轴拉应力-应变关系回归模型,为UHTCC材料在极端温度环境下的性能设计和工程应用提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 超高韧性水泥基复合材料 /
- 中高温 /
- 低温 /
- 力学性能 /
- 本构模型
Abstract: In order to study the mechanical properties of ultra-high toughness cementitious composites (UHTCC) after temperatures of 200-−100℃, UHTCC with different fiber volume content was designed. The basic mechanical properties of UHTCC after medium-high temperatures and cryogenic temperatures were tested, and the mechanical properties of UHTCC after medium-high temperatures and cryogenic temperatures were evaluated by parameters such as strength and deformation of UHTCC. The results show that the incorporation of fibers can effectively improve the brittleness of the material and enhance the toughness of the material. The temperature effect makes the initial defects appear inside the material, which has a significant effect on the mechanical properties of UHTCC, and the effect of low temperature is significantly higher than that of high temperature. When the temperature is reduced to −100℃, the strength of UHTCC is reduced by about 71% at most, and the deformation is reduced by about 92% at most, but the temperature has no significant effect on the Poisson's ratio of UHTCC. On this basis, the regression model of axial compression and axial tensile stress-strain relationship of UHTCC after medium-high temperatures and cryogenic temperatures is proposed, which provides a reference for the performance design and engineering application of UHTCC materials at extreme temperatures. -
表 1 水泥、粉煤灰和硅灰的物理化学性质
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of cement, fly ash and silica fume
Binder Constituent mass fraction/wt% Specific surface area/(cm2·g−1) Density/(g·cm−3) CaO Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 MgO SO3 Cement 64.94 4.50 19.58 3.20 2.14 3.06 3413 3.15 Fly ash 2.44 30.63 48.74 2.61 1.21 1.02 8000 1.90 Silica fume 4.32 0.42 93.52 0.18 0.34 0.15 200000 2.20 表 2 材料配比
Table 2. Ratio of materials
Fly ash/(kg·m−3) Cement/(kg·m−3) Sand/(kg·m−3) Silica fume/(kg·m−3) Water/(kg·m−3) Water reducer/(kg·m−3) Fiber content/vol% 811.6 493.0 386.7 13.3 313.1 4.2 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 表 3 聚乙烯醇(PVA)纤维性能指标
Table 3. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber performance index
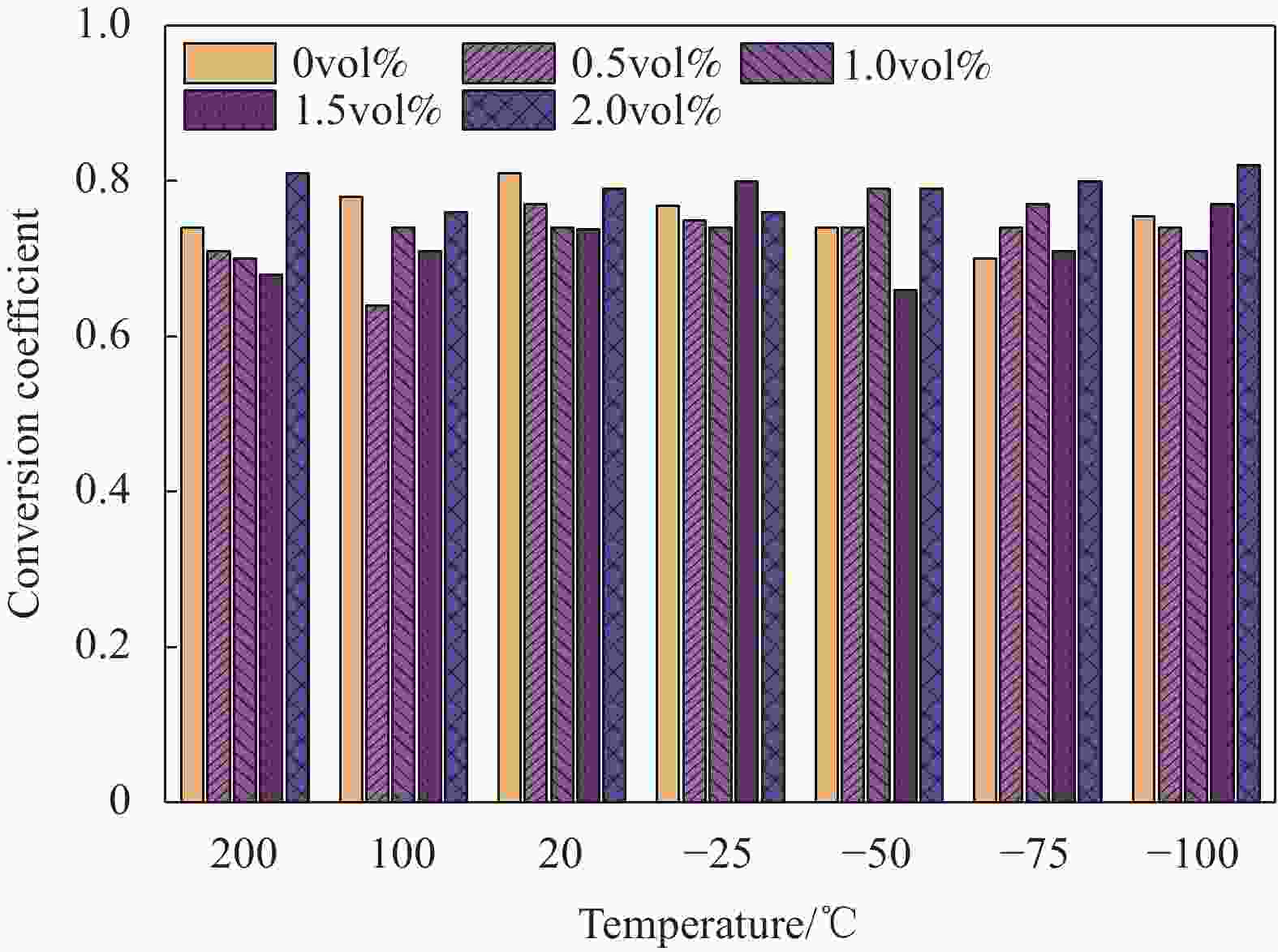
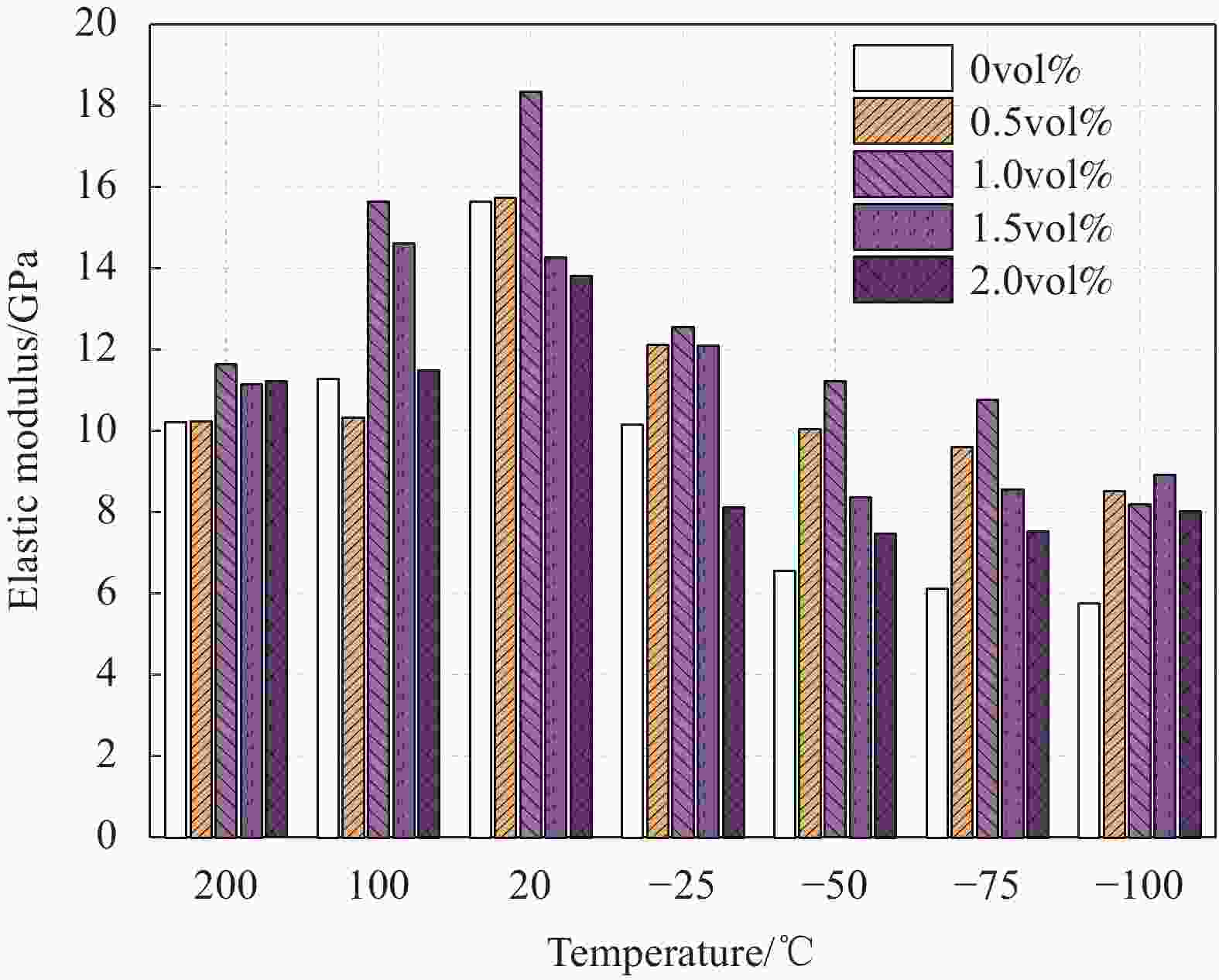
Model Density/(g·cm−3) Diameter/mm Length/mm Elastic modulus/GPa Tensile strength/MPa Elongation/% REC15×12 1.3 0.04 12 42.8 1620 6 表 4 UHTCC强度转换系数α
Table 4. Strength conversion coefficient α of UHTCC
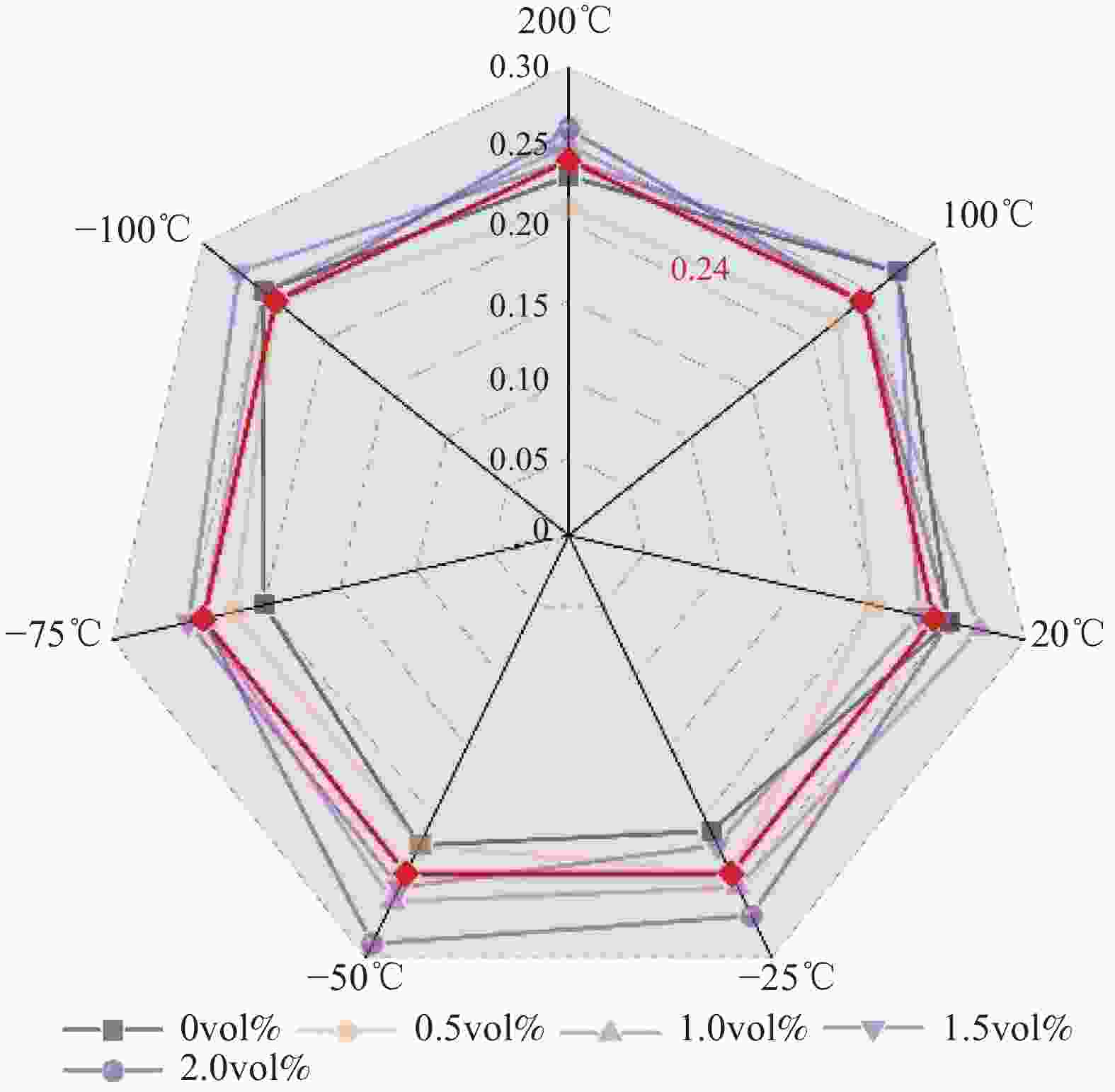
T/℃ α 200 0.73 100 0.73 20 0.77 −25 0.76 −50 0.74 −75 0.74 −100 0.76 Note: T—Temperature. -
[1] 韩广忠. 中国新建 LNG 接收站的经营困境及其对策[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(5):168-173.HAN Guangzhong. The business difficulties in China newly-built LNG receiving terminals and countermeasures[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2014,34(5):168-173(in Chinese). [2] 侯明扬. 全球LNG市场2021年回顾及2022年展望[J]. 油气与新能源, 2022, 34(2):20-24.HOU Mingyang. Review of global LNG market in 2021 and outlook of 2022[J]. Petroleum and New Energy,2022,34(2):20-24(in Chinese). [3] 孙曼丽, 蒙青山, 秦锋, 等. 中国天然气分布式能源“十四五”前景预测及重点区域分析[J]. 国际石油经济, 2022, 30(6):74-79, 86.SUN Manli, MENG Qingshan, QIN Feng, et al. Prospect forecast and key area analysis on natural gas distributed energy in China during the 14th Five-Year Plan period[J]. International Petroleum Economics,2022,30(6):74-79, 86(in Chinese). [4] DEROSA D, HOULT N A, GREEN M F. Effects of varying temperature on the performance of reinforced concrete[J]. Materials and Structures,2015,48(4):1109-1123. doi: 10.1617/s11527-013-0218-y [5] GERWICK B. Eighth international congress of the FIP[J]. Engineering Structures,1978,1(1):55. doi: 10.1016/0141-0296(78)90010-X [6] 蔡向荣, 徐世烺. UHTCC薄板弯曲荷载-变形硬化曲线与单轴拉伸应力-应变硬化曲线对应关系研究[J]. 工程力学, 2010, 27(1):8-16.CAI Xiangrong, XU Shilang. Study on corresponding relationships between flexural load-deformation hardening curves and tensile stress-strain hardening curves of UHTCC[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2010,27(1):8-16(in Chinese). [7] 徐世烺, 李贺东. 超高韧性水泥基复合材料研究进展及其工程应用[J]. 土木工程学报, 2008, 41(6):45-60.XU Shilang, LI Hedong. A review on the development of research and application of ultra high toughness cementitious composites[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2008,41(6):45-60(in Chinese). [8] 张秀芳, 徐世烺, 侯利军. 采用超高韧性水泥基复合材料提高钢筋混凝土梁弯曲抗裂性能研究(II): 试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2009, 42(10):53-66.ZHANG Xiufang, XU Shilang, HOU Lijun. Improvement on flexural and cracking behavior of RC beam using ultra-high toughness cementitious composite II: Experimental study[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2009,42(10):53-66(in Chinese). [9] 李红兵. 超高韧性水泥基复合材料高温性能试验研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016.LI Hongbing. Experimental research on high temperature properties of engineered cementitious composites[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016(in Chinese). [10] 陈猛, 曹宇新, 王瑜婷. 工程水泥基复合材料高温损伤超声特性[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(11):1638-1643.CHEN Meng, CAO Yuxin, WANG Yuting. Ultrasonic characteristics of thermal-damaged engineered cementitious composites[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2022,43(11):1638-1643(in Chinese). [11] 时旭东, 马驰, 张天申, 等. 不同强度等级混凝土–190℃时受压强度性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(3):61-67.SHI Xudong, MA Chi, ZHANG Tianshen, et al. Experimental study on compressive behavior of different strength grade concretes exposed to –190℃[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2017,34(3):61-67(in Chinese). [12] 时旭东, 居易, 郑建华, 等. 混凝土低温受压强度试验研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2014, 44(5):29-33.SHI Xudong, JU Yi, ZHENG Jianhua, et al. Experimental study on compressive strength of concrete exposed to cryogenic temperature[J]. Building Structure,2014,44(5):29-33(in Chinese). [13] 时旭东, 张亮, 郑建华, 等. 低温-常温循环作用下混凝土力学性能试验研究[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2012, 7(7):6-10.SHI Xudong, ZHANG Liang, ZHENG Jianhua, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of concrete under cryogenic-normal temperatures cycles[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products,2012,7(7):6-10(in Chinese). [14] DAHMANI L, KHENANE A, KACI S. Behavior of the reinforced concrete at cryogenic temperatures[J]. Cryogenics,2007,47(9):517-525. [15] DAHMANI L. Behavior of water in the concrete during the freezing process[J]. International Journal of Materials Science,2011,6(2):247-254. [16] MASAD N, ZOLLINGER D, KIM S M, et al. Meso-scale model for simulations of concrete subjected to cryogenic temperatures[J]. Materials and Structures,2016,49(6):2141-2159. doi: 10.1617/s11527-015-0639-x [17] RAHMAN S, GRASLEY Z. A poromechanical model of freezing concrete to elucidate damage mechanisms associated with substandard aggregates[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2014,55:88-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.10.001 [18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2009.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods for long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. Beijing: China Plan Press, 2009(in Chinese). [19] 中国工程建设标准化协会. 纤维混凝土试验方法标准: CECS 13—2009[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2009.China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization. Standard test methods for fiber reinforced concrete: CECS 13—2009[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2009(in Chinese). [20] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构试验方法标准: GB/T 50152—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of concrete structures: GB/T 50152—2012[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2012(in Chinese). [21] 李艳, 刘泽军. 高韧性PVA-FRCC单轴受压力学性能及本构关系[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2014, 17(4):606-612.LI Yan, LIU Zejun. Study on mechanical performance and constitutive equation of high toughness PVA-FRCC under uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2014,17(4):606-612(in Chinese). [22] 过镇海. 混凝土的强度和变形−试验基础和本构关系[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1997: 31-32.GUO Zhenhai. Strength and deformation of concrete—Experimental basis and constitutive relation[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1997: 31-32(in Chinese). [23] 曾志兴. 钢纤维轻骨料混凝土力学性能的试验研究及损伤断裂分析[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2002.ZENG Zhixing. Experimental study on mechanical properties and damage fracture analysis of steel fiber reinforced lightweight aggregate concrete[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2002(in Chinese). [24] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构设计规范: GB/T 50010—2010[S]. 北京: 建筑工业出版社, 2010.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for design of concrete structures: GB/T 50010—2010[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2010(in Chinese). [25] 张勤, 朱潇鹏, 代欢欢, 等. 耐碱玻璃纤维ECC复合材料受压应力-应变关系[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2022, 54(5):82-92.ZHANG Qin, ZHU Xiaopeng, DAI Huanhuan, et al. Stress-strain relationship of alkali-resistant glass fiber ECC composites under compression[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2022,54(5):82-92(in Chinese). [26] HAN T S, FEENSTRA P H, BILLINGTON S L. Simulation of highly ductile fiber-reinforced cement based composite components under cyclic loading[J]. ACI Structural Journal,2003,100(6):749. [27] SKAPSKI A, BILLUPS R, ROONEY A. Capillary cone method for determination of surface tension of solids[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics,1957,26(5):1350-1351. [28] KOGBARA R B, IYENGAR S R, GRASLEY Z C, et al. A review of concrete properties at cryogenic temperatures: Towards direct LNG containment[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2013,47(10):760-770. [29] ROSTÁSY F S, WIEDEMANN G. Stress-strain-behaviour of concrete at extremely low temperature[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,1980,10(4):565-572. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(80)90100-3 -





 下载:
下载: