Damage identification method for fiber-reinforced composite laminates based on element-level damage indicators
-
摘要: 本文针对复合材料层合板结构提出了一种能够综合反映其承载能力缺失的单元级损伤指标−层合单元损伤指标,该指标既可以反映层合板面内外方向刚度的损伤情况,又具有参数数量较少、较易识别的优点。为保证所提损伤指标的合理性,本文利用数学和力学算子对单元级损伤指标与材料级损伤指标进行了等效,并比较了不同损伤指标在表征损伤程度之间的差异性。并提出了基于单元级损伤参数的复合材料结构损伤识别流程,即首先利用单元应变能差值指标对损伤单元进行筛选,然后利用优化方法对候选单元的损伤程度进行辨识。本文所提方法通过数值算例和一个试验进行了验证,分析了单元级损伤参数各个元素之间的相关性,并验证了基于单元级损伤参数的复合材料层合板结构损伤识别流程。本文的研究成果补充了现有复合材料结构健康监测理论。Abstract: An element-level damage index, damage index of laminated element, was proposed for composite laminate structures that can comprehensively reflect the degradation of load-bearing capacity, which can reflect the damage of stiffness in both internal and external directions and has the advantages of fewer parameters and easier identification. In order to ensure the rationality of the proposed damage index, mathematical and mechanical operators was used to equate the element-level damage index with the material-level damage index, and the differences between different damage indexes in characterizing the degree of damage were compared. The damage identification process of composite structures based on element-level damage parameters was also proposed, i.e., the damage elements were firstly screened by using modal strain energy change ratio, and then the damage degree of the candidate elements was identified by using optimization methods. The proposed method was validated by numerical examples and an experiment work, and the correlation between the elements of the element-level damage parameters was analyzed and the damage identification process of the composite laminate structure based on the element-level damage parameters was validated. The results of this paper complement the existing theory of health monitoring of composite structures.
-
图 1 3类损伤指标所需损伤变量个数及特点
Figure 1. Number of damage variables required for the three types of damage indicators and their characteristics
w—Traditional damage variable; ΔAn—Normallized area; ΔAw—Damaged area; Mi—Vector containing material-level damage indicators;f(d1, d2, d3)i—Function of material-level damage indicators
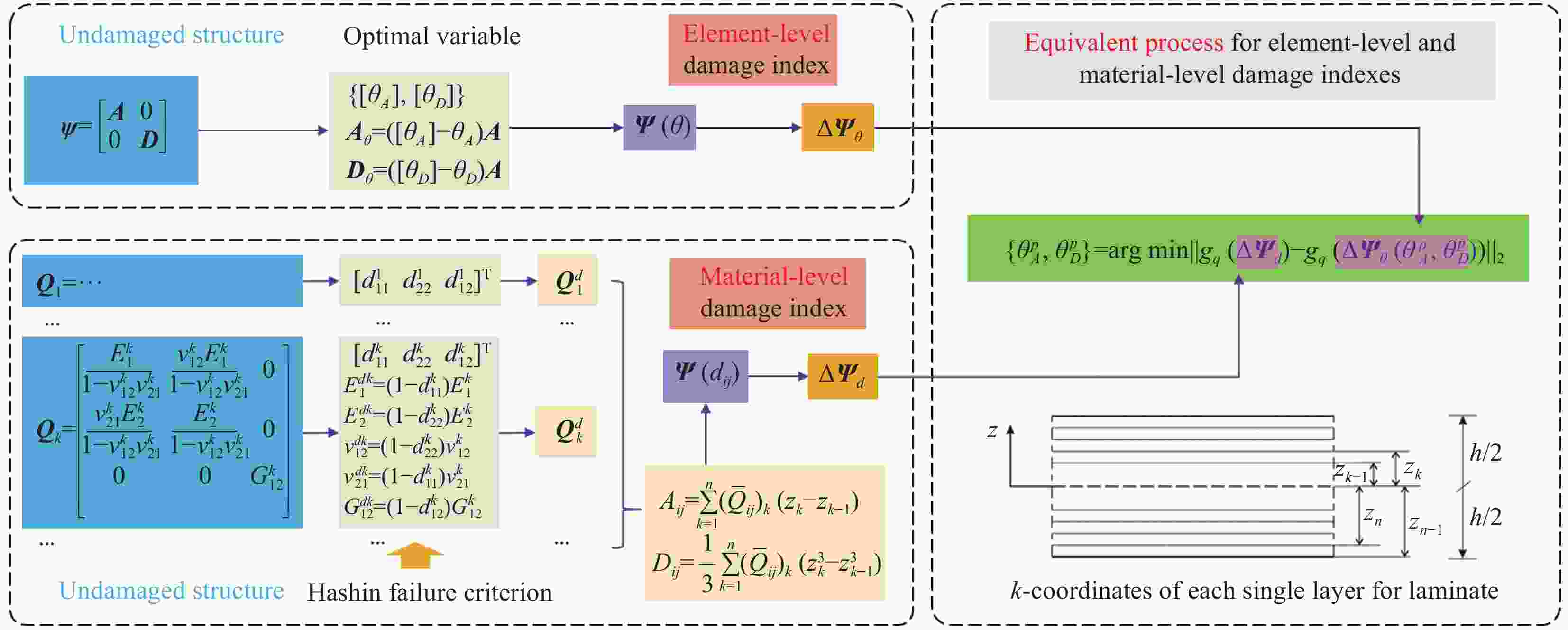
图 2 材料级和单元级损伤指标等效过程示意图
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of equivalent process for material-level and element-level damage indicators
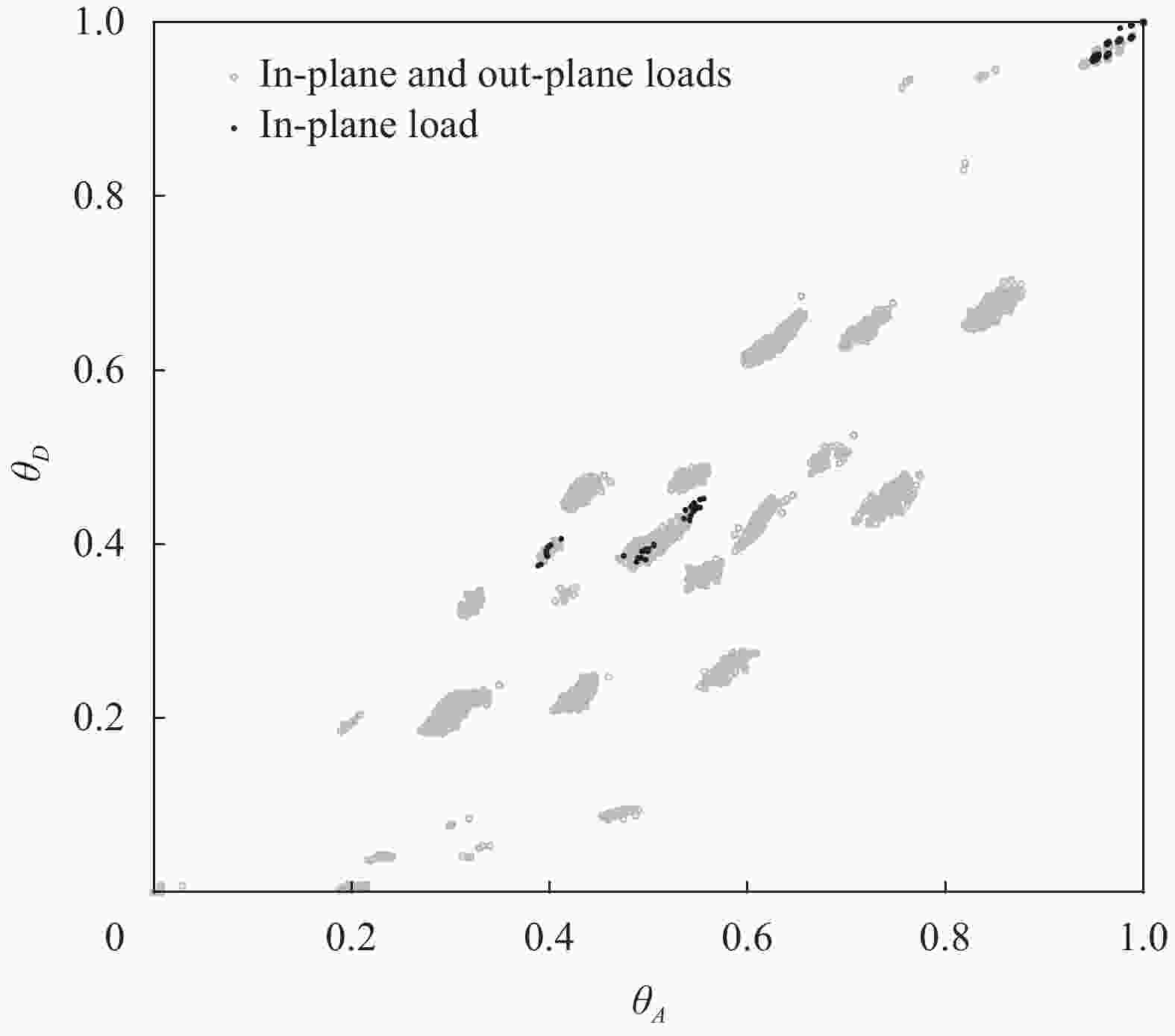
${\boldsymbol{\varPsi }} $—Stiffness matrix of symmetric laminates; A—Tensile stiffness matrix; D—Bending stiffness matrix; Q1—Stiffness matrix of the 1st layer; Q1 d—Stiffness matrix of the 1st layer of the damaged structure; Qk—Stiffness matrix of the kth layer; Qk d—Stiffness matrix of the kth layer of the damaged structure; $E_1^{dk}, E_{\rm{2}}^{dk}, v_{12}^{dk}, v_{{\rm{21}}}^{dk}, G_{{\rm{12}}}^{dk}$—Longitudinal, transverse elastic moduli, Poisson's ratio in both in-face directions, and shear modulus of the kth layer of the damaged structure; $E_1^{k}, E_{\rm{2}}^{k}, v_{12}^{k}, v_{{\rm{21}}}^{k}, G_{{\rm{12}}}^{k}$—Longitudinal, transverse elastic moduli, Poisson's ratio in both in-face directions, and shear modulus of the kth layer of the undamaged structure; $d_{11}^k, d_{22}^k, d_{{\rm{12}}}^k$—Material-level damage parameters in fiber direction, matrix direction and shear direction for the kth layer; ${\boldsymbol{\varPsi }}\left( \theta \right) $—Stiffness matrix expressed by element-level damage parameters; $\Delta {\boldsymbol{\varPsi }}_\theta ^{} $—Residual stiffness matrix expressed by element-level damage parameters; ${\boldsymbol{\varPsi }}\left( {d_{ij}^{}} \right) $—Stiffness matrix expressed by material-level damage parameters; $\Delta{\boldsymbol{ \varPsi}} _d^{} $—Residual stiffness matrix expressed by material-level damage parameters; $\theta _A^p, \theta _D^p$—In-plane and out-of-plane element-level damage indicators under the pth failure mode; $g_q^{} $—The qth kind of operator; $\left\| \cdot \right\|_2 $—The 2-norm of matrix; h—Thickness of laminates; ${z_k} $—Midplane coordinates of the kth layer
表 1 复合材料层合板材料属性
Table 1. Material parameters of composite laminate
E1/GPa E2/GPa G12/GPa ν12 Xt/GPa Xc/GPa Yt/GPa Yc/GPa S12/GPa 140 10 5 0.3 1500 1200 50 250 70 Notes: E1 and E2—Longitudinal and transverse elastic moduli; G12—In-plane shear modulus; v12—Poisson's ratio; Xt and Xc—Longitudinal tensile and compressive strengths; Yt and Yc—Transverse tensile and compressive strengths; S12—In-plane shear strength. 表 2 仿真工况
Table 2. Simulation conditions
Number Description of working conditions and load vectors [Nx; Ny; Nxy] [Mx; My; Mxy] 1 Tensile [100; 100; 0] [0; 0; 0] 2 Tensile and bending [100; 100; 0] [100; 100; 0] Notes: [Nx; Ny; Nxy]—Combined internal force per element width of laminate;[Mx; My; Mxy]—Combined internal moment per element width of laminate. 表 3 层合板两种载荷的失效路径
Table 3. Failure paths of two loads of laminates
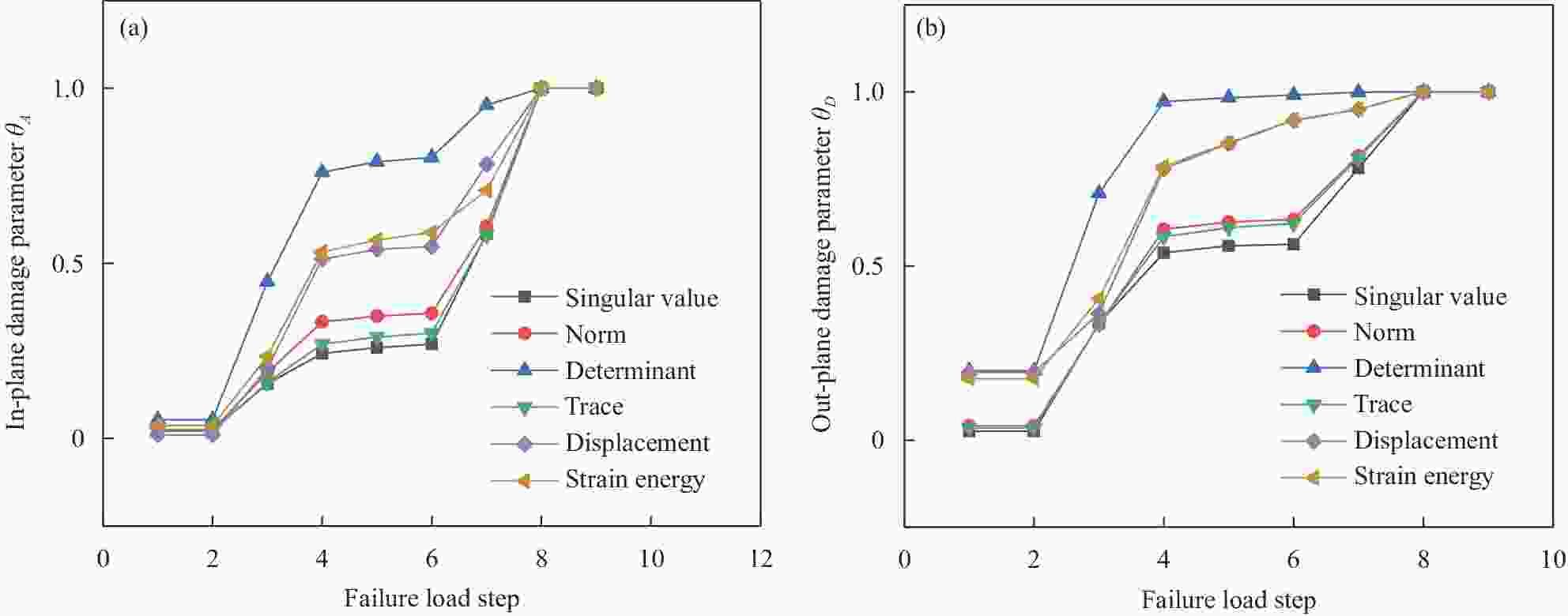
No. Failure paths 1 1MT, 3MT, 5MT, 7MT→2MT, 6MT→4MT→1FT,
2FT, 3FT, 4FT, 5FT, 6FT, 7FT2 6MT, 7MT→1FC, 7FT→5MT→1MC→3MT→2MC→4MT,
5FT, 6FT→3FC→1MT, 4FTNotes: MT and MC—Tensile and compression of matrix; FT and FC—Tensile and compression of fiber. 表 4 损伤工况设置
Table 4. Damage condition settings
Damage condition Damage
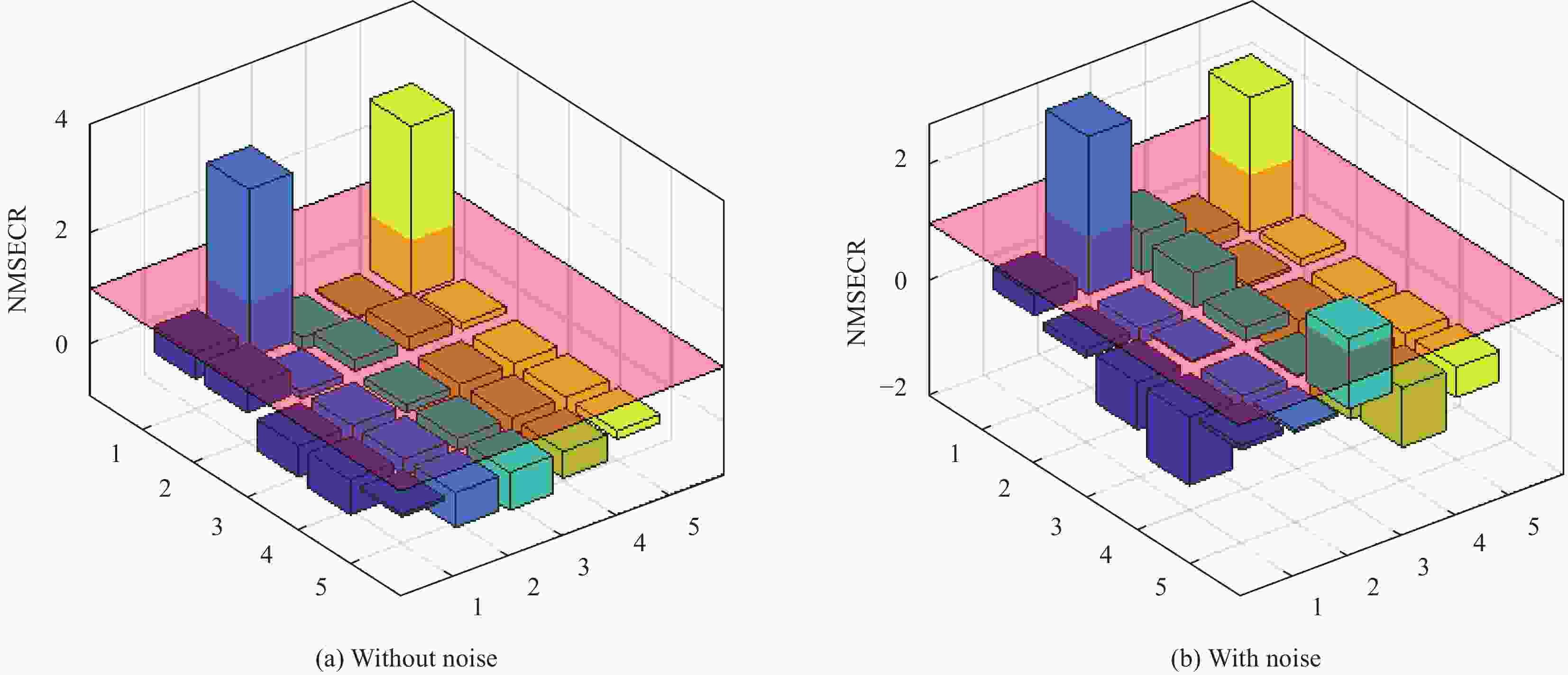
elementExtent of damage θA θD 1 2 0.3 0.25 2 2 0.3 0.25 5 0.2 0.25 表 5 无噪声工况识别结果
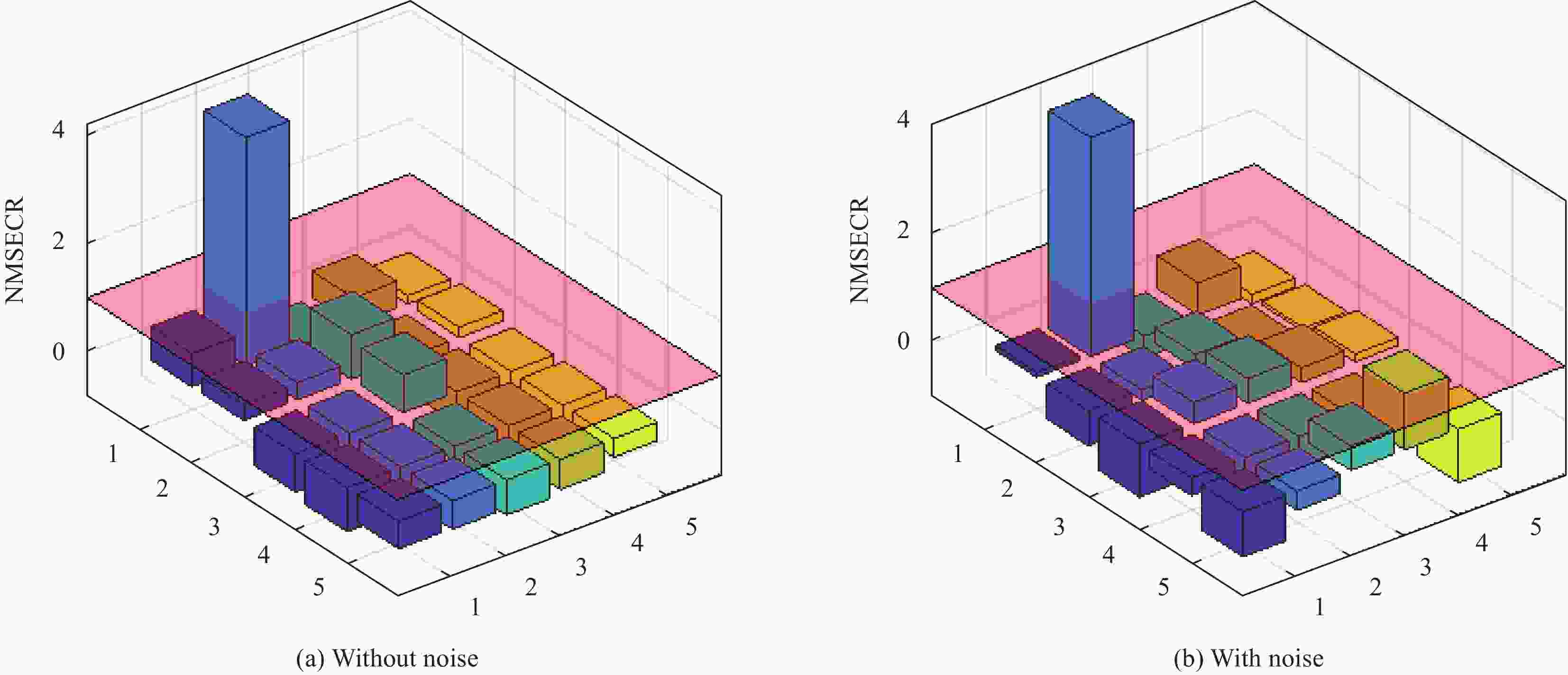
Table 5. Identification results without noise condition
Damage conditions Damaged element θA θD Identified value Error Identified value Error Single damage 2 0.3 0 0.25 0 24 0 — 0 — Multi-damage 2 0.3 0 0.25 0 5 0.2 0 0.25 0 23 0 — 0 — 表 6 含噪声工况识别结果
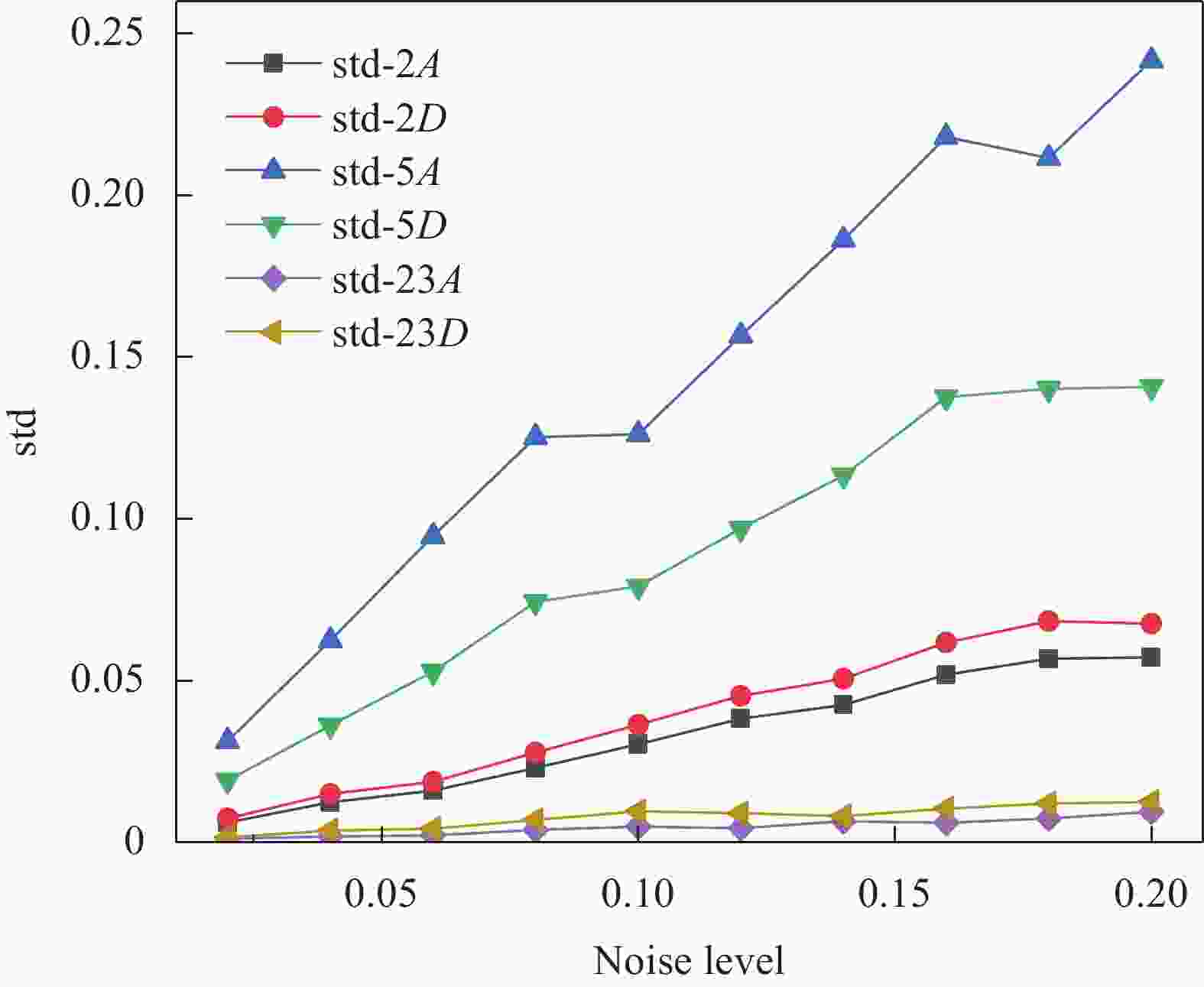
Table 6. Identification results with noise conditions
Damage conditions Damaged element θA θD Identified value Error Identified value Error Single damage 2 0.2993 0.20% 0.2513 −0.52% 24 0 — 0 — Multi-damage 2 0.3002 0.07% 0.2491 −0.36% 5 0.1902 −4.90% 0.2401 −3.96% 23 0.0001 — 0 — 表 7 悬臂梁修正后的固有频率
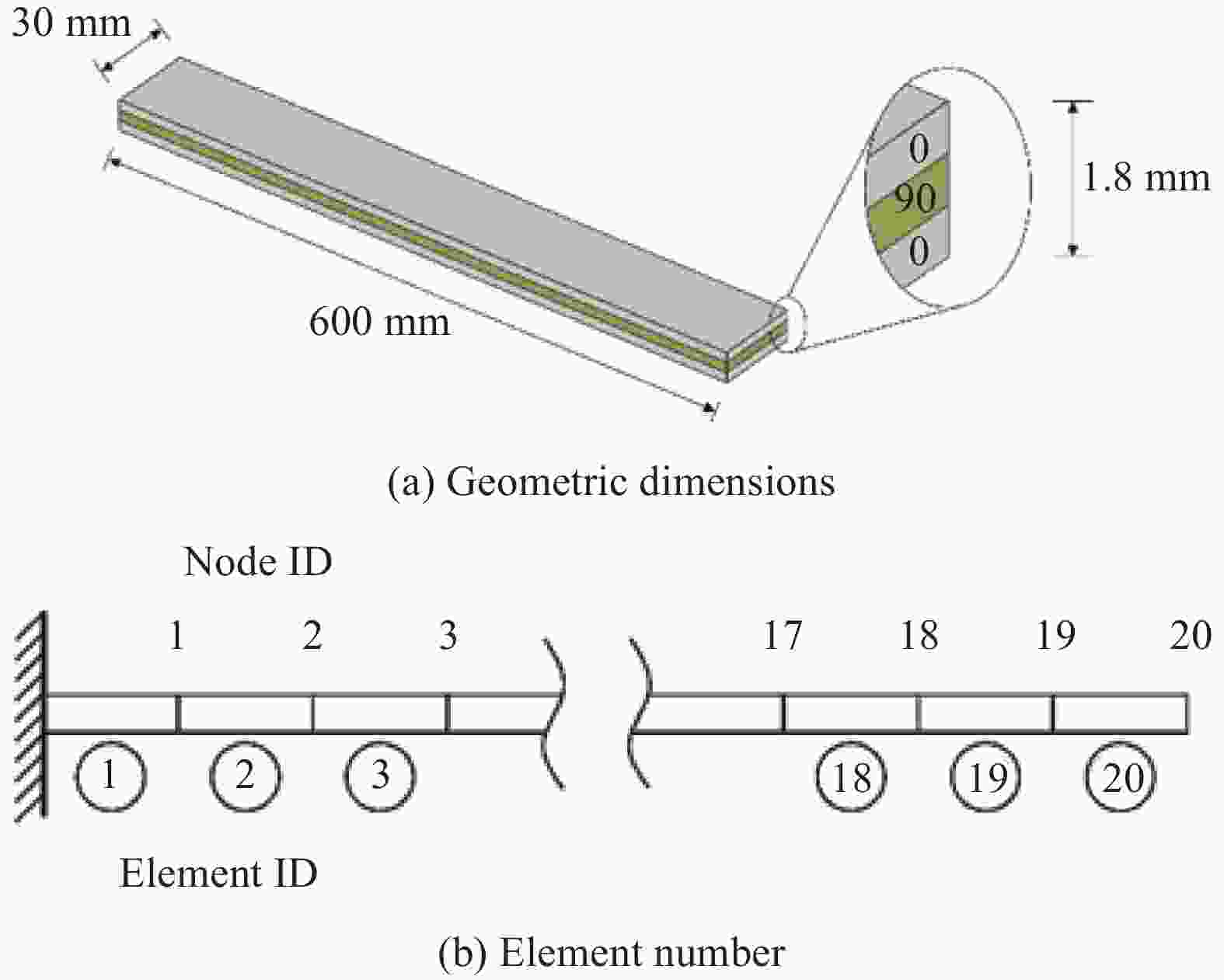
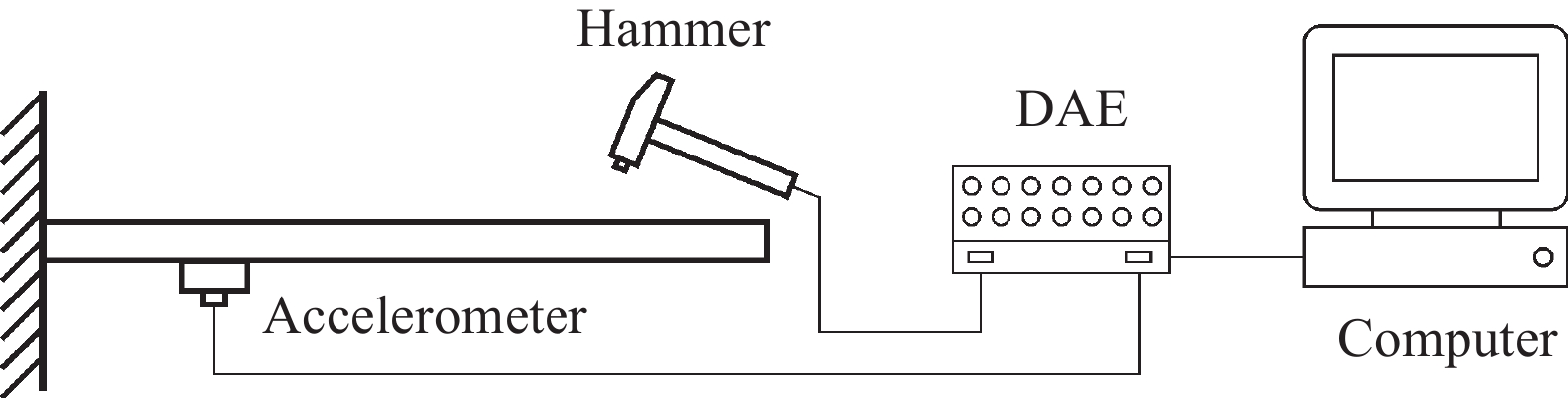
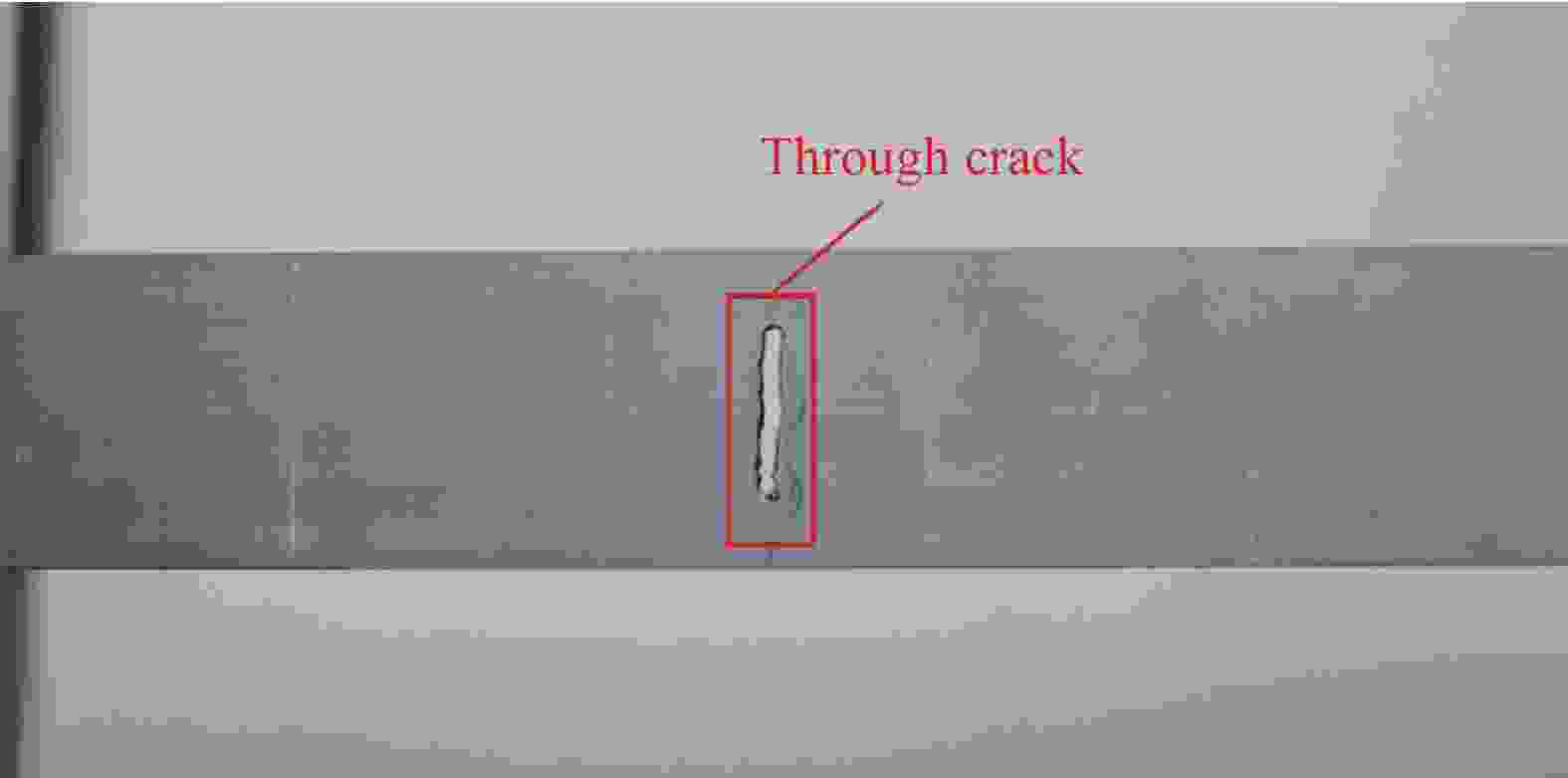
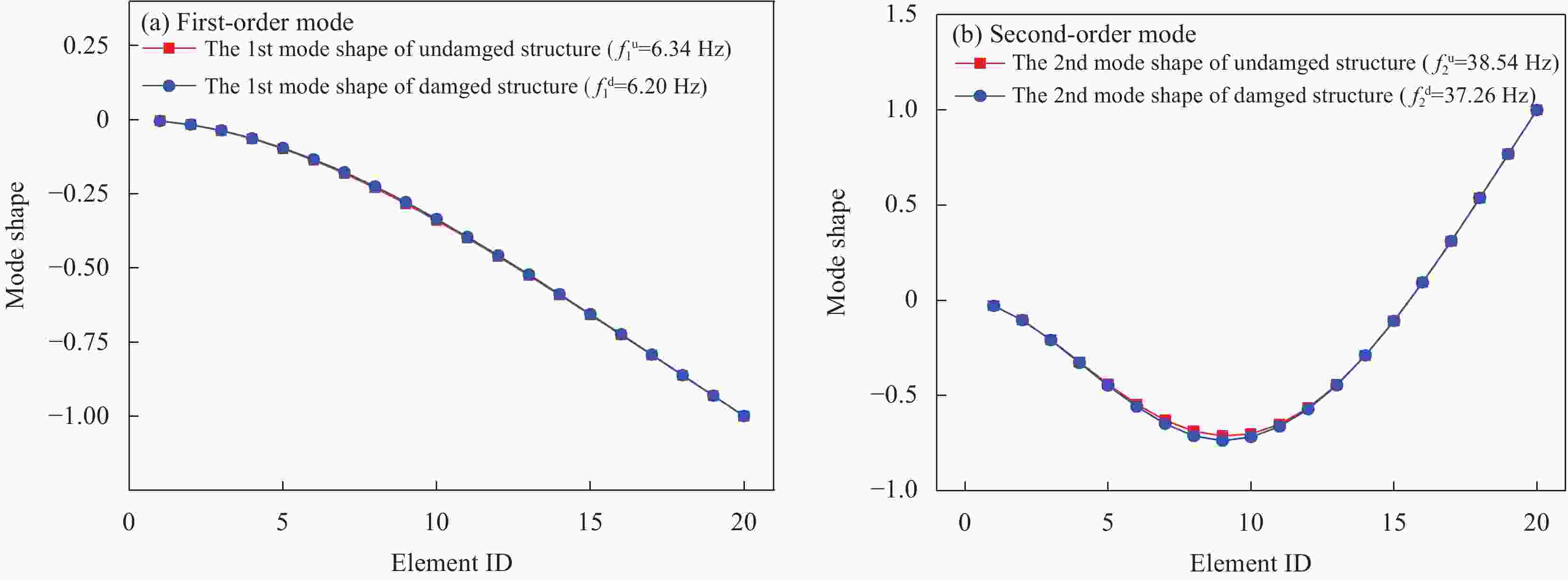
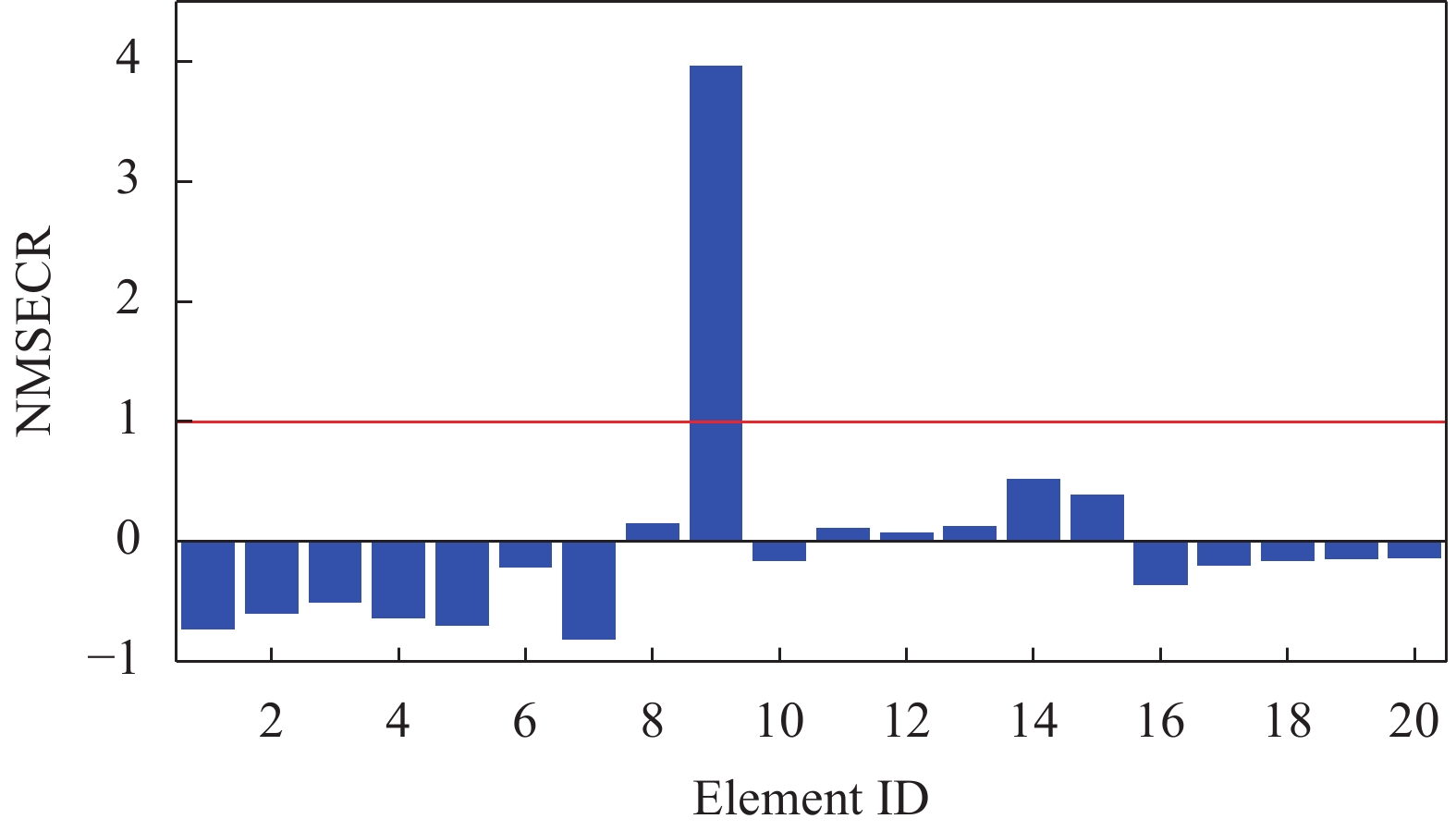
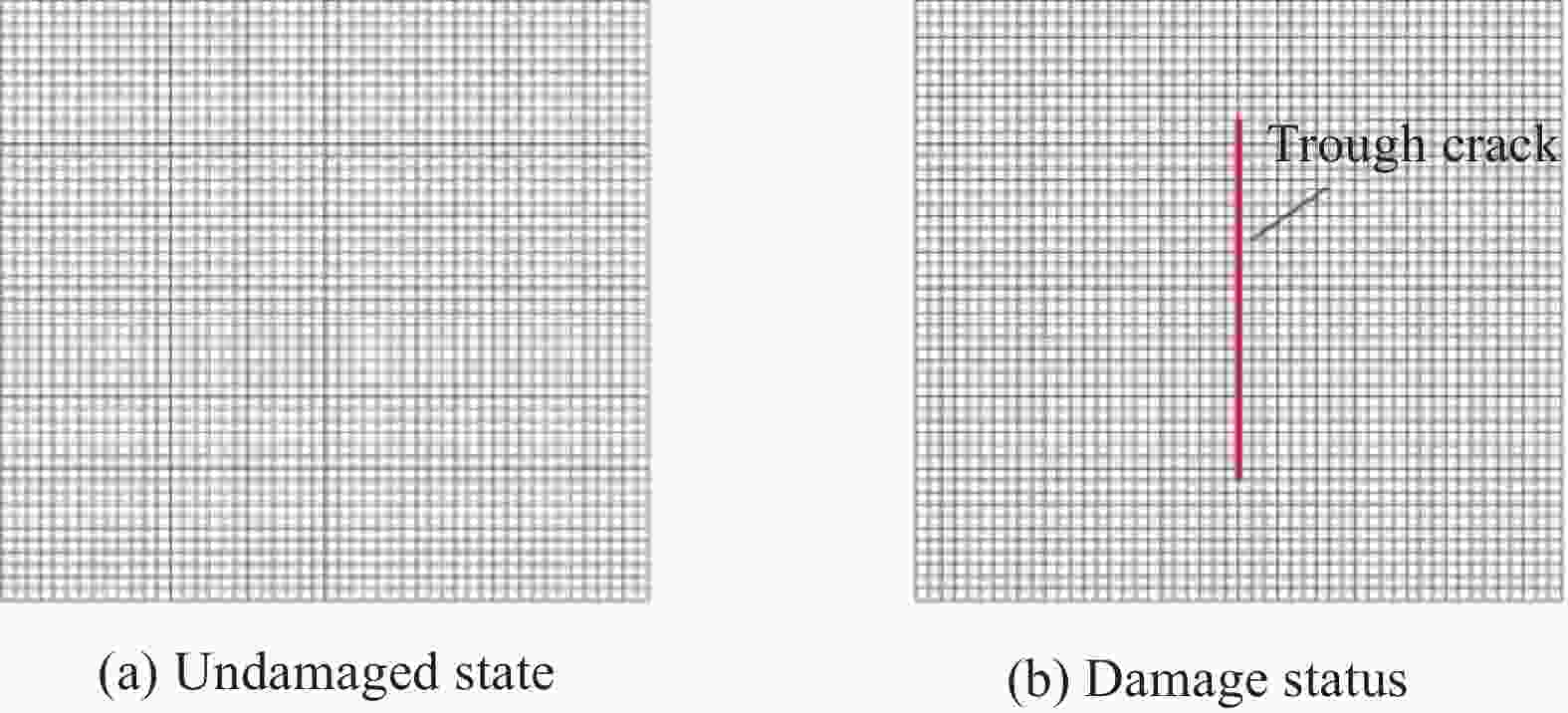
Table 7. Corrected modal frequency of cantilevered beam
Modal order Simulation values/Hz Test values/Hz Relative error/% 1 6.47 6.34 2.21 2 38.72 38.54 0.49 3 96.01 96.57 −0.53 4 188.76 190.91 −1.13 5 336.17 339.77 −1.06 表 8 悬臂梁修正后的弹性参数
Table 8. Elastic parameters of cantilever beam after model updating
E11/GPa E22/GPa G12/GPa v12 ρ/(kg·m−3) 119.57 8.79 5.70 0.30 1794.67 Note: ρ—Density. -
[1] 陈雪峰, 杨志勃, 田绍华, 等. 复合材料结构损伤识别与健康监测展望[J]. 振动测试与诊断, 2018, 38(1):1-10, 202.CHEN Xuefeng, YANG Zhibo, TIAN Shaohua, et al. A review of the damage detection and health monitoring for composite structures[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis,2018,38(1):1-10, 202(in Chinese). [2] 陈健, 袁慎芳. 加筋复合材料结构分层损伤的贝叶斯诊断及预测[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(11):3726-3736. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210202.003CHEN Jian, YUAN Shenfang. Bayesian diagnosis and prognosis of delamination damage in the stiffened composite structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(11):3726-3736(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210202.003 [3] 徐浩, 沙刚刚, 李腾腾, 等. 基于二维连续小波变换与数据融合技术的逆有限元法-伪激励法结构损伤识别方法[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10):3554-3562. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210115.001XU Hao, SHA Ganggang, LI Tengteng, et al. Structure damage identification method of inverse finite element method-pseudo-excitation method based on 2D continuous wavelet transform and data fusion technology[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(10):3554-3562(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210115.001 [4] 颜津玮, 曹善成, 徐超. 基于低秩与稀疏分解的层合板损伤定位[J]. 振动测试与诊断, 2022, 42(6):1220-1225, 1250.YAN Jinwei, CAO Shangcheng, XU Chao. Damage localization of composite laminated plates based on low-rank and sparse decomposition[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis,2022,42(6):1220-1225, 1250(in Chinese). [5] 黄斌, 郭文豪, 鲁溢, 等. 随机梁式结构静力损伤识别的一种改进方法[J]. 计算力学学报, 2018, 35(4): 451-457.HUANG Bin, GUO Wenhao, LU Yi, et al, An improved method of damage identification of random beam structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics , 2018, 35(4): 451-457(in Chinese). [6] 闫天红, 王凤山, 姜民政, 等. 基于模态参数灵敏度分析的结构损伤识别研究[J]. 机械设计, 2019, 36(12): 79-83YAN Tianhong, WANG Fengshan, JIANG Minzheng, et al, Identification of structural damage based on the sensitivity analysis of modal parameters[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2019, 36(12): 79-83(in Chinese). [7] SHI Q H, WANG X J, WANG L, et al. Set-membership identification technique for structural damage based on the dynamic responses with noises[J]. Structural Control & Health Monitoring,2017,24(2):e1868. [8] DU Y, ZHOU S, JING X, et al. Damage detection techniques for wind turbine blades: A review[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2020,141:106445. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106445 [9] WANG X J, SHI Q H, WANG L, et al. Anisotropic reduction factor-based damage identification method for fiber-reinforced composite laminates[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2018,25(11):e2253. doi: 10.1002/stc.2253 [10] 邱家波, 李华东. 复合材料帽型加筋层合板典型板元的等效刚度计算[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2020(7):33-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2020.07.005QIU Jiabo, LI Huadong. Equivalent stiffness calculation of typical plante element of composite cap stiffened laminates[J]. Journal of Composites Science and Engineering,2020(7):33-39(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2020.07.005 [11] 朱秀杰, 熊超, 殷军辉, 等. 基于复合材料层合箱梁改进解析模型计算等效刚度[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6):1483-1495. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190706.001ZHU Xiujie, XIONG Chao, YIN Junhui, et al. Equivalent stiffness calculation based on refined analytical model of composite laminated box beam[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(6):1483-1495(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190706.001 [12] 刘航, 杜国君, 冯岩. 构造上正交各向异性半球形凸起凹凸板等效刚度研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(1):70-80.LIU Hang, DU Guojun, FENG Yan. Study on equivalent stiffnesses of orthotropic hemi-spherical convex plates[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,2020,41(1):70-80(in Chinese). [13] 黄炳生, 秦雨生, 黄泰杰. 基于等效刚度的矩形孔蜂窝梁钢框架结构内力计算方法[J]. 力学季刊, 2023, 44(1):218-226. doi: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2023.01.022HUANG Bingsheng, QIN Yusheng, HUANG Taijie. Internal force calculation of steel frame structure containing castellated beams with rectangular holes based on equivalent stiffness method[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics,2023,44(1):218-226(in Chinese). doi: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2023.01.022 [14] GHODRATI AMIRI G, ZARE HOSSEINZADEH A, JAFARIAN ABYANEH M. A new two-stage method for damage identification in linear-shaped structures via grey system theory and optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Rehabilitation in Civil Engineering,2015,3(2):45-58. [15] VO-DUY T, HO-HUU V, DANG-TRUNG H, et al. A two-step approach for damage detection in laminated composite structures using modal strain energy method and an improved differential evolution algorithm[J]. Composite Structures,2016,147:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.03.027 [16] 郭惠勇, 李正良. 基于应变能等效指标的结构损伤识别技术研究[J]. 固体力学学报, 2013, 34(3):286-291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-7805.2013.03.009GUO Huiyong, LI Zhengliang. Structural damage identification method based on strain energy equivalence parameter[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics,2013,34(3):286-291(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-7805.2013.03.009 [17] XIA Y, HAO H, BROWNJOHN J M W, et al. Damage identification of structures with uncertain frequency and mode shape data[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics,2002,31(5):1053-1066. [18] FANG Y, LIU X, XING J, et al. Substructure damage identification based on sensitivity of power spectral density[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,2023,545:117451. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2022.117451 [19] JALALI S S, MAHZOON M, MOHAMMADI H. Identification of damage properties of glass/epoxy laminates using machine learning models[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 177: 104510. [20] XU D, LIU P F, CHEN Z P, et al. Achieving robust damage mode identification of adhesive composite joints for wind turbine blade using acoustic emission and machine learning[J]. Composite Structures,2020,236:111840. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111840 [21] DINH-CONG D, NGUYEN-THOI T. A chaos game optimization-based model updating technique for structural damage identification under incomplete noisy measurements and temperature variations[J]. Structures,2023,48:1271-1284. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2023.01.032 [22] HUANG M, CHENG X, LEI Y. Structural damage identification based on substructure method and improved whale optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring,2021,11(2):351-380. doi: 10.1007/s13349-020-00456-7 [23] STUBBS N, BROOME T H, OSEGUEDA R. Nondestructive construction error detection in large space structures[J]. AIAA Journal,1990,28(1):146-152. doi: 10.2514/3.10365 [24] 刘康. 基于模型修正的结构损伤识别优化方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2018.LIU Kang. The optimized method for structural damage identification based on model updating technique[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [25] YAM L, YAN Y, JIANG J. Vibration-based damage detection for composite structures using wavelet transform and neural network identification[J]. Composite Structures,2003,60(4):403-412. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(03)00023-0 [26] BEGAMBRE O, LAIER J E. A hybrid particle swarm optimization-simplex algorithm (PSOS) for structural damage identification[J]. Advances in Engineering Software,2009,40(9):883-891. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2009.01.004 [27] HASHIN Z. Failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composites[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1980,47(2):329-334. doi: 10.1115/1.3153664 -






 下载:
下载: