Influences of fiber angle on the vibration damping performance of variable angle laminates
-
摘要: 自动铺丝技术可以实现复杂曲率曲线铺放,可极大提高角度设计的自由度。本文以改善复合材料层合板动态特性为目的,对变角度层合板的减振性能进行了研究分析。首先对不同角度变化变角度层合板进行自由衰减试验,研究了纤维角度变化与变角度层合板阻尼比的关系。然后对含相应角度变角度夹层板进行随机试验,研究了层合板随机激励条件下的振动响应,并采用共振峰处传递函数(Transition function,TF)和拾振点加速度总均方根(Root mean square,RMS)两种指标评价减振效果。结果表明:层合板阻尼比在纤维变化角度为±<45|60>时最大,纤维变化角度为±<73|88>时最小。基于RMS减振评价指标,±<45|60>夹层板较传统直线板减振性能提高27.13%;基于共振峰TF减振评价指标,纤维角度变化对不同共振峰减振效果规律差异明显。研究表明,变角度层合板减振性能明显优于传统直线层合板,相关实验结果将对变角度层合板减振设计及优化提供一定的参考意义。Abstract: With the development of automated fiber placement technology, it is possible to lay complex curves which greatly increase the freedom of angle design. In this paper, with the purpose of improving the dynamic characteristics of composite laminates, the vibration damping performance of variable angle laminates was studied and analyzed. Firstly, the free attenuation experiment was carried out to study the relationship between the change of fiber angle and damping ratio of variable angle laminates. Then, the vibration response of variable angle laminates under random excitation was studied by random experiments. The transition function (TF) at the formant and the root mean square (RMS) of the acceleration at the pick-up point of vibration were used to evaluate the effect of vibration reduction. The results show that the damping ratio of laminates is the largest when the fiber angle is ±<45|60> and the least when the fiber angle is ±<73|88>. Based on the vibration reduction evaluation index of RMS, the vibration reduction performance of ±<45|60> sandwich laminate is 27.13% higher than the traditional linear laminate; Based on the formant vibration reduction evaluation index of TF, the vibration reduction effect of different formants is obviously different with the fiber change. The results show that the vibration reduction performance of the variable angle laminates is obviously better than that of the traditional linear laminates. The relevant experimental results will be helpful for the design and optimization of vibration reduction of variable angle laminates.
-
Key words:
- advanced composites /
- variable angle /
- vibration damping /
- damping /
- vibration response
-
表 1 EM118碳纤维增强树脂预浸料的弹性基础参数
Table 1. Elastic fundation parameters of EM118 carbon fiber reinforced resin prepreg
E1/GPa E2/GPa G12/GPa G13/GPa G23/GPa ${v_{12}}$ 140 7.50 3.69 3.69 2.77 0.27 表 2 EM118碳纤维增强树脂复合材料变角度层合板阻尼比
Table 2. Damping ratio of EM118 carbon fiber reinforced resin variable angle composite laminates
Fiber curve composite laminate Damping ratio ζ/% [±<0|15>]2s 1.588 [±<15|30>]2s 1.440 [±<30|45>]2s 1.161 [±<45|60>]2s 1.775 [±<60|75>]2s 1.381 [±<73|88>]2s 1.056 表 3 EM118碳纤维增强树脂变角度层合板随机激励测点加速度响应共振峰值处传递函数值及减振效果
Table 3. Value of transfer function and vibration reduction effect at the resonance peak of the acceleration response of the random excitation measuring point of EM118 carbon fiber reinforced resin variable angle laminates
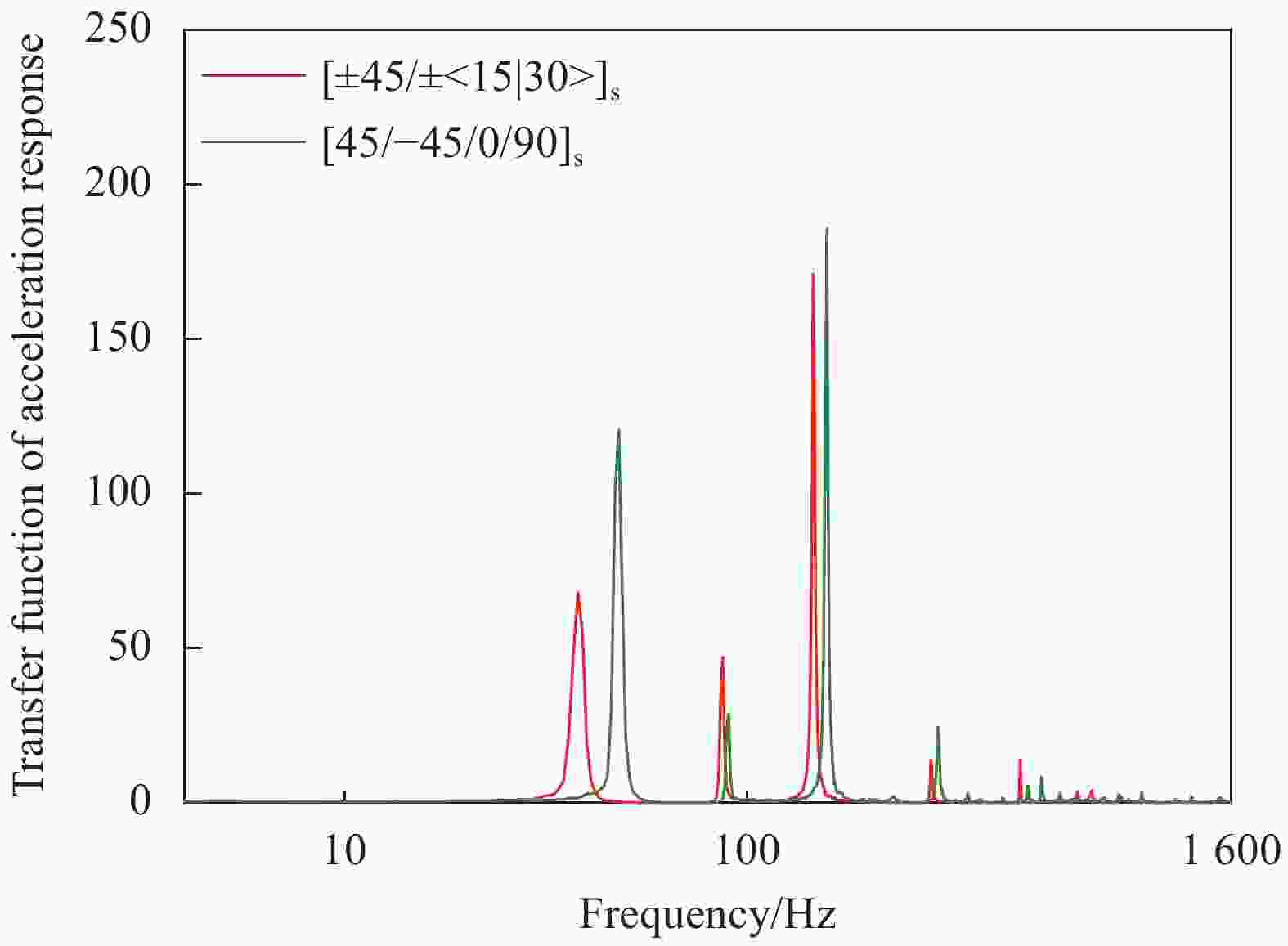
Composite layer sequence Near 48 Hz Near 90 Hz Near 158 Hz Transition function Vibration reduction effect/% Transition function Vibration reduction effect/% Transition function Vibration reduction effect/% [45/−45/0/90]s 120.747 − 28.873 − 185.817 − [±45/±<0|15>]s 39.817 67.02 101.510 −251.57 89.800 51.67 [±45/±<15|30>]s 67.944 43.73 47.002 −62.79 171.014 7.97 [±45/±<30|45>]s 118.434 1.92 110.382 −282.30 25.029 86.53 [±45/±<45|60>]s 37.043 69.32 20.034 30.61 9.504 94.89 [±45/±<60|75>]s 105.821 12.36 25.855 10.45 77.399 58.35 [±45/±<73|88>]s 255.780 −111.83 47.988 −66.20 185.373 0.24 表 4 EM118碳纤维增强树脂变角度层合板随机激励测点响应加速度均方根值及减振效果
Table 4. Random excitation measuring point response acceleration RMS and vibration reduction effect of EM118 carbon fiber reinforced resin variable angle laminates
Composite layer sequence Root mean square/g Vibration reduction effect/% [45/−45/0/90]s 0.3284 − [±45/±<0|15>]s 0.2816 14.25 [±45/±<15|30>]s 0.2893 11.91 [±45/±<30|45>]s 0.3008 8.40 [±45/±<45|60>]s 0.2393 27.13 [±45/±<60|75>]s 0.2944 10.35 [±45/±<73|88>]s 0.3819 −16.29 表 5 不同EM118碳纤维增强树脂变角度层合板相对刚度和相对质量
Table 5. Relative stiffness and relative mass of EM118 carbon fiber reinforced resin laminated plates with different variable angles
Composite layer
sequenceNumber Relative stiffness Relative mass Relative damping Relative stiffness
to mass ratio[45/−45/0/90]s CFRP-T1 1 1 1 1 [±45/±<0|15>]s CFRP-VS1 0.884 1.006 1.490 0.879 [±45/±<15|30>]s CFRP-VS2 0.622 0.993 1.348 0.626 [±45/±<30|45>]s CFRP-VS3 1.031 1.011 1.087 1.020 [±45/±<45|60>]s CFRP-VS4 0.663 1.004 1.662 0.660 [±45/±<60|75>]s CFRP-VS5 1.039 0.997 1.293 1.042 [±45/±<73|88>]s CFRP-VS6 0.949 0.990 0.989 0.959 -
[1] SABA N, JAWAID M, ALOTHMAN OY, et al. A review on dynamic mechanical properties of natural fibre reinforced polymer composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016(106):149-159. [2] 肖军, 李勇, 李建龙. 自动铺放技术在大型飞机复合材料结构件制造中的应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2008(1):50-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2008.01.009XIAO Jun, LI Yong, LI Jianlong. Application of automatic fiber placement in manufacture of composite structures in large aircraft[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2008(1):50-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2008.01.009 [3] AKHAVAN H, RIBEIRO P. Natural modes of vibration of variable stiffness composite laminates with curvilinear fibers[J]. Composite Structures,2011,93(11):3040-3047. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.04.027 [4] 尹先桃, 漆文凯. 变刚度复合材料层合板阻尼性能优化[C]. 中国航空学会第八届航空发动机可靠性学术交流, 2015: 459-463.YIN Xiantao, QI Wenkai. Research on damping properties optimization of variable-stiffness plate[C]. Journal of Physics Conference Series, 2015: 459-463 (in Chinese). [5] 孔斌, 顾杰斐, 陈普会, 等. 变刚度复合材料结构的设计、制造与分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(10):2121-2133.KONG Bin, GU Jiefei, CHEN Puhui, et al. Design, manufacture and analysis of variable stiffness composite structures[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2017,34(10):2121-2133(in Chinese). [6] ABDALLA M, SETOODHE S, GRDAL Z. Design of variable stiffness composite panels for maximum fundamental frequency using lamination parameters[J]. Computers & Strutures,2008,86(9):870-878. [7] 聂国隽, 朱佳瑜. 纤维曲线铺放的复合材料层合板的自由振动分析[J]. 力学季刊, 2016, 37(2):274-283.NIE Guojun, ZHU Jiayu. Free vibration analysis of composite laminates with curvilinear fibers[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics,2016,37(2):274-283(in Chinese). [8] 孙士平, 邓同强, 胡政. 丝束变角度层合板频率性能的参数化分析与优化[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2016, 8:27-32.SUN Shiping, DENG Tongqiang, HU Zheng. Par ametric analysis and optimization of frequency property of variable angle tow laminates[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites,2016,8:27-32(in Chinese). [9] 欧阳小穗, 刘毅. 高速流场中变刚度复合材料层合板颤振分析[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(3):221539.OUTANG X S, LIU Y. Panel flutter of variable stiffness composite laminates in supersonic flow[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2018,39(3):221539(in Chinese). [10] TREVISO A, VAN GENECHTEN B, MUNDO D, et al. Damping in composite materials: Properties and models[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2015,78:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.03.081 [11] TANG X, YAN X. A review on the damping properties of fiber reinforced polymer composites[J]. Journal of Industrial Textiles,2020,49(6):693-721. [12] PEREIRA D A, GUIMARÃES T A M, RESENDE H B, et al. Numerical and experimental analyses of modal frequency and damping in tow-steered CFRP laminates[J]. Composite Structures,2020,244(4):112190. [13] PEREIRA D A, SALES T P, RADE D A. Multi-objective frequency and damping optimization of tow-steered composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures,2020,256:112932. [14] GÜRDAL Z, OLMEDO R. In-plane response of laminates with spatially varying fiber orientations variable stiffness concept[J]. AIAA Journal,1993,31(4):751-758. doi: 10.2514/3.11613 [15] GÜRDAL Z, TATTING B F, WU C K. Variable stiffness composite panels: Effects of stiffness variation on the in-plane and buckling response[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2008,39(5):911-922. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2007.11.015 [16] 漆文凯, 程博. 复合材料层合板阻尼预测分析与验证[J]. 振动测试与诊断, 2013, 33(6):1049-1053.QI Wenkai, CHENG Bo. Predictive analysis and verification of damping for composite laminates[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis,2013,33(6):1049-1053(in Chinese). [17] DHIKARI S, WOODHOUSE J. Identification of damping: Part1, Viscous damping[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,2001,243(1):43-61. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.2000.3391 [18] 李晖, 孙伟, 常永乐, 等. 具有振幅依赖性的纤维增强复合薄板非线性阻尼的时域测试方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(5): 169-174.LI Hui, SUN Wei, CHANG Yongle, et al. Time domain test method for nonlinear damping of a fiber-reinforced composite thin plate with amplitude dependence. Journal of Vibration and Shock [J], 2018, 37(5): 169-174. (in Chinese). [19] FALCÓ O, MAYUGO J A, LOPES C S, et al. Variable-stiffness composite panels: As-manufactured modeling and its influence on the failure behavior[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2014,56:660-669. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.09.003 [20] PEETERS D M J, LOZANO G G, ABDALLA M M. Effect of steering limit constraints on the performance of variable stiffness laminates[J]. Computers & Structures,2018,196:94-111. [21] REDDY J N. Mechanics of laminated composite plates and shells: theory and analysis [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2004: 81-376. [22] 刘建良, 梅志远, 唐宇航, 等. 几种典型复合材料板振动特性综合对比分析及设计规律研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(15):65-72.LIU Jianliang, MEI Zhiyuan, TANG Yuhang, et al. Comprehensive comparative analysis for vibration characteristics of several typical composite panels and their design law[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2019,38(15):65-72(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: