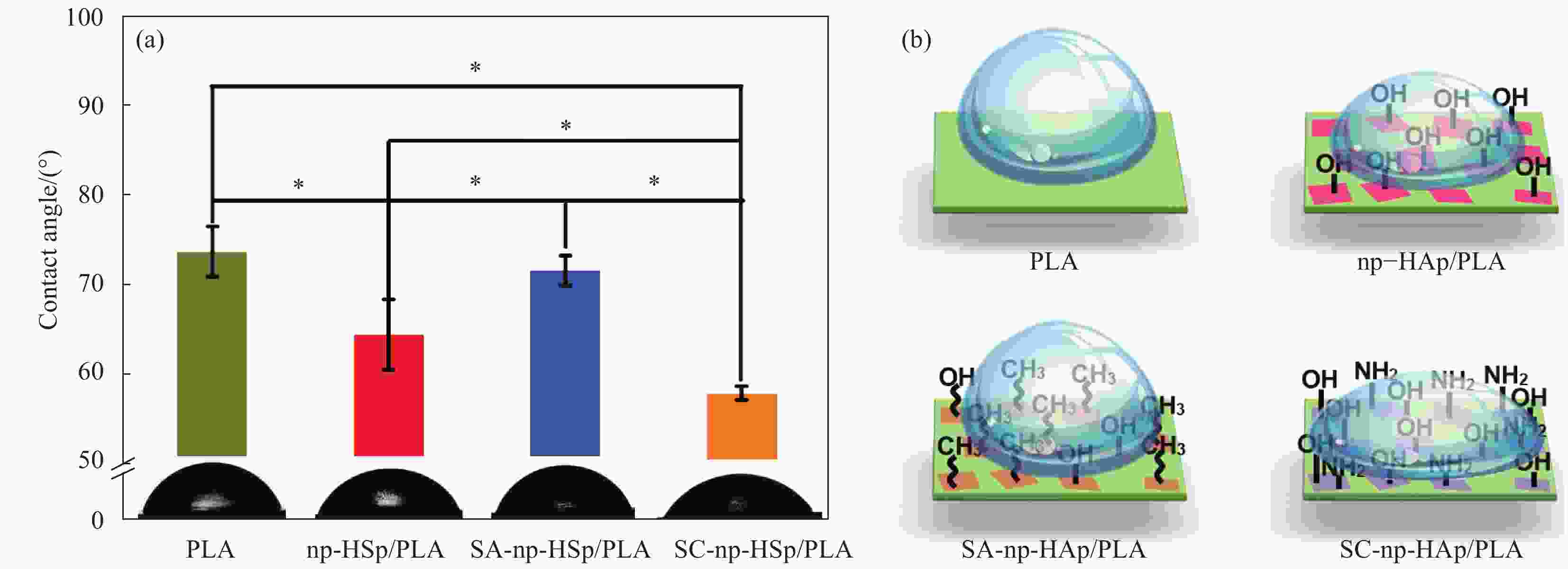
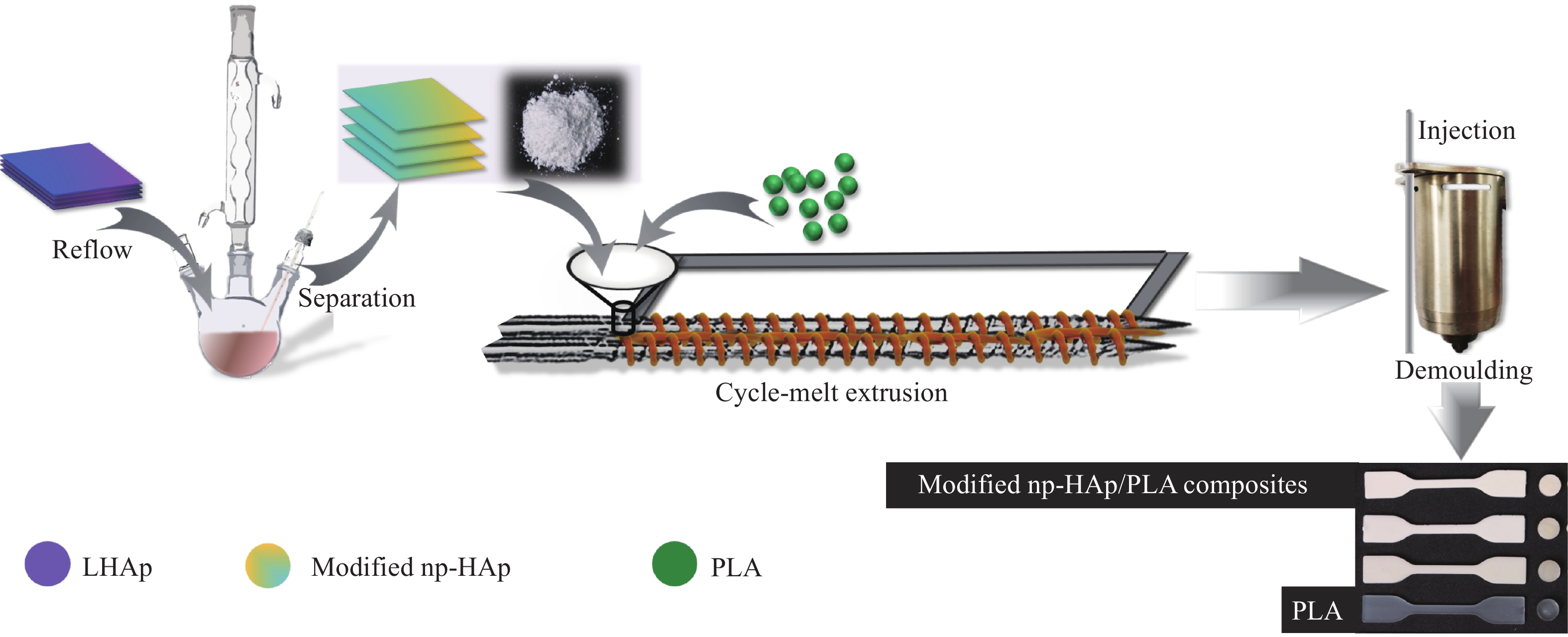
Effect of modifier on properties of nano-platelet hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composites
-
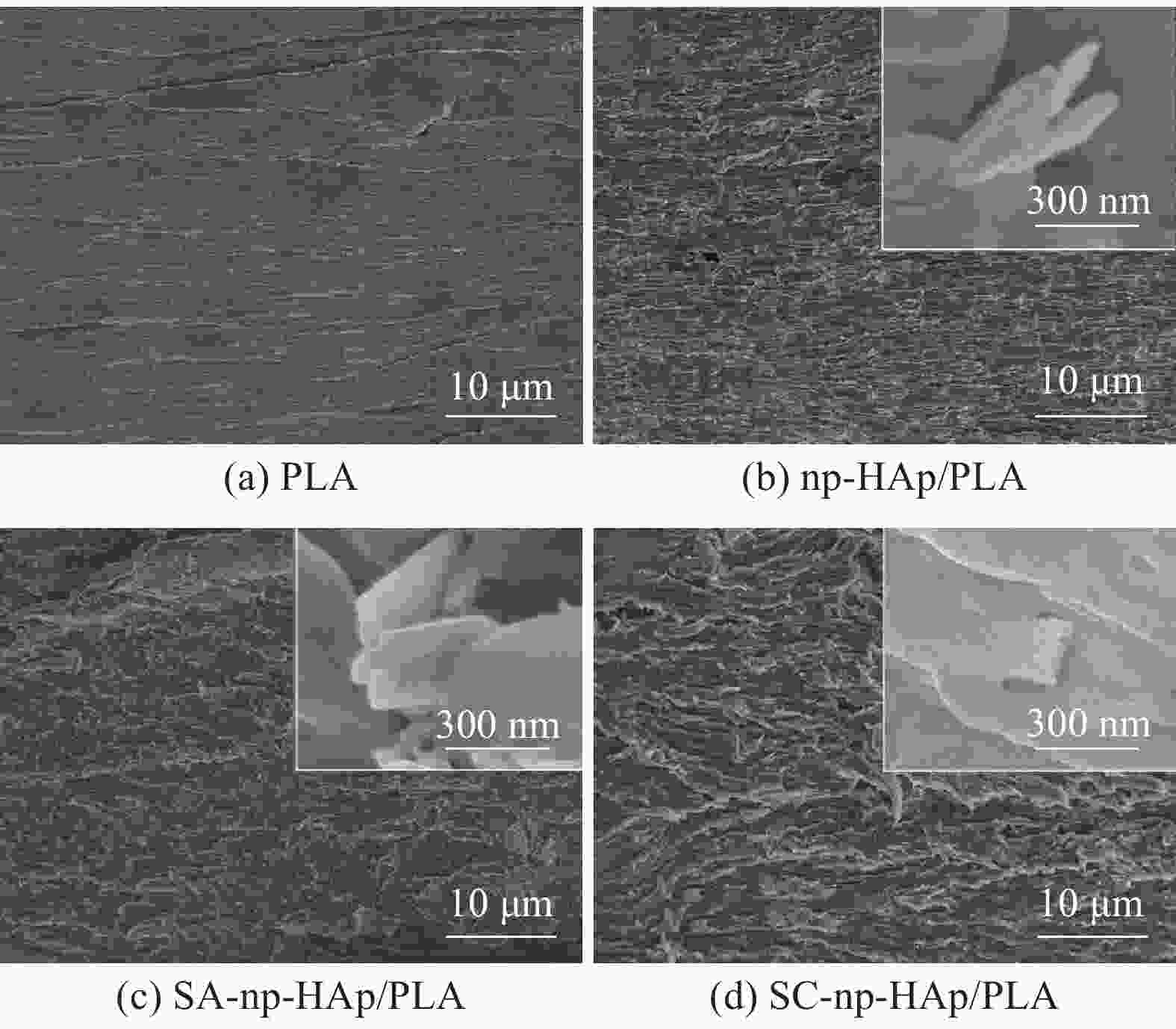
摘要: 分别采用硅烷偶联剂(SC)和硬脂酸(SA)对纳米层片状羟基磷灰石(LHAp)进行表面改性,并通过挤塑工艺制备未改性和两种改性纳米片状羟基磷灰石(np-HAp)增强聚乳酸(PLA) (np-HAp/PLA、SC-np-HAp/PLA和SA-np-HAp/PLA)复合材料。比较了三种复合材料的微观结构、力学性能、热稳定性、结晶性及润湿性。利用XRD、FTIR、XPS、SEM、TGA、DSC、力学性能测试和接触角测试对复合材料的理化性能进行表征。研究发现,np-HAp、SA-np-HAp与PLA界面处存在相分离,而SC-np-HA与PLA两相界面结合紧密;与np-HAp/PLA复合材料相比,SC-np-HAp/PLA复合材料的压缩屈服强度和拉伸强度分别提高了9.4%和6.6%,而SA-np-HAp/PLA复合材料的压缩屈服强度和拉伸强度则出现减小;此外,与np-HAp/PLA复合材料相比,SC-np-HAp/PLA和SA-np-HAp/PLA复合材料的初始分解温度分别提高了7.4%和5.6%,SC-np-HAp/PLA复合材料的结晶度提高了6.7%,SA-np-HAp/PLA复合材料的结晶度则减小了3.5%。水接触角测试结果表明,与np-HAp/PLA复合材料和SA-np-HAp/PLA复合材料相比,SC-np-HAp/PLA复合材料具有更为优异的亲水性。上述结果表明,经SC改性后的np-HAp具有与PLA基体更好的界面结合能力,为制备性能优异的骨植入复合材料提供借鉴。Abstract: The surface modification of nano-lamellar hydroxyapatite (LHAp) was carried out with silane coupling agent (SC) and stearic acid (SA), separately. The unmodified and two modified nano-platelet hydroxyapatite (np-HAp) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) (np-HAp/PLA, SC-np-HAp/PLA, and SA-np-HAp/PLA) composites were prepared by extrusion process. The microstructure, mechanical properties, thermal stability, crystallinity, and wettability of the three composites were compared. XRD, FTIR, XPS, SEM, TGA, DSC, mechanical property test, and contact angle test were conducted to characterize the physiochemical properties of the composites. The results show that there is phase separation at the interface of np-HAp or SA-np-HAp and PLA, and the interface of SC-np-HAp/PLA composite demonstrates strong interface adhesion. Compared with np-HAp/PLA composite, the compressive yield strength and tensile strength of SC-np-HAp/PLA composite increase by 9.4% and 6.6%, respectively, while SA-np-HAp/PLA composite exhibites reductions. Further, compared with np-HAp/PLA composite, the initial decomposition temperature of SC-np-HAp/PLA and SA-np-HAp/PLA composites increases by 7.4% and 5.6%, respectively, and crystallinity of the former increases by 6.7%, while the latter decreases by 3.5%. Compared with np-HAp/PLA and SA-np-HAp/PLA composites, the SC-np-HAp/PLA composite has a significantly lower water contact angle. These results indicate that the SC-modified np-HAp has better interface compatibility with PLA matrix, which will provide a new criterion for the preparation of high-performance bone implant composites.
-
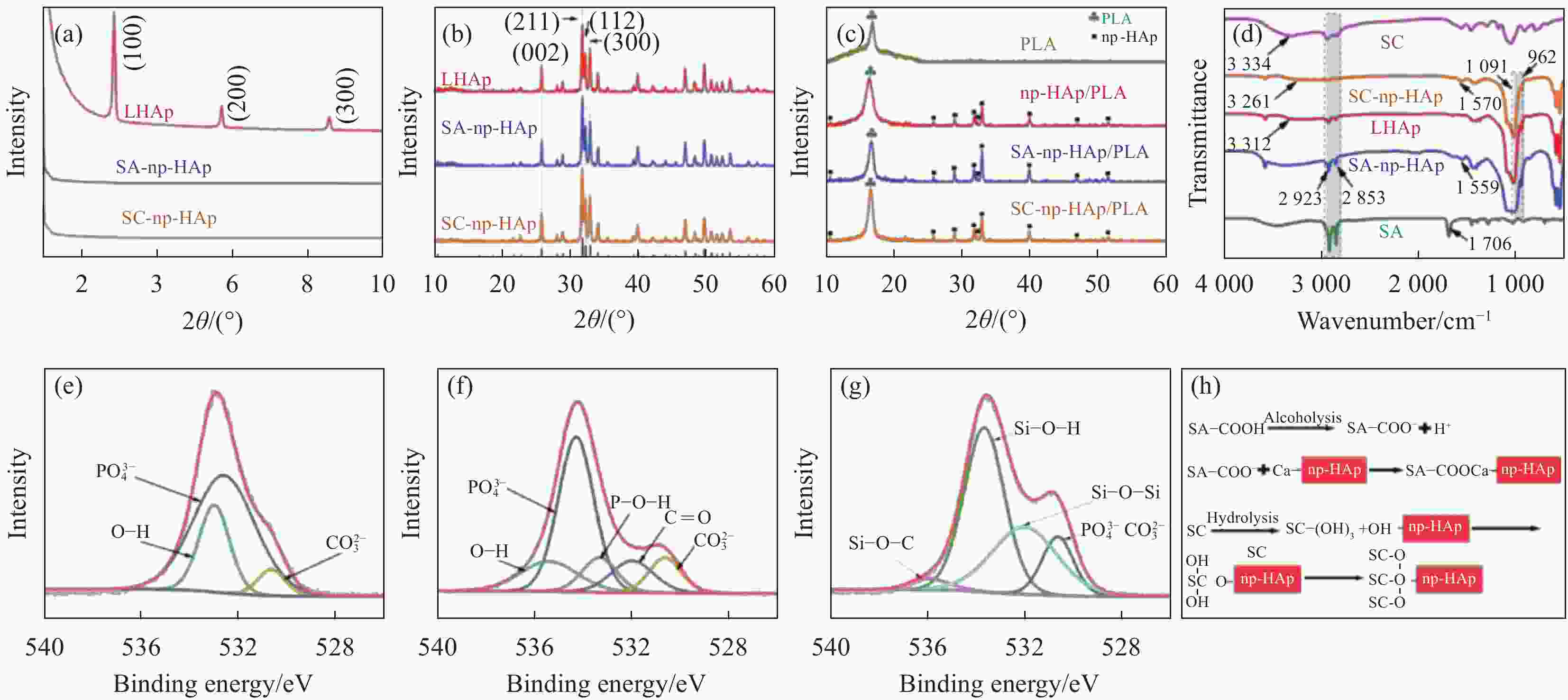
图 2 层片状羟基磷灰石(LHAp)、硬脂酸(SA)-np-HAp、硅烷偶联剂(SC)-np-HAp ((a),(b))及其复合材料(c)的XRD图谱;SC、SA、LHAp、SA-np-HAp和SC-np-HAp的FTIR图谱(d);LHAp (e)、SA-np-HAp (f)和SC-np-HAp (g)的O1s高分辨XPS图谱;SA和SC与np-HAp的结合过程示意图(h)
Figure 2. XRD patterns of lamellar hydroxyapatite (LHAp), stearic acid (SA)-np-HAp, silane coupling agent (SC)-np-HAp ((a), (b)) and PLA compsites (c); FTIR spectra of SC, SA, LHAp, SA-np-HAp and SC-np-HAp (d); High resolution XPS O1s spectra of LHAp (e), SA-np-HAp (f) and SC-np-HAp (g); Schematic illustration showing interaction between SA/SC and np-HAp (h)
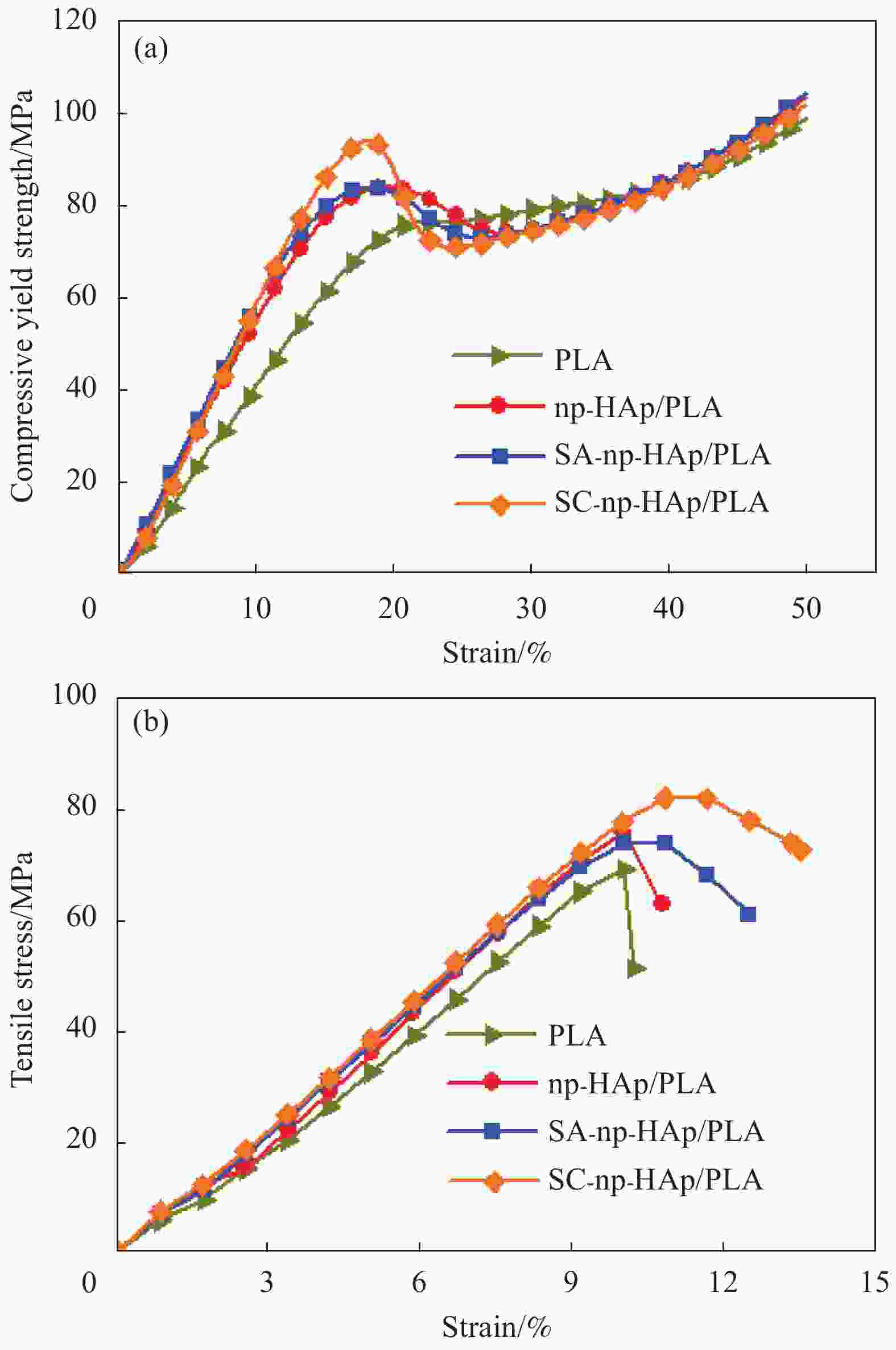
表 1 PLA、np-HAp/PLA、SA-np-HAp/PLA和SC-np-HAp/PLA复合材料的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of PLA, np-HAp/PLA, SA-np-HAp/PLA and SC-np-HAp/PLA composites
Material Compressive yield strength/MPa Compression modulus/MPa Tensile strength/MPa Young’s modulus/MPa PLA 74.6 (4.6) 424.8 (12.2) 68.7 (1.2) 714.9 (21.4) np-HAp/PLA 84.7 (3.4) 525.1 (38.9) 76.0 (1.6) 838.5 (16.2) SA-np-HAp/PLA 76.0 (3.3) 576.6 (44.0) 72.1 (1.1) 797.8 (22.5) SC-np-HAp/PLA 92.7 (1.4) 614.6 (27.6) 81.0 (0.8) 832.1 (12.9) Note: Values in the parentheses represent the standard deviations of replicates. 表 2 PLA、np-HAp/PLA、SA-np-HAp/PLA和SC-np-HAp/PLA复合材料的热稳定性
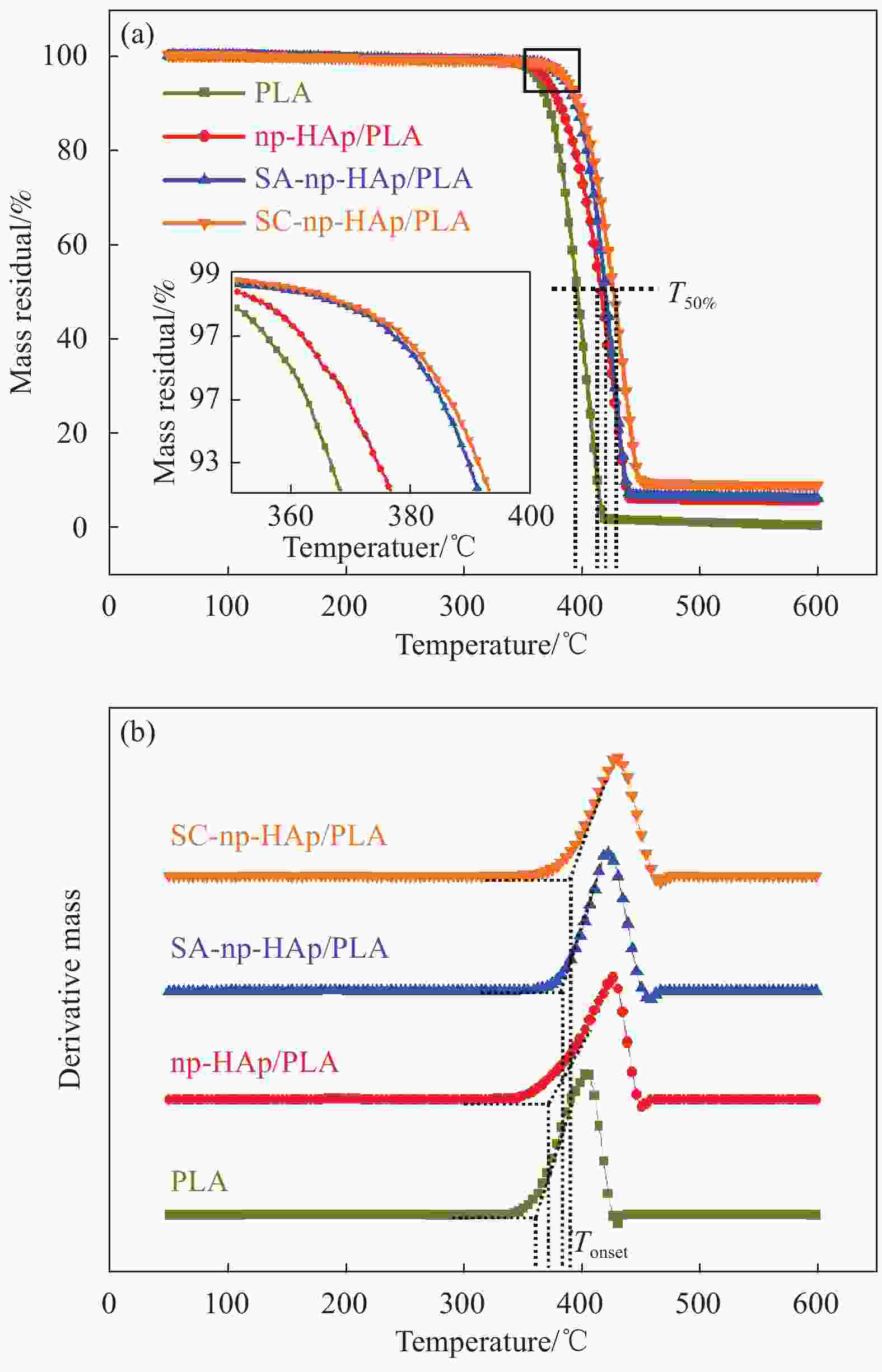
Table 2. Thermal stability of PLA, np-HAp/PLA, SA-np-HAp/PLA and SC-np-HAp/PLA composites
Material PLA np-HAp/PLA SA-np-HAp/PLA SC-np-Ap/PLA Tonset/℃ 353.3 364.0 384.6 391.0 T50%/℃ 395.6 415.6 420.0 426.7 Rm/% 0 5.3 6.0 8.9 Notes: Tonset—Initial decomposition temperature; T50%—Unstable state temperature; Rm—Residual mass at 600℃. 表 3 PLA、np-HAp/PLA、SA-np-HAp/PLA和SC-np-HAp/PLA复合材料在加热和冷却过程中的DSC热参数
Table 3. Thermal parameters of PLA, np-HAp/PLA, SA-np-HAp/PLA and SC-np-HAp/PLA composites in DSC analysis during heating and cooling
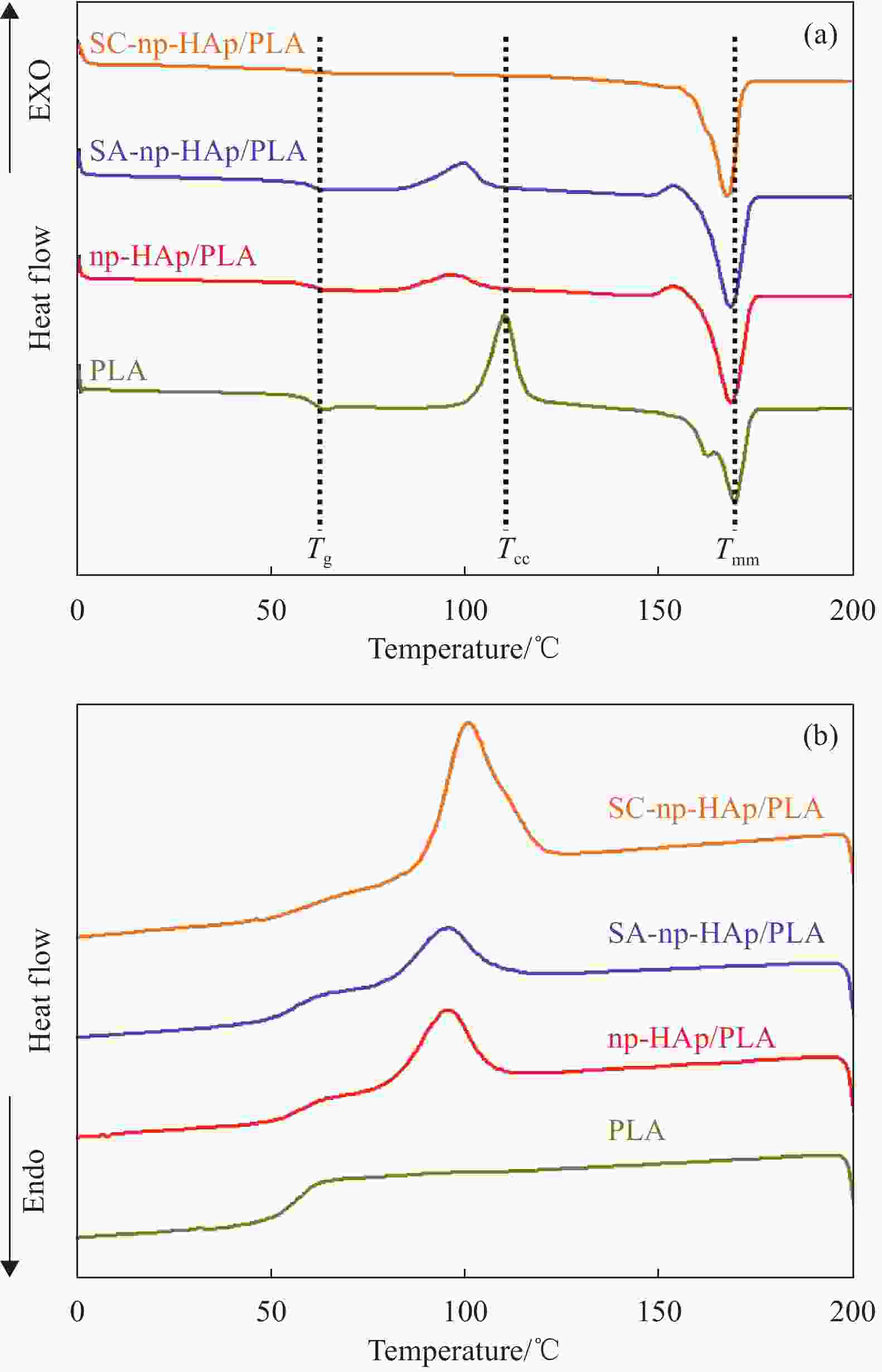
Material Tg/℃ Tcc/℃ ΔHcc/(J·g–1) Tm/℃ ΔHm/(J·g–1) χc/% PLA 60.2 110.2 33.2 169.3 14.7 21.9 np-HAp/PLA 60.5 96.4 9.55 168.1 41.1 37.4 SA-np-HAp/PLA 60.0 99.2 13.6 167.5 42.2 33.9 SC-np-HAp/PLA 60.0 — — 167.1 37.2 44.1 Notes: Tg—Glass transition temperature; Tcc—Cold crystallization temperature; ΔHcc—Cold crystallization enthalpy; Tm—Melting temperature; ΔHm—Melting enthalpy; χc—Crystallinity. -
[1] OLSZTA M J, CHENG X, JEE S S, et al. Bone structure and formation: A new perspective[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports,2007,58(3-5):77-116. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2007.05.001 [2] SARANYA N, SARAVANAN S, MOORTHI A, et al. Enhanced osteoblast adhesion on polymeric nano-scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology,2011,7(2):238-244. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2011.1283 [3] ZHENG J, LI Y, SHI M, et al. Microtribological behaviour of human tooth enamel and artificial hydroxyapatite[J]. Tribology International,2013,63:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2012.04.019 [4] ZHOU H, LAWRENCE J G, BHADURI S B. Fabrication aspects of PLA-CaP/PLGA-CaP composites for orthopedic applications: A review[J]. Acta Biomaterialia,2012,8(6):1999-2016. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.01.031 [5] GUPTA B, REVAGADE N, HILBORN J. Poly(lactic acid) fiber: An overview[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2007,32(4):455-482. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.01.005 [6] KANGO S, KALIA S, CELLI A, et al. Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic-inorganic nanocomposites: A review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2013,38(8):1232-1261. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.02.003 [7] 杨春瑜, 杨春莉, 田晓红, 等. 改性羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸复合材料制备及其生物相容性评价[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2010, 44(12):114-118.YANG C Y, YANG C L, TIAN X H, et al. Preparation and biocompatibility evaluation of modified hydroxyapatite/poly L-lactic acid composites[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2010,44(12):114-118(in Chinese). [8] ZHANG S, LIU J, ZHOU W, et al. Interfacial fabrication and property of hydroxyapatite/polylactide resorbable bone fixation composites[J]. Current Applied Physics,2005,5(5):516-518. doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2005.01.023 [9] SOMASUNDARAM S. Silane coatings of metallic biomaterials for biomedical implants: A preliminary review[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials,2018,106(8):2901-2918. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34151 [10] ZHANG Q, YIE G, LI Y, et al. Studies on the cyclosporin a loaded stearic acid nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2000,200(2):153-159. doi: 10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00361-6 [11] LIU J, ZHENG B, WANG P, et al. Enhance d in vitro and in vivo performance of Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy achieved with APTES pretreatment for drug-eluting vascular stent application[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(28):17842-17858. [12] WANG X, SONG G, LOU T. Fabrication and characterization of nano-composite scaffold of PLLA/silane modified hydroxyapatite[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics,2010,32(4):391-397. [13] SUN J, CAO Z, WU L. Polyvinylidene fluoride/silane-treated hydroxyapatite mixed matrix membrane for enzyme capturing[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2015,126:265-272. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.12.034 [14] DENG C, WENG J, DUAN K, et al. Preparation and mechanical property of poly(s-caprolactone)-matrix composites containing nano-apatite fillers modified by silane coupling agents[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine,2010,21(12):3059-3064. doi: 10.1007/s10856-010-4158-6 [15] DUPRAZ A, MEER S A T V D, DE WIJN J, et al. Biocompatibility screening of silane-treated hydroxyapatite powders, for use as filler in resorbable composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine,1996,7(12):731-738. doi: 10.1007/BF00121408 [16] KIM K J, WHITE J L, SHIM S E, et al. Effects of stearic acid coated talc, CaCO3, and mixed talc/CaCO3 particles on the rheological properties of polypropylene compounds[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2004,93(5):2105-2113. doi: 10.1002/app.20686 [17] ZHANG X, LI Q, LI L, et al. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite/stearic acid composite coating and corrosion behavior of coated magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Letters,2012,88:76-78. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2012.08.011 [18] YANG X, LU X, GE J, et al. Effect of a silane coupling agent on mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite/polycaprolactone composites[J]. Key Engineering Materials,2007,361-363:531-534. [19] GONSALVES J, FERRO J, BARRETO E, et al. Influence of concentration of hydroxyapatite surface modifier agent on bioactive composite characteristics[J]. Ceramics International,2016,42(15):17023-17031. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.07.210 [20] NAIR A, GAUTIERI A, CHANG S W, et al. Molecular mechanics of mineralized collagen fibrils in bone[J]. Nature Communications,2013,4:1724. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2720 [21] REY C, COMBES C, DROUET C, et al. Bone mineral: Update on chemical composition and structure[J]. Osteoporosis International,2009,20(6):1013-1021. doi: 10.1007/s00198-009-0860-y [22] ZHOU H, LEE J. Nanoscale hydroxyapatite particles for bone tissue engineering[J]. Acta Biomaterialia,2011,7(7):2769-2781. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.03.019 [23] JANDAS P J, MOHANTY S, NAYAK S K. Surface treated banana fiber reinforced poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites for disposable applications[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2013,52:392-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.03.033 [24] HUANG Z, WAN Y, PENG M, et al. Incorporating nanoplate-like hydroxyapatite into polylactide for biomimetic nanocomposites via direct melt intercalation[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,185:107903. [25] LIU S, LI Y, SUN H, et al. Preparation and characterisation of a lamellar hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composite[J]. Plastics Rubber & Composites,2019,48(2):66-73. [26] LUO H L, LI W, JI D H, et al. One-step exfoliation and surface modification of lamellar hydroxyapatite by intercalation of glucosamine[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2016,173:262-267. [27] WAN Y, WU C, ZUO G, et al. Controlled template synthesis of lamellar hydroxyapatite nanoplates as a potential carrier for gene delivery[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2015,156:238-246. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.03.011 [28] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料 拉伸性能的测定 第2部分: 模塑和挤塑塑料的试验条件: GB/T 1040.2—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics: Determination of tensile properties Part 2: Test conditions for moulding and extrusion plastics: GB/T 1040.2—2006[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2006(in Chinese). [29] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料 压缩性能的测定: GB/T 1041—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics: Detemination of compressive properties: GB/T 1041—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese). [30] XU H, XIE L, CHEN J B, et al. Strong and tough micro/nanostructured poly(lactic acid) by mimicking the multifunctional hierarchy of shell[J]. Materials Horizons,2014,1(5):546-552. doi: 10.1039/C4MH00085D [31] KOSTOV-KYTIN V V, DYULGEROVA E, ILIEVA R, et al. Powder X-ray diffraction studies of hydroxyapatite and β-TCP mixtures processed by high energy dry milling[J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(7):8664-8671. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.094 [32] RUAN B, WU P, LAI X, et al. Effects of Sphingomonas sp. GY2B on the structure and physicochemical properties of stearic acid-modified montmorillonite in the biodegradation of phenanthrene[J]. Applied Clay Science,2018,156:36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.01.009 [33] MILICEVIC D, SULJOVRUJIC E. The influence of the preparation conditions and filler content on thermal properties of poly-L-lactide and hydroxyapatite/poly-L-lactide nanocomposite[J]. Polymer International,2017,66(9):1275-1283. doi: 10.1002/pi.5382 [34] FUJIMORI H, TOYA H, IOKU K, et al. In situ observation of defects in hydroxyapatite up to 1 200℃ by ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy[J]. Chemical Physics Letters,2000,325(4):383-388. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2614(00)00695-3 [35] LIU S, LI Y, SUN H, et al. Preparation and characterisation of a lamellar hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composite[J]. Plastics Rubber and Composites,2019,48(2):66-73. doi: 10.1080/14658011.2018.1548191 [36] YANG J M, WEN C L, HAO T L. Properties of HTPB based polyurethane membrane prepared by epoxidation method[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2001,183(1):37-47. [37] MARCOMINI A L, REGO B T, SUMAN BRETAS R E. Improvement of the short-and long-term mechanical properties of injection-molded poly(etheretherketone) and hydroxyapatite nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2017,134(7):44476-44490. [38] PAN Y S. Surface modification of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite[J]. Micro & Nano Letters,2011,6(3):129-130. [39] ZUO G, WAN Y, MENG X, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a lamellar hydroxyapatite/DNA nanohybrid[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2011,126(3):470-475. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.060 [40] LI Y, WENG W. Surface modification of hydroxyapatite by stearic acid: characterization and in vitro behaviors[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine,2008,19(1):19-25. doi: 10.1007/s10856-007-3123-5 [41] JIANG L Y, XIONG C D, CHEN D L, et al. Effect of n-HA with different surface-modified on the properties of n-HA/PLGA composite[J]. Applied Surface Science,2012,259:72-78. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.06.091 [42] LAM R, QUARONI L, PEDERSON T, et al. A molecular insight into the nature of crystallographic mismatches in self-assembled fibrillar networks under non-isothermal crystallization conditions[J]. Soft Matter,2010,6(2):404-408. doi: 10.1039/B919477K [43] SALEM H, ABDELRAHIM M, EID K A, et al. Nanosized rods agglomerates as a new approach for formulation of a dry powder inhaler[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine,2011,6(2):311-320. doi: 10.2217/nnm.11.1 [44] WANG X, LI Y, JIE W, et al. Development of biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(hexamethylene adipamide) composites[J]. Biomaterials,2002,23(24):4787-4791. doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00229-6 [45] LIAO J G, WANG X J, ZUO Y, et al. Surface Modification of nano-hydroxyapatite with silane agent[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2008,23(1):145-149. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2008.00145 [46] RAN X, YU X, HE J, et al. Molecular mechanism of nano-hydroxyapatite surface changes from hydrophilic to hydrophobic[J]. Asian Journal of Chemistry,2014,26(17):5355-5359. doi: 10.14233/ajchem.2014.18110 [47] DIAO H, SI Y, ZHU A, et al. Surface modified nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(lactide acid) composite and its osteocyte compatibility[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C,2012,32(7):1796-1801. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2012.04.065 [48] FANG Z, FENG Q. Improved mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite whisker-reinforced poly(L-lactic acid) scaffold by surface modification of hydroxyapatite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C,2014,35:190-194. [49] RAKMAE S, RUKSAKULPIWAT Y, SUTAPUN W, et al. Effect of silane coupling agent treated bovine bone based carbonated hydroxyapatite on in vitro degradation behavior and bioactivity of PLA composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C,2012,32(6):1428-1436. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2012.04.022 [50] ZHU J, UHL F M, MORGAN A B, et al. Studies on the mechanism by which the formation of nanocomposites enhances thermal stability[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2001,13(12):4649-4654. doi: 10.1021/cm010451y [51] NAIR K M, THOMAS S, GROENINCKX G. Thermal and dynamic mechanical analysis of polystyrene composites reinforced with short sisal fibres[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2001,61(16):2519-2529. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(01)00170-1 [52] LEE J H, PARK T G, PARK H S, et al. Thermal and mechanical characteristics of poly(L-lactic acid) nanocomposite scaffold[J]. Biomaterials,2003,24(16):2773-2778. doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00080-2 [53] CHOW W S, LOK S K. Thermal properties of poly(lactic acid)/organo-montmorillonite nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,2009,95(2):627-632. [54] PAUL M A, ALEXANDRE M L, DEGÉE P, et al. New nanocomposite materials based on plasticized poly(L-lactide) and organo-modified montmorillonites: Thermal and morphological study[J]. Polymer,2003,44(2):443-450. [55] MARTIN O, AVÉROUS L. Poly(lactic acid): Plasticization and properties of biodegradable multiphase systems[J]. Polymer,2001,42(14):6209-6219. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00086-6 [56] DAY M, NAWABY A V, LIAO X. A DSC study of the crystallization behaviour of polylactic acid and its nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis & Calorimetry,2006,86(3):623-629. [57] WANG H, SUN X, SEIB P. Strengthening blends of poly(lactic acid) and starch with methylenediphenyl diisocyanate[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2001,82(7):1761-1767. doi: 10.1002/app.2018 [58] SZUSTAKIEWICZ K, GAZIŃSKA M, KRYSZAK B, et al. The influence of hydroxyapatite content on properties of poly(L-lactide)/hydroxyapatite porous scaffolds obtained using thermal induced phase separation technique[J]. European Polymer Journal,2019,113:313-320. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.01.073 [59] SANJAY S L, ANNASO B G, CHAVAN S M, et al. Recent progress in preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces: A review[J]. Journal of Surface Engineered Materials and Advanced Technology,2012,2(2):76-94. -





 下载:
下载: