Development status and future of ceramic-metal co-continuous composite material
-
摘要: 陶瓷-金属双连续相复合材料作为一种采用空间连续网络构型设计的复合材料,具有耐摩擦磨损、抗热震性高、热膨胀系数低等特点,具有广阔的应用前景。其中,多孔陶瓷预制体作为双连续相复合材料中的结构增强相,其本征特性对复合材料的整体性能有重要影响。本文系统分析了现阶段在多孔陶瓷的制备方法与表面改性两个领域内的主要进展,并对陶瓷-金属双连续相复合材料的制备技术与性能研究进行了介绍。最后,展望了陶瓷-金属双连续相复合材料在未来的发展过程中可能会遇到的四大挑战。Abstract: As a kind of composite material designed by space continuous network configuration, the ceramic-metal co-continuous composite owns some special characteristics such as the resistance of friction and wear, high thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion coefficient and so on, which make it has broad application prospects. Inside, the intrinsic properties of porous ceramic preforms as the ceramic reinforcement in the co-continuous composite have important impacts on the overall performance of the composite. In this review, the main progress in the current preparation methods and surface modification of porous ceramics are systematically analyzed, and both the preparation technology and the performance research of ceramic-metal co-continuous composite are summarized. Finally, we outline the four major challenges that may be encountered in the future development of ceramic-metal co-continuous composites.
-
Key words:
- ceramic-metal /
- composite /
- co-continuous reinforcement /
- network configuration /
- technical challenges
-
图 14 通过表面改性和ECP在氧化铝陶瓷上形成铜层的工艺示意图 (a)、多巴胺聚合物改性陶瓷表面与催化颗粒间可能的界面定位机制示意图 (b)[88]
Figure 14. Schematic diagram of the process for creating copper layer on alumina ceramic via modification and ECP (a), schematic illustration about a possible interfacial location mechanism for the modification between ceramic surface and catalytic particles by dopamine polymer (b)[88]
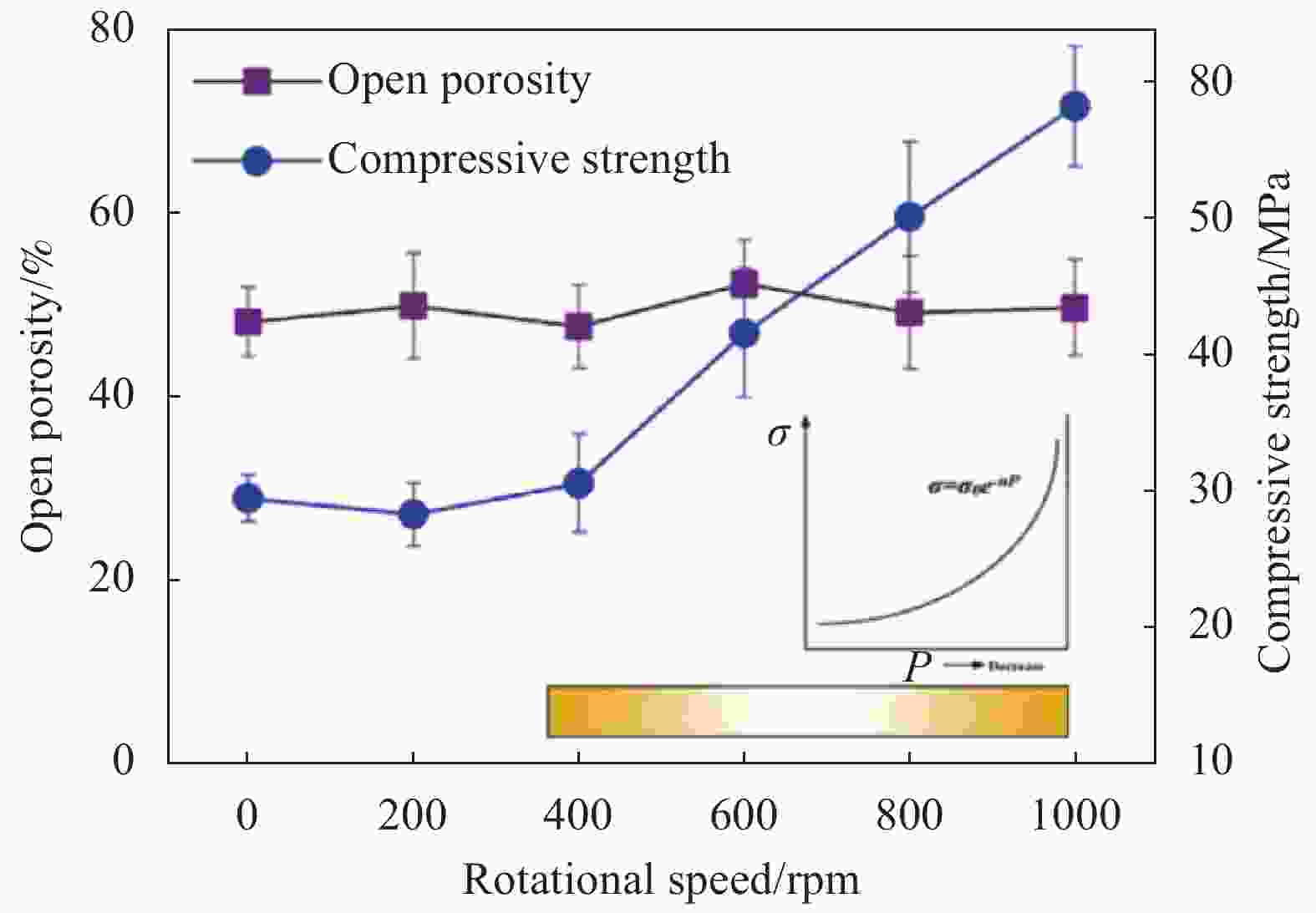
图 22 SiC网络陶瓷的宏观形貌 (a)、SiC多孔陶瓷的微观网络结构 (b)、SiC/Fe-20Cr的宏观形貌 (c)、SiC/Fe-20Cr的微观结构 (d) 和模拟微观力学模型(箭头为加载方向,点表示固定表面) (e)[114]
Figure 22. Macro-appearance of SiC network ceramic (a), microstructure of SiC network ceramic (b), macro-appearance of SiC/Fe-20Cr (c), microstructure of SiC/Fe-20Cr (d), simulated micromechanical model (Arrow is the loadingdirection, points mean the fixed surface) (e)[114]
表 1 几种多孔陶瓷制备方法的工艺性比较
Table 1. Technological comparison of several methods for preparing porous ceramics
Type of technology Aperture size Apparent porosity/% Advantages Disadvantage Organic foam impregnation 100 μm-5 mm 70-90 High porosity, adjustable aperture Low strength, environment pollution Pore forming agent method 10 μm-1 mm 0-50 Adjustable size and shape, high strength Inhomogeneous pores, low porosity Foaming method 10 μm-2 mm 40-90 High strength and porosity Complex process, high production cost Sol-gel >1 nm 30-70 Suitable for micropores, high free degree Limited use, high production cost Solid sintering 1-600 μm 20-30 Simple process, high strength Low porosity, environment pollution Template method 1 nm-100 μm 10-90 Large aperture distribution range, high strength High production cost, complex process -
[1] STANKOVICH S, DIKIN D A, DOMMETT G H B, et al. Graphene-based composite materials[J]. Nature,2006,442(7100):282-286. doi: 10.1038/nature04969 [2] REZWAN K, CHEN Q Z, BLAKER J J, et al. Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Biomaterials,2006,27(18):3413-3431. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.039 [3] 谭毅. 新材料概论[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2004: 5.TAN Yi. Introduction new materials[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2004: 5(in Chinese). [4] 吴人洁. 下世纪我国复合材料的发展机遇与挑战[J]. 复合材料学报, 2000, 17(1):1-4. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.01.001WU Renjie. The prospective opportunities and challenges of composite materials in China during the next century[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2000,17(1):1-4(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.01.001 [5] YIP N Y, TIRAFERRI A, PHILLIP W A, et al. High performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2010,44(10):3812-3818. [6] ZHANG Y, CHAN H F, LEONG K W. Advanced materials and processing for drug delivery: The past and the future[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews,2013,65(1):104-120. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.10.003 [7] BALLAL D R, ZELINA J. Progress in aeroengine technology (1939-2003)[J]. Journal of Aircraft,2015,41(1):43-50. [8] YVON P, CARRÉF. Structural materials challenges for advanced reactor systems[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials,2009,385(2):217-222. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.11.026 [9] LIU W, JIANG X, SHAO Z, et al. A review on nanocarbon-reinforced Cu-matrix nanocomposites with high mechanical strengths[J]. Current Nanoence,2017,13(4):410-420. [10] SHIN S E, KO Y J, BAE D H. Mechanical and thermal properties of nanocarbon-reinforced aluminum matrix composites at elevated temperatures[J]. Composites,2016,106(12):66-73. [11] MELENDEZ I M, NEUBAUER E, ANGERER P, et al. Influence of nano-reinforcements on the mechanical properties and microstructure of titanium matrix composites[J]. Composites Science & Technology,2011,71(8):1154-1162. [12] MOASERI E, KARIMI M, BANIADAM M, et al. Improvements in mechanical properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube-reinforced epoxy composites through novel magnetic-assisted method for alignment of carbon nanotubes[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2014,64:228-233. [13] SINGH T, PATNAIK A, SATAPATHY B K. Friction braking performance of nanofilled hybrid fiber reinforced phenolic composites: Influence of nanoclay and carbon nanotubes[J]. Nano Brief Reports & Reviews,2013,8(3):1-15. [14] ZHANG X, ZHAO N Q, HE C N. The superior mechanical and physical properties of nanocarbon reinforced bulk composites achieved by architecture design-A review[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 113: 100672. [15] MANFREDI D, PAVESE M, BIAMINO S, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of co-continuous metal/ceramic composites obtained from reactive metal penetration of commercial aluminium alloys into cordierite[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing, 2010, 41(5): 639-645. [16] RAMESH R, PRASANTH A S, RAGAVAN M, et al. SiC/aluminium co-continuous composite synthesized by reactive metal penetration[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 592-594: 847-853. [17] MANFREDI D, PAVESE M, BIAMINO S, et al. Preparation and properties of NiAl(Si)/Al2O3 co-continuous compo-sites obtained by reactive metal penetration[J]. Compo-sites Science and Technology, 2009, 69(11-12): 1777-1782. [18] AGRAWAL P, CONLON K, BOWMAN K J, et al. Thermal residual stresses in co-continuous composites[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(4): 1143-1156. [19] YIN Y, ZHAO F, SONG X, et al. Preparation and characterization of hydroxyap-atite/chitosan-gelatin network composite[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2000, 77(13): 2929-2938. [20] MYUNG D, WATERS D, WISEMAN M, et al. Progress in the development of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2008,19(6):647-657. doi: 10.1002/pat.1134 [21] ARAKI K, HALLORAN J W. Porous ceramic bodies with interconnected pore channels by a novel freeze casting technique[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2005,88(5):1108-1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00176.x [22] 陈建春. 铝合金变质、细化、合金化材料及铝熔体物理净化材料的设计、工艺及应用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2011.CHEN J C. Preparation, techniques and applications of Al alloys for modification, refining and alloying, and materials and filtrators for physical purifying[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2011(in Chinese). [23] LV Y, LIU H, WANG Z, et al. Silver nanoparticle-decorated porous ceramic composite for water treatment[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2009,331(1-2):50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2009.01.007 [24] GARCIA-PENA I, HERNANDEZ S, AURIA R, et al. Correlation of biological activity and reactor performance in biofiltration of toluene with the fungus paecilomycesvariotii CBS115145[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2005,71(8):4280-4285. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4280-4285.2005 [25] HAART L G J D. Deposition and electrical properties of thin porous ceramic electrode layers for solid oxide fuel cell application[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,1991,138(7):1970. doi: 10.1149/1.2085910 [26] ÖZGÜR E N, CÜNEYT T A. Preparation of porous Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 and β-Ca3(PO4)2 bioceramics[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2000,83(7):1581-1584. [27] LUKES P, CLUPEK M, BABICKY V, et al. Pulsed electrical discharge in water generated using porous-ceramic-coated electrodes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science,2008,36(4):1146-1147. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2008.920945 [28] JULBE A, FARRUSSENG D, GUIZARD C. Porous ceramic membranes for catalytic reactors-Overview and new ideas[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2001,181(1):3-20. doi: 10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00375-6 [29] OHJI T, FUKUSHIMA M. Macro-porous ceramics: Processing and properties[J]. International Materials Reviews,2012,57(2):115-131. doi: 10.1179/1743280411Y.0000000006 [30] ZHAO C, ZENG L F. Pressurelessly sintering silicon carbide with additives of holmium oxide and alumina[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,1995,30(3):265-270. doi: 10.1016/0025-5408(95)00004-6 [31] MATSUDA S, TAKAHASHI M. Fracture strength distribution of porous ceramics under quasi-static load[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2010,77(13):2601-2609. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2010.06.005 [32] KISELOV V S, LYTVYN P M, YUKHYMCHUK V O, et al. Synthesis and properties of porous SiC ceramics[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2010,107(9):1-6. [33] GUO X Z, YANG H. Sintering and microstructure of silicon carbide ceramic with Y3Al5O12 added by sol-gel method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B,2005,6(3):213-218. [34] DIVECHA A P, FISHMAN S G, KARMARKAR S D. Silicon carbide reinforced aluminum-A formable composite[J]. Journal of Metals,2013,33(9):12-17. [35] CAO J, RUSINA O, SIEBER H. Processing of porous TiO2-ceramics from biological performs γ-Al2O3→α-Al2O3[J]. Ceramics International,2004,30(7):1971-1974. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2003.12.180 [36] KLAWITTER J J, HULBERT S F. Application of porous ceramics for the attachment of load bearing internal orthopedic applications[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A,2010,5(6):161-229. [37] SCHWARTZWALDER K, SOMESS A V. Method of making porous ceramic articles: US, US 30900941[P]. 1963-05-21. [38] COLOMBO P, HELLMANN J R. Ceramic foams from preceramic polymers[J]. Materials Research Innovations,2002,6(5-6):260-272. doi: 10.1007/s10019-002-0209-z [39] BERNARDO E, COLOMBO P, MANIAS E. SiOC glass modified by montmorillonite clay[J]. Ceramics International,2006,32(6):679-686. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2005.05.002 [40] ZHANG X Z, WANG R J, LIU G W, et al. Preparation of silicon carbide reticulated porous ceramics by organic foam impregnation[J]. Materials Science Forum,2015,814:574-578. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.814.574 [41] OKADA K, ISOBE T, KATSUMATA K I, et al. Porous ceramics mimicking nature-preparation and properties of microstructures with unidirectionally oriented pores[J]. Science & Technology of Advanced Materials,2011,12(6):064701. [42] LIU B, DONG Y S, LIN P H, et al. Preparation of polyphosphate porous bioceramics and in vitro cytocompatibility[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2011,26(7):759-764. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2011.00759 [43] SHANG S S, HE X, YANG Y, et al. Preparation of Ti2AlN porous ceramics by organic foam impregnation process[J]. Key Engineering Materials,2016,697:163-168. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.697.163 [44] WANG J, ZHAO J. Investigating the effect of SPRM on mechanical strength and thermal conductivity of highly porous alumina ceramics[J]. Ceramics International,2017,43(18):16430-16435. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.022 [45] ZUO K H, ZHANG Y, ZENG Y P, et al. Pore-forming agent induced microstructure evolution of freeze casted hydroxyapatite[J]. Ceramics International,2011,37(1):407-410. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2010.08.015 [46] QIAN H, CHENG X, ZHANG H, et al. Preparation of porous mullite ceramics using fly ash cenosphere as a pore-forming agent by gelcasting process[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology,2014,11(5):858-863. doi: 10.1111/ijac.12204 [47] ZUZANA Z V, LOCS J, KEUPER M, et al. Microstructural comparison of porous oxide ceramics from the system Al2O3-ZrO2 prepared with starch as a pore-forming agent[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2012,32(10):2163-2172. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.02.005 [48] HAN F, ZHONG Z, ZHANG F, et al. Preparation and characterization of SiC whisker-reinforced SiC porous ceramics for hot gas filtration[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2015,54(1):226-232. [49] COLOMBO P. Engineering porosity in polymer-derived ceramics[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2008,28:1389-1395. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2007.12.002 [50] WANG C, KASUGA T, NOGAMI M. Macroporous Calcium phosphate glass-ceramic prepared by two-step pressing technique and using sucrose as a pore former[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine,2005,16:739-744. doi: 10.1007/s10856-005-2611-8 [51] BAI J G, YANG X H, SHI Y G, et al. Fabrication of directional SiC porous ceramics using Fe2O3 as pore-forming agent[J]. Materials Letters,2012,78:192-194. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2012.03.046 [52] ZHANG Y M, HU L Y, HAN J C, et al. Freeze casting of aqueous alumina slurries with glycerol for porous ceramics[J]. Ceramics International,2010,36:617-621. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.09.036 [53] 吕咏梅. 发泡剂的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 橡胶科技, 2005, 3(6):53-56.LV Yongmei. Present study situation and development tendency of blowing agents[J]. Plastics Science & Technology,2005,3(6):53-56(in Chinese). [54] 赵国玺. 表面活性剂物理化学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1984: 35-48.ZHAO Guoxi. Physico-chemistry of surfactants[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 1984: 35-48(in Chinese). [55] SEPULVEDA P, BINNER J G P. Processing of cellular ceramics by foaming and in situ polymerization of organic monomers[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,1999,19(12):2059-2066. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(99)00024-2 [56] KIM Y W, PARK C B. Processing of microcellular preceramics using carbon dioxide[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2003,63(16):2371-2377. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00270-7 [57] YUAN L, HE Z B, YU J K. Fabrication of Al2O3-based porous ceramic with closed pores by superplastic high-temperature foaming method[J]. Journal of Northeastern University,2013,34(7):939-943. [58] GONZENBACH U T, STUDART A R, TERVOORT E, et al. Macroporous ceramics from particle-stabilized wet foams[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2007,90(1):16-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.01328.x [59] HE X, SU B, TANG Z H, ZHAO B, et al. The comparison of macroporous ceramics fabricated through the protein direct foaming and sponge replica methods[J]. Journal of Porous Materials,2012,19(5):761-766. doi: 10.1007/s10934-011-9528-z [60] BARG S, SOLTMANN C, ANDRADE M, et al. Cellular ceramics by direct foaming of emulsified ceramic powder suspensions[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2008,91(9):2823-2829. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02553.x [61] JIN G Q, GUO X Y. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous silicon carbide[J]. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials,2003,60(1-3):207-212. [62] SIMONENKO E P, SIMONENKO N P, PAPYNOV E K, et al. Preparation of porous SiC-ceramics by sol-gel and spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology,2017,82(3):748-759. doi: 10.1007/s10971-017-4367-2 [63] 黄剑锋. 溶胶-凝胶原理与技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 13-20.HUANG Jianfeng. Principle and technology of sol-gel[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 13-20(in Chinese). [64] KRESGE C T, LEONOWICZ M E, ROTH W J, et al. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism[J]. Nature,1992,359(6397):710-712. doi: 10.1038/359710a0 [65] ALLAN S, STUART W C, MICHAEL W A. 29Si solid-state NMR study of mesoporous M41S materials[J]. Chemistry of Materials,1995,7(10):1829-1832. doi: 10.1021/cm00058a012 [66] 刘栎锟, 叶钢, 陈靖, 等. 冠醚修饰的SBA-15型有序介孔硅基材料及应用: 中国, CN106268653B[P]. 2019-04-05.LIU Likun, YE Gang, CHEN Jing, et al. SBA-15 ordered mesoporous silicon based materials modified by crown ether and its application: China, CN106268653B[P]. 2019-04-05(in Chinese). [67] OGBEMI O O, MARK A J, STEPHEN D N. Gelcasting: From laboratory development toward industrial production[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,1997,17(2):407-413. [68] 任强, 武秀兰. 微米级多孔陶瓷的研究[J]. 中国陶瓷工业, 2003, 10(2):21-23.REN Qiang, WU Xiulan. Development on micron porous ceramics[J]. China Ceramic Industry,2003,10(2):21-23(in Chinese). [69] YANAGISAWA K, IOKU K, YAMASAKI N. Formation of anatase porous ceramics by hydrothermal hot-pressing of amorphous titania spheres[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,1997,80(5):1303-1306. [70] DING S Q, ZHU S, ZENG Y P, et al. Fabrication of mullite-bonded porous silicon carbide ceramics by in situ reaction bonding[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2007,27(4):2095-2102. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.06.003 [71] KISHIMOTO A, OBATA M, ASAOKA H, et al. Fabrication of alumina-based ceramic foams utilizing superplasticity[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2007,27(1):41-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.03.002 [72] JAYASEELAN D D, KONDO N, BRITO M E, et al. High-strength porous alumina ceramics by the pulse electric current sintering technique[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2002,85(1):267-269. [73] MASAYA K, JUNYA Y, YASUSHI S, et al. Preparation and electrochemical characteristics of N-enriched carbon foam[J]. Carbon,2007,45(5):1105-1107. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2007.02.023 [74] ZHANG G J, YANG J F, OHJI T. Fabrication of porous ceramics with unidirectionally aligned continuous pores[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2001,84(6):1395-1397. [75] ZHANG W, LI M, WANG C, et al. Micropatterning of porous structures from Co/continuous polymer blends[J]. Advances in Polymer Technology,2013,32(1):166-179. [76] TANG F Q, FUDOUZI H, UCHIKOSHI T, et al. Preparation of porous materials with controlled pore size and poro-sity[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2004,24(2):341-344. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(03)00223-1 [77] JIANG F Y, WANG J B, HE X H, et al. Morphgenetic Al2O3 porous ceramic with fabric-structure by processed bio-template from ramie fibres[J]. Materials Letters,2017,194(1):242-245. [78] XIONG D B, CAO M, GUO Q, et al. Graphene-and-copper artificial nacre fabricated by a preform impregnation process: Bioinspired strategy for strengthening-toughening of metal matrix composite[J]. ACS Nano,2015,9(7):6934-6943. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01067 [79] LU Y, YANG J F, LU W Z, et al. The mechanical properties of co-continuous Si3N4/Al composites manufactured by squeeze casting[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2010,527(23):6289-6299. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.06.047 [80] DELUCA M A, MCCORMACK J F. Metallization of ceramics: US, US 4604299[P]. 1986-08-05. [81] RODRGUEZ-LORENZO L M, FERREIRA J M F. Development of porous ceramic bodies for applications in tissue engineering and drug delivery systems[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2004,39(1):83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2003.09.014 [82] WOO B H, SONE M, SHIBATA A, et al. Effects of SC-CO2 catalyzation in metallization on polymer by electroless plating[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2009,203(14):1971-1978. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.01.031 [83] LOUIS S. Method of coating metal: US, US 3185596[P]. 1965-05-25. [84] AKHMETZYANOV M, ALBAUT G. Study of large plastic strains and fracture in metal elements by photoelastic coating method[J]. International Journal of Fracture,2004,128(1-4):223-231. [85] GHOSH S, SENGUPTA A, PAL K S, et al. Characterization of metallized alumina ceramics[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy & Materials Science,2012,43(3):912-920. [86] CHENG Y S, YEUNG K L. Effects of electroless plating chemistry on the synthesis of palladium membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2001,182(1-2):195-203. doi: 10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00563-9 [87] SHAFEEV G A, BELLARD L, THEMLIN J M, et al. Uncongruent laser ablation and electroless metallization of SiC[J]. Applied Physics Letters,1996,68(6):773. doi: 10.1063/1.116738 [88] WANG Y, XU Y H, CAO Z Y, et al. A facile process to manufacture high performance copper layer on ceramic material via biomimetic modification and electroless plating[J]. Composites,2019,157(15):123-130. [89] JACSON T R, LIU H, PATRIKALAKIS N M. Modeling and designing functionally graded material components for fabrication with local composition control[J]. Materials & Design,1999,20(2-3):63-75. [90] NIINO M, HIRAI T, WATANABE R. Functionally gradient materials[J]. Journal of Japanese Society of Composite Material,1987,13(6):257. doi: 10.6089/jscm.13.257 [91] DELFOSSE D. Fundamentals of functionally graded materials[J]. Materials Today,1998,1(4):18. doi: 10.1016/S1369-7021(98)80023-0 [92] JIN Z H, PAULINO G H. Transient thermal stress analysis of an edge crack in a functionally graded material[J]. International Journal of Fracture,2001,107(1):73-98. doi: 10.1023/A:1026583903046 [93] 艾桃桃. 梯度多孔陶瓷的制备技术[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2011, 47(3):59-61, 76.AI T T. Preparation techique of gradient porous ceramics[J]. China Ceramic,2011,47(3):59-61, 76(in Chinese). [94] ZHOU W B, ZHANG R B, AI S G, et al. Load distribution in threads of porous metal-ceramic functionally graded composite joints subjected to thermomechanical loading[J]. Composite Structures,2015,134:680-688. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.08.113 [95] ZHANG F, QI C X, WANG S, et al. A study on preparation of cordierite gradient pores porous ceramics from rectorite[J]. Solid State Sciences,2011,13(5):929-933. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2011.02.015 [96] KEN D, CAROLINE R C. Processing of functionally gradient ceramic membrane substrates for enhanced porosity[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,1999,82(8):2073-2079. [97] HALLORAN J. Materials science: Making better ceramic composites with ice[J]. Science,2006,311(5760):479-480. doi: 10.1126/science.1123220 [98] LUCHINI B, HUBÁLKOVÁ J, WETZIG T, et al. Carbon-bonded alumina foam filters produced by centrifugation: A route towards improved homogeneity[J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(12):13832-13840. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.228 [99] AHMED A, SMITH J, ZHANG H. Gradient porous materials by emulsion centrifugation[J]. Chemical Communications,2011,47:11754-11760. doi: 10.1039/c1cc15212b [100] TRUNEC M, MISAK J. Consolidation of nanoparticle suspensions by centrifugation in non-porous moulds[J]. Ceramics International,2014,40(6):7775-7782. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.120 [101] GOMBOTZ W R, HEALY M S, BROWN L R. Very low temperature casting of controlled release microspheres: US, US5019400[P]. 1991-05-28. [102] TANG Y F, WU C, ZHAO K. Fabrication of lamellar porous alumina with graded structures by combining centrifugal and directional freeze casting[J]. Ceramics International,2017,44(5):5794-5798. [103] DEVILLE S, SAIZ E, TOMSIA P A. Freeze casting of hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Biomaterials,2006,27(32):5480-5489. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.06.028 [104] KONOPKA K, OLSZÁWKA-MYALSKA A, SZAFRAN M. Ceramic-metal composites with an interpenetrating network[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2003,81(2-3):329-332. doi: 10.1016/S0254-0584(02)00595-3 [105] ZHENG J, HU Y Y. New insights into compositional dependence of Li-ion transport in polymer-ceramic compo-site electrolytes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(4):4113-4120. [106] AL-KETAN O, ASSAD A, AL-RUB R K A. Mechanical properties of periodic interpenetrating phase composites with novel architected microstructures[J]. Composite Structures,2017,176:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.05.026 [107] ROY S, STOLL O, KAY ANDRÉ W, et al. Analysis of the elastic properties of an interpenetrating AlSi12-Al2O3 composite using ultrasound phase spectroscopy[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2011,71(7):962-968. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.02.014 [108] JANINA D A. Tribological properties of AlSi12-Al2O3 interpenetrating composite layers in comparison with unreinforced matrix alloy[J]. Materials,2017,10(9):1045. doi: 10.3390/ma10091045 [109] SIDDHARTHA R, JENS G, VLADIMIR K, et al. Load partitioning study in a 3D interpenetrating AlSi12/Al2O3 metal/ceramic composite[J]. Materials Science Forum,2013,772(2):103-107. [110] KRISHNA S A M, SHRIDHA T N, KRISHNAMURTHY L. Experimental investigations on thermal analysis and thermal characterization of Al 6061-Sic-Gr hybrid metal matrix composites[J]. International Journal of Material Science Innovations,2015,5(2):54-66. doi: 10.12783/ijmsci.2015.0502.04 [111] WANG D, ZHENG Z, LV J, et al. Enhanced thermal conductive 3D-SiC/Al-Si-Mg interpenetrating composites fabricated by pressureless infiltration[J]. Ceramics International,2016,43(2):1755-1761. [112] YAN H, YE H Y, CHEN W. Dry friction and wear performance of cocontinuous Al-23Si/SiC composites[J]. Materials Research Innovations,2015,19(9):131-135. [113] NAPOLE G E D, GOLDENSTEIN H, CARMO G M D, et al. Aluminium matrix composites reinforced with co-continuous in-terlaced phases aluminium-alumina needles[J]. Materials Research, 2002, 5(3): 337-342. [114] YU L, JIANG YL, LU SK, et al. Numerical simulations of compression properties of SiC/Fe-20Cr Co-continuous composites[C]//1st International Conference on 3D Materials Science. New Jersey: Wiley, 2016: 85-90. [115] SOY U, DEMIR A, CALISKAN F. Effect of bentonite addition on fabrication of reticulated porous SiC ceramics for liquid metal infiltration[J]. Ceramics International, 2011, 37(1): 15-19. [116] KIM J S, KWON Y S, LOMOVSKY O I, et al. A synthetic route for metal-ceramic interpenetrating phase compo-sites[J]. Materials Letters,2006,60(29-30):3723-3726. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.096 [117] SAEID K, HAMID B, ROSHANAK L. The effect of calcination temperature on synthesis of B4C-nano Tib2 compo-site by co-precipitation method[J]. Oriental Journal of Chemistry,2016,32(4):2243-2249. doi: 10.13005/ojc/320457 [118] TOMICZEK B, KUJAWA M, MATULA G, et al. Aluminium AlSi12 alloy matrix composites reinforced by mullite porous preforms[J]. Materialwissenschaft Und Werkstofftechnik,2015,46(4-5):368-376. doi: 10.1002/mawe.201500411 [119] TIHAY F, POURROY G, RICHARD-PLOUET M, et al. Effect of fischer-tropsch synthesis on the microstructure of Fe-Co-based metal/spinel composite materials[J]. Applied Catalysis A General,2001,206(1):29-42. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00595-0 [120] YANG J Y, CHUNG D D L. Casting particulate and fibrous metal-matrix composites by vacuum infiltration of a liquid metal under an inert gas pressure[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1989,24:3605-3612. doi: 10.1007/BF02385746 [121] BINNER J, CHANG H, HIGGINSON R. Processing of ceramic-metal interpenetrating composites[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2009,29(5):837-842. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.07.034 [122] LEE K B, KIM Y S, KWON H. Fabrication of Al-3 Wtpct Mg matrix composites reinforced with Al2O3 and SiC particulates by the pressureless infiltration technique[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science,1998,29(12):3087-3095. doi: 10.1007/s11661-998-0216-9 [123] ISAACS J A, TARICCO F, MICHAUD V J, et al. Chemical stability of zirconia-stabilized alumina fibers during pressure infiltration by aluminum[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A,1991,22(12):2855-2862. doi: 10.1007/BF02650246 [124] ZHU J, WANG F, WANG Y, et al. Interfacial structure and stability of a co-continuous SiC/Al composite prepared by vacuum-pressure infiltration[J]. Ceramics International,2017,43(8):6563-6570. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.085 [125] JHAVER R, TIPPUR H. Processing, compression response and finite element modeling of syntactic foam based interpenetrating phase composite (IPC)[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A,2009,499(1-2):507-517. [126] YU L, JIANG Y L, RU H Q, et al. Microstructures of co-continuous SiC/Fe2Cr13 composite fabricated by vacuum-pressure casting and infiltration processes[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2011,239-242:1661-1664. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.239-242.1661 [127] XING H W, CAO X M, Hu W P, et al. Interfacial reactions in 3D-SiC network reinforced Cu-matrix composites prepared by squeeze casting[J]. Materials Letters,2005,59(12):1563-1566. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2005.01.023 [128] REN W S, RAN G H, ZI W Y, et al. The fabrication method and research progress of the reticulated ceramic reinforcement in metal matrix composites[J]. Materials For Mechanical Engineering,2005,29(12):1-59. [129] QIN S S. Metal-matrix composites for marine applications: Development status and our countermeasures[J]. Materials Review,2003,17(10):68-70. [130] YAN H, YE H Y, CHEN W. Dry friction and wear performance of co-continuous Al-23Si/SiC composites[J]. Material Research Innovations,2015,19(9):131-135. [131] DIMIDUK D M, DUTTON R. Technical report OMB No. 0704-0188[R]. Washington: Materials and Manufacturing Directorate Air Force Research Laboratory, 2004. [132] PENG H X, FAN Z, EVANS J R G. Bi-continuous metal matrix composites[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A,2001,303(1-2):37-45. [133] SEITZ H, RIEDER W, IRSEN S, et al. Three-dimensional printing of porous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials,2010,74B(2):782-788. [134] LEE J Y, TAN W S, AN J, et al. The potential to enhance membrane module design with 3D printing technology[J]. Journal of Membrane ence,2016,499:480-490. [135] MOTAMAN S A H, KIES F, KHNEN P, et al. Optimal design for metal additive manufacturing: An integrated computational materials engineering (ICME) approach[J]. JOM,2020,72(3):1092-1104. doi: 10.1007/s11837-020-04028-4 [136] POST G, KEESTRA M, RUTTING L. An introduction to interdisciplinary research[M]. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press, 2016: 20. [137] SWITHENBANK J. Some unresolved problems in the fluid mechanics of combustion[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering,1975,97(3):287. doi: 10.1115/1.3447305 [138] SURUJHLAL D, SKEWS B W. Three-dimensional shock wave reflection transition in steady flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2019,858:565-587. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2018.747 [139] LUDMILA C. Performance modeling in mapreduce environments: Challenges and opportunities[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd ACM/SPEC International Conference on Performance Engineering. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2011: 5-6. [140] MOON S K, TAN Y E, HWAN J H, et al. Application of 3D printing technology for designing light-weight unmanned aerial vehicle wing structures[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering & Manufacturing Green Technology,2014,1(3):223-228. -






 下载:
下载: