Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 nanocomposites and their adsorption to Pb(II)
-
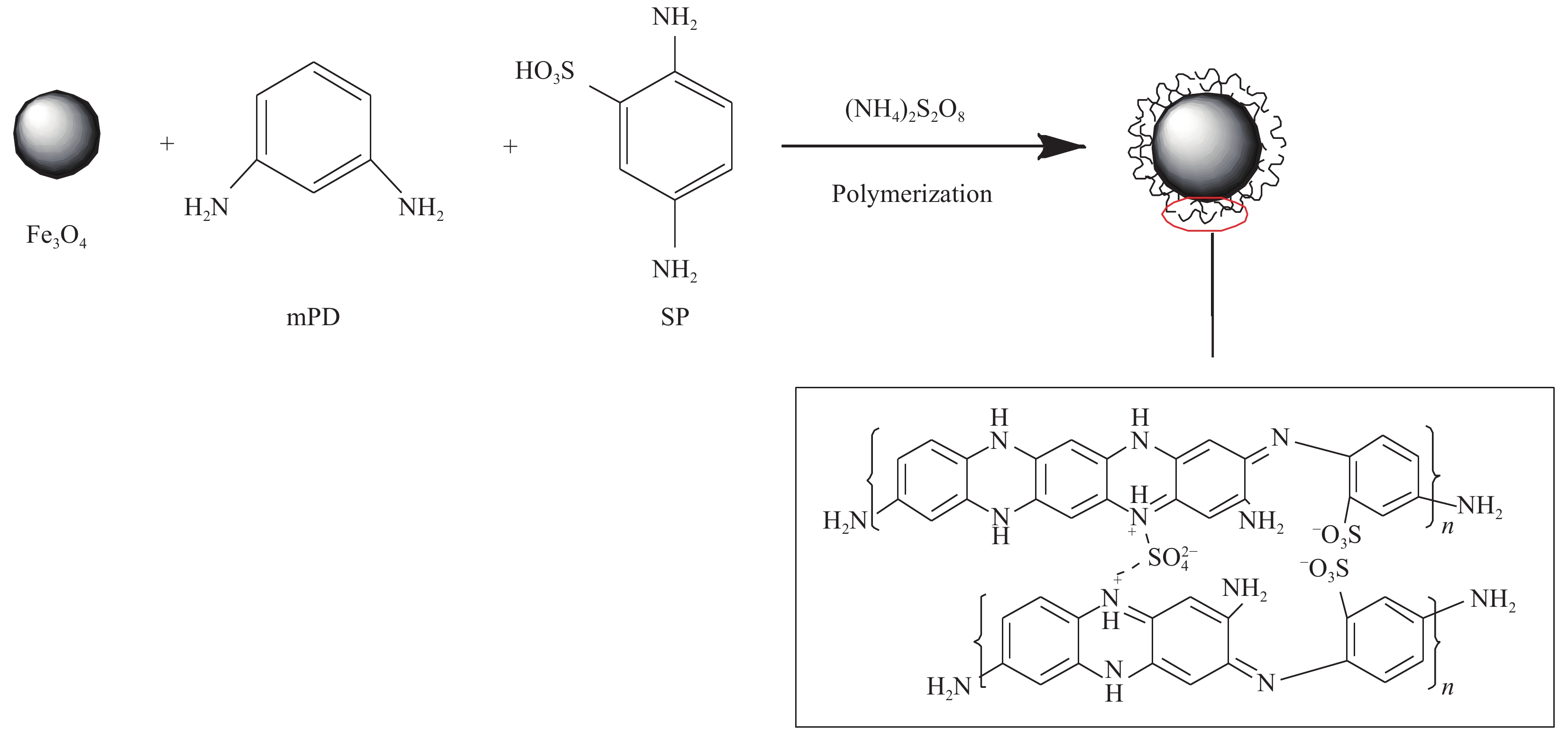
摘要: 为解决磁性纳米Fe3O4易被腐蚀、团聚等问题,可对其进行功能化修饰。在超声波辐照下首先制备磁性纳米Fe3O4颗粒,然后选用2,5-二氨基苯磺酸(SP)和间苯二胺(mPD)单体为引入剂进行功能化修饰,制备得到富含氨基、磺酸基和亚氨基活性官能团的金属基复合材料Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5),并采用FTIR、TEM、XRD等手段对其进行表征,证实了超声波辐照法制得的磁性纳米复合材料具有稳定性好、反应活性高、粒径小和比表面积更大等特点。同时考察其对Pb(II)的吸附性能,结果表明:mPD和SP摩尔比、溶液pH值、竞争性阳离子种类和反应温度等因素均会影响吸附效果;等温吸附过程符合Freundlich模型,吉布斯自由能∆G0<0,吸附是一个自发过程;Pb(II)的吸附行为符合准二级动力学,速率常数k2=3.61×10−3 g·mg−1·min−1,平衡吸附量qe=63.297 mg·g−1;推测得到吸附机制主要为离子交换、络合吸附和静电引力等。Abstract: In order to solve the problem that Fe3O4 nanoparticles were easy to be corroded and agglomerated, it was decided to functionalize it. Magnetic nano-Fe3O4 particles were prepared under ultrasonic irradiation, then 2-diaminobenzenesulfonic acid (SP) and m-phenylenediamine (mPD) monomers were selected as introduction agents to prepare metal matrix composites Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5), which were rich in amino, sulfonic acid and imine active functional groups, and nanocomposites were characterized by FTIR, TEM, XRD and other methods. The characterized results show that the magnetic nanocomposites prepared by ultrasonic strengthening method have the characteristics of good stability, high reaction activity, small particle size and larger specific surface area. The adsorption properties of Pb(II) by Fe3O4-mPD/SP were investigated which showed that the molar percentage of SP and mPD, reaction temperature, sorts of competitive cations and the pH value of solution all had effect on the adsorption of Pb(II). The adsorption isotherm conforms to the Freundlich model, and the adsorption of Pb(II) is a spontaneous process, Gibbs free energy ∆G0<0. It is found that the adsorption behavior of Pb(II) on nanocomposites can be well described by quasi secondary dynamics equation, kinetic constant k2=3.61×10−3 g·mg−1·min−1, equilibrium adsorption capacity qe=63.297 mg·g−1. It is speculated that the adsorption mechanism of this adsorbent includes ion exchange, complex adsorption and electrostatic adsorption.
-
Key words:
- ultrasound /
- magnetic properties /
- metal-matrix composites /
- adsorption /
- freundlich model /
- Fe3O4 nanoparticles
-
表 1 不同吸附剂对Pb(II)的吸附容量比较
Table 1. Comparison of adsorption capacity of Pb(II) by different adsorbents
Adsorbent Saturated adsorption capacity/(mg·g−1) Ref. Magnetic ion-imprinted and —SH functionalized polymer 32.58 [3] MNPs-Ca-alginate immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium 56.18 [6] Magnetic alginate beads 50.00 [7] Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 40.10 [8] Fe3O4@SiO2-NH-COOH 34.27 [9] Magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide 76.94 [13] Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5) 95.24 This study Note: MNPs—Magnetic nanoparticles. 表 2 Pb(II)吸附动力学方程拟合及各参数值
Table 2. Pb(II) adsorption kinetic equation fitting and parameters
Dynamics model R2 Rate constant qe,cal/(mg·g−1) qe,exp/(mg·g−1) Quasi-first-order kinetics 0.627 k1=1.65×10−2 min−1 — — Quasi-second-order kinetics 0.999 k2=3.61×10−3 g·mg−1·min−1 63.297 62.493 Internal diffusion equation 0.557 kp=2.005 mg·(g·min1/2)−1 — — Notes: qe,cal—Theoretical saturated adsorption capacity; qe,exp—Experimental saturated adsorption capacity; k1—Quasi-first-order kinetic constant; k2—Quasi-second-order kinetic constant; kp—Internal diffusion coefficient; R2—Correlation coefficient. 表 3 Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5)对Pb(II)各吸附动力学模型参数
Table 3. Kinetic model parameters of adsorption of Pb(II) by Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5)
Model Parameters and values Langmuir model KL/(L·mg−1) qm/(mg·g−1) R2 0.068 95.24 0.979 Freundlich model KF/(mg1−(1/n)·L1/n·g−1) 1/n R2 23.53 0.268 0.994 Temkin model Kt Bl R2 3.513 13.55 0.952 Notes: KL—Langmuir adsorption constant; KF—Freundlich adsorption coefficient; Kt, Bl—Temkin adsorption isotherm; qm—Saturated adsorption capacity; R2—Linear correlation coefficient; n—Empirical constant. 表 4 Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5)吸附Pb(II)热力学常数
Table 4. Thermodynamic constants of Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5) adsorption of Pb(II)
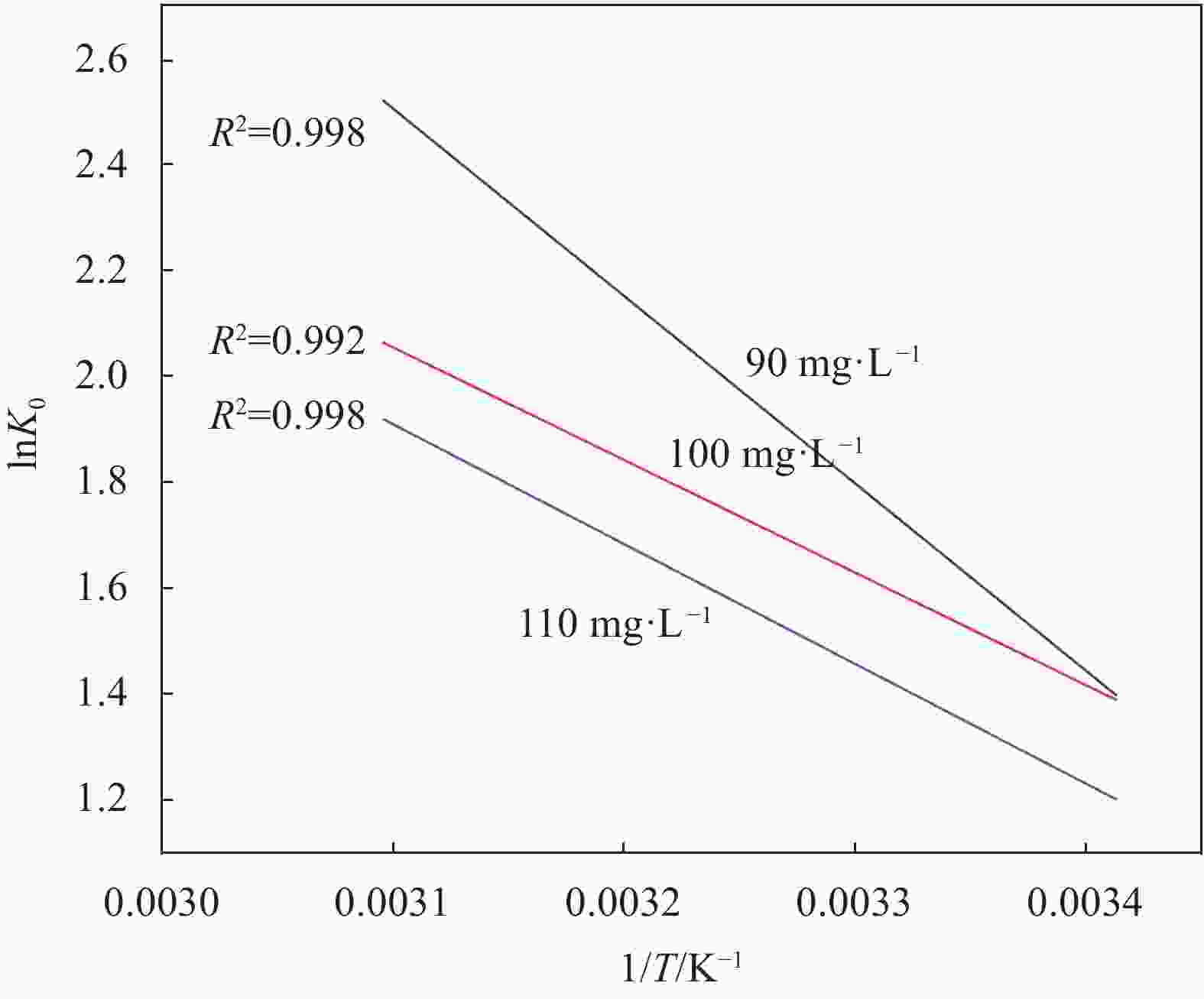
C0/(mg·L−1) ∆G0/(kJ·mol−1) ∆H0/(kJ·mol−1) ∆S0/(J·mol−1·K−1) 293 K 303 K 313 K 323 K 90 3.404 −4.570 5.561 6.807 30.766 116.620 100 3.342 4.197 4.768 5.542 21.703 85.479 110 2.937 −3.677 −4.361 −5.183 18.749 74.014 Notes: C0—Initial concentration of solution; ∆G0—Gibbs free energy; ∆H0—Enthalpy change; ∆S0—Entropy change. 表 5 Fe3O4和Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5)抗氧化性实验
Table 5. Antioxidant activity of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5)
Sample Sample state during adsorption qe/(mg·g−1) Fe3O4 Fresh preparation 23.19 Exposed to air for 48 h 17.51 Fe3O4-mPD/SP(95∶5) Fresh preparation 40.46 Exposed to air for 48 h 37.73 -
[1] 刘崇敏, 黄益宗, 于方明, 等. 改性沸石及添加CaCl2和MgCl2对重金属离子Pb2+吸附特性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(5):803-809. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.05.012LIU Chongmin, HUANG Yizong, YU Fangming, et al. Effect of modified zeolite and addition of CaCl2 and MgCl2 on the adsorption characteristics of heavy metal ion Pb2+[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2013,32(5):803-809(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.05.012 [2] 祝宏山. 高效去除水中铅离子的吸附剂制备与性能研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2019.ZHU Hongshan. Study on preparation and properties of adsorbents for efficient removal of lead ions from water[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2019(in Chinese). [3] 苏欣悦, 丁欣欣, 闫良国. Fe3O4磁性纳米材料的制备及水处理应用进展[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2020, 26(6):1-10.SU Xinyue, DING Xinxin, YAN Liangguo. Progress in preparation and water treatment application of Fe3O4 magnetic nanomaterials[J]. China Powder Technology,2020,26(6):1-10(in Chinese). [4] 郭健, 姚云, 赵小旭, 等. 粮食中重金属铅离子、镉离子的污染现状及对人体的危害[J]. 粮食科技与经济, 2018, 43(3):33-35, 85.GUO Jian, YAO Yun, ZHAO Xiaoxu, et al. Pollution status and harm to human body of heavy metal lead ion and cadmium ion in grain[J]. Grain Science, Technology and Economy,2018,43(3):33-35, 85(in Chinese). [5] KILIÇ H D, KIZIL H. Simultaneous analysis of Pb2+ and Cd2+ at graphene/bismuth nanocomposite film-modified pencil graphite electrode using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry.[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2019,411(30):8113-8121. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-02193-3 [6] 于婉婷. 聚间苯二胺的化学氧化合成及其除Cr(VI)的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013.YU Wanting. Chemical oxidation synthesis of poly(m-phenylenediamine) and its removal of Cr(VI)[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2013(in Chinese). [7] 姜智超, 邓景衡, 李伟. 四氧化三铁-蛭石复合材料制备及其对Pb2+的吸附性能[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(7):1664-1671. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.07.2016110703JIANG Zhichao, DENG Jingheng, LI Wei. Preparation of ferric oxide-vermiculite composite and its adsorption properties for Pb2+[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2017,36(7):1664-1671(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.07.2016110703 [8] XU P, ZENG G M, HUANG D L, et al. Adsorption of Pb(II) by iron oxide nanoparticales immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanisms analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,203:423-431. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.048 [9] IDRIS A, HASSAN N, MISRAN E, et al. Synthesis of magnetic alginate beads based on maghemite nanoparticles for Pb(II) removal in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2012,18(5):1582-1589. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2012.02.018 [10] 金旭. 氨基改性超顺磁纳米微粒的制备及其对污水中重金属的吸附研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2018.JIN Xu. Preparation of amino modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles and their adsorption of heavy metals in wastewater[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [11] 刘煌. 功能性磁性纳米颗粒制备及在重金属和致病菌分离的初步应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2012.LIU Huang. Preparation of functional magnetic nanoparticles and its preliminary application in the separation of heavy metals and pathogenic bacteria[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Industrial and Commercial University, 2012(in Chinese). [12] 张恒, 郑娇, 许宁侠, 等. 磁性四氧化三铁纳米微粒的研究进展[J]. 河南科技, 2020, 39(35):134-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2020.35.045ZHANG Heng, ZHENG Jiao, XU Ningxia, et al. Research progress of magnetic ferric oxide nanoparticles[J]. Henan Science and Technology,2020,39(35):134-136(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2020.35.045 [13] 谭丽莎. 功能化磁性纳米复合材料的制备及其对Pb(II)和Cr(VI)的选择性去除研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015.TAN Lisha. Preparation of functionalized magnetic nanocomposites and their selective removal of Pb(II) and Cr(VI)[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015(in Chinese). [14] MAHER A, SAMI Y, JEAN P, et al. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles, synthesis and surface modification[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,2015,39:641-648. doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2015.05.035 [15] FAN L L, LUO C N, SUN M, et al. Highly selective adsorption of lead ions by water-dispersible magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composites[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2013,103:523-529. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.11.006 [16] SABARIAH K, ZAINATUL A A R, MASITA M, et al. Acrylic acid-grafted polyaniline fibers for nickel ion removal from water: Synthesis, characterization and adsorption kinetics[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2022,79:1699-1711. doi: 10.1007/s00289-021-03585-1 [17] 赵德明, 李敏, 徐新华. 高分散型纳米级Pd/Fe对4-氯苯酚的还原脱氯[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(3):1091-1098. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2013.03.043ZHAO Deming, LI Min, XU Xinhua. Reductive dechlorination of 4-chlorophenol by highly dispersed nanometer Pd/Fe[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering,2013,64(3):1091-1098(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2013.03.043 [18] FIGUEIRA P, LOPES C B, DANIEL A L, et al. Removal of mercury(II) by dithiocarbamate surface functionalized magnetite particles: Application to synthetic and natural spiked waters[J]. Water Research,2011,45(17):5773-5784. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.057 [19] ZHANG W B, DENG M, SUN C X, et al. Ultrasound-enhanced adsorption of chromium(VI) on Fe3O4 magnetic particles[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research,2014,53(1):333-339. doi: 10.1021/ie401497k [20] ZHANG J, ZHAI S, LI S, et al. Pb(II) removal of Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 core-shell nanomaterials prepared via a controllable sol-gel proce[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,215-216:461-471. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.043 [21] YU W T, CHAI L Y, ZHANG L Y, et al. Synthesis of poly(m-phenylenediamine) with improved properties and superior prospect for Cr(VI) removal[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2013,23(11):3490-3498. doi: 0.1016/S1003-6326(13)62893-9 [22] HUANG M R, LU H J, LI X G. Synthesis and strong heavy-metal ion sorption of copolymer microparticles from phenylenediamine and its sulfonate[J]. Journal of Materials Chemitry,2012,22(34):17685-17699. doi: 10.1039/c2jm32361c [23] CRUZLOPES L P, MACENA M, ESTEVES B, et al. Ideal pH for the adsorption of metal ions Cr6+, Ni2+, Pb2+ in aqueous solution with different adsorbent materials[J]. Open Agriculture,2021,6(1):115-123. doi: 10.1515/opag-2021-0225 [24] LI Y C, JIN Z H, LI T L, et al. One-step synthesis and characterization of core-shell Fe@SiO2 nanocomposite for Cr(VI) reduction[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2012,421-422:260-266. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.01.010 [25] LIU C K, BAI R B, LY Q S. Selective removal of copper and lead ions by diethylenetriamine-functionalized adsorbent: Behaviors and mechanisms[J]. Water Research,2008,42(6-7):1511-1522. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.031 -






 下载:
下载: