Mechanical properties and microstructure of hybrid fiber reinforced rubber concrete under sulfate attack
-
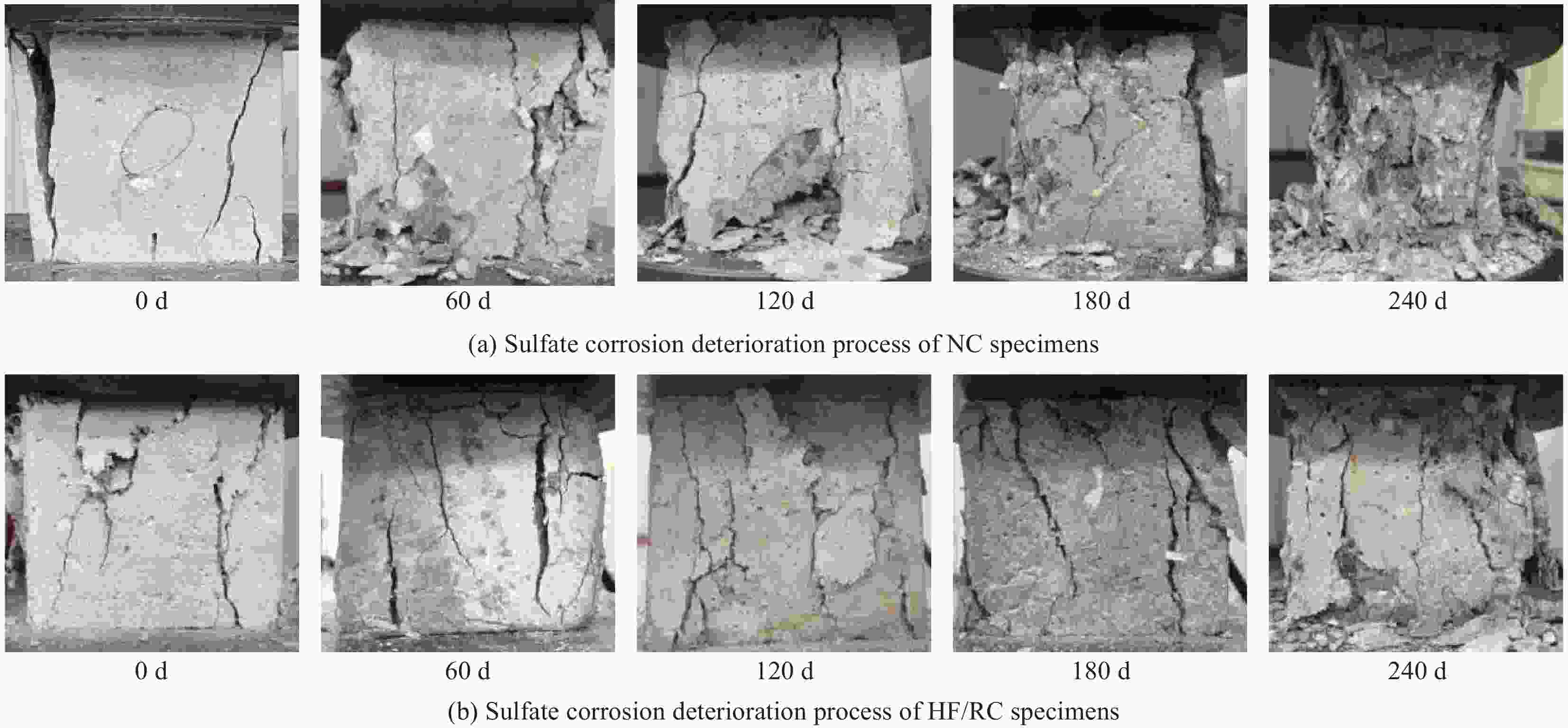
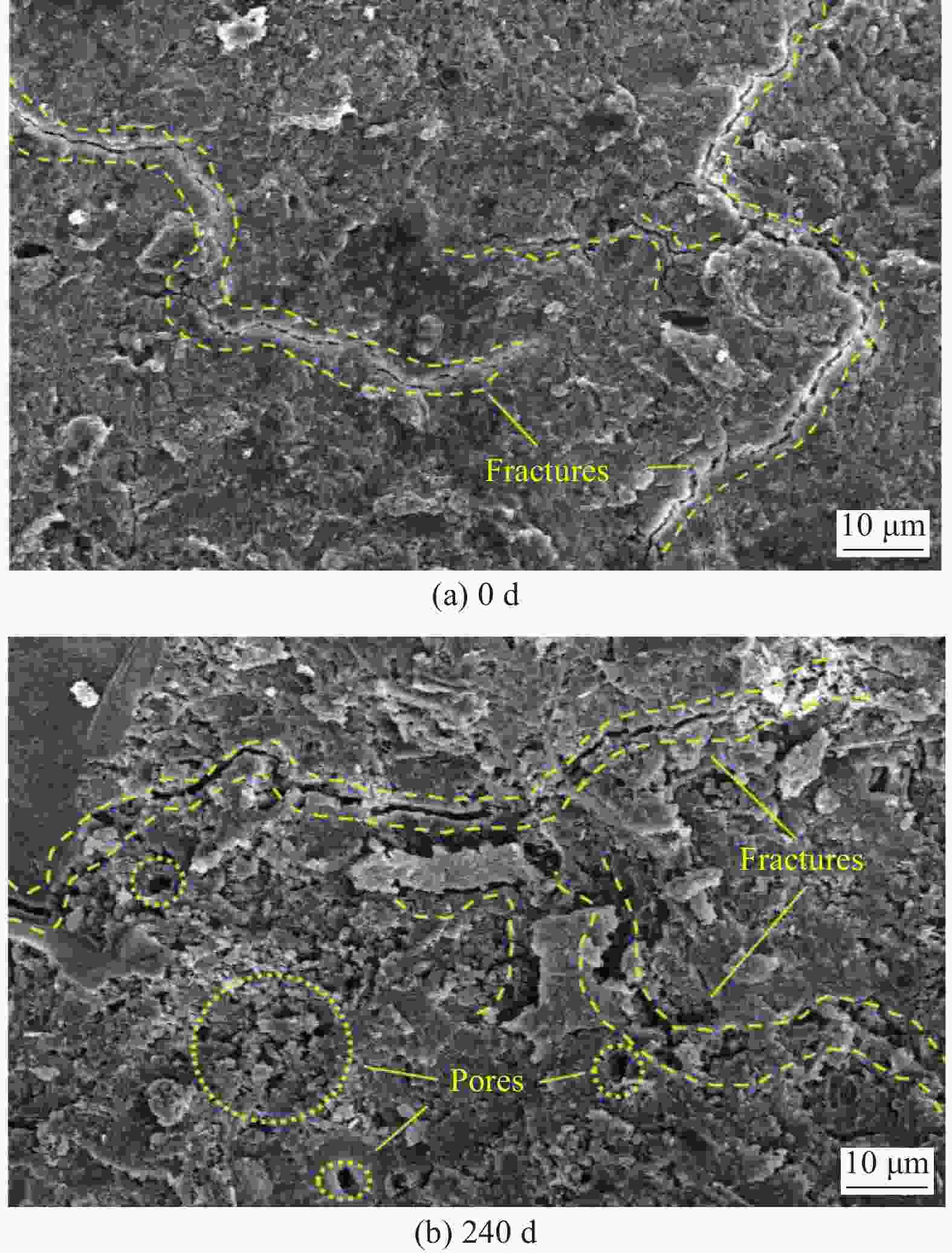
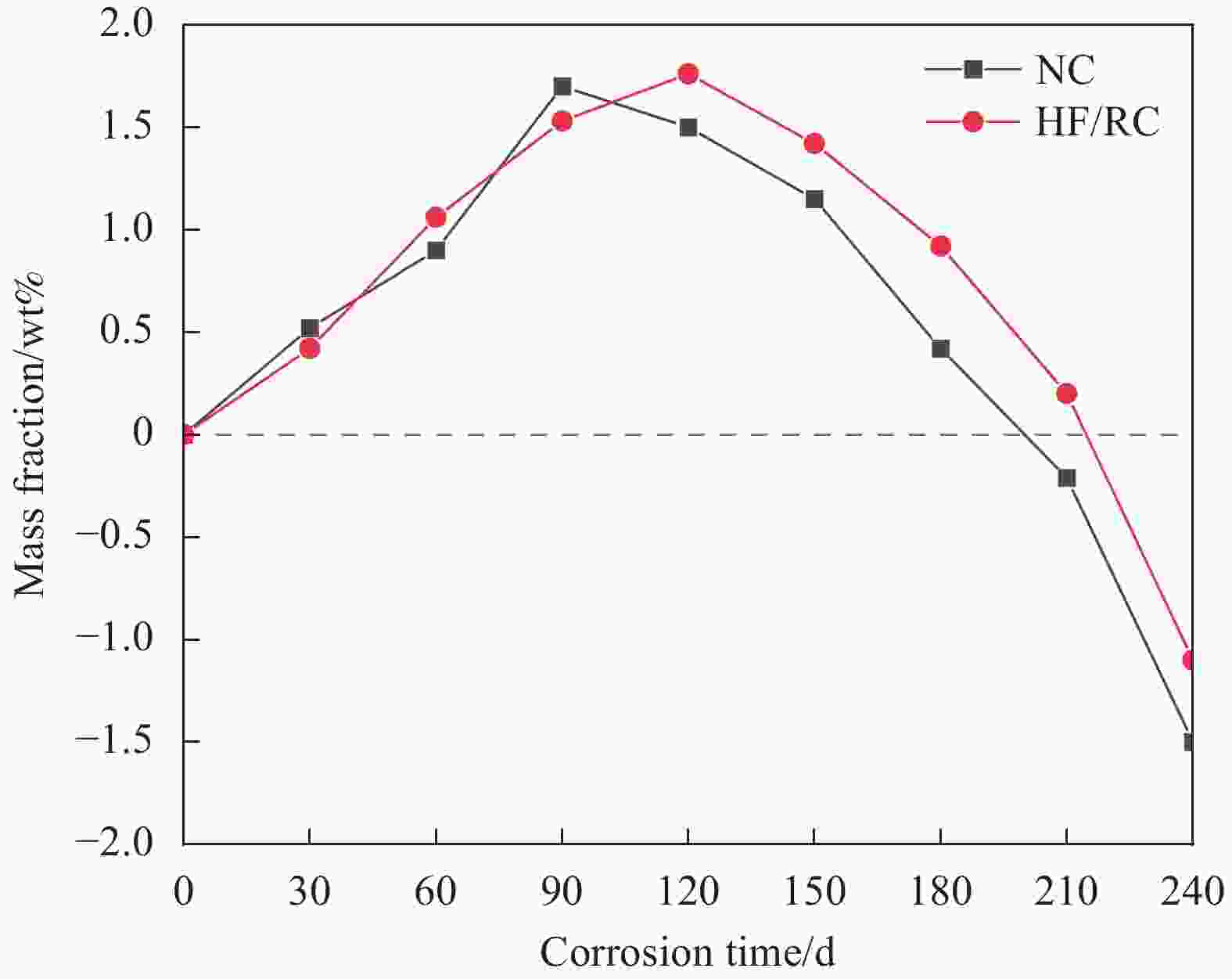
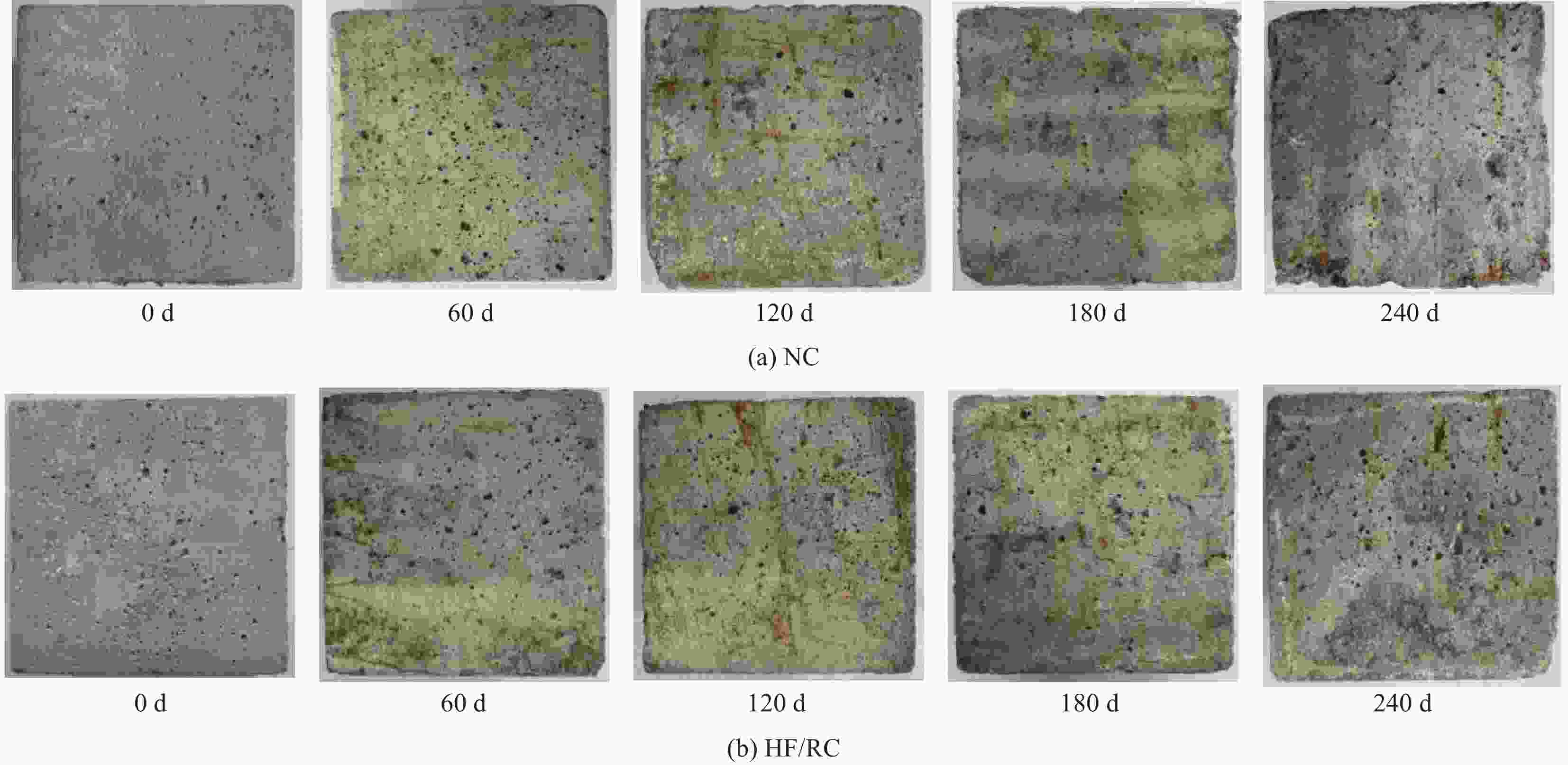
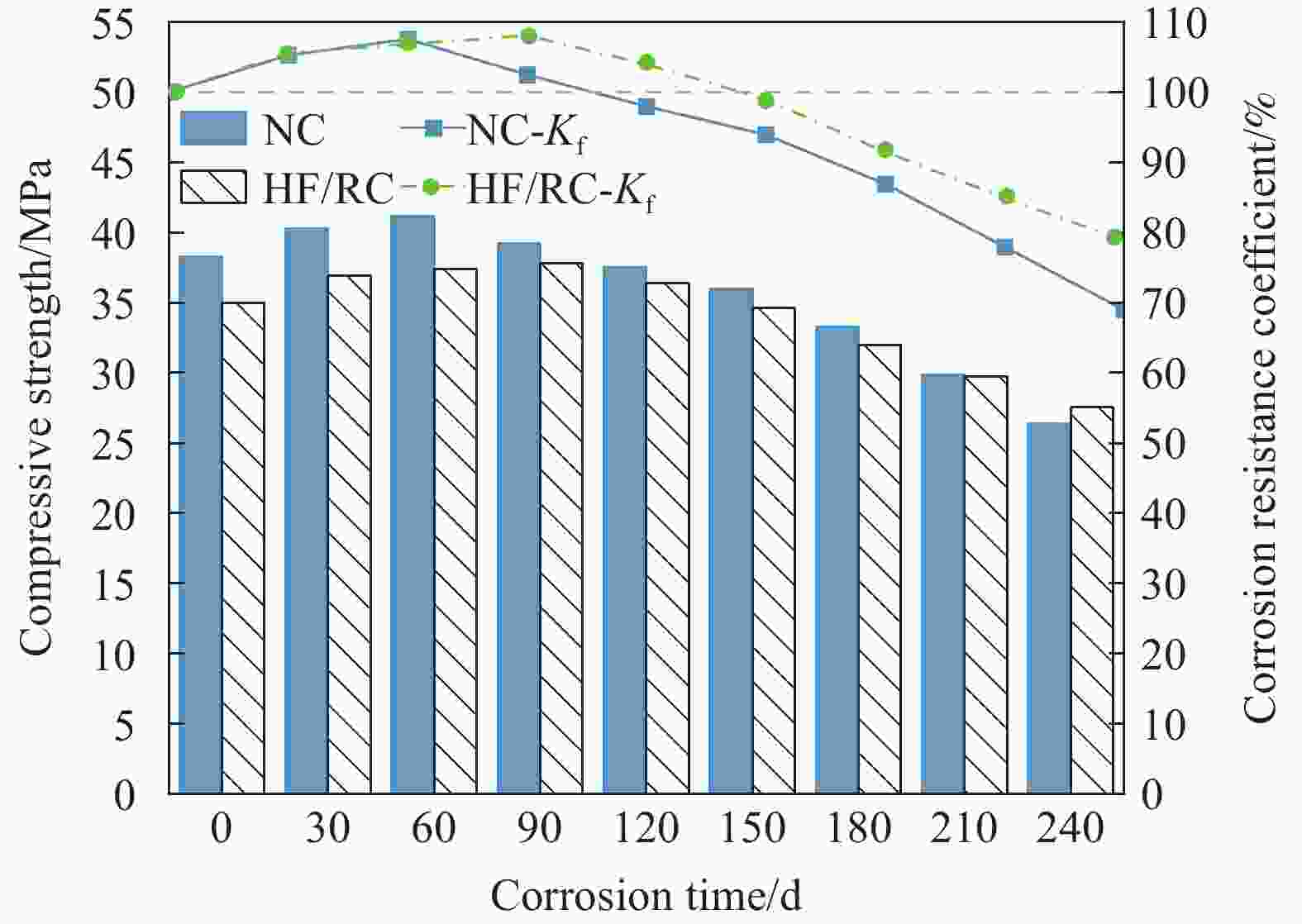
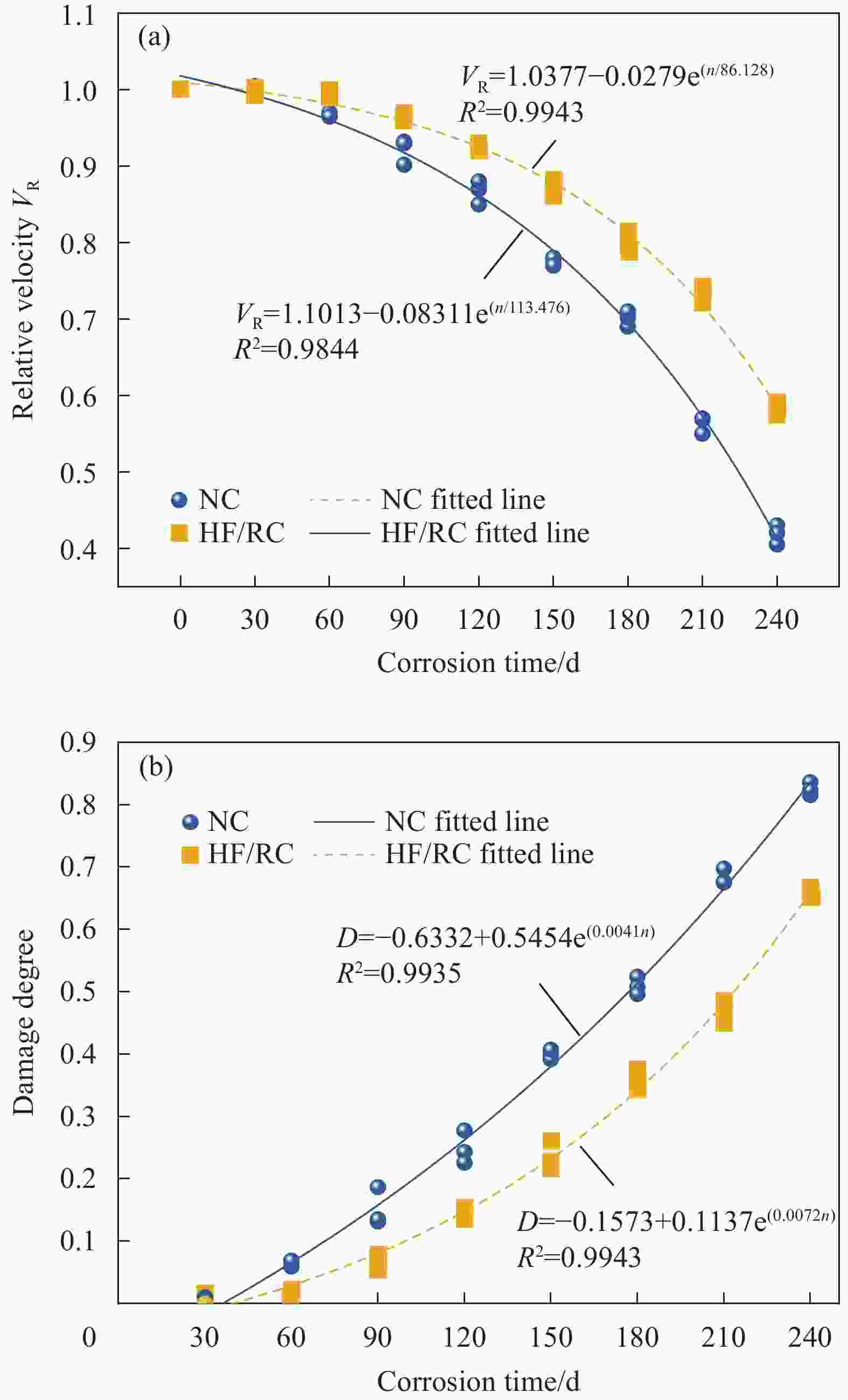
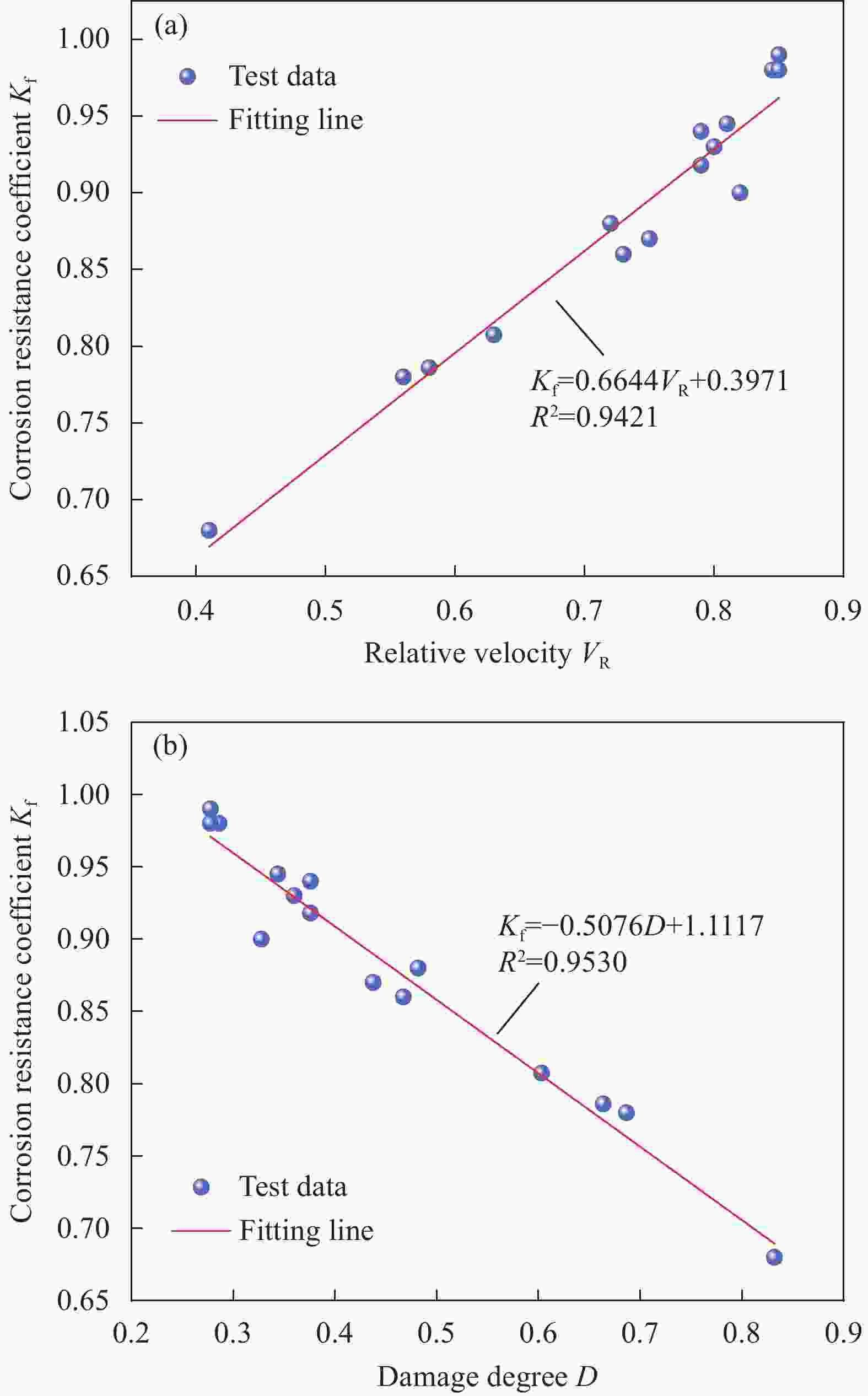
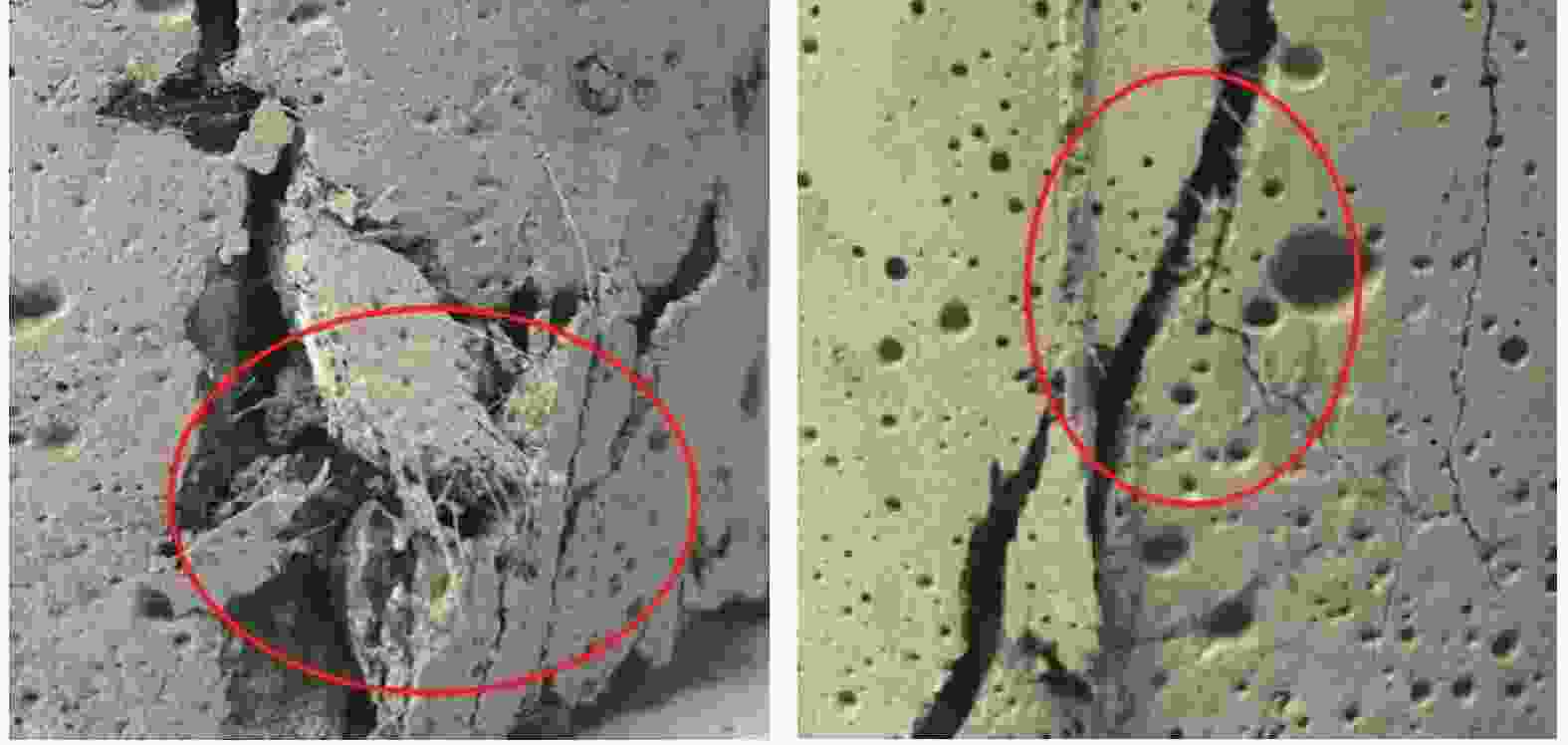
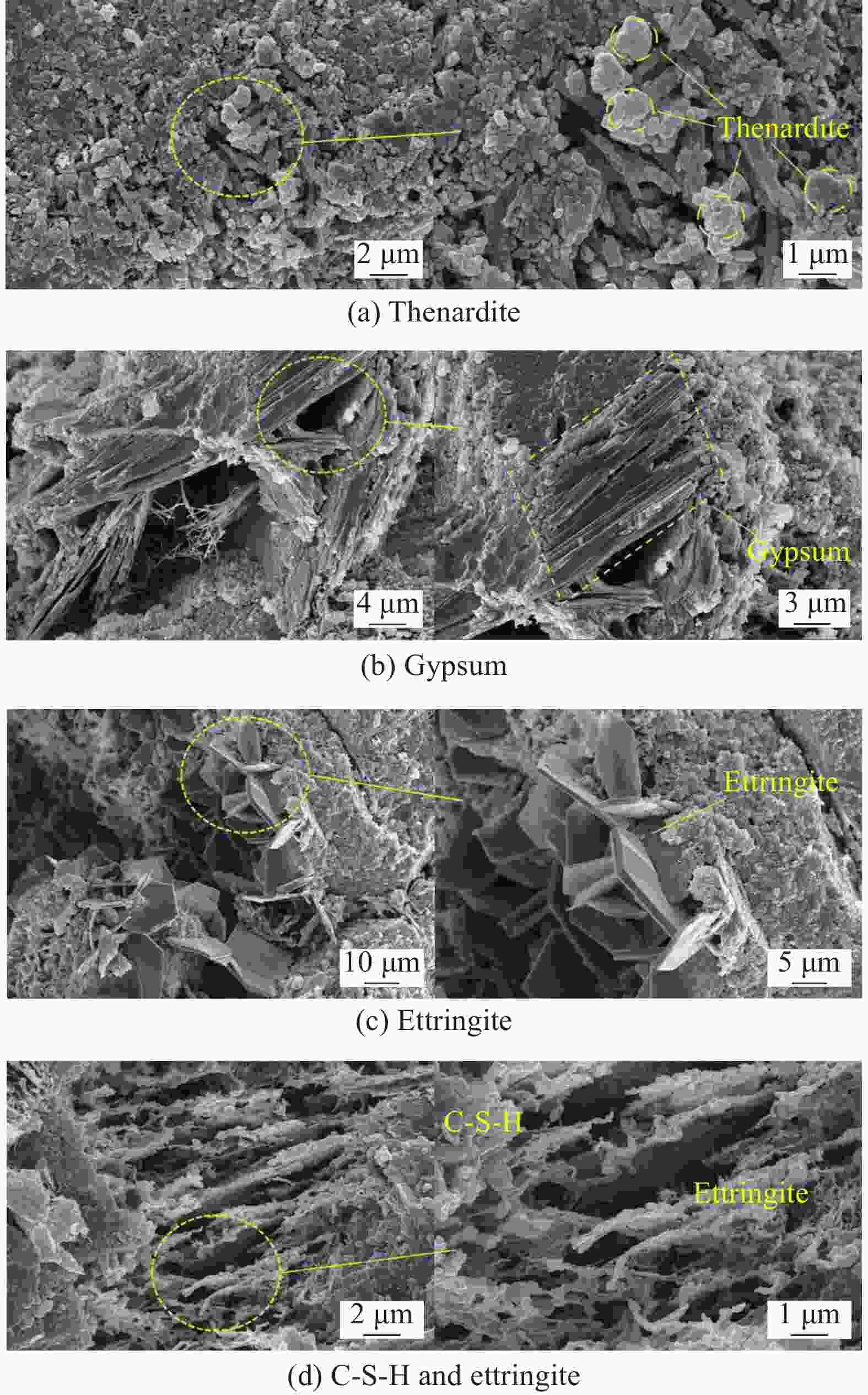
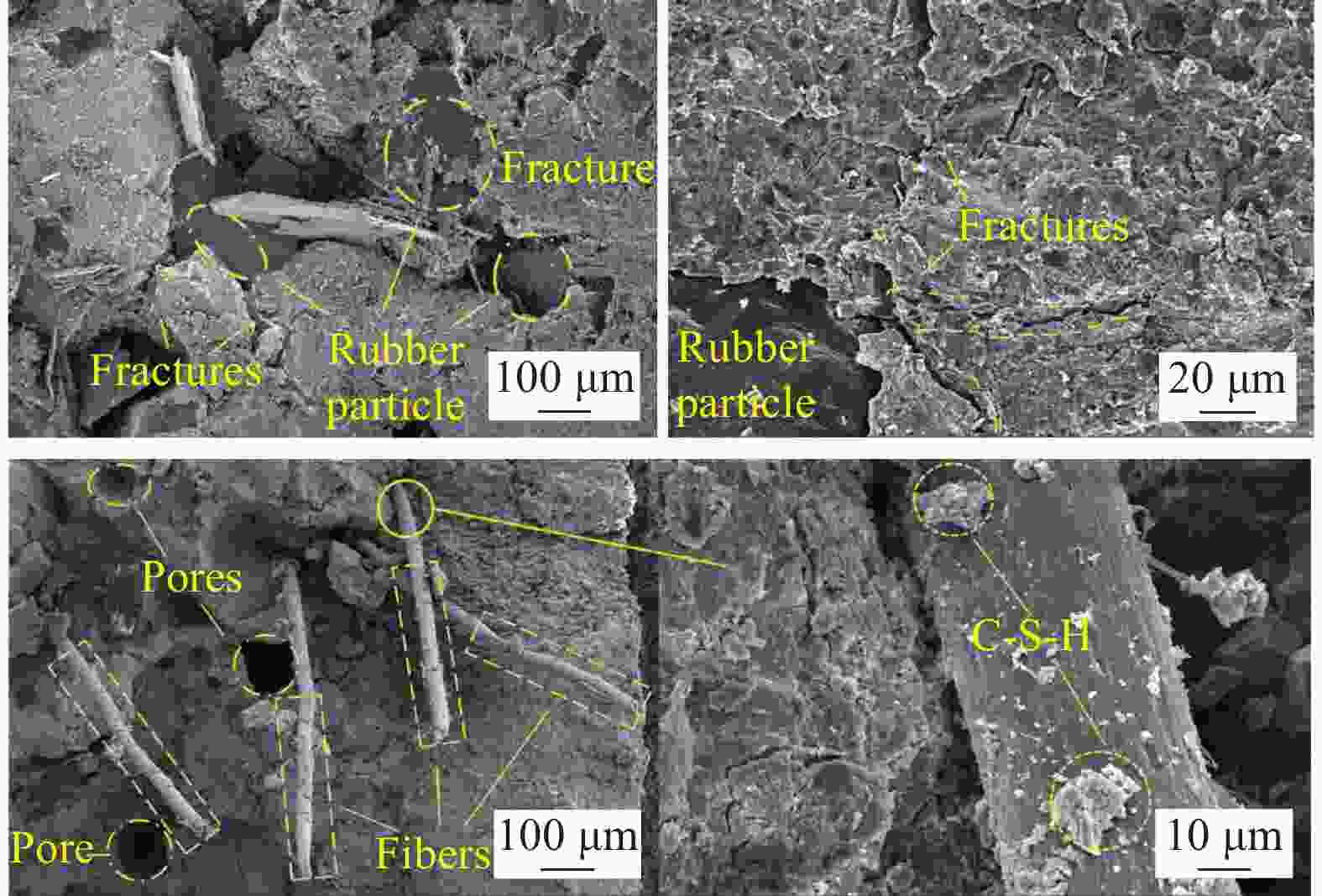
摘要: 为研究混杂纤维/橡胶混凝土(HF/RC)的抗硫酸盐侵蚀性能,对比分析硫酸盐环境下干湿循环240次内,普通混凝土(NC)和HF/RC的表观现象、质量损失、超声参数、抗压强度损失等性能指标劣化过程,采用SEM及XRD微观表征手段分析硫酸盐/干湿循环前后试件微观形貌及物相组成。结果表明:随硫酸盐/干湿循环次数增加,NC、HF/RC试件的质量、抗压强度呈先增后减的趋势,超声参数与抗压强度、耐蚀系数具有密切相关性;侵蚀初期SO4 2−与胶凝物质反应填充原生孔隙,基体密实度提高。侵蚀过程胶凝材料不断被消耗,基体在硫酸钠反复结晶的物理侵蚀及硫酸盐化学侵蚀的共同作用下出现空隙和孔洞。但橡胶颗粒和混杂纤维可阻断裂缝扩展继而减缓SO4 2−扩散,抑制膨胀性产物生成,延缓结晶应力诱发的表层裂纹发育。硫酸盐侵蚀各阶段HF/RC的劣化程度均优于NC,经240次硫酸盐/干湿循环后,NC、HF/RC的耐蚀系数分别为69.00%、78.87%。Abstract: To study the sulfate resistance performance of hybrid fiber reinforced rubber concrete (HF/RC), the apparent phenomena, mass loss, ultrasonic parameters and compressive strength of normal concrete (NC) and HF/RC were analyzed during 240 dry-wet cycles under sulfate environment. SEM and XRD were used to analyze the microstructure and phase composition of the specimen under sulfate attack. The results show that with the increase of dry-wet cycles, the mass and compressive strength of NC and HF/RC specimens increase firstly and then decrease. Ultrasonic parameters are closely related to compressive strength and corrosion resistance coefficient. In the early stage of erosion, SO4 2− reacts with the cementitious material to fill the original pores, and the compactness of the matrix is improved. With the continuous consumption of cementitious materials, voids and pores appear in the matrix due to the physical erosion caused by repeated crystallization of sodium sulfate and the chemical erosion caused by sulfate. Rubber particles and hybrid fibers delay the emergence and development of crack and slow down SO4 2− diffusion. The generation of expansive products is inhibited, and the development of surface cracks induced by crystallization stress is delayed. The damage degree of HF/RC in each stages of sulfate erosion is better than that of NC. After 240 dry-wet cycles, the corrosion resistance coefficient of NC is 69.00% while that of HF/RC is 78.87%.
-
Key words:
- sulfate environment /
- rubber concrete /
- basalt fiber /
- polyvinyl alcohol fiber /
- dry-wet cycle /
- microstructure
-
表 1 纤维基本物理力学性能参数
Table 1. Basic physical and mechanical parameters of fibers
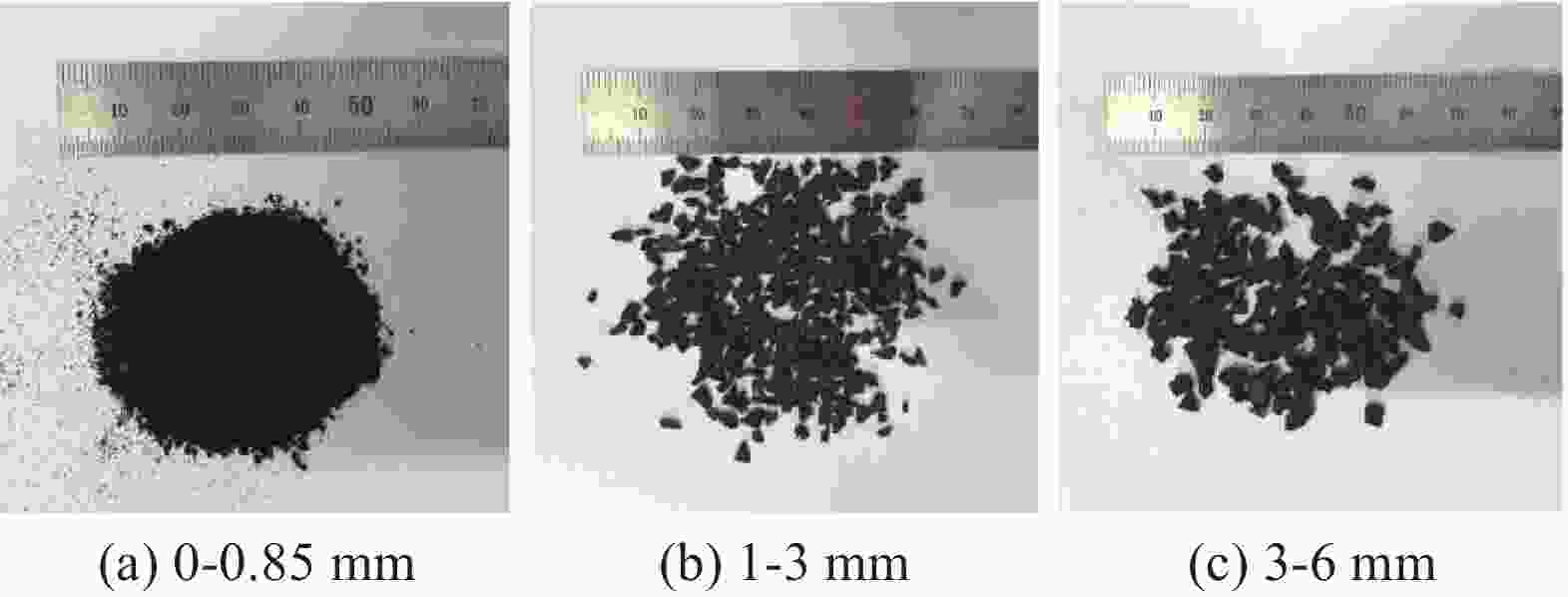
Property Length/mm Tensile strength/MPa Elastic modulus/GPa Elongation at break/% Density/(g·cm−3) Basalt fiber 18 3000-4800 90-110 1.5-3.2 2.63 Polyvinyl alcohol fiber 12 1600-2500 40-80 6.0 1.20 表 2 混凝土配合比
Table 2. Mixing proportions of concrete
Group
numberRubber
particle
size/mmRubber
particle/
(kg·m−3)Basalt
fiber/
(kg·m−3)Polyvinyl
alcohol
fibers/(kg·m−3)Sand/
(kg·m−3)Limestone/
(kg·m−3)Cement/
(kg·m−3)Water
reducer/
(kg·m−3)Water/
(kg·m−3)0# — — — — 885 885 440 3.8 200 1# 0-0.85 46.73 2.63 1.29 796.5 885 440 3.8 200 2# 0-0.85 93.46 5.26 2.58 708 885 440 3.8 200 3# 0-0.85 140.18 7.89 3.87 619.5 885 440 3.8 200 4# 1-3 46.73 5.26 3.87 796.5 885 440 3.8 200 5# 1-3 93.46 7.89 1.29 708 885 440 3.8 200 6# 1-3 140.18 2.63 2.58 619.5 885 440 3.8 200 7# 3-6 46.73 7.89 2.58 796.5 885 440 3.8 200 8# 3-6 93.46 2.63 3.87 708 885 440 3.8 200 9# 3-6 140.18 5.26 1.29 619.5 885 440 3.8 200 表 3 正交试验结果
Table 3. Results of orthogonal experiments
Group number Compressive strength/MPa Splitting tensile strength/MPa Flexural strength/MPa 0# 38.56 3.73 5.60 1# 32.81 3.89 5.65 2# 32.02 4.05 5.71 3# 24.76 3.82 5.66 4# 36.39 4.51 6.28 5# 30.01 4.17 5.51 6# 27.19 3.52 5.28 7# 31.83 4.39 6.03 8# 30.22 3.88 5.15 9# 24.58 3.34 5.24 -
[1] 武强, 涂坤, 曾一凡, 等. 打造我国主体能源(煤炭)升级版面临的主要问题与对策探讨[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(6):1625-1636.WU Qiang, TU Kun, ZENG Yifan, et al. Discussion on the main problems and countermeasures for building an upgrade version of main energy (coal) industry in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(6):1625-1636(in Chinese). [2] SIDDIKA A, AL MAMUN M A, ALYOUSEF R, et al. Properties and utilizations of waste tire rubber in concrete: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,224(10):711-731. [3] GUO Q, WANG S, ZHANG R Y. Intrinsic damage characteristics for recycled crumb rubber concrete subjected to uniaxial pressure employing cohesive zone model[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,317:125773. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125773 [4] 王家滨, 侯泽宇, 张凯峰, 等. 再生混凝土高浓度Mg2+-SO4 2−-Cl−复合盐侵蚀耐久性[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(23):73-83.WANG Jiabin, HOU Zeyu, ZHANG Kaifeng, et al. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete subjected to high concentration Mg2+-SO4 2−-Cl− compound salts[J]. Materials Reports,2022,36(23):73-83(in Chinese). [5] KAEWUNRUEN S, LI D, CHEN Y, et al. Enhancement of dynamic damping in eco-friendly railway concrete sleepers using waste-tyre crumb rubber[J]. Materials,2018,11(7):1169. doi: 10.3390/ma11071169 [6] 于泳, 朱涵, 朱学超, 等. 橡胶粒径和掺量对水泥基材料收缩和抗开裂性能的影响[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2016, 34(4):522-525, 521.YU Yong, ZHU Han, ZHU Xuechao, et al. Influence of particle size and content of rubber on shrinkage and crack resistance of cement-based materials[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering,2016,34(4):522-525, 521(in Chinese). [7] GUPTA T, SIDDIQUE S, SHARMA R K, et al. Behaviour of waste rubber powder and hybrid rubber concrete in aggressive environment[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,217:283-291. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.05.080 [8] THOMAS B S, GUPTA R C. Long term behaviour of cement concrete containing discarded tire rubber[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2015,102(9):78-87. [9] CHAI L J, GUO L P, CHEN B, et al. Mechanical properties of ecological high ductility cementitious composites produced with recycled crumb rubber and recycled asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management,2019,21(3):488-502. doi: 10.1007/s10163-018-0813-7 [10] 赵修敏, 杨海峰, 李雪良, 等. 钢纤维橡胶混凝土的静力和动冲击性能研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2021, 51(8):173-178. doi: 10.13204/j.gyjzG20070301ZHAO Xiumin, YANG Haifeng, LI Xueliang, et al. Study on static and dynamic impact properties of steel-fiber reinforced rubber concrete[J]. Industrial Construction,2021,51(8):173-178(in Chinese). doi: 10.13204/j.gyjzG20070301 [11] HOSSAIN F M Z, SHAHJALAL M, ISLAM K, et al. Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete containing crumb rubber and polypropylene fiber[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,225:983-996. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.245 [12] 贺东青, 王金歌, 王一鸣. 橡胶掺量对CBFRC的物理力学性能影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2015, 18(5):857-860. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2015.05.025HE Dongqing, WANG Jinge, WANG Yiming. Effect of crumb rubber proportion on mechanical properties of chopped basalt fiber reinforced concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2015,18(5):857-860(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2015.05.025 [13] KARIMIPOUR A, GHALEHNOVI M, DE BRITO J. Mechanical and durability properties of steel fibre-reinforced rubberised concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 257: 119463. [14] 张伟, 殷成龙, 李辉, 等. 绿色路用纤维增强水泥基复合材料制备及其韧性表征[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(S2):498-502.ZHANG Wei, YIN Chenglong, LI Hui, et al. Preparation and toughness characterization of fiber reinforced cementitious composites (FRCC) for green roads[J]. Materials Reports,2018,32(S2):498-502(in Chinese). [15] ALWESABI E A H, ABU BAKAR B H, ALSHAIKH I M H, et al. Experimental investigation on mechanical properties of plain and rubberised concretes with steel-polypropylene hybrid fibre[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,233:117194. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117194 [16] 姚韦靖, 刘宜思, 庞建勇, 等. 硫酸盐侵蚀下掺稻壳灰混凝土的劣化性能及损伤模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10):4813-4823. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210923.001YAO Weijing, LIU Yisi, PANG Jianyong, et al. Performance degradation and damage model of concrete incorporating rice husk ash under sulfate attack[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(10):4813-4823(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210923.001 [17] 李华, 孙伟, 左晓宝. 矿物掺合料改善水泥基材料抗硫酸盐侵蚀性能的微观分析[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2012, 40(8):1119-1126.LI Hua, SUN Wei, ZUO Xiaobao. Effect of mineral admixtures on sulfate attack resistance of cement-based materials[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2012,40(8):1119-1126(in Chinese). [18] ZHANG Z Y, ZHOU J T, ZOU Y, et al. Change on shear strength of concrete fully immersed in sulfate solutions[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,235:117463. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117463 [19] ELAHI M M A, SHEARER C R, NASER A, et al. Improving the sulfate attack resistance of concrete by using supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs): A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,281:122628. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122628 [20] LIU Y S, PANG J Y, CHEN Q Q, et al. Study on mechanical properties and pore structure of hybrid fiber reinforced rubber concrete[J]. Crystals,2021,11:1-21. [21] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of concrete physical and mechanical properties: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2019(in Chinese). [22] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2009(in Chinese). [23] LI Y, YANG X B, LOU P, et al. Sulfate attack resistance of recycled aggregate concrete with NaOH-solution-treated crumb rubber[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,287(4):123044. [24] 龚建清, 邓国旗, 单波. 活性粉末混凝土高温后超声研究及微观分析[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(1):68-76. doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2018.01.009GONG Jianqing, DENG Guoqi, SHAN Bo. Ultrasonic test and microscopic analysis of reactive powder concrete exposed to high temperature[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences),2018,45(1):68-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2018.01.009 [25] 姚韦靖, 刘雨姗, 王婷雅, 等. 橡胶/混凝土盐冻循环后性能劣化及微观结构[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(12):4294-4304.YAO Weijing, LIU Yushan, WANG Tingya, et al. Performance degradation and microscopic structure of rubber/concrete after salt freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(12):4294-4304(in Chinese). [26] 解国梁, 杜金胜, 申向东. 粉煤灰轻骨料混凝土抗硫酸盐侵蚀研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2015, 34(2):544-549. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2015.02.055XIE Guoliang, DU Jinsheng, SHEN Xiangdong. Experimental study on fly ash lightweight aggregate concrete resistance to sulfate corrosion[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2015,34(2):544-549(in Chinese). doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2015.02.055 [27] RAGOUG R, METALSSI O O, BARBERON F, et al. Durability of cement pastes exposed to external sulfate attack and leaching: Physical and chemical aspects[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2019,116:134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2018.11.006 [28] YU C, SUN W, SCRIVENER K. Mechanism of expansion of mortars immersed in sodium sulfate solutions[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2013,43:105-111. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2012.10.001 [29] WANG R J, TAO Z, LI Y. Evaluation of microcrack size in rubber concrete ITZ exposed to sulfate attack[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2019,31(12):04019308. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002986 [30] TAHA M M R, ASCE M, EL-DIEB A S, et al. Mechanical, fracture, and microstructural investigations of rubber concrete[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2008,20(10):640-649. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2008)20:10(640) -





 下载:
下载: