Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based nanofiber membranes with temperature-sensitive and excellent mechanical properties
-
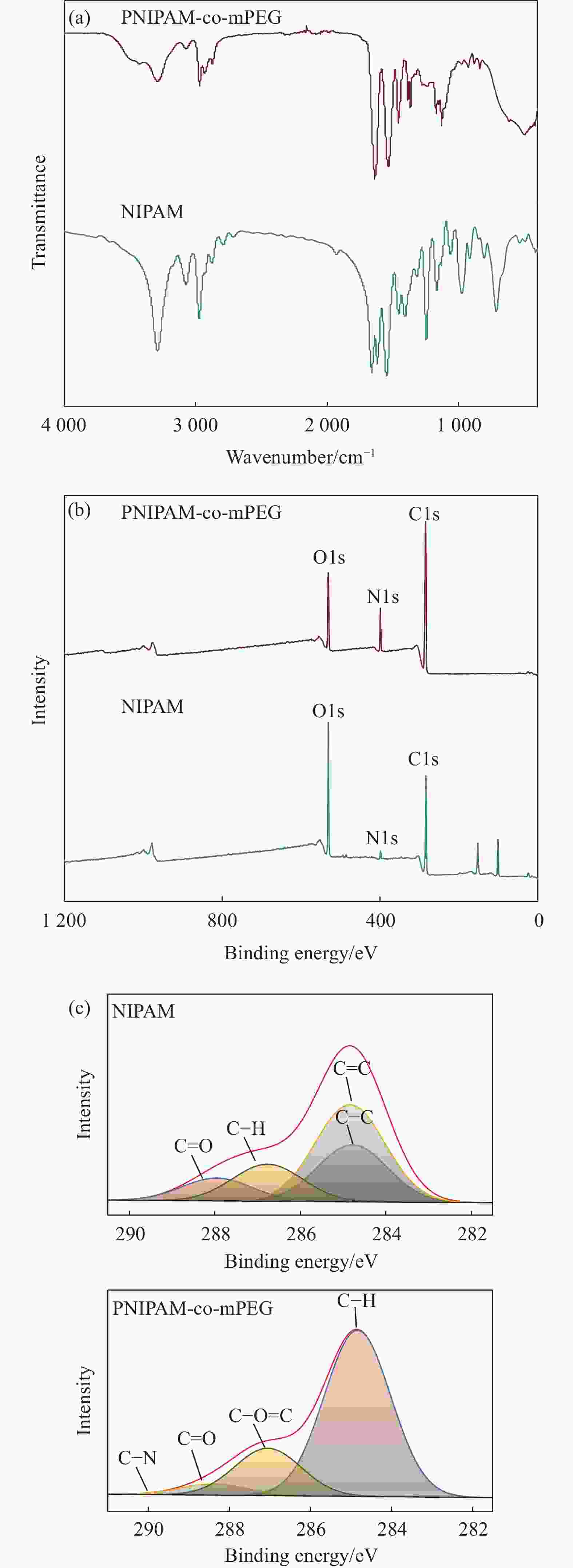
摘要: 聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)(PNIPAM)同时含有亲水性的酰胺基和疏水性的异丙基,是目前应用最广泛的一种具有温度敏感特性的聚合物,其相关产品在组织工程、医疗卫生和智能织物等领域拥有广阔的应用前景。本文应用自由基聚合法成功合成PNIPAM,并创新性地采用静电纺丝技术将其制备成一种具有温度敏感特性的纳米纤维膜,随后尝试将聚乙二醇甲醚(mPEG)与PNIPAM按不同比例进行共聚来探究PNIPAM-co-mPEG的各项性能表现。研究结果表明:制备得到的温敏纤维膜能随着温度的变化呈现出显著的亲、疏水性转变。与纯PNIPAM温敏纤维膜相比,经共聚处理后的温敏纤维膜的力学性能得到显著提升,能在大量吸水溶胀的状态下保持纤维固有形态;共聚后纤维膜的残重率提高321%,初始分解温度提高240%;其在室温下的水接触角减小超过16°,亲水性得到一定程度的提升;其低临界相变温度也从31.7℃提高至43.6℃,温度响应范围扩大。
-
关键词:
- 静电纺丝 /
- 温度敏感特性 /
- 纳米纤维膜 /
- 聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)(PNIPAM) /
- 聚乙二醇甲醚(mPEG)
Abstract: Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), which contains both hydrophilic amide and hydrophobic isopropyl groups, is one of the most widely used temperature-sensitive polymers, and its related products have promising applications in the fields of tissue engineering, medical care and smart fabrics. In this study, PNIPAM was successfully synthesized by free radical polymerization, and PNIPAM was prepared into temperature-sensitive nano-membranes by electrospinning technology innovatively. Then, we tried to copolymerize polyethylene glycol methyl ether (mPEG) and PNIPAM in different proportions to investigate the performance of PNIPAM-co-mPEG. The results showed that the temperature-sensitive nano-membranes exhibited significant hydrophilic and hydrophobic transitions with temperature changes. Compared with the pure PNIPAM temperature-sensitive nano-membranes, the mechanical properties of the PNIPAM-co-mPEG were significantly improved, and it could maintain the inherent fiber morphology under the condition of large water absorption and swelling. The residual weight rate and the initial decomposition temperature of PNIPAM-co-mPEG are increased by 321% and 240%, respectively. The water contact angle of PNIPAM-co-mPEG at room temperature decreases by more than 16°, which improves the hydrophilicity to a certain extent. Moreover, the low critical solution temperature of PNIPAM-co-mPEG is increased from 31.7℃ to 43.6℃, the temperature-sensitive range is expanded. -
图 2 (a) 不同浓度的电纺溶液在接收装置上的成膜状态;(b) 13wt%线型PNIPAM电纺纤维膜的SEM图像;(c) 15wt%线型PNIPAM电纺纤维膜的SEM图 像;(d) 17wt%线型PNIPAM电纺纤维膜的SEM图像;(e) PNIPAM-co-mPEG纳米纤维膜的SEM图像
Figure 2. (a) Nano-membranes state on receiver device with different electrospinning solution concentrations; (b) SEM images of 11wt% PNIPAM nano-membranes; (c) SEM images of 13wt% PNIPAM nano-membranes; (d) SEM images of 15wt% PNIPAM nano-membranes; (e) SEM images of PNIPAM-co-mPEG nano-membranes
图 4 (a) 将 PNIPAM-co-mPEG和纯PNIPAM纤维膜浸入25℃和45℃的水溶液中的状态;(b) PNIPAM和PNIPAM-co-mPEG纳米纤维膜的拉伸强度对比图;(c) PNIPAM和PNIPAM-co-mPEG纳米膜的水接触角图像
Figure 4. (a) Nano-membranes obtained from PNIPAM-co-mPEG and pure PNIPAM were immersed in water at 25℃ and 45°C; (b) Tensile strength comparison of PNIPAM and PNIPAM-co-mPEG nano-membranes; (c) Water contact angle images of PNIPAM and PNIPAM-co-mPEG nano-membranes
CA—Contact angle
表 1 制备聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)(PNIPAM)-co-聚乙二醇甲醚(mPEG)的投料比例
Table 1. Feeding ratio for preparation of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM)-co-polyethylene glycol methyl ether (mPEG)
Sample NIPAM/g mPEG/g 1,4-dioxane/mL AIBN/g PNIPAM-
co-5mPEG5 1.22 30 0.15 PNIPAM-
co-10mPEG5 2.43 30 0.15 PNIPAM-
co-15mPEG5 3.65 30 0.15 Note: AIBN—Azodiisobutyronitrile. 表 2 制备PNIPAM基温敏纤维膜的电纺参数
Table 2. Electrospinning parameters of PNIPAM based membranes
Sample Distance/
cmVoltage
(+/−)/kVVelocity/
(mm·min−1)PNIPAM
(11wt%)18.5 13.45/−2.5 0.15 PNIPAM
(13wt%)19.5 14.94/−2.5 0.20 PNIPAM
(15wt%)20.0 15.65/−2.5 0.20 PNIPAM-
co-mPEG17.0 13.45/−2.5 0.30 表 3 PNIPAM和PNIPAM-co-mPEG的分子量及其分布
Table 3. Molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of PNIPAM and PNIPAM-co-mPEG
Sample Mn/(g·mol−1) Mw/(g·mol−1) PDI PNIPAM 595156 1250589 2.10 PNIPAM-co-5mPEG 434110 1079342 2.49 PNIPAM-co-10mPEG 520070 1784472 3.43 PNIPAM-co-15mPEG 348551 1534512 4.40 Notes: Mn—Number-average molecular weight; Mw—Mass-average molecular mass; PDI—Polydispersity index (Ratio of the mass average molecular mass to the number average molecular mass). 表 4 PNIPAM和不同比例共聚物热失重信息
Table 4. TGA and DTG information of PNIPAM and PNIPAM-co-mPEG
Sample Residue/% T10%/℃ TMax/℃ PNIPAM 0.42 112.12 409.10 PNIPAM-co-5mPEG 1.67 250.50 394.30 PNIPAM-co-10mPEG 1.35 269.29 387.60 PNIPAM-co-15mPEG 1.27 290.46 352.40 Notes: T10%—Initial decomposition temperature; TMax—Maximum decomposition temperature. -
[1] HELLWEG T, DEWHURST C D, EIMER W, et al. PNIPAM-co-polystyrene core-shell microgels: Structure, swelling behavior, and crystallization[J]. Langmuir,2004,20(11):4330-4335. doi: 10.1021/la0354786 [2] FEIL H, BAE Y H, FEIJEN J, et al. Effect of comonomer hydrophilicity and ionization on the lower critical solution temperature of N-isopropylacrylamide copolymers[J]. Macromolecules,1993,26(10):2496-2500. doi: 10.1021/ma00062a016 [3] TANG L, WANG L, YANG X, et al. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based smart hydrogels: Design, properties and applications[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2020,115:100702. [4] CHUANG W J, CHIU W Y. Thermo-responsive nanofibers prepared from poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-methylol acrylamide)[J]. Polymer,2012,53(14):2829-2838. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2012.05.014 [5] HAQ M A, SU Y L, WANG D J. Mechanical properties of PNIPAM based hydrogels: A review[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications,2018,70:842-855. [6] SUN G, ZHANG X Z, CHU C C. Effect of the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the properties of chitosan-PEG-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine,2008,19(8):2865-2872. doi: 10.1007/s10856-008-3410-9 [7] SUN G M, ZHANG X Z, CHU C C. Formulation and characterization of chitosan-based hydrogel films having both temperature and pH sensitivity[J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Medicine,2008,18(8):1563-1577. [8] DEITZEL J M, KLEINMEYER J D, HIRVONEN J K, et al. Controlled deposition of electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) fibers[J]. Polymer,2001,42(19):8163-8170. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00336-6 [9] GUO Y J, WANG X Y, SHEN Y, et al. Research progress, models and simulation of electrospinning technology: A review[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2021,57(1):58-104. [10] THENMOZHI S, DHARMARAJ N, KADIRVELU K, et al. Electrospun nanofibers: New generation materials for advanced applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B-Advanced Functional Solid-State Materials,2017,217:36-48. [11] YANG Z, CHENG Q, JIANG Q, et al. Thermo-sensitive nanoparticles for triggered release of siRNA[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Science—Polymer Edition,2015,26(4):264-276. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2014.997559 [12] AHMAD S, AHMAD M, MANZOOR K, et al. A review on latest innovations in natural gums based hydrogels: Preparations & applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,136:870-890. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.113 [13] WANG H, YAN H, ZHU Y J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of thermo-responsive supramolecular diblock copolymers[J]. Journal of Polymer Research,2016,23(4):73-80. doi: 10.1007/s10965-016-0949-x [14] ALEXANDER A, AJAZUDDIN, KHAN J, et al. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics,2014,88(3):575-585. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.07.005 [15] ABANDANSARI H S, AGHAGHAFARI E, NABID M R, et al. Preparation of injectable and thermoresponsive hydrogel based on penta-block copolymer with improved sol stabi-lity and mechanical properties[J]. Polymer,2013,54(4):1329-1340. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2013.01.004 [16] CHAI Y H, LONG Y P, DONG X Z, et al. Improved functional recovery of rat transected spinal cord by peptide-grafted PNIPAM based hydrogel[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2022,210:112220. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.112220 [17] ZHU D Y, CHEN X J, HONG Z P, et al. Repeatedly Intrinsic self-healing of millimeter-scale wounds in polymer through rapid volume expansion aided host-guest interaction[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(20):22534-22542. [18] 田黎明, 杨丹丹, 聂康明, 等. 多壁碳纳米管/PCL-b-PNIPAM复合材料的制备[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(12):2706-2711. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160125.001TIAN Liming, YANG Dandan, NIE Kangming, et al. Preparation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/PCL-b-PNIPAM composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(12):2706-2711(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160125.001 [19] WANG Y L, SONG S J, CHU X H, et al. A new temperature-responsive controlled-release pesticide formulation-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) modified graphene oxide as the nanocarrier for lambda-cyhalothrin delivery and their application in pesticide transportation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2021,612:125987. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125987 [20] 李妍, 郭彦峰, 付俊, 等. 冷链物流中二元有机相变储能材料的制备与热物性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(6):2679-2689.LI Yan, GUO Yanfeng, FU Jun, et al. Preparation and thermophysical performance of organic phase change energy storage materials in cold chain transportation[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(6):2679-2689(in Chinese). [21] 徐朝阳, 李健昱, 石小梅, 等. 聚乙二醇改性纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合水凝胶的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(4):708-713. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160819.001XU Zhaoyang, LI Jianyu, SHI Xiaomei, et al. Preparation and properties of polyethylene glycol-modified cellulose nanofibers/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(4):708-713(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160819.001 [22] XU D L, ZHENG J F, ZHANG X, et al. Mechanistic insights of a thermoresponsive interface for fouling control of thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2022,56(3):1927-1937. [23] ZHAO Y Y, WEN J P, SUN H G, et al. Thermo-responsive separation membrane with smart anti-fouling and self-cleaning properties[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2020,156:333-342. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2020.02.006 -





 下载:
下载:






