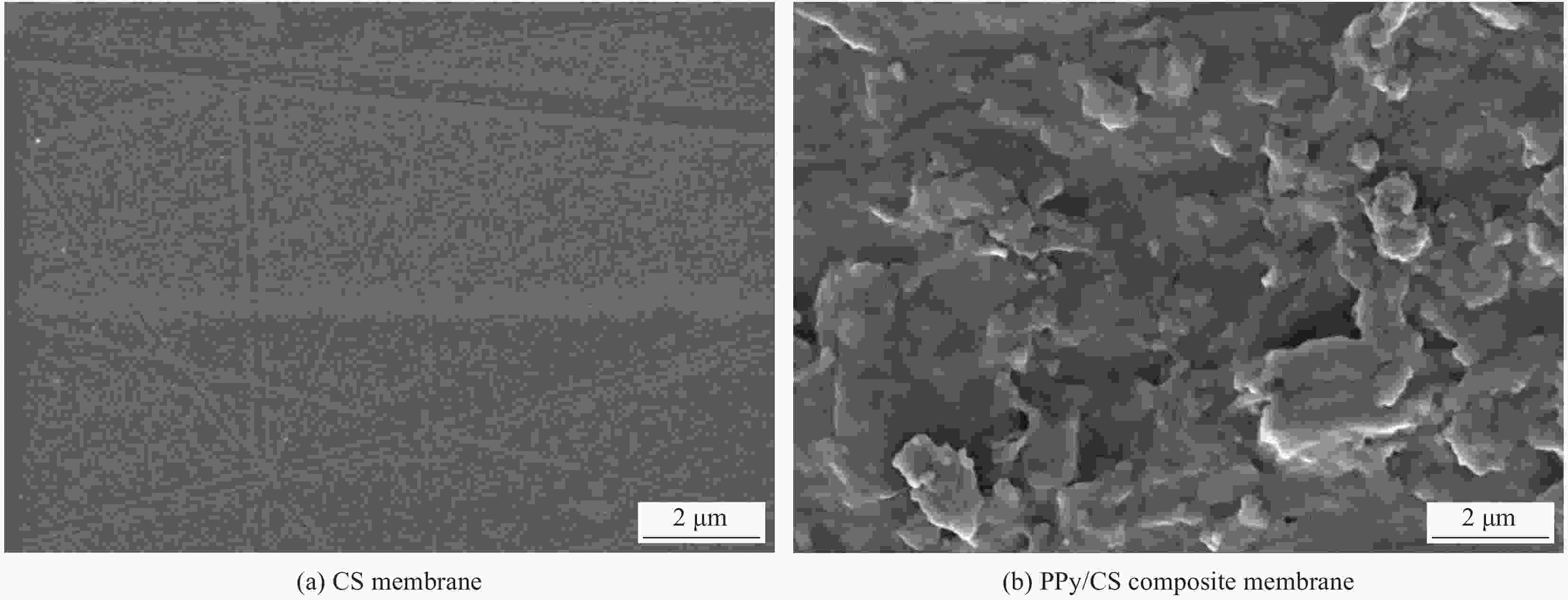
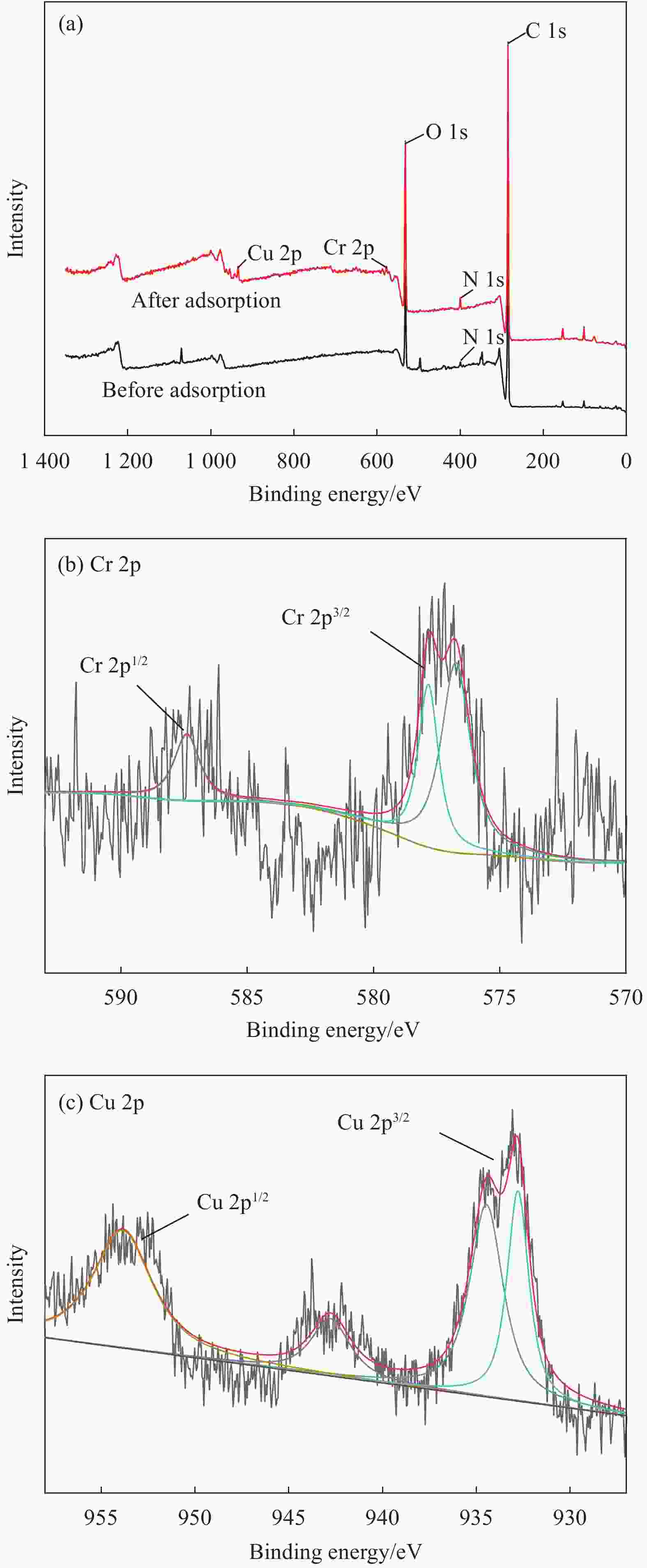
Preparation of polypyrrole/chitosan composite membrane and its adsorption mechanism for Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ)
-
摘要: 以聚吡咯(PPy)和壳聚糖(CS)为原料,制备PPy/CS复合膜,通过红外、孔径分析、热分析和SEM等手段对其结构进行表征,并研究了PPy/CS复合膜对Cu(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)吸附性能的影响及吸附机制,考察了pH值、吸附时间、溶液起始浓度等因素对吸附率的影响。结果表明,初始浓度对吸附率影响最大;在pH=3.5、温度为333 K及速率为100 r·min−1下震荡吸附50 min,20 mg的PPy/CS复合膜吸附6 mg·L−1的Cu(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)混合液时,PPy/CS复合膜对Cu(Ⅱ)表现出很好的选择性,吸附量达2.715 mg·g−1;通过对PPy/CS复合膜和CS膜的吸附性能比较,PPy/CS复合膜对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附率增加至94.14%;采用0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液对吸附Cu(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的PPy/CS复合膜进行脱附再生,循环15次后,其吸附量变化很小,可以多次使用。研究表明,PPy/CS复合膜对Cu(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附符合准二级动力学模型和Langmuir吸附等温式。Abstract: A polypyrrole/chitosan (PPy/CS) composite membrane was prepared using PPy and CS as raw materials, and the structure of the PPy/CS composite membrane was characterized by infrared, pore diameter analysis, thermal analysis and SEM. The effects of PPy/CS composite membrane on the adsorption performance and adsorption mechanism for Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ) were discussed. The effects of pH value, adsorption time, and initial concentration of the solution on the adsorption efficiency were investigated. The results show that the adsorption efficiency of PPy/CS composite membrane for Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ) are greater affected by the initial concentration of the solution. When pH=3.5, temperature is 333 K, the adsorption is shaken at 100 r·min−1 for 50 min, 20 mg of PPy/CS composite membrane adsorbs 6 mg·L−1 of Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ), PPy/CS composite membrane for Cu(Ⅱ) shows good selectivity and adsorption amount reaches 2.715 mg·g−1; Compared with PPy/CS composite membrane and CS membrane, the adsorption rate of PPy/CS composite membrane for Cu(Ⅱ) increases to 94.14%; The PPy/CS composite membrane adsorbing Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ) is desorbed and regenerated with 0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH solution. After circulation for 15 times, its adsorption amount changes very small, it can be used multiple times. The adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ) by PPy/CS composite membrane conforms to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
-
Key words:
- polypyrroles /
- chitosan /
- composite membrane /
- adsorption /
- Cu(Ⅱ) /
- Cr(Ⅵ)
-
表 1 CS膜和PPy/CS复合膜的比表面积和孔径
Table 1. Specific surface area and pore size of CS membrane and PPy/CS composite membrane
Sample SBET/(m2·g−1) DBJH/nm CS 27.32 3.507 PPy/CS 14.08 3.138 Notes: SBET—Specific surface area measured by BET; DBJH—Average pore measured by BJH. 表 2 PPy/CS复合膜吸附Cr(Ⅵ)和Cu(Ⅱ)正交实验数据
Table 2. Orthogonal experimental data for adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cu(Ⅱ) on PPy/CS composite membrane
Experiment number
(Cr/Cu)A/(mg·L−1) B/mg C D/min qe/(mg·g−1) 1 2 20 2.5 40 0.375/0.860 2 2 25 3.0 50 0.484/0.756 3 2 30 3.5 60 0.347/0.630 4 4 20 3.0 60 1.100/1.870 5 4 25 3.5 40 0.980/1.524 6 4 30 2.5 50 0.820/1.280 7 6 20 3.5 50 1.380/2.715 8 6 25 2.5 60 1.160/2.236 9 6 30 3.0 40 0.830/1.857 R 0.721/1.520 0.286/0.559 0.117/0.164 0.167/0.170 Notes: A—Initial mass concentration; B—Dosage of PPy/CS composite membrane; C—pH value; D—Adsorption time; qe—Adsorption quantity. 表 3 PPy/CS复合膜吸附Cr(Ⅵ)、Cu(Ⅱ)的准一级和准二级动力学模型参数
Table 3. Pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic model parameters for adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cu(Ⅱ) on PPy/CS composite membrane
Heavy metal ion qe,exp/(mg·g−1) Pseudo-first-order Pseudo-second-order k1/min−1 qe,cal/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/(g(mg·min)−1) qe,cal/(mg·g−1) R2 Cu(Ⅱ) 1.5060 0.046800 1.9890 0.96560 0.01776 1.9710 0.9982 Cr(Ⅵ) 0.8897 0.009850 0.1131 0.07187 1.61400 0.8249 0.9923 Notes: qe,cal, qe,exp—Adsorption amount at time t and adsorption equilibrium, respectively; k1—Pseudo-first-order adsorption rate constant; k2—Pseudo-second-order adsorption rate constant. 表 4 PPy/CS复合膜吸附Cr(Ⅵ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附等温线参数
Table 4. Adsorption isotherm parameters of PPy/CS composite membrane for Cr(Ⅵ) and Cu(Ⅱ) adsorption
Heavy metal ion Langmuir equation Freundlich equation Q/(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) RL R2 Kf/(mg·g−1) 1/n R2 Cr(Ⅵ) 3.190 0.3731 0.4012 0.9919 0.8349 0.6164 0.9804 Cu(Ⅱ) 1.789 0.2504 0.4996 0.9971 0.3725 0.5966 0.9879 Notes: KL is a constant related to adsorption energy; Q is the saturated adsorption capacity of monolayer adsorption; Kf is a constant related to the adsorption capacity; 1/n is a measure of the adsorption strength. 表 5 PPy/CS复合膜与文献报道的各种吸附剂对Cu(II)和Cr(VI)吸附能力比较
Table 5. Comparison on Cu(II) and Cr(VI) adsorption capacity of PPy/CS composite membrane and various adsorbents reported in literature
Sample m/g c0/ (mg·L−1) qe/(mg·g−1) v/mL Reference PPy/CS Cu(Ⅱ)/Cr(Ⅵ) 0.02 6 2.715/1.308 10 This work Sulfonate PAN ENM Cr(Ⅵ) 0.005 50 220.4 100 [40] RA-5CS/PMAA Cr(Ⅵ) 0.02 6.5 4.980 30 [41] Bagasse before dialdehyde cellulose Cu(Ⅱ)/Cr(Ⅵ) 0.5 50 2.185/0.457 25 [42] Modified pectin-Fe3O4 Cu(Ⅱ) 0.02 500 105.0 10 [43] Bt/Bc/α-Fe2O3 Cr(Ⅵ) 0.04 50 81.70 150 [44] HEBC Cu(Ⅱ) 0.05 40 11.98 50 [45] ZM-CSt-PVA Cu(Ⅱ) 0.1 2 000 199.0 100 [46] GP-CTAB Cr(Ⅵ) 0.02 50 95.30 50 [47] SBA-15-SH Cr(Ⅵ) 0.02 0.8 6.850 100 [48] NMA-LDHs Cr(Ⅵ) 0.05 100 103.4 100 [49] Cedrus atlantica Manetti Cu(Ⅱ) 2.2 200 14.23 400 [50] -
[1] THAO V D, GIANG B L, THU T V. Free-standing polypyrrole/polyaniline composite film fabricated by interfacial polymerization at the vapor/liquid interface for enhanced hexavalent chromium adsorption[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(10):5445-5452. doi: 10.1039/C8RA10478F [2] LINGAMDINNE L P, KODURU J R, KARRI R R. A comprehensive review of applications of magnetic graphene oxide based nanocomposites for sustainable water purification[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2019,231:622-634. [3] 杨宗锜, 刘洋, 张涛, 等. 重金属废水处理技术进展[J]. 绿色环保建材, 2019(11):42, 45.YANG Zongqi, LIU Yang, ZHANG Tao, et al. Progress in heavy metal wastewater treatment technology[J]. Green Environmental Protection Building Materials,2019(11):42, 45(in Chinese). [4] ZHU Y, FAN W, ZHOU T, et al. Removal of chelated heavy metals from aqueous solution: A review of current methods and mechanisms[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,678:253-266. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.416 [5] YAN X, CHAI L, LI Q, et al. Abiological granular sludge formation benefit for heavy metal wastewater treatment using sulfide precipitation[J]. Clean: Soil, Air, Water,2017,45(4):1500730. [6] MOHAMMED K, SAHU O. Recovery of chromium from tannery industry waste water by membrane separation technology: Health and engineering aspects[J]. Scientific African,2019,4:e00096. [7] AZIMI A, AZARI A, REZAKAZEMI M, et al. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: A review[J]. Chembioeng Reviews,2017,4(1):37-59. doi: 10.1002/cben.201600010 [8] BARAN W, ADAMEK E, JAJKO M, et al. Removal of veterinary antibiotics from wastewater by electrocoagulation[J]. Chemosphere,2018,194(9):381-389. [9] TRAN T K, LEU H J, VU T Q, et al. Hydrogen production from the tannery wastewater treatment by using agriculture supports membrane/adsorbents electrochemical system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2020,45(6):3699-3711. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.040 [10] SENGUPTA A K. Ion exchange and ion exchangers: An introduction[M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc., 2017. [11] 邢敏, 雷西萍, 韩丁, 等. Fe3O4/高岭土磁性复合材料对Cu2+的吸附性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(9):2204-2211.XING Min, LEI Xiping, HAN Ding, et al. Adsorption properties of Fe3O4/kaolin magnetic composites for Cu2+[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(9):2204-2211(in Chinese). [12] 王磊, 白成玲, 朱振亚. 氧化石墨烯/海藻酸钠复合膜对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附性能和机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(3):681-689.WANG Lei, BAI Chengling, ZHU Zhenya. Adsorption properties and mechanism of Pb(Ⅱ) ions adsorbed by graphene oxide/sodium alginate composite membrane[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(3):681-689(in Chinese). [13] 陈潇, 张浩宇, 霍神焕, 等. 壳聚糖改性地聚合物的力学及吸附性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(12):2959-2967.CHEN Xiao, ZHANG Haoyu, HUO Shenhuan, et al. Mechanical and adsorption properties of geopolymer modified by chitosan[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(12):2959-2967(in Chinese). [14] REGIEL-FUTYRA A, KUS-LIŚKIEWICZ M, SEBASTIAN V, et al. Development of noncytotoxic chitosan-gold nanocomposites as efficient antibacterial materials[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(2):1087-1099. [15] 刘耀智. 金属有机框架/聚吡咯复合电极在超级电容器中的应用研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2019.LIU Yaozhi. Metal-organic frameworks/polypyrrole composite electrode for supercapacitor[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2019(in Chinese). [16] WANG Y, HUANG L, WANG Z, et al. Application of polypyrrole flexible electrode for electrokinetic remediation of Cr(Ⅵ) contaminated soil in a main-auxiliary electrode system[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,373:131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.016 [17] 代洪秀. 功能化聚吡咯纳米复合材料在电化学传感中的应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018.DAI Hongxiu. Study on funcyionalized polypyrrole nanocomposites-based electrochemical sensors[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2018(in Chinese). [18] GARCIA-CABEZON C, GARCIA-HERNANDEZ C, RODRIGUEZ-MENDEZ M L, et al. A new strategy for corrosion protection of porous stainless steel using polypyrrole films[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2020,37:85-95. [19] CYSEWSKA K, GAZDA M, JASIŃSKI P. Influence of electropolymerization temperature on corrosion, morphological and electrical properties of PPy doped with salicylate on iron[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2017,328:248-255. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.08.055 [20] VATANPOUR V, SALEHI E, SAHEBJAMEE N, et al. Novel chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol thin membrane adsorbents modified with detonation nanodiamonds: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption performance[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,2020,13(1):1731-1740. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.01.010 [21] MO Z, GOU H, HE J, et al. Preparation and characterization of conductive and magnetic PPy/Fe3O4/Ag nanocomposites[J]. Polymer Composites,2014,35(3):450-455. doi: 10.1002/pc.22680 [22] REN H, GAO Z, WU D, et al. Efficient Pb(Ⅱ) removal using sodium alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose gel beads: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanism[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,137:402-409. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.002 [23] 彭惠娥. 壳低聚糖接枝共聚物的制备、表征及其应用[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2009.PENG Huie. Preparation, characterization and application of chitooligosaccharide grafted copolymer[D]. Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2009(in Chinese). [24] 黄春龙. 表面改性二氧化硅纳米颗粒对水泥早期水化影响的研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2018.HUANG Chunlong. Potential effect of surface modified nano-SiO2 on the cement paste hydration on early[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [25] 徐丹丹. EVOH 纳米纤维膜功能化及吸附铬离子和染料的研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2017.XU Dandan. EVOH nanofiber membranes functionalized for chromium ions and dyes adsorption[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2017(in Chinese). [26] WANG J, PAN K, HE Q, et al. Polyacrylonitrile/polypyrrole core/shell nanofiber mat for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013,244-245:121-129. [27] YI M, HAO W, AI Z. Negative impact of oxygen molecular activation on Cr(Ⅵ) removal with core-shell Fe@Fe2O3 nanowires[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,298:1-10. [28] GAUDIN P, FIOUX P, DORGE S, et al. Formation and role of Cu+ species on highly dispersed CuO/SBA-15 mesoporous materials for SOx removal: An XPS study[J]. Fuel Processing Technology,2016,153:129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.07.015 [29] 于长江. 生物炭复合材料的制备及其对重金属离子的吸附行为和机制研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2018.YU Changjiang. Preparation and characterization of biochar composites and its adsorption behavior and mechanism investigation of heavy metal ions[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [30] QIU H, ZHANG S, PAN B, et al. Effect of sulfate on Cu(Ⅱ) sorption to polymer-supported nano-iron oxides: Behavior and XPS study[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2012,366(1):37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.09.070 [31] MARTÍNEZ J M L, ENRIQUE RODRÍGUEZ-CASTELLÓN E, SÁNCHEZ R M T, et al. XPS studies on the Cu(I,Ⅱ)-polyampholyte heterogeneous catalyst: An insight into its structure and mechanism[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical,2011,339(1-2):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2011.02.010 [32] BABU N K C, ASMA K, RAGHUPATHI A, et al. Screening of leather auxiliaries for their role in toxic hexavalent chromium formation in leather: Posing potential health hazards to the users[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2005,13(12):1189-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.07.003 [33] JIA L, WANG J S, GUO Q W, et al. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by cross-linked magnetic hydroxamated chitosan[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 842: 175-179. [34] 潘道皑. 物质结构[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1988.PAN Daoai. Material structure[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1988(in Chinese). [35] MEI J, ZHANG H, LI Z, et al. A novel tetraethylenepentamine crosslinked chitosan oligosaccharide hydrogel for total adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,224(15):115-154. [36] QI X, WEI W, SU T, et al. Fabrication of a new polysaccharide-based adsorbent for water purification[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,195(18):368-377. [37] 刘星群, 谢水波, 曾凡勇, 等. 亚铁铝类水滑石吸附铀的性能与吸附机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(1):183-190.LIU Xingqun, XIE Shuibo, ZENG Fanyong, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of uranium(Ⅵ) adsorption by Fe(Ⅱ)-Al LDH[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(1):183-190(in Chinese). [38] 白成玲, 王磊, 朱振亚, 等. 氧化石墨烯/海藻酸钙水凝胶复合膜对水中Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6):1458-1465.BAI Chengling, WANG Lei, ZHU Zhenya, et al. Adsorption of Cd(II) in water by graphene oxide/calcium alginate hydrogel composite membrane[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(6):1458-1465(in Chinese). [39] MIRBAGHERI S A, HOSSEINI S N. Pilot plant investigation on petrochemical wastewater treatmentfor the removal of copper and chromium with the objective of reuse[J]. Desalination,2005,171(1):85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2004.03.022 [40] 王杰, 汪滨, 杜宗玺, 等. 磺胺化聚丙烯腈纳米纤维膜的制备及其对Cr(Ⅵ)和Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2020, 41(1):1-7.WANG Jie, WANG Bin, DU Zongxi, et al. Preparation of sulfonated polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membranes and adsorption capacity for Cr(Ⅵ) and Pb(Ⅱ)[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2020,41(1):1-7(in Chinese). [41] 钟少锋, 吉婉丽, 刘晓云. 壳聚糖超细纤维的制备及其铬离子吸附性能研究[J]. 化学试剂, 2020, 42(3):226-231.ZHONG Shaofeng, JI Wanli, LIU Xiaoyun. Preparation of chitosan/poly (methacylic acid) superfine fiber mat and application in chromium ion removal[J]. Chemical Reagents,2020,42(3):226-231(in Chinese). [42] 邓啟敏. 双醛蔗渣纤维素对Cu(Ⅱ)、Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(4):251-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2020.04.121DENG Qimin. Dialdehyde bagasse cellulose for Cu(Ⅱ), Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption performance[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2020,47(4):251-253(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2020.04.121 [43] 陈思, 马占玲, 李宁宁, 等. 丙烯酰胺改性果胶-Fe3O4磁性微球的制备及对水和海产品中Cu2+的吸附性能[J]. 中国食品学报, 2019, 19(3):189-194.CHEN Si, MA Zhanling, LI Ningning, et al. Preparation of acrylamide modified Fe3O4-pectin magnetic microspheres and its adsorption property for copper ions in water and marin products[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(3):189-194(in Chinese). [44] RUAN Z H, WU J H, HUANG J F, et al. Facile preparation of rosin-based biochar coated bentonite for supporting α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and its application for Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(8):4595-4603. doi: 10.1039/C4TA06491G [45] 黄菲, 闫梦, 常建宁, 等. 不同菌糠生物炭对水体中Cu2+、Cd2+的吸附性能[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4):1-13.HUANG Fei, YAN Meng, CHANG Jianning, et al. Adsorption performance of Cu2+ and Cd2+ in water by different biochars derived from spent mushroom substrate[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2020,39(4):1-13(in Chinese). [46] 王梓民, 石海信, 王爱荣, 等. 冷冻交联制备ZM-CSt-PVA复合凝胶及吸附Cu2+性能[J]. 精细化工, 2019, 36(6):1198-1202, 1209.WANG Zimin, SHI Haixin, WANG Airong, et al. Preparation of ZM-CSt-PVA composite gel though freezing cross-linking method and its adsorption performance of Cu2+[J]. Fine Chemicals,2019,36(6):1198-1202, 1209(in Chinese). [47] YU Z, SONG W, LI J, et al. Improved simultaneous adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ) of organic modified metakaolin-based geopolymer[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,2020,13(3):93-101. [48] 程福强, 吉田田, 薛敏, 等. 巯基改性SBA-15的制备及其对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2):193-198.CHENG Fuqiang, JI Tiantian, XUE Min, et al. Thiohydroxy-functionalized mesoporous materials: Preparation and its adsorption to Cr(Ⅵ)[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2020,35(2):193-198(in Chinese). [49] LEI C, ZHU X, ZHU B, et al. Superb adsorption capacity of hierarchical calcined Ni/Mg/Al layered double hydroxides for congo red and Cr(Ⅵ) ions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2017,321(5):801-811. [50] HAMDAOUI O. Adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) from aqueous phase by cedar bark[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science & Technology,2016,38(8):1087-1091. -






 下载:
下载: