Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of polyacrylamide in water by cobalt azaphthalocyanine
-
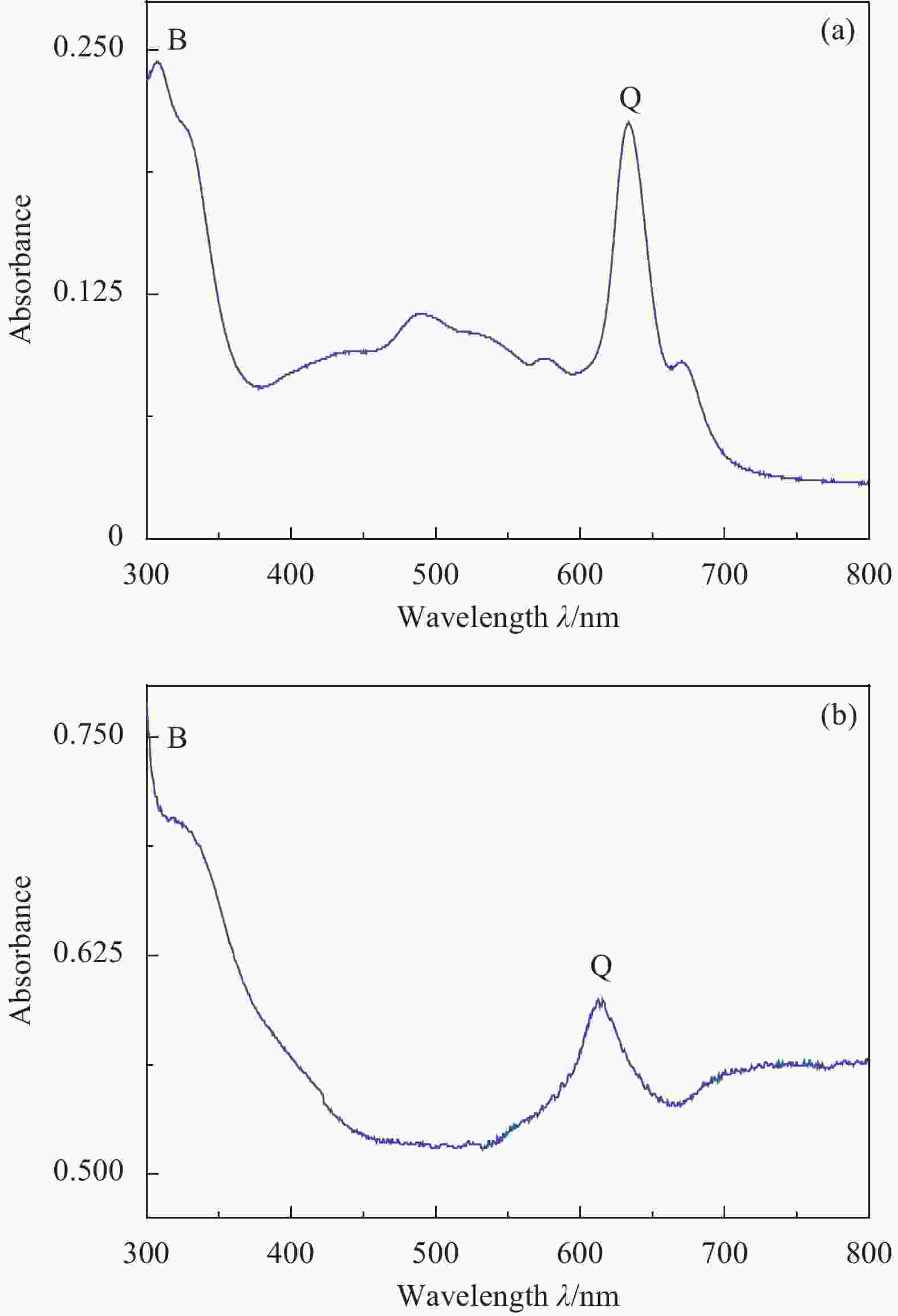
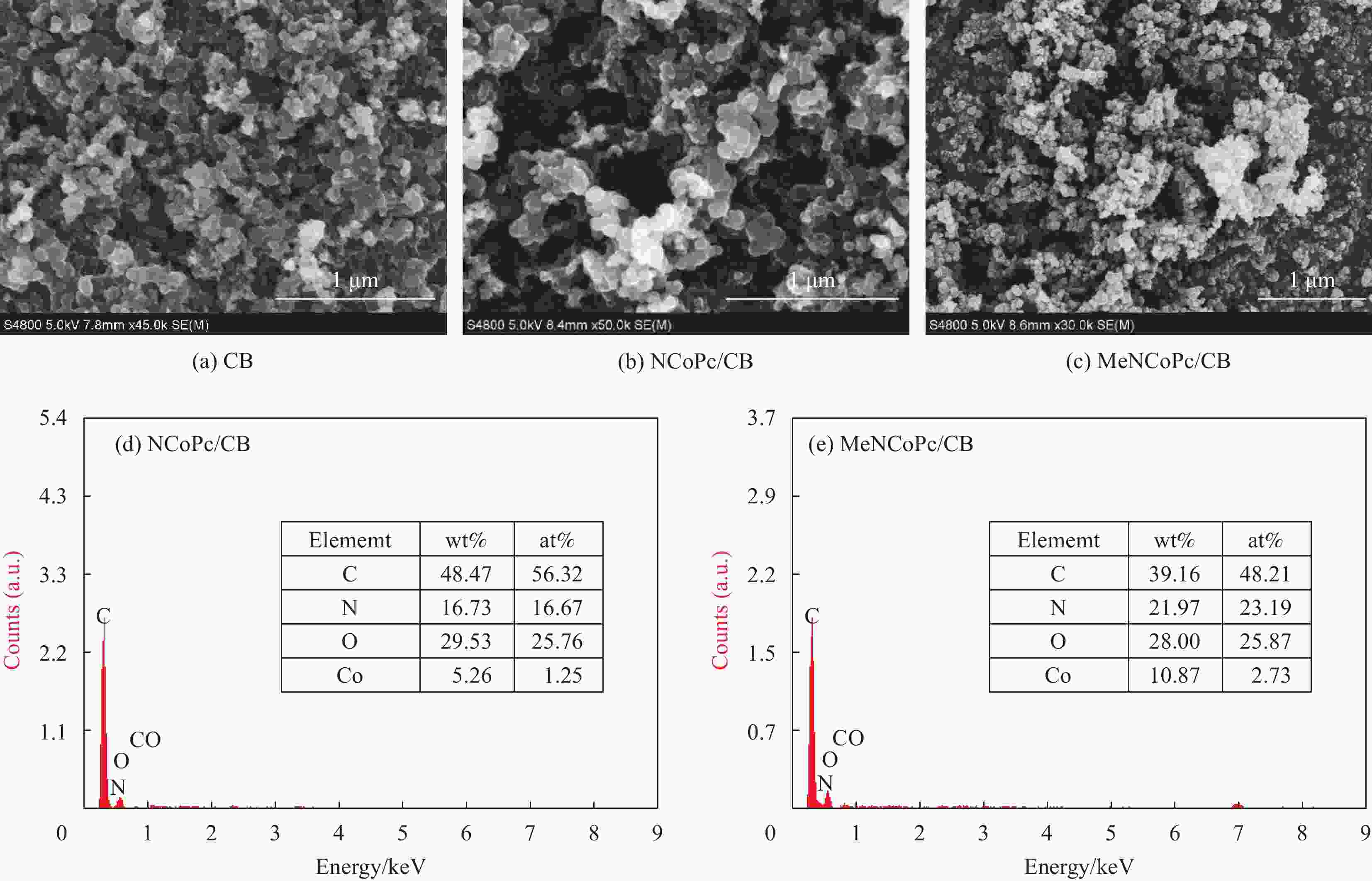
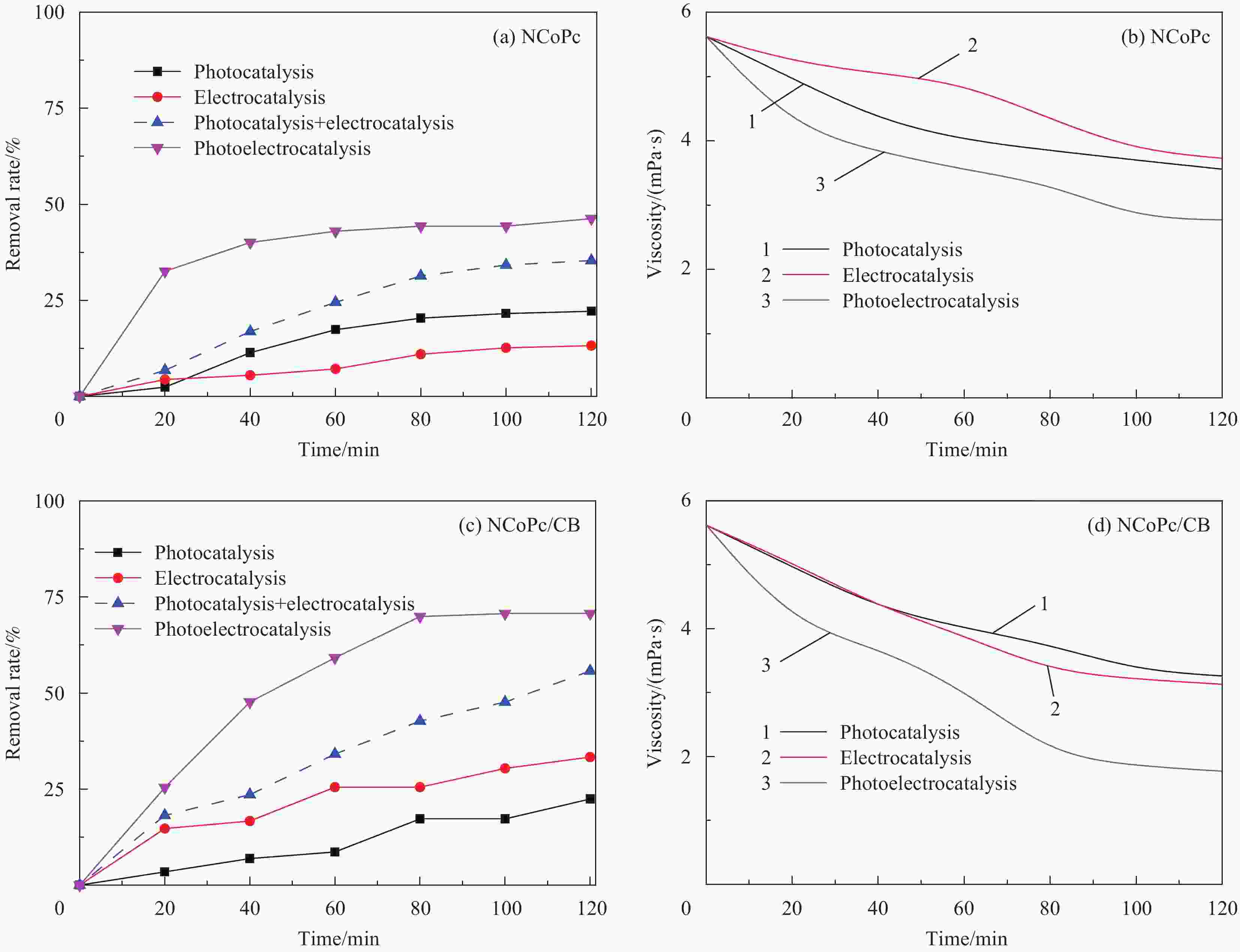
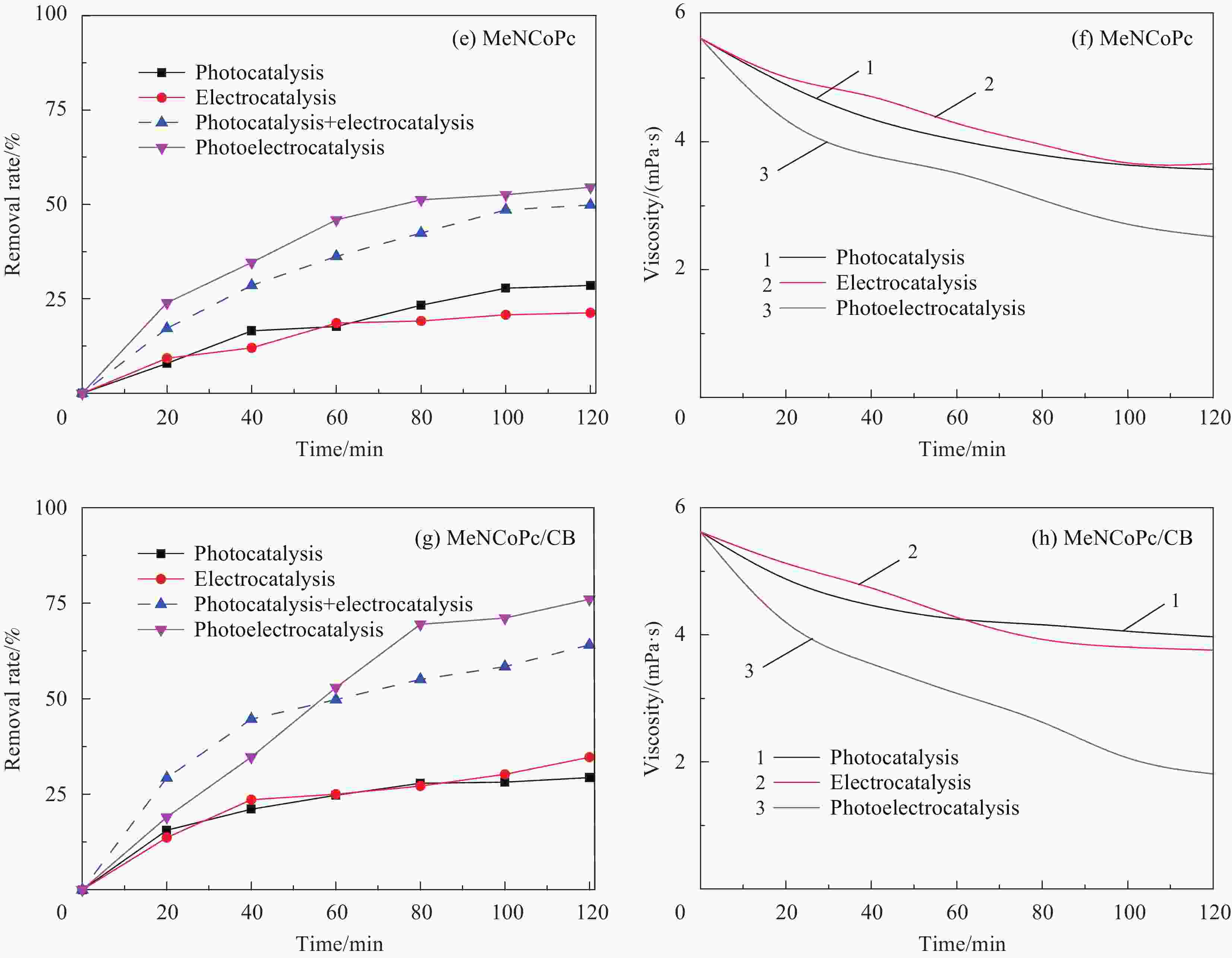
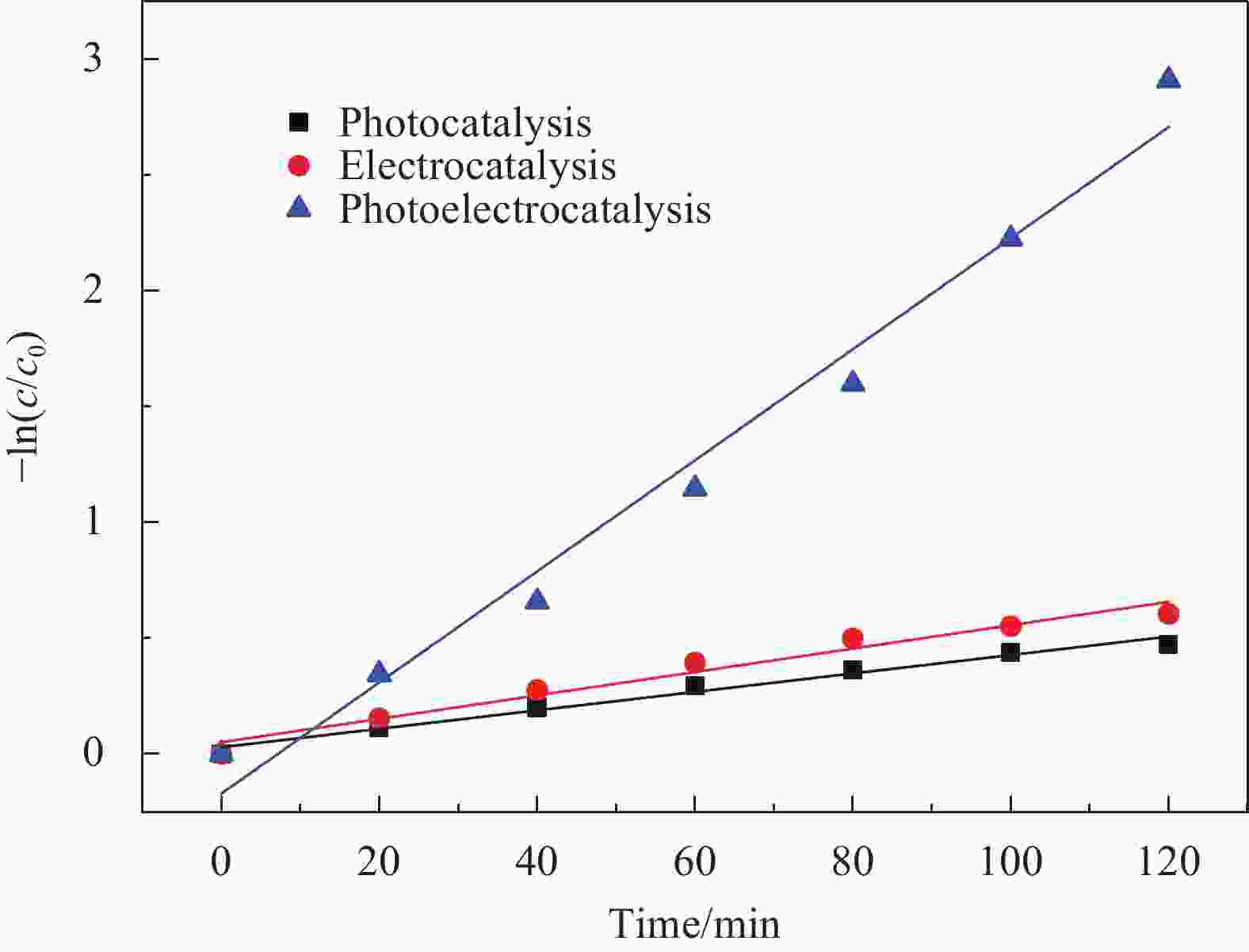
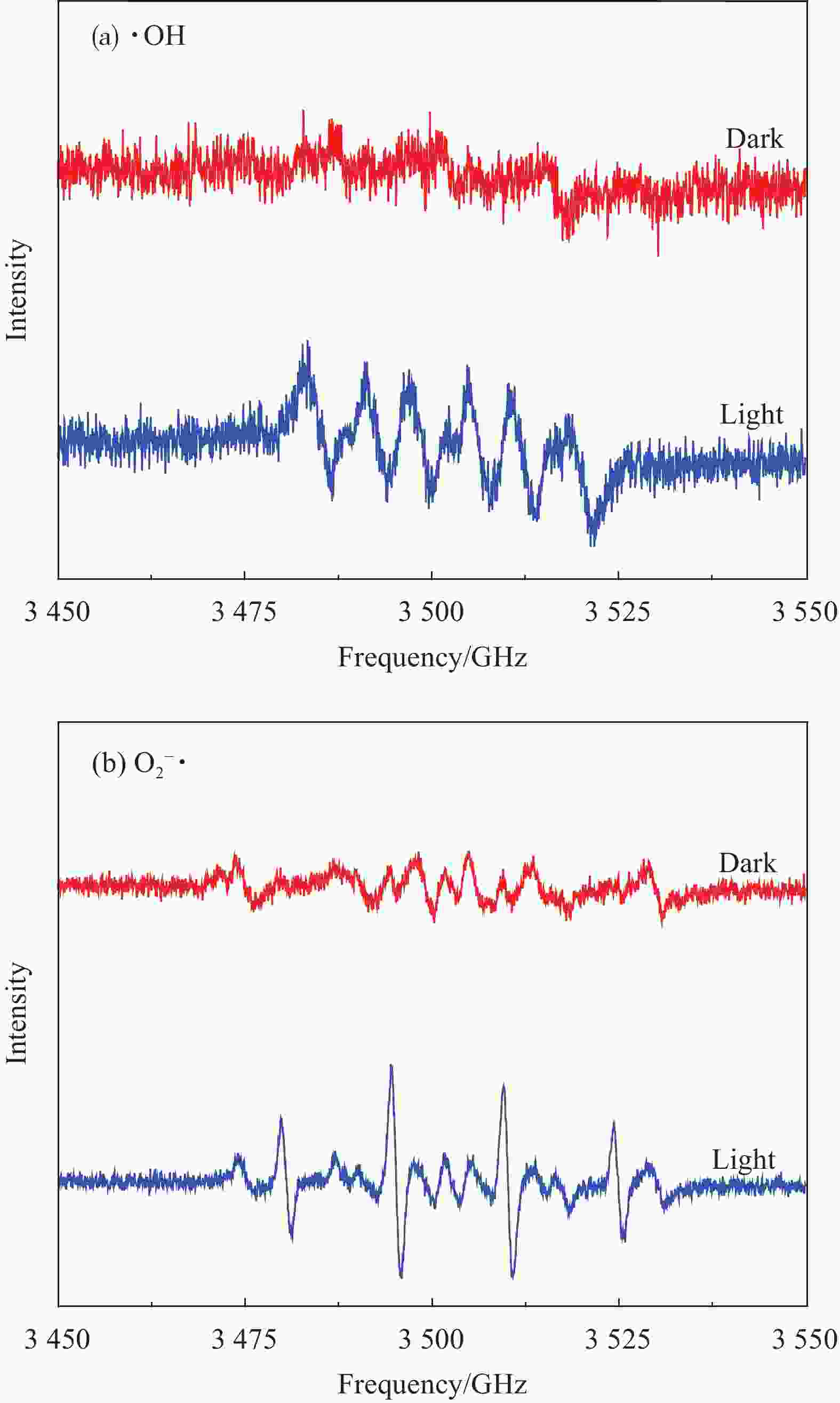
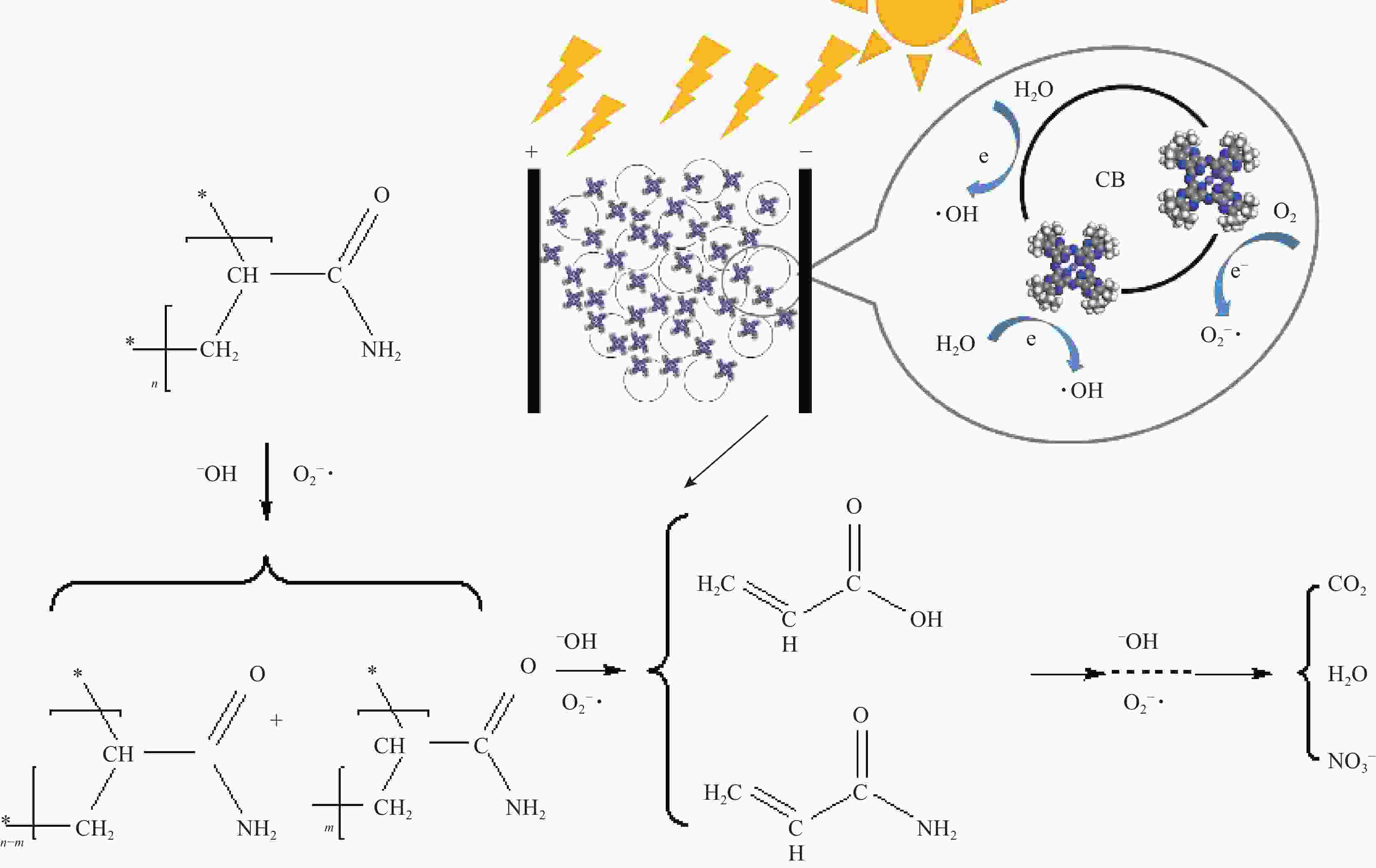
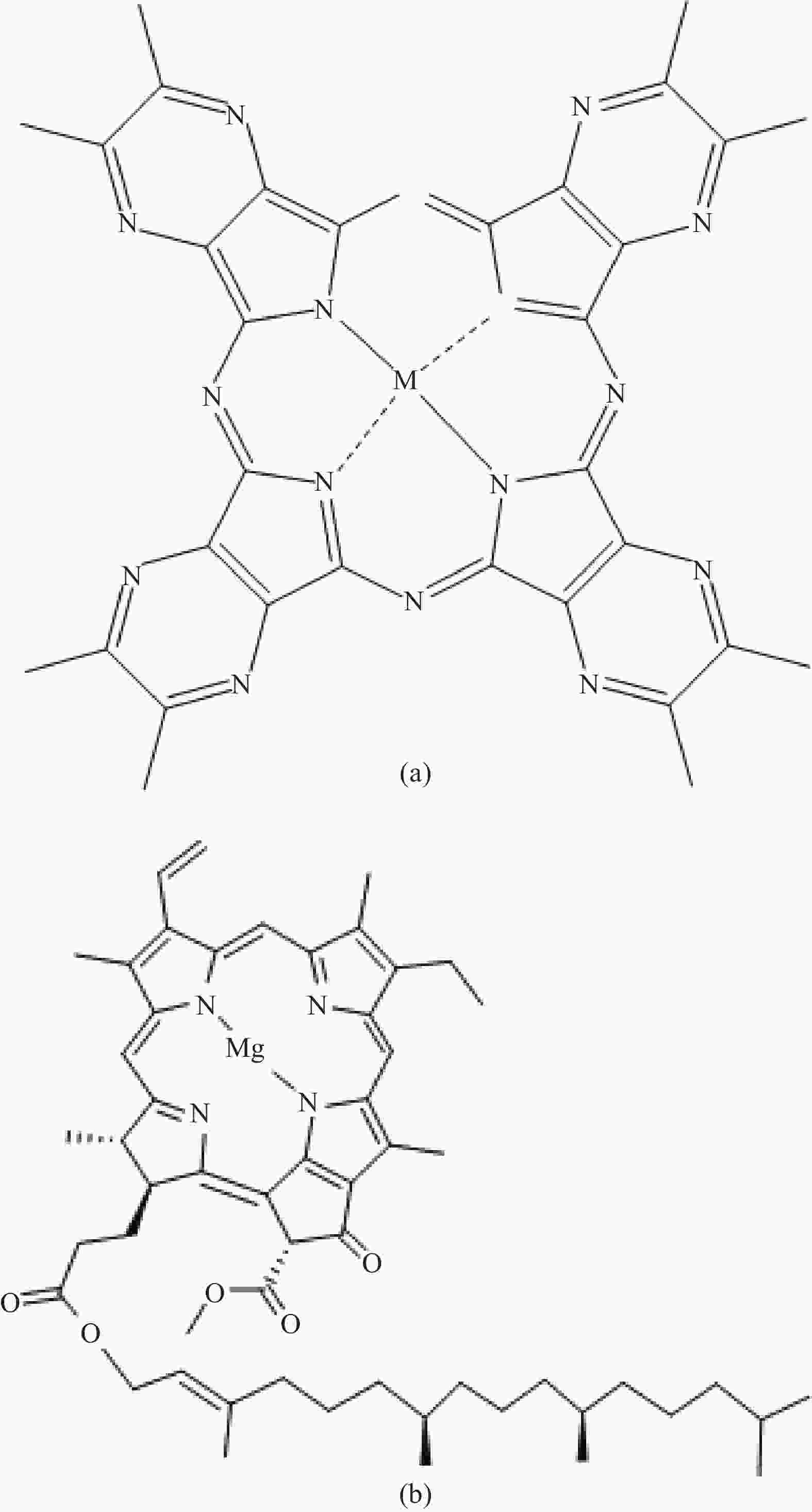
摘要: 针对水环境中聚丙烯酰胺(HPAM)难以被快速去除的问题,以导电炭黑(CB)为载体,制备了负载型氮杂酞菁钴(NCoPc/CB)和甲基取代氮杂酞菁钴(MeNCoPc/CB)复合材料,并对其光电催化降解HPAM的性能进行了研究。搭建分体式光电协同催化体系,选取50 mg/L HPAM水溶液为目标污染物,以Na2SO4为电解质,对NCoPc的理化性能及光电协同催化工艺降解高分子聚合物的性能进行了考察。结果证实,光电协同催化工艺对HPAM去除率不但优于单独光催化和单独电催化工艺,更优于两者的代数和,说明光电联合体系中产生了协同增强效应。其中,以MeNCoPc/CB复合材料效果最佳,污染物去除率达到76.07%,溶液黏度由8.33 mPa·s降至1.81 mPa·s。对协同工艺进行反应动力学分析,证实此过程符合准一级反应动力学,其反应速率常数分别是光催化的6.03倍和电催化的3.97倍。电子自旋共振技术(ESR)证实,反应体系内主要活性物质为·OH和O2−·。Abstract: Supported cobalt azaphthalocyanine (NCoPc/CB) and methyl-substituted cobalt azaphthalocyanine (MeNCoPc/CB) composites were prepared, in which carbon black (CB) was used as a carrier, to solve the problem that polyacrylamide (HPAM) was difficult to be removed in the water. The physical and chemical properties of catalyst and photoelectrocatalytic degradation performance of HPAM was studied in a split photoelectric cooperative catalytic system, with 50 mg/L HPAM aqueous solution as the target pollutant and Na2SO4 as the electrolyte. The results confirm that the removal rate of HPAM by the photoelectrocatalysis is not only superior to the photocatalysis and electrocatalysis, but also to the algebraic sum of the two, which shows that the photoelectric combined system has an obvious synergistic enhancement effect. Among them, MeNCoPc/CB composite has the best effect, the pollutant removal rate reaches 76.07%, and the solution viscosity decreases from 8.33 mPa·s to 1.81 mPa·s. The photoelectrocatalytic reaction confirms that the process conforms to the quasi-first-order reaction kinetics, while the reaction rate constants are 6.03 times that of photocatalysis and 3.97 times that of electrocatalysis. Electron spin resonance technology (ESR) confirms that the main active substances in the reaction system are ·OH and O2·−.
-
Key words:
- cobalt azaphthalocyanine /
- photoelectrocatalysis /
- degradation /
- polyacrylamide /
- reaction mechanism
-
表 1 三种催化工艺降解HPAM动力学反应速率常数
Table 1. Kinetics reaction rate of three catalytic processes for degradation of HPAM
No. Voltage/V Na2SO4/(mol·L−1) Reaction rate/min−1 Correlation coefficient R2 Process 1 — 0.1 3.98×10−3 0.9789 Photocatalysis 2 40 0.1 5.05×10−3 0.9614 Electrocatalysis 3 40 0.1 2.40×10−2 0.9771 Photoelectrocatalysis 表 2 不同反应阶段HPAM降解水样成分分析
Table 2. Analysis of components of HPAM solution sample degradated in different reaction period
No. Water sample after
40 min of reactionWater sample after
80 min of reactionWater sample after
120 min of reactionComposition Content/% Composition Content/% Composition Content/% 1 Water 99.625 Water 99.611 Water 99.562 2 HPAM 0.035 HPAM 0.008 HPAM 0.002 3 AM 0.020 AM 0.009 AM 0.003 4 Acrylic acid 0.040 Acrylic acid 0.055 Acrylic acid 0.002 5 NO3− 0.040 NO3− 0.063 NO3− 0.128 6 Na2SO4 0.230 Na2SO4 0.250 2-(2-Hydroxypropoxy)-1-propanol 0.002 7 DMF 0.010 DMF 0.004 2,4,7,9-Tetramethyl-5-decyne-4,7-diol 0.009 8 — — — — Myristicin 0.002 9 — — — — Na2SO4 0.290 Notes: AM—Acrylamide; DMF—Dimethylformamide. -
[1] BAO M, CHEN Q, LI Y, et al. Biodegradation of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide by bacteria isolated from production water after polymer flooding in an oil field[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,184(1-3):105-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.011 [2] MA F, WEI L, WANG L, et al. Isolation and identification of the sulphate-reducing bacteria strain H1 and its function for hydrolysed polyacrylamide degradation[J]. International Journal of Biotechnology,2008,10(1):55-63. doi: 10.1504/IJBT.2008.017979 [3] RONG X, QIU F, ZHANG C, et al. Preparation of Ag-AgBr/TiO2-graphene and its visible light photocatalytic activity enhancement for the degradation of polyacrylamide[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds,2015,639:153-161. [4] ZHANG H, ZHONG Z, XING W. Application of ceramic membranes in the treatment of oilfield-produced water: Effects of polyacrylamide and inorganic salts[J]. Desalination,2013,309:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2012.09.012 [5] LIU T, HONG Y, CHEN Q. Heterogeneous photo-fenton degradation of polyacrylamid in aqueous solution over Fe(Ⅲ)-SiO2 catalyst[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,162(2-3):860-865. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.110 [6] WEN Q, CHEN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Biodegradation of polyacrylamide by bacteria isolated from activated sludge and oil-contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,175(1-3):955-959. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.102 [7] WEN Q, CHEN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Performance and microbial characteristics of bioaugmentation systems for polyacrylamide degradation[J]. Journal of Polymers & the Environment,2011,19(1):125-132. [8] DONZELLO M P, ERCOLANI C, NOVAKOVA V, et al. Tetrapyrazino-porphyrazines and their metal derivatives Part I: Synthesis and basic structural information[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews,2016,309:107-179. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2015.09.006 [9] MALEKI A, REZAYAN A H. One-pot synthesis of metallopyrazinoporphyrazines using 2,3-diaminomaleonitrile and 1,2-dicarbonyl compounds accelerated by microwave irradiation[J]. Organic Chemistry International,2014,2014:958951. [10] LINSTEAD R P, NOBLE E G, WRIGHT J M. 187. Phthalocyanines Part Ⅸ: Derivatives of thiophen, thionaphthen, pyridine, and pyrazine, and a note on the nomenclature[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society,1937:911-921. doi: 10.1039/jr9370000911 [11] MARIN M L, SANTOS-JUANES L, ARQUES A, et al. Organic photocatalysts for the oxidation of pollutants and model compounds[J]. Chemical Reviews,2012,112(3):1710-1750. doi: 10.1021/cr2000543 [12] LIU J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG F, et al. Dimerization of metal-free sulfonated phthalocyanines in aqueous methanol solution[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,1996,12(2):163-167. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB19960215 [13] 郭黎平, 姜秀娥, 杜锡光, 等. 双核磺化酞菁 钴在混合溶液中聚集现象的光谱和电化学研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2003, 23(5):1031-1034.GUO Liping, JIANG Xiue, DU Xiguang, et al. Spectroscopy and electrochemistry studies on the aggregation of binuclear cobalt phthalocyaninehexasulfonate in mixed solutions[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2003,23(5):1031-1034(in Chinese). [14] 吴星, 袁诗海. 四磺化酞菁钴在水溶液中二 聚作用力的研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 1999, 19(1):113-115.WU Xing, YUAN Shihai. Study on the action force of dimerization of cobalt tetrasulfonate phthalocyanine in aqueous solution[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,1999,19(1):113-115(in Chinese). [15] ILIEV V, ALEXIEV V, BILYARSKA L. Effect of metal phthalocyanine complex aggregation on the catalytic and photocatalytic oxidation of sulfur containing compounds[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical,1999,137(1-3):15-22. doi: 10.1016/S1381-1169(98)00069-7 [16] 沈永嘉. 酞菁的合成与应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2000.SHEN Yongjia. The synthesis and application of phthalocyanine[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000(in Chinese). [17] 许越. 催化剂设计与制备工艺[M]. 北京: 化 学工业出版社, 2003.XU Yue. Catalyst design and preparation process[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003(in Chinese). [18] 赵修太, 王增宝, 邱广敏, 等. 部分水解聚丙烯酰胺水溶液初始黏度的影响因素[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2009, 38(3):231-234.ZHAO Xiutai, WANG Zengbao, QIU Guangmin, et al. Study on influence factors of the initial viscosity of HPAM solution[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil and Gas,2009,38(3):231-234(in Chinese). [19] 张峰. 光催化氧化联合工艺处理不同污染物 的研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.ZHANG Feng. Study on pollutants degradation by combined process of photocatalytic oxidation technique[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011(in Chinese). [20] 张峰, 李文奇, 冯传平, 等. 光催化电化学联 合降解水中苯酚的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(10):2161-2166.ZHANG Feng, LI Wenqi, FENG Chuanping, et al. Study on synergetic degradation of phenol by independent electrochemical and photocatalytic processes[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2011,5(10):2161-2166(in Chinese). [21] 胡春, 王怡中, 汤鸿霄. TiO2光催化氧化苯酚 动力学研究[J]. 环境科学, 1997, 18(4):2-5.HU Chun, WANG Yizhong, TANG Hongxiao. Kinetic study on photocatalytic oxidation of phenol by TiO2[J]. Environmental Science,1997,18(4):2-5(in Chinese). [22] 刘咏, 赵仕林, 李启彬, 等. 苯酚在氯离子体 系中的电化学氧化研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2006, 29(11):21-22.LIU Yong, ZHAO Shilin, LI Qibin, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of phenol in chloride-ion system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2006,29(11):21-22(in Chinese). [23] 陈颖, 崔军明, 王宝辉, 等. 光催化氧化降解水中聚丙烯酰胺的可行性研究[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 2001, 25(2):82-83.CHEN Ying, CUI Junming, WANG Baohui, et al. Feasibility of photocatalytic oxidation of degrading polyacrylamide in water[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute,2001,25(2):82-83(in Chinese). [24] 陈颖, 王宝辉, 张海燕, 等. 纳米级TiO2光催化氧化聚丙烯酰胺[J]. 催化学报, 1999, 20(3):309-312.CHEN Ying, WANG Baohui, ZHANG Haiyan, et al. Photocatalytic oxidation of polyacrylamide in water over nanometer TiO2 particles[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,1999,20(3):309-312(in Chinese). [25] COMNINELLIS C, PULGARIN C. Anodic oxidation of phenol for waste water treatment[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry,1991,21(8):703-708. doi: 10.1007/BF01034049 [26] COMNINELLIS C. Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment[J]. Electrochimica Acta,1994,39(11-12):1857-1862. doi: 10.1016/0013-4686(94)85175-1 [27] 曲久辉, 刘会娟. 水处理电化学原理与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007.QU Jiuhui, LIU Huijuan. Principles and techniques of electrochemistry in water treatment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007(in Chinese). [28] RAJKUMAR D, PALANIVELU K. Electrochemical treatment of industrial wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2004,113(1-3):123-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.05.039 [29] SANJUÁN A, ALVARO M, AGUIRRE G, et al. Intrazeolite photochemistry 21: 2,4,6-Triphenylpyrylium encapsulated inside zeolite y supercages as heterogeneous photocatalyst for the generation of hydroxyl radical[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,1998,120(29):7351-7352. doi: 10.1021/ja980121n [30] SANJUÁN A, AGUIRRE G, ALVARO M, et al. 2,4,6-Triphenylpyrylium ion encapsulated within Y zeolite as photocatalyst for the degradation of methyl parathion.[J]. Water Research,2000,34(1):320-326. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00103-7 [31] SANJUÁN A, AGUIRRE G, ALVARO M, et al. 2,4,6-Triphenylpyrylium ion encapsulated in Y zeolite as photocatalyst: A co-operative contribution of the zeolite host to the photodegradation of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid using solar light[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,1998,15(3-4):247-257. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(97)00052-0 [32] HOFFMANN N. Photochemical reactions as key steps in organic synthesis[J]. Chemical reviews,2008,108(3):1052-1103. doi: 10.1021/cr0680336 [33] JACKSON C V, MICKELSON J K, STRINGER K, et al. Electrolysis-induced myocardial dysfunction: A novel method for the study of free radical mediated tissue injury[J]. Journal of Pharmacological Methods,1986,15(4):305-320. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(86)90010-0 [34] LI D, GE S, HUANG J, et al. Photocatalytic chromogenic identification of chlorophenol pollutants by manganese phthalocyanine under sunlight irradiation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2014,125(14):216- 222. [35] 周抗寒, 周定. 复极性固定床电解槽内电极 电位的分布[J]. 环境化学, 1994, 13(4):318-322.ZHOU Kanghan, ZHOU Ding. Potential distribution in a bipolar packed bed electrolyser[J]. Environmental Chemistry,1994,13(4):318-322(in Chinese). [36] 张青红. 纳米氧化钛光催化材料及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002.ZHANG Qinghong. Nanometer titanium oxide and its application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: