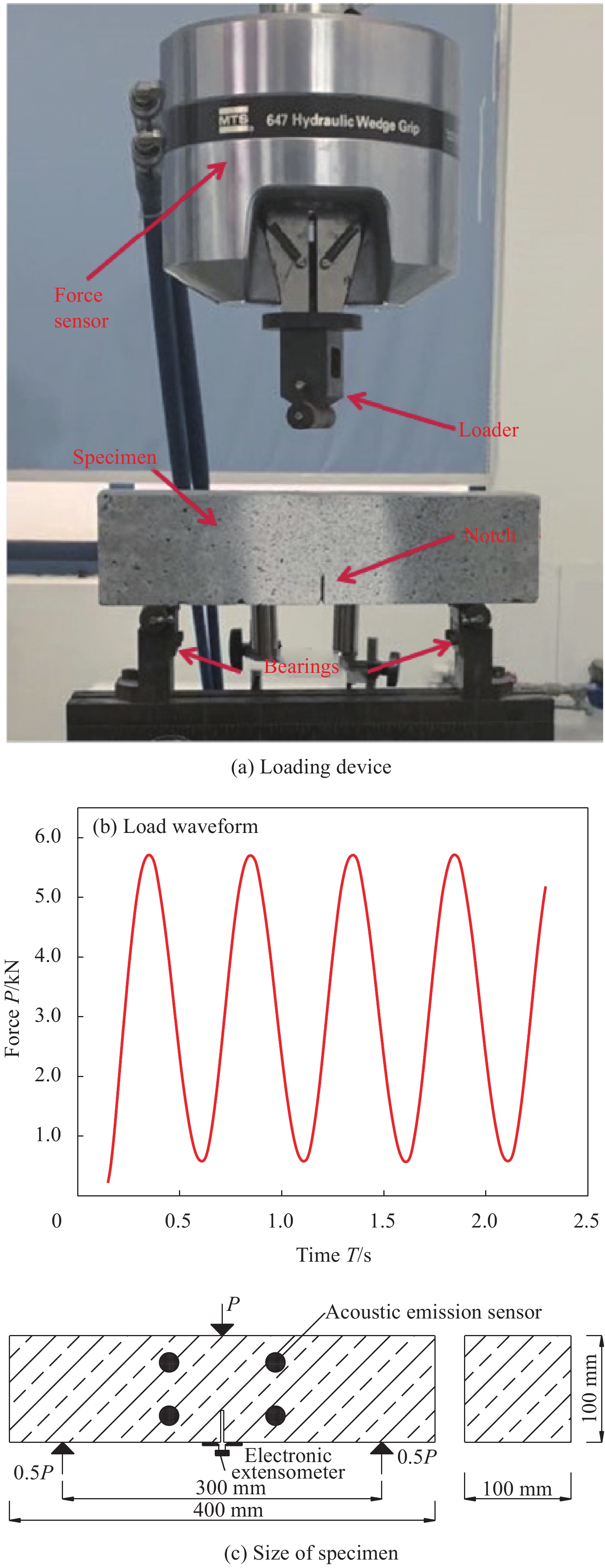
Effect of fatigue load on damage and fracture properties of rubber concrete
-
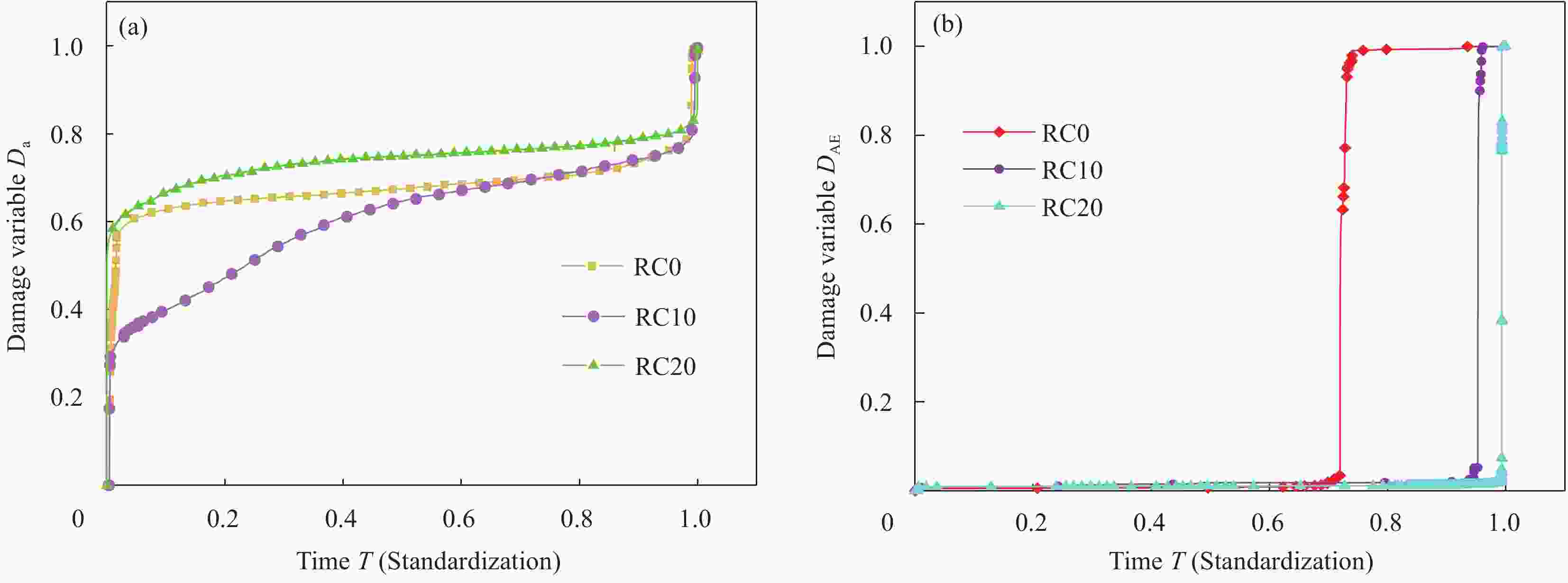
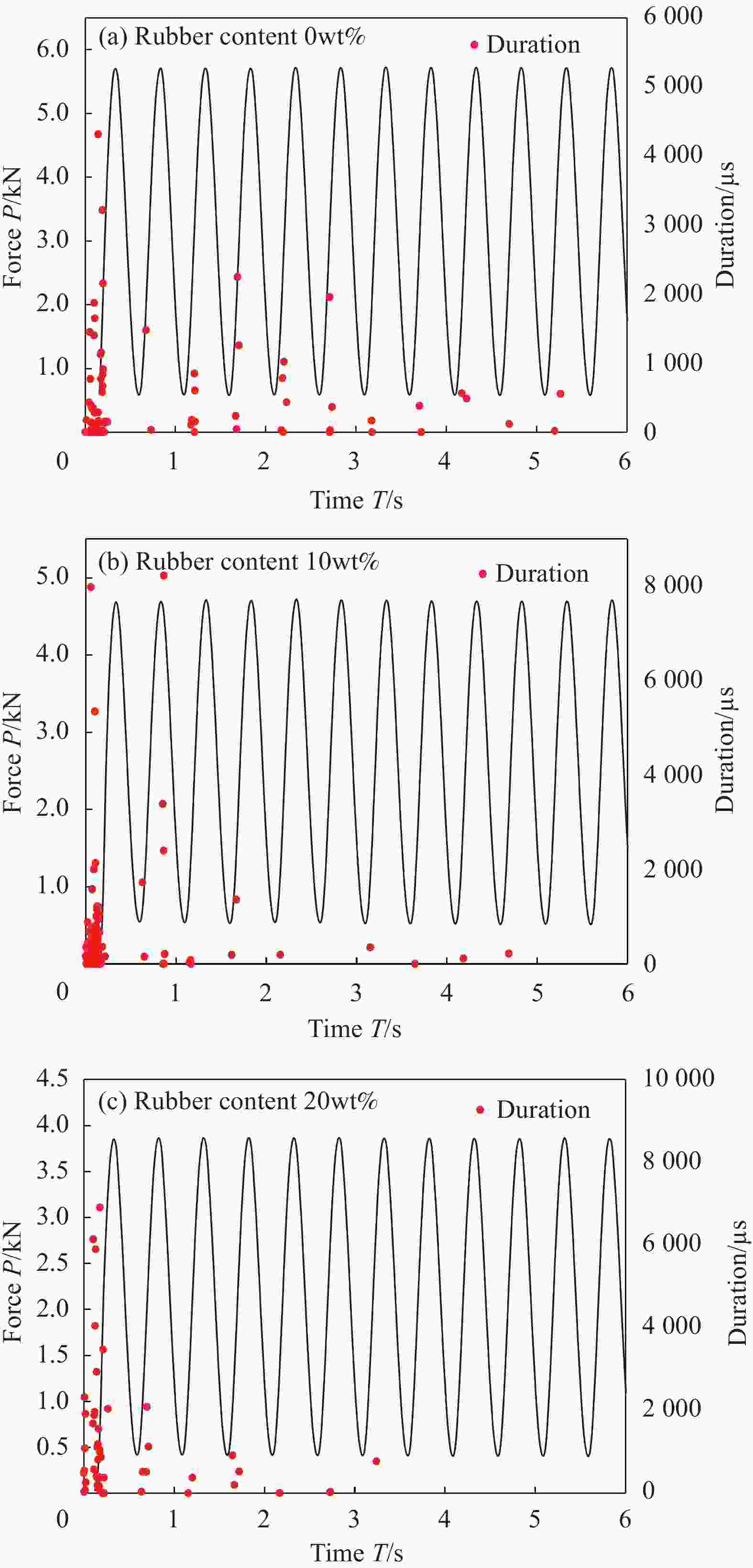
摘要: 虽然橡胶混凝土塑性和疲劳性能较好,但由于掺入橡胶,其在疲劳荷载下离散性增大,损伤过程及最终的断裂机制均不明确。为研究橡胶混凝土在疲劳荷载下的损伤和断裂性能,基于声发射开展了不同橡胶掺量的混凝土在疲劳荷载下的三点弯曲疲劳断裂试验。计算有效裂缝长度,分析疲劳荷载下不同橡胶掺量的混凝土裂缝长度a的变化规律,并利用裂缝长度a和声发射累积能量EAE分别定义了损伤变量Da和DAE;分析疲劳荷载下不同橡胶掺量的混凝土断裂能GF的变化规律;利用声发射中的信号持续时间分析疲劳荷载下橡胶混凝土中裂缝出现和扩展的规律。结果表明,混凝土的断裂能随橡胶掺量的增加呈线性增加;在疲劳荷载下,裂缝长度a和Da均呈倒S型规律变化,而DAE呈正S型规律变化;声发射信号持续时间表明,在疲劳荷载下,橡胶混凝土中的裂缝总在荷载较小时出现或发生扩展。Abstract: Although rubber concrete has better properties of plasticity and fatigue, due to the incorporation of rubber, its dispersion increases under fatigue load and the damage process and the ultimate fracture mechanism are not clear. In order to study the damage and fracture performance of rubber concrete under fatigue load, the three-point bending fatigue fracture test of concrete with different rubber contents under fatigue load based on acoustic emission was carried out. The effective crack length a was calculated and the change law of the crack length a of the rubber concrete with different rubber contents under the fatigue load was analyzed. The crack length ac and the acoustic emission cumulative energy EAE were used to define the damage variables Da and DAE.The variation law of the fracture energy GF of the rubber concrete with different rubber contents under the fatigue load and the law of the occurrence and propagation of cracks in the rubber concrete under the fatigue load were analyzed using the signal duration in the acoustic emission. The results show that the fracture energy of the concrete increases linearly with the increase of the rubber content. Under the fatigue load, both a and Da change in an inverted S-shaped law, while DAE shows a positive S-shaped law; The duration of the acoustic emission signal shows that the cracks in the rubber concrete always appear or expand when the load is small under the fatigue load.
-
Key words:
- rubber concrete /
- fatigue /
- damage variable /
- maximum crack length /
- acoustic emission cumulative energy
-
表 1 橡胶混凝土配比
Table 1. Mix proportion of rubber concrete
Sample Cement/kg Fly ash/kg SiC powder of high purity/kg Gravel/kg Fine aggregate/kg Water/kg Water reducer/kg Sand Rubber RC0 20.56 7.44 1.38 42.64 54.32 0 10.64 0.4 RC10 20.56 7.44 1.38 42.64 48.80 5.44 10.64 0.4 RC20 20.56 7.44 1.38 42.64 43.44 10.88 10.64 0.4 表 2 不同橡胶含量的橡胶混凝土三点弯曲试验结果
Table 2. Three point bending test results of rubber concrete with different rubber contents
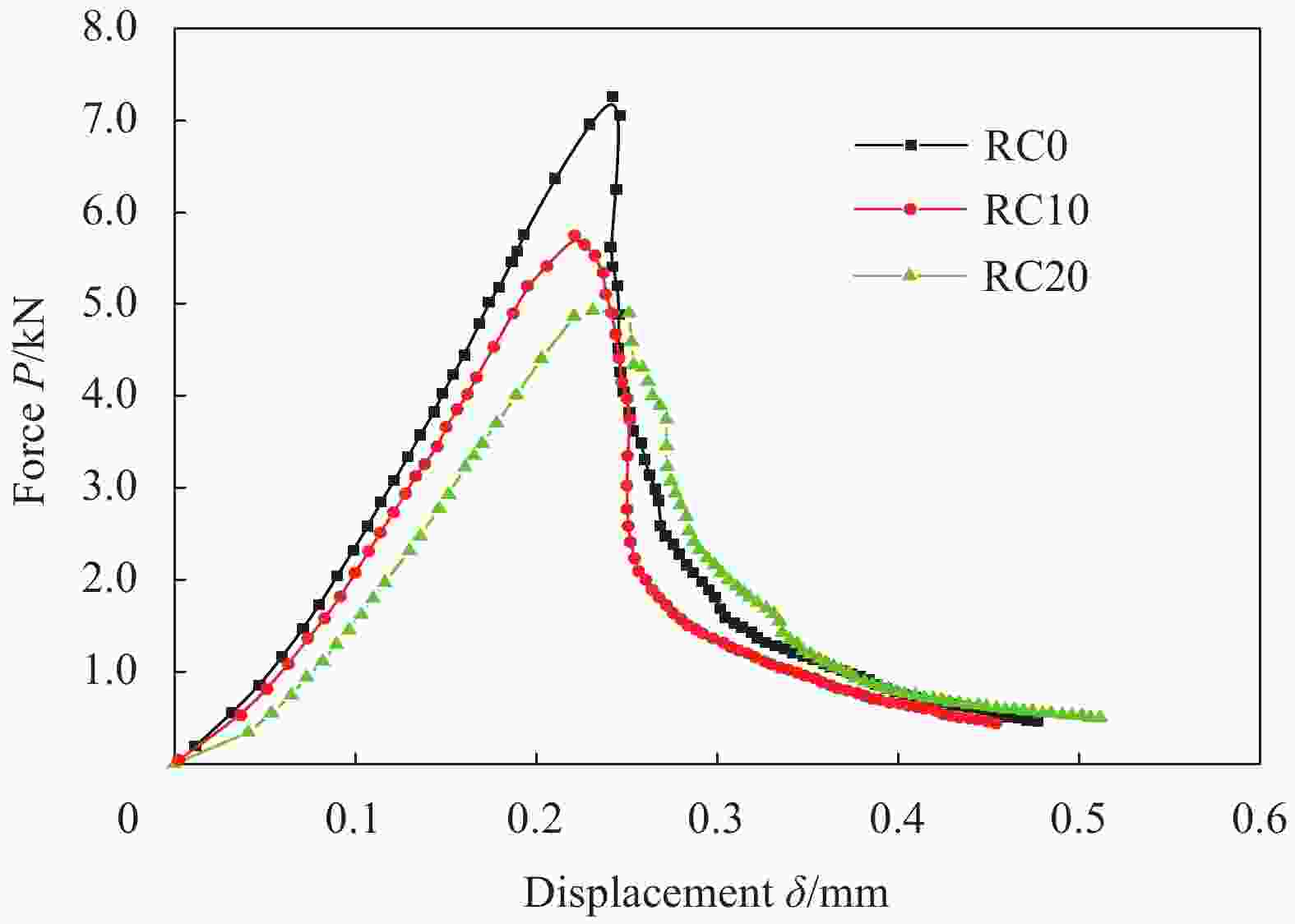
Rubber content Pmax/kN fmax/MPa E/GPa 0wt% 6.932 3.12 38.81 7.301 3.29 50.00 7.160 3.22 48.01 Average 7.131 3.21 45.60 Standard deviation 0.152 0.07 4.87 10wt% 6.084 2.74 30.22 5.723 2.58 39.00 5.780 2.60 42.24 Average 5.862 2.63 37.15 Standard deviation 0.158 0.07 5.08 20wt% 4.889 2.20 24.81 4.556 2.05 27.50 4.965 2.23 30.98 Average 4.803 2.16 27.76 Standard deviation 0.178 0.08 2.53 Notes: Pmax—Maximum load that specimen can bear; fmax—Bending strength; E—Elastic modulus. 表 3 不同橡胶含量的橡胶混凝土三点弯曲疲劳试验结果
Table 3. Three point bending fatigue test results of rubber concrete with different rubber contents
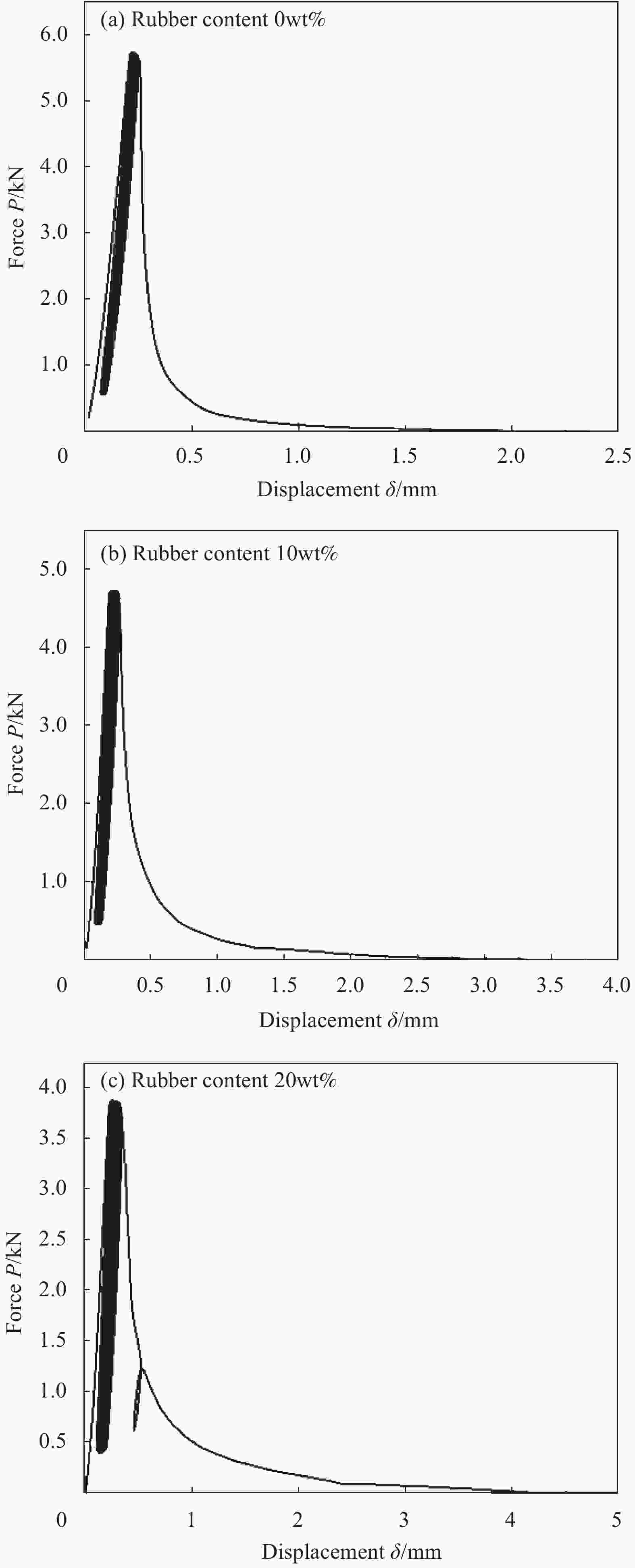
Sample Specimen number Fatigue life N Fracture energy Gf/(kN·m−1) Acoustic emission cultivate energy GAE RC0 1 130 1.73 25491 2 104 0.94 28783 3 71 0.71 28581 Average 102 1.13 27618 Standard deviation 24 0.43 1507 RC10 1 130 1.03 20118 2 23 0.38 40939 3 1188 6.92 27581 4 342 2.61 40496 5 2041 8.85 1841 6 8470 44.10 16849 Average 2033 10.65 24637 Standard deviation 2963 17.09 13703 RC20 1 4354 22.68 42850 2 16557 87.16 70 3 75 0.66 32093 4 9730 46.55 1026 5 728 4.55 28030 6 1820 11.34 21952 Average 5544 28.82 21003 Standard deviation 5876 26.62 15747 -
[1] SIDDIKA A, AL-MAMUN M A, ALYOUSEF R, et al. Properties and utilizations of waste tire rubber in concrete: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,224:711-731. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.108 [2] HAN Q H, YANG G, XU J. Experimental study on the relationship between acoustic emission energy and fracture energy of crumb rubber concrete[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2018,25(10):e2240. [3] KHALIL E, ABD-ELMOHSEN M, ANWAR A M. Impact resistance of rubberized self-compacting concrete[J]. Water Science,2015,29(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.wsj.2014.12.002 [4] YUNG W H, YUNG L C, HUA L H. A study of the durability properties of waste tire rubber applied to self-compacting concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2013,41:665-672. [5] NABILAH A B, NOAMAN N M R, NASIR N A M, et al. Experimental evaluation of flexural behaviour of rubberized concrete beam[J]. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering,2019,20(7):999-1005. doi: 10.1007/s42107-019-00159-5 [6] FENG W, LIU F, YANG F, et al. Experimental study on dynamic split tensile properties of rubber concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,165:675-687. [7] LIU F, ZHENG W, LI L, et al. Mechanical and fatigue performance of rubber concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2013,47:711-719. [8] ZHU X Y, CHEN X D, LIU S S, et al. Experimental study on flexural fatigue performance of rubberised concrete for pavement[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering,2020,21(9):1135-1146. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2018.1521971 [9] CHEN C, CHEN X, ZHANG J. Experimental study on flexural fatigue behavior of self-compacting concrete with waste tire rubber[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures,2019(6):1-12. doi: 10.1080/15376494.2019.1701152 [10] 蒋咏秋. 美国复合材料力学的发展动向[J]. 复合材料学报, 1985, 2(1):101-106.JIANG Yongqiu. Recent advances of mechanics of composites in the united states[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,1985,2(1):101-106(in Chinese). [11] SHAH S G, KISHEN J M C. Fracture behavior of concrete-concrete interface using acoustic emission technique[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2010,77(6):908-924. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2010.01.018 [12] 罗素蓉, 陈伟妹, 王雪芳. 橡胶自密实混凝土断裂性能试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(2):217-222.LUO Surong, CHEN Weimei, WANG Xuefang. Fracture properties of rubberized self-compacting concrete[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2015,46(2):217-222(in Chinese). [13] 曹国瑞, 王娟, 卿龙邦, 等. 橡胶混凝土断裂性能试验研究[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2018, 40(6):94-100.CAO Guorui, WANG Juan, QING Longbang, et al. Experimental study o the fracture characteristics of crumb rubber concrete[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering,2018,40(6):94-100(in Chinese). [14] WANG C, ZHANG Y, MA A. Investigation into the fatigue damage process of rubberized concrete and plain concrete by AE analysis[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2011,23(7):953-960. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000257 [15] SHAN Z, YU Z, LI X, et al. A damage model for concrete under fatigue loading[J]. Applied Sciences,2019,9(13):2768. doi: 10.3390/app9132768 [16] 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 水工混凝土断裂试验规程: DL/T 5332—2005[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2006.National Development and Reform Commission. Norm for fracture test of hydraulic concrete: DL/T 5332—2005[S]. Beijing: China Power Press, 2006(in Chinese). [17] 彭晨. 带预制裂纹混凝土疲劳损伤研究及寿命预测[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2013.PENG Chen. Fatigue damage and life prediction of prefabricated crack concrete[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [18] GUO Y, CHEN X, LI X, et al. Experimental study on fracture behavior of three-graded concrete under cyclic loading after initial static loading[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics,2019,103:102272. doi: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102272 [19] CARPINTERI A, LACIDOGNA G, CORRADO M, et al. Cracking and crackling in concrete-like materials: A dynamic energy balance[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2016,155:130-144. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2016.01.013 [20] LU Y Y, LI Z J. Study of the relationship between concrete fracture energy and AE signal energy under uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2012,24(5):538-547. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000418 [21] 吴香国, 韩相默, 徐世烺. 超高性能水泥基复合材料弯拉作用下虚拟应变硬化机制分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, 25(2):129-134. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.022WU Xiangguo, HAN Xiangmo, XU Shilang. Pseudo strain hardening model of ultra high performance cementitious composites under flexural loading[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2008,25(2):129-134(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.022 [22] RILEM Technical Committee. FMC 1 Determination of the fracture energy of mortar and concrete by means of three-point bend tests on notched beams[M]//RILEM. Recommendations for the testing and use of constructions materials. E & FN SPON, 1994. [23] NOORSUHADA M N. An overview on fatigue damage assessment of reinforced concrete structures with the aid of acoustic emission technique[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016,112:424-439. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.206 [24] 胡少伟, 陆俊, 范向前. 混凝土断裂试验中的声发射特性研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2011, 30(6):16-19.HU Shaowei, LU Jun, FAN Xiangqian. Study on acoustic emission technique for normal concrete fracture test[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering,2011,30(6):16-19(in Chinese). [25] KENNEDY J B, NEVILLE A M. Basic statistical methods for engineers and scientists[M]. Scranton International Textbook Co., 1964. -





 下载:
下载: